The Molecular Pathogenesis of Tumor-Suppressive miR-486-5p and miR-486-3p Target Genes: GINS4 Facilitates Aggressiveness in Lung Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Course of Patients with LUAD Cells
2.2. Cell Lines and Cell Culture
2.3. Construction of the miRNA Expression Signature in LUAD Based on RNA Sequencing
2.4. Identification of Oncogenic Targets Regulated by miR-486-5p and miR-486-3p in LUAD Cells
2.5. Expression Levels of Genes and Prognosis by In Silico Analysis
2.6. Transfection with siRNA and miRNA
2.7. RNA Extraction and Reverse Transcription Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
2.8. Western Blotting
2.9. Cell Proliferation and Cell Cycle Assays
2.10. Plasmid Construction and Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assays
2.11. Immunohistochemical Staining
2.12. Putative miRNA Binding to GINS4 and miRNA Expression
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
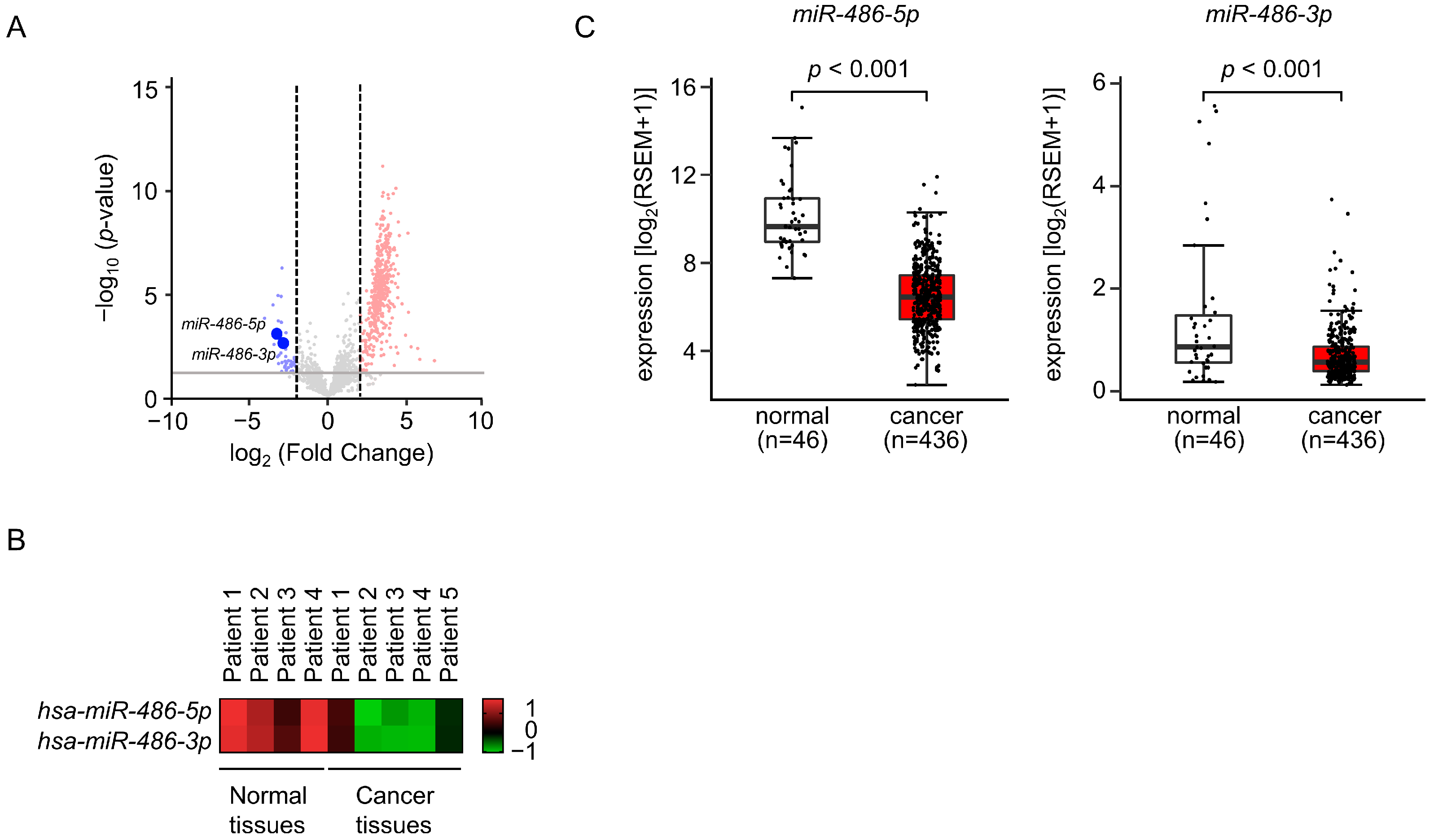
3.1. Selection of Downregulated miRNAs in LUAD Clinical Specimens by Small RNA Sequencing
3.2. Expression Levels of miR-486-5p and miR-486-3p in LUAD Specimens and Cell Lines
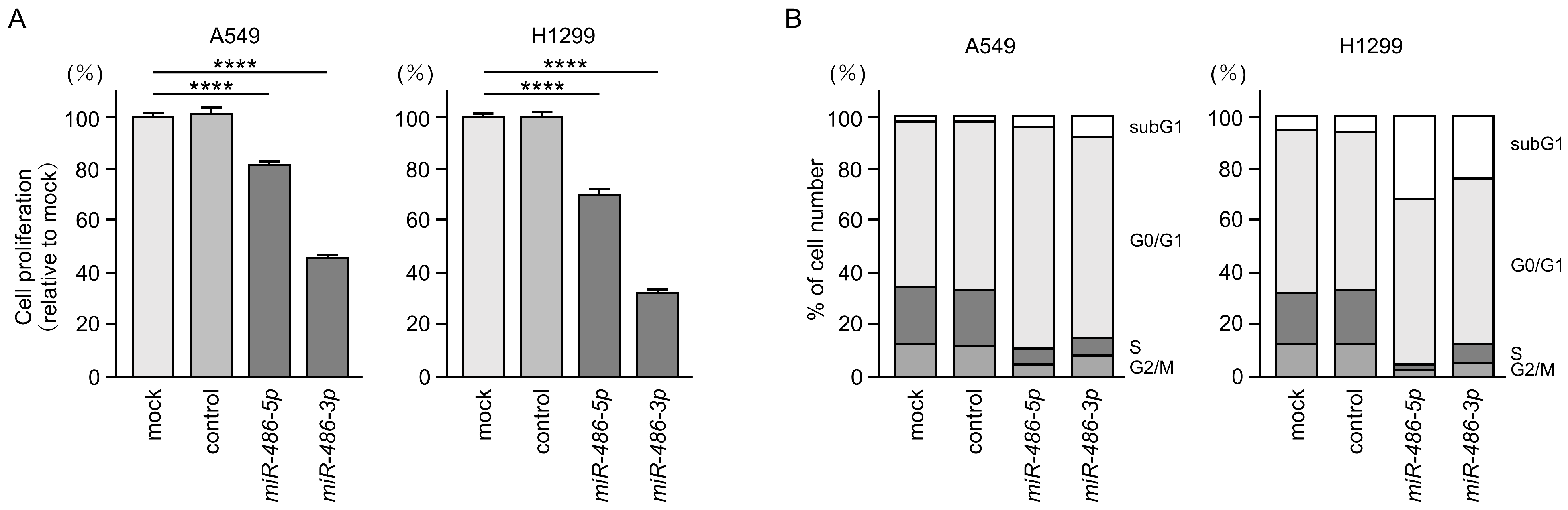
3.3. Antitumor Functions of miR-486-5p and miR-486-3p in LUAD Cells
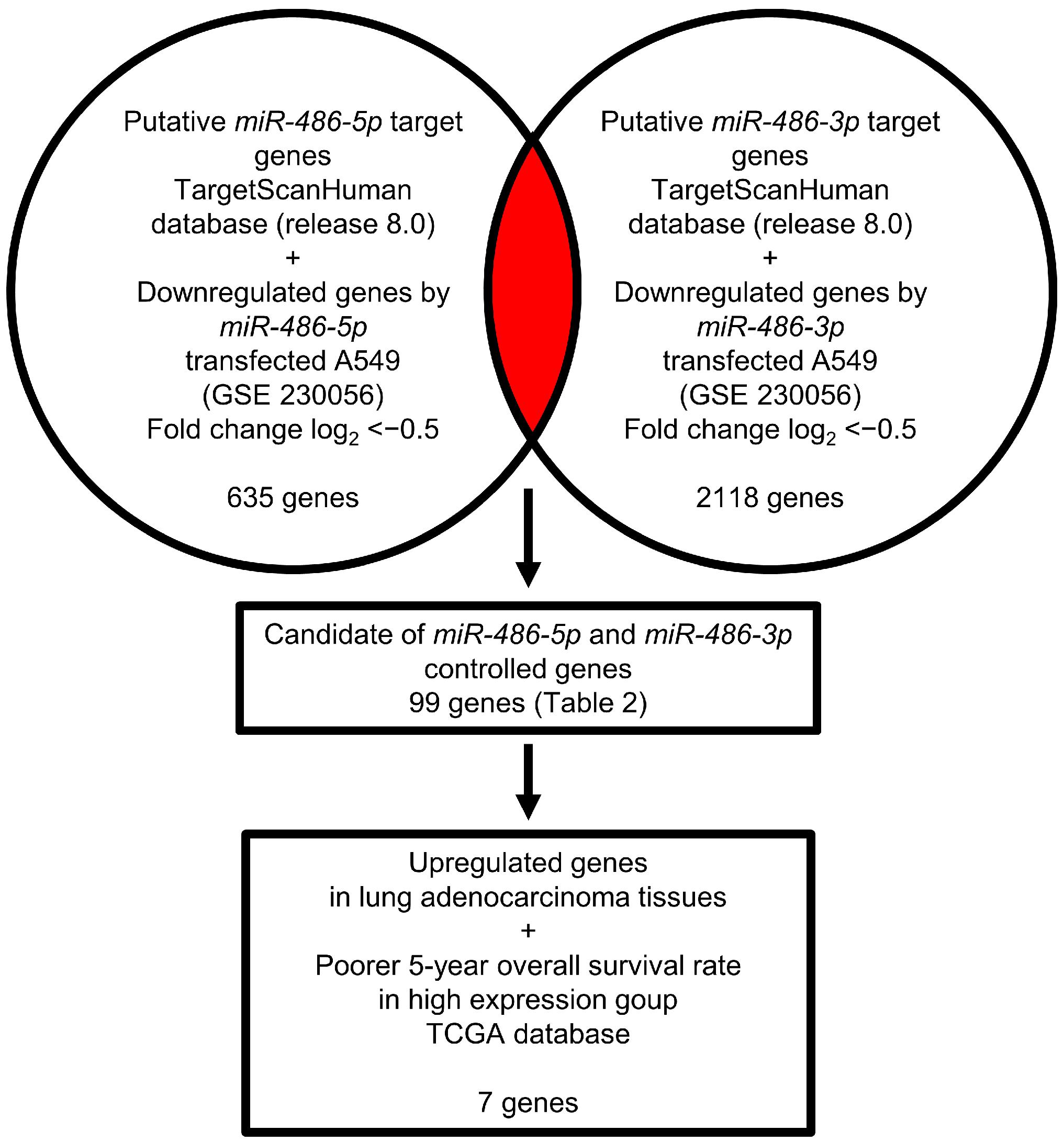
3.4. Identification of Genes Controlled by miR-486-5p and miR-486-3p in LUAD Cells
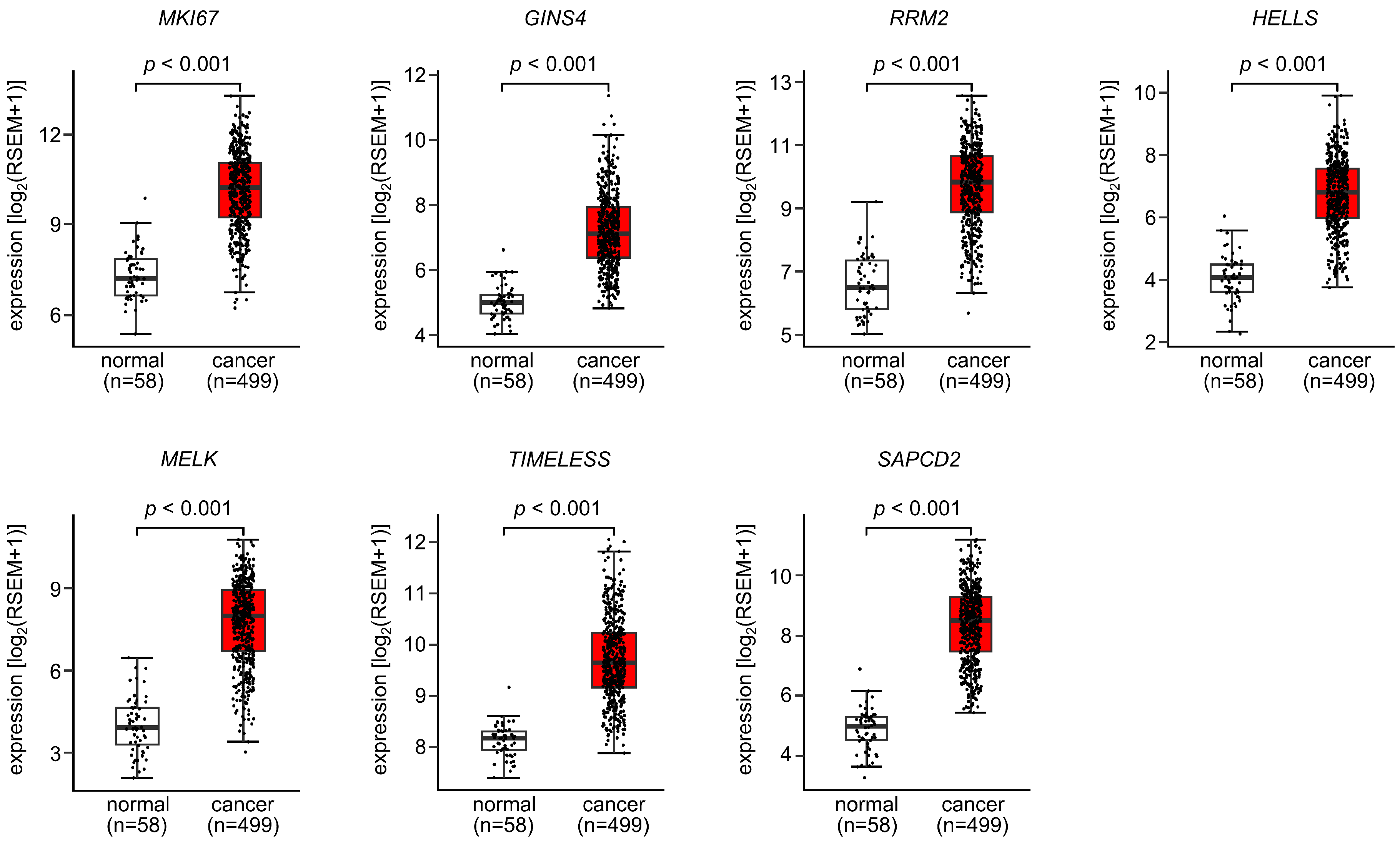
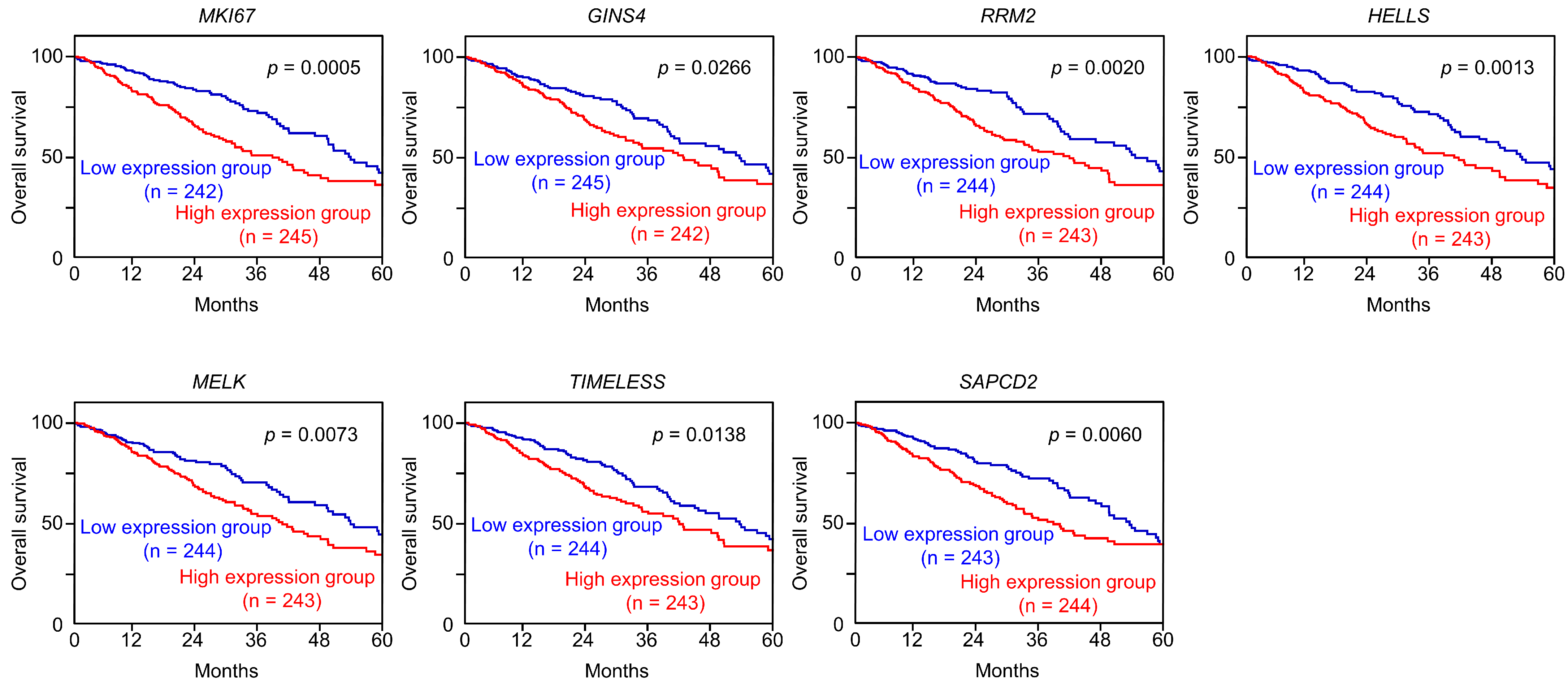
3.5. Expression and Clinical Significance of Both Strands of Pre-miR-486 Target Genes in LUAD
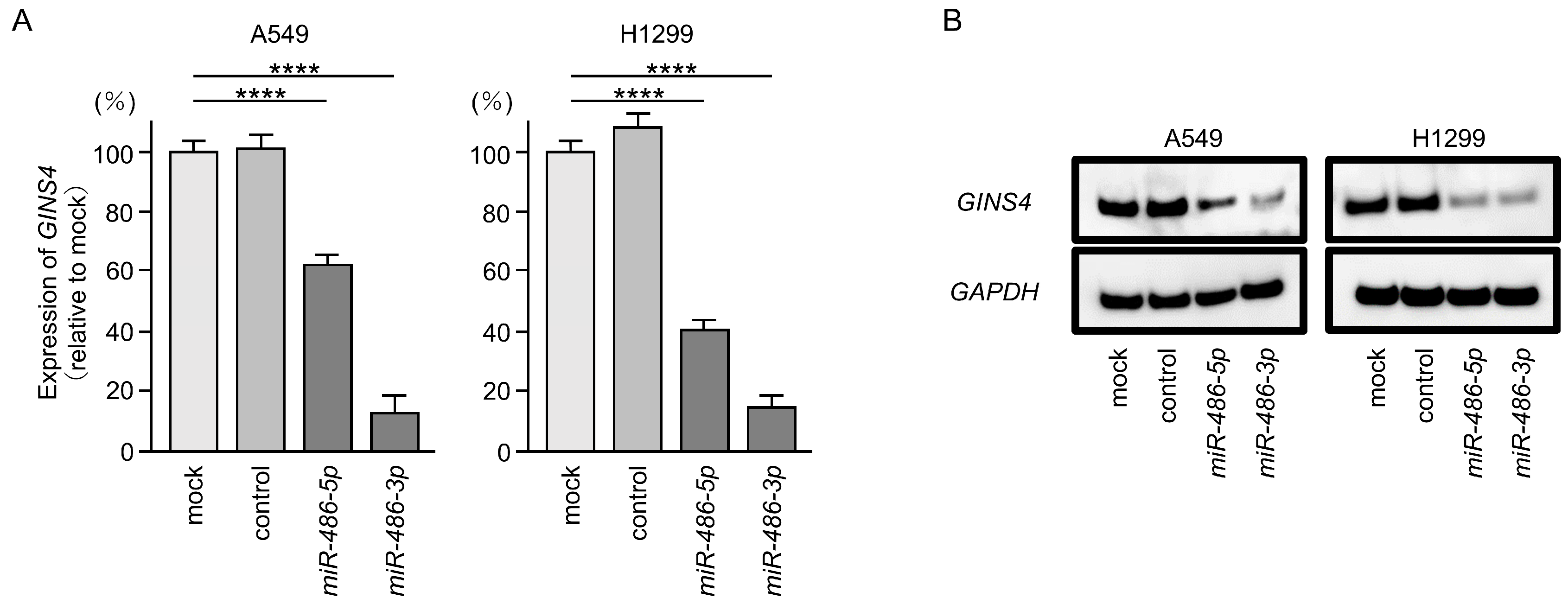
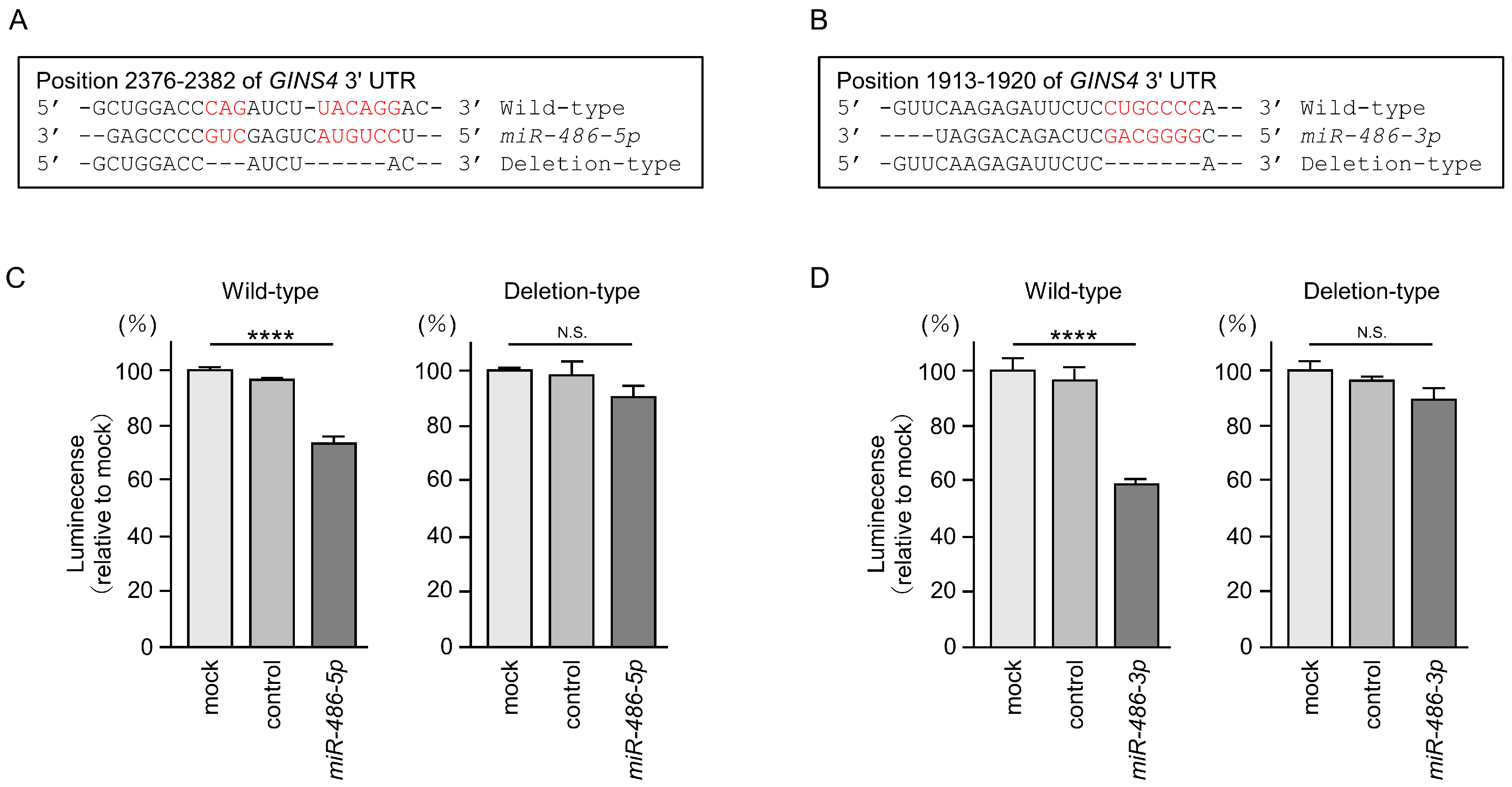
3.6. Direct Regulation of GINS4 by miR-486-5p and miR-486-3p in LUAD Cells
3.7. Functional Significance of GINS4 in LUAD Cells
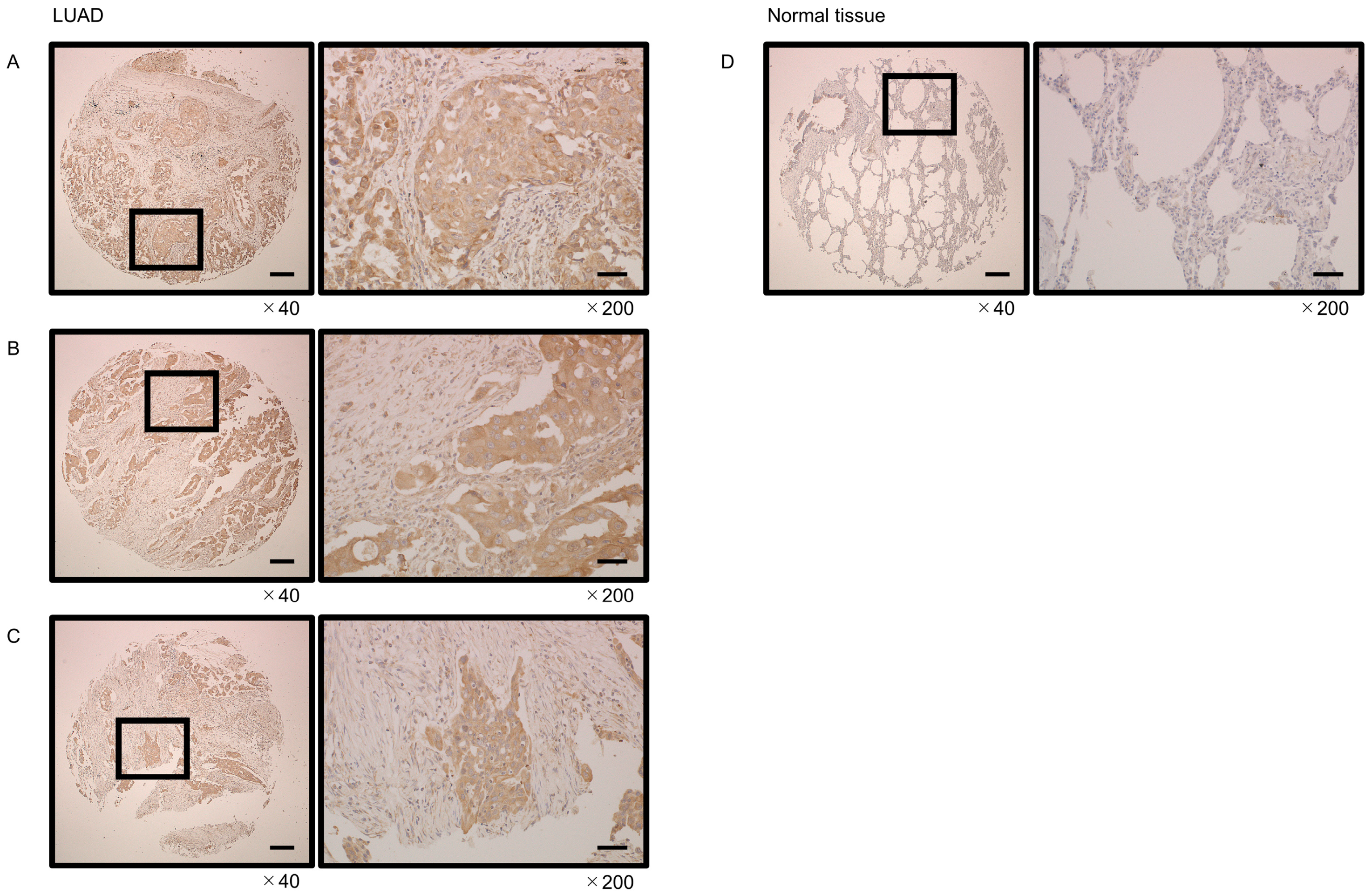
3.8. Immunostaining of GINS4 in LUAD Clinical Tissues
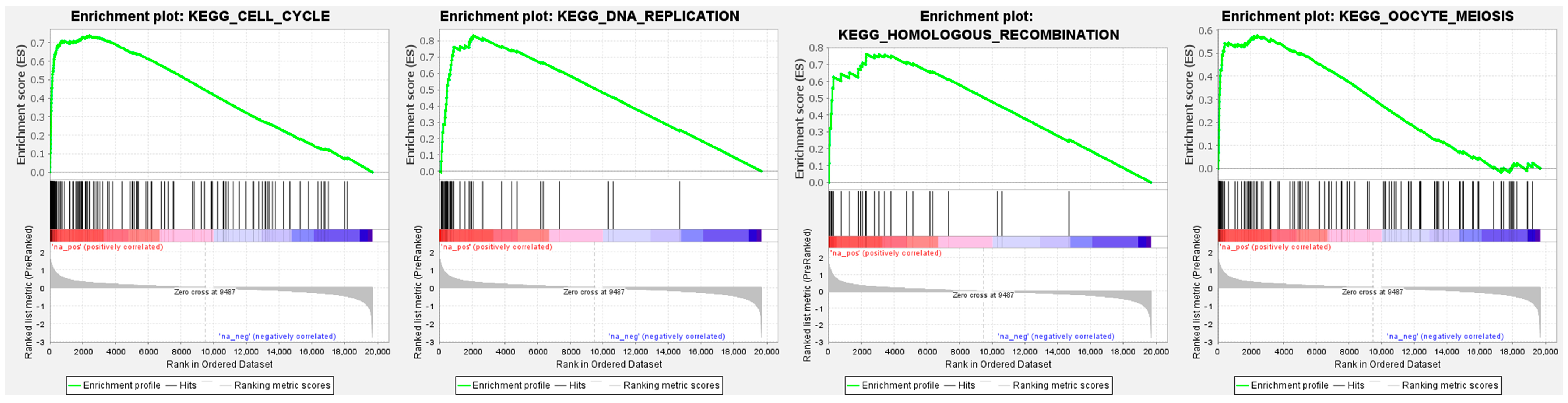
3.9. GINS4-Mediated Pathways Determined by Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schabath, M.B.; Cote, M.L. Cancer Progress and Priorities: Lung Cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2019, 28, 1563–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aokage, K.; Yoshida, J.; Hishida, T.; Tsuboi, M.; Saji, H.; Okada, M.; Suzuki, K.; Watanabe, S.; Asamura, H. Limited resection for early-stage non-small cell lung cancer as function-preserving radical surgery: A review. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 47, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirker, R. Conquering lung cancer: Current status and prospects for the future. Pulmonology 2020, 26, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, A.C.; Tan, D.S.W. Targeted Therapies for Lung Cancer Patients with Oncogenic Driver Molecular Alterations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 611–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reck, M.; Remon, J.; Hellmann, M.D. First-Line Immunotherapy for Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 586–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatica, A.; Bozzoni, I. Long non-coding RNAs: New players in cell differentiation and development. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frías-Lasserre, D.; Villagra, C.A. The Importance of ncRNAs as Epigenetic Mechanisms in Phenotypic Variation and Organic Evolution. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vienberg, S.; Geiger, J.; Madsen, S.; Dalgaard, L.T. MicroRNAs in metabolism. Acta Physiol. 