Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Synthetic Peptides Based on Glucocorticoid-Induced Leucine Zipper (GILZ) Protein for the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (IBDs)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Peptide Synthesis
2.3. In Vitro Cell Activation
2.4. Mice
2.5. DNBS-Induced Colitis
2.6. Tissue Histology
2.7. Leukocyte Isolation from Colon Lamina Propria
2.8. RNA Isolation and qPCR
2.9. Flow Cytometry
2.10. Immunofluorescence
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
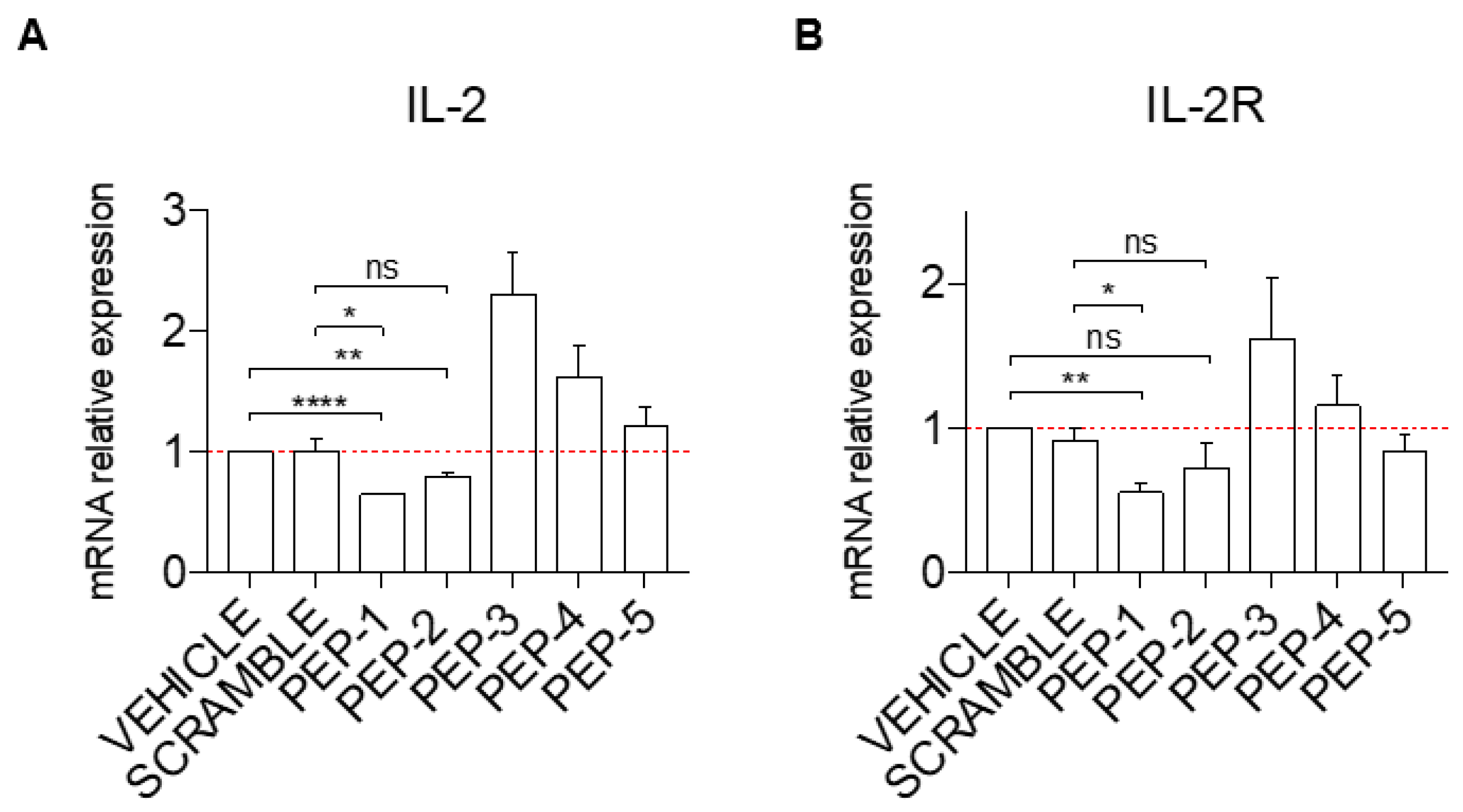
3.1. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of GILZ Peptides in Human Cell Lines
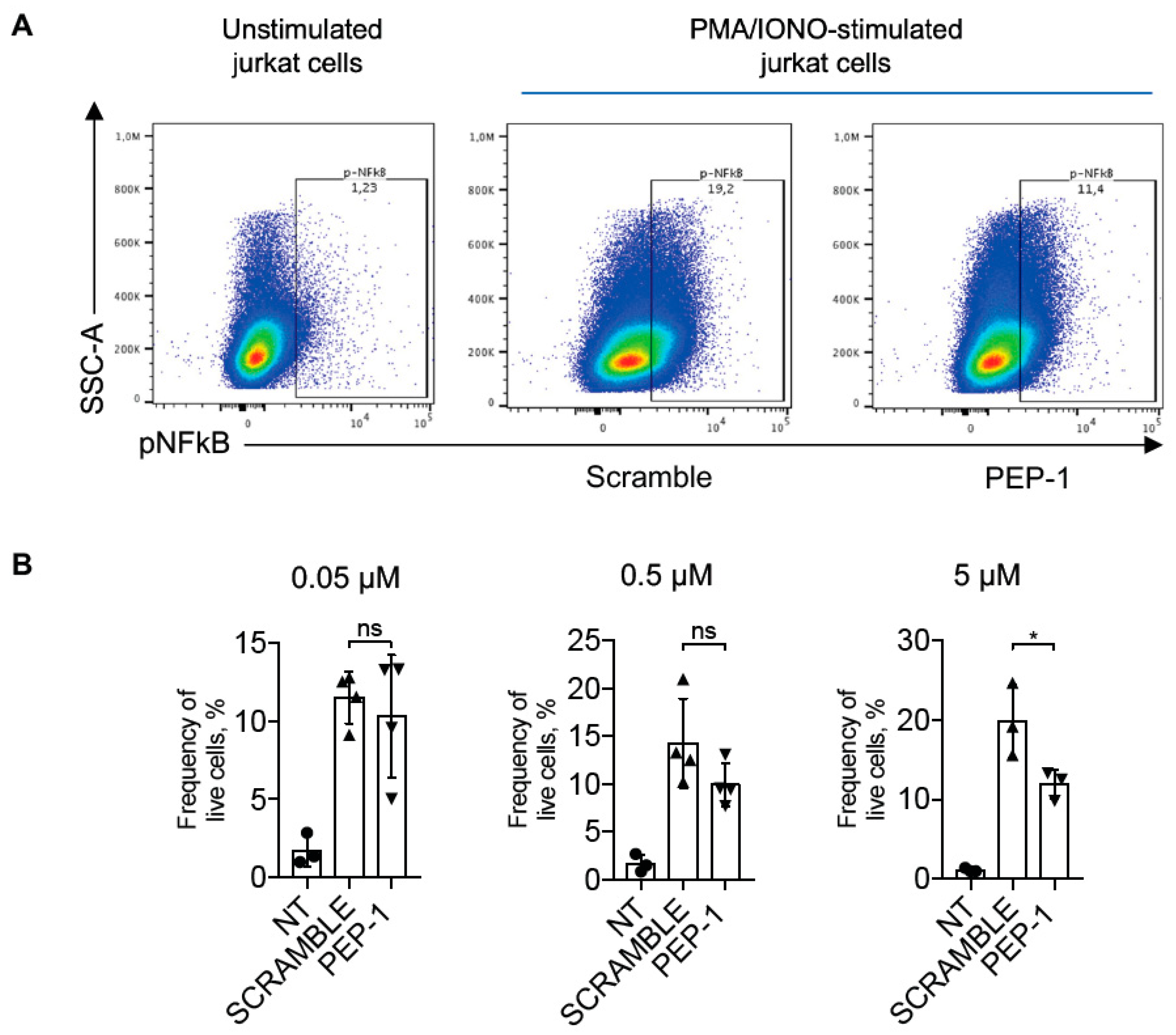
3.2. Evaluation of NF-κB Nuclear Translocation by Flow Cytometry in Jurkat Cells
3.3. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of PEP-1 in Human Monocytes
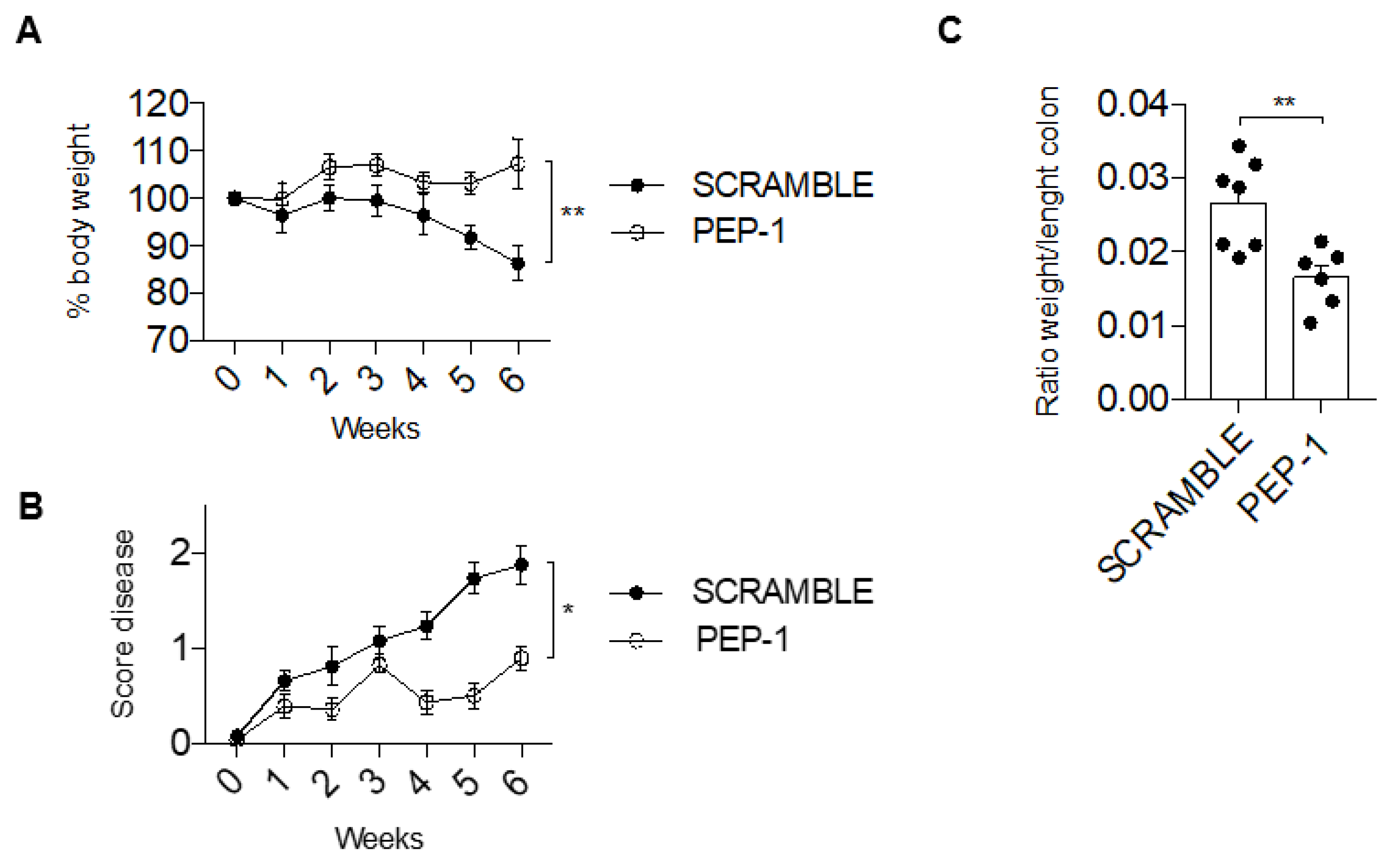
3.4. PEP-1 Peptide Administration Ameliorates Clinical Signs in Colitic IL-10KO Mice
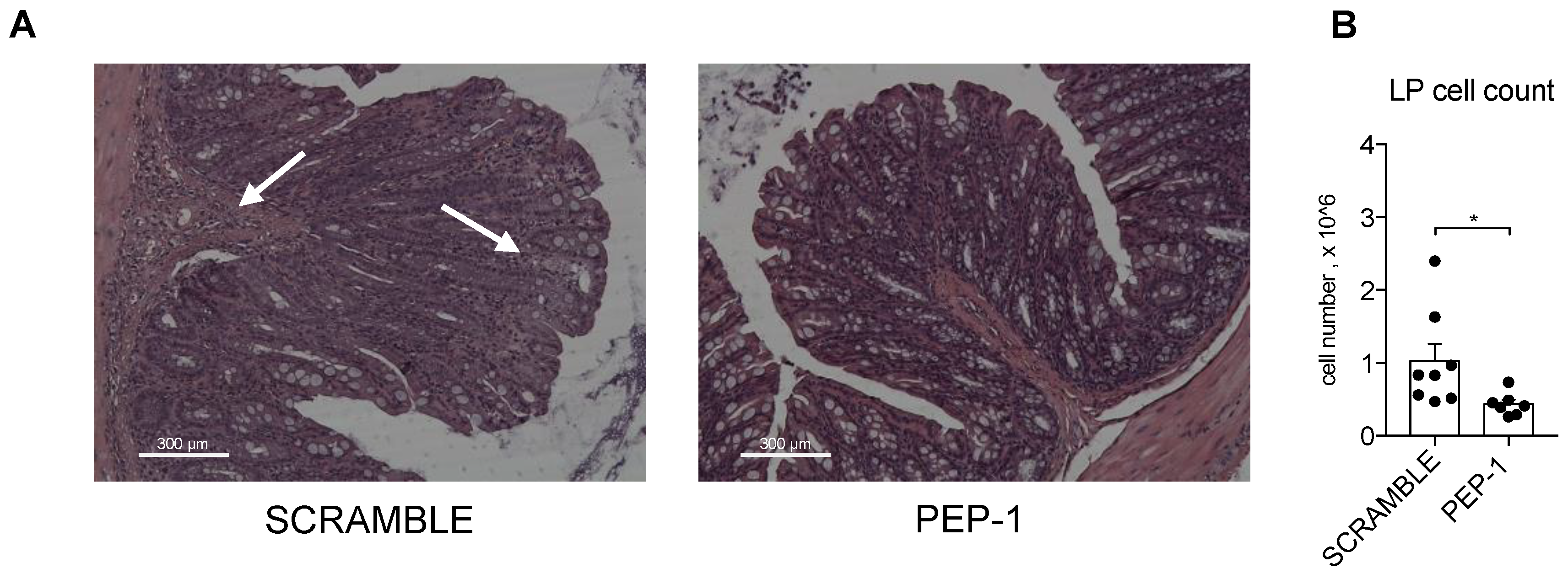
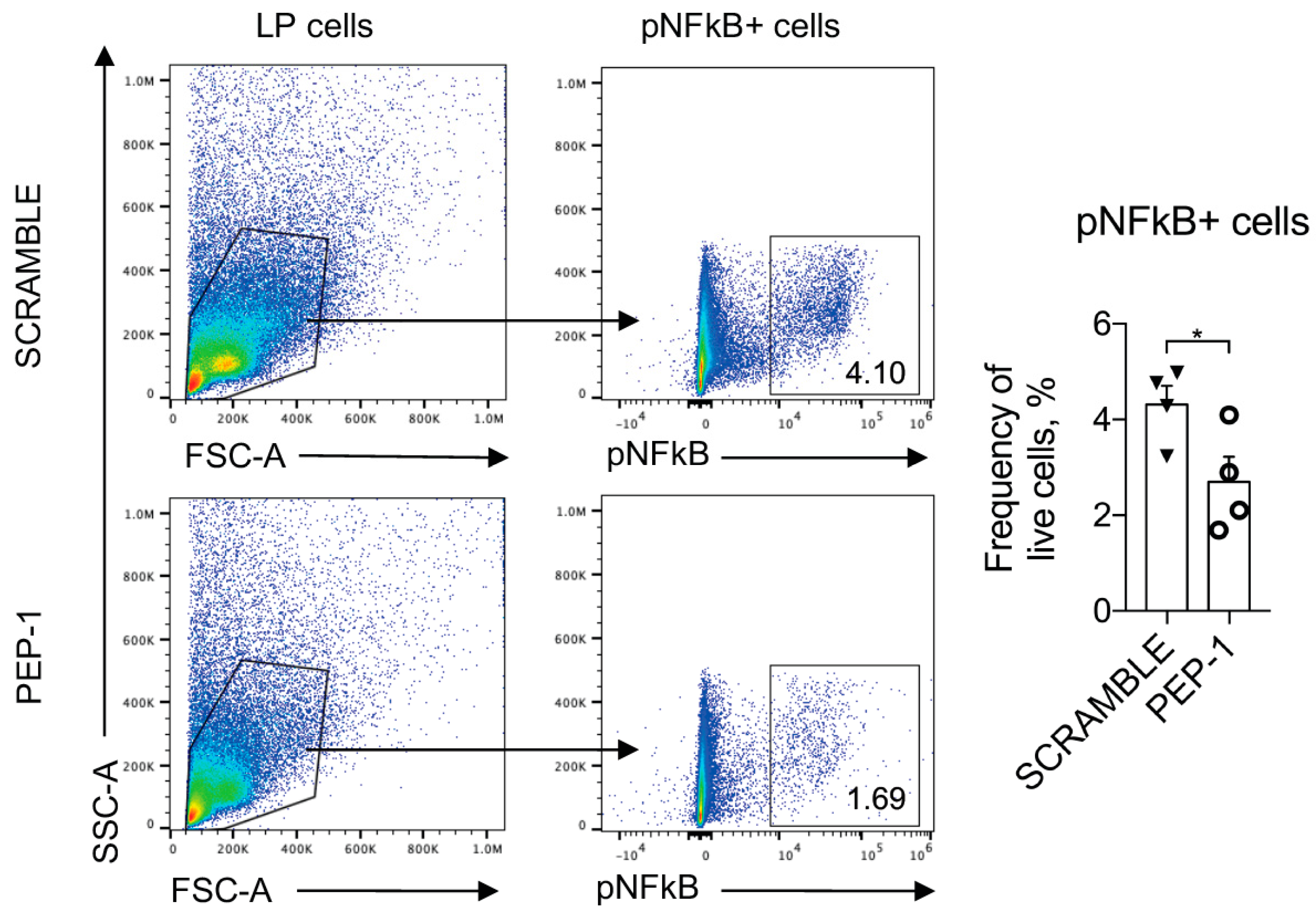
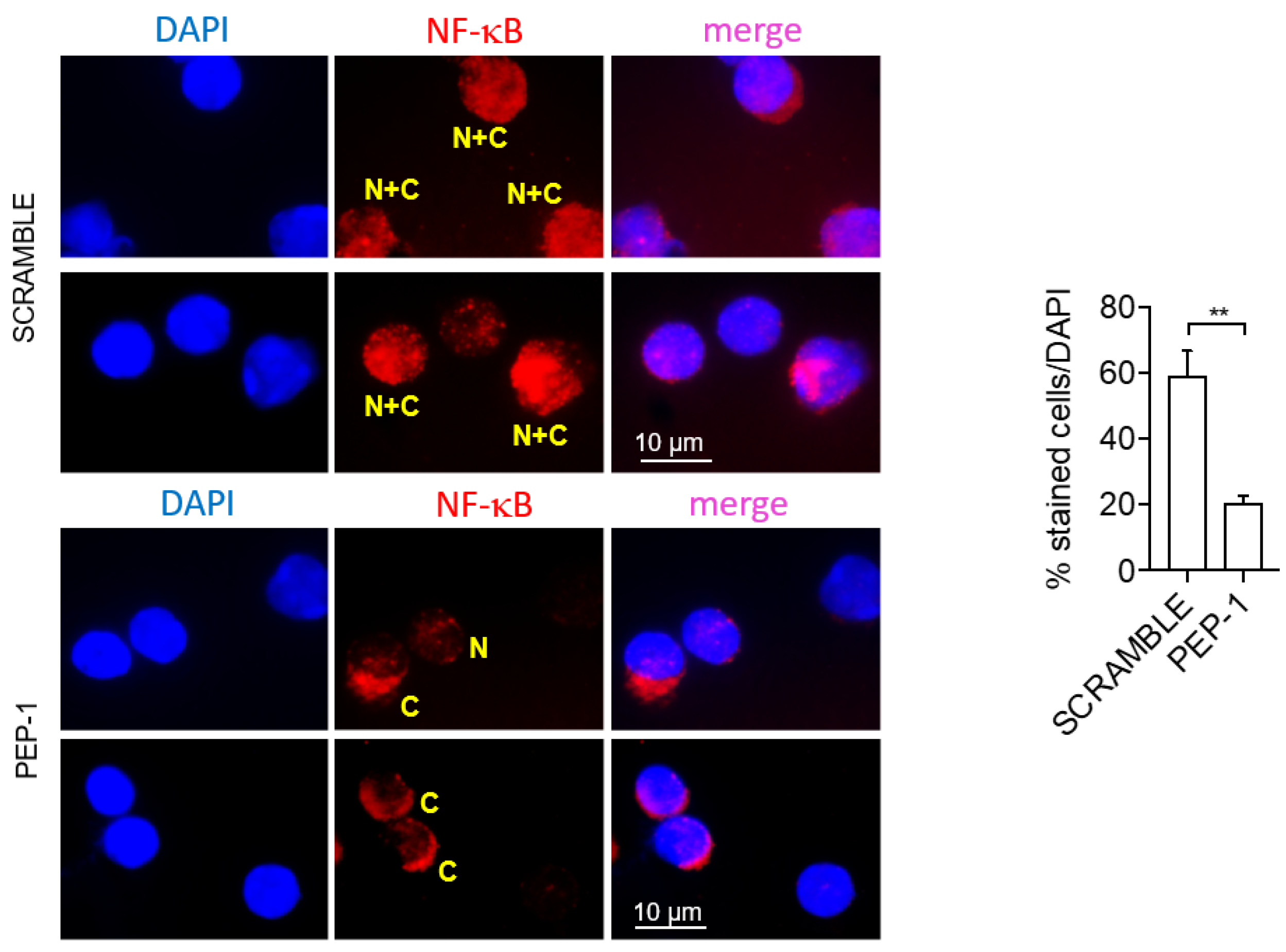
3.5. PEP-1 Peptide Treatment Counteracts Leukocytes Infiltration and Prevents NF-κB Nuclear Translocation in Colon Lamina Propria (LP) of IL-10 KO mice
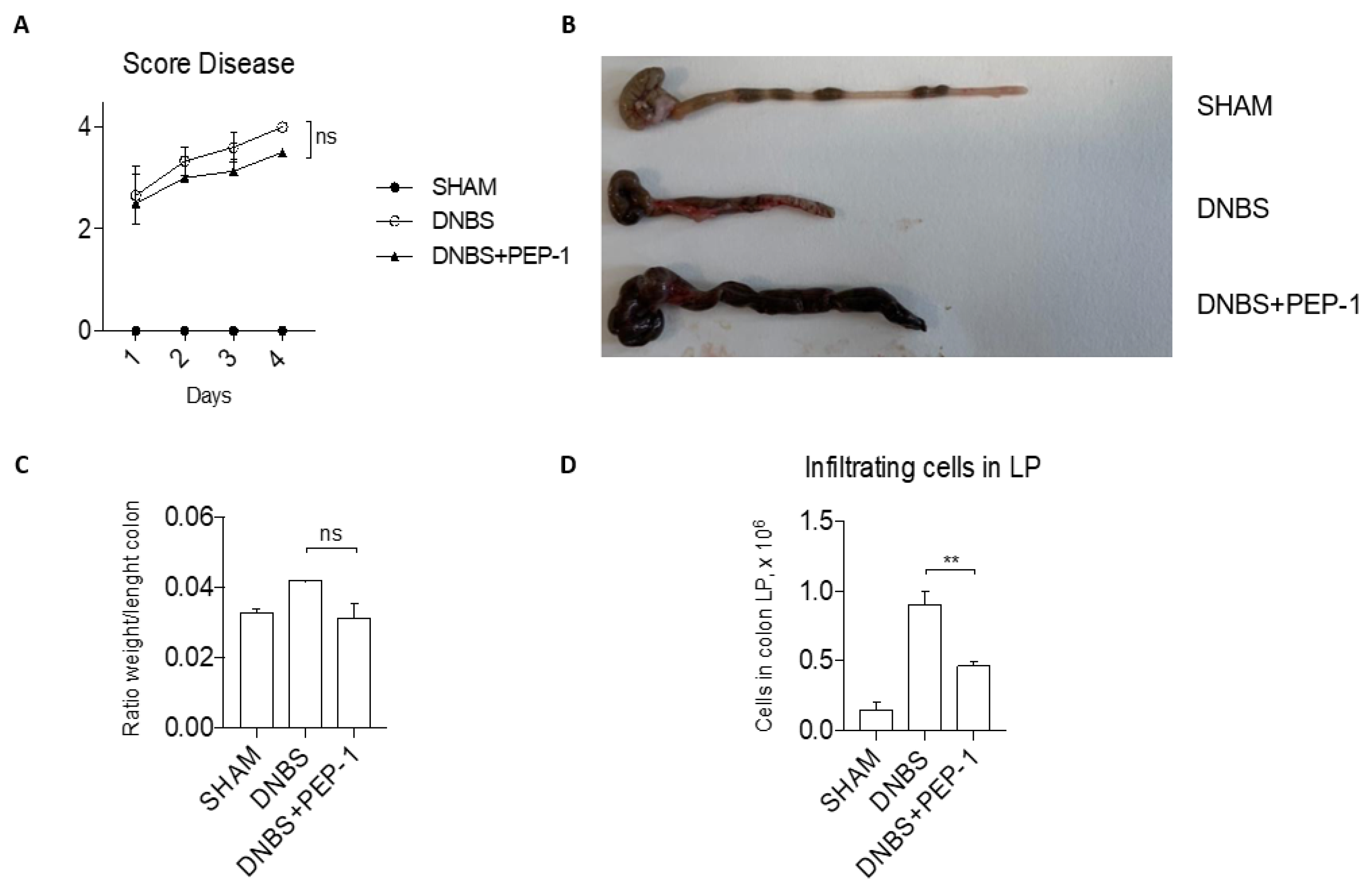
3.6. PEP-1 Protect against the Development of DNBS-Induced Colitis in Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Diaz-Jimenez, D.; Kolb, J.P.; Cidlowski, J.A. Glucocorticoids as Regulators of Macrophage-Mediated Tissue Homeostasis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 669891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronchetti, S.; Migliorati, G.; Bruscoli, S.; Riccardi, C. Defining the role of glucocorticoids in inflammation. Clin. Sci. (Lond) 2018, 132, 1529–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taves, M.D.; Ashwell, J.D. Glucocorticoids in T cell development, differentiation and function. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruscoli, S.; Febo, M.; Riccardi, C.; Migliorati, G. Glucocorticoid Therapy in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Mechanisms and Clinical Practice. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 691480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cain, D.W.; Cidlowski, J.A. Immune regulation by glucocorticoids. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandewalle, J.; Luypaert, A.; De Bosscher, K.; Libert, C. Therapeutic Mechanisms of Glucocorticoids. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 29, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schacke, H.; Docke, W.D.; Asadullah, K. Mechanisms involved in the side effects of glucocorticoids. Pharmacol. Ther. 2002, 96, 23–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, P.J. Glucocorticosteroids. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2017, 237, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, P.J.; Karin, M. Nuclear factor-kappaB: A pivotal transcription factor in chronic inflammatory diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 336, 1066–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Neriah, Y.; Karin, M. Inflammation meets cancer, with NF-kappaB as the matchmaker. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, T. The nuclear factor NF-kappaB pathway in inflammation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a001651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tak, P.P.; Firestein, G.S. NF-kappaB: A key role in inflammatory diseases. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 107, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillooly, K.M.; Pattoli, M.A.; Taylor, T.L.; Chen, L.; Cheng, L.; Gregor, K.R.; Whitney, G.S.; Susulic, V.; Watterson, S.H.; Kempson, J.; et al. Periodic, partial inhibition of IkappaB Kinase beta-mediated signaling yields therapeutic benefit in preclinical models of rheumatoid arthritis. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2009, 331, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.L.; Maeda, S.; Hsu, L.C.; Yagita, H.; Karin, M. Inhibition of NF-kappaB in cancer cells converts inflammation- induced tumor growth mediated by TNFalpha to TRAIL-mediated tumor regression. Cancer Cell 2004, 6, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bosscher, K.; Vanden Berghe, W.; Haegeman, G. The interplay between the glucocorticoid receptor and nuclear factor-kappaB or activator protein-1: Molecular mechanisms for gene repression. Endocr. Rev. 2003, 24, 488–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerber, A.N.; Newton, R.; Sasse, S.K. Repression of transcription by the glucocorticoid receptor: A parsimonious model for the genomics era. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Adamio, F.; Zollo, O.; Moraca, R.; Ayroldi, E.; Bruscoli, S.; Bartoli, A.; Cannarile, L.; Migliorati, G.; Riccardi, C. A new dexamethasone-induced gene of the leucine zipper family protects T lymphocytes from TCR/CD3-activated cell death. Immunity 1997, 7, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannarile, L.; Zollo, O.; D’Adamio, F.; Ayroldi, E.; Marchetti, C.; Tabilio, A.; Bruscoli, S.; Riccardi, C. Cloning, chromosomal assignment and tissue distribution of human GILZ, a glucocorticoid hormone-induced gene. Cell Death Differ. 