Evaluation of the Immunomodulatory Effects of Radiation for Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy in Glioblastoma Multiforme
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
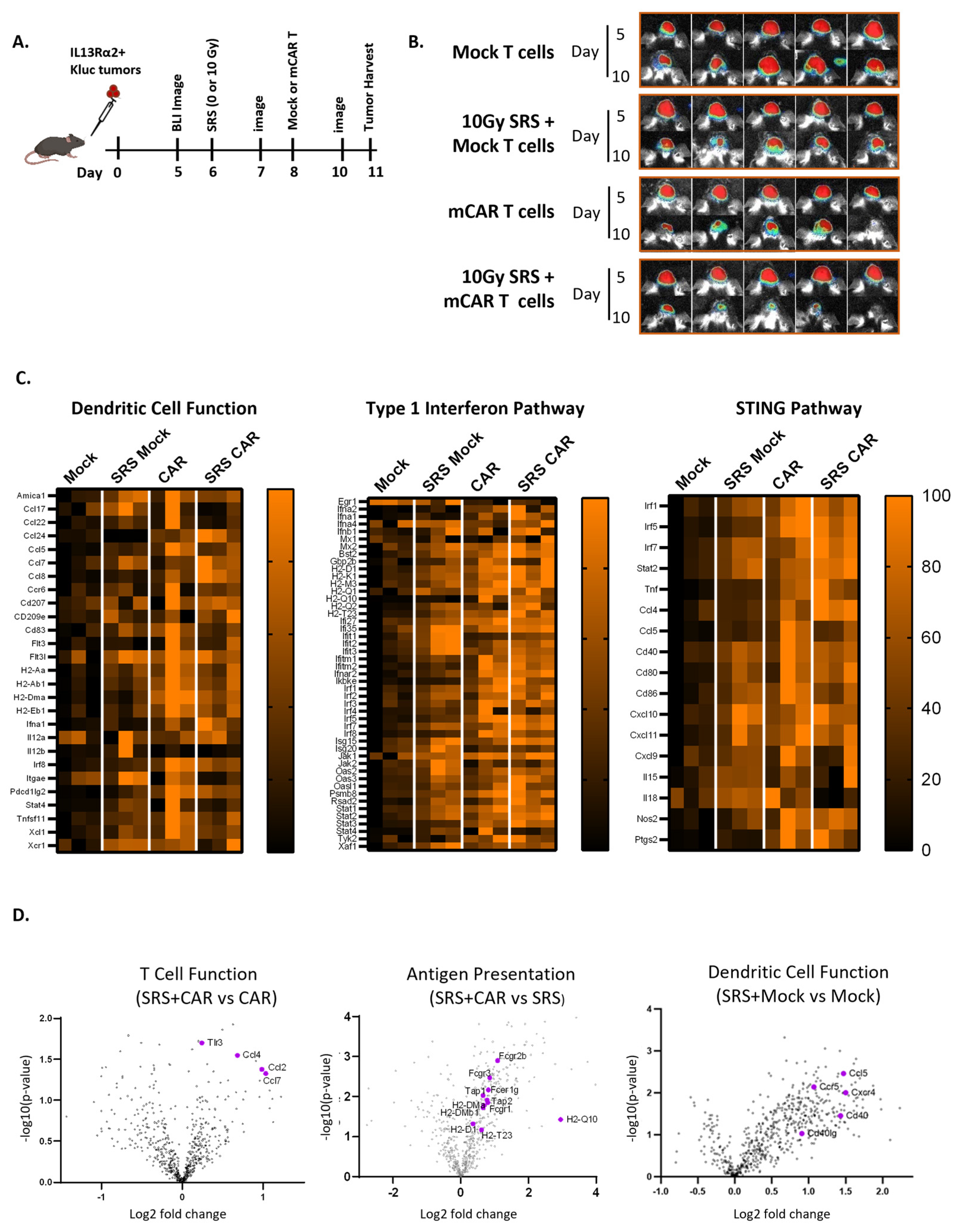
3.1. Conditioning SRS Has Immunomodulatory Effects in Murine GBM
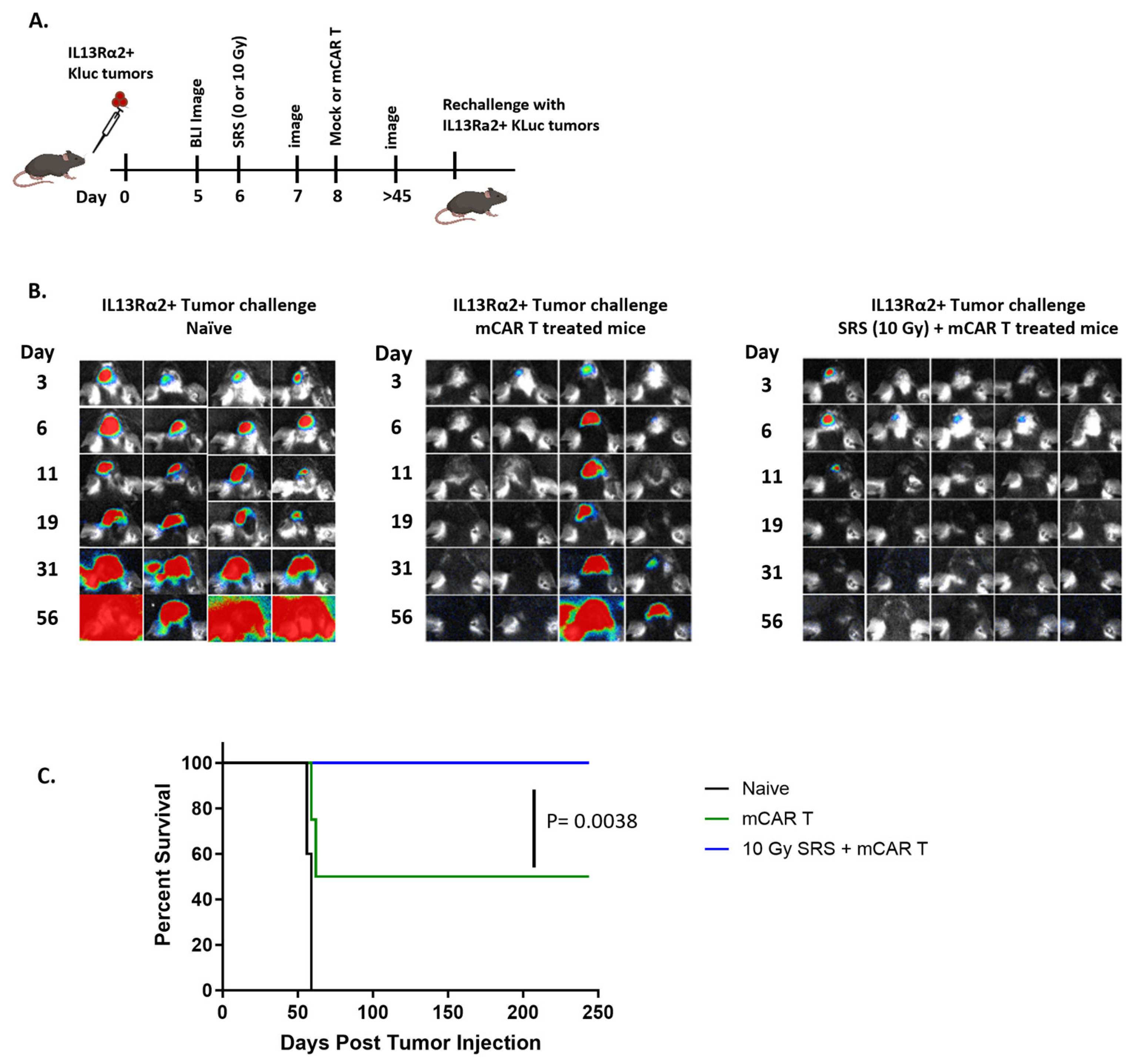
3.2. Conditioning SRS in Combination with mCAR T Therapy Enhances Antitumor Responses
3.3. Conditioning SRS and mCAR T Therapy Enhance Innate and Adaptive Immunity Pathways Involving the cGAS-STING Pathway
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alexander, B.M.; Cloughesy, T.F. Adult Glioblastoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2402–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laperriere, N.; Zuraw, L.; Cairncross, G. Radiotherapy for newly diagnosed malignant glioma in adults: A systematic review. Radiother. Oncol. 2002, 64, 259–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizumoto, M.; Tsuboi, K.; Igaki, H.; Yamamoto, T.; Takano, S.; Oshiro, Y.; Hayashi, Y.; Hashii, H.; Kanemoto, A.; Nakayama, H.; et al. Phase I/II trial of hyperfractionated concomitant boost proton radiotherapy for supratentorial glioblastoma multiforme. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2010, 77, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souhami, L.; Seiferheld, W.; Brachman, D.; Podgorsak, E.B.; Werner-Wasik, M.; Lustig, R.; Schultz, C.J.; Sause, W.; Okunieff, P.; Buckner, J.; et al. Randomized comparison of stereotactic radiosurgery followed by conventional radiotherapy with carmustine to conventional radiotherapy with carmustine for patients with glioblastoma multiforme: Report of Radiation Therapy Oncology Group 93-05 protocol. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2004, 60, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weichselbaum, R.R.; Liang, H.; Deng, L.; Fu, Y.X. Radiotherapy and immunotherapy: A beneficial liaison? Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 365–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filatenkov, A.; Baker, J.; Mueller, A.M.; Kenkel, J.; Ahn, G.O.; Dutt, S.; Zhang, N.; Kohrt, H.; Jensen, K.; Dejbakhsh-Jones, S.; et al. Ablative Tumor Radiation Can Change the Tumor Immune Cell Microenvironment to Induce Durable Complete Remissions. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 3727–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lugade, A.A.; Moran, J.P.; Gerber, S.A.; Rose, R.C.; Frelinger, J.G.; Lord, E.M. Local radiation therapy of B16 melanoma tumors increases the generation of tumor antigen-specific effector cells that traffic to the tumor. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 7516–7523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Probst, H.C.; Vuong, V.; Landshammer, A.; Muth, S.; Yagita, H.; Schwendener, R.; Pruschy, M.; Knuth, A.; van den Broek, M. Radiotherapy promotes tumor-specific effector CD8+ T cells via dendritic cell activation. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reits, E.A.; Hodge, J.W.; Herberts, C.A.; Groothuis, T.A.; Chakraborty, M.; Wansley, E.K.; Camphausen, K.; Luiten, R.M.; de Ru, A.H.; Neijssen, J.; et al. Radiation modulates the peptide repertoire, enhances MHC class I expression, and induces successful antitumor immunotherapy. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 1259–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, J.; See, A.P.; Phallen, J.; Jackson, C.M.; Belcaid, Z.; Ruzevick, J.; Durham, N.; Meyer, C.; Harris, T.J.; Albesiano, E.; et al. Anti-PD-1 blockade and stereotactic radiation produce long-term survival in mice with intracranial gliomas. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2013, 86, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, P.A.; Bang, Y.-J.; Piha-Paul, S.A.; Razak, A.R.A.; Bennouna, J.; Soria, J.-C.; Rugo, H.S.; Cohen, R.B.; O’Neil, B.H.; Mehnert, J.M.; et al. T-Cell–Inflamed Gene-Expression Profile, Programmed Death Ligand 1 Expression, and Tumor Mutational Burden Predict Efficacy in Patients Treated With Pembrolizumab Across 20 Cancers: KEYNOTE-028. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 37, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reardon, D.; Omuro, A.; Brandes, A.; Rieger, J.; Wick, A.; Sepulveda, J.; Phuphanich, S.; De Souza, P.; Ahluwalia, M.; Lim, M. OS10. 3 randomized phase 3 study evaluating the efficacy and safety of nivolumab vs bevacizumab in patients with recurrent glioblastoma: CheckMate 143. Neuro-Oncology 2017, 19, iii21–iii22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muftuoglu, Y.; Liau, L.M. Results From the CheckMate 143 Clinical Trial: Stalemate or New Game Strategy for Glioblastoma Immunotherapy? JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 987–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weller, M.; Vlahovic, G.; Khasraw, M.; Brandes, A.A.; Zwirtes, R.; Tatsuoka, K.; Carpentier, A.F.; Reardon, D.A.; Bent, M. 356TiP—A randomized phase 2, single-blind study of temozolomide (TMZ) and radiotherapy (RT) combined with nivolumab or placebo (PBO) in newly diagnosed adult patients (pts) with tumor O6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase (MGMT)-methylated glioblastoma (GBM)—CheckMate-548. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, vi113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, M.; Lim, M.; Idbaih, A.; Steinbach, J.; Finocchiaro, G.; Raval, R.; Ashby, L.; Ansstas, G.; Baehring, J.; Taylor, J.; et al. CTIM-25. A randomized phase 3 study of nivolumab or placebo combined with radiotherapy plus temozolomide in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma with methylated MGMT promoter: CheckMate 548. Neuro-Oncology 2021, 23, vi55–vi56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, F.L.; Neelapu, S.S.; Bartlett, N.L.; Siddiqi, T.; Chavez, J.C.; Hosing, C.M.; Ghobadi, A.; Budde, L.E.; Bot, A.; Rossi, J.M.; et