2017, 219, 346–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasiadou, E.; Jacob, L.S.; Slack, F.J. Non-coding RNA networks in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.J.; Tay, Y. Noncoding RNA:RNA Regulatory Networks in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadhan, R.; Isidoro, C.; Song, Y.S.; Dhanasekaran, D.N. Signaling by LncRNAs: Structure, Cellular Homeostasis, and Disease Pathology. Cells 2022, 11, 2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smolarz, B.; Durczyński, A.; Romanowicz, H.; Szyłło, K.; Hogendorf, P. miRNAs in Cancer (Review of Literature). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussen, B.M.; Hidayat, H.J.; Salihi, A.; Sabir, D.K.; Taheri, M.; Ghafouri-Fard, S. MicroRNA: A signature for cancer progression. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 138, 111528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.L.; Tsai, Y.M.; Lien, C.T.; Kuo, P.L.; Hung, A.J. The Roles of MicroRNA in Lung Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matranga, C.; Tomari, Y.; Shin, C.; Bartel, D.P.; Zamore, P.D. Passenger-strand cleavage facilitates assembly of siRNA into Ago2-containing RNAi enzyme complexes. Cell 2005, 123, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, K.; Tanigawa, K.; Nohata, N.; Misono, S.; Okada, R.; Asai, S.; Moriya, S.; Suetsugu, T.; Inoue, H.; Seki, N. FAM64A: A Novel Oncogenic Target of Lung Adenocarcinoma Regulated by Both Strands of miR-99a (miR-99a-5p and miR-99a-3p). Cells 2020, 9, 2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, A.; Seki, N.; Mizuno, K.; Misono, S.; Yamada, Y.; Kikkawa, N.; Sanada, H.; Kumamoto, T.; Suetsugu, T.; Inoue, H. Involvement of dual-strand of the miR-144 duplex and their targets in the pathogenesis of lung squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 420–432. [Google Scholar]
- Misono, S.; Seki, N.; Mizuno, K.; Yamada, Y.; Uchida, A.; Arai, T.; Kumamoto, T.; Sanada, H.; Suetsugu, T.; Inoue, H. Dual strands of the miR-145 duplex (miR-145–5p and miR-145–3p) regulate oncogenes in lung adenocarcinoma pathogenesis. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 63, 1015–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misono, S.; Seki, N.; Mizuno, K.; Yamada, Y.; Uchida, A.; Sanada, H.; Moriya, S.; Kikkawa, N.; Kumamoto, T.; Suetsugu, T.; et al. Molecular Pathogenesis of Gene Regulation by the miR-150 Duplex: miR-150–3p Regulates TNS4 in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancers 2019, 11, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanada, H.; Seki, N.; Mizuno, K.; Misono, S.; Uchida, A.; Yamada, Y.; Moriya, S.; Kikkawa, N.; Machida, K.; Kumamoto, T.; et al. Involvement of Dual Strands of miR-143 (miR-143–5p and miR-143–3p) and Their Target Oncogenes in the Molecular Pathogenesis of Lung Adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanigawa, K.; Misono, S.; Mizuno, K.; Asai, S.; Suetsugu, T.; Uchida, A.; Kawano, M.; Inoue, H.; Seki, N. MicroRNA signature of small-cell lung cancer after treatment failure: Impact on oncogenic targets by miR-30a-3p control. Mol. Oncol. 2023, 17, 328–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misono, S.; Mizuno, K.; Suetsugu, T.; Tanigawa, K.; Nohata, N.; Uchida, A.; Sanada, H.; Okada, R.; Moriya, S.; Inoue, H.; et al. Molecular Signature of Small Cell Lung Cancer after Treatment Failure: The MCM Complex as Therapeutic Target. Cancers 2021, 13, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toda, H.; Seki, N.; Kurozumi, S.; Shinden, Y.; Yamada, Y.; Nohata, N.; Moriya, S.; Idichi, T.; Maemura, K.; Fujii, T.; et al. RNA-sequence-based microRNA expression signature in breast cancer: Tumor-suppressive miR-101–5p regulates molecular pathogenesis. Mol. Oncol. 2020, 14, 426–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, R.; Adams, C.M.; Jiang, W.; Greenawalt, E.; Eischen, C.M. Pan-cancer analysis reveals cooperativity of both strands of microRNA that regulate tumorigenesis and patient survival. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, R.; Sun, J.; Zhao, Z. microRNA regulation in cancer: One arm or two arms? Int. J. Cancer 2015, 137, 1516–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, A.E.; Lu, W.T.; Godfrey, J.D.; Antonov, A.V.; Paicu, C.; Moxon, S.; Dalmay, T.; Wilczynska, A.; Muller, P.A.; Bushell, M. The cytoskeleton adaptor protein ankyrin-1 is upregulated by p53 following DNA damage and alters cell migration. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Y.; Li, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zheng, H.; Gao, B.; Guo, X.; Li, Z.; Chen, R.; Chen, C. circNFIB1 inhibits lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis via the miR-486–5p/PIK3R1/VEGF-C axis in pancreatic cancer. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moro, M.; Fortunato, O.; Bertolini, G.; Mensah, M.; Borzi, C.; Centonze, G.; Andriani, F.; Di Paolo, D.; Perri, P.; Ponzoni, M.; et al. MiR-486–5p Targets CD133+ Lung Cancer Stem Cells through the p85/AKT Pathway. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Liu, C.; Yao, R.; Tan, Q.; Wang, Q.; Tian, H. miR-486–5p suppresses gastric cancer cell growth and migration through downregulation of fibroblast growth factor 9. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 24, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faur, C.I.; Roman, R.C.; Jurj, A.; Raduly, L.; Almășan, O.; Rotaru, H.; Chirilă, M.; Moldovan, M.A.; Hedeșiu, M.; Dinu, C. Salivary Exosomal MicroRNA-486–5p and MicroRNA-10b-5p in Oral and Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Medicina 2022, 58, 1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElKhouly, A.M.; Youness, R.A.; Gad, M.Z. MicroRNA-486–5p and microRNA-486–3p: Multifaceted pleiotropic mediators in oncological and non-oncological conditions. Noncoding RNA Res. 2020, 5, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, T.; Yang, K.; Zhang, M.; Wang, K. miR-486–5p suppresses prostate cancer metastasis by targeting Snail and regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition. OncoTargets Ther. 2016, 9, 6909–6914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.; Tian, W.; Zhang, H.; Li, W.; Ji, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y. MicroRNA-486–5p Suppresses Lung Cancer via Downregulating mTOR Signaling In Vitro and In Vivo. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 655236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.A.; Mohamed, E.I.; El-Kaream, S.A.A.; Badawi, M.I.; Darwish, S.H. Underexpression of miR-486–5p but not Overexpression of miR-155 is Associated with Lung Cancer Stages. Microrna 2018, 7, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Q.; Wu, S.; Liao, X.; Liu, C.; Chen, Y. Anesthetic propofol enhances cisplatin-sensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer cells through N6-methyladenosine-dependently regulating the miR-486–5p/RAP1-NF-κB axis. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Qi, X.; Liu, L.; Hu, X.; Liu, J.; Yang, J.; Yang, J.; Lu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, S.; et al. Emerging Epigenetic Regulation of Circular RNAs in Human Cancer. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 16, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.P.; He, Y.J.; Hou, J.C.; Chen, X.; Zhou, S.Y.; Yang, S.J.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.D.; Hu, J.H.; Zhong, S.L.; et al. The role of circRNAs in cancers. Biosci. Rep. 2017, 37, BSR20170750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Liu, X.; Wu, Y.; Lou, Y.; Li, X.; Huang, G. Circular RNA EPB41 expression predicts unfavorable prognoses in NSCLC by regulating miR-486–3p/eIF5A axis-mediated stemness. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, X.; Huang, W.; He, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, S.; Xiong, H. Circ_CSPP1 Regulates the Development of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer via the miR-486–3p/BRD9 Axis. Biochem. Genet. 