The Multifunctional Nature of the MicroRNA/AKT3 Regulatory Axis in Human Cancers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. AKT3-Derived circRNAs
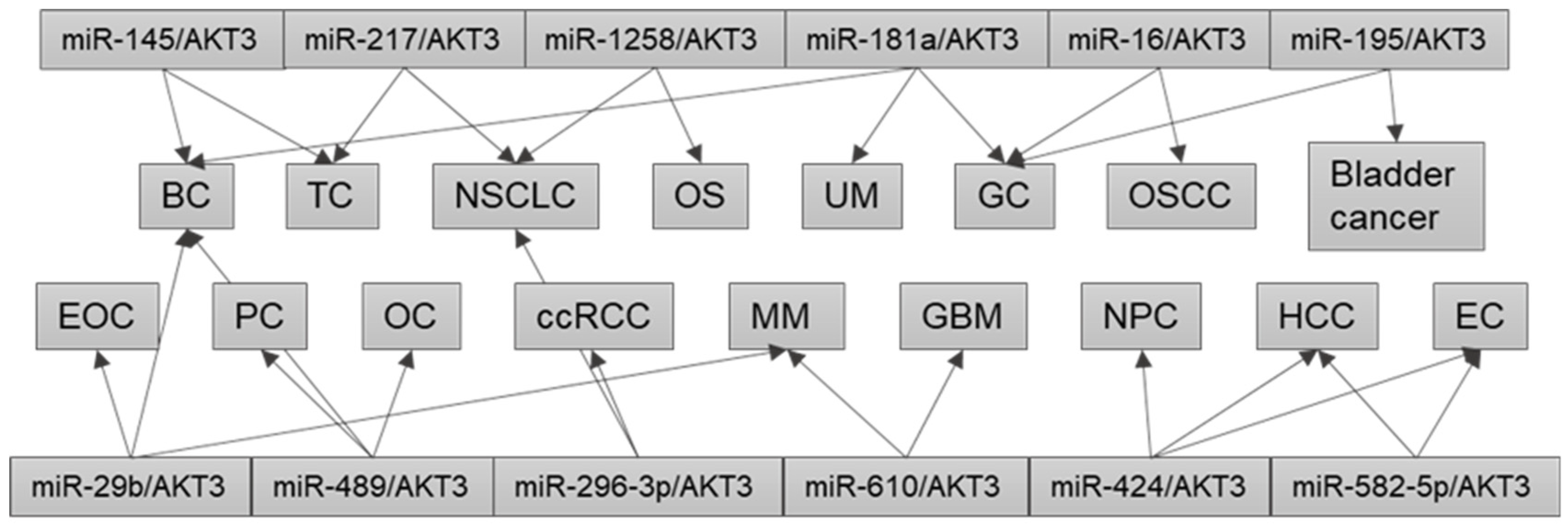
3. AKT3 and miRNA/AKT3 Axes in Human Cancers
3.1. Breast Cancer
| BC Model System | AKT3 or Akt3/Functions | AKT3 Targets | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| K-RAS mutated MDA-MB-231 cells; xenografts | AKT3/cell proliferation↑, tumor growth↑, post-irradiation cell survival↑ | [21] | |
| 3475 subline of MDA-MB-231 cells (lung metastasis); MDA-MB-231 | AKT3/tumor growth↑, metastasis↑, apoptosis↓ | ERK, Bim, Bax | [45] |
| MDA-MB-231; MDA-MB-468 and MCF10DCIS xenografts | AKT3/TNBC growth↑ | p27 | [46] |
| ErbB2(+) BC cells, mammary tumor cells | AKT3/cell proliferation↑, tamoxifen sensitivity↓ | pErbB2/pErbB3, Foxo3a, ERα | [47] |
| MMTV-ErbB2, MMTV-PyMT mice (Neu- and PyMT- driven mammary oncogenesis) | Akt3/no effect on tumorigenesis of mouse BC cells | [48] | |
| PyMT mouse BC cells | Akt3/metastasis of mouse BC cells↓ | [49] | |
| MDA-MB-231 BO cells; xenografts | AKT3/migration↓, invasion↓ bone metastasis↓ | HER2, DDR kinase | [50] |
| IBC cells: SUM149 | AKT3/survival of IBC↑, no effect on invasion | [51] |
| Tumor Tissue/Cell Lines | LncRNA or circRNA/Functions | MiRNAs in the miRNA/AKT3 Axis/Related Functions | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Breast Cancer (BC) | |||
| BC tissues; MDA-MB-231, HUVECs | miR-29b/ angiogenesis↓ tumorigenesis↓ | [36] | |
| Docetaxel resistance of BC MCF7, MDA-MB-231, docetaxel resistant cell lines: MCF7/DTX, MDA-MB-231/DTX | miR-145/ cell viability↓, colony formation↓, docetaxel sensitivity↑ | [53] | |
| MCF10A, MCF10. AT1, MCF10.neoT, CF10. Ca1d, MCF10. Ca1h, MCF10. DCIS | miR-29c/ preneoplastic TNBC cell proliferation↓, colonization ability↓ | [54] | |
| MDA-MB-231 | miR-181a-5p/ viability↓, migration↓, survival↓, Warburg effect↓ | [55] | |
| BC tissues; BT-549, MCF-7, MDA-MB-453, MDA-MB-231 | miR-433/ cell proliferation↓, cell viability↓, apoptosis↑ | [56] | |
| Drug-resistant and drug-sensitive BC tumor tissues; MCF-7, MDA-MB-231, MDA-MB-468, T47D | miR-489/ chemosensitivity↑, cell proliferation↓, invasion↓ | [57] | |
| MCF-7, MDA-MB-231 | miR-3614-3p/ invasion↓, migration↓ | [58] | |
| BC tissues; MDA-MB-231 | circWHSC1/ cell growth↑, proliferation↑, migration↑, invasion↑, glycolysis↑, apoptosis↓ | miR-212-5p | [60] |
| HCC1937, BT549, MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, T47D, BT474 | RP11-480I12.5-004/ cell proliferation↑, colony formation↑, apoptosis↓ | miR-29c-3p | [59] |
| Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) | |||
| NSCLC tissues; cell lines: BEAS-2B, A549, HCC823, NCL-H23, NCL-H358 cells | miR-217/ cell proliferation↓, apoptosis↑ | [61] | |
| NSCLC tissues; A549 | circulating miR-320a/ metastatic potential↓, apoptosis↑ | [62] | |
| NSCLC tissues; NSCLC cell lines: CALU3, CALU6, A549, H1229, H1975 | circWHSC1/ colony formation↑, viability↑, metastasis↑, progression↑ | miR-296-3p | [63] |
| NSCLC tissues; NSCLC cell lines: A549 and H460 | circ_0016760/proliferation↑, migration↑, apoptosis↓ | miR-646 | [64] |
| NSCLC tissues; Cell lines: NCI-H1299, A549, H460, NCI-H2106, H1975 | circ_0000520/ cell growth↑, migration↑, invasion↑ | miR-1258 | [65] |
| Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) | |||
| HCC specimens; HCC cell lines: HepG2 | miR-122, miR-124/ function not validated | [66] | |
| HCC tissue samples and cell lines: Huh-7, SNU-182, SNU-475, Hep3B2, HepG2 | miR-122/ cell growth↓, migration↓, apoptosis↑, | [67] | |
| HCC-BCLC9 cell | miR-122/ cell proliferation↓, dormancy↑ | [68] | |
| HCC specimens; HepG2, HuH7, SMMC-7721 | miR-144/ cell proliferation↓, migration↓, invasion↓ | [69] | |
| HCC tissues of solitary large, nodular, and small HCC; HCC cell lines: SMMC7721, HepG2, HUH7, MHCC97-L, MHCC97-H, HCCLM3 | miR-424/ cell proliferation↓ | [70] | |
| HCC specimens; HCC cell lines: QGY-7703, Huh7, BEL-7402, HepG2, Hep3B | miR-582-5p/ colony formation↓, cell proliferation↓ | [71] | |
| HCC tissues; HCC cell lines: SNU-449, SNU-182, Huh7, LM3, Bel-7405, SK-hep1, Hep3B | LINC00680/stemness behavior↑, chemosensitivity↓ | miR-568 | [72] |
| HCC specimens; HCC cell lines: HepG2, Hep3B, Huh-7, SNU398, NU449, SNU182, SNU475 | miR-519d/AKT3? miR-519d/ cell proliferation↑, migration↑, apoptosis↓ | [73] | |
| Colorectal cancer (CRC) | |||
| CRC cell lines: RKO, HCT116 | miR-124-3p.1/ proliferation↓, metastasis↓ | [74] | |
| CRC tissues; CRC cell lines: SW480, HCT116, LOVO, SW620 | miR-384/ proliferation↓ | [75] | |
| CRC tissues; CRC cell lines: Colo205, SW620, HCT116, HT29, LOVO, SW480 | LINC02163/proliferation↑, metastasis↑ | miR-511-3p | [76] |
| CRC tissues; CRC cell lines: LOVO, PKO, SW480, HT29 | lncRNA DSCAM-AS1/proliferation↑, invasion↑, migration↑ | miR-384 | [77] |
| Gastric carcinoma (GC) | |||
| GC tissues; cell lines: SGC-7901, MKN45, BGC823 | miR-195/ apoptosis↑ | [78] | |
| Gastric adenocarcinoma serum; cell line: MGC-803 | MALAT1/ apoptosis↓ | miR-181a-5p | [79] |
| GC tissues; GC cell lines: MKN28, NCI-N87, AGS, KATOIII, RF1, RF48 | circNF1/cell proliferation↑ | miR-16 | [80] |
| Cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) cell lines: HCCC-9810, RBE | circRNA CDR1a/proliferation↑, invasion↑ | miR-641 | [81] |
| Pancreatic cancer (PC) tissues; cell line: PANC-1 | miR-489/proliferation↓, apoptosis↑ | [82] | |
| Ovarian cancer (OC)/epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) | |||
| EOC tissues; cell lines: SKOV3, A2780, HO8910, 3AO | miR-29b/ Warburg effect↓, tumor growth↓ | [83] | |
| OC cell lines: SKOV3, OVCAR3, cisplatin-resistant SKOV and OVCAR3 cells | miR-489/ survival↓, growth↓, apoptosis↑, sensitivity of cisplatin-resistant OC to cisplatin↑ | [84] | |
