Mechanisms of Atrial Fibrillation in Obstructive Sleep Apnoea
Abstract
1. Clinical Associations between AF and OSA, and Current Treatment Strategies
1.1. OSA Predisposes to AF
1.2. Clinical Management of AF in Patients with OSA
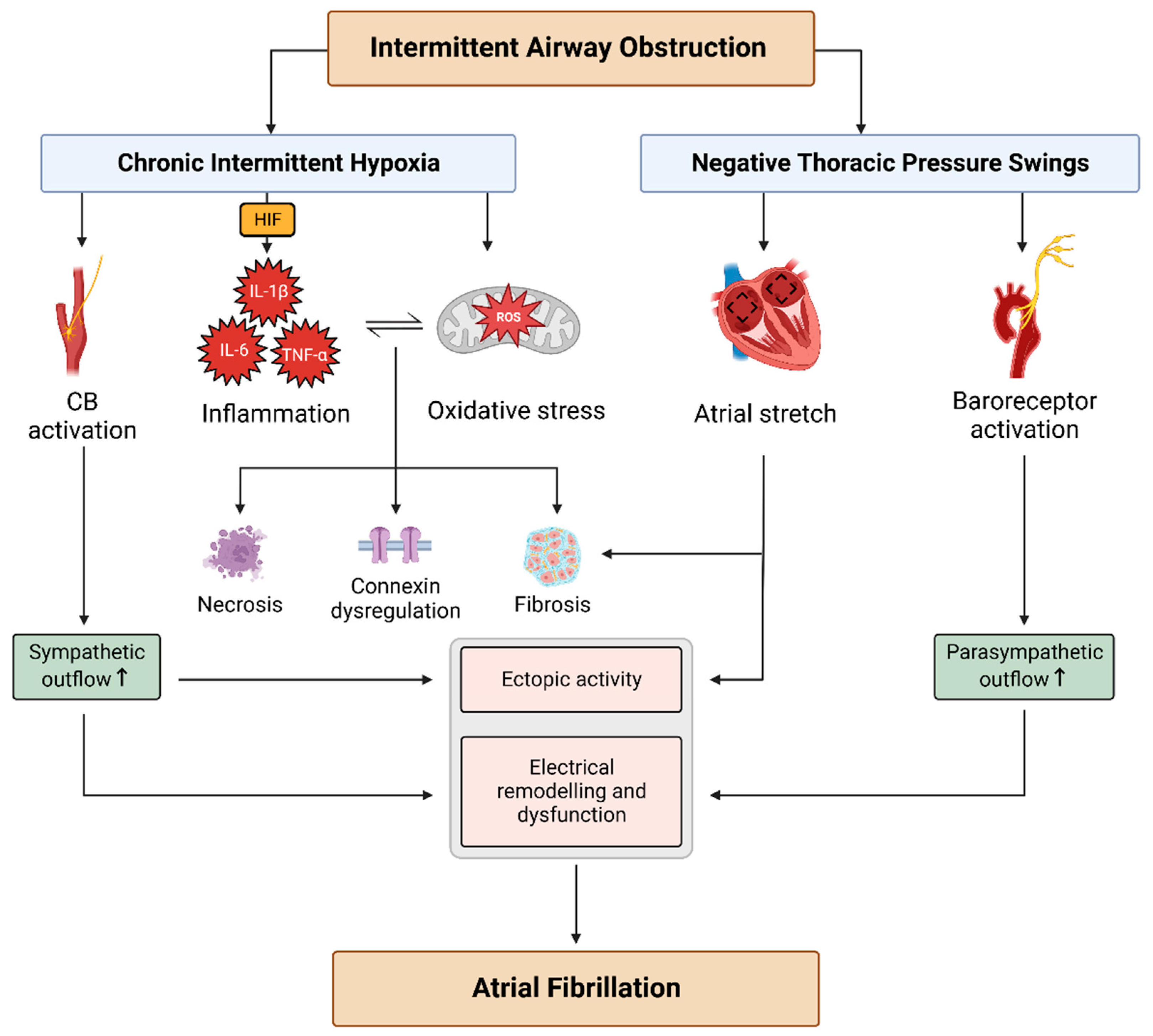
2. Arrhythmogenic Mechanisms in OSA
2.1. Autonomic Imbalance
2.2. NTP Swings
2.3. CIH
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lippi, G.; Sanchis-Gomar, F.; Cervellin, G. Global epidemiology of atrial fibrillation: An increasing epidemic and public health challenge. Int. J. Stroke 2021, 16, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hindricks, G.; Potpara, T.; Dagres, N.; Arbelo, E.; Bax, J.J.; Blomström-Lundqvist, C.; Boriani, G.; Castella, M.; Dan, G.; Dilaveris, P.; et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS): The Task Force for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) of the ESC. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 373–498. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yeghiazarians, Y.; Jneid, H.; Tietjens, J.; Redline, S.; Brown, D.; El-Sherif, N.; Mehra, R.; Bozkurt, B.; Ndumele, C.E.; Somers, V. Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Cardiovascular Disease: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2021, 144, e56–e67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapur, V.; Auckley, D.; Chowdhuri, S.; Kuhlmann, D.; Mehra, R.; Ramar, K.; Harrod, C. Clinical Practice Guideline for Diagnostic Testing for Adult Obstructive Sleep Apnea: An American Academy of Sleep Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Sleep. Med. 2017, 13, 479–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linz, D.; McEvoy, R.D.; Cowie, M.R.; Somers, V.K.; Nattel, S.; Lévy, P.; Kalman, J.; Sanders, P. Associations of Obstructive Sleep Apnea with Atrial Fibrillation and Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Treatment: A Review. JAMA Cardiol. 2018, 3, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moula, A.I.; Parrini, I.; Tetta, C.; Lucà, F.; Parise, G.; Rao, C.M.; Mauro, E.; Parise, O.; Matteucci, F.; Gulizia, M.M.; et al. Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Atrial Fibrillation. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gami, A.S.; Pressman, G.; Caples, S.M.; Kanagala, R.; Gard, J.J.; Davison, D.E.; Maloud, J.; Ammash, N.; Friedman, P.; Somers, V. Association of atrial fibrillation and obstructive sleep apnea. Circulation 2004, 110, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Cai, X.; Yan, H.; Pan, Y. Causal Effect of Obstructive Sleep Apnea on Atrial Fibrillation: A Mendelian Randomization Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 16, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadby, G.; McArdle, N.; Briffa, T.; Hillman, D.R.; Simpson, L.; Knuiman, M.; Hung, J. Severity of OSA is an independent predictor of incident atrial fibrillation hospitalization in a large sleep-clinic cohort. Chest 2015, 148, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmqvist, F.; Guan, N.; Zhu, Z.; Kowey, P.R.; Allen, L.A.; Fonarow, G.C.; Hylek, E.; Mahaffey, K.; Freeman, J.; Chang, P.; et al. Impact of obstructive sleep apnea and continuous positive airway pressure therapy on outcomes in patients with atrial fibrillation—Results from the Outcomes Registry for Better Informed Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation (ORBIT-AF). Am. Heart J. 2015, 169, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalgaard, F.; North, R.; Pieper, K.; Fonarow, G.C.; Kowey, P.R.; Gersh, B.J.; Mahaffey, K.; Pokorney, S.; Steinberg, B.; Naccarrelli, G.; et al. Risk of major cardiovascular and neurologic events with obstructive sleep apnea among patients with atrial fibrillation. Am. Heart J. 2020, 223, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, F.; Raza, A.; Guo, J. Treating obstructive sleep apnea with continuous positive airway pressure reduces risk of recurrent atrial fibrillation after catheter ablation: A meta-analysis. Sleep Med. 2018, 46, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, C.Y.; Liu, T.; Shehata, M.; Stevens, S.; Chugh, S.S.; Wang, X. Meta-analysis of obstructive sleep apnea as predictor of atrial fibrillation recurrence after catheter ablation. Am. J. Cardiol. 