Human Adult Renal Progenitor Cells Prevent Cisplatin-Nephrotoxicity by Inducing CYP1B1 Overexpression and miR-27b-3p Down-Regulation through Extracellular Vesicles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Co-Culture Experiments
2.2. Evaluation of Apoptosis
2.3. Caspase-3 Staining
2.4. Transcriptomic Profile
2.5. RNA Extraction and RT-PCR
2.6. Real-Time PCR
2.7. lncRNA qPCR
2.8. miRNA Analysis
2.9. miRNA Target Analysis
2.10. EV Extraction from tARPC/RPTEC Co-Culture Supernatants
2.11. Urinary EV Purification from Oncological Patients
2.12. KIM-1 ELISA
2.13. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.13.1. tARPCs Immunofluorescence
2.13.2. RCC Immunofluorescence
2.14. Western Blot
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
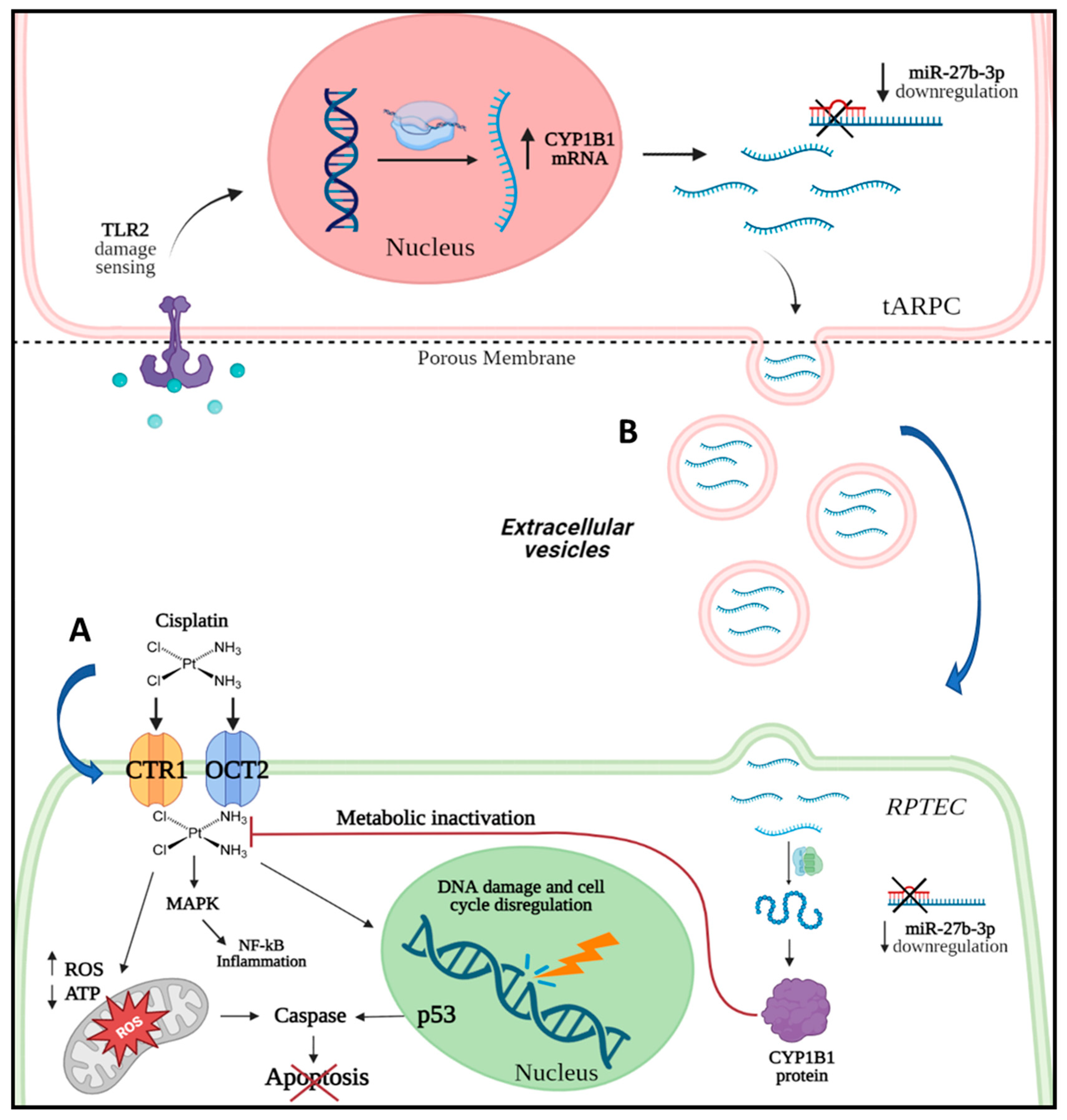
3.1. tARPC Protect RPTEC from Cisplatin-Induced Apoptosis and Necrosis
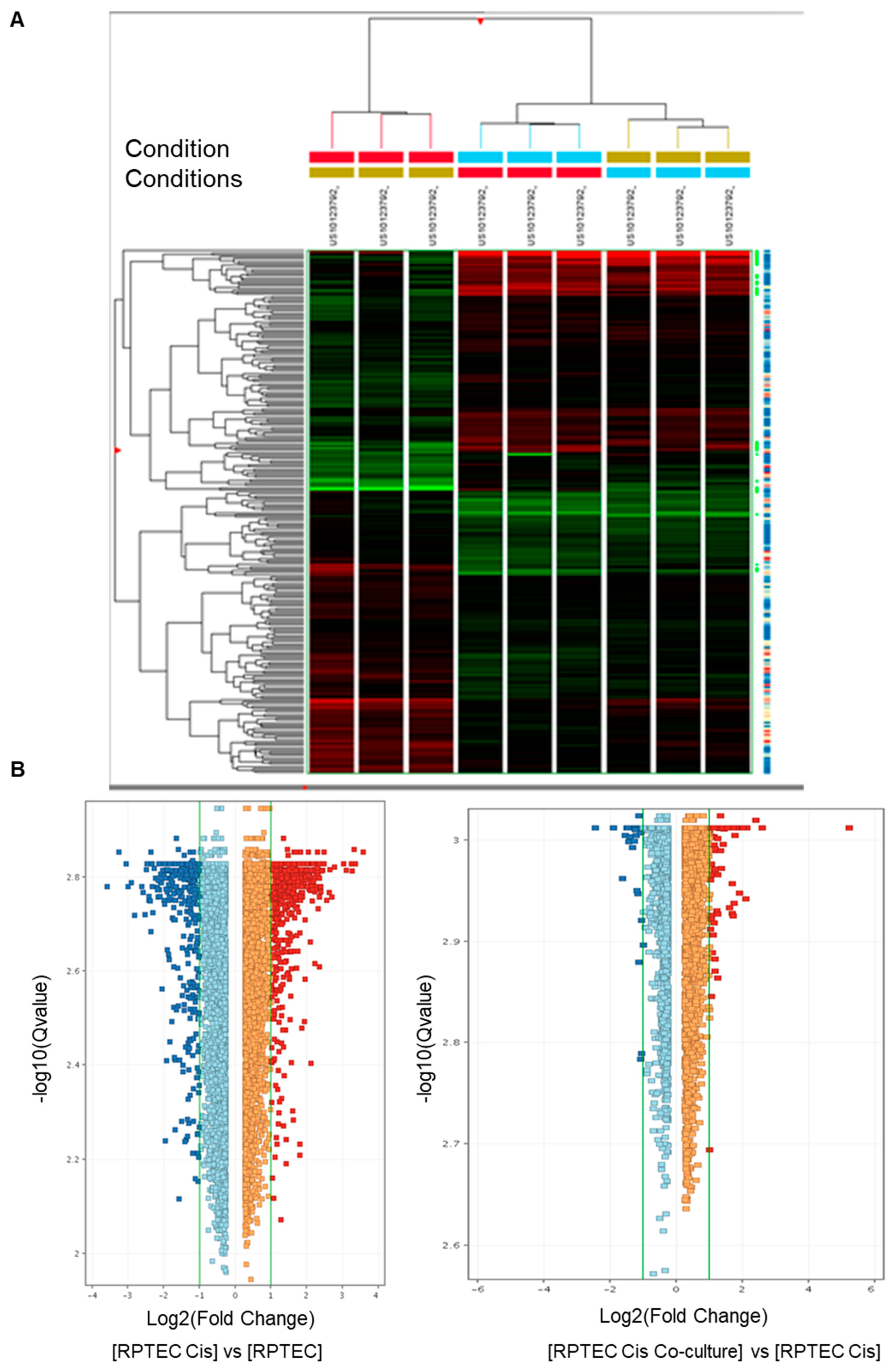
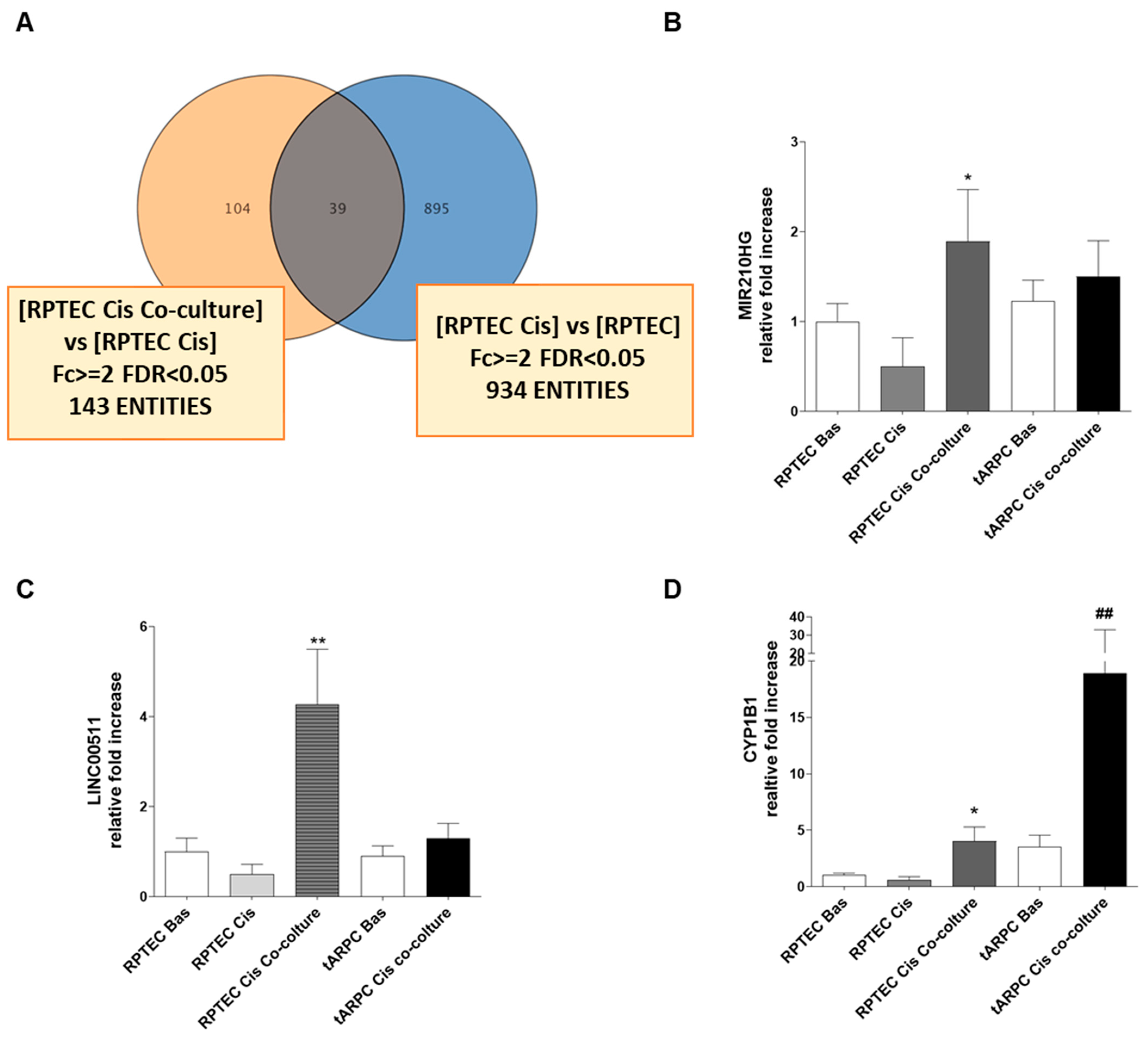
3.2. Transcriptomic Analysis Revealed That tARPC Induce Overexpression of CYP1B1, a Cisplatin-Inactivating Enzyme
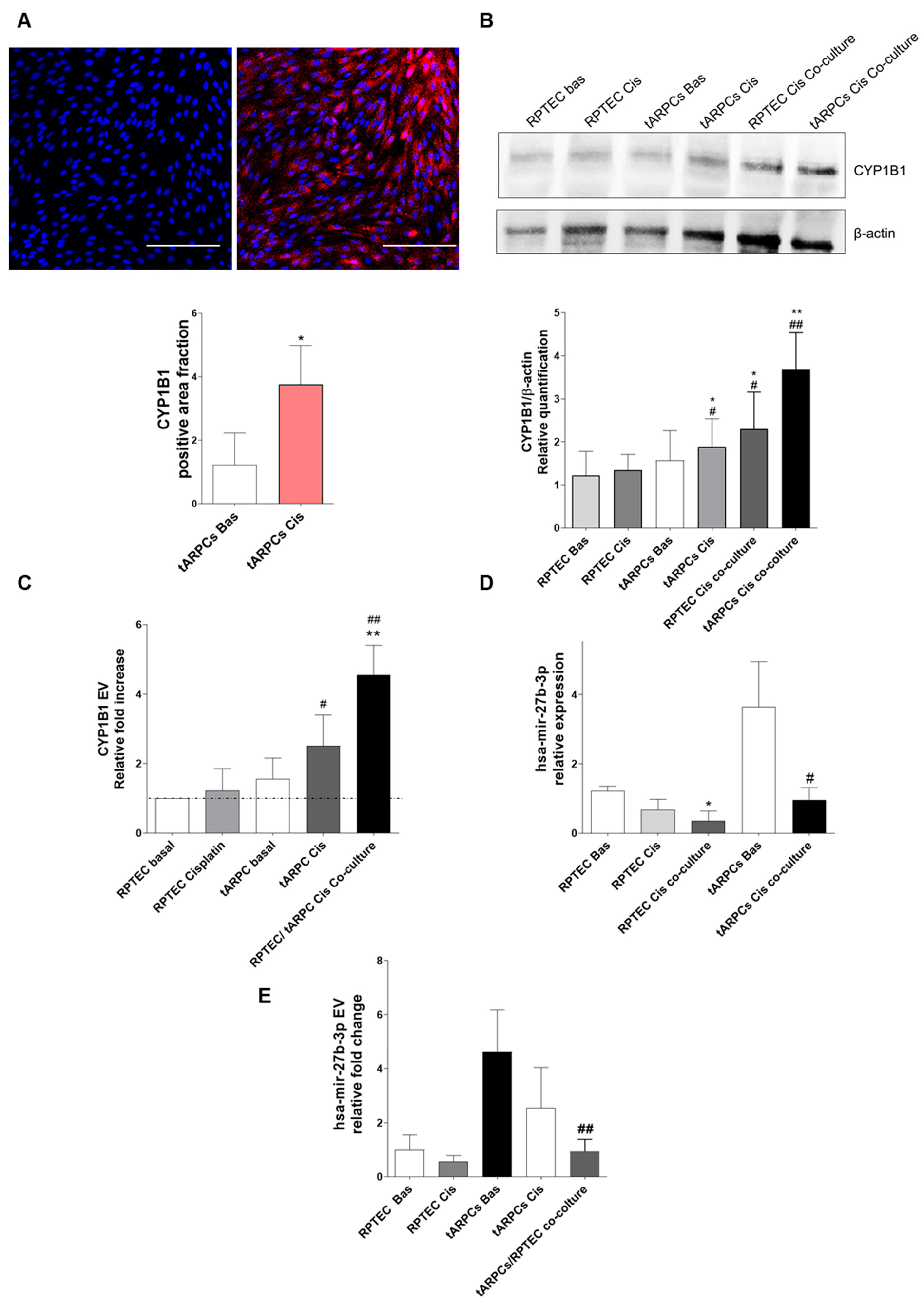
3.3. tARPC Induce Cisplatin Resistance in RPTEC by Releasing EVs Containing CYP1B1
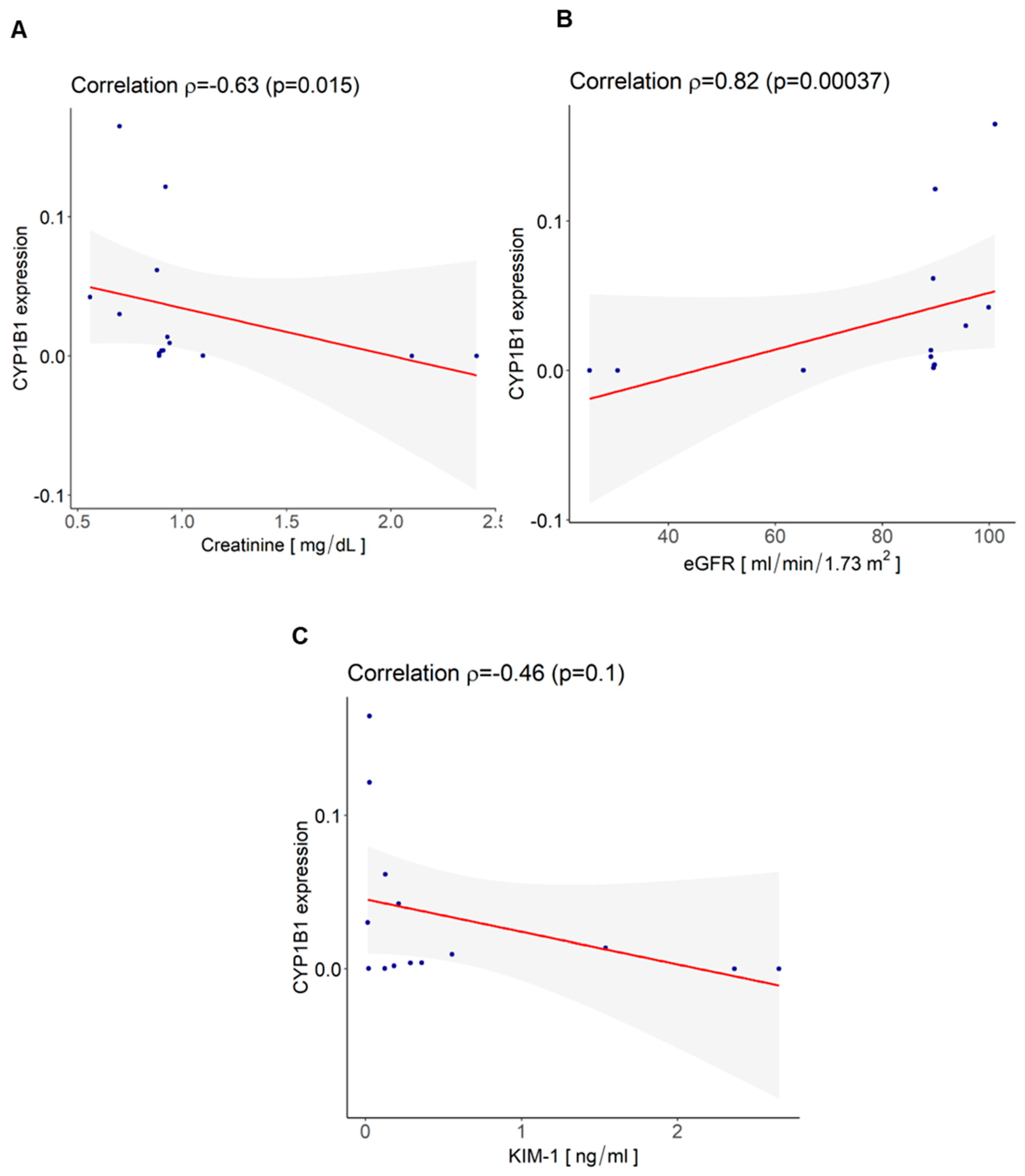
3.4. CYP1B1 Is Expressed in Urinary Extracellular Vesicles from Cisplatin-Treated Patients with Nephrotoxicity and Showed Co-Localization with CD133+ tARPC
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mcsweeney, K.R.; Gadanec, L.K.; Zulli, A. Mechanisms of Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury. Cancers 2021, 13, 1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozkok, A.; Edelstein, C.L. Pathophysiology of Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury. BioMed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 967826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.; Livingston, M.J.; Safirstein, R.; Dong, Z. Cisplatin Nephrotoxicity: New Insights and Therapeutic Implications. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2023, 19, 53–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellum, J.A.; Romagnani, P.; Ashuntantang, G.; Ronco, C.; Zarbock, A.; Anders, H.J. Acute Kidney Injury. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2021, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volarevic, V.; Djokovic, B.; Jankovic, M.G.; Harrell, C.R.; Fellabaum, C.; Djonov, V.; Arsenijevic, N. Molecular Mechanisms of Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity: A Balance on the Knife Edge between Renoprotection and Tumor Toxicity. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019, 9, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.P.; Tadagavadi, R.K.; Ramesh, G.; Reeves, W.B. Mechanisms of Cisplatin Nephrotoxicity. Toxins 2010, 2, 2490–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perazella, M.A. Onco-Nephrology: Renal Toxicities of Chemotherapeutic Agents. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 7, 1713–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hanigan, M.H. Role of Cysteine S-Conjugate Beta-Lyase in the Metabolism of Cisplatin. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2003, 306, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabla, N.; Dong, Z. Cisplatin Nephrotoxicity: Mechanisms and Renoprotective Strategies. Kidney Int. 2008, 73, 994–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasari, S.; Tchounwou, P.B. Cisplatin in Cancer Therapy: Molecular Mechanisms of Action. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 740, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallustio, F.; Serino, G.; Schena, F.P. Potential Reparative Role of Resident Adult Renal Stem/Progenitor Cells in Acute Kidney Injury. BioRes. Open Access 2015, 4, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallustio, F.; Curci, C.; Aloisi, A.; Toma, C.C.; Marulli, E.; Serino, G.; Cox, S.N.; De Palma, G.; Stasi, A.; Divella, C.; et al. Inhibin-A and Decorin Secreted by Human Adult Renal Stem/Progenitor Cells Through the TLR2 Engagement Induce Renal Tubular Cell Regeneration. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nony, P.A.; Schnellmann, R.G. Mechanisms of Renal Cell Repair and Regeneration after Acute Renal Failure. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2003, 304, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, B.D.; Valerius, M.T.; Kobayashi, A.; Mugford, J.W.; Soeung, S.; Duffield, J.S.; McMahon, A.P.; Bonventre, J.V. Intrinsic Epithelial Cells Repair the Kidney after Injury. Cell Stem Cell 2008, 2, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantley, L.G. Adult Stem Cells in the Repair of the Injured Renal Tubule. Nat. Clin. Pract. Nephrol. 2005, 1, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cable, J.; Fuchs, E.; Weissman, I.; Jasper, H.; Glass, D.; Rando, T.A.; Blau, H.; Debnath, S.; Oliva, A.; Park, S.; et al. Adult Stem Cells and Regenerative Medicine-a Symposium Report. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2020, 1462, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciancalepore, A.G.; Sallustio, F.; Girardo, S.; Gioia Passione, L.; Camposeo, A.; Mele, E.; Di Lorenzo, M.; Costantino, V.; Schena, F.P.; Pisignano, D. A Bioartificial Renal Tubule Device Embedding Human Renal Stem/Progenitor Cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzeri, E.; Crescioli, C.; Ronconi, E.; Mazzinghi, B.; Sagrinati, C.; Netti, G.S.; Angelotti, M.L.; Parente, E.; Ballerini, L.; Cosmi, L.; et al. Regenerative Potential of Embryonic Renal Multipotent Progenitors in Acute Renal Failure. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 3128–3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, K.; Kitamura, S.; Sang, Y.; Fukushima, K.; Wada, J. Adult Kidney Stem/Progenitor Cells Contribute to Regeneration through the Secretion of Trophic Factors. Stem Cell Res. 2020, 46, 101865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzin, R.; Stasi, A.; Sallustio, F.; Bruno, S.; Merlotti, G.; Quaglia, M.; Grandaliano, G.; Pontrelli, P.; Thurman, J.M.; Camussi, G.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Patients with Antibody-Mediated Rejection Induce Tubular Senescence and Endothelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Renal Cells. Am. J. Transplant. 2022, 22, 2139–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, J.N.; Collisson, E.A.; Mills, G.B.; Shaw, K.R.M.; Ozenberger, B.A.; Ellrott, K.; Shmulevich, I.; Sander, C.; Stuart, J.M. The Cancer Genome Atlas Pan-Cancer Analysis Project. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonsdale, J.; Thomas, J.; Salvatore, M.; Phillips, R.; Lo, E.; Shad, S.; Hasz, R.; Walters, G.; Garcia, F.; Young, N.; et al. The Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) Project. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 580–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Li, C.; Kang, B.; Gao, G.; Li, C.; Zhang, Z. GEPIA: A Web Server for Cancer and Normal Gene Expression Profiling and Interactive Analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W98–W102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horley, N.J.; Beresford, K.J.; Chawla, T.; McCann, G.J.; Ruparelia, K.C.; Gatchie, L.; Sonawane, V.R.; Williams, I.S.; Tan, H.L.; Joshi, P.; et al. Discovery and characterization of novel CYP1B1 inhibitors based on heterocyclic chalcones: Overcoming cisplatin resistance in CYP1B1-overexpressing lines. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 129, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellano, G.; Franzin, R.; Sallustio, F.; Stasi, A.; Banelli, B.; Romani, M.; De Palma, G.; Lucarelli, G.; Divella, C.; Battaglia, M.; et al. Complement component C5a induces aberrant epigenetic modifications in renal tubular epithelial cells accelerating senescence by Wnt4/βcatenin signaling after ischemia/reperfusion injury. Aging 2019, 11, 4382–4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Liu, G.; Dai, Z.; Wang, L.; Lin, B.; Zhang, J. CYP1B1: A Novel Molecular Biomarker Predicts Molecular Subtype, Tumor Microenvironment, and Immune Response in 33 Cancers. Cancers 2022, 14, 5641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S. Cisplatin: The First Metal Based Anticancer Drug. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 88, 102925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anonymous. Effects and Side-Effects of Cisplatin. Lancet 1982, 1, 682. [Google Scholar]