| OC tissues; Cell lines: CaOV3, OVCAR3, SKOV3 | RHPN1-AS1/proliferation↑, migration↑, invasion↑ | miR-665 | [85] |
| OC tissues; OC cell lines: SKOV-3, ES-2, OVCAR3, A2780, CAOV3 | lncRNA EMX2OS/proliferation↑, invasion↑, tumor growth ↑ | miR-654 | [86] |
| Endometrial carcinoma (EC) | |||
| EC tissues; EC cell line ECC1 | miR-582-5p/proliferation↓, apoptosis↑ | [87] | |
| Endometrial adenocarcinoma cell line: Ishikawa (ISK) cells | lncCDKN2B-AS1/proliferation↑, invasion↑ | miR-424-5p | [88] |
| EC tissues; EC cell lines: HEC1A, HEC1B, Ishikawa | LINC01224/ proliferation↑, apoptosis↓ | miR-485-5p | [89] |
| Thyroid carcinoma (TC)/papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) | |||
| TC tissues; cell lines: TPC-1, FTC-133, 8505C; primary PTC cells; | miR-145/ growth↓, metastasis↓ | [90] | |
| PTC tissues; PTC cell line: K1 | miR-29a/ growth↓, apoptosis↑, metastasis↓ | [91] | |
| TC tissues; PTC cell lines: 8505C, TPC-1, SW1736 | miR-217/ proliferation↓, migration↓, invasion↓ | [92] | |
| PTC tissues; PTC cell lines: B-CPAP, KTC-1 | lncRNA n384546/progression↑, metastasis↑ | miR-145-5p | [93] |
| TC tissues; TC cell lines: BCPAP, K1, H7H83, TPC-1 | circ_0000144/proliferation↑, migration↑, invasion↑ | miR-217 | [94] |
| Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) | |||
| NPC tissues; Human primary NPC cell | miR-424-5p/ proliferation↓, migration↓, apoptosis↑ | [95] | |
| NPC tissues; NPC cell lines: C666-1, SUNE1, 5-8 F, HNE1, HNE2 | circTRAF3/proliferation↑, invasion↑, apoptosis↓ | miR-203a-3p | [96] |
| Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) tissues; cell line: SCC-4, SCC-25, HN-6, CAL-27, TCA-83 | miR-16/ proliferation↓, apoptosis↑ | [97] | |
| Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) | |||
| GBM cell lines: T98G, U87, A172, LN229, LN18 | miR-610/ proliferation↓, anchorage independent growth↓ | [98] | |
| GBM cell lines: LN229, A172, U373, SHG44 | lncRNA, GAS5/proliferation↓, migration↓, invasion↓ | miR-424 | [99] |
| Multiple myeloma (MM) | |||
| Primary MM cells, MM cell lines: MM.1S, RPMI8226 | miR-15a, miR-16-1/ cell proliferation↓ | [100] | |
| MM cell lines: OPM2, RPMI-8226; Endothelial cell: HUVECs | miR-29b/ endothelial cell proliferation↓, migration↓, tube formation↓ | [101] | |
| MM tissues; cell lines: KM3, H929, MM1S, U266 cells | circ_0000142/proliferation↑, metastasis↑ | miR-610 | [102] |
| MM tissues; cell lines: OPM-2, U266, KM3, U1996, H929 | lncRNA FEZF1-AS1/ proliferation↑, apoptosis↓ | miR-610 | [103] |
| Osteosarcoma (OS) | |||
| OS tissues; cell lines: HOS, MG-63, Saos-2, SW1353, U2OS | miR-1258/ proliferation↓ | [104] | |
| OS tissues; OS cell lines: HOS, MG-63, SaOS-2, U2OS, | MALAT1/ glycolysis↑, proliferation↑, metastasis↑ | miR-485-3p | [105] |
| Uveal melanoma (UM) tissues; UM cell line: OCM-1A | miR-224-5p/ proliferation↓, migration↓, invasion↓ | [106] | |
| UM cell lines: OMM2.5, UM001, Mel285, Mel290; UM xenografts | miR-181a-5p/ proliferation↓, colony formation↓, apoptosis↑, tumor growth ↓ | [107] | |
| NK/T cell lymphoma (NKTL) tissues; cell lines: KHYG-1, NK-92, HANK-1, SNK-1, SNK-6 | miR-150/ sensitivity of NKTL to radiation treatment↑ | [108] | |
| Bladder cancer TCGA database | miR-195/ cell proliferation↓ | [109] | |
| Wilms’ tumor tissues; cell lines: 17–94, WIT49 | miR-22-3p/ proliferation↓, invasion↓ | [110] |
3.2. Lung Cancer
3.3. Digestive/Gastrointestinal Cancers
3.4. Gynecologic Cancers
3.5. Thyroid Carcinoma and Head and Neck Cancers
3.6. Other Types of Human Cancer
4. Dysregulation of the Same miRNA/AKT3 Axis in Different Cancers
5. Perspectives and Therapeutic Applications
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Full Name |
| 3′-UTRs | 3′-untranslated region |
| CCA | cholangiocarcinoma |
| ccRCC | clear cell renal cell carcinoma |
| ceRNA | competitive endogenous RNA |
| circRNAs | circular RNAs |
| CRC | colorectal cancer |
| DDR | discoidin domain receptors |
| EC | endometrial carcinoma |
| EOC | epithelial ovarian cancer |
| ERα | estrogen receptor alpha |
| GAS5 | growth arrest-specific 5 |
| GBM | glioblastoma multiforme |
| GC | gastric cancer |
| HCC | hepatocellular carcinoma |
| HER2 | ErbB2 receptor tyrosine kinase 2 |
| HK2 | hexokinase2 |
| HUVEC | human umbilical vein endothelial cells |
| IBC | inflammatory breast cancer |
| lncRNAs | long non-coding RNAs |
| MALAT-1 | metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 |
| miRNA, miR- | microRNA |
| MM | multiple myeloma |
| ncRNAs | non-coding RNAs |
| NKTL | NK/T cell lymphoma |
| NPC | nasopharyngeal carcinoma |
| NSCLC | non-small-cell lung cancer |
| OC | ovarian cancer |
| OS | osteosarcoma |
| OSCC | oral squamous cell carcinoma |
| PC | pancreatic cancer |
| PD-L1 | programmed death-ligand 1 |
| PTC | papillary thyroid carcinoma |
| RCC | renal cell carcinoma |
| TGFβ | transforming growth factor β |
| TNBC | triple-negative breast cancer |
| ULM | uterine leiomyomas |
| UM | uveal melanoma |
| UTR | untranslated region |
References
