Targeting Neuroinflammation with Abscisic Acid Reduces Pain Sensitivity in Females and Hyperactivity in Males of an ADHD Mice Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
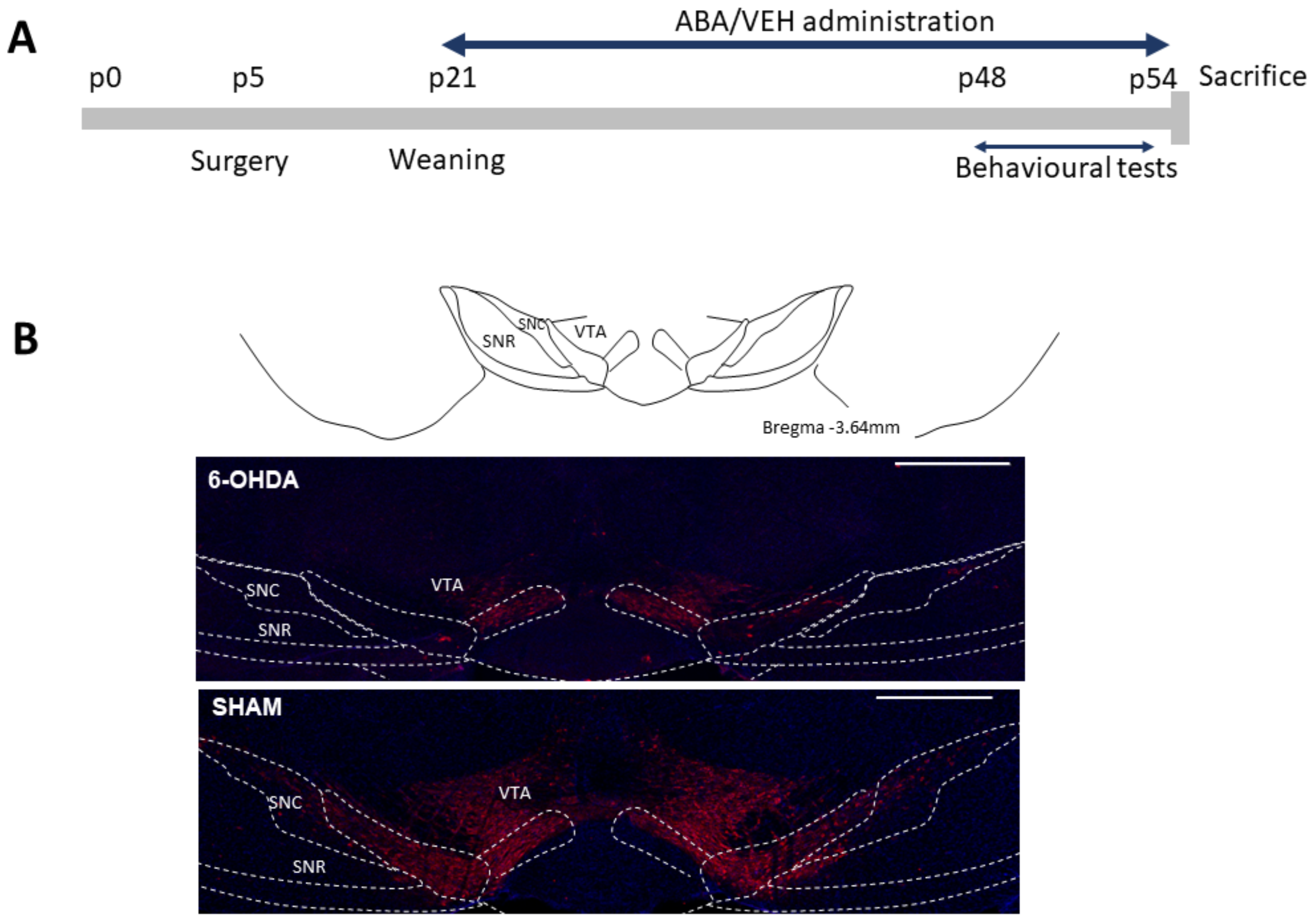
2.1. Animals and Surgical Procedures
2.2. Behavioral Procedures
2.3. Immunofluorescence Procedure
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. 6-OHDA Reduced TH Staining in the Ventral Tegmental Area
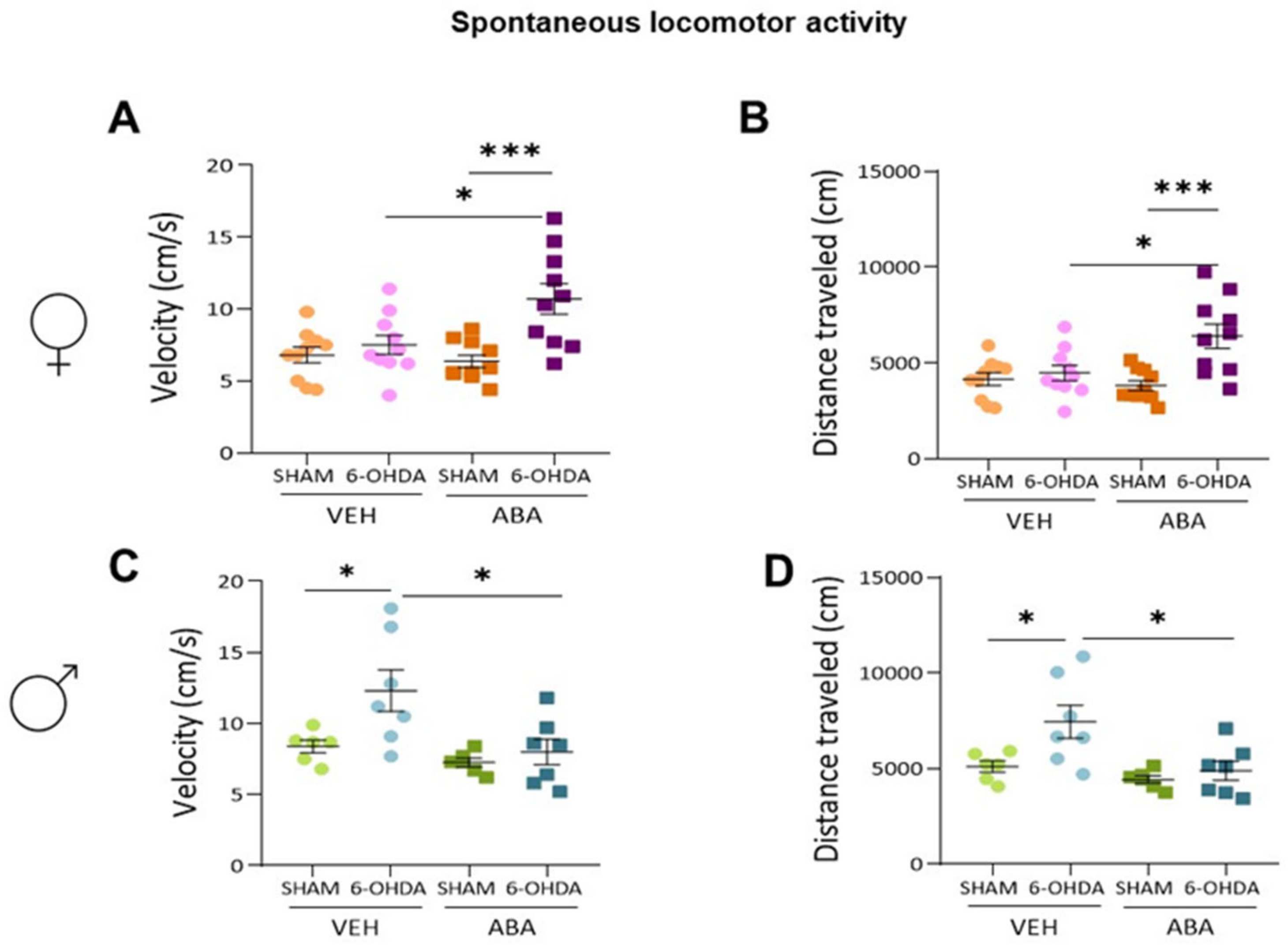
3.2. Effect of Perinatal i.c.v. 6-OHDA Injection and ABA Treatment on Spontaneous Locomotor Activity
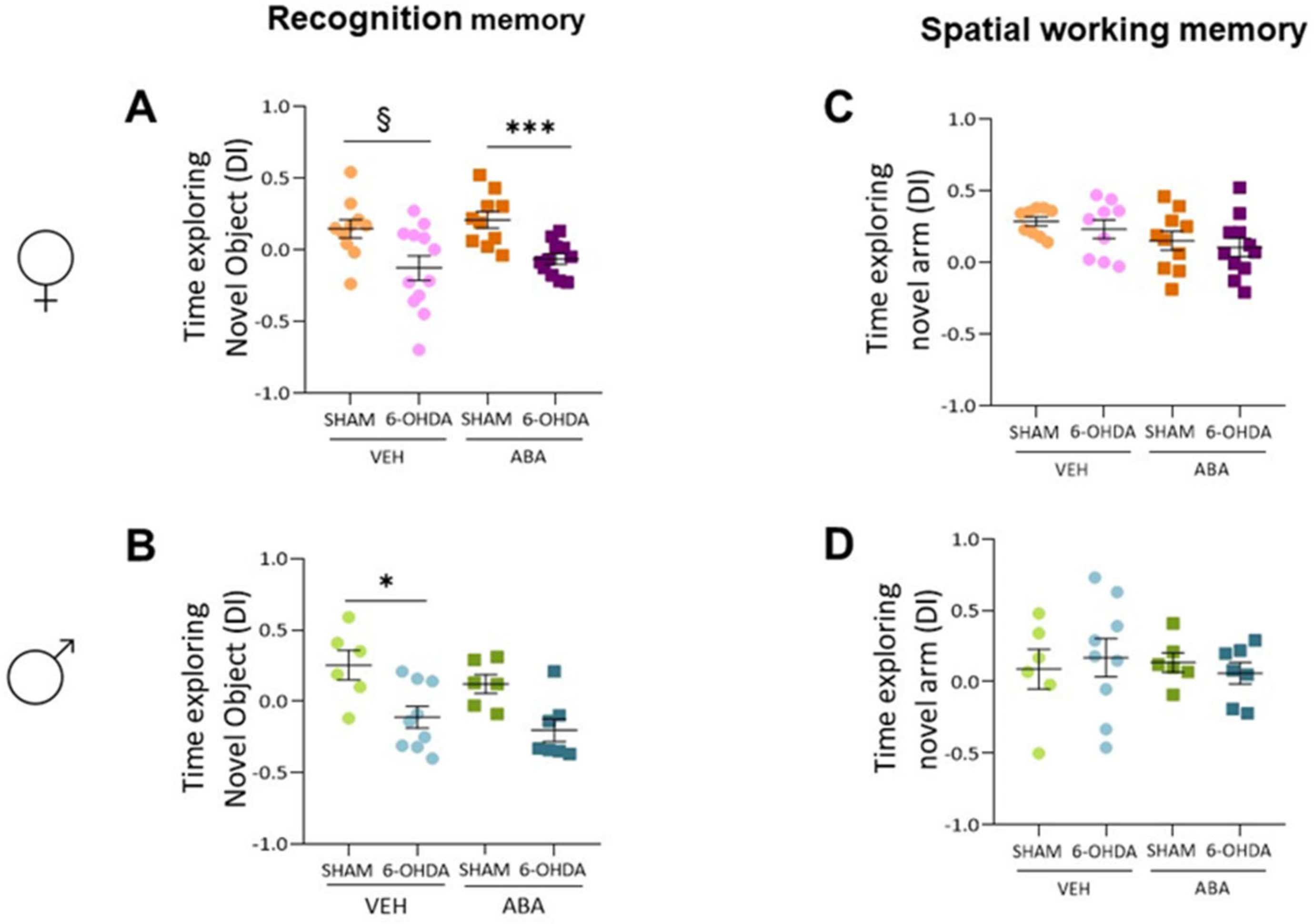
3.3. 6-OHDA Injection Reduces Novel Object Recognition, and ABA Treatment Does Not Rescue the Lesion Effect
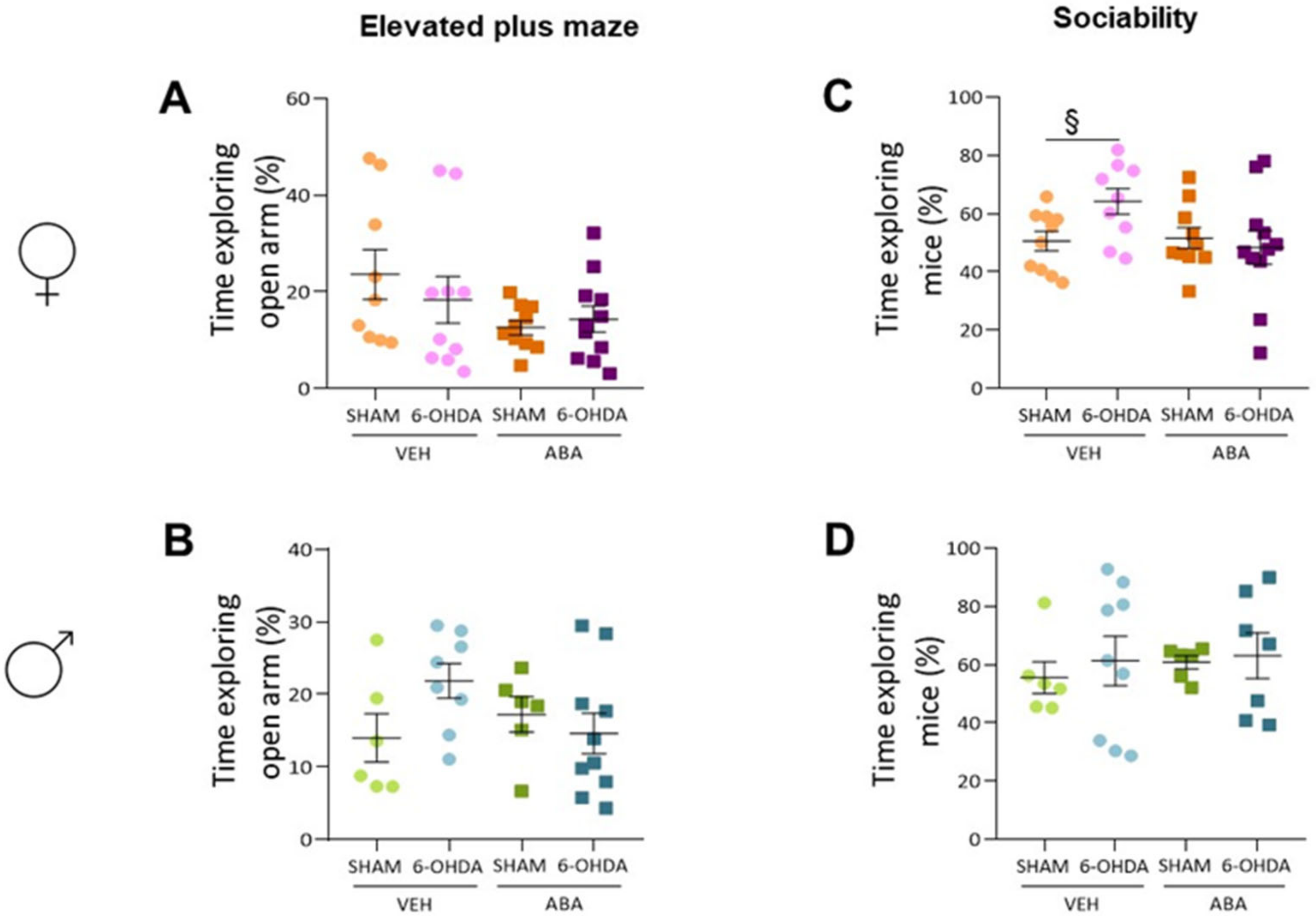
3.4. The 6-OHDA Lesion Did Not Alter Spatial Memory as Measured by Spontaneous Alternation (T-Maze) Nor Anxiety as Measured by Elevated plus Maze
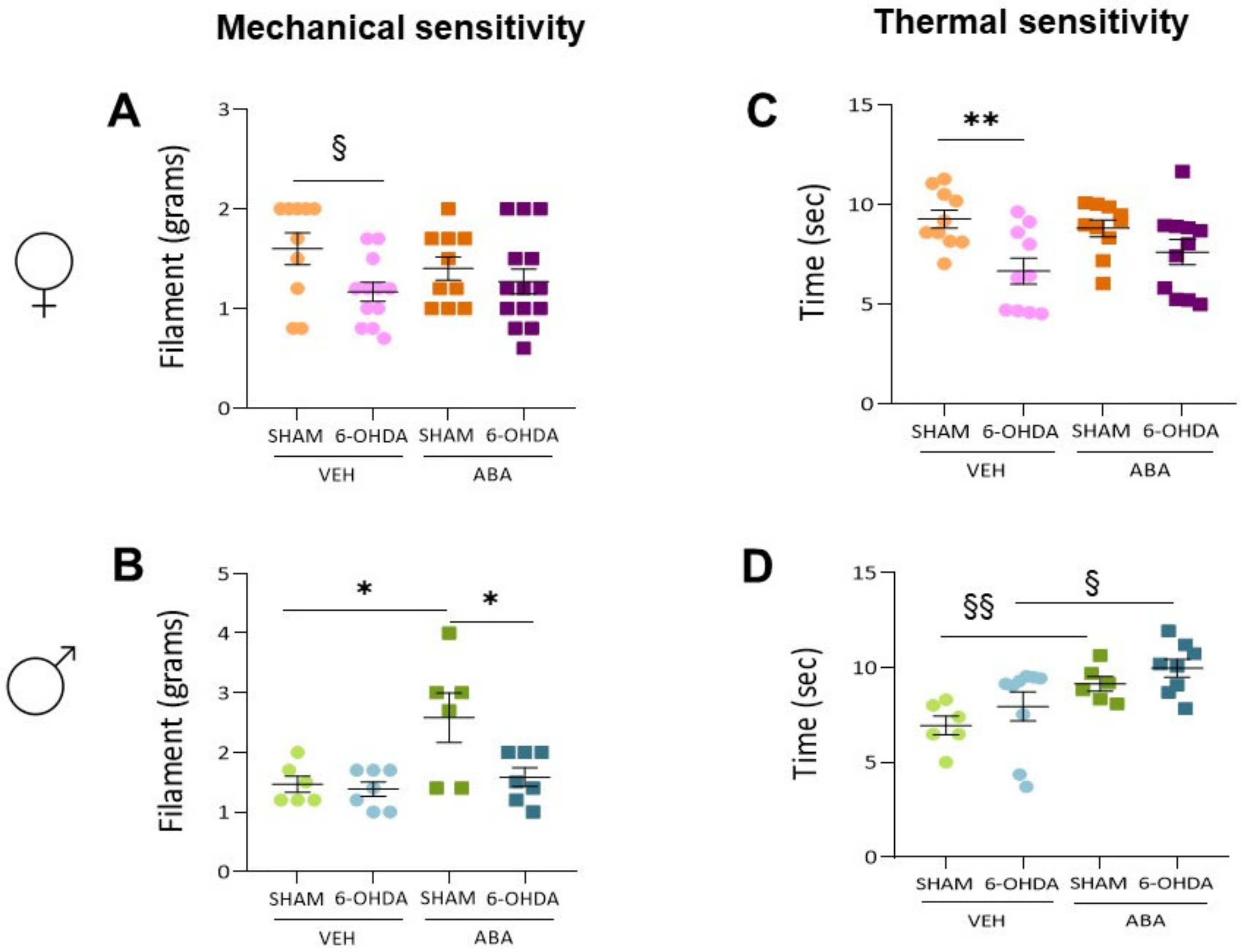
3.5. The 6-OHDA Lesion Had a Sex-Dependent Effect on Pain Sensitivity Tests—ABA Treatment Had a Potential Beneficial Effect Elevating Pain Sensitivity Threshold
3.6. Perinatal Injection of 6-OHDA Lesions Had a Sex-Dependent Effect on Sociability in Two-Month-Old Mice
3.7. Perinatal 6-OHDA Lesion Had a Sex-Dependent Effect on Pain Sensitivity by the Mechanical Stimulus, as Measured by the Von Frey Test
3.8. Perinatal 6-OHDA Lesions Had a Sex-Dependent Effect on Pain Sensitivity by Thermal Stimulus, and ABA Treatment Increased the Threshold in Both Females and Males
3.9. In the Anterior Cingulate Cortex (ACC), the 6-OHDA Lesion Induced Microglia Polarization to a Proinflammatory Status, and ABA Rescued the Effect in Females but Not in Males
3.10. In the Posterior Insular Cortex, 6-OHDA Lesions Induced Microglia Polarization to a Proinflammatory Status Only in Females, and ABA Rescued the Effect
3.11. Perinatal 6-OHDA Lesion and ABA Treatment Affected APE1 Intensity Differently in the ACC of Females and Males
3.12. Perinatal 6-OHDA Lesion Reduces Ape1 Intensity in Both Females’ and Males’ Posterior Insula
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Faraone, S.V.; Asherson, P.; Banaschewski, T.; Biederman, J.; Buitelaar, J.K.; Ramos-Quiroga, J.A.; Rohde, L.A.; Sonuga-Barke, E.J.S.; Tannock, R.; Franke, B. Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2015, 1, 15020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avni, E.; Ben-Itzchak, E.; Zachor, D.A. The Presence of Comorbid ADHD and Anxiety Symptoms in Autism Spectrum Disorder: Clinical Presentation and Predictors. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borschuk, A.P.; Rodweller, C.; Salorio, C.F. The Influence of Comorbid Asthma on the Severity of Symptoms in Children with Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. J. Asthma 2018, 55, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slim, M.; Rico-Villademoros, F.; Calandre, E.P. Psychiatric Comorbidity in Children and Adults with Gluten-Related Disorders: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2018, 10, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, H.; Vivas, D.; Cao, F.; Kazimi, I.F.; Teixeira, A.L.; Zeni, C.P. ADHD Is Associated with Migraine: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eur. Child. Adolesc Psychiatry 2018, 27, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brus, M.J.; Solanto, M.V.; Goldberg, J.F. Adult ADHD vs. Bipolar Disorder in the DSM-5 Era: A Challenging Differentiation for Clinicians. J. Psychiatr. Pr. 2014, 20, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velő, S.; Keresztény, Á.; Ferenczi-Dallos, G.; Pump, L.; Móra, K.; Balázs, J. The Association between Prosocial Behaviour and Peer Relationships with Comorbid Externalizing Disorders and Quality of Life in Treatment-Naïve Children and Adolescents with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawaskar, M.; Fridman, M.; Grebla, R.; Madhoo, M. Comparison of Quality of Life, Productivity, Functioning and Self-Esteem in Adults Diagnosed with ADHD and with Symptomatic ADHD. J. Atten. Disord. 