In Vivo Effects of Bay 11-7082 on Fibroid Growth and Gene Expression: A Preclinical Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fibroid Specimens Collection
2.2. Fibroid Animal Model
2.3. Blood Chemistry Panel
2.4. RNA Sequencing and Bioinformatic Analysis
2.5. Quantitative RT-PCR
2.6. Immunoblotting
2.7. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
2.8. Immunohistochemistry
2.9. Fibroid Explant Culture
2.10. Statistics
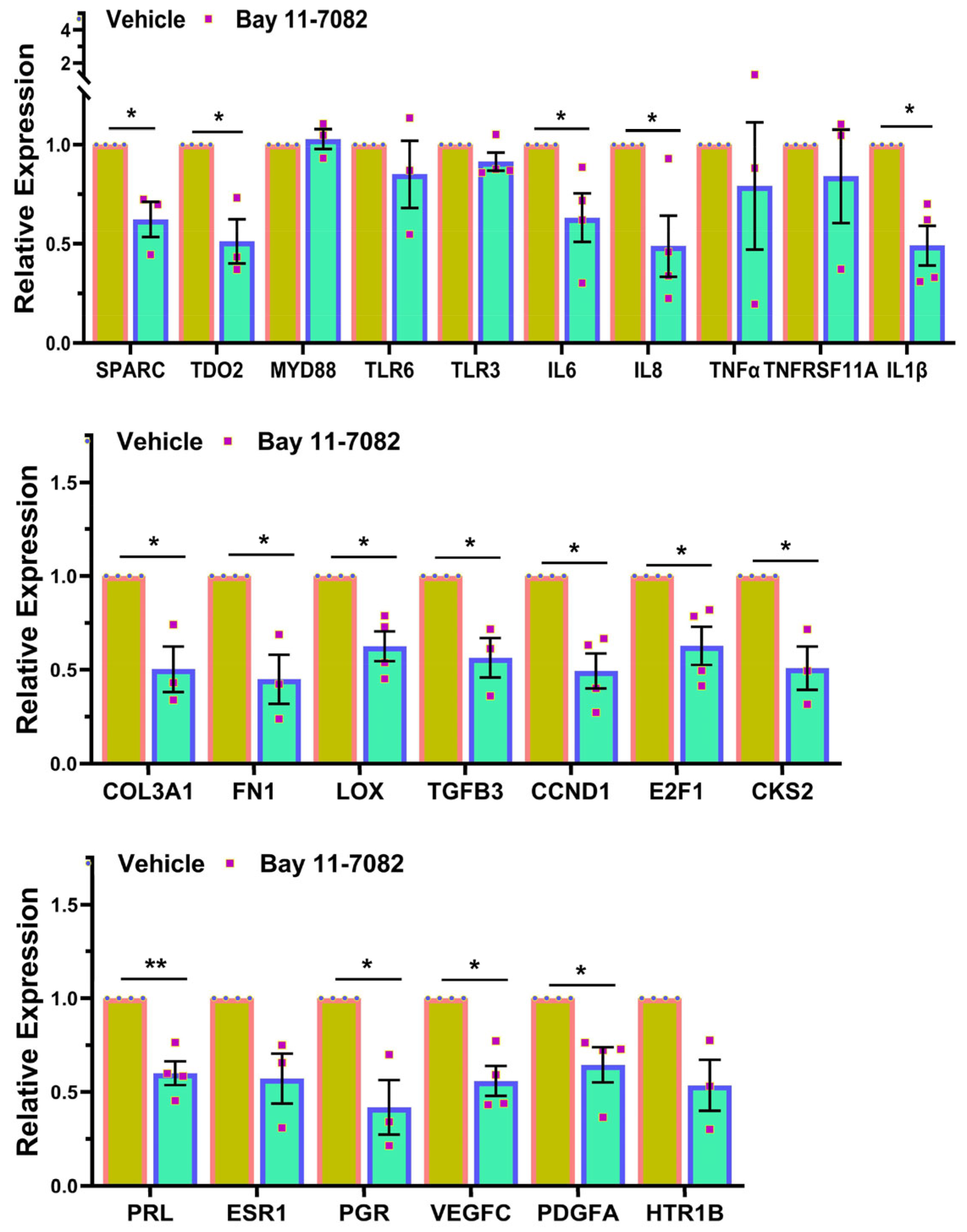
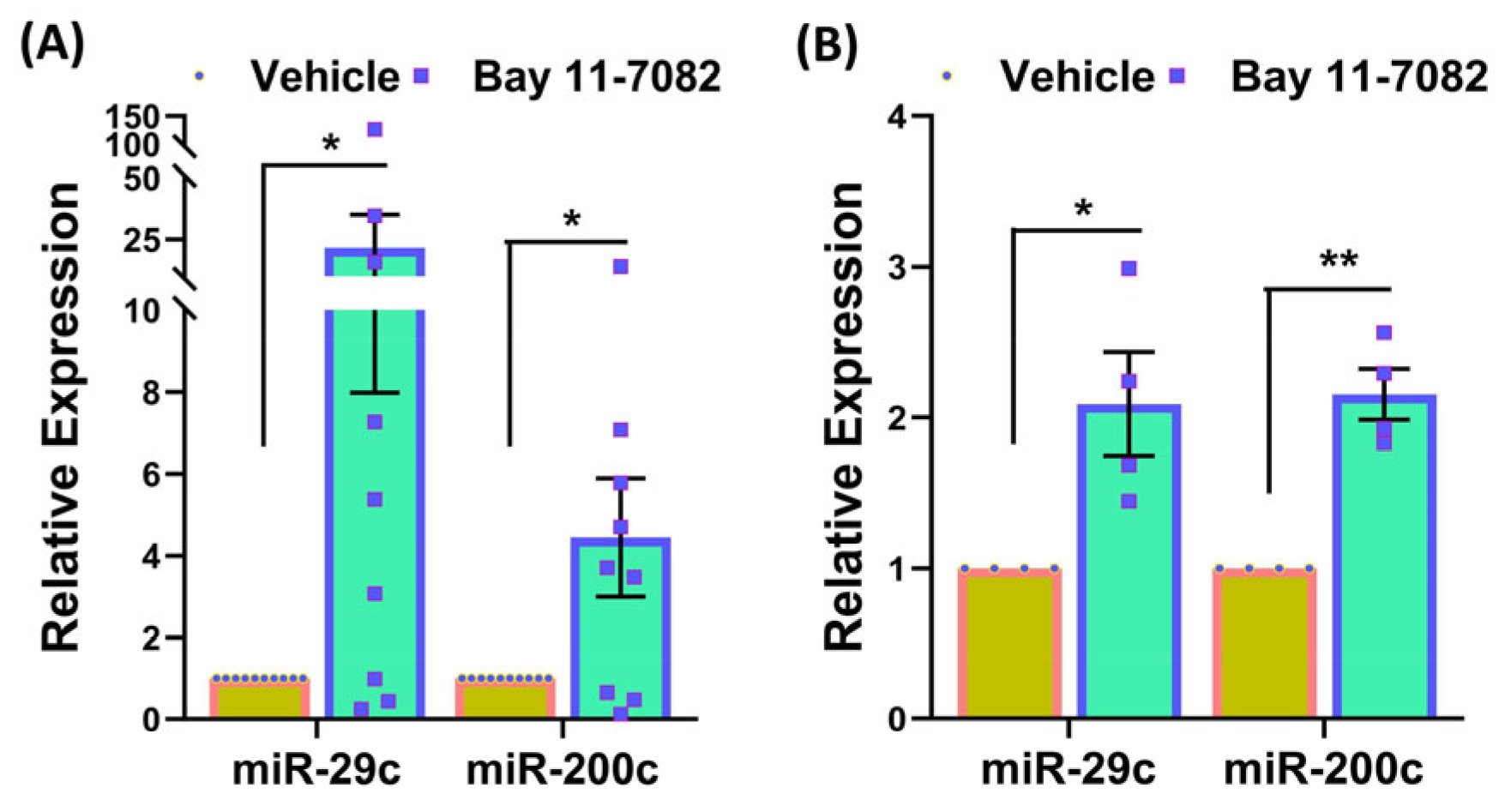
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baranov, V.S.; Osinovskaya, N.S.; Yarmolinskaya, M.I. Pathogenomics of Uterine Fibroids Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, F.M.; Bloise, E.; Ortiga-Carvalho, T.M. Hormones and pathogenesis of uterine fibroids. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2016, 34, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chegini, N. Proinflammatory and profibrotic mediators: Principal effectors of leiomyoma development as a fibrotic disorder. Semin. Reprod. Med. 2010, 28, 180–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konenkov, V.I.; Koroleva, E.G.; Orlov, N.B.; Prokof’ev, V.F.; Shevchenko, A.V.; Novikov, A.M.; Dergacheva, T.I. Blood Serum Levels of Proinflammatory Cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, TNFα, IL-8, IL-12p70, and IFNγ) in Patients with Uterine Myoma. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2018, 165, 698–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orciani, M.; Caffarini, M.; Biagini, A.; Lucarini, G.; Delli Carpini, G.; Berretta, A.; Di Primio, R.; Ciavattini, A. Chronic Inflammation May Enhance Leiomyoma Development by the Involvement of Progenitor Cells. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 2018, 1716246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zannotti, A.; Greco, S.; Pellegrino, P.; Giantomassi, F.; Delli Carpini, G.; Goteri, G.; Ciavattini, A.; Ciarmela, P. Macrophages and Immune Responses in Uterine Fibroids. Cells 2021, 10, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramadass, V.; Vaiyapuri, T.; Tergaonkar, V. Small Molecule NF-κB Pathway Inhibitors in Clinic. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.C. NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2017, 2, 17023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, K.; Karin, M. NF-κB, inflammation, immunity and cancer: Coming of age. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, T.D.; Khorram, O. Mechanisms underlying aberrant expression of miR-29c in uterine leiomyoma. Fertil. Steril. 2016, 105, 236–245.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, T.D.; Khorram, O. miR-200c Regulates IL8 Expression by Targeting IKBKB: A Potential Mediator of Inflammation in Leiomyoma Pathogenesis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlAshqar, A.; Reschke, L.; Kirschen, G.W.; Borahay, M.A. Role of inflammation in benign gynecologic disorders: From pathogenesis to novel therapies. Biol. Reprod. 2021, 105, 7–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahid, A.; Li, B.; Kombe, A.J.K.; Jin, T.; Tao, J. Pharmacological Inhibitors of the NLRP3 Inflammasome. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Rhee, M.H.; Kim, E.; Cho, J.Y. BAY 11-7082 is a broad-spectrum inhibitor with anti-inflammatory activity against multiple targets. Mediat. Inflamm. 2012, 2012, 416036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.L.; Sun, C.M. BAY-11-7082 induces apoptosis of multiple myeloma U266 cells through inhibiting NF-κB pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 2564–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, M.G.; Alaniz, L.; Lopes, E.C.; Blanco, G.; Hajos, S.E.; Alvarez, E. Inhibition of NF-kappaB activity by BAY 11-7082 increases apoptosis in multidrug resistant leukemic T-cell lines. Leuk. Res. 2005, 29, 1425–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, T.D.; Ton, N.; Rysling, S.; Quintanilla, D.; Boos, D.; Gao, J.; McSwiggin, H.; Yan, W.; Khorram, O. The Influence of Race/Ethnicity on the Transcriptomic Landscape of Uterine Fibroids. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, T.D.; Gao, J.; Quintanilla, D.; McSwiggin, H.; Boos, D.; Yan, W.; Khorram, O. Differential Expression of MED12-Associated Coding RNA Transcripts in Uterine Leiomyomas. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, T.D.; Ton, N.; Rysling, S.; Boos, D.; Khorram, O. The Effect of Race/Ethnicity and MED12 Mutation on the Expression of Long Non-Coding RNAs in Uterine Leiomyoma and Myometrium. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, T.D.; Ton, N.; Rysling, S.; Quintanilla, D.; Boos, D.; Khorram, O. Therapeutic effects of in vivo administration of an inhibitor of tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase (680c91) for the treatment of fibroids: A preclinical study. Fertil. Steril. 2024, 121, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, T.D.; Ton, N.; Manrique, N.; Rysling, S.; Khorram, O. Targeting the long non-coding RNA MIAT for the treatment of fibroids in an animal model. Clin. Sci. 2024, 138, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewan, M.Z.; Terashima, K.; Taruishi, M.; Hasegawa, H.; Ito, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Mori, N.; Sata, T.; Koyanagi, Y.; Maeda, M.; et al. Rapid tumor formation of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1-infected cell lines in novel NOD-SCID/gammac(null) mice: Suppression by an inhibitor against NF-kappaB. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 5286–5294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, T.D.; Munoz, L.; Quintanilla, D.; Boos, D.; Khorram, O. Therapeutic Effects of Long-Term Administration of Tranilast in an Animal Model for the Treatment of Fibroids. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, A.; Duitama, C.; Metge, F.; Rosskopp, D.; Boucas, J. Flaski. Flaski (3.12.2). Zenodo 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Franceschini, A.; Wyder, S.; Forslund, K.; Heller, D.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Roth, A.; Santos, A.; Tsafou, K.P.; et al. STRING v10: Protein-protein interaction networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D447–D452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, T.D.; Quintanilla, D.; Boos, D.; Khorram, O. Differential Expression of Super-Enhancer-Associated Long Non-coding RNAs in Uterine Leiomyomas. Reprod. Sci. 2022, 29, 2960–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, T.