Cognitive Functions, Neurotransmitter Alterations, and Hippocampal Microstructural Changes in Mice Caused by Feeding on Western Diet
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
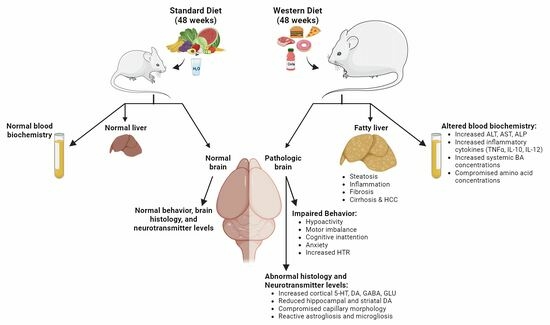
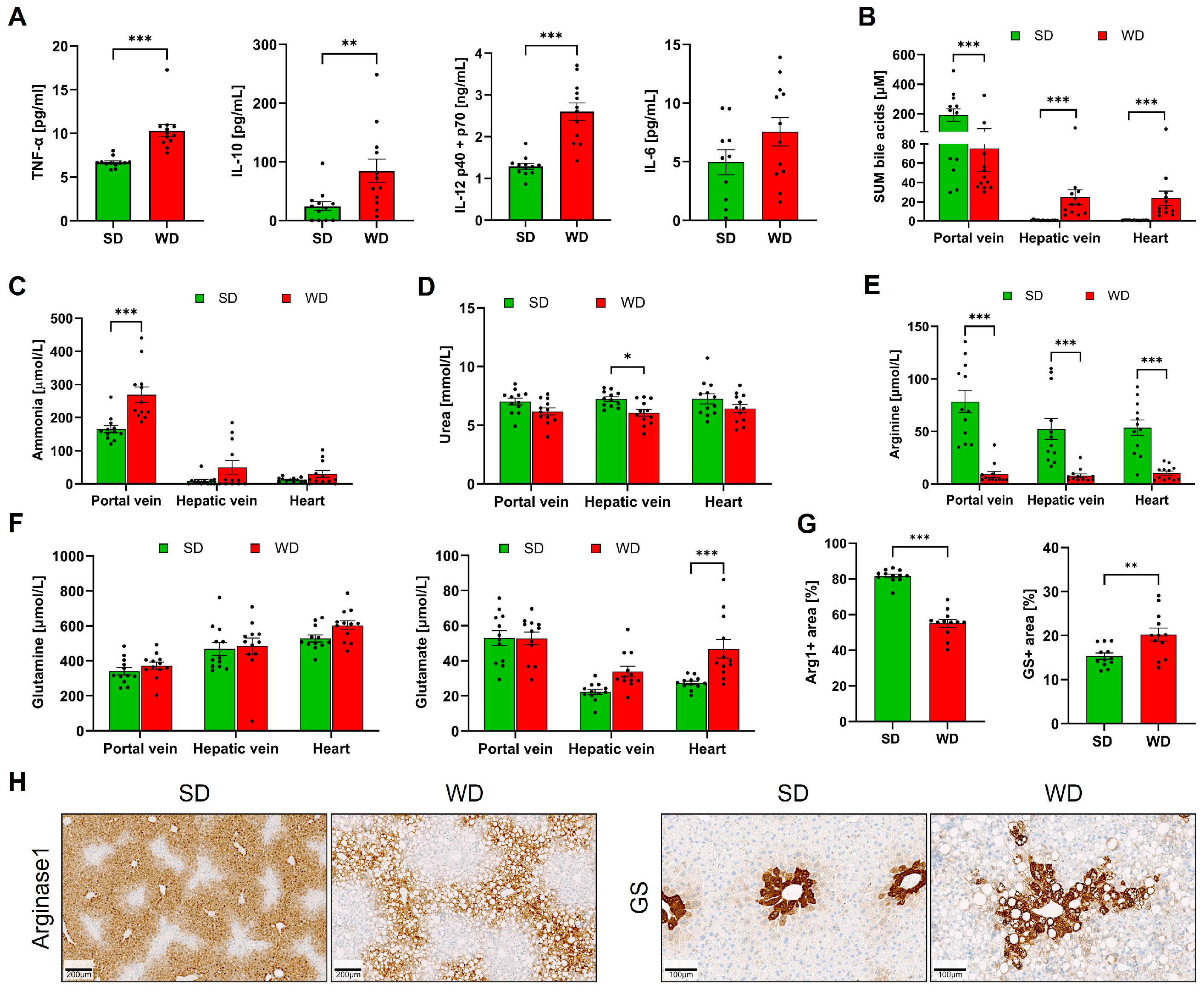
3.1. Long-Term Feeding on Western Diet Induces Steatohepatitis and Compromises Blood Biochemistry in Mice
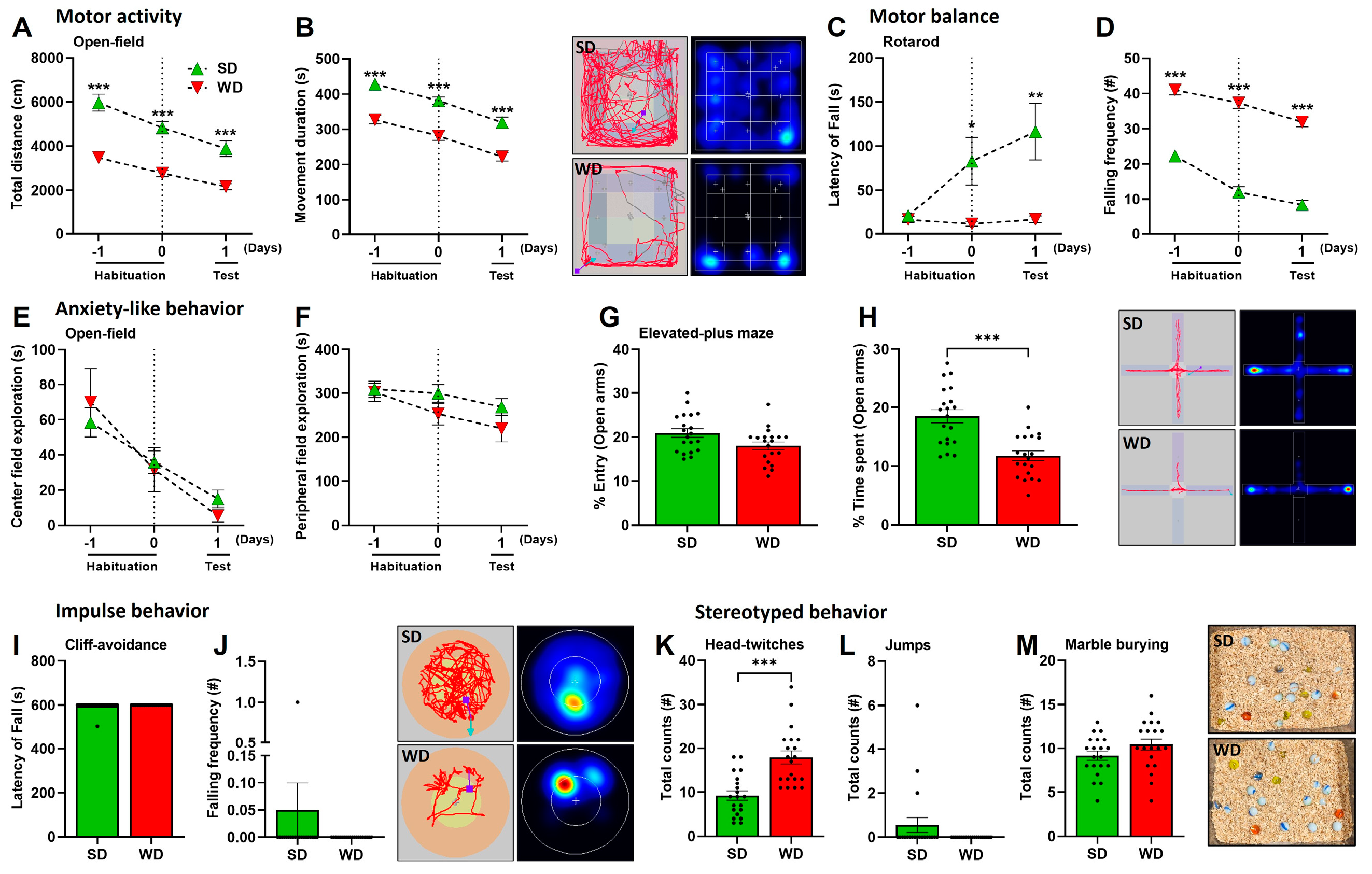
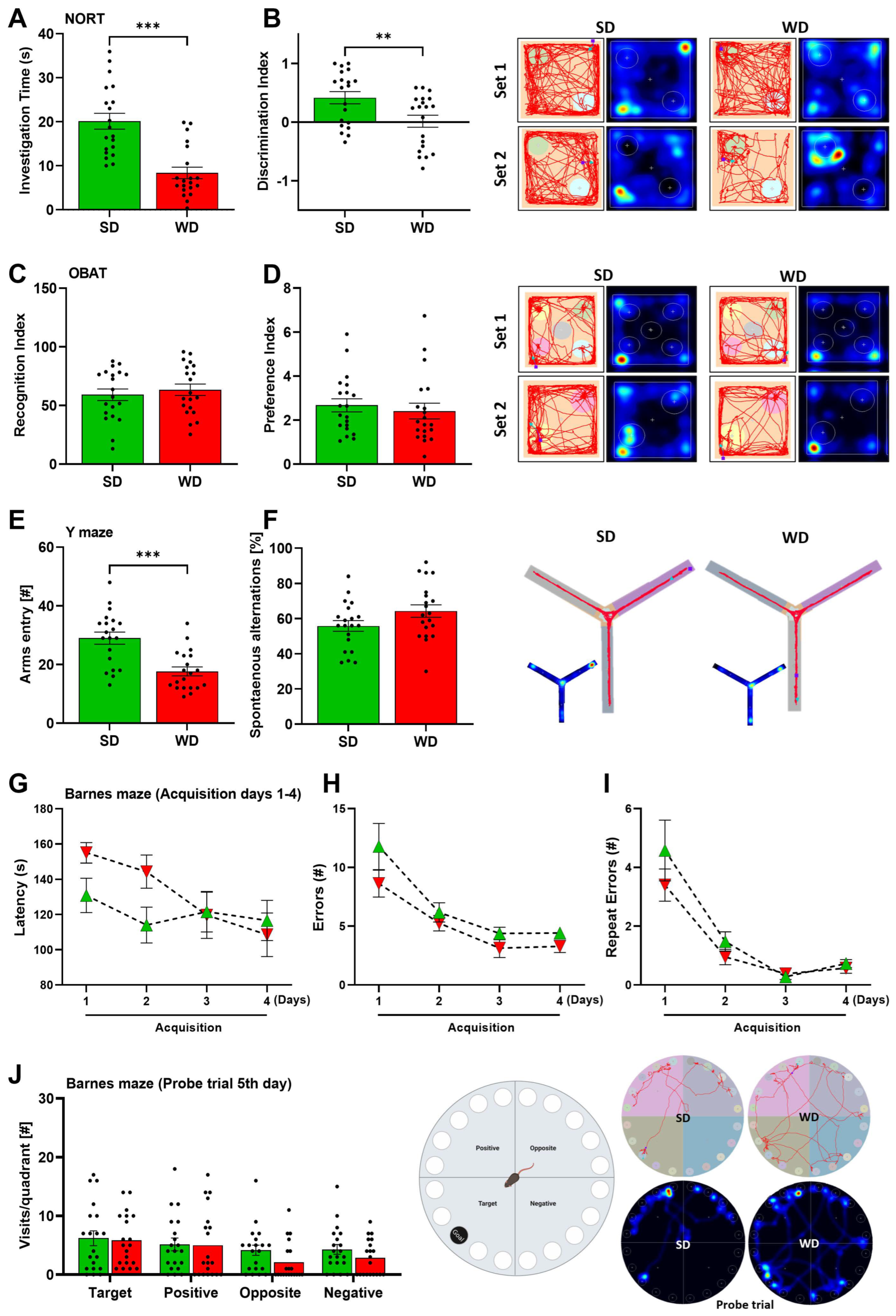
3.2. Induction of Steatohepatitis by Western Diet Coincides with Impaired Behaviors in Mice
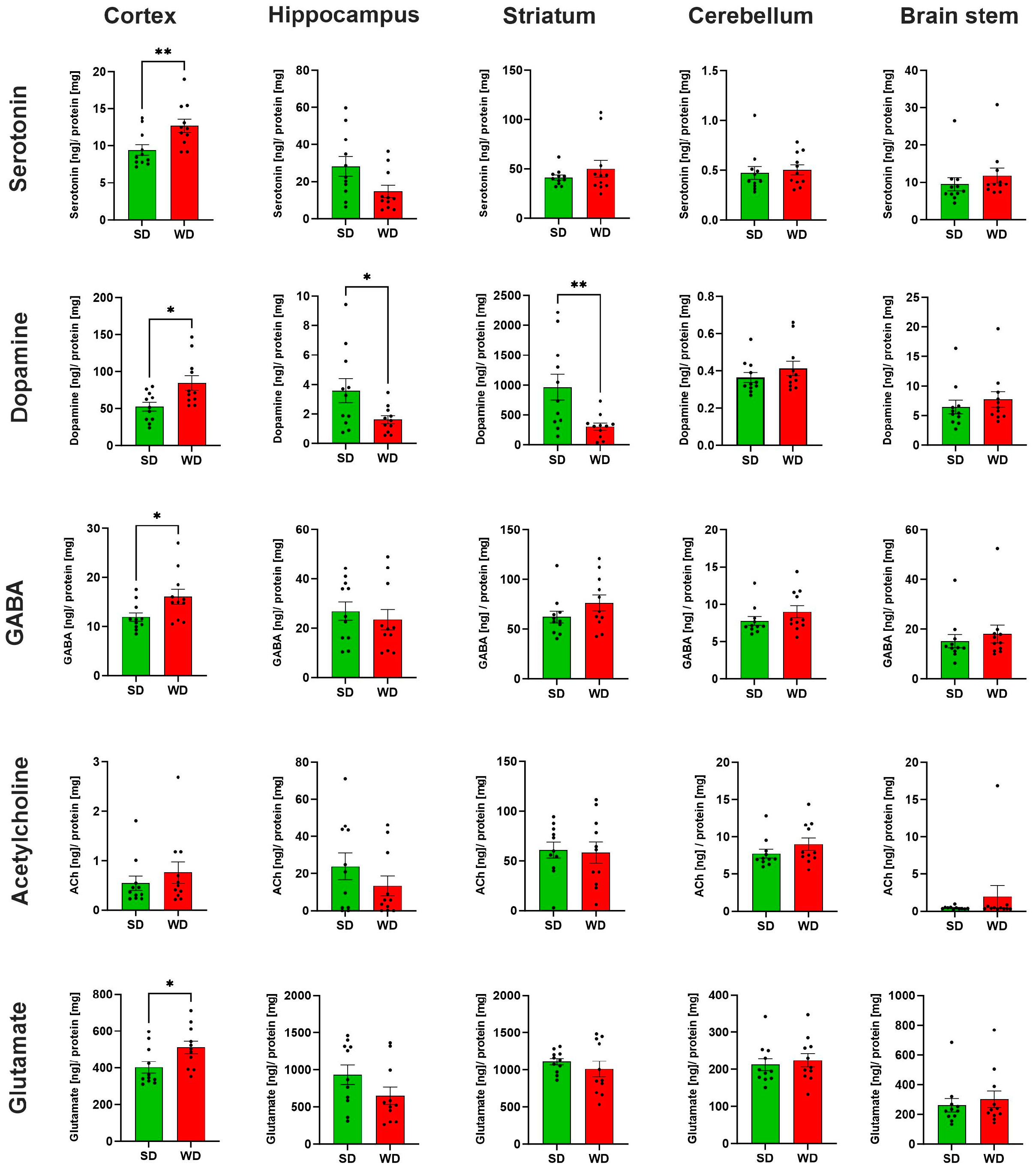
3.3. Region-Specific Alterations of Neurotransmitter Levels in the Brain of Western Diet-Fed Mice
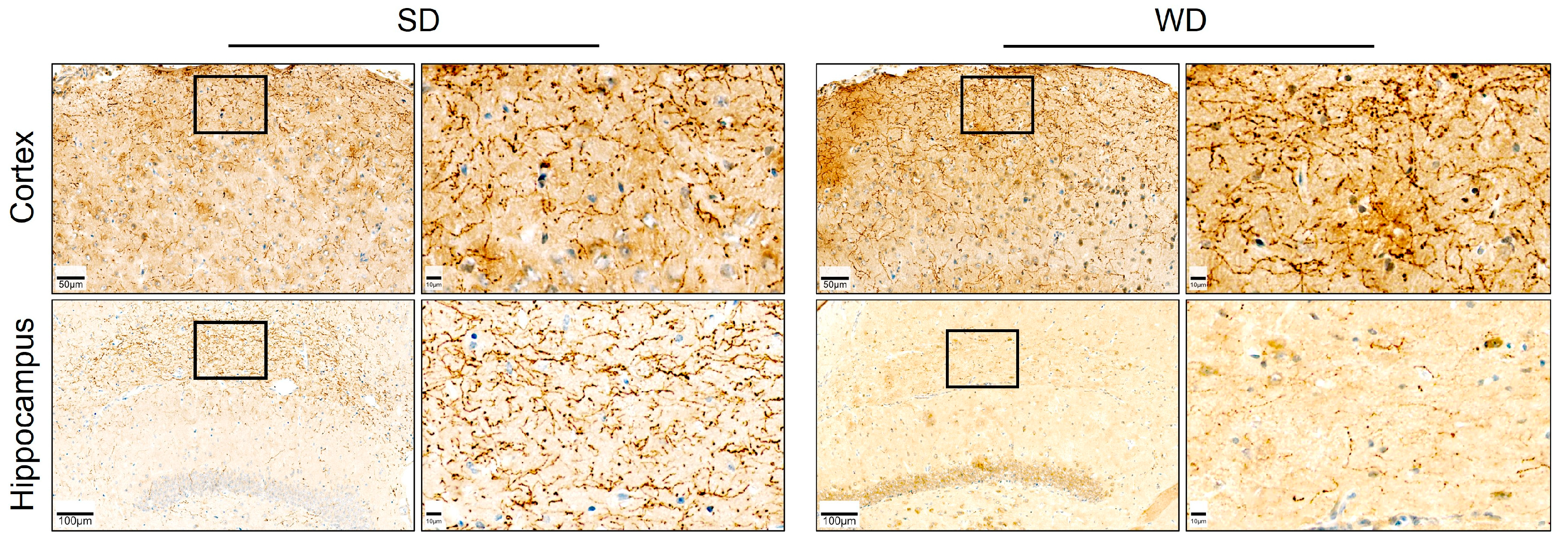
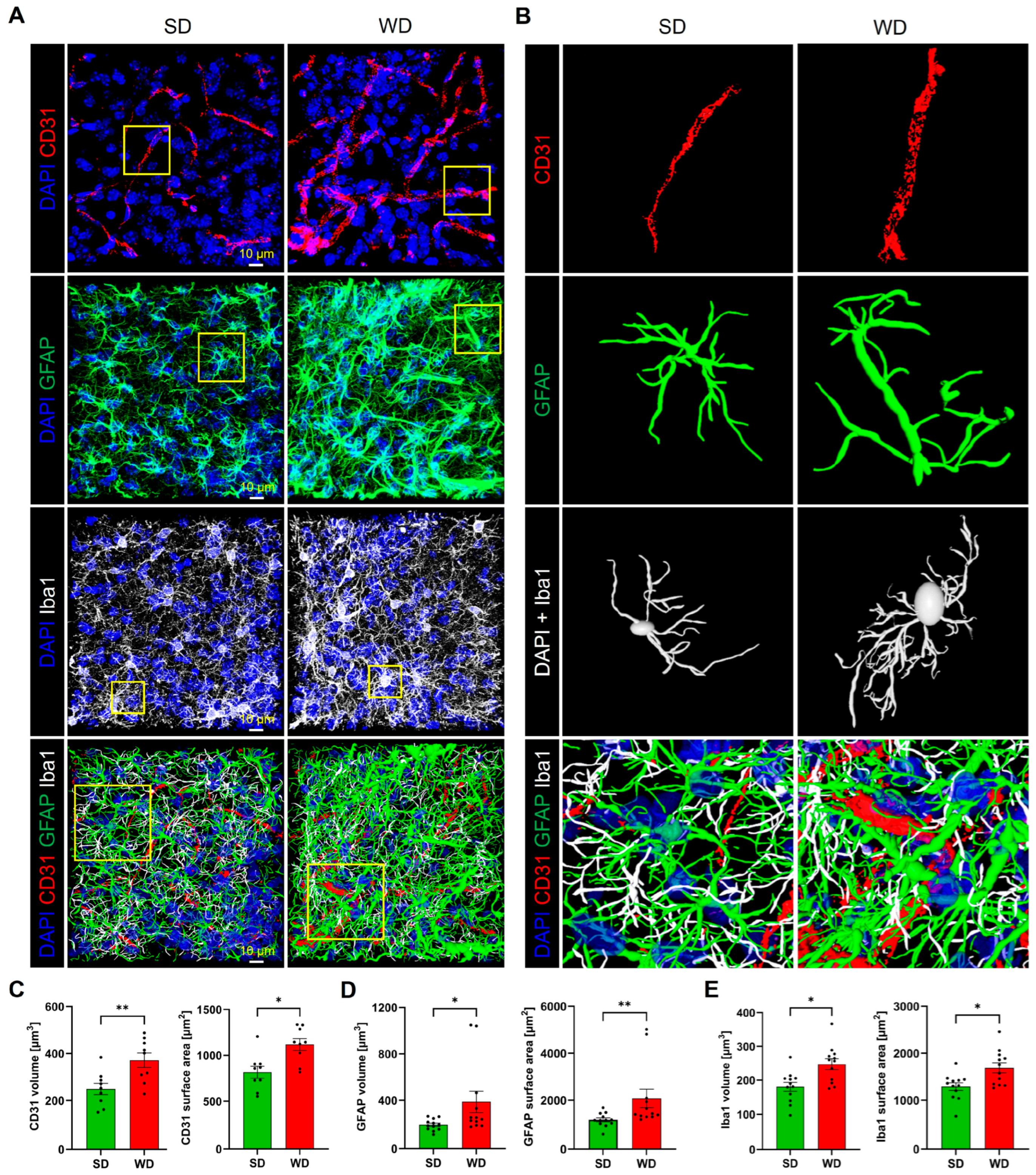
3.4. Compromised Blood Capillaries, Astrogliosis, and Microgliosis in the Brain of Western Diet-Fed Mice
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kouvari, M.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Yannakoulia, M.; Georgousopoulou, E.; Critselis, E.; Chrysohoou, C.; Tousoulis, D.; Pitsavos, C. Transition from Metabolically Benign to Metabolically Unhealthy Obesity and 10-Year Cardiovascular Disease Incidence: The ATTICA Cohort Study. Metabolism 2019, 93, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghallab, A.; Myllys, M.; Friebel, A.; Duda, J.; Edlund, K.; Halilbasic, E.; Vucur, M.; Hobloss, Z.; Brackhagen, L.; Begher-Tibbe, B.; et al. Spatio-Temporal Multiscale Analysis of Western Diet-Fed Mice Reveals a Translationally Relevant Sequence of Events during NAFLD Progression. Cells 2021, 10, 2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell-Wiley, T.M.; Poirier, P.; Burke, L.E.; Després, J.-P.; Gordon-Larsen, P.; Lavie, C.J.; Lear, S.A.; Ndumele, C.E.; Neeland, I.J.; Sanders, P.; et al. Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2021, 143, 984–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edlow, A.G. Maternal Obesity and Neurodevelopmental and Psychiatric Disorders in Offspring. Prenat. Diagn. 2017, 37, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulton, S.; Décarie-Spain, L.; Fioramonti, X.; Guiard, B.; Nakajima, S. The Menace of Obesity to Depression and Anxiety Prevalence. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 33, 18–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratcliff, M.B.; Jenkins, T.M.; Reiter-Purtill, J.; Noll, J.G.; Zeller, M.H. Risk-Taking Behaviors of Adolescents with Extreme Obesity: Normative or Not? Pediatrics 2011, 127, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, M.G.; Majumdar, A. Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease: Addressing a New Era in Liver Transplantation. World J. Hepatol. 