- Cardone, M.H.; Roy, N.; Stennicke, H.R.; Salvesen, G.S.; Franke, T.F.; Stanbridge, E.; Frisch, S.; Reed, J.C. Regulation of cell death pro-tease caspase-9 by phosphorylation. Science 1998, 282, 1318–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinz, N.; Jücker, M. Distinct functions of AKT isoforms in breast cancer: A comprehensive review. Cell Commun. Signal. 2019, 17, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.H.; Yang, M.J.; Choi, S.; Kim, J.; Koh, G.Y. Refractoriness of STING therapy is relieved by AKT inhibitor through effective vascular disruption in tumour. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilanges, B.; Posor, Y.; Vanhaesebroeck, B. PI3K isoforms in cell signalling and vesicle trafficking. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 515–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Jiang, W.; Hou, P. Emerging role of PI3K/AKT in tumor-related epigenetic regulation. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2019, 59, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yen, C.; Liaw, D.; Podsypanina, K.; Bose, S.; Wang, S.I.; Puc, J.; Miliaresis, C.; Rodgers, L.; McCombie, R.; et al. PTEN, a putative protein tyrosine phosphatase gene mutated in human brain, breast, and prostate cancer. Science 1997, 275, 1943–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Mo, Y.Y. The Akt-associated microRNAs. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2012, 69, 3601–3612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, F.F. Non-coding RNAs: New players in eukaryotic biology. Gene 2005, 357, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvakumar, S.C.; Preethi, K.A.; Sekar, D. MicroRNAs as important players in regulating cancer through PTEN/PI3K/AKT signalling pathways. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2023, 1878, 188904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebbesen, K.K.; Hansen, T.B.; Kjems, J. Insights into circular RNA biology. RNA Biol. 2017, 14, 1035–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, J.N.; Cieslik, M.; Zhang, Y.; Shukla, S.; Xiao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.M.; Dhanasekaran, S.M.; Engelke, C.G.; Cao, X.; et al. The Landscape of Circular RNA in Cancer. Cell 2019, 176, 869–881.e813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, T.B.; Jensen, T.I.; Clausen, B.H.; Bramsen, J.B.; Finsen, B.; Damgaard, C.K.; Kjems, J. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature 2013, 495, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, B.; Chao, J.; Yao, H. Circular RNA and its mechanisms in disease: From the bench to the clinic. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 187, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, C.; Li, G.; Lu, J.; Li, L. Crosstalk between circRNAs and the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in cancer progression. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Statello, L.; Guo, C.-J.; Chen, L.-L.; Huarte, M. Gene regulation by long non-coding RNAs and its biological functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 96–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattick, J.S.; Amaral, P.P.; Carninci, P.; Carpenter, S.; Chang, H.Y.; Chen, L.-L.; Chen, R.; Dean, C.; Dinger, M.E.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; et al. Long non-coding RNAs: Definitions, functions, challenges and recommendations. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 24, 430–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercer, T.R.; Dinger, M.E.; Mattick, J.S. Long non-coding RNAs: Insights into functions. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Askari, A.; Hussen, B.M.; Taheri, M.; Mokhtari, M. A long non-coding RNA with important roles in the carcinogenesis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 1037149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffer, P.J.; Woodgett, J.R. Molecular cloning and characterisation of a novel putative protein-serine kinase related to the cAMP-dependent and protein kinase C families. Eur. J. Biochem./FEBS 1991, 201, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, K.M.; Anderson, N.G. The protein kinase B/Akt signalling pathway in human malignancy. Cell. Signal. 2002, 14, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toulany, M.; Maier, J.; Iida, M.; Rebholz, S.; Holler, M.; Grottke, A.; Jüker, M.; Wheeler, D.L.; Rothbauer, U.; Rodemann, H.P. Akt1 and Akt3 but not Akt2 through interaction with DNA-PKcs stimulate proliferation and post-irradiation cell survival of K-RAS-mutated cancer cells. Cell Death Discov. 2017, 3, 17072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, A.; Lambring, C.B. Akt Isoforms: A Family Affair in Breast Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.S.; Xu, P.Z.; Gottlob, K.; Chen, M.L.; Sokol, K.; Shiyanova, T.; Roninson, I.; Weng, W.; Suzuki, R.; Tobe, K.; et al. Growth retardation and increased apoptosis in mice with homozygous disruption of the Akt1 gene. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 2203–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.; Mu, J.; Kim, J.K.; Thorvaldsen, J.L.; Chu, Q.; Crenshaw, E.B., 3rd; Kaestner, K.H.; Bartolomei, M.S.; Shulman, G.I.; Birnbaum, M.J. Insulin resistance and a diabetes mellitus-like syndrome in mice lacking the protein kinase Akt2 (PKB beta). Science 2001, 292, 1728–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tschopp, O.; Yang, Z.Z.; Brodbeck, D.; Dummler, B.A.; Hemmings-Mieszczak, M.; Watanabe, T.; Michaelis, T.; Frahm, J.; Hemmings, B.A. Essential role of protein kinase B gamma (PKB gamma/Akt3) in postnatal brain development but not in glucose homeostasis. Development 2005, 132, 2943–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wainstein, E.; Maik-Rachline, G.; Blenis, J.; Seger, R. AKTs do not translocate to the nucleus upon stimulation but AKT3 can constitutively signal from the nuclear envelope. Cell Rep. 2022, 41, 111733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatani, K.; Thompson, D.A.; Barthel, A.; Sakaue, H.; Liu, W.; Weigel, R.J.; Roth, R.A. Up-regulation of Akt3 in estrogen receptor-deficient breast cancers and androgen-independent prostate cancer lines. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 21528–21532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risso, G.; Blaustein, M.; Pozzi, B.; Mammi, P.; Srebrow, A. Akt/PKB: One kinase, many modifications. Biochem. J. 2015, 468, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishi, H.; Kuroda, S.; Tanaka, M.; Matsuzaki, H.; Ono, Y.; Kameyama, K.; Haga, T.; Kikkawa, U. Molecular cloning and characterization of a new member of the RAC protein kinase family: Association of the pleckstrin homology domain of three types of RAC protein kinase with protein kinase C subspecies and beta gamma subunits of G proteins. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995, 216, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.A.; Stemke-Hale, K.; Tellez, C.; Calderone, T.L.; Deng, W.; Prieto, V.G.; Lazar, A.J.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Mills, G.B. A novel AKT3 mutation in melanoma tumours and cell lines. Br. J. Cancer 2008, 99, 1265–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeganeh, P.N.; Richardson, C.; Bahrani-Mostafavi, Z.; Tait, D.L.; Mostafavi, M.T. Dysregulation of AKT3 along with a small panel of mRNAs stratifies high-grade serous ovarian cancer from both normal epithelia and benign tumor tissues. Genes Cancer 2017, 8, 784–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhunapantula, S.V.; Robertson, G.P. Targeting protein kinase-b3 (akt3) signaling in melanoma. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2017, 21, 273–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, F.-M.; Yost, S.E.; Wen, W.; Frankel, P.H.; Schmolze, D.; Chu, P.-G.; Yuan, Y.-C.; Liu, Z.; Yim, J.; Chen, Z. Differential gene expression and AKT targeting in triple negative breast cancer. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 4356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joy, A.; Kapoor, M.; Georges, J.; Butler, L.; Chang, Y.; Li, C.; Crouch, A.; Smirnov, I.; Nakada, M.; Hepler, J.; et al. The role of AKT isoforms in glioblastoma: AKT3 delays tumor progression. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2016, 130, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Chen, L.; Tang, L. Upregulation of AKT1 and downregulation of AKT3 caused by dysregulation of microRNAs contributes to pathogenesis of hemangioma by promoting proliferation of endothelial cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 21342–21351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Cai, B.; Shen, L.; Dong, Y.; Lu, Q.; Sun, S.; Liu, S.; Ma, S.; Ma, P.X.; Chen, J. MiRNA-29b suppresses tumor growth through simultaneously inhibiting angiogenesis and tumorigenesis by targeting Akt3. Cancer Lett. 2017, 397, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Jiang, T.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Y. CircAKT3 inhibits glycolysis balance in lung cancer cells by regulating miR-516b-5p/STAT3 to inhibit cisplatin sensitivity. Biotechnol. Lett. 2020, 42, 1123–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, W.; Li, B.; Wang, L.; Xu, Z.; Zeng, A.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; et al. Circular RNA AKT3 upregulates PIK3R1 to enhance cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer via miR-198 suppression. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xu, W.; Xia, Z.; Liu, W.; Pan, G.; Ding, J.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Xie, X.; Jiang, D. Hsa_circ_0000199 facilitates chemo-tolerance of triple-negative breast cancer by interfering with miR-206/613-led PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling. Aging 2021, 13, 4522–4551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, D.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Shen, D.; Lu, J.; Wang, M.; Zebibula, A.; Xu, L.; Wu, H.; Li, G.; et al. Circ-AKT3 inhibits clear cell renal cell carcinoma metastasis via altering miR-296-3p/E-cadherin signals. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Li, X.; Li, F.; Wu, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, H.; Huang, N.; Yang, X.; Xiao, F.; Liu, D.; et al. A novel tumor suppressor protein encoded by circular AKT3 RNA inhibits glioblastoma tumorigenicity by competing with active phosphoinositide-dependent Kinase-1. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmani, F.; Ferns, G.A.; Talebian, S.; Nourbakhsh, M.; Avan, A.; Shahidsales, S. Role of regulatory miRNAs of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in the pathogenesis of breast cancer. Gene 2020, 737, 144459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, K.M.; Sun, Y.; Ji, P.; Granberg, K.J.; Bernard, B.; Hu, L.; Cogdell, D.E.; Zhou, X.; Yli-Harja, O.; Nykter, M.; et al. Genomically amplified Akt3 activates DNA repair pathway and promotes glioma progression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 3421–3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerji, S.; Cibulskis, K.; Rangel-Escareno, C.; Brown, K.K.; Carter, S.L.; Frederick, A.M.; Lawrence, M.S.; Sivachenko, A.Y.; Sougnez, C.; Zou, L.; et al. Sequence analysis of mutations and translocations across breast cancer subtypes. Nature 2012, 486, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suyama, K.; Yao, J.; Liang, H.; Benard, O.; Loudig, O.D.; Amgalan, D.; McKimpson, W.M.; Phillips, G.R.; Segall, J.; Wang, Y.; et al. An Akt3 Splice Variant Lacking the Serine 472 Phosphorylation Site Promotes Apoptosis and Suppresses Mammary Tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, Y.R.; Yoshida, T.; Marusyk, A.; Beck, A.H.; Polyak, K.; Toker, A. Targeting Akt3 signaling in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 964–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabinski, N.; Möllmann, K.; Milde-Langosch, K.; Müller, V.; Schumacher, U.; Brandt, B.; Pantel, K.; Jücker, M. AKT3 regulates ErbB2, ErbB3 and estrogen receptor α expression and contributes to endocrine therapy resistance of ErbB2+ breast tumor cells from Balb-neuT mice. Cell. Signal. 