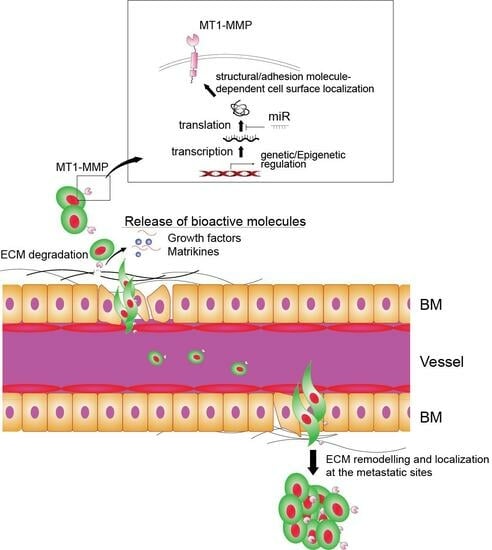
MT1-MMP as a Key Regulator of Metastasis
Abstract
1. Introduction
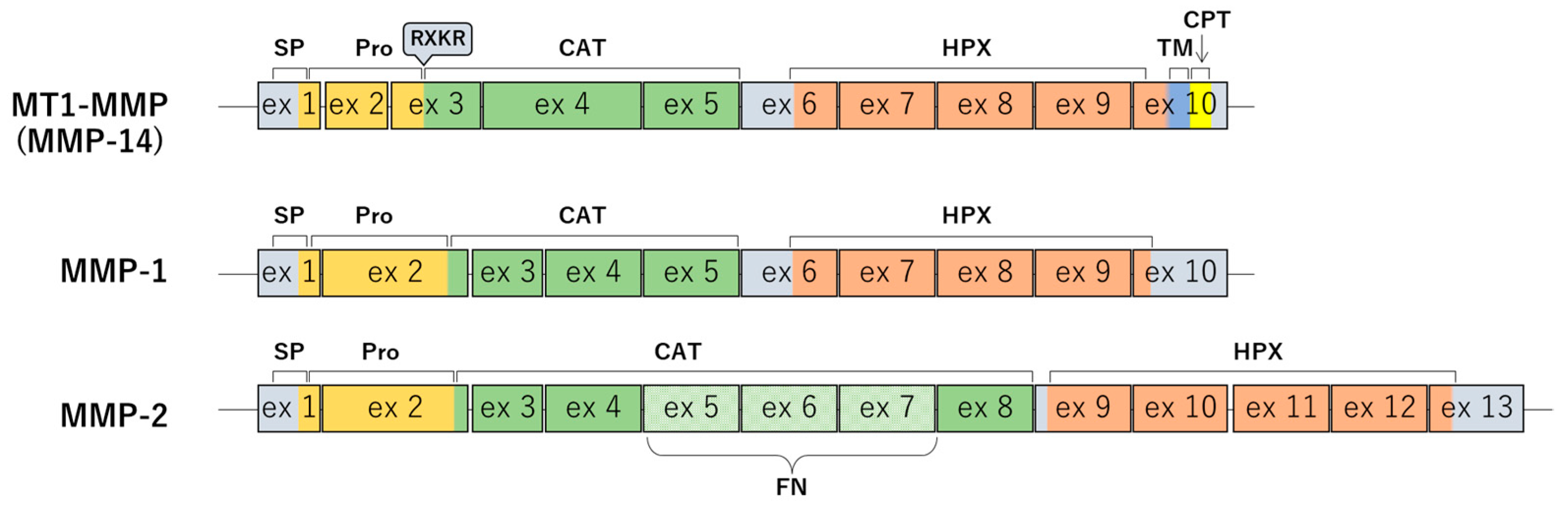
2. The Fundamentals of MT1-MMP
2.1. The Structure of MT1-MMP
2.2. How MT1-MMP Expressions Are Regulated
2.3. Intracellular Localization of MT1-MMP
2.4. MT1-MMP-Dependent Processing of Other MMPs
2.5. ECM Components as Substrates of MT1-MMP
2.6. Non-ECM-Related Substrates of MT1-MMP
2.7. Beyond Its Function as Proteinase
3. The Impact of MT1-MMP on Cancer Metastasis
3.1. ECM Remodeling by MT1-MMP
3.2. The Activation of Oncogenic Signaling by MT1-MMP
3.3. Metastasis Promotion via the Non-Proteolytic Activity of MT1-MMP
4. Negative Regulators of MT1-MMP
4.1. Endogenous Negative Regulators of MT1-MMP
4.2. Artificial Inhibitors of MT1-MMP
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sato, H.; Takino, T.; Okada, Y.; Cao, J.; Shinagawa, A.; Yamamoto, E.; Seiki, M. A matrix metalloproteinase expressed on the surface of invasive tumour cells. Nature 1994, 370, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessenbrock, K.; Plaks, V.; Werb, Z. Matrix metalloproteinases: Regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Cell 2010, 141, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, T.; Seiki, M. Integrated functions of membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase in regulating cancer malignancy: Beyond a proteinase. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 1095–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, Y. Membrane-type matrix metalloproteinases: Their functions and regulations. Matrix Biol. 2015, 44–46, 207–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woskowicz, A.M.; Weaver, S.A.; Shitomi, Y.; Ito, N.; Itoh, Y. MT-LOOP-dependent localization of membrane type I matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP) to the cell adhesion complexes promotes cancer cell invasion. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 35126–35137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yana, I.; Weiss, S.J. Regulation of membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase activation by proprotein convertases. Mol. Biol. Cell 2000, 11, 2387–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohi, J.; Lehti, K.; Valtanen, H.; Parks, W.C.; Keski-Oja, J. Structural analysis and promoter characterization of the human membrane-type matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MT1-MMP) gene. Gene 2000, 242, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafleur, M.A.; Xu, D.; Hemler, M.E. Tetraspanin proteins regulate membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase-dependent pericellular proteolysis. Mol. Biol. Cell 2009, 20, 2030–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.P.; Li, Q.; Lin, F.X.; Li, J.; Wu, L.M.; Li, W.; Yang, Q.Z. MT1-MMP is not a good prognosticator of cancer survival: Evidence from 11 studies. Tumour Biol. 2014, 35, 12489–12495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.W.; Ma, W.; Jiang, F.; Xie, Y.; Tang, L. Upregulation of matrix metalloproteinase 14 (MMP14) is associated with poor prognosis in renal clear cell carcinoma-a bioinformatics analysis. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2022, 11, 1523–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, Y.; Ishida, M.; Yamaka, R.; Ueno, Y.; Sakagami, T.; Fujisawa, T.; Iwai, H.; Tsuta, K. MMP14 expression levels accurately predict the presence of extranodal extensions in oral squamous cell carcinoma: A retrospective cohort study. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brookes, M.J.; Roundhill, E.A.; Jeys, L.; Parry, M.; Burchill, S.A.; Rankin, K.S. Membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase as predictor of survival and candidate therapeutic target in Ewing sarcoma. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2022, 69, e29959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apte, S.S.; Fukai, N.; Beier, D.R.; Olsen, B.R. The matrix metalloproteinase-14 (MMP-14) gene is structurally distinct from other MMP genes and is co-expressed with the TIMP-2 gene during mouse embryogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 25511–25517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, G.M.; Crow, M.T.; Bilato, C.; Gluzband, Y.; Ryu, W.S.; Li, Z.; Stetler-Stevenson, W.; Nater, C.; Froehlich, J.P.; Lakatta, E.G.; et al. Increased expression of membrane-type matrix metalloproteinase and preferential localization of matrix metalloproteinase-2 to the neointima of balloon-injured rat carotid arteries. Circulation 1998, 97, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madlener, M.; Parks, W.C.; Werner, S. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and their physiological inhibitors (TIMPs) are differentially expressed during excisional skin wound repair. Exp. Cell Res. 1998, 242, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, T.L.; Stitelman, D.; Davis, S.J.; Apte, S.S.; Madri, J.A. Egr-1 mediates extracellular matrix-driven transcription of membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase in endothelium. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 22679–22685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, B.K.; Shakya, A.; Turk, J.R.; Apte, S.S.; Ray, A. Induction of the MMP-14 gene in macrophages of the atherosclerotic plaque: Role of SAF-1 in the induction process. Circ. Res. 2004, 95, 1082–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramolelli, S.; Cheng, J.; Martinez-Corral, I.; Vaha-Koskela, M.; Elbasani, E.; Kaivanto, E.; Rantanen, V.; Tuohinto, K.; Hautaniemi, S.; Bower, M.; et al. PROX1 is a transcriptional regulator of MMP14. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasurinen, A.; Gramolelli, S.; Hagstrom, J.; Laitinen, A.; Kokkola, A.; Miki, Y.; Lehti, K.; Yashiro, M.; Ojala, P.M.; Bockelman, C.; et al. High tissue MMP14 expression predicts worse survival in gastric cancer, particularly with a low PROX1. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 6995–7005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cathcart, J.M.; Banach, A.; Liu, A.; Chen, J.; Goligorsky, M.; Cao, J. Interleukin-6 increases matrix metalloproteinase-14 (MMP-14) levels via down-regulation of p53 to drive cancer progression. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 61107–61120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, L.D.; Le, T.; Fan, G. DNA methylation and its basic function. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fry, C.J.; Peterson, C.L. Chromatin remodeling enzymes: Who’s on first? Curr. Biol. 2001, 11, R185–R197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Yan, Q. Histone ubiquitination and deubiquitination in transcription, DNA damage response, and cancer. Front. Oncol. 2012, 2, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernov, A.V.; Sounni, N.E.; Remacle, A.G.; Strongin, A.Y. Epigenetic control of the invasion-promoting MT1-MMP/MMP-2/TIMP-2 axis in cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 12727–12734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Wu, F.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Tang, H. DNMT1 recruited by EZH2-mediated silencing of miR-484 contributes to the malignancy of cervical cancer cells through MMP14 and HNF1A. Clin. Epigenetics 2019, 11, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Dai, C.; Yu, X.; Yin, X.B.; Zhou, F. microRNA-485-5p inhibits the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma through blocking the WBP2/Wnt signaling pathway. Cell. Signal. 2020, 66, 109466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Hu, G.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Y.; Xue, W.; Xu, Y.; Zhai, W. circPTCH1 promotes invasion and metastasis in renal cell carcinoma via regulating miR-485-5p/MMP14 axis. Theranostics 2020, 10, 10791–10807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zuo, X.; Wang, K.; Han, Q.; Zuo, J.; Ni, H.; Liu, W.; Bao, H.; Tu, Y.; Xie, P. MicroRNA-485-5p attenuates cell proliferation in glioma by directly targeting paired box 3. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2018, 8, 2507–2517. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, D.; Feng, X.D.; Zhu, W.Q.; Bao, Y.N. LncRNA BLACAT1 regulates the viability, migration and invasion of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells by targeting miR-142-5p. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 10313–10323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.T. Proteolytic activity of specialized surface protrusions formed at rosette contact sites of transformed cells. J. Exp. Zool. 1989, 251, 167–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Machesky, L.M. Cells assemble invadopodia-like structures and invade into matrigel in a matrix metalloprotease dependent manner in the circular invasion assay. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrowska-Podhorodecka, Z.; Ali, A.; Norouzi, M.; Ding, I.; Abbasi, S.; Arora, P.D.; Wong, T.H.F.; Magalhaes, M.; McCulloch, C.A. Vimentin-mediated myosin 10 aggregation at tips of cell extensions drives MT1-MMP-dependent collagen degradation in colorectal cancer. FASEB J. 2023, 37, e23097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Lou, G.; Zhou, J. MT1-MMP promotes the proliferation and invasion of gastric carcinoma cells via regulating vimentin and E-cadherin. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 19, 2519–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, L.; Cao, H.; Chen, J.; Weller, S.G.; Krueger, E.W.; Zhang, L.; Razidlo, G.L.; McNiven, M.A. Pancreatic tumor cell metastasis is restricted by MT1-MMP binding protein MTCBP-1. J. Cell Biol. 2019, 218, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uekita, T.; Gotoh, I.; Kinoshita, T.; Itoh, Y.; Sato, H.; Shiomi, T.; Okada, Y.; Seiki, M. Membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase cytoplasmic tail-binding protein-1 is a new member of the Cupin superfamily. A possible multifunctional protein acting as an invasion suppressor down-regulated in tumors. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 12734–12743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, R.; Martin, G.; Tagit, O.; Guichard, A.; Cambi, A.; Voituriez, R.; Vassilopoulos, S.; Chavrier, P. MT1-MMP directs force-producing proteolytic contacts that drive tumor cell invasion. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uekita, T.; Tanaka, S.S.; Sato, H.; Seiki, M.; Tojo, H.; Tachi, C. Expression of membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP) mRNA in trophoblast and endometrial epithelial cell populations of the synepitheliochorial placenta of goats (Capra hircus). Arch. Histol. Cytol. 2001, 64, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, A.; Lehti, K.; Wang, X.; Weiss, S.J.; Keski-Oja, J.; Pei, D. Regulation of membrane-type matrix metalloproteinase 1 activity by dynamin-mediated endocytosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 13693–13698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remacle, A.; Murphy, G.; Roghi, C. Membrane type I-matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP) is internalised by two different pathways and is recycled to the cell surface. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 3905–3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takino, T.; Miyamori, H.; Kawaguchi, N.; Uekita, T.; Seiki, M.; Sato, H. Tetraspanin CD63 promotes targeting and lysosomal proteolysis of membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 304, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyagawa, T.; Hasegawa, K.; Aoki, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Otagiri, Y.; Arasaki, K.; Wakana, Y.; Asano, K.; Tanaka, M.; Yamaguchi, H.; et al. MT1-MMP recruits the ER-Golgi SNARE Bet1 for efficient MT1-MMP transport to the plasma membrane. J. Cell Biol. 2019, 218, 3355–3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo-Cordero, J.J.; Marrero-Diaz, R.; Megias, D.; Genis, L.; Garcia-Grande, A.; Garcia, M.A.; Arroyo, A.G.; Montoya, M.C. MT1-MMP proinvasive activity is regulated by a novel Rab8-dependent exocytic pathway. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 1499–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linder, S.; Scita, G. RABGTPases in MT1-MMP trafficking and cell invasion: Physiology versus pathology. Small GTPases 2015, 6, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sharma, P.; Parveen, S.; Shah, L.V.; Mukherjee, M.; Kalaidzidis, Y.; Kozielski, A.J.; Rosato, R.; Chang, J.C.; Datta, S. SNX27-retromer assembly recycles MT1-MMP to invadopodia and promotes breast cancer metastasis. J. Cell Biol. 2020, 219, e201812098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kean, M.J.; Williams, K.C.; Skalski, M.; Myers, D.; Burtnik, A.; Foster, D.; Coppolino, M.G. VAMP3, syntaxin-13 and SNAP23 are involved in secretion of matrix metalloproteinases, degradation of the extracellular matrix and cell invasion. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 4089–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamberland, J.P.; Ritter, B. Retromer revisited: Evolving roles for retromer in endosomal sorting. J. Cell Biol. 2017, 216, 3433–3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burd, C.; Cullen, P.J. Retromer: A master conductor of endosome sorting. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a016774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmert-Buck, M.R.; Emonard, H.P.; Corcoran, M.L.; Krutzsch, H.C.; Foidart, J.M.; Stetler-Stevenson, W.G. Cell surface binding of TIMP-2 and pro-MMP-2/TIMP-2 complex. FEBS Lett. 1995, 364, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strongin, A.Y.; Collier, I.; Bannikov, G.; Marmer, B.L.; Grant, G.A.; Goldberg, G.I. Mechanism of cell surface activation of 72-kDa type IV collagenase. Isolation of the activated form of the membrane metalloprotease. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 5331–5338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strongin, A.Y.; Marmer, B.L.; Grant, G.A.; Goldberg, G.I. Plasma membrane-dependent activation of the 72-kDa type IV collagenase is prevented by complex formation with TIMP-2. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 14033–14039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knauper, V.; Will, H.; Lopez-Otin, C.; Smith, B.; Atkinson, S.J.; Stanton, H.; Hembry, R.M.; Murphy, G. Cellular mechanisms for human procollagenase-3 (MMP-13) activation. Evidence that MT1-MMP (MMP-14) and gelatinase a (MMP-2) are able to generate active enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 17124–17131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knauper, V.; Bailey, L.; Worley, J.R.; Soloway, P.; Patterson, M.L.; Murphy, G. Cellular activation of proMMP-13 by MT1-MMP depends on the C-terminal domain of MMP-13. FEBS Lett. 2002, 532, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naba, A.; Clauser, K.R.; Ding, H.; Whittaker, C.A.; Carr, S.A.; Hynes, R.O. The extracellular matrix: Tools and insights for the “omics” era. Matrix Biol. 2016, 49, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iozzo, R.V.; Schaefer, L. Proteoglycan form and function: A comprehensive nomenclature of proteoglycans. Matrix Biol. 2015, 42, 11–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouw, J.K.; Ou, G.; Weaver, V.M. Extracellular matrix assembly: A multiscale deconstruction. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 771–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egeblad, M.; Rasch, M.G.; Weaver, V.M. Dynamic interplay between the collagen scaffold and tumor evolution. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2010, 22, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzi, A.; Yurchenco, P.D.; Iozzo, R.V. The nature and biology of basement membranes. Matrix Biol. 2017, 57–58, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayadev, R.; Sherwood, D.R. Basement membranes. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, R207–R211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohuchi, E.; Imai, K.; Fujii, Y.; Sato, H.; Seiki, M.; Okada, Y. Membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase digests interstitial collagens and other extracellular matrix macromolecules. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 2446–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajita, M.; Itoh, Y.; Chiba, T.; Mori, H.; Okada, A.; Kinoh, H.; Seiki, M. Membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase cleaves CD44 and promotes cell migration. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 153, 893–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deryugina, E.I.; Bourdon, M.A.; Jungwirth, K.; Smith, J.W.; Strongin, A.Y. Functional activation of integrin ?v?3 in tumor cells expressing membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase. Int. J. Cancer 2000, 86, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshikawa, N.; Schenk, S.; Moeckel, G.; Sharabi, A.; Miyazaki, K.; Gardner, H.; Zent, R.; Quaranta, V. Proteolytic processing of laminin-5 by MT1-MMP in tissues and its effects on epithelial cell morphology. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 364–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshikawa, N.; Giannelli, G.; Cirulli, V.; Miyazaki, K.; Quaranta, V. Role of cell surface metalloprotease MT1-MMP in epithelial cell migration over laminin-5. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 148, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ornitz, D.M.; Marie, P.J. FGF signaling pathways in endochondral and intramembranous bone development and human genetic disease. Genes. Dev. 2002, 16, 1446–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peduto, L.; Reuter, V.E.; Shaffer, D.R.; Scher, H.I.; Blobel, C.P. Critical function for ADAM9 in mouse prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 9312–9319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, K.M.; Wong, H.L.; Jin, G.; Liu, B.; Cao, R.; Cao, Y.; Lehti, K.; Tryggvason, K.; Zhou, Z. MT1-MMP inactivates ADAM9 to regulate FGFR2 signaling and calvarial osteogenesis. Dev. Cell 2012, 22, 1176–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suenaga, N.; Mori, H.; Itoh, Y.; Seiki, M. CD44 binding through the hemopexin-like domain is critical for its shedding by membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase. Oncogene 2005, 24, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, H.; Tomari, T.; Koshikawa, N.; Kajita, M.; Itoh, Y.; Sato, H.; Tojo, H.; Yana, I.; Seiki, M. CD44 directs membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase to lamellipodia by associating with its hemopexin-like domain. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 3949–3959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Asthana, P.; Gurung, S.; Zhang, S.; Wong, S.K.K.; Fallah, S.; Chow, C.F.W.; Che, S.; Zhai, L.; Wang, Z.; et al. Regulation of age-associated insulin resistance by MT1-MMP-mediated cleavage of insulin receptor. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Chi, C. Interaction of Mint3 with Furin regulates the localization of Furin in the trans-Golgi network. J. Cell Sci. 2008, 121, 2217–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, T.; Seiki, M. Mint3 enhances the activity of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) in macrophages by suppressing the activity of factor inhibiting HIF-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 30350–30359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, T.; Seiki, M. A membrane protease regulates energy production in macrophages by activating hypoxia-inducible factor-1 via a non-proteolytic mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 29951–29964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, I.; Li, X.Y.; Hu, Y.; Weiss, S.J. Induction of a MT1-MMP and MT2-MMP-dependent basement membrane transmigration program in cancer cells by Snail1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 20318–20323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, H.S.; Robertson, A.E.; Stoletov, K.; Leith, S.J.; Chin, C.A.; Chien, A.E.; Hague, M.N.; Ablack, A.; Carmine-Simmen, K.; McPherson, V.A.; et al. Invadopodia are required for cancer cell extravasation and are a therapeutic target for metastasis. Cell Rep. 2014, 8, 1558–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, L.; Liu, H.G.; Dong, S.Y.; Yang, F.; Wang, Q.X.; Guo, G.L.; Pan, Y.F.; Zhang, X.H. Upregulation of CD44v6 contributes to acquired chemoresistance via the modulation of autophagy in colon cancer SW480 cells. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 8811–8824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugahara, K.N.; Murai, T.; Nishinakamura, H.; Kawashima, H.; Saya, H.; Miyasaka, M. Hyaluronan oligosaccharides induce CD44 cleavage and promote cell migration in CD44-expressing tumor cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 32259–32265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, I.; Kawano, Y.; Murakami, D.; Sasayama, T.; Araki, N.; Miki, T.; Wong, A.J.; Saya, H. Proteolytic release of CD44 intracellular domain and its role in the CD44 signaling pathway. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 155, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.H.; Wang, W.M.; Yang, J.G.; Xia, H.F.; Xiao, B.L.; Chen, G.H.; Huang, J.; Li, R.F.; Chen, G. ALIX promotes cell migration and invasion of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by regulating the expression of MMP9, MMP14, VEGF-C. Arch. Oral. Biol. 2023, 151, 105696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazono, K.; Olofsson, A.; Colosetti, P.; Heldin, C.H. A role of the latent TGF-beta 1-binding protein in the assembly and secretion of TGF-beta 1. EMBO J. 1991, 10, 1091–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, J.; Lameiras, P.; Beljebbar, A.; Berquand, A.; Villemin, M.; Ramont, L.; Dukic, S.; Nuzillard, J.M.; Molinari, M.; Gautier, M.; et al. Structural characterization and in vivo pro-tumor properties of a highly conserved matrikine. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 17839–17857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mecham, R.P.; Broekelmann, T.J.; Fliszar, C.J.; Shapiro, S.D.; Welgus, H.G.; Senior, R.M. Elastin degradation by matrix metalloproteinases. Cleavage site specificity and mechanisms of elastolysis. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 18071–18076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannelli, G.; Falk-Marzillier, J.; Schiraldi, O.; Stetler-Stevenson, W.G.; Quaranta, V. Induction of cell migration by matrix metalloprotease-2 cleavage of laminin-5. Science 1997, 277, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schenk, S.; Hintermann, E.; Bilban, M.; Koshikawa, N.; Hojilla, C.; Khokha, R.; Quaranta, V. Binding to EGF receptor of a laminin-5 EGF-like fragment liberated during MMP-dependent mammary gland involution. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 161, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, M.; Koshikawa, N.; Schenk, S.; Quaranta, V. The LG3 module of laminin-5 harbors a binding site for integrin alpha3beta1 that promotes cell adhesion, spreading, and migration. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 33045–33053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gingras, D.; Bousquet-Gagnon, N.; Langlois, S.; Lachambre, M.P.; Annabi, B.; Beliveau, R. Activation of the extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase (ERK) cascade by membrane-type-1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP). FEBS Lett. 2001, 507, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alessio, S.; Ferrari, G.; Cinnante, K.; Scheerer, W.; Galloway, A.C.; Roses, D.F.; Rozanov, D.V.; Remacle, A.G.; Oh, E.S.; Shiryaev, S.A.; et al. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2 binding to membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase induces MAPK activation and cell growth by a non-proteolytic mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyalendo, C.; Michaud, M.; Beaulieu, E.; Roghi, C.; Murphy, G.; Gingras, D.; Beliveau, R. Src-dependent phosphorylation of membrane type I matrix metalloproteinase on cytoplasmic tyrosine 573: Role in endothelial and tumor cell migration. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 15690–15699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenach, P.A.; Roghi, C.; Fogarasi, M.; Murphy, G.; English, W.R. MT1-MMP regulates VEGF-A expression through a complex with VEGFR-2 and Src. J. Cell Sci. 2010, 123, 4182–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippov, S.; Koenig, G.C.; Chun, T.H.; Hotary, K.B.; Ota, I.; Bugge, T.H.; Roberts, J.D.; Fay, W.P.; Birkedal-Hansen, H.; Holmbeck, K.; et al. MT1-matrix metalloproteinase directs arterial wall invasion and neointima formation by vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 202, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehti, K.; Allen, E.; Birkedal-Hansen, H.; Holmbeck, K.; Miyake, Y.; Chun, T.H.; Weiss, S.J. An MT1-MMP-PDGF receptor-beta axis regulates mural cell investment of the microvasculature. Genes. Dev. 2005, 19, 979–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, T.H.; Sabeh, F.; Ota, I.; Murphy, H.; McDonagh, K.T.; Holmbeck, K.; Birkedal-Hansen, H.; Allen, E.D.; Weiss, S.J. MT1-MMP-dependent neovessel formation within the confines of the three-dimensional extracellular matrix. J. Cell Biol. 2004, 167, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valacca, C.; Tassone, E.; Mignatti, P. TIMP-2 Interaction with MT1-MMP Activates the AKT Pathway and Protects Tumor Cells from Apoptosis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uekita, T.; Itoh, Y.; Yana, I.; Ohno, H.; Seiki, M. Cytoplasmic tail-dependent internalization of membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase is important for its invasion-promoting activity. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 155, 1345–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anilkumar, N.; Uekita, T.; Couchman, J.R.; Nagase, H.; Seiki, M.; Itoh, Y. Palmitoylation at Cys574 is essential for MT1-MMP to promote cell migration. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 1326–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galvez, B.G.; Matias-Roman, S.; Yanez-Mo, M.; Sanchez-Madrid, F.; Arroyo, A.G. ECM regulates MT1-MMP localization with beta1 or alphavbeta3 integrins at distinct cell compartments modulating its internalization and activity on human endothelial cells. J. Cell Biol. 2002, 159, 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grafinger, O.R.; Gorshtein, G.; Stirling, T.; Brasher, M.I.; Coppolino, M.G. Beta1 integrin-mediated signaling regulates MT1-MMP phosphorylation to promote tumor cell invasion. J. Cell Sci. 2020, 133, jcs239152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grafinger, O.R.; Gorshtein, G.; Stirling, T.; Geddes-McAlister, J.; Coppolino, M.G. Inhibition of beta1 integrin induces its association with MT1-MMP and decreases MT1-MMP internalization and cellular invasiveness. Cell Signal. 2021, 83, 109984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, T.; Seiki, M. Cytoplasmic tail of MT1-MMP regulates macrophage motility independently from its protease activity. Genes Cells 2009, 14, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, T.; Niiya, D.; Seiki, M. Targeting the Warburg effect that arises in tumor cells expressing membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 14691–14704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, T.; Murakami, Y.; Seiki, M.; Sakamoto, T. Mint3 in bone marrow-derived cells promotes lung metastasis in breast cancer model mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 490, 688–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, J.; Ohe, C.; Tanaka, N.; Yoshida, T.; Saito, R.; Atsumi, N.; Kobayashi, T.; Kinoshita, H.; Tsuta, K.; Sakamoto, T. Hypoxia inducible factor-1 activator munc-18-interacting protein 3 promotes tumour progression in urothelial carcinoma. Clin. Transl. Discov. 2023, 3, e158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanamori, A.; Matsubara, D.; Saitoh, Y.; Fukui, Y.; Gotoh, N.; Kaneko, S.; Seiki, M.; Murakami, Y.; Inoue, J.I.; Sakamoto, T. Mint3 depletion restricts tumor malignancy of pancreatic cancer cells by decreasing SKP2 expression via HIF-1. Oncogene 2020, 39, 6218–6230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, C.; Kusubata, K.; Tashiro, Y.; Gritli, I.; Sato, A.; Ohki-Koizumi, M.; Morita, Y.; Nagano, M.; Sakamoto, T.; Koshikawa, N.; et al. MT1-MMP plays a critical role in hematopoiesis by regulating HIF-mediated chemokine/cytokine gene transcription within niche cells. Blood 2012, 119, 5405–5416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shofuda, K.; Moriyama, K.; Nishihashi, A.; Higashi, S.; Mizushima, H.; Yasumitsu, H.; Miki, K.; Sato, H.; Seiki, M.; Miyazaki, K. Role of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2 (TIMP-2) in regulation of pro-gelatinase A activation catalyzed by membrane-type matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MT1-MMP) in human cancer cells. J. Biochem. 1998, 124, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, A.N.; Unsworth, E.J.; Stetler-Stevenson, W.G. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2 inhibits bFGF-induced human microvascular endothelial cell proliferation. J. Cell Physiol. 1993, 157, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoegy, S.E.; Oh, H.R.; Corcoran, M.L.; Stetler-Stevenson, W.G. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2 (TIMP-2) suppresses TKR-growth factor signaling independent of metalloproteinase inhibition. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 3203–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, D.W.; Li, H.; Guedez, L.; Wingfield, P.T.; Diaz, T.; Salloum, R.; Wei, B.Y.; Stetler-Stevenson, W.G. TIMP-2 mediated inhibition of angiogenesis: An MMP-independent mechanism. Cell 2003, 114, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.; Takahashi, R.; Kondo, S.; Mizoguchi, A.; Adachi, E.; Sasahara, R.M.; Nishimura, S.; Imamura, Y.; Kitayama, H.; Alexander, D.B.; et al. The membrane-anchored MMP inhibitor RECK is a key regulator of extracellular matrix integrity and angiogenesis. Cell 2001, 107, 789–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, C.; Sheng, Z.; Horan, T.P.; Kitayama, H.; Maki, M.; Hitomi, K.; Kitaura, Y.; Takai, S.; Sasahara, R.M.; Horimoto, A.; et al. Regulation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and inhibition of tumor invasion by the membrane-anchored glycoprotein RECK. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 13221–13226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsoulidis, E.; Mavrommatis, E.; Woodard, J.; Shields, M.A.; Sassano, A.; Carayol, N.; Sawicki, K.T.; Munshi, H.G.; Platanias, L.C. Role of interferon alpha (IFNalpha)-inducible Schlafen-5 in regulation of anchorage-independent growth and invasion of malignant melanoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 40333–40341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassano, A.; Mavrommatis, E.; Arslan, A.D.; Kroczynska, B.; Beauchamp, E.M.; Khuon, S.; Chew, T.L.; Green, K.J.; Munshi, H.G.; Verma, A.K.; et al. Human Schlafen 5 (SLFN5) Is a Regulator of Motility and Invasiveness of Renal Cell Carcinoma Cells. Mol. Cell Biol. 2015, 35, 2684–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Guo, L.; Li, C.; Yang, Y.; Gu, X.; Deng, L.L.; Lu, C. SLFN5 suppresses cancer cell migration and invasion by inhibiting MT1-MMP expression via AKT/GSK-3beta/beta-catenin pathway. Cell Signal. 2019, 59, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneeggen, M.; Pedersen, N.M.; Campsteijn, C.; Haugsten, E.M.; Stenmark, H.; Schink, K.O. WDFY2 restrains matrix metalloproteinase secretion and cell invasion by controlling VAMP3-dependent recycling. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clancy, J.W.; Sedgwick, A.; Rosse, C.; Muralidharan-Chari, V.; Raposo, G.; Method, M.; Chavrier, P.; D’Souza-Schorey, C. Regulated delivery of molecular cargo to invasive tumour-derived microvesicles. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodillinsky, C.; Fuhrmann, L.; Irondelle, M.; Pylypenko, O.; Li, X.Y.; Bonsang-Kitzis, H.; Reyal, F.; Vacher, S.; Calmel, C.; De Wever, O.; et al. Metastasis-suppressor NME1 controls the invasive switch of breast cancer by regulating MT1-MMP surface clearance. Oncogene 2021, 40, 4019–4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtowicz-Praga, S.; Low, J.; Marshall, J.; Ness, E.; Dickson, R.; Barter, J.; Sale, M.; McCann, P.; Moore, J.; Cole, A.; et al. Phase I trial of a novel matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor batimastat (BB-94) in patients with advanced cancer. Investig. New Drugs 1996, 14, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuniasse, P.; Devel, L.; Makaritis, A.; Beau, F.; Georgiadis, D.; Matziari, M.; Yiotakis, A.; Dive, V. Future challenges facing the development of specific active-site-directed synthetic inhibitors of MMPs. Biochimie 2005, 87, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, J.T. The importance of estimating the therapeutic index in the development of matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors. Cardiovasc. Res. 2006, 69, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winer, A.; Adams, S.; Mignatti, P. Matrix Metalloproteinase Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy: Turning Past Failures Into Future Successes. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 1147–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Youn, I.; Demissie, R.; Vaid, T.M.; Che, C.T.; Azar, D.T.; Han, K.Y. Identification of small molecule inhibitors against MMP-14 via High-Throughput screening. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2023, 85, 117289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devy, L.; Huang, L.; Naa, L.; Yanamandra, N.; Pieters, H.; Frans, N.; Chang, E.; Tao, Q.; Vanhove, M.; Lejeune, A.; et al. Selective inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-14 blocks tumor growth, invasion, and angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 1517–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, B.; Watt, K.; Banerjee, S.; Newsted, D.; Truesdell, P.; Adams, J.; Sidhu, S.S.; Craig, A.W.B. A novel immunotherapy targeting MMP-14 limits hypoxia, immune suppression and metastasis in triple-negative breast cancer models. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 58372–58385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tanaka, N.; Sakamoto, T. MT1-MMP as a Key Regulator of Metastasis. Cells 2023, 12, 2187. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12172187
Tanaka N, Sakamoto T. MT1-MMP as a Key Regulator of Metastasis. Cells. 2023; 12(17):2187. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12172187
Chicago/Turabian StyleTanaka, Noritaka, and Takeharu Sakamoto. 2023. "MT1-MMP as a Key Regulator of Metastasis" Cells 12, no. 17: 2187. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12172187
APA StyleTanaka, N., & Sakamoto, T. (2023). MT1-MMP as a Key Regulator of Metastasis. Cells, 12(17), 2187. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12172187