2020, 12, 1168–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estes, C.; Anstee, Q.M.; Arias-Loste, M.T.; Bantel, H.; Bellentani, S.; Caballeria, J.; Colombo, M.; Craxi, A.; Crespo, J.; Day, C.P.; et al. Modeling NAFLD Disease Burden in China, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Spain, United Kingdom, and United States for the Period 2016–2030. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 896–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarus, J.V.; Ekstedt, M.; Marchesini, G.; Mullen, J.; Novak, K.; Pericàs, J.M.; Roel, E.; Romero-Gómez, M.; Ratziu, V.; Tacke, F.; et al. A Cross-Sectional Study of the Public Health Response to Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Europe. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Angona, Ó.; Anmella, G.; Valdés-Florido, M.J.; De Uribe-Viloria, N.; Carvalho, A.F.; Penninx, B.W.J.H.; Berk, M. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) as a Neglected Metabolic Companion of Psychiatric Disorders: Common Pathways and Future Approaches. BMC Med. 2020, 18, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berzigotti, A.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Bosch, J.; Grace, N.D.; Burroughs, A.K.; Morillas, R.; Escorsell, A.; Garcia-Pagan, J.C.; Patch, D.; Matloff, D.S.; et al. Obesity Is an Independent Risk Factor for Clinical Decompensation in Patients with Cirrhosis. Hepatology 2011, 54, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanyal, A.J.; Van Natta, M.L.; Clark, J.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Diehl, A.; Dasarathy, S.; Loomba, R.; Chalasani, N.; Kowdley, K.; Hameed, B.; et al. Prospective Study of Outcomes in Adults with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1559–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mort, E.J.; Fordington, S.; Heritage, S.; Fowden, A.L.; Jones, S.; Camm, E.J. Age and an Obesogenic Diet Affect Mouse Behaviour in a Sex-Dependent Manner. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2023, 58, 2451–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghallab, A.; Cellière, G.; Henkel, S.G.; Driesch, D.; Hoehme, S.; Hofmann, U.; Zellmer, S.; Godoy, P.; Sachinidis, A.; Blaszkewicz, M.; et al. Model-Guided Identification of a Therapeutic Strategy to Reduce Hyperammonemia in Liver Diseases. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 860–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schenk, A.; Ghallab, A.; Hofmann, U.; Hassan, R.; Schwarz, M.; Schuppert, A.; Schwen, L.O.; Braeuning, A.; Teutonico, D.; Hengstler, J.G.; et al. Physiologically-Based Modelling in Mice Suggests an Aggravated Loss of Clearance Capacity after Toxic Liver Damage. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, R.; González, D.; Hobloss, Z.; Brackhagen, L.; Myllys, M.; Friebel, A.; Seddek, A.-L.; Marchan, R.; Cramer, B.; Humpf, H.-U.; et al. Inhibition of Cytochrome P450 Enhances the Nephro- and Hepatotoxicity of Ochratoxin A. Arch. Toxicol. 