al. Phase 1 Results of ZUMA-1: A Multicenter Study of KTE-C19 Anti-CD19 CAR T Cell Therapy in Refractory Aggressive Lymphoma. Mol. Ther. 2017, 25, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maude, S.L.; Laetsch, T.W.; Buechner, J.; Rives, S.; Boyer, M.; Bittencourt, H.; Bader, P.; Verneris, M.R.; Stefanski, H.E.; Myers, G.D.; et al. Tisagenlecleucel in Children and Young Adults with B-Cell Lymphoblastic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Brawley, V.; Hegde, M.; Bielamowicz, K.; Kalra, M.; Landi, D.; Robertson, C.; Gray, T.L.; Diouf, O.; Wakefield, A.; et al. HER2-Specific Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Modified Virus-Specific T Cells for Progressive Glioblastoma: A Phase 1 Dose-Escalation Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 1094–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, C.E.; Alizadeh, D.; Starr, R.; Weng, L.; Wagner, J.R.; Naranjo, A.; Ostberg, J.R.; Blanchard, M.S.; Kilpatrick, J.; Simpson, J.; et al. Regression of Glioblastoma after Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 2561–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, M.; Joseph, S.K.; Pashankar, F.; DeRenzo, C.; Sanber, K.; Navai, S.; Byrd, T.T.; Hicks, J.; Xu, M.L.; Gerken, C.; et al. Tumor response and endogenous immune reactivity after administration of HER2 CAR T cells in a child with metastatic rhabdomyosarcoma. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Rourke, D.M.; Nasrallah, M.P.; Desai, A.; Melenhorst, J.J.; Mansfield, K.; Morrissette, J.J.D.; Martinez-Lage, M.; Brem, S.; Maloney, E.; Shen, A.; et al. A single dose of peripherally infused EGFRvIII-directed CAR T cells mediates antigen loss and induces adaptive resistance in patients with recurrent glioblastoma. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaaa0984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, C.; Hibbard, J.; Alizadeh, D.; Blanchard, M.; Natri, H.; Wang, D.; Ostberg, J.; Aguilar, B.; Wagner, J.; Paul, J. Phase I Trial Evaluating Locoregionally-delivered IL13Rα2-targeting CAR T Cells in High-Grade Glioma. Res. Sq. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, D.; Wong, R.A.; Gholamin, S.; Maker, M.; Aftabizadeh, M.; Yang, X.; Pecoraro, J.R.; Jeppson, J.D.; Wang, D.; Aguilar, B.; et al. IFNγ Is Critical for CAR T Cell-Mediated Myeloid Activation and Induction of Endogenous Immunity. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 2248–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murty, S.; Haile, S.T.; Beinat, C.; Aalipour, A.; Alam, I.S.; Murty, T.; Shaffer, T.M.; Patel, C.B.; Graves, E.E.; Mackall, C.L.; et al. Intravital imaging reveals synergistic effect of CAR T-cells and radiation therapy in a preclinical immunocompetent glioblastoma model. Oncoimmunology 2020, 9, 1757360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reilly, K.M.; Loisel, D.A.; Bronson, R.T.; McLaughlin, M.E.; Jacks, T. Nf1;Trp53 mutant mice develop glioblastoma with evidence of strain-specific effects. Nat. Genet. 