The Sebaceous Gland: A Key Player in the Balance Between Homeostasis and Inflammatory Skin Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. SG Physiology
3.1. SG Anatomy and Differentiation
3.2. Sebum Composition and Regulation
3.3. SG Role in Skin Immunobiology
3.4. SG Role in Crosstalk with Other Cell Populations
4. Acne
5. Seborrheic Dermatitis
6. Eosinophilic Pustular Folliculitis
7. Rosacea
8. Atopic Dermatitis
9. Psoriasis
10. Hidradenitis Suppurativa
11. Melasma
12. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Zouboulis, C.C.; Picardo, M.; Ju, Q.; Kurokawa, I.; Törcsik, D.; Bíró, T.; Schneider, M.R. Beyond Acne: Current Aspects of Sebaceous Gland Biology and Function. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2016, 17, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludovici, M.; Kozul, N.; Materazzi, S.; Risoluti, R.; Picardo, M.; Camera, E. Influence of the Sebaceous Gland Density on the Stratum Corneum Lipidome. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forni, M.F.; Trombetta-Lima, M.; Sogayar, M.C. Stem Cells in Embryonic Skin Development. Biol. Res. 2012, 45, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, M.R.; Schmidt-Ullrich, R.; Paus, R. The Hair Follicle as a Dynamic Miniorgan. Curr. Biol. 2009, 19, R132–R142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemann, C. Differentiation of the Sebaceous Gland. Dermato-Endocrinology 2009, 1, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kligman, A.M. The Uses of Sebum. Br. J. Dermatol. 1963, 75, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyden, J.J.; McGinley, K.J.; Mills, O.H.; Kligman, A.M. Propionibacterium Levels in Patients With and Without Acne Vulgaris. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1975, 65, 382–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiboutot, D. Regulation of Human Sebaceous Glands. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2004, 123, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agak, G.W.; Qin, M.; Nobe, J.; Kim, M.-H.; Krutzik, S.R.; Tristan, G.R.; Elashoff, D.; Garbán, H.J.; Kim, J. Propionibacterium Acnes Induces an Interleukin-17 Response in Acne Vulgaris That Is Regulated by Vitamin A and Vitamin D. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schachner, L.A.; Alexis, A.F.; Andriessen, A.; Berson, D.; Gold, M.; Goldberg, D.J.; Hu, S.; Keri, J.; Kircik, L.; Woolery-Lloyd, H. Insights into Acne and the Skin Barrier: Optimizing Treatment Regimens with Ceramide-Containing Skincare. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2023, 22, 2902–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.R.; Thiboutot, D.M. Thematic Review Series: Skin Lipids. Sebaceous Gland Lipids: Friend or Foe? J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picardo, M.; Ottaviani, M.; Camera, E.; Mastrofrancesco, A. Sebaceous Gland Lipids. Dermato-Endocrinology 2009, 1, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zouboulis, C.C.; Coenye, T.; He, L.; Kabashima, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Niemann, C.; Nomura, T.; Oláh, A.; Picardo, M.; Quist, S.R.; et al. Sebaceous Immunobiology—Skin Homeostasis, Pathophysiology, Coordination of Innate Immunity and Inflammatory Response and Disease Associations. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1029818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderwolf, K.; Kyle, C.; Davy, C. A Review of Sebum in Mammals in Relation to Skin Diseases, Skin Function, and the Skin Microbiome. PeerJ 2023, 11, e16680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouboulis, C.C.; Yoshida, G.J.; Wu, Y.; Xia, L.; Schneider, M.R. Sebaceous Gland: Milestones of 30-Year Modelling Research Dedicated to the “Brain of the Skin”. Exp. Dermatol. 2020, 29, 1069–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoro, O.E.; Camera, E.; Flori, E.; Ottaviani, M. Insulin and the Sebaceous Gland Function. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1252972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knop, E.; Knop, N.; Millar, T.; Obata, H.; Sullivan, D.A. The International Workshop on Meibomian Gland Dysfunction: Report of the Subcommittee on Anatomy, Physiology, and Pathophysiology of the Meibomian Gland. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 1938–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butovich, I.A. Meibomian Glands, Meibum, and Meibogenesis. Exp. Eye Res. 2017, 163, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halperin, V.; Kolas, S.; Jefferis, K.R.; Huddleston, S.O.; Robinson, H.B.G. The Occurrence of Fordyce Spots, Benign Migratory Glossitis, Median Rhomboid Glossitis, and Fissured Tongue in 2,478 Dental Patients. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 1953, 6, 1072–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, M.G.; Puia, S.A. Sebaceous Cyst in the Oral Cavity. Ann. Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 8, 137–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.R.; Paus, R. Sebocytes, Multifaceted Epithelial Cells: Lipid Production and Holocrine Secretion. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2010, 42, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, R.W.; Göbel, K.; Niessen, C.M.; Paus, R.; Steensel, M.A.M.; Lim, X. Homeostasis of the Sebaceous Gland and Mechanisms of Acne Pathogenesis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2019, 181, 677–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, R.W.; Langan, E.A.; Ansell, D.M.; de Vos, I.J.H.M.; Göbel, K.; Schneider, M.R.; Picardo, M.; Lim, X.; van Steensel, M.A.M.; Paus, R. Neuroendocrinology and Neurobiology of Sebaceous Glands. Biol. Rev. 2020, 95, 592–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.; Tam, J.; Jalian, H.R.; Anderson, R.R.; Evans, C.L. Longitudinal, 3D in Vivo Imaging of Sebaceous Glands by Coherent Anti-Stokes Raman Scattering Microscopy—Normal Function and Response to Cryotherapy. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 135, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.; Hansmann, F.; Loeffler-Wirth, H.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Binder, H.; Schneider, M.R. A Spatial Portrait of the Human Sebaceous Gland Transcriptional Program. J. Biol. Chem. 2024, 300, 107442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaba, A.; Thalheim, T.; Schneider, M.R. The Role of Cell–Cell and Cell–Matrix Junctional Complexes in Sebaceous Gland Homeostasis and Differentiation. Cell Commun. Signal. 2024, 22, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thody, A.J.; Shuster, S. Control and Function of Sebaceous Glands. Physiol. Rev. 1989, 69, 383–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isom, M.; Desaire, H. Skin Surface Sebum Analysis by ESI-MS. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouboulis, C.C.; Chen, W.-C.; Thornton, M.J.; Qin, K.; Rosenfield, R. Sexual Hormones in Human Skin. Horm. Metab. Res. 2007, 39, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi, C. Hormone Therapy in Acne. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2013, 79, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pochi, P.E.; Strauss, J.S.; Downing, D.T. Age-Related Changes in Sebaceous Gland Activity. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1979, 73, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farage, M.A.; Neill, S.; MacLean, A.B. Physiological Changes Associated with the Menstrual Cycle: A Review. Obstet. Gynecol. Surv. 2009, 64, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid-wendtner, M.H.; Korting, H.C. The pH of the Skin Surface and Its Impact on the Barrier Function. Ski. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2006, 19, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoover, E.; Aslam, S.; Krishnamurthy, K. Physiology, Sebaceous Glands; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA; StatPearls: Petersburg, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Banyś, A.; Hartman-Petrycka, M.; Kras, K.; Kamińska, M.; Krusiec-Świdergoł, B.; Popielski, P.; Lebiedowska, A.; Wilczyński, S. The Influence of Sebum on Directional Reflectance of the Skin. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisinger, M.; Li, W.