2022, 96, 3349–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, C.H.; Ramirez Flores, R.O.; Myllys, M.; Hassan, R.; Edlund, K.; Hofmann, U.; Marchan, R.; Cadenas, C.; Reinders, J.; Hoehme, S.; et al. Transcriptomic Cross-Species Analysis of Chronic Liver Disease Reveals Consistent Regulation Between Humans and Mice. Hepatol. Commun. 2022, 6, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, R.; Friebel, A.; Brackhagen, L.; Hobloss, Z.; Myllys, M.; González, D.; Albrecht, W.; Mohammed, E.S.I.; Seddek, A.-L.; Marchan, R.; et al. Hypoalbuminemia Affects the Spatio-Temporal Tissue Distribution of Ochratoxin A in Liver and Kidneys: Consequences for Organ Toxicity. Arch. Toxicol. 2022, 96, 2967–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, K.J.; Pratt, B.; Bose, N.; Dubois, L.G.; St John-Williams, L.; Perrott, K.M.; Ky, K.; Kapahi, P.; Sharma, V.; MacCoss, M.J.; et al. Skyline for Small Molecules: A Unifying Software Package for Quantitative Metabolomics HHS Public Access. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 1447–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghallab, A.; Hassan, R.; Hofmann, U.; Friebel, A.; Hobloss, Z.; Brackhagen, L.; Begher-Tibbe, B.; Myllys, M.; Reinders, J.; Overbeck, N.; et al. Interruption of Bile Acid Uptake by Hepatocytes after Acetaminophen Overdose Ameliorates Hepatotoxicity. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianmoena, K.; Gasparoni, N.; Jashari, A.; Gabrys, P.; Grgas, K.; Ghallab, A.; Nordström, K.; Gasparoni, G.; Reinders, J.; Edlund, K.; et al. Epigenomic and Transcriptional Profiling Identifies Impaired Glyoxylate Detoxification in NAFLD as a Risk Factor for Hyperoxaluria. Cell Rep. 2021, 36, 109526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghallab, A.; Myllys, M.; Holland, C.H.; Zaza, A.; Murad, W.; Hassan, R.; Ahmed, Y.A.; Abbas, T.; Abdelrahim, E.A.; Schneider, K.M.; et al. Influence of Liver Fibrosis on Lobular Zonation. Cells 2019, 8, 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weishaupt, A.K.; Kubens, L.; Ruecker, L.; Schwerdtle, T.; Aschner, M.; Bornhorst, J. A Reliable Method Based on Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry for the Simultaneous Quantification of Neurotransmitters in Caenorhabditis elegans. Molecules 2023, 28, 5373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Custodio, R.J.P.; Botanas, C.J.; de la Peña, J.B.; dela Peña, I.J.; Kim, M.; Sayson, L.V.; Abiero, A.; Ryoo, Z.Y.; Kim, B.N.; Kim, H.J.; et al. Overexpression of the Thyroid Hormone-Responsive (THRSP) Gene in the Striatum Leads to the Development of Inattentive-like Phenotype in Mice. Neuroscience 2018, 390, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dela Peña, I.J.I.; Botanas, C.J.; de la Peña, J.B.; Custodio, R.J.; dela Peña, I.; Ryoo, Z.Y.; Kim, B.N.; Ryu, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; Cheong, J.H. The Atxn7-Overexpressing Mice Showed Hyperactivity and Impulsivity Which Were Ameliorated by Atomoxetine Treatment: A Possible Animal Model of the Hyperactive-Impulsive Phenotype of ADHD. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 88, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botanas, C.J.; Custodio, R.J.P.; Kim, H.J.; de la Pena, J.B.; Sayson, L.V.; Ortiz, D.M.; Kim, M.; Lee, H.J.; Acharya, S.; Kim, K.M.; et al. R (−)-Methoxetamine Exerts Rapid and Sustained Antidepressant Effects and Fewer Behavioral Side Effects Relative to S (+)-Methoxetamine. Neuropharmacology 2021, 193, 108619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayson, L.V.; Ortiz, D.M.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, M.; Custodio, R.J.P.; Yun, J.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Cha, H.J.; Cheong, J.H.; et al. Deletion of Cryab Increases the Vulnerability of Mice to the Addiction-like Effects of the Cannabinoid JWH-018 via Upregulation of Striatal NF-ΚB Expression. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1135929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custodio, R.J.P.; Sayson, L.V.; Botanas, C.J.; Abiero, A.; You, K.Y.; Kim, M.; Lee, H.J.; Yoo, S.Y.; Lee, K.W.; Lee, Y.S.; et al. 25B-NBOMe, a Novel N-2-Methoxybenzyl-Phenethylamine (NBOMe) Derivative, May Induce Rewarding and Reinforcing Effects via a Dopaminergic Mechanism: Evidence of Abuse Potential. Addict. Biol. 2020, 25, e12850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.; Lee, H.; Choi, Y.; Kang, H.; Jeon, S.J.; Ryu, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; Cheong, J.H.; Lim, S.; Kim, B.N.; et al. Maturational Delay and Asymmetric Information Flow of Brain Connectivity in SHR Model of ADHD Revealed by Topological Analysis of Metabolic Networks. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custodio, R.J.P.; Kim, M.; Sayson, L.V.; Lee, H.J.; Ortiz, D.M.; Kim, B.-N.; Kim, H.J.; Cheong, J.H. Low Striatal T3 Is Implicated in Inattention and Memory Impairment in an ADHD Mouse Model Overexpressing Thyroid Hormone-Responsive Protein. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custodio, R.J.P.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.; Ortiz, D.M.; Kim, M.; Buctot, D.; Sayson, L.V.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, B.-N.; Yi, E.C.; et al. Hippocampal Dentate Gyri Proteomics Reveals Wnt Signaling Involvement in the Behavioral Impairment in the THRSP-Overexpressing ADHD Mouse Model. Commun. Biol. 2023, 6, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsthoorn, L.; Vreeken, D.; Kiliaan, A.J. Gut Microbiome, Inflammation, and Cerebrovascular Function: Link Between Obesity and Cognition. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 761456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, E.; Hay, P.; Campbell, L.; Trollor, J.N. A Review of the Association between Obesity and Cognitive Function across the Lifespan: Implications for Novel Approaches to Prevention and Treatment. Obes. Rev. 2011, 12, 740–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geginat, J.; Larghi, P.; Paroni, M.; Nizzoli, G.; Penatti, A.; Pagani, M.; Gagliani, N.; Meroni, P.; Abrignani, S.; Flavell, R.A. The Light and the Dark Sides of Interleukin-10 in Immune-Mediated Diseases and Cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2016, 30, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kany, S.; Vollrath, J.T.; Relja, B. Cytokines in Inflammatory Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Wu, X.; Liang, S.; Jin, F. Elevated Blood Ammonia Level Is a Potential Biological Risk Factor of Behavioral Disorders in Prisoners. Behav. Neurol. 2015, 2015, 797862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qvartskhava, N.; Lang, P.A.; Görg, B.; Pozdeev, V.I.; Ortiz, M.P.; Lang, K.S.; Bidmon, H.J.; Lang, E.; Leibrock, C.B.; Herebian, D.; et al. Hyperammonemia in Gene-Targeted Mice Lacking Functional Hepatic Glutamine Synthetase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5521–5526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claeys, W.; Van Hoecke, L.; Geerts, A.; Van Vlierberghe, H.; Lefere, S.; Van Imschoot, G.; Van Wonterghem, E.; Ghesquière, B.; Vandenbroucke, R.E.; Van Steenkiste, C. A Mouse Model of Hepatic Encephalopathy: Bile Duct Ligation Induces Brain Ammonia Overload, Glial Cell Activation and Neuroinflammation. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 17558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapper, E.B.; Jiang, Z.G.; Patwardhan, V.R. Refining the Ammonia Hypothesis: A Physiology-Driven Approach to the Treatment of Hepatic Encephalopathy. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2015, 90, 646–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Wang, X.; Jiang, R.; Zhao, A.; Yan, J.; Zheng, X.; Huang, F.; Liu, X.; Panee, J.; Rajani, C.; et al. Dysregulated Bile Acid Signaling Contributes to the Neurological Impairment in Murine Models of Acute and Chronic Liver Failure. EBioMedicine 2018, 37, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, E.A.; Weissenborn, K. Neurology and the Liver. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1997, 63, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Albhaisi, S.; Sanyal, A.J. Behavioral Health Disorders Related to Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Clin. Liver Dis. 2022, 20, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, G.; Taneja, A.; Kandiah, P.A. Brain and the Liver: Cerebral Edema, Hepatic Encephalopathy and Beyond. Hepatic Crit. Care 2017, 7, 83–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, P.; Chellian, R.; Wilson, R.; Behnood-Rod, A.; Panunzio, S.; Bruijnzeel, A.W. Sex