-D.; Khorram, O. Cross-talk between miR-29c and transforming growth factor-β3 is mediated by an epigenetic mechanism in leiomyoma. Fertil. Steril. 2019, 112, 1180–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, T.D.; Quintanilla, D.; Boos, D.; Khorram, O. Long Noncoding RNA MIAT Modulates the Extracellular Matrix Deposition in Leiomyomas by Sponging MiR-29 Family. Endocrinology 2021, 162, bqab186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, T.D.; Quintanilla, D.; Boos, D.; Khorram, O. Tryptophan catabolism is dysregulated in leiomyomas. Fertil. Steril. 2021, 116, 1160–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, T.D.; Quintanilla, D.; Boos, D.; Khorram, O. Further characterization of tryptophan metabolism and its dysregulation in fibroids. F S Sci. 2022, 3, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klavert, J.; van der Eerden, B.C.J. Fibronectin in Fracture Healing: Biological Mechanisms and Regenerative Avenues. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 663357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deguine, J.; Barton, G.M. MyD88: A central player in innate immune signaling. F1000Prime Rep. 2014, 6, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borahay, M.A.; Asoglu, M.R.; Mas, A.; Adam, S.; Kilic, G.S.; Al-Hendy, A. Estrogen Receptors and Signaling in Fibroids: Role in Pathobiology and Therapeutic Implications. Reprod. Sci. 2017, 24, 1235–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.J.; Sefton, E.C. The role of progesterone signaling in the pathogenesis of uterine leiomyoma. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2012, 358, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiMauro, A.; Seger, C.; Minor, B.; Amitrano, A.M.; Okeke, I.; Taya, M.; Rackow, A.R.; Kumar, D.; Kottman, R.M.; Bhagavath, B.; et al. Prolactin is Expressed in Uterine Leiomyomas and Promotes Signaling and Fibrosis in Myometrial Cells. Reprod. Sci. 2022, 29, 2525–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, R.A.; Mora, S.; Diehl, T.; Rhoades, A.R.; Stewart, E.A. Prolactin is an autocrine or paracrine growth factor for human myometrial and leiomyoma cells. Gynecol. Obstet. Investig. 1999, 48, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cetin, E.; Al-Hendy, A.; Ciebiera, M. Non-hormonal mediators of uterine fibroid growth. Curr. Opin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 32, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentry, C.C.; Okolo, S.O.; Fong, L.F.; Crow, J.C.; Maclean, A.B.; Perrett, C.W. Quantification of vascular endothelial growth factor-A in leiomyomas and adjacent myometrium. Clin. Sci. 2001, 101, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, S.; Wang, Z. Expression and functional analysis of platelet-derived growth factor in uterine leiomyomata. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2006, 5, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolcet, X.; Llobet, D.; Pallares, J.; Matias-Guiu, X. NF-kB in development and progression of human cancer. Virchows Arch. 2005, 446, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Dutta, J.; Gupta, N.; Fan, G.; Gélinas, C. Regulation of programmed cell death by NF-kappaB and its role in tumorigenesis and therapy. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2008, 615, 223–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verzella, D.; Pescatore, A.; Capece, D.; Vecchiotti, D.; Ursini, M.V.; Franzoso, G.; Alesse, E.; Zazzeroni, F. Life, death, and autophagy in cancer: NF-κB turns up everywhere. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, S.; Saghari, S.; Bassiri, F.; Raesi, R.; Zarrabi, A.; Hushmandi, K.; Sethi, G.; Tergaonkar, V. NF-κB as a regulator of cancer metastasis and therapy response: A focus on epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Cell. Physiol. 2022, 237, 2770–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, D.W.; Huang, L.R.; Chen, Y.W.; Huang, C.F.; Chuang, T.H. Interplay between Inflammation and Stemness in Cancer Cells: The Role of Toll-Like Receptor Signaling. J. Immunol. Res. 2016, 2016, 4368101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhang, J.; Arfuso, F.; Chinnathambi, A.; Zayed, M.E.; Alharbi, S.A.; Kumar, A.P.; Ahn, K.S.; Sethi, G. NF-κB in cancer therapy. Arch. Toxicol. 2015, 89, 711–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, T.D.; Khorram, O. Regulation of Cell Cycle Regulatory Proteins by MicroRNAs in Uterine Leiomyoma. Reprod. Sci. 2019, 26, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, B.; Abeler, V.M.; Hellesylt, E.; Holth, A.; Shih Ie, M.; Skeie-Jensen, T.; Chen, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, T.L. Gene expression signatures differentiate uterine endometrial stromal sarcoma from leiomyosarcoma. Gynecol. Oncol. 2013, 128, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Levine, A.J. p53 and E2F-1 cooperate to mediate apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 3602–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, H.; Lin, H.; Zhang, Z. CKS2 in human cancers: Clinical roles and current perspectives (Review). Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 3, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Ruan, Y.; Wang, X.; Min, L.; Shen, Z.; Sun, Y.; Qin, X. BAY 11-7082, a nuclear factor-kappaB inhibitor, induces apoptosis and S phase arrest in gastric cancer cells. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 49, 864–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, L.V.; Tamayo, A.T.; Yoshimura, L.C.; Lo, P.; Ford, R.J. Inhibition of constitutive NF-kappa B activation in mantle cell lymphoma B cells leads to induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauert-Wunderlich, H.; Siegmund, D.; Maier, E.; Giner, T.; Bargou, R.C.; Wajant, H.; Stühmer, T. The IKK inhibitor Bay 11-7082 induces cell death independent from inhibition of activation of NFκB transcription factors. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, C.; Oronsky, B.; Carter, C.A.; Oronsky, A.; Knox, S.J.; Sher, D.; Reid, T.R. TGF-beta: A master immune regulator. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2020, 24, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.M.; Nikolic-Paterson, D.J.; Lan, H.Y. TGF-β: The master regulator of fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2016, 12, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caja, L.; Dituri, F.; Mancarella, S.; Caballero-Diaz, D.; Moustakas, A.; Giannelli, G.; Fabregat, I. TGF-β and the Tissue Microenvironment: Relevance in Fibrosis and Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, S.K.; Goodwin, J.S.; Al-Hendy, A. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 reduces TGF-beta3-induced fibrosis-related gene expression in human uterine leiomyoma cells. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, E754–E762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norian, J.M.; Malik, M.; Parker, C.Y.; Joseph, D.; Leppert, P.C.; Segars, J.H.; Catherino, W.H. Transforming growth factor beta3 regulates the versican variants in the extracellular matrix-rich uterine leiomyomas. Reprod. Sci. 2009, 16, 1153–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arici, A.; Sozen, I. Transforming growth factor-beta3 is expressed at high levels in leiomyoma where it stimulates fibronectin expression and cell proliferation. Fertil. Steril. 2000, 73, 1006–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, D.S.; Malik, M.; Nurudeen, S.; Catherino, W.H. Myometrial cells undergo fibrotic transformation under the influence of transforming growth factor beta-3. Fertil. Steril. 2010, 93, 1500–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freudlsperger, C.; Bian, Y.; Contag Wise, S.; Burnett, J.; Coupar, J.; Yang, X.; Chen, Z.; Van Waes, C. TGF-β and NF-κB signal pathway cross-talk is mediated through TAK1 and SMAD7 in a subset of head and neck cancers. Oncogene 2013, 32, 1549–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Gonzalez, A. TGF-β and NF-κB Cross-Talk: Unexpected Encounters in the Developing Lung. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2021, 64, 275–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rameshwar, P.; Narayanan, R.; Qian, J.; Denny, T.N.; Colon, C.; Gascon, P. NF-kappa B as a central mediator in the induction of TGF-beta in monocytes from patients with idiopathic myelofibrosis: An inflammatory response beyond the realm of homeostasis. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 2271–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandl, M.; Seidler, B.; Haller, F.; Adamski, J.; Schmid, R.M.; Saur, D.; Schneider, G. IKK(alpha) controls canonical TGF(ss)-SMAD signaling to regulate genes expressing SNAIL and SLUG during EMT in panc1 cells. J. Cell Sci. 2010, 123 Pt 24, 4231–4239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.I.; Choi, M.E. TGF-β-activated kinase-1: New insights into the mechanism of TGF-β signaling and kidney disease. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2012, 31, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallet, S.D.; Ricard-Blum, S. Lysyl oxidases: From enzyme activity to extracellular matrix cross-links. Essays Biochem. 