-H.; Anthonavage, M.; Pappas, A.; Zhang, L.; Rossetti, D.; Huang, Q.; Seiberg, M. A Melanocortin Receptor 1 and 5 Antagonist Inhibits Sebaceous Gland Differentiation and the Production of Sebum-Specific Lipids. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2011, 63, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theoharides, T.C.; Stewart, J.M.; Taracanova, A.; Conti, P.; Zouboulis, C.C. Neuroendocrinology of the Skin. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2016, 17, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrofrancesco, A.; Ottaviani, M.; Cardinali, G.; Flori, E.; Briganti, S.; Ludovici, M.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Lora, V.; Camera, E.; Picardo, M. Pharmacological PPARγ Modulation Regulates Sebogenesis and Inflammation in SZ95 Human Sebocytes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 138, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béke, G.; Dajnoki, Z.; Kapitány, A.; Gáspár, K.; Medgyesi, B.; Póliska, S.; Hendrik, Z.; Péter, Z.; Törőcsik, D.; Bíró, T.; et al. Immunotopographical Differences of Human Skin. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatsuji, T.; Kao, M.C.; Zhang, L.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Gallo, R.L.; Huang, C.-M. Sebum Free Fatty Acids Enhance the Innate Immune Defense of Human Sebocytes by Upregulating β-Defensin-2 Expression. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Törőcsik, D.; Kovács, D.; Póliska, S.; Szentkereszty-Kovács, Z.; Lovászi, M.; Hegyi, K.; Szegedi, A.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Ståhle, M. Genome Wide Analysis of TLR1/2- and TLR4-Activated SZ95 Sebocytes Reveals a Complex Immune-Competence and Identifies Serum Amyloid A as a Marker for Activated Sebaceous Glands. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattii, M.; Lovászi, M.; Garzorz, N.; Atenhan, A.; Quaranta, M.; Lauffer, F.; Konstantinow, A.; Küpper, M.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Kemeny, L.; et al. Sebocytes Contribute to Skin Inflammation by Promoting the Differentiation of T Helper 17 Cells. Br. J. Dermatol. 2018, 178, 722–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.-Y.; Huang, C.-M.; Nakatsuji, T.; Thiboutot, D.; Kang, S.-A.; Monestier, M.; Gallo, R.L. Histone H4 Is a Major Component of the Antimicrobial Action of Human Sebocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2009, 129, 2489–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolakis, G.; Seltmann, H.; Hossini, A.M.; Makrantonaki, E.; Knolle, J.; Zouboulis, C.C. Ex Vivo Human Skin and SZ95 Sebocytes Exhibit a Homoeostatic Interaction in a Novel Coculture Contact Model. Exp. Dermatol. 2015, 24, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Hossini, A.M.; Nikolakis, G.; Balthasar, O.; Kurtz, A.; Zouboulis, C.C. 3D-SeboSkin Model for Human Ex Vivo Studies of Hidradenitis Suppurativa/Acne Inversa. Dermatology 2022, 238, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouboulis, C.C.; Hou, X.; von Waldthausen, H.; Zouboulis, K.C.; Hossini, A.M. HS 3D-SeboSkin Model Enables the Preclinical Exploration of Therapeutic Candidates for Hidradenitis Suppurativa/Acne Inversa. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Naser, M.B.; Seltmann, H.; Zouboulis, C.C. SZ95 Sebocytes Induce Epidermal Melanocyte Dendricity and Proliferation in Vitro. Exp. Dermatol. 2012, 21, 393–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Naser, M.B.; Nikolakis, G.; Zouboulis, C.C. Preservation of Epidermal Melanocyte Integrity in an Ex Vivo Co-Culture Skin Model with Sebocytes. Exp. Dermatol. 2023, 32, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flori, E.; Mastrofrancesco, A.; Mosca, S.; Ottaviani, M.; Briganti, S.; Cardinali, G.; Filoni, A.; Cameli, N.; Zaccarini, M.; Zouboulis, C.C.; et al. Sebocytes Contribute to Melasma Onset. iScience 2022, 25, 103871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuchayi, S.M.; Makrantonaki, E.; Ganceviciene, R.; Dessinioti, C.; Feldman, S.R.; Zouboulis, C.C. Acne Vulgaris. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 1, 15029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouboulis, C.C.; Jourdan, E.; Picardo, M. Acne Is an Inflammatory Disease and Alterations of Sebum Composition Initiate Acne Lesions. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2014, 28, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, S.-W.; Park, E.-S.; Lee, D.-H.; Huh, C.-H.; Park, K.-C. Does Facial Sebum Excretion Really Affect the Development of Acne? Br. J. Dermatol. 2005, 153, 919–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomholt, H.B.; Kilian, M. Population Genetic Analysis of Propionibacterium Acnes Identifies a Subpopulation and Epidemic Clones Associated with Acne. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDowell, A. Over a Decade of recA and Tly Gene Sequence Typing of the Skin Bacterium Propionibacterium Acnes: What Have We Learnt? Microorganisms 2017, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spittaels, K.-J.; Ongena, R.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Crabbé, A.; Coenye, T. Cutibacterium Acnes Phylotype I and II Strains Interact Differently With Human Skin Cells. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 575164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dréno, B.; Dagnelie, M.A.; Khammari, A.; Corvec, S. The Skin Microbiome: A New Actor in Inflammatory Acne. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2020, 21, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.; Kang, D.; Barnard, E.; Li, H. Strain-Level Differences in Porphyrin Production and Regulation in Propionibacterium Acnes Elucidate Disease Associations. mSphere 2016, 1, e00023-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessinioti, C.; Katsambas, A.D. The Role of Propionibacterium Acnes in Acne Pathogenesis: Facts and Controversies. Clin. Dermatol. 2010, 28, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottaviani, M.; Camera, E.; Picardo, M. Lipid Mediators in Acne. Mediat. Inflamm. 2010, 2010, 858176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Permatasari, F.; Xu, Y.; Wu, D.; Yin, Z.; Luo, D. Palmitic Acid Induces Production of Proinflammatory Cytokines Interleukin-6, Interleukin-1β, and Tumor Necrosis Factor-α via a NF-κB-Dependent Mechanism in HaCaT Keratinocytes. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 530429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josse, G.; Mias, C.; Le Digabel, J.; Filiol, J.; Ipinazar, C.; Villaret, A.; Gomiero, C.; Bevilacqua, M.; Redoules, D.; Nocera, T.; et al. High Bacterial Colonization and Lipase Activity in Microcomedones. Exp. Dermatol. 2020, 29, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouboulis, C.C. Propionibacterium Acnes and Sebaceous Lipogenesis: A Love-Hate Relationship? J. Investig. Dermatol. 2009, 129, 2093–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iinuma, K.; Sato, T.; Akimoto, N.; Noguchi, N.; Sasatsu, M.; Nishijima, S.; Kurokawa, I.; Ito, A. Involvement of Propionibacterium Acnes in the Augmentation of Lipogenesis in Hamster Sebaceous Glands in Vivo and in Vitro. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2009, 129, 2113–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovács, D.; Camera, E.; Póliska, S.; Cavallo, A.; Maiellaro, M.; Dull, K.; Gruber, F.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Szegedi, A.; Törőcsik, D. Linoleic Acid Induced Changes in SZ95 Sebocytes-Comparison with Palmitic Acid and Arachidonic Acid. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flori, E.; Mastrofrancesco, A.; Ottaviani, M.; Maiellaro, M.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Camera, E. Desaturation of Sebaceous-Type Saturated Fatty Acids through the SCD1 and the FADS2 Pathways Impacts Lipid Neosynthesis and Inflammatory Response in Sebocytes in Culture. Exp. Dermatol. 2023, 32, 808–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.-R.; Shin, J.-M.; Kim, C.-H.; Kim, S.; Kim, C.-D.; Seo, Y.-J.; Lee, J.-H.; Im, M.; Lee, Y.; Lee, Y.H. Activation of NLRP3 Inflammasome by Palmitic Acid in Human Sebocytes. Ann. Dermatol. 2021, 33, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Törőcsik, D.; Fazekas, F.; Póliska, S.; Gregus, A.; Janka, E.A.; Dull, K.; Szegedi, A.