The Biologist’s Guide to the Glucocorticoid Receptor’s Structure
Abstract
1. Introduction
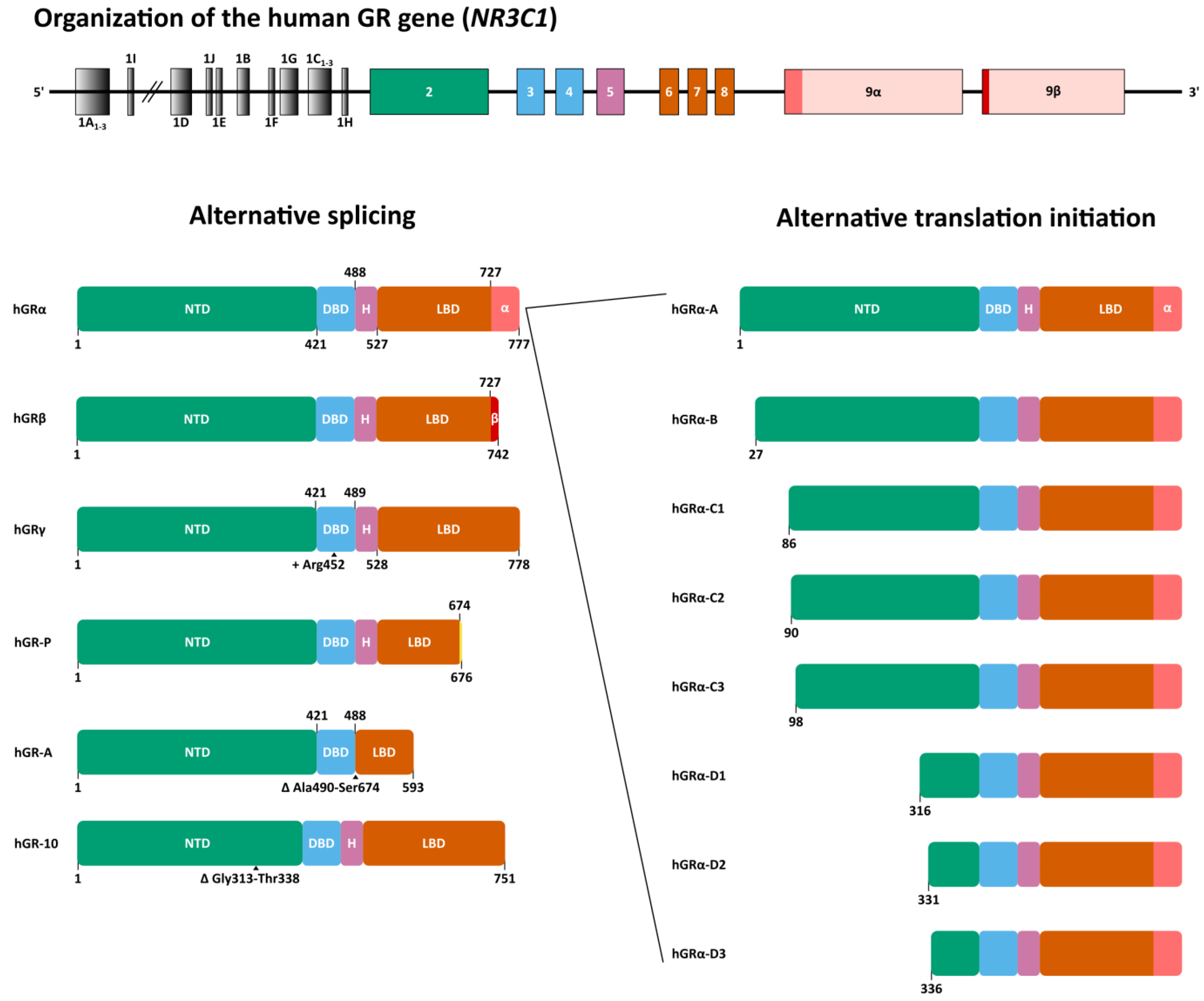
2. Glucocorticoid Receptor Gene and Isoforms
3. Glucocorticoid Receptor Structure
3.1. N-Terminal Domain (NTD)
3.1.1. Secondary Structure
3.1.2. Phosphorylation
3.1.3. Intrinsic Disorder of the NTD
3.2. DNA-Binding Domain (DBD)
3.2.1. DBD Structure
3.2.2. GR Binding to Glucocorticoid Response Elements (GREs)
3.2.3. GR Binding to Inverted-Repeat Negative Glucocorticoid Response Element (IR-nGRE)
3.2.4. GR Binding to Half-Sites
3.2.5. GR Binding to TRE
3.2.6. GR Binding to κBRE
3.2.7. GR Binding to RNA
3.3. Carboxy-Terminal Ligand-Binding Domain (LBD)
3.3.1. Agonist-Bound Form
3.3.2. Antagonist-Bound Form
3.4. GR in Complex with Hsp
4. GR Dimerization and Oligomerization
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arriza, J.L.; Weinberger, C.; Cerelli, G.; Glaser, T.M.; Handelin, B.L.; Housman, D.E.; Evans, R.M. Cloning of Human Mineralocorticoid Receptor Complementary DNA: Structural and Functional Kinship with the Glucocorticoid Receptor. Science 1987, 237, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busada, J.T.; Cidlowski, J.A. Mechanisms of Glucocorticoid Action during Development. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2017, 125, 147–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, T.; McQueen, A.; Chen, T.-C.; Wang, J.-C. Regulation of Glucose Homeostasis by Glucocorticoids. In Glucocorticoid Signaling: From Molecules to Mice to Man; Wang, J.-C., Harris, C., Eds.; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 99–126. ISBN 978-1-4939-2895-8. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz-Topete, D.; Cidlowski, J.A. One Hormone, Two Actions: Anti- and Pro-Inflammatory Effects of Glucocorticoids. NIM 2015, 22, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouanes, S.; Popp, J. High Cortisol and the Risk of Dementia and Alzheimer’s Disease: A Review of the Literature. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2019, 11, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madalena, K.M.; Lerch, J.K. The Effect of Glucocorticoid and Glucocorticoid Receptor Interactions on Brain, Spinal Cord, and Glial Cell Plasticity. Neural. Plast. 2017, 2017, e8640970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousa, S.A.; Dehe, L.; Aboryag, N.; Shaqura, M.; Beyer, A.; Schäfer, M.; Treskatsch, S. Identification of Glucocorticoid Receptors as Potential Modulators of Parasympathetic and Sympathetic Neurons within Rat Intracardiac Ganglia. Front. Neuroanat. 2022, 16, 902738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhang, T.-N.; Knight, J.K.; Goodwin, J.E. The Glucocorticoid Receptor in Cardiovascular Health and Disease. Cells 2019, 8, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Topete, D.; Myers, P.H.; Foley, J.F.; Willis, M.S.; Cidlowski, J.A. Corticosteroids Are Essential for Maintaining Cardiovascular Function in Male Mice. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 2759–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, R.W.; Ivy, J.R.; Bailey, M.A. Glucocorticoids and Renal Na+ Transport: Implications for Hypertension and Salt Sensitivity. J. Physiol. 2014, 592, 1731–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkins, U.A.; Gomez-Sanchez, E.P.; Gomez-Sanchez, C.M.; Gomez-Sanchez, C.E. The Ubiquitous Mineralocorticoid Receptor: Clinical Implications. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2012, 14, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maradonna, F.; Gioacchini, G.; Notarstefano, V.; Fontana, C.M.; Citton, F.; Dalla Valle, L.; Giorgini, E.; Carnevali, O. Knockout of the Glucocorticoid Receptor Impairs Reproduction in Female Zebrafish. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whirledge, S.; Cidlowski, J.A. Glucocorticoids and Reproduction: Traffic Control on the Road to Reproduction. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 28, 399–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whirledge, S.D.; Oakley, R.H.; Myers, P.H.; Lydon, J.P.; DeMayo, F.; Cidlowski, J.A. Uterine Glucocorticoid Receptors Are Critical for Fertility in Mice through Control of Embryo Implantation and Decidualization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 15166–15171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caratti, G.; Iqbal, M.; Hunter, L.; Kim, D.; Wang, P.; Vonslow, R.M.; Begley, N.; Tetley, A.J.; Woodburn, J.L.; Pariollaud, M.; et al. REVERBa Couples the Circadian Clock to Hepatic Glucocorticoid Action. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 4454–4471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, B.P.; Birnie, M.T.; Kershaw, Y.M.; Pauza, A.G.; Kim, S.; Baek, S.; Rogers, M.F.; Paterson, A.R.; Stavreva, D.A.; Murphy, D.; et al. Corticosterone Pattern-Dependent Glucocorticoid Receptor Binding and Transcriptional Regulation within the Liver. PLoS Genet. 2021, 17, e1009737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanovski, J.A.; Cutler, G.B. Glucocorticoid Action and the Clinical Features of Cushing’s Syndrome. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 1994, 23, 487–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fardet, L.; Feve, B. Systemic Glucocorticoid Therapy: A Review of Its Metabolic and Cardiovascular Adverse Events. Drugs 2014, 74, 1731–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anonymous. On the Constitutional and Local Effects of Disease of the Supra-Renal Capsules. Br. Foreign Med.-Chir. Rev. 1856, 18, 404–413. [Google Scholar]
- Oakley, R.H.; Cidlowski, J.A. The Biology of the Glucocorticoid Receptor: New Signaling Mechanisms in Health and Disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 1033–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheschowitsch, K.; Leite, J.; Assreuy, J. New Insights in Glucocorticoid Receptor Signaling–More than Just a Ligand Binding Receptor. Front. Endocrinol. 2017, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weikum, E.R.; Knuesel, M.T.; Ortlund, E.A.; Yamamoto, K.R. Glucocorticoid Receptor Control of Transcription: Precision and Plasticity via Allostery. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmermans, S.; Vandewalle, J.; Libert, C. Dimerization of the Glucocorticoid Receptor and Its Importance in (Patho)Physiology: A Primer. Cells 2022, 11, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmermans, S.; Souffriau, J.; Libert, C. A General Introduction to Glucocorticoid Biology. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groeneweg, F.L.; Karst, H.; de Kloet, E.R.; Joëls, M. Rapid Non-Genomic Effects of Corticosteroids and Their Role in the Central Stress Response. J. Endocrinol. 2011, 209, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiebaut, C.; Vlaeminck-Guillem, V.; Trédan, O.; Poulard, C.; Le Romancer, M. Non-Genomic Signaling of Steroid Receptors in Cancer. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2021, 538, 111453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leis, H.; Page, A.; Ramírez, A.; Bravo, A.; Segrelles, C.; Paramio, J.; Barettino, D.; Jorcano, J.L.; Pérez, P. Glucocorticoid Receptor Counteracts Tumorigenic Activity of Akt in Skin through Interference with the Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase Signaling Pathway. Mol. Endocrinol. 2004, 18, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayroldi, E.; Cannarile, L.; Migliorati, G.; Nocentini, G.; Delfino, D.V.; Riccardi, C. Mechanisms of the Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Glucocorticoids: Genomic and Nongenomic Interference with MAPK Signaling Pathways. FASEB J. 2012, 26, 4805–4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, I.-H.; Buttgereit, F. Non-Genomic Glucocorticoid Effects to Provide the Basis for New Drug Developments. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2006, 246, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hench, P.S.; Kendall, E.C. The Effect of a Hormone of the Adrenal Cortex (17-Hydroxy-11-Dehydrocorticosterone; Compound E) and of Pituitary Adrenocorticotropic Hormone on Rheumatoid Arthritis. Proc. Staff Meet. Mayo Clin. 1949, 24, 181–197. [Google Scholar]
- Lantz, J.C. The 1950 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2000, 75, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutinho, A.E.; Chapman, K.E. The Anti-Inflammatory and Immunosuppressive Effects of Glucocorticoids, Recent Developments and Mechanistic Insights. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2011, 335, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caratti, G.; Matthews, L.; Poolman, T.; Kershaw, S.; Baxter, M.; Ray, D. Glucocorticoid Receptor Function in Health and Disease. Clin. Endocrinol. 2015, 83, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, V.; Metcalf, L.; Versnel, J.; Upton, J.; Walker, S.; Horne, R. Patient-Reported Side Effects, Concerns and Adherence to Corticosteroid Treatment for Asthma, and Comparison with Physician Estimates of Side-Effect Prevalence: A UK-Wide, Cross-Sectional Study. NPJ Prim. Care Respir. Med. 2015, 25, 15026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäcke, H.; Döcke, W.