2019, 63, 349–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.; Gao, L.; Wu, C.; Qin, F.; Yuan, J. Role of the lysyl oxidase family in organ development (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 20, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, K.A.; Lopez, K.M. Lysyl oxidase in cancer inhibition and metastasis. Cancer Lett. 2018, 417, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.H.; Hsia, S.M.; Shieh, T.M. Lysyl Oxidase and the Tumor Microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 18, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Yang, A.; Jia, J.; Popov, Y.V.; Schuppan, D.; You, H. Lysyl Oxidase (LOX) Family Members: Rationale and Their Potential as Therapeutic Targets for Liver Fibrosis. Hepatology 2020, 72, 729–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamopoulos, C.; Piperi, C.; Gargalionis, A.N.; Dalagiorgou, G.; Spilioti, E.; Korkolopoulou, P.; Diamanti-Kandarakis, E.; Papavassiliou, A.G. Advanced glycation end products upregulate lysyl oxidase and endothelin-1 in human aortic endothelial cells via parallel activation of ERK1/2-NF-κB and JNK-AP-1 signaling pathways. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 1685–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laczko, R.; Csiszar, K. Lysyl Oxidase (LOX): Functional Contributions to Signaling Pathways. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moravek, M.B.; Bulun, S.E. Endocrinology of uterine fibroids: Steroid hormones, stem cells, and genetic contribution. Curr. Opin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2015, 27, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakas, P.; Liapis, A.; Vlahopoulos, S.; Giner, M.; Logotheti, S.; Creatsas, G.; Meligova, A.K.; Alexis, M.N.; Zoumpourlis, V. Estrogen receptor alpha and beta in uterine fibroids: A basis for altered estrogen responsiveness. Fertil. Steril. 2008, 90, 1878–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKay, L.I.; Cidlowski, J.A. Cross-talk between nuclear factor-kappa B and the steroid hormone receptors: Mechanisms of mutual antagonism. Mol. Endocrinol. 1998, 12, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deroo, B.J.; Archer, T.K. Differential activation of the IkappaBalpha and mouse mammary tumor virus promoters by progesterone and glucocorticoid receptors. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2002, 81, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, A.E.; Collins, F.; Klonisch, T.; Sallenave, J.M.; Critchley, H.O.; Saunders, P.T. An additive interaction between the NFkappaB and estrogen receptor signalling pathways in human endometrial epithelial cells. Hum. Reprod. 2010, 25, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uimari, O.; Subramaniam, K.S.; Vollenhoven, B.; Tapmeier, T.T. Uterine Fibroids (Leiomyomata) and Heavy Menstrual Bleeding. Front. Reprod. Health 2022, 4, 818243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Al-Hendy, A. Update on the Role and Regulatory Mechanism of Extracellular Matrix in the Pathogenesis of Uterine Fibroids. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimamura, T.; Hsu, T.C.; Colburn, N.H.; Bejcek, B.E. Activation of NF-kappaB is required for PDGF-B chain to transform NIH3T3 cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2002, 274, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurbuz, N.; Asoglu, M.R.; Ashour, A.A.; Salama, S.; Kilic, G.S.; Ozpolat, B. A selective serotonin 5-HT1B receptor inhibition suppresses cells proliferation and induces apoptosis in human uterine leiomyoma cells. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2016, 206, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnabei, L.; Laplantine, E.; Mbongo, W.; Rieux-Laucat, F.; Weil, R. NF-κB: At the Borders of Autoimmunity and Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 716469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumin, J.; Wilcox, B.D.; Otterness, I.; Melendez, J.A.; Huang, C.; Jeffrey, J.J. Serotonin-mediated production of interstitial collagenase by uterine smooth muscle cells requires interleukin-1alpha, but not interleukin-1beta. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 25488–25494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. Toll-like receptors and their crosstalk with other innate receptors in infection and immunity. Immunity 2011, 34, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, K.H.; Staudt, L.M. Toll-like receptor signaling. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a011247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Lin, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Hu, H. Targeting NF-κB pathway for the therapy of diseases: Mechanism and clinical study. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Zheng, L.; Chen, L.; Luo, N.; Yang, W.; Qu, X.; Liu, M.; Cheng, Z. Lipopolysaccharide activated TLR4/NF-kappaB signaling pathway of fibroblasts from uterine fibroids. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 10014–10025. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.; Sun, H.F.; Li, S.; Zhang, N.; Chen, J.S.; Liu, J.X. SPARC: A potential target for functional nanomaterials and drugs. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10, 1235428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Zhao, Y.; Pei, Y.; Lian, F.; Lin, H. Role of the NF-kB signalling pathway in heterotopic ossification: Biological and therapeutic significance. Cell Commun. Signal. 2024, 22, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, B.; Naczki, C.; Patel, C.; Ghoneum, A.; Qasem, S.; Salih, Z.; Said, N. Regulation of the bi-directional cross-talk between ovarian cancer cells and adipocytes by SPARC. Oncogene 2019, 38, 4366–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amato, N.C.; Rogers, T.J.; Gordon, M.A.; Greene, L.I.; Cochrane, D.R.; Spoelstra, N.S.; Nemkov, T.G.; D’Alessandro, A.; Hansen, K.C.; Richer, J.K. A TDO2-AhR signaling axis facilitates anoikis resistance and metastasis in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 4651–4664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Zhou, M. TDO2 deficiency attenuates the hepatic lipid deposition and liver fibrosis in mice with diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Heliyon 2023, 9, e22464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Yan, L.; Lin, J.; Ke, K.; Yang, W. Constitutive TDO2 expression promotes liver cancer progression by an autocrine IL-6 signaling pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, T.D.; Rehan, A.; Khorram, O. Tranilast induces MiR-200c expression through blockade of RelA/p65 activity in leiomyoma smooth muscle cells. Fertil. Steril. 