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Kovács, D. Epidermal Growth Factor Modulates Palmitic Acid-Induced Inflammatory and Lipid Signaling Pathways in SZ95 Sebocytes. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 600017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.; Jin, M.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Lee, Y. Increased Lipid Accumulation under Hypoxia in SZ95 Human Sebocytes. Dermatology 2020, 237, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alestas, T.; Ganceviciene, R.; Fimmel, S.; Müller-Decker, K.; Zouboulis, C.C. Enzymes Involved in the Biosynthesis of Leukotriene B4 and Prostaglandin E2 Are Active in Sebaceous Glands. J. Mol. Med. 2006, 84, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dozsa, A.; Dezso, B.; Toth, B.I.; Bacsi, A.; Poliska, S.; Camera, E.; Picardo, M.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Bíró, T.; Schmitz, G.; et al. PPARγ-Mediated and Arachidonic Acid—Dependent Signaling Is Involved in Differentiation and Lipid Production of Human Sebocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 910–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Gao, M.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, R.; Liu, J.; Sun, S.; Li, S.; Hu, L.; Xiang, R.; Mo, R.; et al. TRPV3 Promotes Sebocyte Inflammation via Transcriptional Modulating TLR2 in Acne. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Basis Dis. 2024, 1870, 167195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossini, A.M.; Hou, X.; Exner, T.; Fauler, B.; Eberle, J.; Rabien, A.; Makrantonaki, E.; Zouboulis, C.C. Free Fatty Acids Induce Lipid Accumulation, Autophagy, and Apoptosis in Human Sebocytes. Ski. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2023, 36, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downing, D.T.; Stewart, M.E.; Wertz, P.W.; Strauss, J.S. Essential Fatty Acids and Acne. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1986, 14, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Wang, F.; He, L. Skin Barrier Dysfunction in Acne Vulgaris: Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Approaches. Med. Sci. Monit. 2024, 30, e945336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simard, M.; Tremblay, A.; Morin, S.; Martin, C.; Julien, P.; Fradette, J.; Flamand, N.; Pouliot, R. α-Linolenic Acid and Linoleic Acid Modulate the Lipidome and the Skin Barrier of a Tissue-Engineered Skin Model. Acta Biomater. 2022, 140, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, M.E.; Grahek, M.O.; Cambier, L.S.; Wertz, P.W.; Downing, D.T. Dilutional Effect of Increased Sebaceous Gland Activity on the Proportion of Linoleic Acid in Sebaceous Wax Esters and in Epidermal Acylceramides. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1986, 87, 733–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirdamadi, Y.; Thielitz, A.; Wiede, A.; Goihl, A.; Papakonstantinou, E.; Hartig, R.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Reinhold, D.; Simeoni, L.; Bommhardt, U.; et al. Insulin and Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 Can Modulate the Phosphoinositide-3-Kinase/Akt/FoxO1 Pathway in SZ95 Sebocytes in Vitro. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2015, 415, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capitanio, B.; Lora, V.; Ludovici, M.; Sinagra, J.-L.; Ottaviani, M.; Mastrofrancesco, A.; Ardigò, M.; Camera, E. Modulation of Sebum Oxidation and Interleukin-1α Levels Associates with Clinical Improvement of Mild Comedonal Acne. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2014, 28, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tochio, T.; Tanaka, H.; Nakata, S.; Ikeno, H. Accumulation of Lipid Peroxide in the Content of Comedones May Be Involved in the Progression of Comedogenesis and Inflammatory Changes in Comedones. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2009, 8, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottaviani, M.; Alestas, T.; Flori, E.; Mastrofrancesco, A.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Picardo, M. Peroxidated Squalene Induces the Production of Inflammatory Mediators in HaCaT Keratinocytes: A Possible Role in Acne Vulgaris. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2006, 126, 2430–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, K.; Yoshizawa, K.; Makino, I.; Kawakami, K.; Onoue, M. Comedogenicity of Squalene Monohydroperoxide in the Skin After Topical Application. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2000, 25, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saint-Leger, D.; Bague, A.; Cohen, E.; Lchivot, M. A Possible Role for Squalene in the Pathogenesis of Acne. I. In Vitro Study of Squalene Oxidation. Br. J. Dermatol. 1986, 114, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrault, C.; Garnier, J.; Pedretti, N.; Cordier-Dirikoc, S.; Ratineau, E.; Deguercy, A.; Bernard, F.-X. Androgens Induce Sebaceous Differentiation in Sebocyte Cells Expressing a Stable Functional Androgen Receptor. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 152, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imperato-McGinley, J.; Gautier, T.; Cai, L.Q.; Yee, B.; Epstein, J.; Pochi, P. The Androgen Control of Sebum Production. Studies of Subjects with Dihydrotestosterone Deficiency and Complete Androgen Insensitivity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1993, 76, 524–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tincello, D.G.; Saunders, P.T.; Hodgins, M.B.; Simpson, N.B.; Edwards, C.R.; Hargreaves, T.B.; Wu, F.C. Correlation of Clinical, Endocrine and Molecular Abnormalities with in Vivo Responses to High-Dose Testosterone in Patients with Partial Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome. Clin. Endocrinol. 1997, 46, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnik, B.C.; Schmitz, G. Role of Insulin, Insulin-like Growth Factor-1, Hyperglycaemic Food and Milk Consumption in the Pathogenesis of Acne Vulgaris. Exp. Dermatol. 2009, 18, 833–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Obermayer-Pietsch, B.; Hong, J.-B.; Melnik, B.; Yamasaki, O.; Dessinioti, C.; Ju, Q.; Liakou, A.; Al-Khuzaei, S.; Katsambas, A.; et al. Acne-Associated Syndromes: Models for Better Understanding of Acne Pathogenesis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2011, 25, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, R.; Pasupuletti, V.; Antonipillai, I. Androgen Induction of Steroid 5 Alpha-Reductase May Be Mediated via Insulin-like Growth Factor-I. Endocrinology 1993, 133, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Yanase, T.; Morinaga, H.; Okabe, T.; Nomura, M.; Daitoku, H.; Fukamizu, A.; Kato, S.; Takayanagi, R.; Nawata, H. Insulin-like Growth Factor 1/Insulin Signaling Activates Androgen Signaling through Direct Interactions of Foxo1 with Androgen Receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 7329–7338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Rosso, J.Q.; Kircik, L. The Primary Role of Sebum in the Pathophysiology of Acne Vulgaris and Its Therapeutic Relevance in Acne Management. J. Dermatolog. Treat. 2024, 35, 2296855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briganti, S.; Flori, E.; Mastrofrancesco, A.; Ottaviani, M. Acne as an Altered Dermato-Endocrine Response Problem. Exp. Dermatol. 2020, 29, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agamia, N.F.; Abdallah, D.M.; Sorour, O.; Mourad, B.; Younan, D.N. Skin Expression of Mammalian Target of Rapamycin and Forkhead Box Transcription Factor O1, and Serum Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 in Patients with Acne Vulgaris and Their Relationship with Diet. Br. J. Dermatol. 2016, 174, 1299–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappel, M.; Mauger, D.; Thiboutot, D. Correlation between Serum Levels of Insulin-like Growth Factor 1, Dehydroepiandrosterone Sulfate, and Dihydrotestosterone and Acne Lesion Counts in Adult Women. Arch. Dermatol. 2005, 141, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monfrecola, G.; Lembo, S.; Caiazzo, G.; De Vita, V.; Di Caprio, R.; Balato, A.; Fabbrocini, G. Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) Expression Is Increased in Acne Patients’ Skin. Exp. Dermatol. 2016, 25, 153–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Amitai, D.; Laron, Z. Effect of Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 Deficiency or Administration on the Occurrence of Acne. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2011, 25, 950–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meixiong, J.; Ricco, C.; Vasavda, C.; Ho, B.K. Diet and Acne: A Systematic Review. JAAD Int. 2022, 7, 95–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnik, B.C. Acne Transcriptomics: Fundamentals of Acne Pathogenesis and Isotretinoin Treatment. Cells 2023, 12, 2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clatici, V.G.; Voicu, C.; Voaides, C.; Roseanu, A.; Icriverzi, M.; Jurcoane, S. Diseases of Civilization—Cancer, Diabetes, Obesity and Acne—The Implication of Milk, IGF-1 and mTORC1. Maedica 2018, 13, 273–281. [Google Scholar]