2011, 108, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Yan, M.; Yuan, J.; Wang, Y.; Qiao, S. Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Treatment Decreases the Risk of Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea after Radiofrequency Ablation. Int. Heart J. 2022, 63, 716–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanagala, R.; Murali, N.S.; Friedman, P.A.; Ammash, N.M.; Gersh, B.J.; Ballman, K.V.; Shamsuzzaman, A.; Somers, V. Obstructive sleep apnea and the recurrence of atrial fibrillation. Circulation 2003, 107, 2589–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, S.B.; Upender, R.; Walters, A.S.; Goodpaster, R.L.; Stanley, J.J.; Wang, L.; Chandrasekhar, R. Effective Apnea-Hypopnea Index (“Effective AHI”): A New Measure of Effectiveness for Positive Airway Pressure Therapy. Sleep 2016, 39, 1961–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEvoy, R.D.; Antic, N.A.; Heeley, E.; Luo, Y.; Ou, Q.; Zhang, X.; Mediano, O.; Chen, R.; Drager, L.; Liu, Z.; et al. CPAP for Prevention of Cardiovascular Events in Obstructive Sleep Apnea. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 919–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, H.; Takahashi, M.; Yaegashi, H.; Eda, S.; Tsunemoto, H.; Kamikozawa, M.; Koyama, J.; Yamazaki, K.; Ikeda, U. Efficacy of continuous positive airway pressure on arrhythmias in obstructive sleep apnea patients. Heart Vessel. 2010, 25, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, W.T.; Nasir, U.B.; Alqalyoobi, S.; O’Neal, W.T.; Mawri, S.; Sabbagh, S.; Soliman, E.; Al-Mallah, M. Meta-Analysis of Continuous Positive Airway Pressure as a Therapy of Atrial Fibrillation in Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Am. J. Cardiol. 2015, 116, 1767–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, X.; Xu, X.; Dai, J.; Chen, C.; Ma, L.; Li, J.; Mao, W.; Zhu, M. Effects of continuous positive airway pressure treatment in obstructive sleep apnea patients with atrial fibrillation: A meta-analysis. Medicine 2021, 100, e25438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, D.; Mohanty, P.; Di Biase, L.; Shaheen, M.; Lewis, W.; Quan, K.; Cummings, J.; Wang, P.; Al-Ahmad, A.; Venkatraman, P.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Pulmonary Vein Antral Isolation in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2010, 3, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anter, E.; Di Biase, L.; Contreras-Valdes, F.; Gianni, C.; Mohanty, S.; Tschabrunn, C. Atrial Substrate and Triggers of Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2017, 10, e005407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalliah, C.; Wong, G.; Lee, G.; Voskoboinik, A.; Kee, K.; Goldin, J.; Watts, T.; Linz, D.; Wirth, D.; Parameswaran, R.; et al. Sleep apnoea has a dose-dependent effect on atrial remodelling in paroxysmal but not persistent atrial fibrillation: A high-density mapping study. Europace 2021, 23, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalliah, C.; Wong, G.; Lee, G.; Voskoboinik, A.; Kee, K.; Goldin, J.; Watts, T.; Linz, D.; Parameswaran, R.; Sugumar, H.; et al. Impact of CPAP on the Atrial Fibrillation Substrate in Obstructive Sleep Apnea. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. EP 2022, 8, 869–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Ge, X.; Guo, L.; Wang, Y.; Guo, W.; Jiang, C.; Ma, C. Efficacy of catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea with and without continuous positive airway pressure treatment: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Europace 2014, 16, 1309–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchhof, P.; Camm, A.J.; Goette, A.; Brandes, A.; Eckardt, L.; Elvan, A.; Fetsch, T.; van Gelder, I.; Haase, D.; Haegli, L.; et al. Early Rhythm-Control Therapy in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1305–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirchhof, P.; Benussi, S.; Kotecha, D.; Ahlsson, A.; Atar, D.; Casadei, B.; Castella, M.; Diener, H.; Heidbuchel, H.; Hendricks, J.; et al. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with EACTS. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 2893–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nattel, S.; Heijman, J.; Zhou, L.; Dobrev, D. Molecular Basis of Atrial Fibrillation Pathophysiology and Therapy. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 51–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syeda, F.; Holmes, A.; Yu, T.; Tull, S.; Kuhlmann, S.; Pavlovic, D.; Betney, D.; Riley, G.; Kucera, J.; Jousset, F.; et al. PITX2 Modulates Atrial Membrane Potential and the Antiarrhythmic Effects of Sodium-Channel Blockers. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 1881–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, A.; Saxena, P.; Kabir, S.; O’Shea, C.; Kuhlmann, S.; Gupta, S.; Fobian, D.; Apicella, C.; O’Reilly, M.; Syeda, F.; et al. Atrial resting membrane potential confers sodium current sensitivity to propafenone, flecainide and dronedarone. Heart Rhythm. 2021, 18, 1212–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monahan, K.; Brewster, J.; Wang, L.; Parvez, B.; Goyal, S.; Roden, D.; Darbar, D. Relation of the severity of obstructive sleep apnea in response to anti-arrhythmic drugs in patients with atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter. Am. J. Cardiol. 2012, 110, 369–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, S.K.; Wang, L.; Upender, R.; Darbar, D.; Monahan, K. Severity of obstructive sleep apnea influences the effect of genotype on response to anti-arrhythmic drug therapy for atrial fibrillation. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2014, 10, 503–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardi, C.; Faini, A.; Mariani, D.; Gironi, F.; Castiglioni, P.; Parati, G. Nocturnal Arrhythmias and Heart-Rate Swings in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome Treated with Beta Blockers. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e015926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowie, M.; Linz, D.; Redline, S.; Somers, V.; Simonds, A. Sleep Disordered Breathing and Cardiovascular Disease: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 78, 608–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ucak, S.; Dissanayake, H.; Sutherland, K.; de Chazal, P.; Cistulli, P. Heart rate variability and obstructive sleep apnea: Current perspectives and novel technologies. J. Sleep Res. 2021, 30, e13274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, M.; Gervès-Pinquié, C.; Feuilloy, M.; Le Vaillant, M.; Trzepizur, W.; Meslier, N.; Paris, A.; Pigeanne, T.; Racineux, J.; Balusson, F.; et al. Association of Nocturnal Hypoxemia and Pulse Rate Variability with Incident Atrial Fibrillation in Patients Investigated for Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2021, 18, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.J. Vagal cardiac efferent innervation in F344 rats: Effects of chronic intermittent hypoxia. Auton. Neurosci. 2017, 203, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, H.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, S. Cardiac Sympathetic Denervation Suppresses Atrial Fibrillation and Blood Pressure in a Chronic Intermittent Hypoxia Rat Model of Obstructive Sleep Apnea. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e010254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Xu, W.; Yun, F.; Zhao, H.; Li, W.; Gong, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Yan, S.; Zhang, S.; Ding, X.; et al. Chronic obstructive sleep apnea causes atrial remodeling in canines: Mechanisms and implications. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2014, 109, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Yan, S.; Wang, X.; Zhao, S.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Lu, S.; Dong, X.; Zhao, J.; Yu, S.; et al. Metoprolol prevents chronic obstructive sleep apnea-induced atrial fibrillation by inhibiting structural, sympathetic nervous and metabolic remodeling of the atria. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deneke, T.; Chaar, H.; de Groot, J.; Wilde, A.; Lawo, T.; Mundig, J.; Bösche, L.; Mügge, A.; Grewe, P. Shift in the pattern of autonomic atrial innervation in subjects with persistent atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm. 2011, 8, 1357–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gould, P.; Yii, M.; McLean, C.; Finch, S.; Marshall, T.; Lambert, G.; Kaye, D. Evidence for increased atrial sympathetic innervation in persistent human atrial fibrillation. Pacin. Clin. Electrophysiol. 2006, 29, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linz, D.; Hohl, M.; Ukena, C.; Mahfoud, F.; Wirth, K.; Neuberger, H.R.; Böhm, M. Obstructive respiratory events and premature atrial contractions after cardioversion. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 45, 1332–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bober, S.L.; Ciriello, J.; Jones, D.L. Atrial arrhythmias and autonomic dysfunction in rats exposed to chronic intermittent hypoxia. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2018, 314, H1160–H1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, S.; Yang, Y.; Li, R.; Yin, L.; Zhang, K.; Cheng, L.; Xu, X.; Wang, W.; Zhao, Z.; Li, G. The Potential Effects of Aliskiren on Atrial Remodeling Induced by Chronic Intermittent Hypoxia in Rats. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2020, 14, 3755–3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ma, C.; Li, R.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, K.; Cheng, L.; Yuan, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; et al. Improving effects of eplerenone on atrial remodeling induced by chronic intermittent hypoxia in rats. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2022, 60, 107432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Ma, Z.; Song, C.; Duan, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, G. Role of ion channels in chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced atrial remodeling in rats. Life Sci. 2020, 254, 117797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, A.O. Cardiac ion channels. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2009, 2, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, R.M.; Colecraft, H.M. L-type calcium channel targeting and local signalling in cardiac myocytes. Cardiovasc. Res. 2013, 98, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiferaw, Y.; Aistrup, G.; Wasserstrom, J. Intracellular Ca2+ waves, afterdepolarizations, and triggered arrhythmias. Cardiovasc. Res. 2012, 95, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yan, S.; Zhao, J.; Ding, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, D.; Liu, L.; Peng, W.; Li, H.; Wang, D.; et al. Metoprolol Inhibits Cardiac Apoptosis and Fibrosis in a Canine Model of Chronic Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 36, 1131–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, J.; López, J.M. Understanding MAPK Signaling Pathways in Apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLarty, J.L.; Meléndez, G.C.; Brower, G.L.; Janicki, J.S.; Levick, S.P. Tryptase/Protease-activated receptor 2 interactions induce seletive mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling and collagen synthesis by cardiac fibroblasts. Hypertension 2011, 58, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Ma, Z.; Wang, W.; Liu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, M.; Li, G. Beneficial effects of tolvaptan on atrial remodeling induced by chronic intermittent hypoxia in rats. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2018, 36, e12466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, K.; Li, X.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, M.; Suo, Y.; Liang, X.; Tse, G.; Goudis, C.; et al. Doxycycline attenuates chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced atrial fibrosis in rats. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2018, 36, e12321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Rio, R.; Andrade, D.C.; Lucero, C.; Arias, P.; Iturriaga, R. Carotid Body Ablation Abrogates Hypertension and Autonomic Alterations Induced by Intermittent Hypoxia in Rats. Hypertension 2016, 68, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linz, D.; Hohl, M.; Nickel, A.; Mahfoud, F.; Wagner, M.; Ewen, S.; Schotten, U.; Maack, C.; Wirth, K.; Böhm, M. Effect of renal denervation on neurohumoral activation triggering atrial fibrillation in obstructive sleep apnea. Hypertension 2013, 62, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarenbach, C.F.; Camen, G.; Sievi, N.A.; Wyss, C.; Stradling, J.R.; Kohler, M. Effect of simulated obstructive hypopnea and apnea on thoracic aortic wall transmural pressures. J. Appl. Physiol. 2013, 115, 613–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, Y.K.; Shi, Y.; Benito, B.; Gillis, M.A.; Mizuno, K.; Tardif, J.C.; Nattel, S. Determinants of atrial fibrillation in an animal model of obesity and acute obstructive sleep apnea. Heart Rhythm. 2012, 9, 1409–1416.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linz, D.; Schotten, U.; Neuberger, H.R.; Böhm, M.; Wirth, K. Negative tracheal pressure during obstructive respiratory events promotes atrial fibrillation by vagal activation. Heart Rhythm. 2011, 8, 1436–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linz, D.; Hohl, M.; Khoshkish, S.; Mahfoud, F.; Ukena, C.; Neuberger, H.R.; Wirth, K.; Böhm, M. Low-Level But not High-Level Baroreceptor Stimulation Inhibits Atrial Fibrillation in a Pig Model of Sleep Apnea. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2016, 27, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Xiaokereti, J.; Meng, Q.; Cao, G.; Sun, H.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, L.; Tang, B. Low-Level Vagus Nerve Stimulation Reverses Obstructive Sleep Apnea-Related Atrial Fibrillation by Ameliorating Sympathetic Hyperactivity and Atrial Myocyte Injury. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 620655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, M.J.; Shinohara, T.; Park, H.W.; Frick, K.; Ice, D.S.; Choi, E.K.; Han, S.; Maruyama, M.; Sharma, R.; Shen, C.; et al. Continuous low-level vagus nerve stimulation reduces stellate ganglion nerve activity and paroxysmal atrial tachyarrhythmias in ambulatory canines. Circulation 2011, 123, 2204–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, X.; Scherlag, B.J.; Yu, L.; Li, S.; Ali, R.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, G.; Nakagawa, H.; Jackman, W.; Lazzara, R.; et al. Prevention and reversal of atrial fibrillation inducibility and autonomic remodeling by low-level vagosympathetic nerve stimulation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 57, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, K.; Singh, J.P.; Parks, K.A.; Katritsis, D.G.; Stavrakis, S.; Armoundas, A.A. Low-Level Tragus Stimulation Modulates Atrial Alternans and Fibrillation Burden in Patients with Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e020865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stavrakis, S.; Humphrey, M.B.; Scherlag, B.J.; Hu, Y.; Jackman, W.M.; Nakagawa, H.; Lockwood, D.; Lazzara, R.; Po, S. Low-level