Differences in the Elevated Plus-Maze Test and Large Open Field Test in Adult Wistar Rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2021, 204, 173168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Figueiredo Cerqueira, M.M.; Castro, M.M.L.; Vieira, A.A.; Kurosawa, J.A.A.; do Amaral Junior, F.L.; de Siqueira, F.D.C.C.; Sosthenes, M.C.K. Comparative Analysis between Open Field and Elevated Plus Maze Tests as a Method for Evaluating Anxiety-like Behavior in Mice. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennaceur, A.; Michalikova, S.; Chazot, P.L. Do Rats Really Express Neophobia towards Novel Objects? Experimental Evidence from Exposure to Novelty and to an Object Recognition Task in an Open Space and an Enclosed Space. Behav. Brain Res. 2009, 197, 417–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lécuyer, M.A.; Kebir, H.; Prat, A. Glial Influences on BBB Functions and Molecular Players in Immune Cell Trafficking. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1862, 472–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Jia, H.; Qi, Y.; Tu, S.; Shao, A. Affective Immunology: The Crosstalk Between Microglia and Astrocytes Plays Key Role? Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, L.C.; Harder, J.M.; Soto, I.; De Vries, W.N.; John, S.W.M.; Howell, G.R. Chronic Consumption of a Western Diet Induces Robust Glial Activation in Aging Mice and in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizarbe, B.; Soares, A.F.; Larsson, S.; Duarte, J.M.N. Neurochemical Modifications in the Hippocampus, Cortex and Hypothalamus of Mice Exposed to Long-Term High-Fat Diet. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.-J.; Li, M.-Q.; Zhao, L.; Chen, W.-G.; Wang, J.-L. Short-Term High-Fat Diet Favors the Appearances of Apoptosis and Gliosis by Activation of ERK1/2/P38MAPK Pathways in Brain. Aging 2021, 13, 23133–23148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, M.O.; Battagello, D.S.; Cardoso, A.R.; Hauser, D.N.; Bittencourt, J.C.; Correa, R.G. Dopamine: Functions, Signaling, and Association with Neurological Diseases. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 39, 31–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerfen, C.R. Segregation of D1 and D2 Dopamine Receptors in the Striatal Direct and Indirect Pathways: An Historical Perspective. Front. Synaptic Neurosci. 2023, 14, 1002960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kempadoo, K.A.; Mosharov, E.V.; Choi, S.J.; Sulzer, D.; Kandel, E.R. Dopamine Release from the Locus Coeruleus to the Dorsal Hippocampus Promotes Spatial Learning and Memory. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 14835–14840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colognesi, M.; Gabbia, D.; De Martin, S. Depression and Cognitive Impairment-Extrahepatic Manifestations of NAFLD and NASH. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbaş, O.; Akseki, H.S.; Aktuğ, H.; Taşkıran, D. Low-Grade Chronic Inflammation Induces Behavioral Stereotypy in Rats. Metab Brain Dis. 2015, 30, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higarza, S.G.; Arboleya, S.; Gueimonde, M.; Gómez-Lázaro, E.; Arias, J.L.; Arias, N. Neurobehavioral Dysfunction in Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis Is Associated with Hyperammonemia, Gut Dysbiosis, and Metabolic and Functional Brain Regional Deficits. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radford-Smith, D.E.; Patel, P.J.; Irvine, K.M.; Russell, A.; Siskind, D.; Anthony, D.C.; Powell, E.E.; Probert, F. Depressive Symptoms in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Are Identified by Perturbed Lipid and Lipoprotein Metabolism. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0261555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corne, S.J.; Pickering, R.W.; Warner, B.T. A Method for Assessing the Effects of Drugs on the Central Actions of 5-Hydroxytryptamine. Br. J. Pharmacol. Chemother. 1963, 20, 106–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willins, D.L.; Meltzer, H.Y. Direct Injection of 5-HT2A Receptor Agonists into the Medial Prefrontal Cortex Produces a Head-Twitch Response in Rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1997, 282, 699–706. [Google Scholar]
- Malaquias, M.J.; Pinto, C.M.; Ramos, C.; Ferreira, S.; Gandara, J.; Almeida, A.; Cavaco, S.; Miranda, H.P.; Magalhães, M. Acquired Hepatocerebral Degeneration and Hepatic Encephalopathy: One or Two Entities? Eur. J. Neurol. 2020, 27, 2396–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, A.L.; Salgado, P.; Alves, J.E.; Silva, S.; Ferreira, S.; Magalhães, M. Uncommon Movement Disorders in Chronic Hepatic Disease with Response to Rifaximin. Tremor Other Hyperkinetic Mov. 2019, 9, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dury, S.; Molinaro, A.; Hedenström, P. Propranolol-Induced Hallucinations Mimicking Encephalopathy in a Patient with Liver Cirrhosis. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 56, 829–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halberstadt, A.L.; Geyer, M.A. Characterization of the Head-Twitch Response Induced by Hallucinogens in Mice: Detection of the Behavior Based on the Dynamics of Head Movement. Psychopharmacology 2013, 227, 727–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Berg, M.; Magaraggia, I.; Schreiber, R.; Hillhouse, T.M.; Porter, J.H. How to Account for Hallucinations in the Interpretation of the Antidepressant Effects of Psychedelics: A Translational Framework. Psychopharmacology 2022, 239, 1853–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Danbolt, N.C. Glutamate as a Neurotransmitter in the Healthy Brain. J. Neural Transm. 