- Melnik, B.C. Linking Diet to Acne Metabolomics, Inflammation, and Comedogenesis: An Update. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 8, 371–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.N.; Braue, A.; Varigos, G.A.; Mann, N.J. The Effect of a Low Glycemic Load Diet on Acne Vulgaris and the Fatty Acid Composition of Skin Surface Triglycerides. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2008, 50, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Törőcsik, D.; Kovács, D.; Camera, E.; Lovászi, M.; Cseri, K.; Nagy, G.G.; Molinaro, R.; Rühl, R.; Tax, G.; Szabó, K.; et al. Leptin Promotes a Proinflammatory Lipid Profile and Induces Inflammatory Pathways in Human SZ95 Sebocytes. Br. J. Dermatol. 2014, 171, 1326–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esler, W.P.; Tesz, G.J.; Hellerstein, M.K.; Beysen, C.; Sivamani, R.; Turner, S.M.; Watkins, S.M.; Amor, P.A.; Carvajal-Gonzalez, S.; Geoly, F.J.; et al. Human Sebum Requires de Novo Lipogenesis, Which Is Increased in Acne Vulgaris and Suppressed by Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase Inhibition. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaau8465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semenza, G.L. HIF-1 Mediates Metabolic Responses to Intratumoral Hypoxia and Oncogenic Mutations. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 3664–3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, J.G.; Li, X.M.; Lee, J.K.; Park, S.; Hong, D.; Jung, K.E.; Lee, Y.; Seo, Y.-J.; Kim, C.D.; Shin, J.-M.; et al. Azidothymidine Downregulates Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 Induced Lipogenesis by Suppressing Mitochondrial Biogenesis and Mitophagy in Immortalized Human Sebocytes. Ann. Dermatol. 2021, 33, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Huang, S.; Lu, S.; Liu, F.; Luo, X.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Shi, G. Paeoniflorin Mitigates Insulin-like Growth Factor 1-Induced Lipogenesis and Inflammation in Human Sebocytes by Inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/FoxO1 and JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathways. Nat. Prod. Bioprospect. 2024, 14, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.-M.; Kim, K.M.; Kim, C.D.; Lee, Y.; Park, S. The Possible Role of Yes-Associated Protein (YAP) on IGF-1-Induced Sebum Production. Exp. Dermatol. 2023, 32, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, D.; Feng, T.; Wang, C. Clinical Efficacy of Etonogestrel Implants on Relieving Dysmenorrhea in Endometriosis and Adenomyosis Women for up to 3 years. Front. Med. 2025, 12, 1460578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitano, T.; Koiwai, T.; Fujikawa, K.; Mori, S.; Matsumoto, T.; Sato, T. Ozenoxacin Suppresses Sebum Production by Inhibiting mTORC1 Activation in Differentiated Hamster Sebocytes. J. Dermatol. 2024, 51, 1187–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottaviani, M.; Flori, E.; Mastrofrancesco, A.; Briganti, S.; Lora, V.; Capitanio, B.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Picardo, M. Sebocyte Differentiation as a New Target for Acne Therapy: An In Vivo Experience. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34, 1803–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briganti, S.; Mosca, S.; Di Nardo, A.; Flori, E.; Ottaviani, M. New Insights into the Role of PPARγ in Skin Physiopathology. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camera, E.; Ludovici, M.; Tortorella, S.; Sinagra, J.-L.; Capitanio, B.; Goracci, L.; Picardo, M. Use of Lipidomics to Investigate Sebum Dysfunction in Juvenile Acne. J. Lipid Res. 2016, 57, 1051–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouboulis, C.C.; Ní Raghallaigh, S.; Schmitz, G.; Powell, F.C. The Pro-Differentiation Effect of Doxycycline on Human SZ95 Sebocytes. Dermatology 2020, 237, 792–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picardo, M.; Cardinali, C.; La Placa, M.; Lewartowska-Białek, A.; Lora, V.; Micali, G.; Montisci, R.; Morbelli, L.; Nova, A.; Parodi, A.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of N-Acetyl-GED-0507-34-LEVO Gel in Patients with Moderate-to Severe Facial Acne Vulgaris: A Phase IIb Randomized Double-Blind, Vehicle-Controlled Trial. Br. J. Dermatol. 2022, 187, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piacentini, F.; Camera, E.; Di Nardo, A.; Dell’Anna, M.L. Seborrheic Dermatitis: Exploring the Complex Interplay with Malassezia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borda, L.J.; Wikramanayake, T.C. Seborrheic Dermatitis and Dandruff: A Comprehensive Review. J. Clin. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 3, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, J.M.; Alexis, A.; Zirwas, M.; Taylor, S. Unmet Needs for Patients with Seborrheic Dermatitis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2024, 90, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, V.Y.; Leo, M.; Hassoun, L.; Chahal, D.S.; Maibach, H.I.; Sivamani, R.K. Role of Sebaceous Glands in Inflammatory Dermatoses. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2015, 73, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamloul, G.; Khachemoune, A. An Updated Review of the Sebaceous Gland and Its Role in Health and Diseases Part 2: Pathophysiological Clinical Disorders of Sebaceous Glands. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 34, e14862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, J.R.; Messenger, A.G.; Tosti, A.; Todd, G.; Hordinsky, M.; Hay, R.J.; Wang, X.; Zachariae, C.; Kerr, K.M.; Henry, J.P.; et al. A Comprehensive Pathophysiology of Dandruff and Seborrheic Dermatitis—Towards a More Precise Definition of Scalp Health. Acta Derm.-Venereol. 2013, 93, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adalsteinsson, J.A.; Kaushik, S.; Muzumdar, S.; Guttman-Yassky, E.; Ungar, J. An Update on the Microbiology, Immunology and Genetics of Seborrheic Dermatitis. Exp. Dermatol. 2020, 29, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeAngelis, Y.M.; Gemmer, C.M.; Kaczvinsky, J.R.; Kenneally, D.C.; Schwartz, J.R.; Dawson, T.L. Three Etiologic Facets of Dandruff and Seborrheic Dermatitis: Malassezia Fungi, Sebaceous Lipids, and Individual Sensitivity. J. Investig. Dermatol. Symp. Proc. 2005, 10, 295–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousel, J.; Nădăban, A.; Saghari, M.; Pagan, L.; Zhuparris, A.; Theelen, B.; Gambrah, T.; van der Wall, H.E.C.; Vreeken, R.J.; Feiss, G.L.; et al. Lesional Skin of Seborrheic Dermatitis Patients Is Characterized by Skin Barrier Dysfunction and Correlating Alterations in the Stratum Corneum Ceramide Composition. Exp. Dermatol. 2024, 33, e14952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ro, B.I.; Dawson, T.L. The Role of Sebaceous Gland Activity and Scalp Microfloral Metabolism in the Etiology of Seborrheic Dermatitis and Dandruff. J. Investig. Dermatol. Symp. Proc. 2005, 10, 194–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dessinioti, C.; Katsambas, A. Seborrheic Dermatitis: Etiology, Risk Factors, and Treatments:: Facts and Controversies. Clin. Dermatol. 2013, 31, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeAngelis, Y.M.; Saunders, C.W.; Johnstone, K.R.; Reeder, N.L.; Coleman, C.G.; Kaczvinsky, J.R.; Gale, C.; Walter, R.; Mekel, M.; Lacey, M.P.; et al. Isolation and Expression of a Malassezia Globosa Lipase Gene, LIP1. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 2138–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, S.N.; Kim, A.-R.; Kim, Y.R.; Kim, M.J.; Park, W.-S.; Lee, J.H.; Jung, W.H.; Lee, Y.W.; et al. Isolation and Identification of Malassezia Species from Chinese and Korean Patients with Seborrheic Dermatitis and in Vitro Studies on Their Bioactivity on Sebaceous Lipids and IL-8 Production. Mycoses 2016, 59, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijaz, N.; Fitzgerald, D. Seborrhoeic Dermatitis. Br. J. Hosp. Med. 2017, 78, C88–C91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsic Arsenijevic, V.S.; Milobratovic, D.; Barac, A.M.; Vekic, B.; Marinkovic, J.; Kostic, V.S. A Laboratory-Based Study on Patients with Parkinson’s Disease and Seborrheic Dermatitis: The Presence and Density of Malassezia Yeasts, Their Different Species and Enzymes Production. BMC Dermatol. 2014, 14, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, W.-H.; Anthonavage, M.; Pappas, A.; Rossetti, D.; Cavender, D.; Seiberg, M.; Eisinger, M. Melanocortin-5 Receptor and Sebogenesis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 660, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, M.; Nomura, T.; Miyachi, Y.; Kabashima, K. Eosinophilic Pustular Folliculitis: A Review of the Japanese Published Works. J. Dermatol. 2013, 40, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhou, X.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, M.; Yao, X.; Lu, J.; Hu, X. Clinical and Pathological Analysis of 10 Cases of Eosinophilic Pustular Folliculitis. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2023, 16, 2467–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, A.; Kobayashi, N.; Fukumoto, T.; Asada, H. A Case of Eosinophilic Pustular Folliculitis with Response to Infliximab. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2012, 67, e136–e137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagiwara, A.; Fujimura, T.; Furudate, S.; Kambayashi, Y.; Kagatani, S.; Aiba, S. Induction of CD163+ M2 Macrophages in the Lesional Skin of Eosinophilic Pustular Folliculitis. Acta Derm.-Venereol. 2014, 94, 104–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, A.; Doi, H.; Miyachi, Y.; Kabashima, K. Treatment of Eosinophilic Pustular Folliculitis with Ciclosporin: Suppression of mRNA Expression of IL-4 and IL-13. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2010, 24, 1489–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; Chiba, T.; Nakahara, T.; Furue, M. Upregulation of IL-36 Cytokines in Folliculitis and Eosinophilic Pustular Folliculitis. Australas. J. Dermatol. 2020, 61, e39–e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakahigashi, K.; Doi, H.; Otsuka, A.; Hirabayashi, T.; Murakami, M.; Urade, Y.; Tanizaki, H.; Egawa, G.; Miyachi, Y.; Kabashima, K. PGD2 Induces Eotaxin-3 via PPARγ from Sebocytes: A Possible Pathogenesis of Eosinophilic Pustular Folliculitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 129, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukamachi, S.; Kabashima, K.; Sugita, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Tokura, Y. Therapeutic Effectiveness of Various Treatments for Eosinophilic Pustular Folliculitis. Acta Derm.-Venereol. 2009, 89, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkin, J.; Dahl, M.; Detmar, M.; Drake, L.; Feinstein, A.; Odom, R.; Powell, F. Standard Classification of Rosacea: Report of the National Rosacea Society Expert Committee on the Classification and Staging of Rosacea. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2002, 46, 584–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, R.L.; Granstein, R.D.; Kang, S.; Mannis, M.; Steinhoff, M.; Tan, J.; Thiboutot, D. Standard Classification and Pathophysiology of Rosacea: The 2017 Update by the National Rosacea Society Expert Committee. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2018, 78, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, P.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Cao, Y.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Q. Exploring the Pathogenesis and Mechanism-Targeted Treatments of Rosacea: Previous Understanding and Updates. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Lee, S.B.; Heo, J.H.; Yoon, H.S.; Byun, J.W.; Choi, G.S.; Shin, J. Sebaceous Glands Participate in the Inflammation of Rosacea. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34, e144–e146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazier, W.; Zemtsov, R.K.; Yufei, G. Rosacea: Common Questions and Answers. Am. Fam. Physician 2024, 109, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Crawford, G.H.; Pelle, M.T.; James, W.D. Rosacea: I. Etiology, Pathogenesis, and Subtype Classification. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2004, 51, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shemer, A.; Gupta, A.K.; Kassem, R.; Sharon, N.; Quinlan, E.M.; Galili, E. Low-Dose Isotretinoin versus Minocycline in the Treatment of Rosacea. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 34, e14986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picosse, F.; Rocha, M.A.; Costa, C.S.; Enokihara, M.M.S.E.S.; Sanudo, A.; Bagatin, E. A Comparative Exploration of Immunohistochemical Markers in Patients with Papulopustular Rosacea Undergoing Treatment with Oral Isotretinoin versus Doxycycline. Int. J. Dermatol. 2025, 64, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assiri, A.; Hobani, A.H.; AlKaabi, H.A.; Mojiri, M.E.; Daghriri, S.A.; Suwaid, O.A.; Alameer, M.I.; Akkam, M.M.; Alamir, M.A.; Albarr, A.A.; et al. Efficacy of Low-Dose Isotretinoin in the Treatment of Rosacea: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cureus 2024, 16, e57085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, C.S.; Huang, W.W. Rosacea Pathogenesis. Dermatol. Clin. 2018, 36, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, R.S.Q.; Bourkas, A.N.; Mufti, A.; Sibbald, R.G. Rosacea: Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Correlates. J. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2024, 28, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnar, E.; Eustace, P.; Powell, F.C. The Demodex Mite Population in Rosacea. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1993, 28, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Hamblin, M.R.; Wen, X. Role of the Skin Microbiota and Intestinal Microbiome in Rosacea. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1108661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacey, N.; Russell-Hallinan, A.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Powell, F.C. Demodex Mites Modulate Sebocyte Immune Reaction: Possible Role in the Pathogenesis of Rosacea. Br. J. Dermatol. 2018, 179, 420–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, K.; Di Nardo, A.; Bardan, A.; Murakami, M.; Ohtake, T.; Coda, A.; Dorschner, R.A.; Bonnart, C.; Descargues, P.; Hovnanian, A.; et al. Increased Serine Protease Activity and Cathelicidin Promotes Skin Inflammation in Rosacea. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 975–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamasaki, K.; Kanada, K.; Macleod, D.T.; Borkowski, A.W.; Morizane, S.; Nakatsuji, T.; Cogen, A.L.; Gallo, R.L. TLR2 Expression Is Increased in Rosacea and Stimulates Enhanced Serine Protease Production by Keratinocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 688–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.-Y.; Yamasaki, K.; Rudsil, J.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Park, G.T.; Yang, J.-M.; Gallo, R.L. Sebocytes Express Functional Cathelicidin Antimicrobial Peptides and Can Act to Kill Propionibacterium Acnes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 1863–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovács, D.; Lovászi, M.; Póliska, S.; Oláh, A.; Bíró, T.; Veres, I.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Ståhle, M.; Rühl, R.; Remenyik, É.; et al. Sebocytes Differentially Express and Secrete Adipokines. Exp. Dermatol. 2016, 25, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovács, D.; Fazekas, F.; Oláh, A.; Törőcsik, D. Adipokines in the Skin and in Dermatological Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dajnoki, Z.; Béke, G.; Kapitány, A.; Mócsai, G.; Gáspár, K.; Rühl, R.; Hendrik, Z.; Juhász, I.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Bácsi, A.; et al. Sebaceous Gland-Rich Skin Is Characterized by TSLP Expression and Distinct Immune Surveillance Which Is Disturbed in Rosacea. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 1114–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drucker, A.M.; Wang, A.R.; Li, W.-Q.; Sevetson, E.; Block, J.K.; Qureshi, A.A. The Burden of Atopic Dermatitis: Summary of a Report for the National Eczema Association. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmela Avena-Woods, B.P. Overview of Atopic Dermatitis. Am. J. Manag. Care 2017, 23, S115–S123. [Google Scholar]