2020, 24, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, R.; Goldenberg, M.; Perry, R.; William IsHak, W. The Quality of Life of Adults with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: A Systematic Review. Innov. Clin. Neurosci. 2012, 9, 10–21. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Weibman, D.; Halperin, J.M.; Li, X. A Review of Heterogeneity in Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rucklidge, J.J. Gender Differences in Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2010, 33, 357–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loyer Carbonneau, M.; Demers, M.; Bigras, M.; Guay, M.C. Meta-Analysis of Sex Differences in ADHD Symptoms and Associated Cognitive Deficits. J. Atten. Disord. 2021, 25, 1640–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudre, G.; Frederick, J.; Sharp, W.; Ishii-Takahashi, A.; Mangalmurti, A.; Choudhury, S.; Shaw, P. Mapping Associations between Polygenic Risks for Childhood Neuropsychiatric Disorders, Symptoms of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, Cognition, and the Brain. Mol. Psychiatry 2020, 25, 2482–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolas, M.A.; Burt, S.A. Genetic and Environmental Influences on ADHD Symptom Dimensions of Inattention and Hyperactivity: A Meta-Analysis. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 2010, 119, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, D.; Colpo, G.D.; Zeni, G.; Zeni, C.P.; Teixeira, A.L. Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder and Inflammation: What Does Current Knowledge Tell Us? A Systematic Review. Front. Psychiatry 2017, 8, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leffa, D.; Torres, I.; Rohde, L. A Review on the Role of Inflammation in Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Neuroimmunomodulation 2018, 25, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkougka, D.; Mitropoulos, K.; Tzanakaki, G.; Panagouli, E.; Psaltopoulou, T.; Thomaidis, L.; Tsolia, M.; Sergentanis, T.N.; Tsitsika, A. Gut Microbiome and Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Systematic Review. Pediatr. Res. 2022, 92, 1507–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellul, P.; Acquaviva, E.; Peyre, H.; Rosenzwajg, M.; Gressens, P.; Klatzmann, D.; Delorme, R. Parental Autoimmune and Autoinflammatory Disorders as Multiple Risk Factors for Common Neurodevelopmental Disorders in Offspring: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Transl. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saccaro, L.F.; Schilliger, Z.; Perroud, N.; Piguet, C. Inflammation, Anxiety, and Stress in Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerekes, N.; Sanchéz-Pérez, A.M.; Landry, M. Neuroinflammation as a Possible Link between Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and Pain. Med. Hypotheses 2021, 157, 110717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yao, T.; Cai, J.; Fu, X.; Li, H.; Wu, J. Systemic Inflammatory Regulators and 7 Major Psychiatric Disorders: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2022, 116, 110534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, M.E.; Teixeira, A.L. Inflammation in Psychiatric Disorders: What Comes First? Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2019, 1437, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, S.W.; Yoon, H.K.; Kim, Y.K. Role of Inflammation in Psychiatric Disorders. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1192, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, G.A.; Nigg, J.T.; Sullivan, E.L. Neuroinflammation as a Risk Factor for Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2019, 182, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, C.; Koyama, M.; Ota, E.; Swa, T.; Mlunde, L.B.; Amiya, R.M.; Tachibana, Y.; Yamamoto-Hanada, K.; Mori, R. Allergic Diseases in Children with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Psychiatry 2017, 17, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schans, J.v.d.; Çiçek, R.; de Vries, T.W.; Hak, E.; Hoekstra, P.J. Association of Atopic Diseases and Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 74, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordeleau, M.; Fernández de Cossío, L.; Chakravarty, M.M.; Tremblay, M.È. From Maternal Diet to Neurodevelopmental Disorders: A Story of Neuroinflammation. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2021, 14, 612705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, V.X.; Patel, S.; Jones, H.F.; Dale, R.C. Maternal Immune Activation and Neuroinflammation in Human Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2021, 17, 564–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thürmann, L.; Herberth, G.; Rolle-Kampczyk, U.; Röder, S.; Borte, M.; von Bergen, M.; Lehmann, I.; Trump, S. Elevated Gestational IL-13 During Fetal Development Is Associated with Hyperactivity and Inattention in Eight-Year-Old Children. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, B.W.; Karoly, P. Effects of Attentional Focusing on Pain Perception. Motiv. Emot. 1989, 13, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longe, S.E.; Wise, R.; Bantick, S.; Lloyd, D.; Johansen-Berg, H.; McGlone, F.; Tracey, I. Counter-Stimulatory Effects on Pain Perception and Processing Are Significantly Altered by Attention: An FMRI Study. Neuroreport 2001, 12, 2021–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.C.C.; Chan, C.C.H.; Kwan, A.S.K.; Ting, K.H.; Chui, T. yi Orienting Attention Modulates Pain Perception: An ERP Study. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asztély, K.; Kopp, S.; Gillberg, C.; Waern, M.; Bergman, S. Chronic Pain and Health-Related Quality of Life in Women with Autism And/or ADHD: A Prospective Longitudinal Study. J. Pain Res. 2019, 12, 2925–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasahara, S.; Niwa, S.I.; Matsudaira, K.; Sato, N.; Oka, H.; Yamada, Y. Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder and Chronic Pain. Psychosom. Med. 2020, 82, 346–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stray, L.L.; Kristensen, Ø.; Lomeland, M.; Skorstad, M.; Stray, T.; Tønnessen, F.E. Motor Regulation Problems and Pain in Adults Diagnosed with ADHD. Behav. Brain Funct. 