2001, 8, 201–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bereshchenko, O.; Migliorati, G.; Bruscoli, S.; Riccardi, C. Glucocorticoid-Induced Leucine Zipper: A Novel Anti-inflammatory Molecule. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soundararajan, R.; Wang, J.; Melters, D.; Pearce, D. Differential activities of glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper protein isoforms. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 36303–36313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Marco, B.; Massetti, M.; Bruscoli, S.; Macchiarulo, A.; Di Virgilio, R.; Velardi, E.; Donato, V.; Migliorati, G.; Riccardi, C. Glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper (GILZ)/NF-kappaB interaction: Role of GILZ homo-dimerization and C-terminal domain. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoppstadter, J.; Diesel, B.; Eifler, L.K.; Schmid, T.; Brune, B.; Kiemer, A.K. Glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper is downregulated in human alveolar macrophages upon Toll-like receptor activation. Eur. J. Immunol. 2012, 42, 1282–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berrebi, D.; Bruscoli, S.; Cohen, N.; Foussat, A.; Migliorati, G.; Bouchet-Delbos, L.; Maillot, M.C.; Portier, A.; Couderc, J.; Galanaud, P.; et al. Synthesis of glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper (GILZ) by macrophages: An anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive mechanism shared by glucocorticoids and IL-10. Blood 2003, 101, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, R.T.; Hoppstadter, J.; Hirschfelder, K.; Hachenthal, N.; Diesel, B.; Kessler, S.M.; Huwer, H.; Kiemer, A.K. Downregulation of the glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper (GILZ) promotes vascular inflammation. Atherosclerosis 2014, 234, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vago, J.P.; Tavares, L.P.; Garcia, C.C.; Lima, K.M.; Perucci, L.O.; Vieira, E.L.; Nogueira, C.R.; Soriani, F.M.; Martins, J.O.; Silva, P.M.; et al. The role and effects of glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper in the context of inflammation resolution. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 4940–4950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flamini, S.; Sergeev, P.; Viana de Barros, Z.; Mello, T.; Biagioli, M.; Paglialunga, M.; Fiorucci, C.; Prikazchikova, T.; Pagano, S.; Gagliardi, A.; et al. Glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper regulates liver fibrosis by suppressing CCL2-mediated leukocyte recruitment. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannarile, L.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Santucci, L.; Agostini, M.; Mazzon, E.; Esposito, E.; Muia, C.; Coppo, M.; Di Paola, R.; Riccardi, C. Glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper is protective in Th1-mediated models of colitis. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 530–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannarile, L.; Fallarino, F.; Agostini, M.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Mazzon, E.; Vacca, C.; Genovese, T.; Migliorati, G.; Ayroldi, E.; Riccardi, C. Increased GILZ expression in transgenic mice up-regulates Th-2 lymphokines. Blood 2006, 107, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gentili, M.; Hidalgo-Garcia, L.; Vezza, T.; Ricci, E.; Migliorati, G.; Rodriguez-Nogales, A.; Riccardi, C.; Galvez, J.; Ronchetti, S. A recombinant glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper protein ameliorates symptoms of dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis by improving intestinal permeability. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, J.A.M.; Carvalho, A.F.S.; Grossi, L.C.; Zaidan, I.; de Oliveira, L.C.; Vago, J.P.; Cardoso, C.; Machado, M.G.; Souza, G.V.S.; Queiroz-Junior, C.M.; et al. Glucocorticoid-Induced Leucine Zipper Alleviates Lung Inflammation and Enhances Bacterial Clearance during Pneumococcal Pneumonia. Cells 2022, 11, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, E.; Bruscoli, S.; Mazzon, E.; Paterniti, I.; Coppo, M.; Velardi, E.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Riccardi, C. Glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper (GILZ) over-expression in T lymphocytes inhibits inflammation and tissue damage in spinal cord injury. Neurotherapeutics 2012, 9, 210–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruscoli, S.; Sorcini, D.; Flamini, S.; Gagliardi, A.; Adamo, F.; Ronchetti, S.; Migliorati, G.; Bereshchenko, O.; Riccardi, C. Glucocorticoid-Induced Leucine Zipper Inhibits Interferon-Gamma Production in B Cells and Suppresses Colitis in Mice. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaulieu, E.; Ngo, D.; Santos, L.; Yang, Y.H.; Smith, M.; Jorgensen, C.; Escriou, V.; Scherman, D.; Courties, G.; Apparailly, F.; et al. Glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper is an endogenous antiinflammatory mediator in arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 2651–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellouze, M.; Vigouroux, L.; Tcherakian, C.; Woerther, P.L.; Guguin, A.; Robert, O.; Surenaud, M.; Tran, T.; Calmette, J.; Barbin, T.; et al. Overexpression of GILZ in macrophages limits systemic inflammation while increasing bacterial clearance in sepsis in mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 2020, 50, 589–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, I.; Dejager, L.; Petta, I.; Vandevyver, S.; Puimege, L.; Mahieu, T.; Ballegeer, M.; Van Hauwermeiren, F.; Riccardi, C.; Vuylsteke, M.; et al. LPS resistance of SPRET/Ei mice is mediated by Gilz, encoded by the Tsc22d3 gene on the X chromosome. EMBO Mol. Med. 2013, 5, 456–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayroldi, E.; Migliorati, G.; Bruscoli, S.; Marchetti, C.; Zollo, O.; Cannarile, L.; D’Adamio, F.; Riccardi, C. Modulation of T-cell activation by the glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper factor via inhibition of nuclear factor kappaB. Blood 2001, 98, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riccardi, C.; Bruscoli, S.; Ayroldi, E.; Agostini, M.; Migliorati, G. GILZ, a glucocorticoid hormone induced gene, modulates T lymphocytes activation and death through interaction with NF-kB. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2001, 495, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppstadter, J.; Diesel, B.; Linnenberger, R.; Hachenthal, N.; Flamini, S.; Minet, M.; Leidinger, P.; Backes, C.; Grasser, F.; Meese, E.; et al. Amplified Host Defense by Toll-Like Receptor-Mediated Downregulation of the Glucocorticoid-Induced Leucine Zipper (GILZ) in Macrophages. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppstadter, J.; Hachenthal, N.; Valbuena-Perez, J.V.; Lampe, S.; Astanina, K.; Kunze, M.M.; Bruscoli, S.; Riccardi, C.; Schmid, T.; Diesel, B.; et al. Induction of Glucocorticoid-induced Leucine Zipper (GILZ) Contributes to Anti-inflammatory Effects of the Natural Product Curcumin in Macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 22949–22960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valbuena Perez, J.V.; Linnenberger, R.; Dembek, A.; Bruscoli, S.; Riccardi, C.; Schulz, M.H.; Meyer, M.R.; Kiemer, A.K.; Hoppstadter, J. Altered glucocorticoid metabolism represents a feature of macroph-aging. Aging Cell 2020, 19, e13156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Andaloussi, S.; Jarver, P.; Johansson, H.J.; Langel, U. Cargo-dependent