Activation of the Rat P2X7 Receptor by Functionally Different ATP Activation Sites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Cloning of rP2X7 Concatamers
2.3. Obtaining X. laevis Oocytes for In Vitro Experiments
2.4. Electrophysiological Characterization of rP2X7 Concatamers by Two-Electrode Voltage Clamp
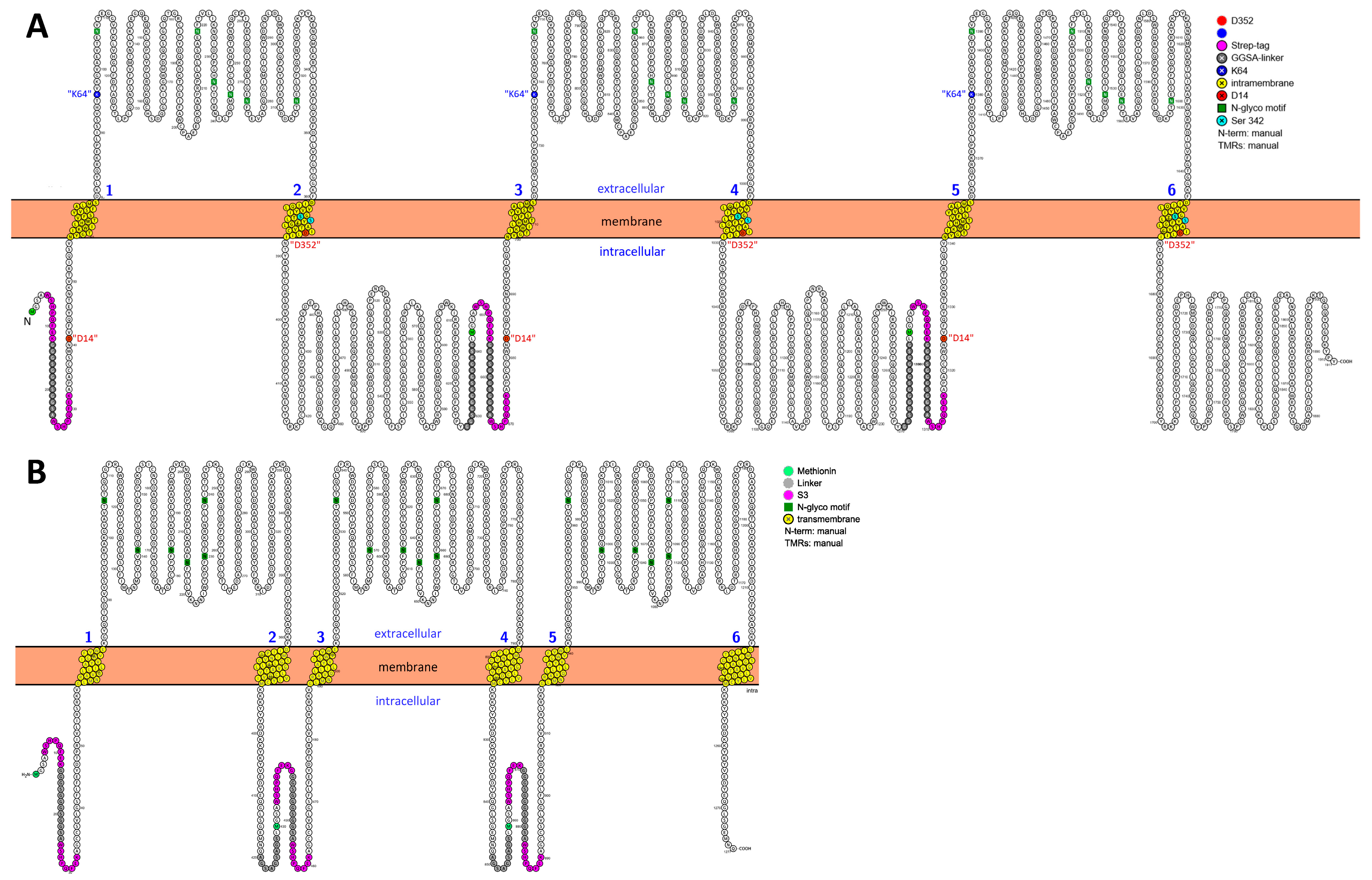
2.5. Biochemical Visualization of the Intactness of Plasma Membrane-Bound P2X7 Concatamers
2.6. Two-Electrode Voltage-Clamp Recording (TEVC)
2.7. Alphafold2 Structure Predictions of Concatenated and Non-Concatenated rP2X7 Homotrimers
2.8. Positioning of the Alphafold2 Models of the rP2X7 and 7-7-7 Concatamer in the Membrane
2.9. Comparison of the Alphafold2-Modeled Structures of the rP2X7 and 7-7-7 with PyMOL 3
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of the Proteoloytic Stability of Homodimeric and Homotrimeric rP2X7 Concatamers

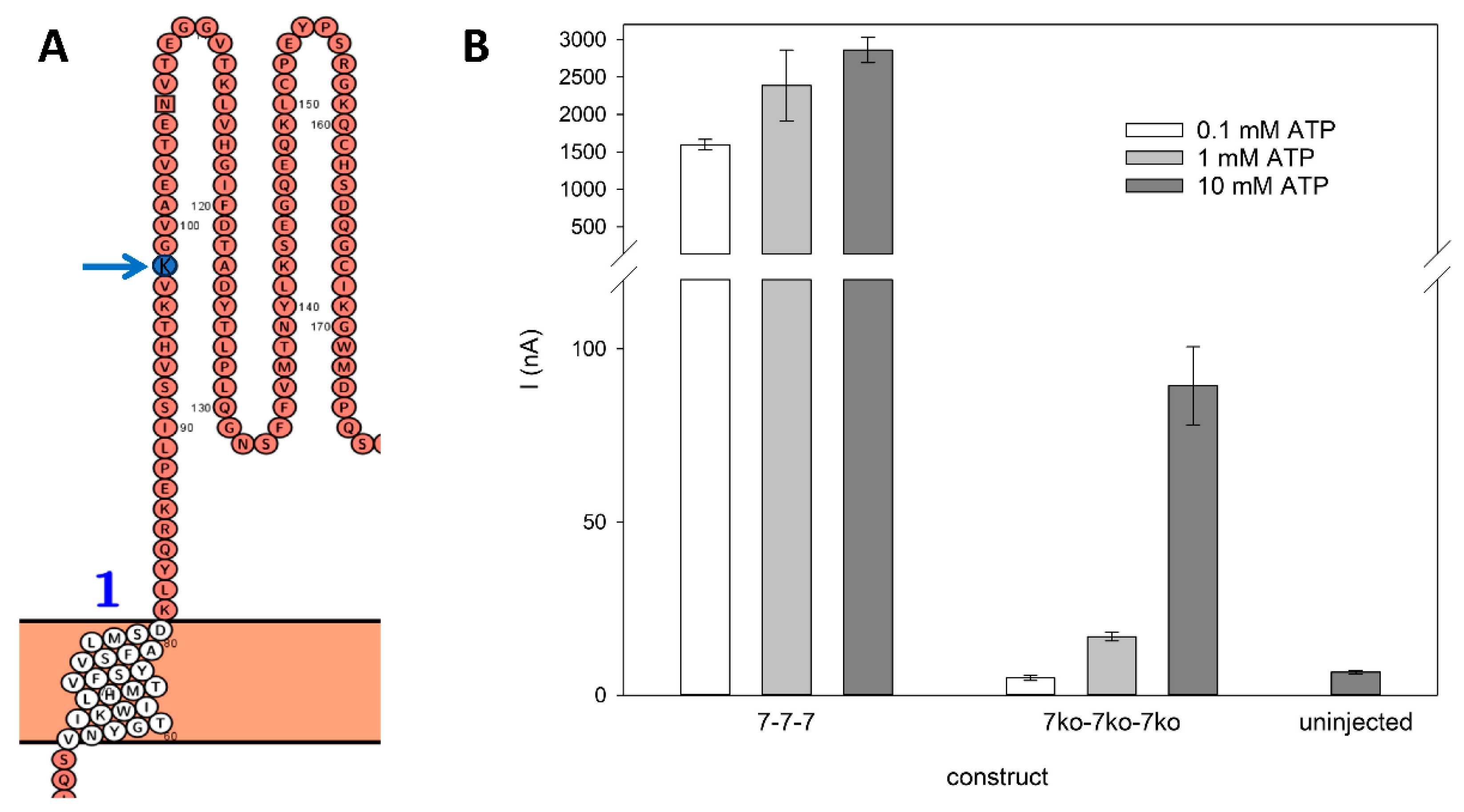
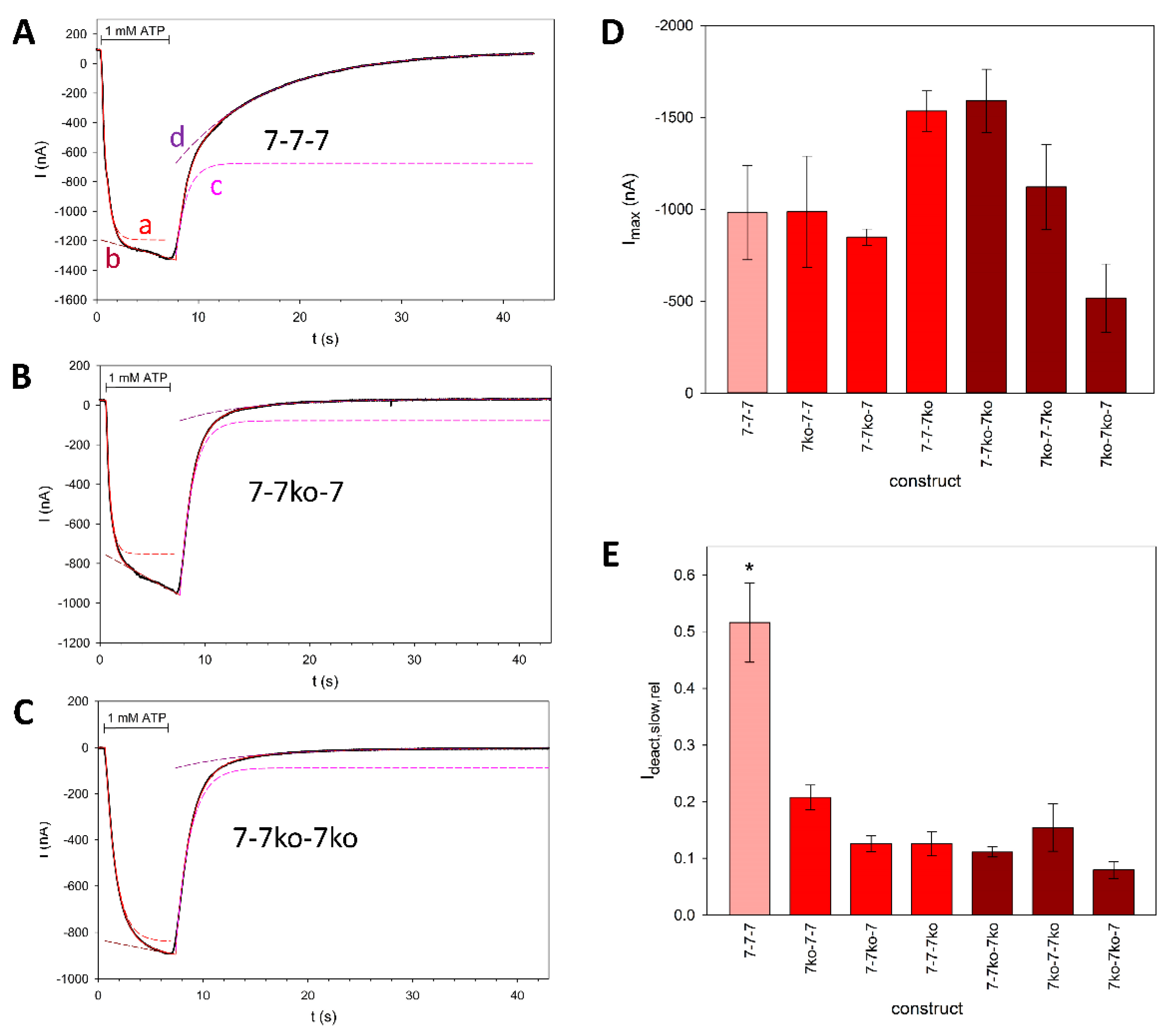
3.2. Electrophysiological Characterization of Knockouts of Individual ATP Binding Sites in Trimeric rP2X7 Concatamers
4. Discussion
4.1. Homotrimeric rP2X7 Concatamers, in Contrast to Their Homodimeric Precursors, Are Proteolytically Stable
4.2. Binding of One ATP Is Sufficient to Open the rP2X7 Channel Pore
4.3. Functionally Distinct Activation Sites at P2X Receptors
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aschrafi, A.; Sadtler, S.; Niculescu, C.; Rettinger, J.; Schmalzing, G. Trimeric architecture of homomeric P2X2 and heteromeric P2X1+2 receptor subtypes. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 342, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicke, A.; Bäumert, H.G.; Rettinger, J.; Eichele, A.; Lambrecht, G.; Mutschler, E.; Schmalzing, G. P2X1 and P2X3 receptors form stable trimers: A novel structural motif of ligand-gated ion channels. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 3016–3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicke, A.; Rettinger, J.; Büttner, C.; Eichele, A.; Lambrecht, G.; Schmalzing, G. Evolving view of quaternary structures of ligand-gated ion channels. Prog. Brain Res. 1999, 120, 61–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oken, A.C.; Lisi, N.E.; Krishnamurthy, I.; McCarthy, A.E.; Godsey, M.H.; Glasfeld, A.; Mansoor, S.E. High-affinity agonism at the P2X7 receptor is mediated by three residues outside the orthosteric pocket. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, D.; Woltersdorf, R.; Boldt, W.; Schmitz, S.; Braam, U.; Schmalzing, G.; Markwardt, F. The P2X7 carboxyl tail is a regulatory module of P2X7 receptor channel activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 25725–25734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Virgilio, F.; Schmalzing, G.; Markwardt, F. The elusive P2X7 macropore. Trends Cell Biol. 2018, 28, 392–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Virgilio, F.; Sarti, A.C.; Coutinho-Silva, R. Purinergic signaling, DAMPs, and inflammation. Am. J. Physiol. 2020, 318, C832–C835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klapperstück, M.; Büttner, C.; Böhm, T.; Schmalzing, G.; Markwardt, F. Characteristics of P2X7 receptors from human B lymphocytes expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1467, 444–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markwardt, F.; Löhn, M.; Böhm, T.; Klapperstück, M. Purinoceptor-operated cationic channels in human B lymphocytes. J. Physiol. 1997, 498, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Silberberg, S.D.; Swartz, K.J. Subtype-specific control of P2X receptor channel signaling by ATP and Mg2+. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E3455–E3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Banerjee, R.; Marinelli, F.; Silberberg, S.; Faraldo-Gomez, J.D.; Hattori, M.; Swartz, K.J. Molecular mechanisms of human P2X3 receptor channel activation and modulation by divalent cation bound ATP. eLife 2019, 8, e47060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, A.E.; Yoshioka, C.; Mansoor, S.E. Full-Length P2X7 structures reveal how palmitoylation prevents channel desensitization. Cell 2019, 179, 659–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawate, T. P2X receptor activation. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 1051, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klapperstück, M.; Büttner, C.; Schmalzing, G.; Markwardt, F. Functional evidence of distinct ATP activation sites at the human P2X7 receptor. J. Physiol. 2001, 534, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel, T.; Lozinsky, I.; Schmalzing, G.; Markwardt, F. Kinetics of P2X7 receptor-operated single channels currents. Biophys. J. 2007, 92, 2377–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surprenant, A.; Rassendren, F.; Kawashima, E.; North, R.A.; Buell, G. The cytolytic P2Z receptor for extracellular ATP identified as a P2X receptor (P2X7). Science 1996, 272, 735–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gloor, S.; Pongs, O.; Schmalzing, G. A vector for the synthesis of cRNAs encoding Myc epitope-tagged proteins in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Gene 1995, 160, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.; Prudic, K.; Pippel, A.; Klapperstück, M.; Braam, U.; Müller, C.E.; Schmalzing, G.; Markwardt, F. Interaction of purinergic P2X4 and P2X7 receptor subunits. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicke, A.; Rettinger, J.; Schmalzing, G. Monomeric and dimeric byproducts are the principal functional elements of higher order P2X1 concatamers. Mol. Pharmacol. 2003, 63, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braman, J.; Papworth, C.; Greener, A. Site-directed mutagenesis using double-stranded plasmid DNA templates. Methods Mol. Biol. 1996, 57, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, K.I.; Basic, M.; Varjosalo, M.; Mäkinen, K. One-step purification of twin-strep-tagged proteins and their complexes on strep-tactin resin cross-linked with bis(sulfosuccinimidyl) suberate (BS3). J. Vis. Exp. 2014, 86, e51536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pult, F.; Fallah, G.; Braam, U.; Detro-Dassen, S.; Niculescu, C.; Laube, B.; Schmalzing, G. Robust post-translocational N-glycosylation at the extreme C-terminus of membrane and secreted proteins in Xenopus laevis oocytes and HEK293 cells. Glycobiology 2011, 21, 1147–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennion, S.; Hagan, S.; Evans, R.J. The role of positively charged amino acids in ATP recognition by human P2X1 receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 29361–29367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmalzing, G.; Markwardt, F. Established protocols for cRNA expression and voltage-clamp characterization of the P2X7 receptor in Xenopus laevis oocytes. In The P2X7 Receptor: Methods and Protocols; Nicke, A., Ed.; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 157–192. [Google Scholar]
- Grudzien-Nogalska, E.; Stepinski, J.; Jemielity, J.; Zuberek, J.; Stolarski, R.; Rhoads, R.E.; Darzynkiewicz, E. Synthesis of anti-reverse cap analogs (ARCAs) and their applications in mRNA translation and stability. Methods Enzymol. 2007, 431, 203–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmalzing, G.; Kröner, S.; Schachner, M.; Gloor, S. The adhesion molecule on glia (AMOG/b2) and a1 subunits assemble to functional sodium pumps in Xenopus oocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 20212–20216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallah, G.; Römer, T.; Braam, U.; Detro-Dassen, S.; Markwardt, F.; Schmalzing, G. TMEM16A(a)/anoctamin-1 shares a homodimeric architecture with CLC chloride channels. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2011, 10, M110.004697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Zidek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomize, M.A.; Pogozheva, I.D.; Joo, H.; Mosberg, H.I.; Lomize, A.L. OPM database and PPM web server: Resources for positioning of proteins in membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D370–D376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omasits, U.; Ahrens, C.H.; Muller, S.; Wollscheid, B. Protter: Interactive protein feature visualization and integration with experimental proteomic data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 884–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabsch, W. A solution for the best rotation to relate two sets of vectors. Acta Cryst. A 1976, A32, 922–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomize, A.L.; Todd, S.C.; Pogozheva, I.D. Spatial arrangement of proteins in planar and curved membranes by PPM 3.0. Protein Sci. 2022, 31, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellgaard, L.; Helenius, A. Quality control in the endoplasmic reticulum. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003, 4, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, R. Statistical methods for model discrimination: Application to gating kinetics and permeation of the acetylcholine receptor channel. Biophys. J. 1987, 51, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelmashenko, O.; Lalo, U.; Yang, Y.; Bragg, L.; North, R.A.; Compan, V. Activation of trimeric P2X2 receptors by fewer than three ATP molecules. Mol. Pharmacol. 2012, 82, 760–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.H.; Sachs, F. Single channel properties of P2X2 purinoceptors. J. Gen. Physiol. 1999, 113, 695–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karoly, R.; Mike, A.; Illes, P.; Gerevich, Z. The unusual state-dependent affinity of P2X3 receptors can be explained by an allosteric two-open-state model. Mol. Pharmacol. 2007, 73, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Khadra, A.; Li, S.; Tomic, M.; Sherman, A.; Stojilkovic, S.S. Experimental characterization and mathematical modeling of P2X7 receptor channel gating. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 14213–14224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browne, L.E.; Cao, L.; Broomhead, H.E.; Bragg, L.; Wilkinson, W.J.; North, R.A. P2X receptor channels show threefold symmetry in ionic charge selectivity and unitary conductance. Nat. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 17–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keceli, B.; Kubo, Y. Signal transmission within the P2X2 trimeric receptor. J. Gen. Physiol. 2014, 143, 761–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, R.; Evans, R.J. ATP-gated P2X receptor channels: Molecular insights into functional roles. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2018, 81, 43–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattler, C.; Eick, T.; Hummert, S.; Schulz, E.; Schmauder, R.; Schweinitz, A.; Unzeitig, C.; Schwede, F.; Benndorf, K. Unravelling the intricate cooperativity of subunit gating in P2X2 ion channels. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gusic, M.; Benndorf, K.; Sattler, C. Dissecting activation steps in P2X7 receptors. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 569, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattori, M.; Gouaux, E. Molecular mechanism of ATP binding and ion channel activation in P2X receptors. Nature 2012, 485, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoor, S.E.; Lu, W.; Oosterheert, W.; Shekhar, M.; Tajkhorshid, E.; Gouaux, E. X-ray structures define human P2X3 receptor gating cycle and antagonist action. Nature 2016, 538, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markwardt, F.; Schön, E.C.; Raycheva, M.; Malisetty, A.; Hawro, Y.S.; Berthold, M.; Schmalzing, G. Two serial filters control P2X7 cation selectivity, Ser342 in the central pore and lateral acidic residues at the cytoplasmic interface. PNAS Nexus 2024, 3, ae349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, M.E.; Chen, F.; Saven, J.G.; Roos, D.S.; Babbitt, P.C.; Sali, A. Evolutionary constraints on structural similarity in orthologs and paralogs. Protein Sci. 2009, 18, 1306–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flittiger, B.; Klapperstück, M.; Schmalzing, G.; Markwardt, F. Effects of protons on macroscopic and single-channel currents mediated by the human P2X7 receptor. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2010, 1798, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuehnel, M.P.; Reiss, M.; Anand, P.K.; Treede, I.; Holzer, D.; Hoffmann, E.; Klapperstueck, M.; Steinberg, T.H.; Markwardt, F.; Griffiths, G. Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptors stimulate macrophage plasma-membrane actin assembly via ADP release, ATP synthesis and P2X7R activation. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trang, M.; Schmalzing, G.; Müller, C.E.; Markwardt, F. Dissection of P2X4 and P2X7 receptor current components in BV-2 microglia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santillan, M. On the use of the Hill functions in mathematical models of gene regulatory networks. Math. Model. Nat. Phenom. 2008, 3, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khakh, B.S.; Bao, X.R.; Labarca, C.; Lester, H.A. Neuronal P2X transmitter-gated cation channels change their ion selectivity in seconds. Nat. Neurosci. 