2013, 9, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treister, R.; Eisenberg, E.; Demeter, N.; Pud, D. Alterations in Pain Response Are Partially Reversed by Methylphenidate (Ritalin) in Adults with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). Pain Pr. 2015, 15, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasanetz, F.; Acuña, M.A.; Nevian, T. Anterior Cingulate Cortex, Pain Perception, and Pathological Neuronal Plasticity during Chronic Pain. Book Neurobiol. Physiol. Psychol. Pain 2022, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, L.A.; McGaughy, J. Attentional Effects of Lesions to the Anterior Cingulate Cortex: How Prior Reinforcement Influences Distractibility. Behav. Neurosci. 2011, 125, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Ma, L.T.; Chen, Y.B.; Ren, D.; Chen, Y.B.; Li, Y.Q.; Sun, H.K.; Qiu, X.T.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, M.M.; et al. Anterior Insular Cortex Mediates Hyperalgesia Induced by Chronic Pancreatitis in Rats. Mol. Brain 2019, 12, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isbrandt, D. A Mechanistic Link between Glia and Neuronal Excitability in Acute Neuroinflammation. J. Physiol. 2017, 595, 603–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villemure, C.; Bushnell, M.C. Cognitive Modulation of Pain: How Do Attention and Emotion Influence Pain Processing? Pain 2002, 95, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.F.; Guan, S.Y.; Luo, L.; Li, Y.J.; Yang, L.; Zhou, X.X.; Guo, G.D.; Zhao, M.G.; Yang, Q.; Liu, G. Tetrahydroxystilbene Glucoside Relieves the Chronic Inflammatory Pain by Inhibiting Neuronal Apoptosis, Microglia Activation, and GluN2B Overexpression in Anterior Cingulate Cortex. Mol. Pain 2018, 14, 1744806918814367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, R.R.; Nackley, A.; Huh, Y.; Terrando, N.; Maixner, W. Neuroinflammation and Central Sensitization in Chronic and Widespread Pain. Anesthesiology 2018, 129, 343–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchatta, O.; Manouze, H.; Bouali-benazzouz, R.; Kerekes, N.; Ba-M’hamed, S.; Fossat, P.; Landry, M.; Bennis, M. Neonatal 6-OHDA Lesion Model in Mouse Induces Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)-like Behaviour. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Sarasúa, S.; Moustafa, S.; García-Avilés, Á.; López-Climent, M.F.; Gómez-Cadenas, A.; Olucha-Bordonau, F.E.; Sánchez-Pérez, A.M. The Effect of Abscisic Acid Chronic Treatment on Neuroinflammatory Markers and Memory in a Rat Model of High-Fat Diet Induced Neuroinflammation. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 13, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa-Fernández, V.; Mañas-Ojeda, A.; Pacheco-Herrero, M.; Castro-Salazar, E.; Ros-Bernal, F.; Sánchez-Pérez, A.M. Early Intervention with ABA Prevents Neuroinflammation and Memory Impairment in a Triple Transgenic Mice Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Behav. Brain Res. 2019, 374, 112106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxinos, G.; Franklin, K.B.J. Paxinos and Franklin’s the Mouse Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates; Elsevier: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, K.E.; Burnett, K.; Gigg, J. Water and T-Maze Protocols Are Equally Efficient Methods to Assess Spatial Memory in 3xTg Alzheimer’s Disease Mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2017, 331, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komada, M.; Takao, K.; Miyakawa, T. Elevated plus Maze for Mice. J. Vis. Exp. 2008, 22, e1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaky, A.; Bouali-Benazzouz, R.; Favereaux, A.; Tell, G.; Landry, M. APE1/Ref-1 Redox Function Contributes to Inflammatory Pain Sensitization. Exp. Neurol. 2018, 307, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Sarasúa, S.; Ribes-Navarro, A.; Beltrán-Bretones, M.T.; Sánchez-Pérez, A.M. AAV Delivery of ShRNA against IRS1 in GABAergic Neurons in Rat Hippocampus Impairs Spatial Memory in Females and Male Rats. Anat. Embryol. 2020, 226, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karperien, A. “FracLac for ImageJ”. Available online: https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/plugins/fraclac/FLHelp/Introduction.htm (accessed on 7 June 2022).