-D.; Asadullah, K. Mechanisms Involved in the Side Effects of Glucocorticoids. Pharmacol. Ther. 2002, 96, 23–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokkinopoulou, I.; Diakoumi, A.; Moutsatsou, P. Glucocorticoid Receptor Signaling in Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, D.A.; Smith, R.E. Steroid-Induced Psychiatric Syndromes: A Report of 14 Cases and a Review of the Literature. J. Affect. Disord. 1983, 5, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, R.S.; Jilka, R.L.; Parfitt, A.M.; Manolagas, S.C. Inhibition of Osteoblastogenesis and Promotion of Apoptosis of Osteoblasts and Osteocytes by Glucocorticoids-Potential Mechanisms of Their Deleterious Effects on Bone. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 102, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, F.; Pouwels, S.; Lammers, J.W.J.; Leufkens, H.G.M.; Bracke, M.; Cooper, C.; Van Staa, T.P. Use of Inhaled and Oral Glucocorticoids, Severity of Inflammatory Disease and Risk of Hip/Femur Fracture: A Population-Based Case–Control Study. J. Intern. Med. 2007, 261, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; MacDonald, T.M.; Walker, B.R. Taking Glucocorticoids by Prescription Is Associated with Subsequent Cardiovascular Disease. Ann. Intern. Med. 2004, 141, 764–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souverein, P.C.; Berard, A.; Staa, T.P.V.; Cooper, C.; Egberts, A.C.G.; Leufkens, H.G.M.; Walker, B.R. Use of Oral Glucocorticoids and Risk of Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Disease in a Population Based Case–Control Study. Heart 2004, 90, 859–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, G.C.; Millar, J.C.; Clark, A.F. Glucocorticoid Receptor Transactivation Is Required for Glucocorticoid-Induced Ocular Hypertension and Glaucoma. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2019, 60, 1967–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daskalakis, N.; Yehuda, R. Site-Specific Methylation Changes in the Glucocorticoid Receptor Exon 1F Promoter in Relation to Life Adversity: Systematic Review of Contributing Factors. Front. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.D.; Muller, C.P. Structure of the Glucocorticoid Receptor (NR3C1) Gene 5′ Untranslated Region: Identification, and Tissue Distribution of Multiple New Human Exon 1. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2005, 35, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiger, H.; Labonté, B.; Groleau, P.; Turecki, G.; Israel, M. Methylation of the Glucocorticoid Receptor Gene Promoter in Bulimic Women: Associations with Borderline Personality Disorder, Suicidality, and Exposure to Childhood Abuse. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2013, 46, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollenberg, S.; Weinberger, C.; Ong, E.; Cerelli, G.; Oro, A.; Lebo, R.; Thompson, E.B.; Rosenfeld, M.; Evans, R. Primary Structure and Expression of a Functional Human Glucocorticoid Receptor CDNA. Nature 1985, 318, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francke, U.; Foellmer, B.E. The Glucocorticoid Receptor Gene Is in 5q–Q32. Genomics 1989, 4, 610–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Ramírez, P.; Tliba, O. Glucocorticoid Receptor β (GRβ): Beyond Its Dominant-Negative Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamberger, C.M.; Bamberger, A.M.; de Castro, M.; Chrousos, G.P. Glucocorticoid Receptor Beta, a Potential Endogenous Inhibitor of Glucocorticoid Action in Humans. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 95, 2435–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kino, T.; Su, Y.A.; Chrousos, G.P. Human Glucocorticoid Receptor (GR) Isoform β: Recent Understanding of Its Potential Implications in Physiology and Pathophysiology. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 3435–3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivers, C.; Levy, A.; Hancock, J.; Lightman, S.; Norman, M. Insertion of an Amino Acid in the DNA-Binding Domain of the Glucocorticoid Receptor as a Result of Alternative Splicing. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1999, 84, 4283–4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, D.J.; Poolman, T.M.; Williamson, A.J.K.; Wang, Z.; Clark, N.R.; Ma’ayan, A.; Whetton, A.D.; Brass, A.; Matthews, L.C.; Ray, D.W. Glucocorticoid Receptor Isoforms Direct Distinct Mitochondrial Programs to Regulate ATP Production. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasai, Y. Two Naturally-Occurring Isoforms and Their Expression of a Glucocorticoid Receptor Gene from an Androgen-Dependent Mouse Tumor. FEBS Lett. 1990, 274, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meijsing, S.H.; Pufall, M.A.; So, A.Y.; Bates, D.L.; Chen, L.; Yamamoto, K.R. DNA Binding Site Sequence Directs Glucocorticoid Receptor Structure and Activity. Science 2009, 324, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivers, C.; Flynn, A.; Qian, X.; Matthews, L.; Lightman, S.; Ray, D.; Norman, M. Characterization of Conserved Tandem Donor Sites and Intronic Motifs Required for Alternative Splicing in Corticosteroid Receptor Genes. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 4958–4967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moalli, P.A.; Pillay, S.; Krett, N.L.; Rosen, S.T. Alternatively Spliced Glucocorticoid Receptor Messenger RNAs in Glucocorticoid-Resistant Human Multiple Myeloma Cells1. Cancer Res. 1993, 53, 3877–3879. [Google Scholar]
- de Lange, P.; Segeren, C.M.; Koper, J.W.; Wiemer, E.; Sonneveld, P.; Brinkmann, A.O.; White, A.; Brogan, I.J.; de Jong, F.H.; Lamberts, S.W.J. Expression in Hematological Malignancies of a Glucocorticoid Receptor Splice Variant That Augments Glucocorticoid Receptor-Mediated Effects in Transfected Cells1. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 3937–3941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krett, N.L.; Pillay, S.; Moalli, P.A.; Greipp, P.R.; Rosen, S.T. A Variant Glucocorticoid Receptor Messenger RNA Is Expressed in Multiple Myeloma Patients1. Cancer Res. 1995, 55, 2727–2729. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, J.D.; Schote, A.B.; Keipes, M.; Muller, C.P. A New Transcript Splice Variant of the Human Glucocorticoid Receptor. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2007, 1095, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, Y.; Iwasaki, Y.; Tsugita, M.; Nishiyama, M.; Taguchi, T.; Okazaki, M.; Nakayama, S.; Kambayashi, M.; Hashimoto, K.; Terada, Y. Glucocorticoid Receptor-β and Receptor-γ Exert Dominant Negative Effect on Gene Repression But Not on Gene Induction. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 3204–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yudt, M.R.; Cidlowski, J.A. Molecular Identification and Characterization of A and B Forms of the Glucocorticoid Receptor. Mol. Endocrinol. 2001, 15, 1093–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, N.Z.; Cidlowski, J.A. Translational Regulatory Mechanisms Generate N-Terminal Glucocorticoid Receptor Isoforms with Unique Transcriptional Target Genes. Mol. Cell 2005, 18, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weikum, E.R.; Liu, X.; Ortlund, E.A. The Nuclear Receptor Superfamily: A Structural Perspective. Protein Sci. 2018, 27, 1876–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Thompson, E.B. Folding of the Glucocorticoid Receptor N-Terminal Transactivation Function: Dynamics and Regulation. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2012, 348, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giguère, V.; Hollenberg, S.M.; Rosenfeld, M.G.; Evans, R.M. Functional Domains of the Human Glucocorticoid Receptor. Cell 1986, 46, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollenberg, S.M.; Giguere, V.; Segui, P.; Evans, R.M. Colocalization of DNA-Binding and Transcriptional Activation Functions in the Human Glucocorticoid Receptor. Cell 1987, 49, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollenberg, S.M.; Evans, R.M. Multiple and Cooperative Trans-Activation Domains of the Human Glucocorticoid Receptor. Cell 1988, 55, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Lee, J.C.; Bolen, D.W.; Thompson, E.B. The Conformation of the Glucocorticoid Receptor AF1/Tau1 Domain Induced by Osmolyte Binds Co-Regulatory Proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 18146–18152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogatsky, I.; Wang, J.C.; Derynck, M.K.; Nonaka, D.F.; Khodabakhsh, D.B.; Haqq, C.M.; Darimont, B.D.; Garabedian, M.J.; Yamamoto, K.R. Target-Specific Utilization of Transcriptional Regulatory Surfaces by the Glucocorticoid Receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 13845–13850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlman-Wright, K.; Almlöf, T.; McEwan, I.J.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Wright, A.P. Delineation of a Small Region within the Major Transactivation Domain of the Human Glucocorticoid Receptor That Mediates Transactivation of Gene Expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 1619–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlman-Wright, K.; Baumann, H.; McEwan, I.J.; Almlöf, T.; Wright, A.P.