2023, 61, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Xie, J.; Wang, H.; Hou, S.; Feng, J. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0011298 enhances Taxol resistance of non-small cell lung cancer by regulating miR-486–3p/CRABP2 axis. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2022, 36, e24408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, J.; Huang, G.; Yin, Z.; Cai, X.; Gong, E.; Li, Y.; Xu, C.; Ye, Z.; Cao, Z.; Cheng, W. Circular RNA FLNA acts as a sponge of miR-486–3p in promoting lung cancer progression via regulating XRCC1 and CYP1A1. Cancer Gene Ther. 2022, 29, 101–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morikawa, T.; Maeda, D.; Kume, H.; Homma, Y.; Fukayama, M. Ribonucleotide reductase M2 subunit is a novel diagnostic marker and a potential therapeutic target in bladder cancer. Histopathology 2010, 57, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aye, Y.; Li, M.; Long, M.J.; Weiss, R.S. Ribonucleotide reductase and cancer: Biological mechanisms and targeted therapies. Oncogene 2015, 34, 2011–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Xue, F.; Chen, H.; Shen, L.; Yuan, X.; Yu, Y.; Zong, Y.; Zhong, L.; Huang, F. MiR-202–3p inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma cells by targeting RRM2. Ann. Transl. Med. 2022, 10, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, K.; Tanigawa, K.; Misono, S.; Suetsugu, T.; Sanada, H.; Uchida, A.; Kawano, M.; Machida, K.; Asai, S.; Moriya, S.; et al. Regulation of Oncogenic Targets by Tumor-Suppressive miR-150–3p in Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, C.T.; Wei, L.; Tsang, F.H.; Chan, C.Y.; Xu, I.M.; Lai, R.K.; Ho, D.W.; Lee, J.M.; Wong, C.C.; Ng, I.O.; et al. HELLS Regulates Chromatin Remodeling and Epigenetic Silencing of Multiple Tumor Suppressor Genes in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology 2019, 69, 2013–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lungu, C.; Muegge, K.; Jeltsch, A.; Jurkowska, R.Z. An ATPase-deficient variant of the SNF2 family member HELLS shows altered dynamics at pericentromeric heterochromatin. J. Mol. Biol. 2015, 427, 1903–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, A.L.; Du, L. The Function and Regulation of SAPCD2 in Physiological and Oncogenic Processes. J. Cancer 2022, 13, 2374–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, D. MiR-486–5p specifically suppresses SAPCD2 expression, which attenuates the aggressive phenotypes of lung adenocarcinoma cells. Histol. Histopathol. 2022, 37, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kamada, K. The GINS complex: Structure and function. Subcell. Biochem. 2012, 62, 135–156. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Gristwood, T.; Hodgson, B.; Trinidad, J.C.; Albers, S.V.; Bell, S.D. Archaeal orthologs of Cdc45 and GINS form a stable complex that stimulates the helicase activity of MCM. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 13390–13395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usman, M.; Okla, M.K.; Asif, H.M.; AbdElgayed, G.; Muccee, F.; Ghazanfar, S.; Ahmad, M.; Iqbal, M.J.; Sahar, A.M.; Khaliq, G.; et al. A pan-cancer analysis of GINS complex subunit 4 to identify its potential role as a biomarker in multiple human cancers. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2022, 12, 986–1008. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Liu, N.; Chen, L.; Jiang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Mao, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; Lai, W.; Tang, H.; et al. LSH interacts with and stabilizes GINS4 transcript that promotes tumourigenesis in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, F.; Zhu, X.; Yi, X.; Luo, C.; Lin, K.; Zhu, J.; Hu, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, J.; Huang, C.; et al. Expression Profile of GINS Complex Predicts the Prognosis of Pancreatic Cancer Patients. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 11433–11444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Cao, Y.; Ma, J.; Luo, L.; Ma, B. Expression and prognosis analysis of GINS subunits in human breast cancer. Medicine 2021, 100, e24827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Zeng, J.; Gao, L.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, L. GINS Complex Subunit 2 Facilitates Gastric Adenocarcinoma Proliferation and Indicates Poor Prognosis. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2021, 255, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Chen, S.; Fan, H.; Ji, D.; Chen, C.; Sheng, W. GINS2 promotes EMT in pancreatic cancer via specifically stimulating ERK/MAPK signaling. Cancer Gene Ther. 2021, 28, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| MicroRNA | miRBase Accession No. | Guide or Passenger Strand | Log2 FC | p-Value | FDR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hsa-miR-517b-3p | MIMAT0002857 | Guide strand | −4.00 | <0.001 | 0.002 |
| hsa-miR-518a-3p | MIMAT0002863 | Guide strand | −3.46 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| hsa-miR-551b-5p | MIMAT0004794 | Passenger strand | −3.39 | 0.004 | 0.022 |
| hsa-miR-523-5p | MIMAT0005449 | Passenger strand | −3.18 | 0.014 | 0.071 |
| hsa-miR-4703-3p | MIMAT0019802 | Guide strand | −3.15 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| hsa-miR-6722-5p | MIMAT0025853 | Passenger strand | −3.12 | <0.001 | 0.002 |
| hsa-miR-34c-5p | MIMAT0000686 | Guide strand | −3.11 | 0.030 | 0.129 |
| hsa-miR-486-5p | MIMAT0002177 | Guide strand | −3.11 | 0.002 | 0.009 |
| hsa-miR-218-1-3p | MIMAT0004565 | Passenger strand | −3.07 | 0.012 | 0.061 |
| hsa-miR-518e-5p | MIMAT0005450 | Passenger strand | −3.01 | 0.001 | 0.008 |
| hsa-miR-34c-3p | MIMAT0004677 | Passenger strand | −2.96 | 0.010 | 0.050 |
| hsa-miR-1208 | MIMAT0005873 | Guide strand | −2.95 | <0.001 | 0.002 |
| hsa-miR-4795-3p | MIMAT0019969 | Passenger strand | −2.95 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| hsa-miR-4455 | MIMAT0018977 | Guide strand | −2.92 | <0.001 | 0.002 |
| hsa-miR-34b-3p | MIMAT0004676 | Guide strand | −2.90 | 0.027 | 0.119 |
| hsa-miR-603 | MIMAT0003271 | Guide strand | −2.90 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| hsa-miR-519a-3p | MIMAT0002869 | Guide strand | −2.90 | 0.002 | 0.012 |
| hsa-miR-486-3p | MIMAT0004762 | Passenger strand | −2.86 | 0.003 | 0.016 |
| hsa-miR-34b-5p | MIMAT0000685 | Passenger strand | −2.73 | 0.046 | 0.175 |
| hsa-miR-4532 | MIMAT0019071 | Guide strand | −2.70 | 0.024 | 0.106 |
| hsa-miR-4655-3p | MIMAT0019722 | Passenger strand | −2.70 | 0.039 | 0.157 |
| hsa-miR-4281 | MIMAT0016907 | Guide strand | −2.66 | 0.006 | 0.035 |
| hsa-miR-518f-3p | MIMAT0002842 | Guide strand | −2.66 | 0.014 | 0.068 |
| hsa-miR-6813-3p | MIMAT0027527 | Passenger strand | −2.65 | 0.001 | 0.007 |
| hsa-miR-940 | MIMAT0004983 | Guide strand | −2.63 | 0.030 | 0.127 |
| hsa-miR-371b-3p | MIMAT0019893 | Passenger strand | −2.50 | 0.047 | 0.178 |
| hsa-miR-516b-5p | MIMAT0002859 | Guide strand | −2.50 | 0.022 | 0.100 |
| hsa-miR-4483 | MIMAT0019017 | Guide strand | −2.36 | 0.034 | 0.141 |
| hsa-miR-523-3p | MIMAT0002840 | Guide strand | −2.34 | 0.023 | 0.106 |
| hsa-miR-758-5p | MIMAT0022929 | Passenger strand | −2.31 | 0.038 | 0.153 |
| hsa-miR-1258 | MIMAT0005909 | Guide strand | −2.31 | 0.040 | 0.158 |
| hsa-miR-4529-5p | MIMAT0019236 | Passenger strand | −2.22 | 0.028 | 0.120 |