- Solanto, M.V. Dopamine Dysfunction in AD/HD: Integrating Clinical and Basic Neuroscience Research. Behav. Brain Res. 2002, 130, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avale, M.E.; Falzone, T.L.; Gelman, D.M.; Low, M.J.; Grandy, D.K.; Rubinstein, M. The Dopamine D4 Receptor Is Essential for Hyperactivity and Impaired Behavioral Inhibition in a Mouse Model of Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Mol. Psychiatry 2004, 9, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, P.M.; Pacheco, R. Targeting the Dopaminergic System in Autoimmunity. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2020, 15, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broome, S.T.; Louangaphay, K.; Keay, K.; Leggio, G.; Musumeci, G.; Castorina, A. Dopamine: An Immune Transmitter. Neural Regen. Res. 2020, 15, 2173–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribes-Navarro, A.; Atef, M.; Sánchez-Sarasúa, S.; Beltrán-Bretones, M.T.; Olucha-Bordonau, F.; Sánchez-Pérez, A.M. Abscisic Acid Supplementation Rescues High Fat Diet-Induced Alterations in Hippocampal Inflammation and IRSs Expression. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 56, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchatta, O.; Manouze, H.; Ba-M’Hamed, S.; Landry, M.; Bennis, M. Neonatal 6-OHDA Lesion Model in Mouse Induces Cognitive Dysfunctions of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) During Young Age. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurzina, N.; Belskaya, A.; Gromova, A.; Ignashchenkova, A.; Gainetdinov, R.R.; Volnova, A. Modulation of Spatial Memory Deficit and Hyperactivity in Dopamine Transporter Knockout Rats via A2A-Adrenoceptors. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slobodin, O.; Davidovitch, M. Gender Differences in Objective and Subjective Measures of ADHD Among Clinic-Referred Children. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa Macedo, L.L.B.; Antunes, F.T.T.; de Andrade Alvarenga, W.; Batista, M.C.C.; de Moura, M.S.B.; Farias, M.N.L.; Caminski, E.S.; Dallegrave, E.; Grivicich, I.; de Souza, A.H. Curcumin for Attention-Deficit-Hyperactivity Disorder: A Systematic Review and Preliminary Behavioral Investigation. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2022, 395, 803–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denninger, J.K.; Smith, B.M.; Kirby, E.D. Novel Object Recognition and Object Location Behavioral Testing in Mice on a Budget. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 2018, e58593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, C.; Mulraney, M.; Rinehart, N.; Sciberras, E. An Examination of the Association between Anxiety and Social Functioning in Youth with ADHD: A Systematic Review. Psychiatry Res. 2019, 273, 402–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ros, R.; Graziano, P.A. Social Functioning in Children with or At Risk for Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Meta-Analytic Review. J. Clin. Child. Adolesc Psychol. 