- Picerno, A.; Castellano, G.; Curci, C.; Kopaczka, K.; Stasi, A.; Pertosa, G.B.; Sabbà, C.; Gesualdo, L.; Gramignoli, R.; Sallustio, F. The Icarus Flight of Perinatal Stem and Renal Progenitor Cells Within Immune System. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 840146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romagnani, P.; Lasagni, L.; Remuzzi, G. Renal Progenitors: An Evolutionary Conserved Strategy for Kidney Regeneration. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2013, 9, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picerno, A.; Giannuzzi, F.; Curci, C.; De Palma, G.; Di Chiano, M.; Simone, S.; Franzin, R.; Gallone, A.; Di Lorenzo, V.F.; Stasi, A.; et al. The Long Non-coding RNA HOTAIR Controls the Self-renewal, Cell Senescence, and Secretion of Anti-aging Protein α-Klotho in Human Adult Renal Progenitor Cells. Stem Cells 2022, 40, 963–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallustio, F.; Gesualdo, L.; Pisignano, D. The Heterogeneity of Renal Stem Cells and Their Interaction with Bio- and Nano-Materials. Stem Cells Heterog. -Nov. Concepts 2019, 1123, 195–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romoli, S.; Angelotti, M.L.; Antonelli, G.; Kumar Vr, S.; Mulay, S.R.; Desai, J.; Anguiano Gomez, L.; Thomasova, D.; Eulberg, D.; Klussmann, S.; et al. CXCL12 Blockade Preferentially Regenerates Lost Podocytes in Cortical Nephrons by Targeting an Intrinsic Podocyte-Progenitor Feedback Mechanism. Kidney Int. 2018, 94, 1111–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfaki, I.; Mir, R.; Almutairi, F.M.; Duhier, F.M.A. Cytochrome P450: Polymorphisms and Roles in Cancer, Diabetes and Atherosclerosis. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2018, 19, 2057–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, H.; Patel, M.; Shrivastava, N. Gene Expression Study of Phase I and II Metabolizing Enzymes in RPTEC/TERT1 Cell Line: Application in in Vitro Nephrotoxicity Prediction. Xenobiotica 2017, 47, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, L.; Liu, X.; Shi, Y.; Ocansey, D.K.W.; Hu, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, C.; Xu, W.; Qian, H. Therapeutic Advances of Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Regenerative Medicine. Cells 2020, 9, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.A.A.; Bhambra, U.; Charalambous, M.P.; David, R.M.; Edwards, R.J.; Lightfoot, T.; Boobis, A.R.; Gooderham, N.J. Interleukin-6 Mediated Upregulation of CYP1B1 and CYP2E1 in Colorectal Cancer Involves DNA Methylation, MiR27b and STAT3. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 2287–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, R.; Liu, K.; Yang, C.; Zheng, J.; Shi, D.; Lin, X.; Wei, C.; Zhang, C.; Fang, Y.; Huang, S.; et al. EMT-Cancer Cells-Derived Exosomal MiR-27b-3p Promotes Circulating Tumour Cells-Mediated Metastasis by Modulating Vascular Permeability in Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Transl. Med. 2021, 11, e595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peraza-Vega, R.I.; Valverde, M.; Rojas, E. MiR-27b-3p a Negative Regulator of DSB-DNA Repair. Genes 2021, 12, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, W.; Hu, C.; Zhang, H.; Qu, Z.; Cen, J.; Qiu, Z.; Li, C.; Ren, H.; Li, Y.; He, X.; et al. MiR-27b Synergizes with Anticancer Drugs via P53 Activation and CYP1B1 Suppression. Cell Res. 2015, 25, 477–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conserva, F.; Barozzino, M.; Pesce, F.; Divella, C.; Oranger, A.; Papale, M.; Sallustio, F.; Simone, S.; Laviola, L.; Giorgino, F.; et al. Urinary MiRNA-27b-3p and MiRNA-1228-3p Correlate with the Progression of Kidney Fibrosis in Diabetic Nephropathy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchiya, Y.; Nakajima, M.; Takagi, S.; Taniya, T.; Yokoi, T. MicroRNA Regulates the Expression of Human Cytochrome P450 1B1. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 9090–9098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Rong, Y.; Deng, Y.; Li, L.; Hu, J.; Yuan, X.; He, H.; Li, L.; Wang, J. MiR-27b-3p Inhibits Estrogen Secretion of Goose Granulosa Cells by Targeting CYP1B1 through the AMPK Signaling Pathway. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Wei, N.; Ma, R.; Jiang, S.-H.; Song, D. Long Noncoding RNA MIR210HG Promotes the Warburg Effect and Tumor Growth by Enhancing HIF-1α Translation in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 580176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.Y.; Lee, G.H.; Khanal, T.; Jin, S.W.; Lee, S.-Y.; Kim, H.G.; Hyon, J.-Y.; Chung, Y.-H.; Ha, S.K.; Han, E.H.; et al. Upregulation of CYP1B1 by Hypoxia Is Mediated by ERα Activation in Breast Cancer Cells. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2022, 12, 2798. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Zhou, F.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Ren, F.; Xu, S. Knockdown of LINC00511 Decreased Cisplatin Resistance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer by Elevating MiR-625 Level to Suppress the Expression of Leucine Rich Repeat Containing Eight Volume-Regulated Anion Channel Subunit E. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2022, 41, 9603271221089000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bournique, B.; Lemarié, A. Docetaxel (Taxotere) Is Not Metabolized by Recombinant Human CYP1B1 in Vitro, but Acts as an Effector of This Isozyme. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2002, 30, 1149–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, V.G.; O’Connor, R.; Liang, Y.; Clynes, M. CYP1B1 Expression Is Induced by Docetaxel: Effect on Cell Viability and Drug Resistance. Br. J. Cancer 2008, 98, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Mu, Y.; Qi, C.; Wang, J.; Xi, G.; Guo, J.; Mi, R.; Zhao, F. CYP1B1 Enhances the Resistance of Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Cells to Paclitaxel in Vivo and in Vitro. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2015, 35, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Wang, S.; Cao, C.; Ye, W.; Wang, M.; Zhou, C.; Chen, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, K.; Zhou, W. α-Naphthoflavone-Derived Cytochrome P450 (CYP)1B1 Degraders Specific for Sensitizing CYP1B1-Mediated Drug Resistance to Prostate Cancer DU145: Structure Activity Relationship. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 116, 105295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Cao, J.; Du, X.; Yang, K.; Yang, X.; Liang, Z.; Shi, J.; Zhang, J. CYP1B1-Catalyzed 4-OHE2 Promotes the Castration Resistance of Prostate Cancer Stem Cells by Estrogen Receptor α-Mediated IL6 Activation. Cell Commun. Signal. 2022, 20, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashcroft, J.; Leighton, P.; Elliott, T.R.; Hosgood, S.A.; Nicholson, M.L.; Kosmoliaptsis, V. Extracellular Vesicles in Kidney Transplantation: A State-of-the-Art Review. Kidney Int. 2022, 101, 485–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, I.O.; Lerman, L.O. Urinary Extracellular Vesicles as Biomarkers of Kidney Disease: From Diagnostics to Therapeutics. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimuccio, V.; Ranghino, A.; Praticò Barbato, L.; Fop, F.; Biancone, L.; Camussi, G.; Bussolati, B. Urinary CD133+ Extracellular Vesicles Are Decreased in Kidney Transplanted Patients with Slow Graft Function and Vascular Damage. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Variables | Values |
|---|---|
| Male | 70% (n = 10) |
| Female | 30% (n = 4) |
| Age (years) | 66.7 ± 7.9 |
| Reason for Chemotherapy | colon adenocarcinoma (n = 6) |
| lung adenocarcinoma (n = 2) | |
| stomach adenocarcinoma (n = 2) | |
| head and neck cancer (n = 2) | |
| breast cancer (n = 2) | |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) mean ± SD | 1.07 ± 0.65 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) mean ± SD | 79.26 ± 24.16 |
| Oxaliplatin (n = 6) | |
| Treatments | Cisplatin (n = 8) |
| Carboplatin (n = 1) |
| Up-Regulated Genes | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| ProbeName | Fold Change | GeneSymbol | Description |
| A_23_P33759 | 37.55951 | DHRS3 | Homo sapiens dehydrogenase/reductase (SDR family) member 3 (DHRS3). mRNA [NM_004753] |