| hsa-miR-518c-3p | MIMAT0002848 | Guide strand | −2.16 | 0.027 | 0.117 |
| hsa-miR-6768-5p | MIMAT0027436 | Guide strand | −2.13 | 0.016 | 0.076 |
| hsa-miR-3622a-5p | MIMAT0018003 | Guide strand | −2.12 | 0.034 | 0.141 |
| hsa-miR-144-5p | MIMAT0004600 | Passenger strand | −2.12 | 0.018 | 0.086 |
| hsa-miR-373-3p | MIMAT0000726 | Guide strand | −2.09 | 0.038 | 0.152 |
| hsa-miR-451a | MIMAT0001631 | Guide strand | −2.07 | 0.038 | 0.153 |
| hsa-miR-144-3p | MIMAT0000436 | Guide strand | −2.06 | 0.024 | 0.107 |
| hsa-miR-4723-5p | MIMAT0019838 | Guide strand | −2.05 | 0.041 | 0.161 |
| hsa-miR-5011-5p | MIMAT0021045 | Passenger strand | −2.02 | 0.025 | 0.110 |
| Gene ID | Gene Symbol | Gene Name | miR-486-5p Total Sites | miR-486-3p Total Sites | miR-486-5p Transfectant Log2 FC | miR-486-3p Transfectant Log2 FC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5141 | PDE4A | Phosphodiesterase 4A | 1 | 3 | −2.25 | −1.06 |
| 9783 | RIMS3 | Regulating synaptic membrane Exocytosis 3 | 1 | 1 | −2.22 | −0.67 |
| 79856 | SNX22 | Sorting nexin 22 | 2 | 1 | −2.15 | −2.67 |
| 4300 | MLLT3 | MLLT3 super-elongation complex subunit | 1 | 2 | −2.10 | −1.18 |
| 2012 | EMP1 | Epithelial membrane protein 1 | 2 | 1 | −2.06 | −0.90 |
| 79628 | SH3TC2 | SH3 domain and tetratricopeptide repeats 2 | 3 | 1 | −1.96 | −1.97 |
| 195828 | ZNF367 | Zinc finger protein 367 | 1 | 1 | −1.94 | −1.10 |
| 115650 | TNFRSF13C | TNF-receptor superfamily member 13C | 1 | 5 | −1.85 | −0.61 |
| 84959 | UBASH3B | Ubiquitin-associated and SH3 domain containing B | 1 | 2 | −1.62 | −2.16 |
| 246243 | RNASEH1 | Ribonuclease H1 | 1 | 1 | −1.60 | −1.21 |
| 339768 | ESPNL | Espin-like | 1 | 2 | −1.55 | −1.46 |
| 220988 | HNRNPA3 | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A3 | 1 | 2 | −1.51 | −1.20 |
| 9411 | ARHGAP29 | Rho GTPase-activating protein 29 | 2 | 1 | −1.48 | −3.37 |
| 81491 | GPR63 | G-protein-coupled receptor 63 | 2 | 2 | −1.47 | −0.82 |
| 56906 | THAP10 | THAP domain containing 10 | 1 | 1 | −1.47 | −1.63 |
| 54751 | FBLIM1 | Filamin-binding LIM protein 1 | 1 | 1 | −1.46 | −0.76 |
| 248 | ALPI | Alkaline phosphatase, intestinal | 1 | 3 | −1.40 | −1.09 |
| 122953 | JDP2 | Jun dimerization protein 2 | 2 | 3 | −1.38 | −1.73 |
| 6689 | SPIB | Spi-B transcription factor | 1 | 4 | −1.37 | −0.77 |
| 6722 | SRF | Serum response factor | 1 | 4 | −1.32 | −0.72 |
| 64710 | NUCKS1 | Nuclear casein kinase and cyclin-dependent kinase substrate 1 | 1 | 1 | −1.30 | −1.45 |
| 29920 | PYCR2 | Pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase 2 | 1 | 1 | −1.28 | −1.40 |
| 81621 | KAZALD1 | Kazal-type serine peptidase-inhibitor domain 1 | 1 | 1 | −1.27 | −1.76 |
| 7433 | VIPR1 | Vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor 1 | 1 | 2 | −1.26 | −2.74 |
| 2304 | FOXE1 | Forkhead box E1 | 1 | 1 | −1.21 | −0.68 |
| 4288 | MKI67 | Marker of proliferation Ki-67 | 2 | 1 | −1.21 | −3.01 |
| 84296 | GINS4 | GINS complex subunit 4 | 1 | 1 | −1.21 | −2.72 |
| 6241 | RRM2 | Ribonucleotide reductase regulatory subunit M2 | 1 | 1 | −1.21 | −3.92 |
| 201292 | TRIM65 | Tripartite motif containing 65 | 1 | 1 | −1.17 | −0.65 |
| 57153 | SLC44A2 | Solute carrier family 44 member 2 | 1 | 4 | −1.17 | −1.67 |
| 2649 | NR6A1 | Nuclear receptor subfamily 6 group A member 1 | 1 | 4 | −1.11 | −0.96 |
| 6720 | SREBF1 | Sterol regulatory element-binding transcription factor 1 | 1 | 1 | −1.09 | −1.68 |
| 339834 | CCDC36 | Coiled-coil domain containing 36 | 2 | 1 | −1.08 | −1.65 |
| 57506 | MAVS | Mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein | 4 | 4 | −1.07 | −0.51 |
| 85014 | TMEM141 | Transmembrane protein 141 | 1 | 2 | −1.06 | −1.54 |
| 283349 | RASSF3 | Ras association domain family member 3 | 1 | 1 | −1.04 | −1.81 |
| 160518 | DENND5B | DENN domain containing 5B | 1 | 1 | −1.04 | −0.65 |