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Härd, T. Structural Characterization of a Minimal Functional Transactivation Domain from the Human Glucocorticoid Receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 1699–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wärnmark, A.; Gustafsson, J.-Å.; Wright, A. Architectural Principles for the Structure and Function of the Glucocorticoid Receptor Τ1 Core Activation Domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 15014–15018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.-H.; Wright, A.; Han, K.-H. An NMR Study on the Intrinsically Disordered Core Transactivation Domain of Human Glucocorticoid Receptor. BMB Rep. 2017, 50, 522–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-H.; Kim, D.-H.; Han, J.J.; Cha, E.-J.; Lim, J.-E.; Cho, Y.-J.; Lee, C.; Han, K.-H. Understanding Pre-Structured Motifs (PreSMos) in Intrinsically Unfolded Proteins. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2012, 13, 34–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Motlagh, H.N.; Chakuroff, C.; Thompson, E.B.; Hilser, V.J. Thermodynamic Dissection of the Intrinsically Disordered N-Terminal Domain of Human Glucocorticoid Receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 26777–26787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismaili, N.; Garabedian, M.J. Modulation of Glucocorticoid Receptor Function via Phosphorylation. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2004, 1024, 86–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Dang, T.; Blind, R.D.; Wang, Z.; Cavasotto, C.N.; Hittelman, A.B.; Rogatsky, I.; Logan, S.K.; Garabedian, M.J. Glucocorticoid Receptor Phosphorylation Differentially Affects Target Gene Expression. Mol. Endocrinol. 2008, 22, 1754–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garza, A.M.S.; Khan, S.H.; Kumar, R. Site-Specific Phosphorylation Induces Functionally Active Conformation in the Intrinsically Disordered N-Terminal Activation Function (AF1) Domain of the Glucocorticoid Receptor. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2010, 30, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrovolna, J.; Chinenov, Y.; Kennedy, M.A.; Liu, B.; Rogatsky, I. Glucocorticoid-Dependent Phosphorylation of the Transcriptional Coregulator GRIP1. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2012, 32, 730–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krstic, M.D.; Rogatsky, I.; Yamamoto, K.R.; Garabedian, M.J. Mitogen-Activated and Cyclin-Dependent Protein Kinases Selectively and Differentially Modulate Transcriptional Enhancement by the Glucocorticoid Receptor. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1997, 17, 3947–3954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Frederick, J.; Garabedian, M.J. Deciphering the Phosphorylation “Code” of the Glucocorticoid Receptor in Vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 26573–26580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.H.; McLaughlin, W.A.; Kumar, R. Site-Specific Phosphorylation Regulates the Structure and Function of an Intrinsically Disordered Domain of the Glucocorticoid Receptor. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iñiguez-Lluhí, J.A.; Lou, D.Y.; Yamamoto, K.R. Three Amino Acid Substitutions Selectively Disrupt the Activation but Not the Repression Function of the Glucocorticoid Receptor N Terminus. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 4149–4156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Moortel, L.; Thommis, J.; Maertens, B.; Staes, A.; Clarisse, D.; De Sutter, D.; Libert, C.; Meijer, O.C.; Eyckerman, S.; Gevaert, K.; et al. Novel Assays Monitoring Direct Glucocorticoid Receptor Protein Activity Exhibit High Predictive Power for Ligand Activity on Endogenous Gene Targets. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 152, 113218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Baskakov, I.V.; Srinivasan, G.; Bolen, D.W.; Lee, J.C.; Thompson, E.B. Interdomain Signaling in a Two-Domain Fragment of the Human Glucocorticoid Receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 24737–24741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Volk, D.E.; Li, J.; Lee, J.C.; Gorenstein, D.G.; Thompson, E.B. TATA Box Binding Protein Induces Structure in the Recombinant Glucocorticoid Receptor AF1 Domain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 16425–16430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.H.; Ling, J.; Kumar, R. TBP Binding-Induced Folding of the Glucocorticoid Receptor AF1 Domain Facilitates Its Interaction with Steroid Receptor Coactivator-1. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.H.; Awasthi, S.; Guo, C.; Goswami, D.; Ling, J.; Griffin, P.R.; Simons, S.S.; Kumar, R. Binding of the N-Terminal Region of Coactivator TIF2 to the Intrinsically Disordered AF1 Domain of the Glucocorticoid Receptor Is Accompanied by Conformational Reorganizations. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 44546–44560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabari, B.R.; Dall’Agnese, A.; Boija, A.; Klein, I.A.; Coffey, E.L.; Shrinivas, K.; Abraham, B.J.; Hannett, N.M.; Zamudio, A.V.; Manteiga, J.C.; et al. Coactivator Condensation at Super-Enhancers Links Phase Separation and Gene Control. Science 2018, 361, eaar3958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, S.; Dugast-Darzacq, C.; Liu, Z.; Dong, P.; Dailey, G.M.; Cattoglio, C.; Heckert, A.; Banala, S.; Lavis, L.; Darzacq, X.; et al. Imaging Dynamic and Selective Low-Complexity Domain Interactions That Control Gene Transcription. Science 2018, 361, eaar2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, F.; Liu, X.; Ortlund, E.A. Glucocorticoid Receptor Condensates Link DNA-Dependent Receptor Dimerization and Transcriptional Transactivation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2024685118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, D.A.; Johnson, T.A.; Presman, D.M.; Fettweis, G.; Wagh, K.; Rinaldi, L.; Stavreva, D.A.; Paakinaho, V.; Jensen, R.A.M.; Mandrup, S.; et al. An Intrinsically Disordered Region-Mediated Confinement State Contributes to the Dynamics and Function of Transcription Factors. Mol. Cell 2021, 81, 1484–1498.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luisi, B.F.; Xu, W.X.; Otwinowski, Z.; Freedman, L.P.; Yamamoto, K.R.; Sigler, P.B. Crystallographic Analysis of the Interaction of the Glucocorticoid Receptor with DNA. Nature 1991, 352, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez, L.D.; Presman, D.M.; Pecci, A. Molecular Dynamics Simulations of the Glucocorticoid Receptor DNA-Binding Domain Suggest a Role of the Lever-Arm Mobility in Transcriptional Output. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, L.C.; Kuchenbecker, K.M.; Schiller, B.J.; Gross, J.D.; Pufall, M.A.; Yamamoto, K.R. The Glucocorticoid Receptor Dimer Interface Allosterically Transmits Sequence-Specific DNA Signals. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2013, 20, 876–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, H.; Paulsen, K.; Kovacs, H.; Berglund, H.; Wright, A.P.H.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Haerd, T. Refined Solution Structure of the Glucocorticoid Receptor DNA-Binding Domain. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 13463–13471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Tilborg, M.A.A.; Bonvin, A.M.J.J.; Hård, K.; Davis, A.L.; Maler, B.; Boelens, R.; Yamamoto, K.R.; Kaptein, R. Structure Refinement of the Glucocorticoid Receptor-DNA Binding Domain from NMR Data by Relaxation Matrix Calculations. J. Mol. Biol. 1995, 247, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, F.; Okafor, C.D.; Ortlund, E.A. The First Crystal Structure of a DNA-Free Nuclear Receptor DNA Binding Domain Sheds Light on DNA-Driven Allostery in the Glucocorticoid Receptor. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gewirth, D.T.; Sigler, P.B. The Basis for Half-Site Specificity Explored through a Non-Cognate Steroid Receptor-DNA Complex. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 1995, 2, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, W.H.; Youn, C.; Ortlund, E.A. The Structural Basis of Direct Glucocorticoid-Mediated Transrepression. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2013, 20, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, W.H.; Kossmann, B.R.; de Vera, I.M.S.; Chuo, S.-W.; Weikum, E.R.; Eick, G.N.; Thornton, J.W.; Ivanov, I.N.; Kojetin, D.J.; Ortlund, E.A. Distal Substitutions Drive Divergent DNA Specificity among Paralogous Transcription Factors through Subdivision of Conformational Space. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, W.H.; de Vera, I.M.S.; Nwachukwu, J.C.; Weikum, E.R.; Herbst, A.G.; Yang, Q.; Bain, D.L.; Nettles, K.W.; Kojetin, D.J.; Ortlund, E.A. Cryptic Glucocorticoid Receptor-Binding Sites Pervade Genomic NF-ΚB Response Elements. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.; Lian, T.; Gu, C.; Yu, K.; Gao, Y.Q.; Su, X.-D. The Effects of Cytosine Methylation on General Transcription Factors. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weikum, E.R.; de Vera, I.M.S.; Nwachukwu, J.C.; Hudson, W.H.; Nettles, K.W.; Kojetin, D.J.; Ortlund, E.A. Tethering Not Required: The Glucocorticoid Receptor Binds Directly to Activator Protein-1 Recognition Motifs to Repress Inflammatory Genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 8596–8608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Weikum, E.R.; Tilo, D.; Vinson, C.; Ortlund, E.A. Structural Basis for Glucocorticoid Receptor Recognition of Both Unmodified and Methylated Binding Sites, Precursors of a Modern Recognition Element. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 8923–8933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surjit, M.; Ganti, K.P.; Mukherji, A.; Ye, T.; Hua, G.; Metzger, D.; Li, M.; Chambon, P. Widespread Negative Response Elements Mediate Direct Repression by Agonist-Liganded Glucocorticoid Receptor. Cell 2011, 145, 224–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiller, B.J.; Chodankar, R.; Watson, L.C.; Stallcup, M.R.; Yamamoto, K.R. Glucocorticoid Receptor Binds Half Sites as a Monomer and Regulates Specific Target Genes. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.-W.; Uhlenhaut, N.H.; Rauch, A.; Weiner, J.; Hübner, S.; Hübner, N.; Won, K.-J.; Lazar, M.A.; Tuckermann, J.; Steger, D.J. Genomic Redistribution of GR Monomers and Dimers Mediates Transcriptional Response to Exogenous Glucocorticoid in Vivo. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kino, T.; Hurt, D.E.; Ichijo, T.; Nader, N.; Chrousos, G.P. Noncoding RNA Gas5 Is a Growth Arrest- and Starvation-Associated Repressor of the Glucocorticoid Receptor. Sci. Signal. 2010, 3, ra8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, W.H.; Pickard, M.R.; de Vera, I.M.S.; Kuiper, E.G.; Mourtada-Maarabouni, M.; Conn, G.L.; Kojetin, D.J.; Williams, G.T.; Ortlund, E.A. Conserved Sequence-Specific LincRNA–Steroid Receptor Interactions Drive Transcriptional Repression and Direct Cell Fate. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, O.H.; Do, E.; Kim, Y.K. A New Function of Glucocorticoid Receptor: Regulation of MRNA Stability. BMB Rep. 2015, 48, 367–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsonnet, N.V.; Lammer, N.C.; Holmes, Z.E.; Batey, R.T.; Wuttke, D.S. The Glucocorticoid Receptor DNA-Binding Domain Recognizes RNA Hairpin Structures with High Affinity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 8180–8192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hörberg, J.; Reymer, A. Decoding the Dual Recognition Mechanism of Glucocorticoid Receptor for DNA and RNA: Sequence vs. Shape. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miner, J.N.; Yamamoto, K.R. The Basic Region of AP-1 Specifies Glucocorticoid Receptor Activity at a Composite Response Element. Genes Dev. 1992, 6, 2491–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bosscher, K.; Vanden Berghe, W.; Haegeman, G. Glucocorticoid Repression of AP-1 Is Not Mediated by Competition for Nuclear Coactivators. Mol. Endocrinol. 2001, 15, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luecke, H.F.; Yamamoto, K.R. The Glucocorticoid Receptor Blocks P-TEFb Recruitment by NFκB to Effect Promoter-Specific Transcriptional Repression. Genes Dev. 2005, 19, 1116–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, N.A.S.; McCalman, M.T.; Moulos, P.; Francoijs, K.-J.; Chatziioannou, A.; Kolisis, F.N.; Alexis, M.N.; Mitsiou, D.J.; Stunnenberg, H.G. Coactivation of GR and NFKB Alters the Repertoire of Their Binding Sites and Target Genes. Genome Res. 2011, 21, 1404–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacta, M.A.; Tharmalingam, B.; Coppo, M.; Rollins, D.A.; Deochand, D.K.; Benjamin, B.; Yu, L.; Zhang, B.; Hu, X.; Li, R.; et al. Gene-Specific Mechanisms Direct Glucocorticoid-Receptor-Driven Repression of Inflammatory Response Genes in Macrophages. eLife 2018, 7, e34864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klock, G.; Strähle, U.; Schütz, G. Oestrogen and Glucocorticoid Responsive Elements Are Closely Related but Distinct. Nature 1987, 329, 734–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordeen, S.K.; Suh, B.J.; Kühnel, B.; Hutchison, C.A., III. Structural Determinants of a Glucocorticoid Receptor Recognition Element. Mol. Endocrinol. 1990, 4, 1866–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, A.Y.-L.; Chaivorapol, C.; Bolton, E.C.; Li, H.; Yamamoto, K.R. Determinants of Cell- and Gene-Specific Transcriptional Regulation by the Glucocorticoid Receptor. PLoS Genet. 