| A_23_P416965 | 6.0632515 | FAM149A | Homo sapiens family with sequence similarity 149. member A (FAM149A). transcript variant 1. mRNA [NM_015398] |
| A_23_P349406 | 5.2752495 | RIMKLA | Homo sapiens ribosomal modification protein rimK-like family member A (RIMKLA). mRNA [NM_173642] |
| A_33_P3290343 | 4.349999 | CYP1B1 | Homo sapiens cytochrome P450. family 1. subfamily B. polypeptide 1 (CYP1B1). mRNA [NM_000104] |
| A_22_P00005242 | 4.348923 | lnc-DLX2-4 | LNCipedia lincRNA (lnc-DLX2-4). lincRNA [lnc-DLX2-4:3] |
| A_23_P209625 | 4.2065525 | CYP1B1 | Homo sapiens cytochrome P450. family 1. subfamily B. polypeptide 1 (CYP1B1). mRNA [NM_000104] |
| A_23_P81158 | 4.171087 | ADH1C | Homo sapiens alcohol dehydrogenase 1C (class I). gamma polypeptide (ADH1C). mRNA [NM_000669] |
| A_23_P35414 | 3.626841 | PPP1R3C | Homo sapiens protein phosphatase 1. regulatory subunit 3C (PPP1R3C). mRNA [NM_005398] |
| A_22_P00016430 | 3.2619064 | HIF1A | HIF1A antisense RNA 2 [Source:HGNC Symbol;Acc:HGNC:43015] [ENST00000554254] |
| A_23_P208937 | 3.2162015 | TLE6 | Homo sapiens transducin-like enhancer of split 6 (TLE6). transcript variant 2. mRNA [NM_024760] |
| A_23_P132027 | 3.0906937 | SPAG4 | Homo sapiens sperm associated antigen 4 (SPAG4). mRNA [NM_003116] |
| A_24_P362904 | 3.0134628 | PFKFB4 | Homo sapiens 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2.6-biphosphatase 4 (PFKFB4). mRNA [NM_004567] |
| A_33_P3247175 | 2.9417257 | C4orf47 | Homo sapiens chromosome 4 open reading frame 47 (C4orf47). mRNA [NM_001114357] |
| A_22_P00014909 | 2.8318717 | TPBGL | Homo sapiens trophoblast glycoprotein-like (TPBGL). mRNA [NM_001195528] |
| A_22_P00002306 | 2.7089448 | MIR210HG | Homo sapiens MIR210 host gene (non-protein coding) (MIR210HG). long non-coding RNA [NR_038262] |
| A_21_P0009360 | 2.4929426 | LINC00673 | Homo sapiens long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 673 (LINC00673). long non-coding RNA [NR_036488] |
| A_22_P00014796 | 2.3685126 | LINC00673 | Homo sapiens long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 673 (LINC00673). long non-coding RNA [NR_036488] |
| A_24_P37441 | 2.3357887 | PDK1 | Homo sapiens pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase. isozyme 1 (PDK1). transcript variant 2. mRNA [NM_002610] |
| A_23_P76071 | 2.2893877 | B3GNT4 | Homo sapiens UDP-GlcNAc:betaGal beta-1.3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase 4 (B3GNT4). mRNA [NM_030765] |
| A_23_P24077 | 2.2306385 | C10orf54 | Homo sapiens chromosome 10 open reading frame 54 (C10orf54). mRNA [NM_022153] |
| A_24_P237586 | 2.2281685 | ANKRD37 | Homo sapiens ankyrin repeat domain 37 (ANKRD37). mRNA [NM_181726] |
| A_21_P0011646 | 2.137652 | LINC00511 | Homo sapiens long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 511 (LINC00511). long non-coding RNA [NR_033876] |