- Mayba, J.N.; Gooderham, M.J. Review of Atopic Dermatitis and Topical Therapies. J. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2017, 21, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maliyar, K.; Sibbald, C.; Pope, E.; Gary Sibbald, R. Diagnosis and Management of Atopic Dermatitis: A Review. Adv. Ski. Wound Care 2018, 31, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, R.; Wolf, D. Abnormal Epidermal Barrier in the Pathogenesis of Atopic Dermatitis. Clin. Dermatol. 2012, 30, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavel, P.; Blunder, S.; Moosbrugger-Martinz, V.; Elias, P.M.; Dubrac, S. Atopic Dermatitis: The Fate of the Fat. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Seok, J.K.; Kang, H.C.; Cho, Y.-Y.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, J.Y. Skin Barrier Abnormalities and Immune Dysfunction in Atopic Dermatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, L.A.; Cork, M.J.; Amagai, M.; De Benedetto, A.; Kabashima, K.; Hamilton, J.D.; Rossi, A.B. Type 2 Inflammation Contributes to Skin Barrier Dysfunction in Atopic Dermatitis. JID Innov. 2022, 2, 100131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flori, E.; Cavallo, A.; Mosca, S.; Kovacs, D.; Cota, C.; Zaccarini, M.; Di Nardo, A.; Bottillo, G.; Maiellaro, M.; Camera, E.; et al. JAK/STAT Inhibition Normalizes Lipid Composition in 3D Human Epidermal Equivalents Challenged with Th2 Cytokines. Cells 2024, 13, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, N.A.; Pirozzi, G.; Graham, N.M.H. Commonality of the IL-4/IL-13 Pathway in Atopic Diseases. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 13, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttman-Yassky, E.; Irvine, A.D.; Brunner, P.M.; Kim, B.S.; Boguniewicz, M.; Parmentier, J.; Platt, A.M.; Kabashima, K. The Role of Janus Kinase Signaling in the Pathology of Atopic Dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 152, 1394–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, A.; Nomura, T.; Mizuno, A.; Imokawa, G. Reevaluation of the Non-Lesional Dry Skin in Atopic Dermatitis by Acute Barrier Disruption: An Abnormal Permeability Barrier Homeostasis with Defective Processing to Generate Ceramide. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2014, 306, 427–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijaljica, D.; Townley, J.P.; Spada, F.; Harrison, I.P. The Heterogeneity and Complexity of Skin Surface Lipids in Human Skin Health and Disease. Prog. Lipid Res. 2024, 93, 101264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovászi, M.; Mattii, M.; Eyerich, K.; Gácsi, A.; Csányi, E.; Kovács, D.; Rühl, R.; Szegedi, A.; Kemény, L.; Ståhle, M.; et al. Sebum Lipids Influence Macrophage Polarization and Activation. Br. J. Dermatol. 2017, 177, 1671–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, H.; Gloor, M.; Stoika, D. Sebaceous Glands in Uninvolved Skin of Patients Suffering from Atopic Dermatitis. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 1981, 270, 167–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajka, G. Surface Lipid Estimation on the Back of the Hands in Atopic Dermatitis. Arch. Dermatol. Forsch. 1974, 251, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuichi, M.; Makino, T.; Matsunaga, K.; Hamade, E.; Yokoi, H.; Shimizu, T. The Usefulness of Sebum Check Film for Measuring the Secretion of Sebum. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2010, 302, 657–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sator, P.-G.; Schmidt, J.B.; Hönigsmann, H. Comparison of Epidermal Hydration and Skin Surface Lipids in Healthy Individuals and in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2003, 48, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firooz, A.; Gorouhi, F.; Davari, P.; Atarod, M.; Hekmat, S.; Rashighi-Firoozabadi, M.; Solhpour, A. Comparison of Hydration, Sebum and pH Values in Clinically Normal Skin of Patients with Atopic Dermatitis and Healthy Controls. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2007, 32, 321–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, X.; Chen, B.; Yin, H.; Gu, C.; Fang, X.; Zhu, R.; Yu, T.; Mi, W.; et al. A Dysregulated Sebum–Microbial Metabolite–IL-33 Axis Initiates Skin Inflammation in Atopic Dermatitis. J. Exp. Med. 2022, 219, e20212397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Qiu, Z.; Zhu, R.; Wang, S.; Gu, C.; Yao, X.; Li, W. Dysregulated Lipidome of Sebum in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis. Allergy 2023, 78, 1524–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liddell, K. A Familial Study of Acne and Eczema. Br. J. Dermatol. 1976, 94, 633–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thyssen, J.P.; Nymand, L.K.; Maul, J.-T.; Schmid-Grendelmeier, P.; Wu, J.J.; Thomsen, S.F.; Egeberg, A. Incidence, Prevalence and Risk of Acne in Adolescent and Adult Patients with Atopic Dermatitis: A Matched Cohort Study. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022, 36, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallo, A.; Camera, E.; Bottillo, G.; Maiellaro, M.; Truglio, M.; Marini, F.; Chavagnac-Bonneville, M.; Fauger, A.; Perrier, E.; Pigliacelli, F.; et al. Biosignatures of Defective Sebaceous Gland Activity in Sebum-Rich and Sebum-Poor Skin Areas in Adult Atopic Dermatitis. Exp. Dermatol. 2024, 33, e15066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T.; Kuwano, T.; Uehara, Y.; Yano, M.; Oya, N.; Takada, N.; Tanaka, S.; Ueda, Y.; Hachiya, A.; Takahashi, Y.; et al. Non-Invasive Human Skin Transcriptome Analysis Using mRNA in Skin Surface Lipids. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seiringer, P.; Hillig, C.; Schäbitz, A.; Jargosch, M.; Pilz, A.C.; Eyerich, S.; Szegedi, A.; Sochorová, M.; Gruber, F.; Zouboulis, C.C.; et al. Spatial Transcriptomics Reveals Altered Lipid Metabolism and Inflammation-Related Gene Expression of Sebaceous Glands in Psoriasis and Atopic Dermatitis. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1334844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Chinnappan, M.; Prestwood, C.A.; Edwards, M.; Artami, M.; Thompson, B.M.; Eckert, K.M.; Vale, G.; Zouboulis, C.C.; McDonald, J.G.; et al. Interleukins 4 and 13 Drive Lipid Abnormalities in Skin Cells through Regulation of Sex Steroid Hormone Synthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2100749118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumont, M.; Luu-The, V.; Dupont, E.; Pelletier, G.; Labrie, F. Characterization, Expression, and Immunohistochemical Localization of 3β-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase/Δ5-Δ4 Isomerase in Human Skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1992, 99, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sugita, K. Adipose Tissue Remodeling via TSLP-Mediated IL-4/IL-13 Signaling: Implications for Atopic Dermatitis and Skin Barrier. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2024, 154, 282–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choa, R.; Harris, J.C.; Yang, E.; Yokoyama, Y.; Okumura, M.; Kim, M.; To, J.; Lou, M.; Nelson, A.; Kambayashi, T. Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin Induces IL-4/IL-13 from T Cells to Promote Sebum Secretion and Adipose Loss. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2024, 154, 480–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.-J.; Huang, Y.-H.; Tsao, C.-H.; Hsieh, W.-C.; Lo, Y.-H.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Chen, H.-L.; Liu, F.-T. Galectin-12 Regulates Immune Responses in the Skin through Sebaceous Glands. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2023, 143, 2120–2131.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Maillet, I.; Mackowiak, C.; Viala, C.; Di Padova, F.; Li, M.; Togbe, D.; Quesniaux, V.; Lai, Y.; Ryffel, B. Experimental Atopic Dermatitis Depends on IL-33R Signaling via MyD88 in Dendritic Cells. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molofsky, A.B.; Savage, A.; Locksley, R.M. Interleukin-33 in Tissue Homeostasis, Injury and Inflammation. Immunity 2015, 42, 1005–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehncke, W.-H.; Schön, M.P. Psoriasis. Lancet 2015, 386, 983–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, C.E.M.; Armstrong, A.W.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; Barker, J.N.W.N. Psoriasis. Lancet 2021, 397, 1301–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, A.W.; Read, C. Pathophysiology, Clinical Presentation, and Treatment of Psoriasis: A Review. JAMA 2020, 323, 1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkes, J.E.; Chan, T.C.; Krueger, J.G. Psoriasis Pathogenesis and the Development of Novel, Targeted Immune Therapies. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drakou, K.; Tsianni, A.; Vrani, F.; Kefala, V.; Rallis, E. Revealing the Correlation between Altered Skin Lipids Composition and Skin Disorders. Cosmetics 2021, 8, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liakou, A.I.; Nyengaard, J.R.; Bonovas, S.; Knolle, J.; Makrantonaki, E.; Zouboulis, C.C. Marked Reduction of the Number and Individual Volume of Sebaceous Glands in Psoriatic Lesions. Dermatology 2016, 232, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittié, L.; Tejasvi, T.; Harms, P.W.; Xing, X.; Nair, R.P.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; Swindell, W.R.; Elder, J.T. Sebaceous Gland Atrophy in Psoriasis: An Explanation for Psoriatic Alopecia? J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 1792–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hau, C.S.; Kanda, N.; Noda, S.; Tatsuta, A.; Kamata, M.; Shibata, S.; Asano, Y.; Sato, S.; Watanabe, S.; Tada, Y. Visfatin Enhances the Production of Cathelicidin Antimicrobial Peptide, Human β-Defensin-2, Human β-Defensin-3, and S100A7 in Human Keratinocytes and Their Orthologs in Murine Imiquimod-Induced Psoriatic Skin. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 182, 1705–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guet-Revillet, H.; Coignard-Biehler, H.; Jais, J.-P.; Quesne, G.; Frapy, E.; Poirée, S.; Le Guern, A.-S.; Le Flèche-Matéos, A.; Hovnanian, A.; Consigny, P.-H.; et al. Bacterial Pathogens Associated with Hidradenitis Suppurativa, France. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1990–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Duca, E.; Morelli, P.; Bennardo, L.; Di Raimondo, C.; Nisticò, S.P. Cytokine Pathways and Investigational Target Therapies in Hidradenitis Suppurativa. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scala, E.; Cacciapuoti, S.; Garzorz-Stark, N.; Megna, M.; Marasca, C.; Seiringer, P.; Volz, T.; Eyerich, K.; Fabbrocini, G. Hidradenitis Suppurativa: Where We Are and Where We Are Going. Cells 2021, 10, 2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napolitano, M.; Megna, M.; Timoshchuk, E.A.; Patruno, C.; Balato, N.; Fabbrocini, G.; Monfrecola, G. Hidradenitis Suppurativa: From Pathogenesis to Diagnosis and Treatment. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 10, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melnik, B.C.; Plewig, G. Impaired Notch-MKP-1 Signalling in Hidradenitis Suppurativa: An Approach to Pathogenesis by Evidence from Translational Biology. Exp. Dermatol. 2013, 22, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vossen, A.R.J.V.; Ardon, C.B.; van der Zee, H.H.; Lubberts, E.; Prens, E.P. The Anti-inflammatory Potency of Biologics Targeting Tumour Necrosis Factor-α, Interleukin (IL)-17A, IL-12/23 and CD20 in Hidradenitis Suppurativa: An Ex Vivo Study. Br. J. Dermatol. 2019, 181, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.; Alhusayen, R.; Amini-Nik, S. The Critical Role of Macrophages in the Pathogenesis of Hidradenitis Suppurativa. Inflamm. Res. 2017, 66, 931–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, J.; Le Jan, S.; Muller, C.; François, C.; Renard, Y.; Durlach, A.; Bernard, P.; Reguiai, Z.; Antonicelli, F. Matrix Remodelling and MMP Expression/Activation Are Associated with Hidradenitis Suppurativa Skin Inflammation. Exp. Dermatol. 2019, 28, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Lin, M.-H.; Tian, X.; Cheng, H.-T.; Gridley, T.; Shen, J.; Kopan, R. γ-Secretase Functions through Notch Signaling to Maintain Skin Appendages but Is Not Required for Their Patterning or Initial Morphogenesis. Dev. Cell 2004, 7, 731–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamp, S.; Fiehn, A.M.; Stenderup, K.; Rosada, C.; Pakkenberg, B.; Kemp, K.; Dam, T.N.; Jemec, G.B. Hidradenitis Suppurativa: A Disease of the Absent Sebaceous Gland? Sebaceous Gland Number and Volume Are Significantly Reduced in Uninvolved Hair Follicles from Patients with Hidradenitis Suppurativa. Br. J. Dermatol. 2011, 164, 1017–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, S.; Niessen, M.T.; Prox, J.; Lüllmann-Rauch, R.; Schmitz, A.; Schwanbeck, R.; Blobel, C.P.; Jorissen, E.; de Strooper, B.; Niessen, C.M.; et al. The Disintegrin/Metalloproteinase Adam10 Is Essential for Epidermal Integrity and Notch-Mediated Signaling. Development 2011, 138, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbrocini, G.; De Vita, V.; Donnarumma, M.; Russo, G.; Monfrecola, G. South Italy: A Privileged Perspective to Understand the Relationship between Hidradenitis Suppurativa and Overweight/Obesity. Ski. Appendage Disord. 2016, 2, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A.; Birabaharan, M.; Strunk, A. Prevalence of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus among Patients with Hidradenitis Suppurativa in the United States. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2018, 79, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivanand, A.; Gulliver, W.P.; Josan, C.K.; Alhusayen, R.; Fleming, P.J. Weight Loss and Dietary Interventions for Hidradenitis Suppurativa: A Systematic Review. J. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2020, 24, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balato, A.; Caiazzo, G.; Annunziata, M.C.; Marasca, C.; Scala, E.; Cacciapuoti, S.; Fabbrocini, G. Anti-TNF-α Therapy Modulates mTORC1 Signalling in Hidradenitis Suppurativa. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2019, 33, e43–e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitriev, A.; König, A.; Lang, V.; Diehl, S.; Kaufmann, R.; Pinter, A.; Buerger, C. mTORC1—A Potential Player in the Pathogenesis of Hidradenitis Suppurativa? J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2021, 35, e444–e447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marasca, C.; Balato, A.; Annunziata, M.C.; Cacciapuoti, S.; Fabbrocini, G. Insulin Resistance, mTOR and Hidradenitis Suppurativa. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2019, 33, e106–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouboulis, C.C.; Nogueira da Costa, A.; Makrantonaki, E.; Hou, X.X.; Almansouri, D.; Dudley, J.T.; Edwards, H.; Readhead, B.; Balthasar, O.; Jemec, G.B.E.; et al. Alterations in Innate Immunity and Epithelial Cell Differentiation Are the Molecular Pillars of Hidradenitis Suppurativa. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34, 846–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Hu, Z.; Lone, A.G.; Artami, M.; Edwards, M.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Stein, M.; Harris-Tryon, T.A. Small Proline-Rich Proteins (SPRRs) Are Epidermally Produced Antimicrobial Proteins That Defend the Cutaneous Barrier by Direct Bacterial Membrane Disruption. eLife 2022, 11, e76729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espósito, A.C.C.; Cassiano, D.P.; da Silva, C.N.; Lima, P.B.; Dias, J.A.F.; Hassun, K.; Bagatin, E.; Miot, L.D.B.; Miot, H.A. Update on Melasma—Part I: Pathogenesis. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 12, 1967–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.; Pan, R.; Meng, X.; Liu, T.; Zhong, H.; Chen, N.; Xu, Y. What Lies behind Melasma: A Review of the Related Skin Microenvironment. Int. J. Dermatol. 2025, 64, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.-H.; Na, J.-I.; Choi, J.-Y.; Park, K.-C. Melasma: Updates and Perspectives. Exp. Dermatol. 2019, 28, 704–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passeron, T.; Picardo, M. Melasma, a Photoaging Disorder. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2018, 31, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.C.; Park, T.J.; Kang, H.Y. Skin-Aging Pigmentation: Who Is the Real Enemy? Cells 2022, 11, 2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, S.-H.; Hwang, Y.-J.; Lee, S.-K.; Park, K.-C. Heterogeneous Pathology of Melasma and Its Clinical Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Barrera, R.; Torres-Alvarez, B.; Castanedo-Cazares, J.P.; Oros-Ovalle, C.; Moncada, B. Solar Elastosis and Presence of Mast Cells as Key Features in the Pathogenesis of Melasma. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2008, 33, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Álvarez, B.; Mesa-Garza, I.G.; Castanedo-Cázares, J.P.; Fuentes-Ahumada, C.; Oros-Ovalle, C.; Navarrete-Solis, J.; Moncada, B. Histochemical and Immunohistochemical Study in Melasma: Evidence of Damage in the Basal Membrane. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 2011, 33, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukari, F.; Jourdan, E.; Fontas, E.; Montaudié, H.; Castela, E.; Lacour, J.-P.; Passeron, T. Prevention of Melasma Relapses with Sunscreen Combining Protection against UV and Short Wavelengths of Visible Light: A Prospective Randomized Comparative Trial. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2015, 72, 189–190.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duteil, L.; Cardot-Leccia, N.; Queille-Roussel, C.; Maubert, Y.; Harmelin, Y.; Boukari, F.; Ambrosetti, D.; Lacour, J.-P.; Passeron, T. Differences in Visible Light-Induced Pigmentation According to Wavelengths: A Clinical and Histological Study in Comparison with UVB Exposure. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2014, 27, 822–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handel, A.C.; Lima, P.B.; Tonolli, V.M.; Miot, L.D.B.; Miot, H.A. Risk Factors for Facial Melasma in Women: A Case–Control Study. Br. J. Dermatol. 2014, 171, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zeng, J.; Lu, J. Mechanisms of Ultraviolet-Induced Melasma Formation: A Review. J. Dermatol. 2022, 49, 1201–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, J.W.; Park, I.S.; Choi, G.S.; Shin, J. Role of Fibroblast-Derived Factors in the Pathogenesis of Melasma. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2016, 41, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, K.; Fujiwara, R.; Sato, K.; Shin, J.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, M.; Kang, H.Y. Possible Involvement of Keratinocyte Growth Factor in the Persistence of Hyperpigmentation in Both Human Facial Solar Lentigines and Melasma. Ann. Dermatol. 2015, 27, 626–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, R.; Dhatwalia, S.k.; Kumar, R.; Rani, S.; Parsad, D. Emerging Role of Dermal Compartment in Skin Pigmentation: Comprehensive Review. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34, 2757–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Viennet, C.; Robin, S.; Berthon, J.-Y.; He, L.; Humbert, P. Precise Role of Dermal Fibroblasts on Melanocyte Pigmentation. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2017, 88, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolognia, J.L.; Pawelek, J.M. Biology of Hypopigmentation. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1988, 19, 217–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picardo, M.; Zompetta, C.; De Luca, C.; Cirone, M.; Faggioni, A.; Nazzaro-Porro, M.; Passi, S.; Prota, G. Role of Skin Surface Lipids in UV-Induced Epidermal Cell Changes. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 1991, 283, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foolad, N.; Shi, V.Y.; Prakash, N.; Kamangar, F.; Sivamani, R.K. The Association of the Sebum Excretion Rate with Melasma, Erythematotelangiectatic Rosacea, and Rhytides. Dermatol. Online J. 2015, 21, 13030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, F.; Marchetti-Deschmann, M.; Kremslehner, C.; Schosserer, M. The Skin Epilipidome in Stress, Aging, and Inflammation. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 11, 607076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohli, J.; Wang, B.; Brandenburg, S.M.; Basisty, N.; Evangelou, K.; Varela-Eirin, M.; Campisi, J.; Schilling, B.; Gorgoulis, V.; Demaria, M. Algorithmic Assessment of Cellular Senescence in Experimental and Clinical Specimens. Nat. Protoc. 2021, 16, 2471–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narzt, M.-S.; Pils, V.; Kremslehner, C.; Nagelreiter, I.-M.; Schosserer, M.; Bessonova, E.; Bayer, A.; Reifschneider, R.; Terlecki-Zaniewicz, L.; Waidhofer-Söllner, P.; et al. Epilipidomics of Senescent Dermal Fibroblasts Identify Lysophosphatidylcholines as Pleiotropic Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP) Factors. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 141, 993–1006.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
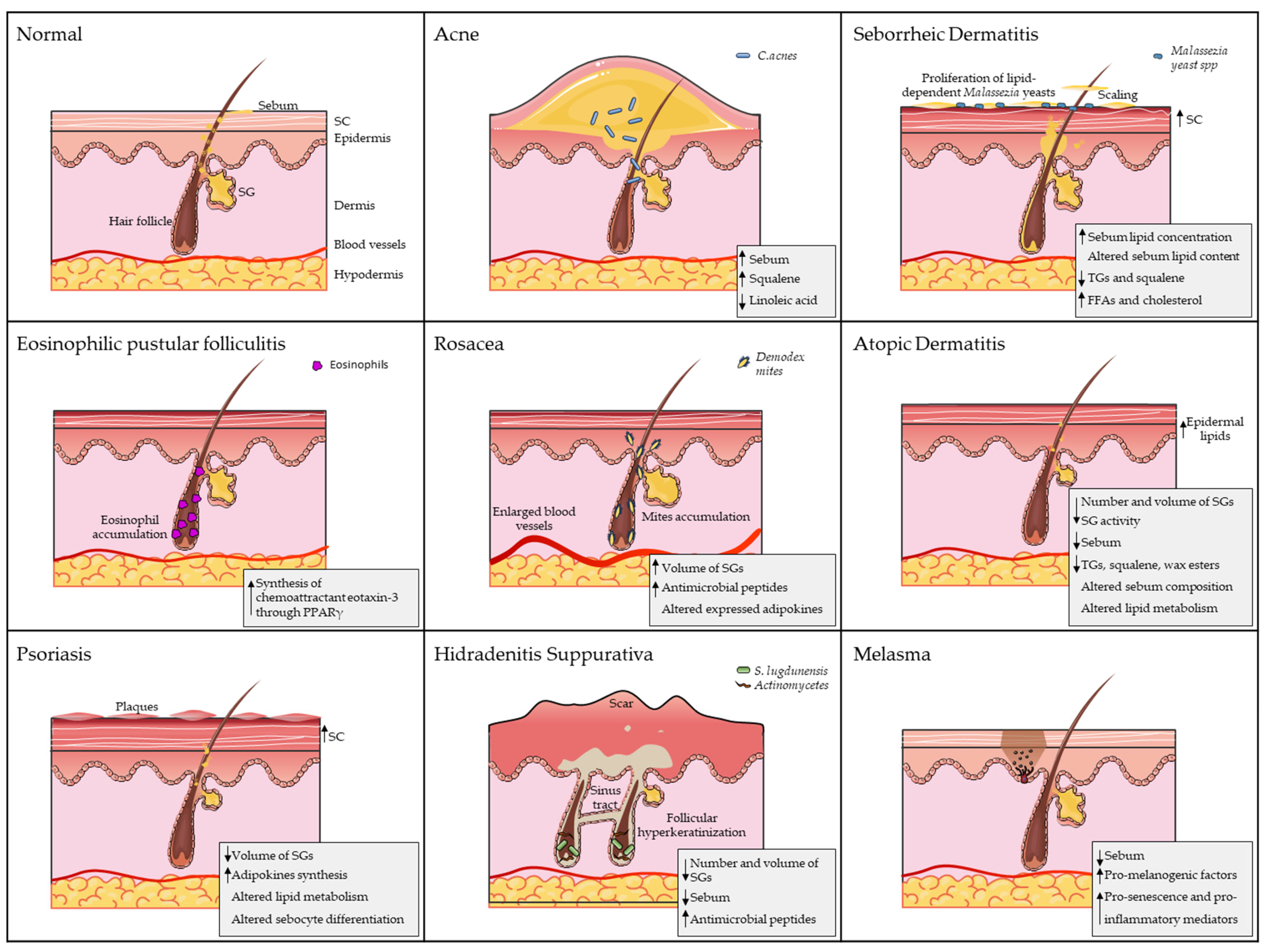
| Skin Condition | SG-Related Pathological Features | References |
|---|---|---|
| Acne | -sebum overproduction -C. acnes overgrowth -qualitative sebum changes (linoleic acid decrease, squalene, squalene peroxides, and sapienic acid increase) -inflammatory process -insulin/IGF-1 axis involvement | [38,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,59,77,78,79,80,81,82,86,94,109] |
| Seborrheic dermatitis | -sebum overproduction -Malassezia yeast spp. overgrowth -qualitative sebum changes (oleic acid and arachidonic acid surplus) -inflammatory process | [114,115,116,117,118,119,120,121,123,125,126] |
| Eosinophilic pustular folliculitis | -eosinophilic chemoattractant eotaxin-3 increase -PPARγ involvement | [133,134,135,136,137] |
| Rosacea | -SG hyperplasia -pro-inflammatory mediators upregulation (cathelicidin peptides) -adipokine altered presence | [149,150,151,152,153,154,155,156,157] |
| Atopic Dermatitis | -SG number and volume reduction -SG reduced activity -sebum reduced production -qualitative sebum changes (triglycerides and squalene decrease) -alteration of lipid metabolism-related gene expression -inflammatory process -3β-HSD1 involvement | [172,173,174,175,176,177,178,181,182,183,184,185,186,187,188] |
| Psoriasis | -SG volume reduction -sebocyte altered differentiation -inflammatory process -adipokine production | [183,194,195,196,197,198] |
| Hidradenitis suppurativa | -SG number and volume reduction -sebum reduced production -antimicrobial peptides overproduction -Notch signalling impairment | [203,207,208,209,217] |
| Melasma | -sebum reduced production -production of pro-melanogenic factors -production of pro-inflammatory and SASP factors | [47,48,49,155,235,236] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mosca, S.; Ottaviani, M.; Briganti, S.; Di Nardo, A.; Flori, E. The Sebaceous Gland: A Key Player in the Balance Between Homeostasis and Inflammatory Skin Diseases. Cells 2025, 14, 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14100747
Mosca S, Ottaviani M, Briganti S, Di Nardo A, Flori E. The Sebaceous Gland: A Key Player in the Balance Between Homeostasis and Inflammatory Skin Diseases. Cells. 2025; 14(10):747. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14100747
Chicago/Turabian StyleMosca, Sarah, Monica Ottaviani, Stefania Briganti, Anna Di Nardo, and Enrica Flori. 2025. "The Sebaceous Gland: A Key Player in the Balance Between Homeostasis and Inflammatory Skin Diseases" Cells 14, no. 10: 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14100747
APA StyleMosca, S., Ottaviani, M., Briganti, S., Di Nardo, A., & Flori, E. (2025). The Sebaceous Gland: A Key Player in the Balance Between Homeostasis and Inflammatory Skin Diseases. Cells, 14(10), 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14100747