2020, 113, 1308–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Garzon, R.; Sun, H.; Ladner, K.J.; Singh, R.; Dahlman, J.; Cheng, A.; Hall, B.M.; Qualman, S.J.; Chandler, D.S.; et al. NF-kappaB-YY1-miR-29 regulatory circuitry in skeletal myogenesis and rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancer Cell 2008, 14, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikhena, D.E.; Liu, S.; Kujawa, S.; Esencan, E.; Coon, J.S.t.; Robins, J.; Bulun, S.E.; Yin, P. RANKL/RANK Pathway and Its Inhibitor RANK-Fc in Uterine Leiomyoma Growth. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 1842–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
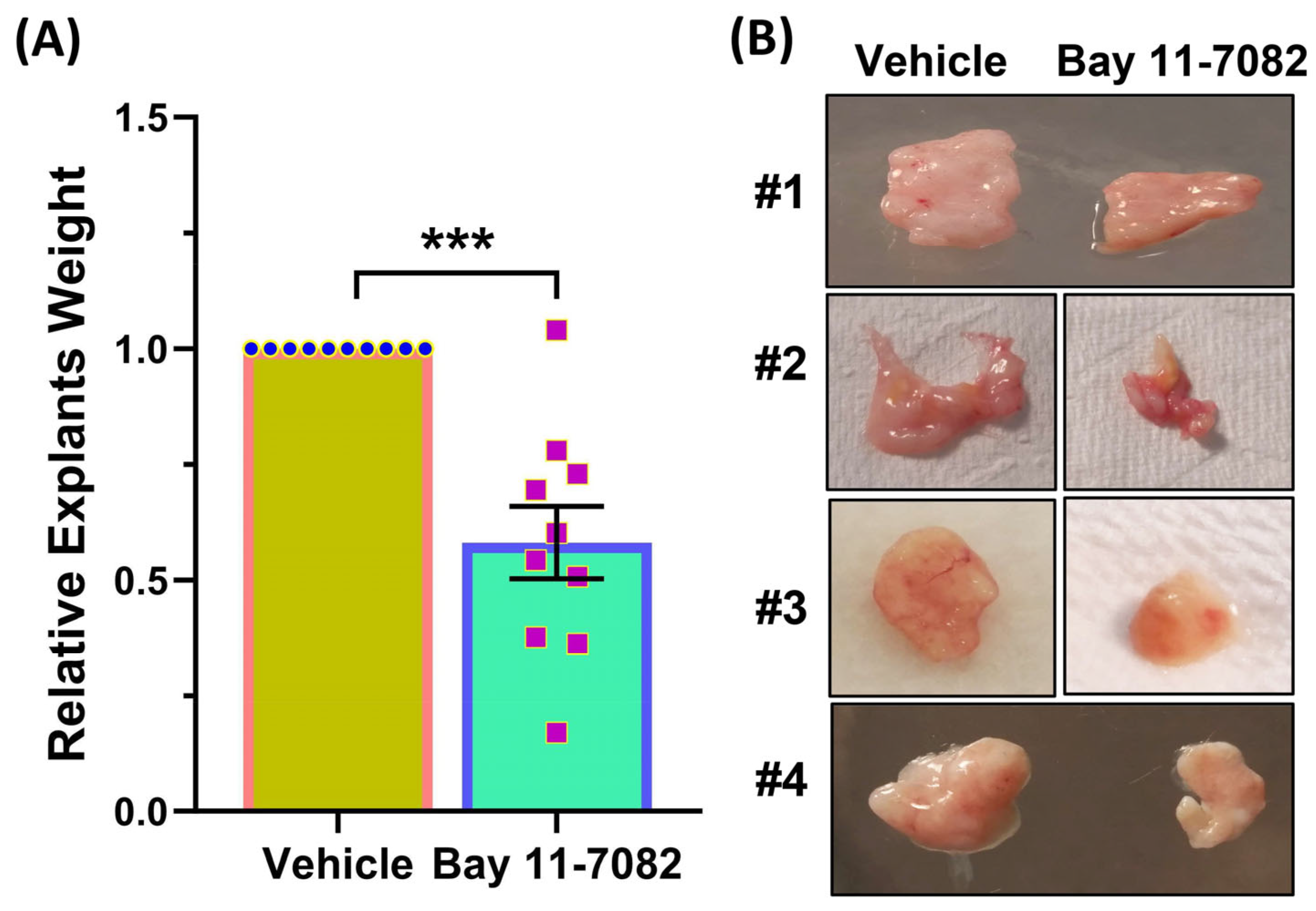
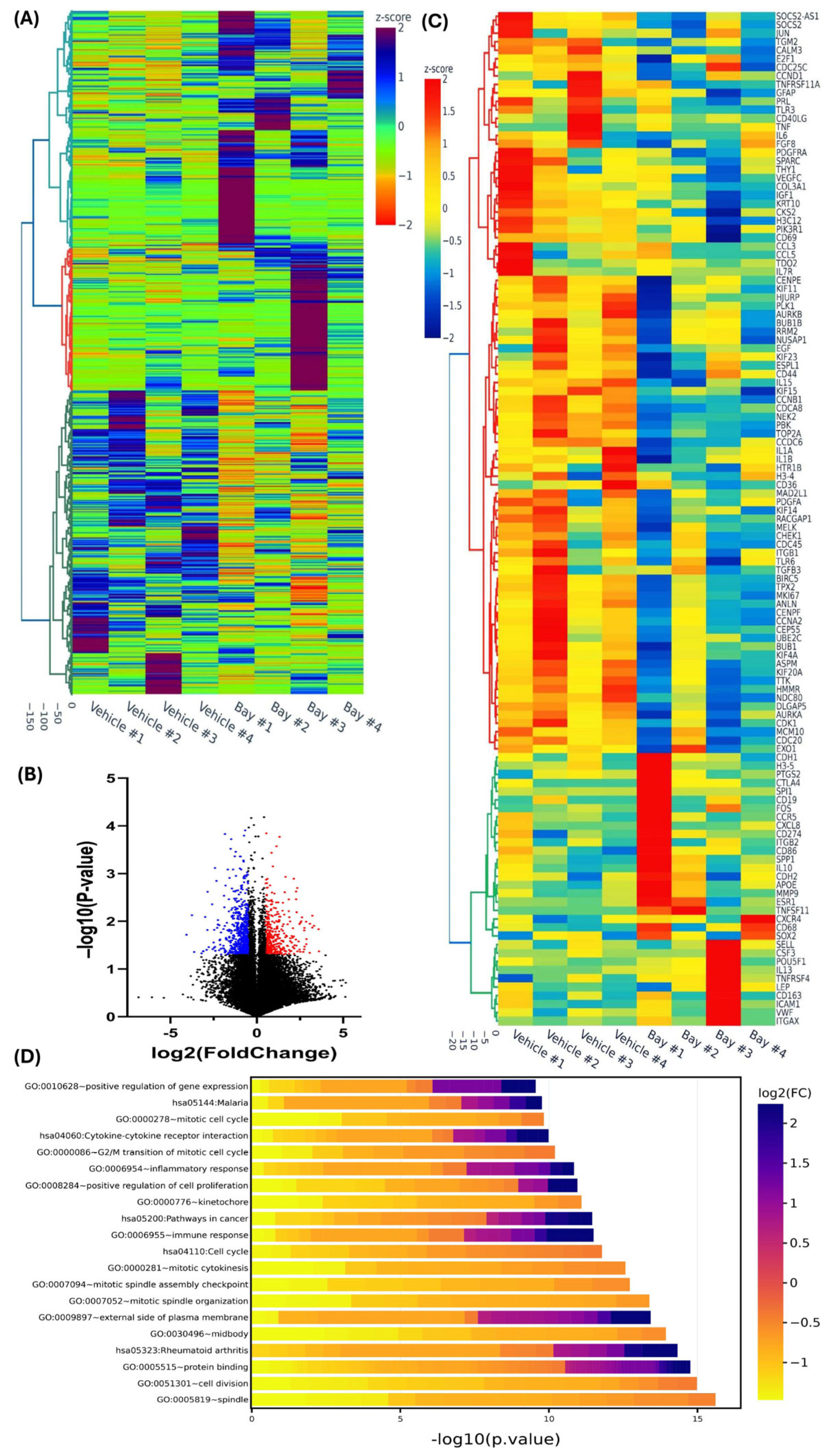

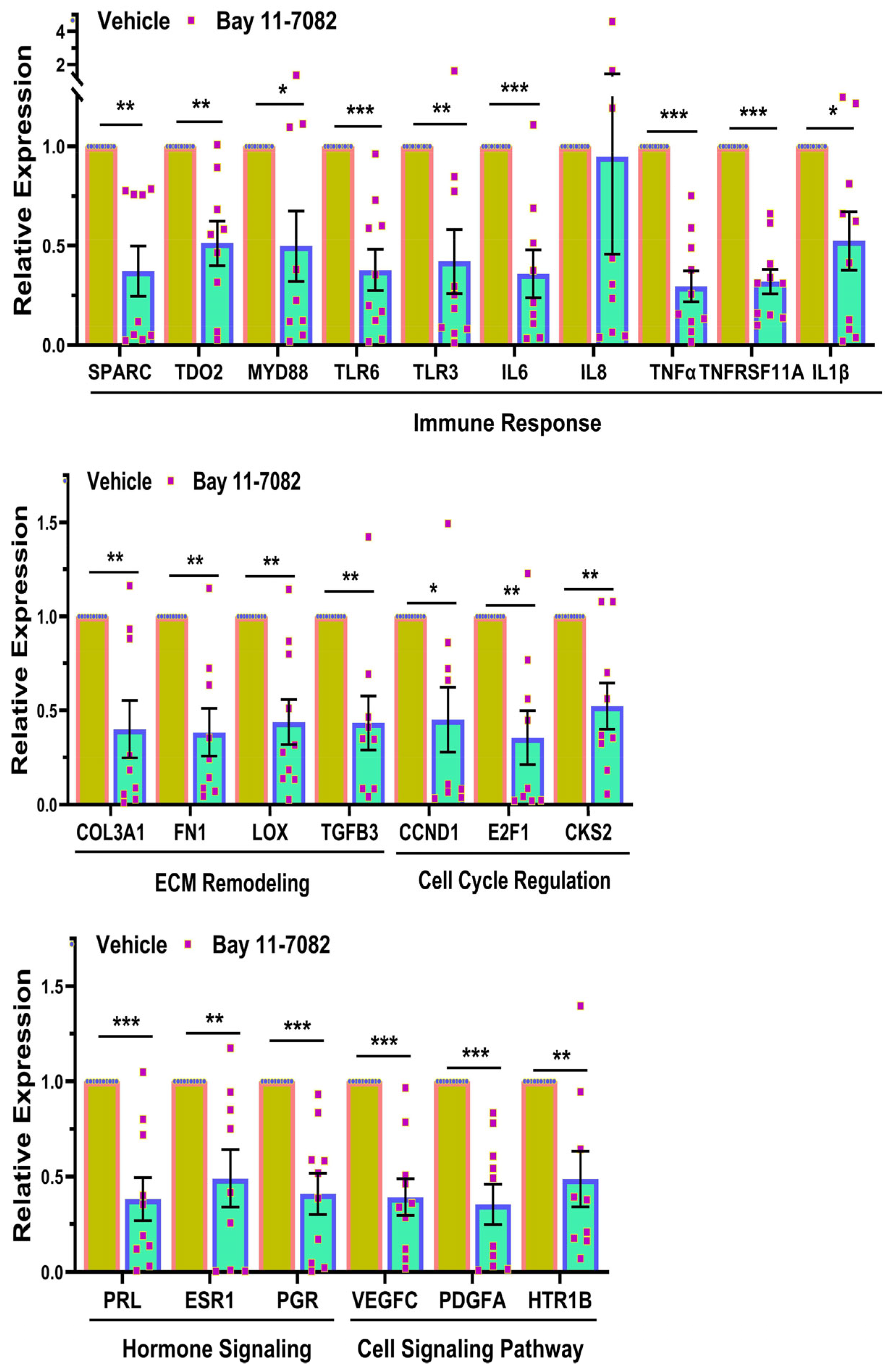

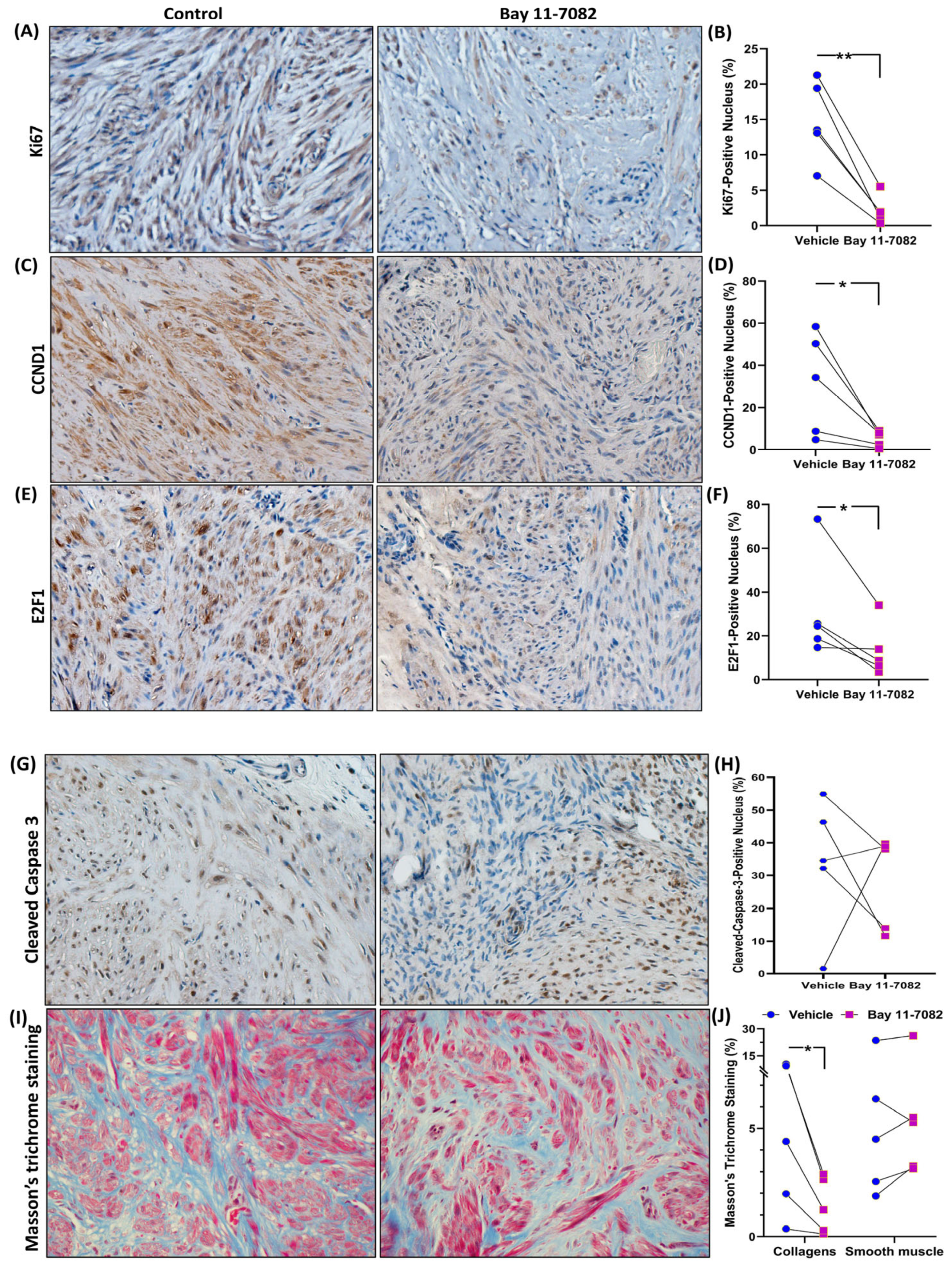

| Chemistry Panel Marker | Vehicle | Bay 11-7082 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| (Mean ± SEM) | (Mean ± SEM) | ||
| General metabolism | |||
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 230.9 ± 17.73 | 261.0 ± 14.63 | 0.069 |
| Kidney function | |||
| BUN (mg/dL) | 24.3 ± 2.8 | 27.1 ± 5.75 | 0.648 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.2 ± 0.29 | 0.4 ± 0.03 | 0.939 |
| Electrolytes | |||
| Sodium (mEq/L) | 154.4 ± 0.98 | 155.3 ± 1.35 | 0.628 |
| Phosphorus (mg/dL) | 8.7 ± 0.77 | 10.1 ± 0.53 | 0.988 |
| Liver function | |||
| Alkaline phosphatase (U/L) | 105 ± 16.95 | 91.9 ± 20.05 | 0.355 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.9 ± 0.12 | 3.5 ± 0.14 | 0.063 |
| SGPT (ALT) (U/L) | 44 ± 10.3 | 54.5 ± 8.71 | 0.504 |
| Total protein (g/dL) | 5.2 ± 0.61 | 4.6 ± 0.16 | 0.326 |
| Globulin (g/dL) | 1.3 ± 0.5 | 1.1 ± 0.24 | 0.786 |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.2 ± 0.02 | 0.3 ± 0.04 | 0.732 |
| Pancreas function | |||
| Amylase (U/L) | 703.9 ± 32.93 | 643.0 ± 36.82 | 0.074 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chuang, T.-D.; Ton, N.; Rysling, S.; Khorram, O. In Vivo Effects of Bay 11-7082 on Fibroid Growth and Gene Expression: A Preclinical Study. Cells 2024, 13, 1091. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13131091
Chuang T-D, Ton N, Rysling S, Khorram O. In Vivo Effects of Bay 11-7082 on Fibroid Growth and Gene Expression: A Preclinical Study. Cells. 2024; 13(13):1091. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13131091
Chicago/Turabian StyleChuang, Tsai-Der, Nhu Ton, Shawn Rysling, and Omid Khorram. 2024. "In Vivo Effects of Bay 11-7082 on Fibroid Growth and Gene Expression: A Preclinical Study" Cells 13, no. 13: 1091. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13131091
APA StyleChuang, T.-D., Ton, N., Rysling, S., & Khorram, O. (2024). In Vivo Effects of Bay 11-7082 on Fibroid Growth and Gene Expression: A Preclinical Study. Cells, 13(13), 1091. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13131091