2014, 121, 799–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czapski, G.A.; Strosznajder, J.B. Glutamate and GABA in Microglia-Neuron Cross-Talk in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitton, P.S. Glutamatergic Control over Brain Dopamine Release In Vivo and In Vitro. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 1997, 21, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauli, O.; Llansola, M.; Erceg, S.; Felipo, V. Hypolocomotion in Rats with Chronic Liver Failure Is due to Increased Glutamate and Activation of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors in Substantia Nigra. J. Hepatol. 2006, 45, 654–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Rabaza, V.; Cabrera-Pastor, A.; Taoro-Gonzalez, L.; Gonzalez-Usano, A.; Agusti, A.; Balzano, T.; Llansola, M.; Felipo, V. Neuroinflammation Increases GABAergic Tone and Impairs Cognitive and Motor Function in Hyperammonemia by Increasing GAT-3 Membrane Expression. Reversal by Sulforaphane by Promoting M2 Polarization of Microglia. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoerbelt, P.; Lindsley, T.A.; Fleck, M.W. Dopamine Directly Modulates GABAA Receptors. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 3525–3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Custodio, R.J.P.; Hobloss, Z.; Myllys, M.; Hassan, R.; González, D.; Reinders, J.; Bornhorst, J.; Weishaupt, A.-K.; Seddek, A.-l.; Abbas, T.; et al. Cognitive Functions, Neurotransmitter Alterations, and Hippocampal Microstructural Changes in Mice Caused by Feeding on Western Diet. Cells 2023, 12, 2331. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12182331
Custodio RJP, Hobloss Z, Myllys M, Hassan R, González D, Reinders J, Bornhorst J, Weishaupt A-K, Seddek A-l, Abbas T, et al. Cognitive Functions, Neurotransmitter Alterations, and Hippocampal Microstructural Changes in Mice Caused by Feeding on Western Diet. Cells. 2023; 12(18):2331. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12182331
Chicago/Turabian StyleCustodio, Raly James Perez, Zaynab Hobloss, Maiju Myllys, Reham Hassan, Daniela González, Jörg Reinders, Julia Bornhorst, Ann-Kathrin Weishaupt, Abdel-latif Seddek, Tahany Abbas, and et al. 2023. "Cognitive Functions, Neurotransmitter Alterations, and Hippocampal Microstructural Changes in Mice Caused by Feeding on Western Diet" Cells 12, no. 18: 2331. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12182331
APA StyleCustodio, R. J. P., Hobloss, Z., Myllys, M., Hassan, R., González, D., Reinders, J., Bornhorst, J., Weishaupt, A.-K., Seddek, A.-l., Abbas, T., Friebel, A., Hoehme, S., Getzmann, S., Hengstler, J. G., van Thriel, C., & Ghallab, A. (2023). Cognitive Functions, Neurotransmitter Alterations, and Hippocampal Microstructural Changes in Mice Caused by Feeding on Western Diet. Cells, 12(18), 2331. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12182331