transcutaneous electrical vagus nerve stimulation suppresses atrial fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 65, 867–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, A.M.; Maass, A.H.; Oberdorf-Maass, S.U.; Van Veldhuisen, D.J.; Van Gilst, W.H.; Van Gelder, I.C. Mechanisms of atrial structural changes caused by stretch occurring before and during early atrial fibrillation. Cardiovasc. Res. 2011, 89, 754–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, Y.K.; Kato, T.; Xiong, F.; Shi, Y.F.; Naud, P.; Maguy, A.; Mizuno, K.; Tardif, J.; Comtois, P.; Nattel, S. Atrial fibrillation promotion with long-term repetitive obstructive sleep apnea in a rat model. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 64, 2013–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, L.; Wang, L.; Yang, X.; Jiang, X.; Hua, F. Recombinant human glucagon-like peptide-1 protects against chronic intermittent hypoxia by improving myocardial energy metabolism and mitochondrial biogenesis. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2019, 481, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, D.C.; Brady, D.C.; Po, P.; Chuang, L.P.; Marcondes, L.; Kim, E.; Keenan, B.; Guo, X.; Maislin, G.; Galante, R.; et al. Simulating obstructive sleep apnea patients’ oxygenation characteristics into a mouse model of cyclical intermittent hypoxia. J. Appl. Physiol. 2015, 118, 544–5755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gami, A.S.; Hodge, D.O.; Herges, R.M.; Olson, E.J.; Nykodym, J.; Kara, T.; Somers, V. Obstructive Sleep Apnea, Obesity, and the Risk of Incident Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 49, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, P.; Levitzky, Y.S.; Wang, R.; Weng, J.; Quan, S.F.; Gottlieb, D.J.; Rueschman, M.; Punjabi, N.; Mehra, R.; Bertisch, S.; et al. Obstructive and Central Sleep Apnea and the Risk of Incident Atrial Fibrillation in a Community Cohort of Men and Women. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Zhang, K.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Yang, Y.; Liang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, G. Doxycycline Improves Fibrosis-Induced Abnormalities in Atrial Conduction and Vulnerability to Atrial Fibrillation in Chronic Intermittent Hypoxia Rats. Med. Sci. Monit. 2020, 26, e918883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Ma, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, M.; Li, G. Ameliorative Impact of Liraglutide on Chronic Intermittent Hypoxia-Induced Atrial Remodeling. J. Immunol. Res. 2022, 2022, 8181474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Zhao, L.; Ma, Z.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, M.; Liang, X.; Li, G. Doxycycline Attenuates Atrial Remodeling by Interfering with MicroRNA-21 and Downstream Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog (PTEN)/Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase (PI3K) Signaling Pathway. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 5580–5587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Guan, S.; Wang, M.; Song, F.; Shangguan, W.; Miao, S.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; et al. Establishment of a lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA network in a rat model of atrial fibrosis by whole transcriptome sequencing. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2022, 63, 723–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, P.; Rubies, C.; Torres, M.; Batlle, M.; Farre, R.; Brugada, J.; Montserrat, J.; Almendros, I.; Mont, L. Atrial fibrosis in a chronic murine model of obstructive sleep apnea: Mechanisms and prevention by mesenchymal stem cells. Respir. Res. 2014, 15, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.L.; Chen, Y.C.; Wang, H.T.; Chang, Y.T.; Fang, Y.N.; Hsueh, S.; Liu, W.; Lin, P.; Hsu, P.; Su, M.; et al. The Impact of Intermittent Hypoxemia on Left Atrial Remodeling in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome. Life 2022, 12, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linz, B.; Hohl, M.; Lang, L.; Wong, D.W.L.; Nickel, A.G.; De La Torre, C.; Sticht, C.; Wirth, K.; Boor, P.; Maack, C.; et al. Repeated exposure to transient obstructive sleep apnea-related conditions causes an atrial fibrillation substrate in a chronic rat model. Heart Rhythm. 