2000, 26, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovo, E.E.; Moreira, A.; Barahona, K.C.; Ramirez, J.; Campos, F.; Tobar, C.; Caceros, V.; Sallabanda, M.; Sallabanda, K. Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Recurrent Glioblastoma Multiforme: A Retrospective Multi-Institutional Experience. Cureus 2021, 13, e18480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, D.E.; Bernard, M.E.; Quan, K.; Clump, D.A.; Engh, J.A.; Burton, S.A.; Heron, D.E. Salvage stereotactic radiosurgery for recurrent glioblastoma multiforme with prior radiation therapy. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2016, 12, 1243–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores, C.T.; Wildes, T.J.; Drake, J.A.; Moore, G.L.; Dean, B.D.; Abraham, R.S.; Mitchell, D.A. Lin− CCR2+ hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells overcome resistance to PD-1 blockade. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klinke, D.J., 2nd; Cheng, N.; Chambers, E. Quantifying crosstalk among interferon-γ, interleukin-12, and tumor necrosis factor signaling pathways within a TH1 cell model. Sci. Signal. 2012, 5, ra32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Chen, P.; Wang, L.; Li, W.; Chen, B.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhao, S.; Ye, L.; He, Y.; et al. cGAS-STING, an important pathway in cancer immunotherapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szatmári, T.; Lumniczky, K.; Désaknai, S.; Trajcevski, S.; Hídvégi, E.J.; Hamada, H.; Sáfrány, G. Detailed characterization of the mouse glioma 261 tumor model for experimental glioblastoma therapy. Cancer Sci. 2006, 97, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, T.; Schneider, H.; Silginer, M.; Steinle, A.; Pruschy, M.; Polić, B.; Weller, M.; Roth, P. NKG2D-Dependent Antitumor Effects of Chemotherapy and Radiotherapy against Glioblastoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 882–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Toro, J.A.; Luo, D.; Gopinath, A.; Sarkisian, M.R.; Campbell, J.J.; Charo, I.F.; Singh, R.; Schall, T.J.; Datta, M.; Jain, R.K.; et al. CCR2 inhibition reduces tumor myeloid cells and unmasks a checkpoint inhibitor effect to slow progression of resistant murine gliomas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 1129–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karachi, A.; Yang, C.; Dastmalchi, F.; Sayour, E.J.; Huang, J.; Azari, H.; Long, Y.; Flores, C.; Mitchell, D.A.; Rahman, M. Modulation of temozolomide dose differentially affects T-cell response to immune checkpoint inhibition. Neuro-Oncology 2019, 21, 730–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores, C.; Pham, C.; Snyder, D.; Yang, S.; Sanchez-Perez, L.; Sayour, E.; Cui, X.; Kemeny, H.; Friedman, H.; Bigner, D.D.; et