| A_23_P347610 | 2.0365067 | HAVCR1 | Homo sapiens hepatitis A virus cellular receptor 1 (HAVCR1). transcript variant 1. mRNA [NM_012206] |
| A_33_P3420416 | 2.0136702 | LGALS9 | Homo sapiens lectin. galactoside-binding. soluble. 9 (LGALS9). transcript variant 2. mRNA [NM_002308] |
| A_23_P16058 | 2.0103858 | ZNF296 | Homo sapiens zinc finger protein 296 (ZNF296). mRNA [NM_145288] |
| Down-Regulated Genes | |||
| ProbeName | Fold Change | GeneSymbol | Description |
| A_22_P00006779 | −2.0106018 | FXR1 | Homo sapiens fragile X mental retardation. autosomal homolog 1 (FXR1). transcript variant 3. mRNA [NM_001013439] |
| A_24_P376129 | −2.0714304 | DFNB31 | Homo sapiens deafness. autosomal recessive 31 [Source:HGNC Symbol;Acc:HGNC:16361] [ENST00000374057] |
| A_33_P3261054 | −2.1762295 | CCDC114 | Homo sapiens coiled-coil domain containing 114 (CCDC114). mRNA [NM_144577] |
| A_32_P171061 | −2.5465722 | ASCL2 | Homo sapiens achaete-scute family bHLH transcription factor 2 (ASCL2). mRNA [NM_005170] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Franzin, R.; Stasi, A.; De Palma, G.; Picerno, A.; Curci, C.; Sebastiano, S.; Campioni, M.; Cicirelli, A.; Rizzo, A.; Di Lorenzo, V.F.; et al. Human Adult Renal Progenitor Cells Prevent Cisplatin-Nephrotoxicity by Inducing CYP1B1 Overexpression and miR-27b-3p Down-Regulation through Extracellular Vesicles. Cells 2023, 12, 1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12121655
Franzin R, Stasi A, De Palma G, Picerno A, Curci C, Sebastiano S, Campioni M, Cicirelli A, Rizzo A, Di Lorenzo VF, et al. Human Adult Renal Progenitor Cells Prevent Cisplatin-Nephrotoxicity by Inducing CYP1B1 Overexpression and miR-27b-3p Down-Regulation through Extracellular Vesicles. Cells. 2023; 12(12):1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12121655
Chicago/Turabian StyleFranzin, Rossana, Alessandra Stasi, Giuseppe De Palma, Angela Picerno, Claudia Curci, Serena Sebastiano, Monica Campioni, Antonella Cicirelli, Alessandro Rizzo, Vito Francesco Di Lorenzo, and et al. 2023. "Human Adult Renal Progenitor Cells Prevent Cisplatin-Nephrotoxicity by Inducing CYP1B1 Overexpression and miR-27b-3p Down-Regulation through Extracellular Vesicles" Cells 12, no. 12: 1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12121655
APA StyleFranzin, R., Stasi, A., De Palma, G., Picerno, A., Curci, C., Sebastiano, S., Campioni, M., Cicirelli, A., Rizzo, A., Di Lorenzo, V. F., Pontrelli, P., Pertosa, G. B., Castellano, G., Gesualdo, L., & Sallustio, F. (2023). Human Adult Renal Progenitor Cells Prevent Cisplatin-Nephrotoxicity by Inducing CYP1B1 Overexpression and miR-27b-3p Down-Regulation through Extracellular Vesicles. Cells, 12(12), 1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12121655