1999, 2, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clyne, J.D.; Brown, T.C.; Hume, R.I. Expression level dependent changes in the properties of P2X2 receptors. Neuropharmacology 2003, 44, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Chang, T.H.; Silberberg, S.D.; Swartz, K.J. Gating the pore of P2X receptor channels. Nat. Neurosci. 2008, 11, 883–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.H.; Rassendren, F.; Spelta, V.; Surprenant, A.; North, R.A. Amino acid residues involved in gating identified in the first membrane-spanning domain of the rat P2X2 receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 14902–14908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clyne, J.D.; LaPointe, L.D.; Hume, R.I. The role of histidine residues in modulation of the rat P2X2 purineceptor by zinc and pH. J. Physiol. 2002, 539, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.H.; Liang, Z.D.; Tomic, M.; Obsil, T.; Stojilkovic, S.S. Molecular determinants of the agonist binding domain of a P2X receptor channel. Mol. Pharmacol. 2005, 67, 1078–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Concatamer | A1act (nA) | R1act (1/s) | A2act (nA) | R2act (1/s) | A1deact (nA) | R1deact (1/s) | A2deact (nA) | R2deact (1/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7wt-7wt-7wt | −1286.7 | 1.81 | −6572.4 | 0.00284 | −626.6 | 0.95 | −756.1 | 0.11 |
| 7wt -7ko-7wt | −783.1 | 2.3 | −7595.2 | 0.00382 | −872.5 | 0.84 | −108.7 | 0.15 |
| 7ko-7ko-7wt | −838.2 | 0.98 | −3485.1 | 0.00259 | −785.1 | 0.72 | −86.1 | 0.13 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Markwardt, F.; Berthold, M.; Hawro Yakoob, S.; Schmalzing, G. Activation of the Rat P2X7 Receptor by Functionally Different ATP Activation Sites. Cells 2025, 14, 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14120855
Markwardt F, Berthold M, Hawro Yakoob S, Schmalzing G. Activation of the Rat P2X7 Receptor by Functionally Different ATP Activation Sites. Cells. 2025; 14(12):855. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14120855
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarkwardt, Fritz, Malte Berthold, Sanaria Hawro Yakoob, and Günther Schmalzing. 2025. "Activation of the Rat P2X7 Receptor by Functionally Different ATP Activation Sites" Cells 14, no. 12: 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14120855
APA StyleMarkwardt, F., Berthold, M., Hawro Yakoob, S., & Schmalzing, G. (2025). Activation of the Rat P2X7 Receptor by Functionally Different ATP Activation Sites. Cells, 14(12), 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14120855