2018, 47, 213–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene, R.W.; Biederman, J.; Faraone, S.V.; Monuteaux, M.C.; Mick, E.; Dupre, E.P.; Fine, C.S.; Goring, J.C. Social Impairment in Girls with ADHD: Patterns, Gender Comparisons, and Correlates. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2001, 40, 704–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biele, G.; Overgaard, K.R.; Friis, S.; Zeiner, P.; Aase, H. Cognitive, Emotional, and Social Functioning of Preschoolers with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Problems. BMC Psychiatry 2022, 22, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anastopoulos, A.D.; Smith, T.F.; Garrett, M.E.; Morrissey-Kane, E.; Schatz, N.K.; Sommer, J.L.; Kollins, S.H.; Ashley-Koch, A. Self-Regulation of Emotion, Functional Impairment, and Comorbidity Among ChildrenWith AD/HD. J. Atten. Disord. 2011, 15, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Liu, L.; Chen, W.; Preece, D.A.; Liu, Q.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Qian, Q. Affective-Cognitive-Behavioral Heterogeneity of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): Emotional Dysregulation as a Sentinel Symptom Differentiating “ADHD-Simplex” and “ADHD-Complex” Syndromes? J. Affec.t Disord. 2022, 307, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McQuade, J.D. ADHD Symptoms, Peer Problems, and Emotion Dysregulation as Longitudinal and Concurrent Predictors of Adolescent Borderline Personality Features. J. Atten. Disord. 2022, 26, 1711–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruton, A.M.; Senders, A.; Tost, G.; Ast, H.; Robinette, L.M.; Leung, B.; Hatsu, I.E.; Arnold, L.E.; Johnstone, J.M. Pain Sensitivity and Perceptual Sensitivity Are Associated with Severity of Emotional Dysregulation in Children with ADHD: A Cross-Sectional Analysis Using the Temperament in Middle Childhood Questionnaire. Disabil. Rehabil. 2022. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Northover, C.; Thapar, A.; Langley, K.; van Goozen, S. Pain Sensitivity in Adolescent Males with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: Testing for Associations with Conduct Disorder and Callous and Unemotional Traits. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stickley, A.; Koyanagi, A.; Takahashi, H.; Kamio, Y. ADHD Symptoms and Pain among Adults in England. Psychiatry Res. 2016, 246, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, N.; Rubia, K.; Knopf, H.; Hölling, H.; Martini, J.; Ehrlich, S.; Roessner, V. Reduced Pain Perception in Children and Adolescents with ADHD Is Normalized by Methylphenidate. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry Ment. Health 2016, 10, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, M.; Noda, K.; Akita, H.; Ishibashi, H. Characterization of Nociceptive Response to Chemical, Mechanical, and Thermal Stimuli in Adolescent Rats with Neonatal Dopamine Depletion. Neuroscience 2015, 289, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchatta, O.; Aby, F.; Sifeddine, W.; Bouali-Benazzouz, R.; Brochoire, L.; Manouze, H.; Fossat, P.; Ba M’Hamed, S.; Bennis, M.; Landry, M. Pain Hypersensitivity in a Pharmacological Mouse Model of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2114094119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, R.; Hattori, S.; Funasaka, T.; Huang, F.L.; Miyakawa, T. Decreased Nesting Behavior, Selective Increases in Locomotor Activity in a Novel Environment, and Paradoxically Increased Open Arm Exploration in Neurogranin Knockout Mice. Neuropsychopharmacol. Rep. 2021, 41, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, A.S.; Miller, S.M.; Sun, Y.; Xu, X.; Zweifel, L.S. Sexual Congruency in the Connectome and Translatome of VTA Dopamine Neurons. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monroe, T.B.; Gore, J.C.; Bruehl, S.P.; Benningfield, M.M.; Dietrich, M.S.; Chen, L.M.; Newhouse, P.; Fillingim, R.; Chodkowski, B.A.; Atalla, S.; et al. Sex Differences in Psychophysical and Neurophysiological Responses to Pain in Older Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study. Biol. Sex Differ. 2015, 6, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, J.L.; Robinson, M.E.; Wise, E.A.; Myers, C.D.; Fillingim, R.B. Sex Differences in the Perception of Noxious Experimental Stimuli: A Meta-Analysis. Pain 1998, 74, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unruh, A.M. Gender Variations in Clinical Pain Experience. Pain 1996, 65, 123–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogil, J.S.; Chesler, E.J.; Wilson, S.G.; Juraska, J.M.; Sternberg, W.F. Sex Differences in Thermal Nociception and Morphine Antinociception in Rodents Depend on Genotype. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2000, 24, 375–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maixner, D.W.; Christy, D.; Kong, L.; Viatchenko-Karpinski, V.; Horner, K.A.; Hooks, S.B.; Weng, H.-R. Phytohormone Abscisic Acid Ameliorates Neuropathic Pain via Regulating LANCL2 Protein Abundance and Glial Activation at the Spinal Cord. Mol. Pain 2022, 18, 174480692211077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, S.; Gandhi, W.; Schweinhardt, P. Cerebral Interactions of Pain and Reward and Their Relevance for Chronic Pain. Neurosci. Lett. 2012, 520, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leknes, S.; Brooks, J.C.W.; Wiech, K.; Tracey, I. Pain Relief as an Opponent Process: A Psychophysical Investigation. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 794–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Arjona, M.d.M.; Grondona, J.M.; Granados-Durán, P.; Fernández-Llebrez, P.; López-Ávalos, M.D. Microglia Morphological Categorization in a Rat Model of Neuroinflammation by Hierarchical Cluster and Principal Components Analysis. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, K.; Morrison, H. Quantifying Microglia Morphology from Photomicrographs of Immunohistochemistry Prepared Tissue Using ImageJ. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 2018, e57648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovens, I.; Nyakas, C.; Schoemaker, R. A Novel Method for Evaluating Microglial Activation Using Ionized Calcium-Binding Adaptor Protein-1 Staining: Cell Body to Cell Size Ratio. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2014, 1, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matisz, C.E.; Gruber, A.J. Neuroinflammatory Remodeling of the Anterior Cingulate Cortex as a Key Driver of Mood Disorders in Gastrointestinal Disease and Disorders. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 133, 104497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Kim, K.; Kwon, M.; Bai, S.J.; Cha, M.; Lee, B.H. Modulation of Neuropathic Pain by Glial Regulation in the Insular Cortex of Rats. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 815945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona, J.C. Role of Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation in Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caston, R.A.; Gampala, S.; Armstrong, L.; Messmann, R.A.; Fishel, M.L.; Kelley, M.R. The Multifunctional APE1 DNA Repair-Redox Signaling Protein as a Drug Target in Human Disease. Drug Discov. Today 2021, 26, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijit, M.; Caston, R.; Gampala, S.; Fishel, M.L.; Fehrenbacher, J.; Kelley, M.R. APE1/Ref-1—One Target with Multiple Indications: Emerging Aspects and New Directions. J. Cell. Signal. 2021, 2, 151–161. [Google Scholar]