cytotoxicity and delivery efficacy of cell-penetrating peptides: A comparative study. Biochem. J. 2007, 407, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, R.; Lohler, J.; Rennick, D.; Rajewsky, K.; Muller, W. Interleukin-10-deficient mice develop chronic enterocolitis. Cell 1993, 75, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorcini, D.; Bruscoli, S.; Frammartino, T.; Cimino, M.; Mazzon, E.; Galuppo, M.; Bramanti, P.; Al-Banchaabouchi, M.; Farley, D.; Ermakova, O.; et al. Wnt/beta-Catenin Signaling Induces Integrin alpha4beta1 in T Cells and Promotes a Progressive Neuroinflammatory Disease in Mice. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 3031–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruscoli, S.; Riccardi, C.; Ronchetti, S. GILZ as a Regulator of Cell Fate and Inflammation. Cells 2021, 11, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, D.A.; Ruscetti, F.W.; Gallo, R. Selective in vitro growth of T lymphocytes from normal human bone marrows. Science 1976, 193, 1007–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Los, M.; Schenk, H.; Hexel, K.; Baeuerle, P.A.; Droge, W.; Schulze-Osthoff, K. IL-2 gene expression and NF-kappa B activation through CD28 requires reactive oxygen production by 5-lipoxygenase. EMBO J. 1995, 14, 3731–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, F.; Smith, E.L.; Carmody, R.J. The Regulation of NF-kappaB Subunits by Phosphorylation. Cells 2016, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elson, C.O.; Cong, Y.; McCracken, V.J.; Dimmitt, R.A.; Lorenz, R.G.; Weaver, C.T. Experimental models of inflammatory bowel disease reveal innate, adaptive, and regulatory mechanisms of host dialogue with the microbiota. Immunol. Rev. 2005, 206, 260–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois-Camacho, K.; Ottum, P.A.; Franco-Munoz, D.; De la Fuente, M.; Torres-Riquelme, A.; Diaz-Jimenez, D.; Olivares-Morales, M.; Astudillo, G.; Quera, R.; Hermoso, M.A. Glucocorticosteroid therapy in inflammatory bowel diseases: From clinical practice to molecular biology. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 6628–6638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovgren, A.K.; Kovarova, M.; Koller, B.H. cPGES/p23 is required for glucocorticoid receptor function and embryonic growth but not prostaglandin E2 synthesis. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 27, 4416–4430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, J.; Stunnenberg, H.G. The glucocorticoid receptor hormone binding domain mediates transcriptional activation in vitro in the absence of ligand. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993, 21, 2673–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Srinivasan, M.; Janardhanam, S. Novel p65 binding glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper peptide suppresses experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 44799–44810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, R.; Tang, W.; Lei, B.; Jiang, C.; Song, F.; Xu, G. Synthesized glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper peptide inhibits photoreceptor apoptosis and protects retinal function in light-induced retinal degeneration model. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2019, 47, 646–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neurath, M.F.; Fuss, I.; Schurmann, G.; Pettersson, S.; Arnold, K.; Muller-Lobeck, H.; Strober, W.; Herfarth, C.; Buschenfelde, K.H. Cytokine gene transcription by NF-kappa B family members in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1998, 859, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.C. NF-kappaB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2017, 2, 17023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhawan, S.; Singh, S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Induction of endothelial cell surface adhesion molecules by tumor necrosis factor is blocked by protein tyrosine phosphatase inhibitors: Role of the nuclear transcription factor NF-kappa B. Eur. J. Immunol. 1997, 27, 2172–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujihara, S.M.; Cleaveland, J.S.; Grosmaire, L.S.; Berry, K.K.; Kennedy, K.A.; Blake, J.J.; Loy, J.; Rankin, B.M.; Ledbetter, J.A.; Nadler, S.G. A D-amino acid peptide inhibitor of NF-kappa B nuclear localization is efficacious in models of inflammatory disease. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 1004–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.; Sudandiradoss, C. Andrographolide-based potential anti-inflammatory transcription inhibitors against nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p50 subunit (NF-kappaB p50): An integrated molecular and quantum mechanical approach. 3 Biotech 2023, 13, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuldo, J.M.; Westra, J.; Asgeirsdottir, S.A.; Kok, R.J.; Oosterhuis, K.; Rots, M.G.; Schouten, J.P.; Limburg, P.C.; Molema, G. Differential effects of NF-kappaB and p38 MAPK inhibitors and combinations thereof on TNF-alpha- and IL-1beta-induced proinflammatory status of endothelial cells in vitro. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2005, 289, C1229–C1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neurath, M.F.; Pettersson, S.; Meyer zum Buschenfelde, K.H.; Strober, W. Local administration of antisense phosphorothioate oligonucleotides to the p65 subunit of NF-kappa B abrogates established experimental colitis in mice. Nat. Med. 1996, 2, 998–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torgerson, T.R.; Colosia, A.D.; Donahue, J.P.; Lin, Y.Z.; Hawiger, J. Regulation of NF-kappa B, AP-1, NFAT, and STAT1 nuclear import in T lymphocytes by noninvasive delivery of peptide carrying the nuclear localization sequence of NF-kappa B p50. J. Immunol. 1998, 161, 6084–6092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paglialunga, M.; Flamini, S.; Contini, R.; Febo, M.; Ricci, E.; Ronchetti, S.; Bereshchenko, O.; Migliorati, G.; Riccardi, C.; Bruscoli, S. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Synthetic Peptides Based on Glucocorticoid-Induced Leucine Zipper (GILZ) Protein for the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (IBDs). Cells 2023, 12, 2294. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12182294
Paglialunga M, Flamini S, Contini R, Febo M, Ricci E, Ronchetti S, Bereshchenko O, Migliorati G, Riccardi C, Bruscoli S. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Synthetic Peptides Based on Glucocorticoid-Induced Leucine Zipper (GILZ) Protein for the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (IBDs). Cells. 2023; 12(18):2294. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12182294
Chicago/Turabian StylePaglialunga, Musetta, Sara Flamini, Raffaele Contini, Marta Febo, Erika Ricci, Simona Ronchetti, Oxana Bereshchenko, Graziella Migliorati, Carlo Riccardi, and Stefano Bruscoli. 2023. "Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Synthetic Peptides Based on Glucocorticoid-Induced Leucine Zipper (GILZ) Protein for the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (IBDs)" Cells 12, no. 18: 2294. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12182294
APA StylePaglialunga, M., Flamini, S., Contini, R., Febo, M., Ricci, E., Ronchetti, S., Bereshchenko, O., Migliorati, G., Riccardi, C., & Bruscoli, S. (2023). Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Synthetic Peptides Based on Glucocorticoid-Induced Leucine Zipper (GILZ) Protein for the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (IBDs). Cells, 12(18), 2294. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12182294