2014, 26, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroulakou, I.G.; Oemler, W.; Naber, S.P.; Tsichlis, P.N. Akt1 ablation inhibits, whereas Akt2 ablation accelerates, the development of mammary adenocarcinomas in mouse mammary tumor virus (MMTV)-ErbB2/neu and MMTV-polyoma middle T transgenic mice. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.; Yao, J.; Suyama, K.; Bajaj, S.; Qian, X.; Loudig, O.D.; Eugenin, E.A.; Phillips, G.R.; Hazan, R.B. N-cadherin regulates mammary tumor cell migration through Akt3 suppression. Oncogene 2013, 32, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinz, N.; Baranowsky, A.; Horn, M.; Kriegs, M.; Sibbertsen, F.; Smit, D.J.; Clezardin, P.; Lange, T.; Schinke, T.; Jücker, M. Knockdown of AKT3 Activates HER2 and DDR Kinases in Bone-Seeking Breast Cancer Cells, Promotes Metastasis In Vivo and Attenuates the TGFβ/CTGF Axis. Cells 2021, 10, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehman, H.L.; Van Laere, S.J.; van Golen, C.M.; Vermeulen, P.B.; Dirix, L.Y.; van Golen, K.L. Regulation of inflammatory breast cancer cell invasion through Akt1/PKBα phosphorylation of RhoC GTPase. Mol. Cancer Res. MCR 2012, 10, 1306–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabi, Y.; Bendifallah, S.; Suisse, S.; Haury, J.; Touboul, C.; Puchar, A.; Favier, A.; Daraï, E. Overview of non-coding RNAs in breast cancers. Transl. Oncol. 2022, 25, 101512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Cai, W.; Lu, H. Overexpression of microRNA-145 enhanced docetaxel sensitivity in breast cancer cells via inactivation of protein kinase B gamma-mediated phosphoinositide 3-kinase -protein kinase B pathway. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 11310–11320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, A.; Singh, H.; Rajapakshe, K.; Tachibana, K.; Ganesan, N.; Pan, Y.; Gunaratne, P.H.; Coarfa, C.; Bedrosian, I. Regulation of miRNA-29c and its downstream pathways in preneoplastic progression of triple-negative breast cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 19645–19660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Tahiri, H.; Yang, C.; Gu, M.; Ruan, X.; Hardy, P. Overexpression of miR-181a regulates the Warburg effect in triple-negative breast cancer. Climacteric J. Int. Menopause Soc. 2023, 26, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Wang, J.; He, W.; Zhao, P.; Ye, C. MicroRNA-433 targets AKT3 and inhibits cell proliferation and viability in breast cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 3998–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Y.W.; Xing, A.Y.; Xiang, S.; Shi, D.B.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.X.; Gao, P. Suppression of SPIN1-mediated PI3K-Akt pathway by miR-489 increases chemosensitivity in breast cancer. J. Pathol. 2016, 239, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Jing, X.; Li, F.; Chen, Y.; Huang, C. miR-3614-3p suppresses cell aggressiveness of human breast cancer by targeting AKT3 and HDAC1 expression. Transl. Cancer Res. 2022, 11, 1565–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, W.; Ding, B.; Zhong, G.; Yao, J.; Fan, W.; Fu, P. RP11-480I12.5-004 Promotes Growth and Tumorigenesis of Breast Cancer by Relieving miR-29c-3p-Mediated AKT3 and CDK6 Degradation. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 21, 916–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Xie, Z. CircWHSC1 regulates malignancy and glycolysis by the miR-212-5p/AKT3 pathway in triple-negative breast cancer. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2021, 123, 104704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.J.; Zha, W.J.; Zhang, W. MicroRNA-217 alleviates development of non-small cell lung cancer by inhibiting AKT3 via PI3K pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 5972–5979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khandelwal, A.; Sharma, U.; Barwal, T.S.; Seam, R.K.; Gupta, M.; Rana, M.K.; Vasquez, K.M.; Jain, A. Circulating miR-320a Acts as a Tumor Suppressor and Prognostic Factor in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 645475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, F.; Yang, Q.; Shen, D.; Chen, J. CircRNA WHSC1 promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression via sponging microRNA-296-3p and up-regulating expression of AKT serine/threonine kinase 3. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2021, 35, e23865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, L.; Ran, R.; Huang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Xing, M.; Cai, Y. Circ_0016760 accelerates non-small-cell lung cancer progression through miR-646/AKT3 signaling in vivo and in vitro. Thorac. Cancer 2021, 12, 3223–3235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Yang, H.; Wei, W.; Hu, F.; Yuan, L. Hsa_circ_0000520 Promotes Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Progression through the miR-1258/AKT3 Axis. J. Oncol. 2022, 2022, 3676685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Xiong, L.; Yu, L.; Li, Z.; Guo, Q.; Li, Z.; Li, B.; Lin, N. Comprehensive analysis of microRNA-regulated protein interaction network reveals the tumor suppressive role of microRNA-149 in human hepatocellular carcinoma via targeting AKT-mTOR pathway. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, M.; Xie, X.; Liu, Z.; Du, X. Regulation of Tumorigenesis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma via the AKT3 Pathway in Cell Lines. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2021, 2021, 3267536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boix, L.; López-Oliva, J.M.; Rhodes, A.C.; Bruix, J. Restoring miR122 in human stem-like hepatocarcinoma cells, prompts tumor dormancy through Smad-independent TGF-β pathway. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 71309–71329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; She, X.G.; Ming, Y.Z.; Wan, Q.Q.; Ye, Q.F. MicroRNA-144 suppresses tumorigenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting AKT3. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 11, 1378–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zheng, W.; Shuai, X.; Chang, R.M.; Yu, L.; Fang, F.; Yang, L.Y. MicroRNA-424 inhibits Akt3/E2F3 axis and tumor growth in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 27736–27750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, W.; Ran, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Fan, X.; Wang, Z.; Ye, Q. miR-582-5p inhibits proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting CDK1 and AKT3. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 8309–8316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, G.; Su, H.; Wang, Z.; Lai, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Dai, L.; Bi, Y.; Chen, W.; Huang, W.; et al. LINC00680 enhances hepatocellular carcinoma stemness behavior and chemoresistance by sponging miR-568 to upregulate AKT3. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. CR 2021, 40, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fornari, F.; Milazzo, M.; Chieco, P.; Negrini, M.; Marasco, E.; Capranico, G.; Mantovani, V.; Marinello, J.; Sabbioni, S.; Callegari, E.; et al. In hepatocellular carcinoma miR-519d is up-regulated by p53 and DNA hypomethylation and targets CDKN1A/p21, PTEN, AKT3 and TIMP2. J. Pathol. 2012, 227, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Dong, W.; Yang, H.; Xiao, G. Propofol suppresses proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer cells by regulating miR-124-3p.1/AKT3. Biotechnol. Lett. 2020, 42, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.X.; Zhu, H.F.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Ren, F.; Hu, Y.H. MiR-384 inhibits the proliferation of colorectal cancer by targeting AKT3. Cancer Cell Int. 2018, 18, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhang, L.; Shang, A.; Song, H.; Huo, J.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, L. LINC02163 promotes colorectal cancer progression via miR-511-3p/AKT3 axis. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2020, 48, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Sun, H.; Zhang, J. LncRNA DSCAM-AS1 promotes colorectal cancer progression by acting as a molecular sponge of miR-384 to modulate AKT3 expression. Aging 2020, 12, 9781–9792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, F.; Zhang, J.; Sun, R.; Li, F.; Li, Y.; Chang, S.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, L.; et al. EGR1 interacts with DNMT3L to inhibit the transcription of miR-195 and plays an anti-apoptotic role in the development of gastric cancer. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 7372–7381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Luo, T.; Pang, T.; Du, Z.; Yin, X.; Cui, H.; Fang, G.; Xue, X. MALAT1 promotes gastric adenocarcinoma through the MALAT1/miR-181a-5p/AKT3 axis. Open Biol. 2019, 9, 190095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ma, K.; Pitts, S.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, X.; Ke, X.; Kovaka, S.; Ashktorab, H.; Smoot, D.T.; Schatz, M.; et al. Novel circular RNA circNF1 acts as a molecular sponge, promoting gastric cancer by absorbing miR-16. Endocr.-Relat. Cancer 2019, 26, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Tang, Z.; Gao, Z.; Shen, P.; Liu, Z.; Dang, X. Circular RNA CDR1as Exerts Oncogenic Properties Partially through Regulating MicroRNA 641 in Cholangiocarcinoma. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2020, 40, e00042-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, M.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.; Wang, J. Role of miR-489 in the proliferation and apoptosis of pancreatic carcinoma. J. Buon 2019, 24, 1574–1580. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Teng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qu, K.; Yang, X.; Fu, J.; Chen, W.; Li, X. MicroRNA-29B (mir-29b) regulates the Warburg effect in ovarian cancer by targeting AKT2 and AKT3. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 40799–40814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Xiao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, K.; Liu, W.; Hao, Q. MiR-489 modulates cisplatin resistance in human ovarian cancer cells by targeting Akt3. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2014, 25, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Yang, T.; Ji, J.; Zhao, F.; Li, C.; Han, X. RHPN1-AS1 promotes cell proliferation and migration via miR-665/Akt3 in ovarian cancer. Cancer Gene Ther. 2021, 28, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, M.; Fang, M.; Wang, C.; Wang, H.; Li, M. LncRNA EMX2OS Induces Proliferation, Invasion and Sphere Formation of Ovarian Cancer Cells via Regulating the miR-654-3p/AKT3/PD-L1 Axis. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 2141–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ma, L. Upregulation of miR-582-5p regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis by targeting AKT3 in human endometrial carcinoma. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 25, 965–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yi, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, L.; Cao, L.; Zhou, Y.; Fang, X. Effects of CDKN2B-AS1 on cellular proliferation, invasion and AKT3 expression are attenuated by miR-424-5p in a model of ovarian endometriosis. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2021, 42, 1057–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, X.; Li, W.; Yan, X.; Ma, T.; Ren, Y.; Hua, M.; Yang, H.; Wu, H.; Zhu, H. Long non-coding RNA LINC01224 promotes cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis by regulating AKT3 expression via targeting miR-485-5p in endometrial carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 46, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boufraqech, M.; Zhang, L.; Jain, M.; Patel, D.; Ellis, R.; Xiong, Y.; He, M.; Nilubol, N.; Merino, M.J.; Kebebew, E. miR-145 suppresses thyroid cancer growth and metastasis and targets AKT3. Endocr.-Relat. Cancer 2014, 21, 517–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Liu, J.; Li, Q.; Chen, G.; Yu, X. miR-29a suppresses growth and metastasis in papillary thyroid carcinoma by targeting AKT3. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 3987–3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Cheng, K.; Wang, T.; Xie, Q.; Chen, M.; Chen, Q.; Wen, Q. miR-217 inhibits proliferation, migration, and invasion via targeting AKT3 in thyroid cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 95, 1718–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Zhou, Q.; Yi, H.; Ma, S.; Li, D.; Xu, Y.; Wang, J.; Yin, S. A novel lncRNA n384546 promotes thyroid papillary cancer progression and metastasis by acting as a competing endogenous RNA of miR-145-5p to regulate AKT3. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.X.; Shi, H.Y.; Hu, Y.L.; Jin, X.L. Circ_0000144 facilitates the progression of thyroid cancer via the miR-217/AKT3 pathway. J. Gene Med. 2020, 22, e3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Zhao, F.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Su, J. MicroRNA-424-5p inhibits the proliferation, migration, and invasion of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by decreasing AKT3 expression. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2020, 53, e9029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Huang, W.; Wu, P.; Zeng, J.; Li, X. CircRNA circTRAF3 promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma metastasis through targeting miR-203a-3p/AKT3 axis. Pathol. Res. Pr. 2021, 221, 153438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, G.H. MicroRNA-16 functions as a tumor-suppressor gene in oral squamous cell carcinoma by targeting AKT3 and BCL2L2. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 9447–9457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, X.; Cao, Q.; Liang, H.; Liu, J.; Li, H.; Liu, F. MicroRNA-610 suppresses the proliferation of human glioblastoma cells by repressing CCND2 and AKT3. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 1961–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Z.P.; Wu, M.; Li, J.; Xiao, G.L.; Liu, B.; Liao, Y.X.; Liu, J.P. Long non-coding RNA GAS5, by up-regulating PRC2 and targeting the promoter methylation of miR-424, suppresses multiple malignant phenotypes of glioma. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2020, 148, 529–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roccaro, A.M.; Sacco, A.; Thompson, B.; Leleu, X.; Azab, A.K.; Azab, F.; Runnels, J.; Jia, X.; Ngo, H.T.; Melhem, M.R. MicroRNAs 15a and 16 regulate tumor proliferation in multiple myeloma. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2009, 113, 6669–6680. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Ye, Q.; Liu, L.; Bihl, J.C.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Cheng, Q. C6-ceramide treatment inhibits the proangiogenic activity of multiple myeloma exosomes via the miR-29b/Akt pathway. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Wang, Y.L.; Wei, J.M.; Huang, Z.D. Upregulation of circ_0000142 promotes multiple myeloma progression by adsorbing miR-610 and upregulating AKT3 expression. J. Biochem. 2021, 169, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.Y.; Chen, L.; Hu, N.; Zhao, H. Long non-coding RNA FEZF1-AS1 promotes cell growth in multiple myeloma via miR-610/Akt3 axis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 103, 1727–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Rong, Y.; Li, L.; Luo, Y.; Wang, J.; Yin, G.; Lv, C.; Cai, W. Overexpression of miR-1258 inhibits cell proliferation by targeting AKT3 in osteosarcoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 510, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, M.J.; Bu, J.; Deng, J.L.; Jiang, B.Y.; Jiang, L.D.; He, X.J. miR-485-3p regulated by MALAT1 inhibits osteosarcoma glycolysis and metastasis by directly suppressing c-MET and AKT3/mTOR signalling. Life Sci. 2021, 268, 118925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, X.; Li, C.; Wang, W. miR-224-5p inhibits proliferation, migration, and invasion by targeting PIK3R3/AKT3 in uveal melanoma. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 12412–12421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Tahiri, H.; Yang, C.; Landreville, S.; Callejo, S.; Hardy, P. MiR-181a-5p inhibits uveal melanoma development by targeting GNAQ and AKT3. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2023, 13, 293–306. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.J.; Chen, J.; Wu, B.; Wang, Y.J.; Guo, K.Y. MicroRNA-150 enhances radiosensitivity by inhibiting the AKT pathway in NK/T cell lymphoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. CR 2018, 37, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ding, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y. Identification of the Key Factors Related to Bladder Cancer by lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA Three-Layer Network. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, B.; Ma, L.; Xing, X.; Wang, Z.R.; Teng, Q.; Li, S.G. MiR-22-3p regulates the proliferation and invasion of Wilms’ tumor cells by targeting AKT3. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 5996–6004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabinski, N.; Bartkowiak, K.; Grupp, K.; Brandt, B.; Pantel, K.; Jücker, M. Distinct functional roles of Akt isoforms for proliferation, survival, migration and EGF-mediated signalling in lung cancer derived disseminated tumor cells. Cell. Signal. 2011, 23, 1952–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Ge, G.; Pan, T.; Wen, D.; Chen, L.; Yu, X.; Zhou, X.; Gan, J. A serum microRNA panel as potential biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma related with hepatitis B virus. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, G.B.; Jeong, J.Y.; Kim, D. GLUT5 regulation by AKT1/3-miR-125b-5p downregulation induces migratory activity and drug resistance in TLR-modified colorectal cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 2020, 41, 1329–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mure, H.; Matsuzaki, K.; Kitazato, K.T.; Mizobuchi, Y.; Kuwayama, K.; Kageji, T.; Nagahiro, S. Akt2 and Akt3 play a pivotal role in malignant gliomas. Neuro-Oncology 2010, 12, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerner, M.; Harada, M.; Lovén, J.; Castro, J.; Davis, Z.; Oscier, D.; Henriksson, M.; Sangfelt, O.; Grandér, D.; Corcoran, M.M. DLEU2, frequently deleted in malignancy, functions as a critical host gene of the cell cycle inhibitory microRNAs miR-15a and miR-16-1. Exp. Cell Res. 2009, 315, 2941–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.T.P.; Suman, K.H.; Nguyen, T.B.; Nguyen, H.T.; Do, D.N. The Role of miR-29s in Human Cancers-An Update. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, B.; Guo, Q.; Fu, F.J.; Wang, Z.; Yin, Z.; Wei, Y.B.; Yang, J.R. The role of miR-29b in cancer: Regulation, function, and signaling. OncoTargets Ther. 2015, 8, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Chen, C.; Qi, M.; Huang, Y.; Wang, L.; Gao, Y.; Dong, H.; Ling, K. Type Iγ phosphatidylinositol phosphate kinase regulates PD-L1 expression by activating NF-κB. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 42414–42427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, P.; Xiong, Y.; Yue, J.; Hanley, S.J.B.; Watari, H. Tumor-Intrinsic PD-L1 Signaling in Cancer Initiation, Development and Treatment: Beyond Immune Evasion. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valihrach, L.; Androvic, P.; Kubista, M. Circulating miRNA analysis for cancer diagnostics and therapy. Mol. Asp. Med. 2020, 72, 100825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, N.; Leidinger, P.; Becker, K.; Backes, C.; Fehlmann, T.; Pallasch, C.; Rheinheimer, S.; Meder, B.; Stähler, C.; Meese, E. Distribution of miRNA expression across human tissues. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 3865–3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, P.S.; Parkin, R.K.; Kroh, E.M.; Fritz, B.R.; Wyman, S.K.; Pogosova-Agadjanyan, E.L.; Peterson, A.; Noteboom, J.; O’Briant, K.C.; Allen, A. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10513–10518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merckaert, T.; Zwaenepoel, O.; Gevaert, K.; Gettemans, J. Development and characterization of protein kinase B/AKT isoform-specific nanobodies. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passos Gibson, V.; Tahiri, H.; Yang, C.; Phan, Q.T.; Banquy, X.; Hardy, P. Hyaluronan decorated layer-by-layer assembled lipid nanoparticles for miR-181a delivery in glioblastoma treatment. Biomaterials 2023, 302, 122341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabatabaei, S.N.; Derbali, R.M.; Yang, C.; Superstein, R.; Hamel, P.; Chain, J.L.; Hardy, P. Co-delivery of miR-181a and melphalan by lipid nanoparticles for treatment of seeded retinoblastoma. J. Control Release 2019, 298, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Tumor Tissue/Cell Lines | CircAKT3/Functions | Targets | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lung cancer tissues; cell lines: A549 and H1299 | hsa_circ_0000199/ glycolysis↑, cell growth↑, drug sensitivity↓ | miR-516b-5p, STAT3 | [37] |
| GC tissues; cell lines: SGC7901, BGC823, CDDP-resistant SGC7901, CDDP-resistant BGC823 | hsa_circ_0000199/ DNA damage repair↑, cell survival↑ | miR-198 | [38] |
| TNBC tissues; cell lines: MCF-10A, MDA-MB-231, MDA-MB-468, SK-BR-3 | hsa_circ_0000199/ chemo-tolerance↑, proliferation↑, migration↑, invasion↑ | miR-206, miR-613 | [39] |
| ccRCC tissues; cell lines: OSRC-2, Caki-1, SN12-PM6, A498, SW839 | hsa_circ_0017252/ metastasis↓ | miR-296-3p | [40] |
| GBM tissues; cell lines: U251, HS683, SW1783, U373, glioma-initiating cells | hsa_circ_0017250/ proliferation↓, invasiveness↓ | AKT | [41] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, C.; Hardy, P. The Multifunctional Nature of the MicroRNA/AKT3 Regulatory Axis in Human Cancers. Cells 2023, 12, 2594. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12222594
Yang C, Hardy P. The Multifunctional Nature of the MicroRNA/AKT3 Regulatory Axis in Human Cancers. Cells. 2023; 12(22):2594. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12222594
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Chun, and Pierre Hardy. 2023. "The Multifunctional Nature of the MicroRNA/AKT3 Regulatory Axis in Human Cancers" Cells 12, no. 22: 2594. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12222594
APA StyleYang, C., & Hardy, P. (2023). The Multifunctional Nature of the MicroRNA/AKT3 Regulatory Axis in Human Cancers. Cells, 12(22), 2594. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12222594