| 92126 | DSEL | Dermatan sulfate epimerase-like | 1 | 1 | −1.03 | −0.72 |
| 3070 | HELLS | Helicase, lymphoid specific | 1 | 2 | −1.02 | −1.90 |
| 11051 | NUDT21 | Nudix hydrolase 21 | 1 | 2 | −1.01 | −1.06 |
| 345557 | PLCXD3 | Phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C X domain containing 3 | 1 | 1 | −1.00 | −2.20 |
| 11113 | CIT | Citron rho-interacting serine/threonine kinase | 1 | 1 | −1.00 | −2.89 |
| 145508 | CEP128 | Centrosomal protein 128 | 1 | 1 | −0.99 | −2.54 |
| 3707 | ITPKB | Inositol-trisphosphate 3-kinase B | 1 | 2 | −0.97 | −1.07 |
| 59269 | HIVEP3 | HIVEP zinc finger 3 | 1 | 3 | −0.97 | −1.29 |
| 81563 | C1orf21 | Chromosome 1 open reading frame 21 | 1 | 1 | −0.94 | −0.66 |
| 84515 | MCM8 | Minichromosome maintenance 8 homologous recombination repair factor | 1 | 1 | −0.94 | −1.80 |
| 93129 | ORAI3 | ORAI calcium release-activated calcium modulator 3 | 1 | 1 | −0.94 | −0.62 |
| 119 | ADD2 | Adducin 2 | 2 | 1 | −0.92 | −4.18 |
| 5939 | RBMS2 | RNA binding motif single-stranded interacting protein 2 | 1 | 2 | −0.90 | −0.51 |
| 55512 | SMPD3 | Sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase 3 | 1 | 3 | −0.89 | −2.43 |
| 9833 | MELK | Maternal embryonic leucine zipper kinase | 1 | 1 | −0.86 | −2.20 |
| 30815 | ST6GALNAC6 | ST6 N-acetylgalactosaminide alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase 6 | 1 | 2 | −0.85 | −0.73 |
| 64077 | LHPP | Phospholysine phosphohistidine inorganic pyrophosphate phosphatase | 2 | 3 | −0.84 | −1.38 |
| 6526 | SLC5A3 | Solute carrier family 5 member 3 | 2 | 1 | −0.83 | −0.78 |
| 10272 | FSTL3 | Follistatin-like 3 | 1 | 2 | −0.80 | −0.71 |
| 10613 | ERLIN1 | ER lipid raft-associated 1 | 1 | 2 | −0.80 | −1.48 |
| 651746 | ANKRD33B | Ankyrin repeat domain 33B | 1 | 3 | −0.79 | −1.28 |
| 26468 | LHX6 | LIM homeobox 6 | 1 | 1 | −0.78 | −1.80 |
| 196743 | PAOX | Polyamine oxidase | 1 | 3 | −0.77 | −1.82 |
| 8624 | PSMG1 | Proteasome assembly chaperone 1 | 2 | 2 | −0.76 | −1.27 |
| 57546 | PDP2 | Pyruvate dehyrogenase phosphatase catalytic subunit 2 | 1 | 3 | −0.75 | −1.31 |
| 10592 | SMC2 | Structural maintenance of chromosomes 2 | 2 | 1 | −0.74 | −1.92 |
| 54475 | NLE1 | Notchless homolog 1 | 1 | 2 | −0.73 | −1.95 |
| 8573 | CASK | Calcium/calmodulin-dependent serine protein kinase | 2 | 1 | −0.72 | −0.51 |
| 153443 | SRFBP1 | Serum response factor-binding protein 1 | 1 | 1 | −0.72 | −0.65 |
| 10217 | CTDSPL | CTD small-phosphatase-like | 1 | 1 | −0.72 | −0.76 |
| 81029 | WNT5B | Wnt family member 5B | 1 | 1 | −0.70 | −2.63 |
| 60312 | AFAP1 | Actin filament-associated protein 1 | 1 | 3 | −0.70 | −1.66 |
| 23216 | TBC1D1 | TBC1 domain family member 1 | 1 | 1 | −0.68 | −1.20 |
| 7301 | TYRO3 | TYRO3 protein tyrosine kinase | 1 | 1 | −0.67 | −1.52 |
| 2000 | ELF4 | E74-like ETS transcription factor 4 | 1 | 2 | −0.67 | −1.49 |
| 5064 | PALM | Paralemmin | 1 | 3 | −0.67 | −1.87 |
| 79622 | SNRNP25 | Small nuclear ribonucleoprotein U11/U12 subunit 25 | 1 | 1 | −0.66 | −0.71 |
| 64399 | HHIP | Hedgehog interacting protein | 1 | 2 | −0.65 | −0.65 |
| 23075 | SWAP70 | Switching B-cell complex subunit SWAP70 | 1 | 1 | −0.64 | −0.88 |
| 118980 | SFXN2 | Aideroflexin 2 | 1 | 1 | −0.64 | −2.07 |
| 4087 | SMAD2 | SMAD family member 2 | 1 | 1 | −0.64 | −0.86 |
| 317762 | CCDC85C | Coiled-coil domain containing 85C | 1 | 1 | −0.63 | −2.02 |
| 84440 | RAB11FIP4 | RAB11 family interacting protein 4 | 1 | 8 | −0.60 | −0.73 |
| 131566 | DCBLD2 | Discoidin, CUB and LCCL domain containing 2 | 1 | 1 | −0.60 | −2.78 |
| 4771 | NF2 | Neurofibromin 2 | 1 | 1 | −0.59 | −1.88 |
| 84083 | ZRANB3 | Zinc finger RANBP2-type containing 3 | 2 | 1 | −0.59 | −1.62 |
| 8914 | TIMELESS | Timeless circadian regulator | 1 | 1 | −0.58 | −1.65 |