al. Novel role of hematopoietic stem cells in immunologic rejection of malignant gliomas. Oncoimmunology 2015, 4, e994374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omuro, A.; Brandes, A.A.; Carpentier, A.F.; Idbaih, A.; Reardon, D.A.; Cloughesy, T.; Sumrall, A.; Baehring, J.; van den Bent, M.; Bähr, O.; et al. Radiotherapy combined with nivolumab or temozolomide for newly diagnosed glioblastoma with unmethylated MGMT promoter: An international randomized phase III trial. Neuro-Oncology 2022, 25, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, M.; Sato, S.; Hemmi, H.; Hoshino, K.; Kaisho, T.; Sanjo, H.; Takeuchi, O.; Sugiyama, M.; Okabe, M.; Takeda, K.; et al. Role of adaptor TRIF in the MyD88-independent toll-like receptor signaling pathway. Science 2003, 301, 640–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeSelm, C.; Palomba, M.L.; Yahalom, J.; Hamieh, M.; Eyquem, J.; Rajasekhar, V.K.; Sadelain, M. Low-Dose Radiation Conditioning Enables CAR T Cells to Mitigate Antigen Escape. Mol. Ther. 2018, 26, 2542–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, S.; Pestka, S.; Jubin, R.G.; Lyu, Y.L.; Tsai, Y.C.; Liu, L.F. Chemotherapeutics and radiation stimulate MHC class I expression through elevated interferon-beta signaling in breast cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accolla, R.; Lombardo, L.; Abdallah, R.; Raval, G.; Forlani, G.; Tosi, G. Boosting the MHC Class II-Restricted Tumor Antigen Presentation to CD4+ T Helper Cells: A Critical Issue for Triggering Protective Immunity and Re-Orienting the Tumor Microenvironment Toward an Anti-Tumor State. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreiter, S.; Vormehr, M.; van de Roemer, N.; Diken, M.; Löwer, M.; Diekmann, J.; Boegel, S.; Schrörs, B.; Vascotto, F.; Castle, J.C.; et al. Mutant MHC class II epitopes drive therapeutic immune responses to cancer. Nature 2015, 520, 692–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Filippo, K.; Dudeck, A.; Hasenberg, M.; Nye, E.; van Rooijen, N.; Hartmann, K.; Gunzer, M.; Roers, A.; Hogg, N. Mast cell and macrophage chemokines CXCL1/CXCL2 control the early stage of neutrophil recruitment during tissue inflammation. Blood 2013, 121, 4930–4937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe-Querol, E.; Rosales, C. Neutrophils in Cancer: Two Sides of the Same Coin. J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 2015, 983698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, C.E.; Pollard, J.W. Distinct role of macrophages in different tumor microenvironments. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.C.; Nishikawa, T.; Chang, C.Y.; Tai, J.A.; Kaneda, Y. CXCL2 combined with HVJ-E suppresses tumor growth and lung metastasis in breast cancer and enhances anti-PD-1 antibody therapy. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2021, 20, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.Y.H.; Gerber, S.A.; Murphy, S.P.; Lord, E.M. Type I interferons induced by radiation therapy mediate recruitment and effector function of CD8(+) T cells. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. CII 2014, 63, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnette, B.C.; Liang, H.; Lee, Y.; Chlewicki, L.; Khodarev, N.N.; Weichselbaum, R.R.; Fu, Y.X.; Auh, S.L. The efficacy of radiotherapy relies upon induction of type i interferon-dependent innate and adaptive immunity. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 2488–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goedegebuure, R.S.A.; Vonk, C.; Kooij, L.P.; Derks, S.; Thijssen, V. Combining Radiation Therapy With Interferons: Back to the Future. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2020, 108, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baird, J.R.; Friedman, D.; Cottam, B.; Dubensky, T.W., Jr.; Kanne, D.B.; Bambina, S.; Bahjat, K.; Crittenden, M.R.; Gough, M.J. Radiotherapy Combined with Novel STING-Targeting Oligonucleotides Results in Regression of Established Tumors. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Crowe, W.N.; Wang, L.; Lu, Y.; Petty, W.J.; Habib, A.A.; Zhao, D. An inhalable nanoparticulate STING agonist synergizes with radiotherapy to confer long-term control of lung metastases. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akhavan, D.; Subham, S.; Jeppson, J.D.; Aguilar, B.; Wong, R.A.; Hibbard, J.C.; Hui, S.; Wong, J.Y.C.; Forman, S.J.; Alizadeh, D.; et al. Evaluation of the Immunomodulatory Effects of Radiation for Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy in Glioblastoma Multiforme. Cells 2024, 13, 1075. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13131075
Akhavan D, Subham S, Jeppson JD, Aguilar B, Wong RA, Hibbard JC, Hui S, Wong JYC, Forman SJ, Alizadeh D, et al. Evaluation of the Immunomodulatory Effects of Radiation for Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy in Glioblastoma Multiforme. Cells. 2024; 13(13):1075. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13131075
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkhavan, David, Siddharth Subham, John D. Jeppson, Brenda Aguilar, Robyn A. Wong, Jonathan C. Hibbard, Susanta Hui, Jeffrey Y. C. Wong, Stephen J. Forman, Darya Alizadeh, and et al. 2024. "Evaluation of the Immunomodulatory Effects of Radiation for Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy in Glioblastoma Multiforme" Cells 13, no. 13: 1075. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13131075
APA StyleAkhavan, D., Subham, S., Jeppson, J. D., Aguilar, B., Wong, R. A., Hibbard, J. C., Hui, S., Wong, J. Y. C., Forman, S. J., Alizadeh, D., & Brown, C. E. (2024). Evaluation of the Immunomodulatory Effects of Radiation for Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy in Glioblastoma Multiforme. Cells, 13(13), 1075. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13131075