2021, 18, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemel, J.; Su, Z.; Gileles-Hillel, A.; Khalyfa, A.; Gozal, D.; Beyer, E. Intermittent hypoxia causes NOX2-dependent remodeling of atrial connexins. BMC Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Jackson, R.M. Reactive species mechanisms of cellular hypoxia-reoxygenation injury. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2002, 282, C227–C241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabryelska, A.; Szmyd, B.; Szemraj, J.; Stawski, R.; Sochal, M.; Białasiewicz, P. Patients with obstructive sleep apnea present with chronic upregulation of serum HIF-1α protein. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2020, 16, 1761–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabryelska, A.; Szmyd, B.; Panek, M.; Szemraj, J.; Kuna, P.; Białasiewicz, P. Serum hypoxia-inducible factor-1α protein level as a diagnostic marker of obstructive sleep apnea. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2020, 130, 158–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, K.; Parikh, K.; Heinrich, E.C. Hypoxia and Inflammation: Insights from High-Altitude Physiology. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 676782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Htoo, A.K.; Greenberg, H.; Tongia, S.; Chen, G.; Henderson, T.; Wilson, D.; Liu, S.F. Activation of nuclear factor κB in obstructive sleep apnea: A pathway leading to systemic inflammation. Sleep Breath. 2006, 10, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, E.; Lesske, J.; Behm, R.; Miller, C., 3rd; Stauss, H.; Unger, T. Carotid chemoreceptors, systemic blood pressure, and chronic episodic hypoxia mimicking sleep apnea. J. Appl. Physiol. 1992, 72, 1978–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Overholt, J.; Kline, D.; Prabhakar, N. Induction of sensory long-term facilitation in the carotid body by intermittent hypoxia: Implications for recurrent apneas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 10073–10078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, A.; Cao, L.; Aldossary, H.; Nathanael, D.; Fu, J.; Ray, C.; Brain, K.; Kumar, P.; Coney, A.; Holmes, A. β-Adrenoceptor blockade prevents carotid body hyperactivity and elevated vascular sympathetic nerve density induced by chronic intermittent hypoxia. Pflug. Arch. 2021, 473, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saleeb-Mousa, J.; Nathanael, D.; Coney, A.M.; Kalla, M.; Brain, K.L.; Holmes, A.P. Mechanisms of Atrial Fibrillation in Obstructive Sleep Apnoea. Cells 2023, 12, 1661. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12121661
Saleeb-Mousa J, Nathanael D, Coney AM, Kalla M, Brain KL, Holmes AP. Mechanisms of Atrial Fibrillation in Obstructive Sleep Apnoea. Cells. 2023; 12(12):1661. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12121661
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaleeb-Mousa, James, Demitris Nathanael, Andrew M. Coney, Manish Kalla, Keith L. Brain, and Andrew P. Holmes. 2023. "Mechanisms of Atrial Fibrillation in Obstructive Sleep Apnoea" Cells 12, no. 12: 1661. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12121661
APA StyleSaleeb-Mousa, J., Nathanael, D., Coney, A. M., Kalla, M., Brain, K. L., & Holmes, A. P. (2023). Mechanisms of Atrial Fibrillation in Obstructive Sleep Apnoea. Cells, 12(12), 1661. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12121661