- Sahakian, L.; Filippone, R.T.; Stavely, R.; Robinson, A.M.; Yan, X.S.; Abalo, R.; Eri, R.; Bornstein, J.C.; Kelley, M.R.; Nurgali, K. Inhibition of APE1/Ref-1 Redox Signaling Alleviates Intestinal Dysfunction and Damage to Myenteric Neurons in a Mouse Model of Spontaneous Chronic Colitis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2021, 27, 388–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Jiang, C.; Kang, Y.; Dai, Y.; Fang, W.; Huang, P. Curcumin Exerts Protective Effects against Hypoxia-reoxygenation Injury via the Enhancement of Apurinic/Apyrimidinic Endonuclease 1 in SH-SY5Y Cells: Involvement of the PI3K/AKT Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 45, 993–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaky, A.; Bassiouny, A.; Farghaly, M.; El-Sabaa, B.M. A Combination of Resveratrol and Curcumin Is Effective Against Aluminum Chloride-Induced Neuroinflammation in Rats. J. Alzheimers. Dis. 2017, 60, S221–S222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torregrosa-Muñumer, R.; Gómez, A.; Vara, E.; Kireev, R.; Barja, G.; Tresguerres, J.A.F.; Gredilla, R. Reduced Apurinic/Apyrimidinic Endonuclease 1 Activity and Increased DNA Damage in Mitochondria Are Related to Enhanced Apoptosis and Inflammation in the Brain of Senescence- Accelerated P8 Mice (SAMP8). Biogerontology 2016, 17, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.L.; Lin, Y.T.; Chuang, P.C.; Bohr, V.A.; Mattson, M.P. BDNF and Exercise Enhance Neuronal DNA Repair by Stimulating CREB-Mediated Production of Apurinic/Apyrimidinic Endonuclease 1. Neuromolecular Med. 2014, 16, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaky, A.; Mohammad, B.; Moftah, M.; Kandeel, K.M.; Bassiouny, A.R. Apurinic/Apyrimidinic Endonuclease 1 Is a Key Modulator of Aluminum-Induced Neuroinflammation. BMC Neurosci. 2013, 14, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meseguer-Beltrán, M.; Sánchez-Sarasúa, S.; Landry, M.; Kerekes, N.; Sánchez-Pérez, A.M. Targeting Neuroinflammation with Abscisic Acid Reduces Pain Sensitivity in Females and Hyperactivity in Males of an ADHD Mice Model. Cells 2023, 12, 465. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12030465
Meseguer-Beltrán M, Sánchez-Sarasúa S, Landry M, Kerekes N, Sánchez-Pérez AM. Targeting Neuroinflammation with Abscisic Acid Reduces Pain Sensitivity in Females and Hyperactivity in Males of an ADHD Mice Model. Cells. 2023; 12(3):465. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12030465
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeseguer-Beltrán, María, Sandra Sánchez-Sarasúa, Marc Landry, Nora Kerekes, and Ana María Sánchez-Pérez. 2023. "Targeting Neuroinflammation with Abscisic Acid Reduces Pain Sensitivity in Females and Hyperactivity in Males of an ADHD Mice Model" Cells 12, no. 3: 465. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12030465
APA StyleMeseguer-Beltrán, M., Sánchez-Sarasúa, S., Landry, M., Kerekes, N., & Sánchez-Pérez, A. M. (2023). Targeting Neuroinflammation with Abscisic Acid Reduces Pain Sensitivity in Females and Hyperactivity in Males of an ADHD Mice Model. Cells, 12(3), 465. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12030465