| 8125 | ANP32A | Acidic nuclear phosphoprotein 32 family member A | 1 | 2 | −0.57 | −1.57 |
| 25937 | WWTR1 | WW domain containing transcription regulator 1 | 2 | 2 | −0.57 | −1.46 |
| 255104 | TMCO4 | Transmembrane and coiled-coil domains 4 | 1 | 1 | −0.56 | −1.09 |
| 51308 | REEP2 | Receptor accessory protein 2 | 1 | 2 | −0.56 | −1.45 |
| 84908 | FAM136A | Family with sequence similarity 136 member A | 1 | 1 | −0.56 | −0.82 |
| 25961 | NUDT13 | Nudix hydrolase 13 | 1 | 1 | −0.55 | −1.49 |
| 81839 | VANGL1 | VANGL planar cell polarity protein 1 | 2 | 2 | −0.55 | −0.78 |
| 54820 | NDE1 | NudE neurodevelopment protein 1 | 1 | 1 | −0.55 | −1.40 |
| 117584 | RFFL | Ring finger and FYVE-like domain containing E3 ubiquitin protein ligase | 1 | 1 | −0.54 | −0.73 |
| 6839 | SUV39H1 | Suppressor of variegation 3–9 homolog 1 | 1 | 3 | −0.53 | −3.23 |
| 154810 | AMOTL1 | Angiomotin-like 1 | 1 | 2 | −0.51 | −1.09 |
| 79096 | C11orf49 | Chromosome 11 open reading frame 49 | 1 | 2 | −0.51 | −1.84 |
| 89958 | SAPCD2 | Suppressor APC domain containing 2 | 1 | 4 | −0.51 | −1.98 |
| 9801 | MRPL19 | Mitochondrial ribosomal protein L19 | 1 | 2 | −0.51 | −0.78 |
| 84948 | TIGD5 | Tigger transposable element-derived 5 | 1 | 1 | −0.50 | −0.91 |
| Pathway | Enrichment Score | Normalized Enrichment Score | p-Value | FDR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG_CELL_CYCLE | 0.74 | 2.91 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| KEGG_DNA_REPLICATION | 0.83 | 2.61 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| KEGG_HOMOLOGOUS_RECOMBINATION | 0.76 | 2.24 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| KEGG_MISMATCH_REPAIR | 0.77 | 2.22 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| KEGG_OOCYTE_MEIOSIS | 0.58 | 2.20 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| KEGG_SPLICEOSOME | 0.56 | 2.17 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| KEGG_PROTEASOME | 0.61 | 2.02 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| KEGG_P53_SIGNALING_PATHWAY | 0.53 | 1.92 | <0.001 | 0.001 |
| KEGG_NUCLEOTIDE_EXCISION_REPAIR | 0.58 | 1.88 | <0.001 | 0.002 |
| KEGG_BASAL_TRANSCRIPTION_FACTORS | 0.59 | 1.86 | <0.001 | 0.002 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tomioka, Y.; Suetsugu, T.; Seki, N.; Tanigawa, K.; Hagihara, Y.; Shinmura, M.; Asai, S.; Kikkawa, N.; Inoue, H.; Mizuno, K. The Molecular Pathogenesis of Tumor-Suppressive miR-486-5p and miR-486-3p Target Genes: GINS4 Facilitates Aggressiveness in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cells 2023, 12, 1885. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12141885
Tomioka Y, Suetsugu T, Seki N, Tanigawa K, Hagihara Y, Shinmura M, Asai S, Kikkawa N, Inoue H, Mizuno K. The Molecular Pathogenesis of Tumor-Suppressive miR-486-5p and miR-486-3p Target Genes: GINS4 Facilitates Aggressiveness in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cells. 2023; 12(14):1885. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12141885
Chicago/Turabian StyleTomioka, Yuya, Takayuki Suetsugu, Naohiko Seki, Kengo Tanigawa, Yoko Hagihara, Masahiro Shinmura, Shunichi Asai, Naoko Kikkawa, Hiromasa Inoue, and Keiko Mizuno. 2023. "The Molecular Pathogenesis of Tumor-Suppressive miR-486-5p and miR-486-3p Target Genes: GINS4 Facilitates Aggressiveness in Lung Adenocarcinoma" Cells 12, no. 14: 1885. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12141885
APA StyleTomioka, Y., Suetsugu, T., Seki, N., Tanigawa, K., Hagihara, Y., Shinmura, M., Asai, S., Kikkawa, N., Inoue, H., & Mizuno, K. (2023). The Molecular Pathogenesis of Tumor-Suppressive miR-486-5p and miR-486-3p Target Genes: GINS4 Facilitates Aggressiveness in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cells, 12(14), 1885. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12141885