2007, 3, e94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postel, S.; Wissler, L.; Johansson, C.A.; Gunnarsson, A.; Gordon, E.; Collins, B.; Castaldo, M.; Köhler, C.; Öling, D.; Johansson, P.; et al. Quaternary Glucocorticoid Receptor Structure Highlights Allosteric Interdomain Communication. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2023, 30, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köhler, C.; Carlström, G.; Gunnarsson, A.; Weininger, U.; Tångefjord, S.; Ullah, V.; Lepistö, M.; Karlsson, U.; Papavoine, T.; Edman, K.; et al. Dynamic Allosteric Communication Pathway Directing Differential Activation of the Glucocorticoid Receptor. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabb5277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, T.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Carlstedt-Duke, J. Glucocorticoid-Dependent Transcriptional Repression of the Osteocalcin Gene by Competitive Binding at the TATA Box. DNA Cell Biol. 1997, 16, 919–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas-Chollier, M.; Watson, L.C.; Cooper, S.B.; Pufall, M.A.; Liu, J.S.; Borzym, K.; Vingron, M.; Yamamoto, K.R.; Meijsing, S.H. A Naturally Occuring Insertion of a Single Amino Acid Rewires Transcriptional Regulation by Glucocorticoid Receptor Isoforms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 17826–17831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichardt, H.M.; Kaestner, K.H.; Tuckermann, J.; Kretz, O.; Wessely, O.; Bock, R.; Gass, P.; Schmid, W.; Herrlich, P.; Angel, P.; et al. DNA Binding of the Glucocorticoid Receptor Is Not Essential for Survival. Cell 1998, 93, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heck, S.; Kullmann, M.; Gast, A.; Ponta, H.; Rahmsdorf, H.J.; Herrlich, P.; Cato, A.C. A Distinct Modulating Domain in Glucocorticoid Receptor Monomers in the Repression of Activity of the Transcription Factor AP-1. EMBO J. 1994, 13, 4087–4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, M.; Meijer, O.C.; Wang, J.; Bhargava, A.; Pearce, D. Homodimerization of the Glucocorticoid Receptor Is Not Essential for Response Element Binding: Activation of the Phenylethanolamine N-Methyltransferase Gene by Dimerization-Defective Mutants. Mol. Endocrinol. 2003, 17, 2583–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presman, D.M.; Ogara, M.F.; Stortz, M.; Alvarez, L.D.; Pooley, J.R.; Schiltz, R.L.; Grøntved, L.; Johnson, T.A.; Mittelstadt, P.R.; Ashwell, J.D.; et al. Live Cell Imaging Unveils Multiple Domain Requirements for In Vivo Dimerization of the Glucocorticoid Receptor. PLoS Biol. 2014, 12, e1001813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, D.D.; Helms, S.; Carlstedt-Duke, J.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Rottman, F.M.; Yamamoto, K.R. Hormone-Mediated Repression: A Negative Glucocorticoid Response Element from the Bovine Prolactin Gene. Genes Dev. 1988, 2, 1144–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, E.P.; Hesse, H.; Müller, J.M.; Beato, M. Glucocorticoid Receptor Binding Site in the Mouse Alpha-Amylase 2 Gene Mediates Response to the Hormone. Mol. Endocrinol. 1993, 7, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuetz, J.D.; Schuetz, E.G.; Thottassery, J.V.; Guzelian, P.S.; Strom, S.; Sun, D. Identification of a Novel Dexamethasone Responsive Enhancer in the Human CYP3A5 Gene and Its Activation in Human and Rat Liver Cells. Mol. Pharm. 1996, 49, 63–72. [Google Scholar]
- Berman, H.; Henrick, K.; Nakamura, H. Announcing the Worldwide Protein Data Bank. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2003, 10, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, A.T.; Kim, M.-Y.; Cho, J.Y. TAK1/AP-1-Targeted Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Barringtonia Augusta Methanol Extract. Molecules 2021, 26, 3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.-C. NF-ΚB Signaling in Inflammation. Sig. Transduct. Target. 2017, 2, 17023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Vedeckis, W.V. The Glucocorticoid Receptor Protein Binds to Transfer RNA. Science 1987, 235, 467–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, C.; King, R.M.; Philipson, L. Genes Specifically Expressed at Growth Arrest of Mammalian Cells. Cell 1988, 54, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourtada-Maarabouni, M.; Pickard, M.R.; Hedge, V.L.; Farzaneh, F.; Williams, G.T. GAS5, a Non-Protein-Coding RNA, Controls Apoptosis and Is Downregulated in Breast Cancer. Oncogene 2009, 28, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickard, M.R.; Mourtada-Maarabouni, M.; Williams, G.T. Long Non-Coding RNA GAS5 Regulates Apoptosis in Prostate Cancer Cell Lines. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2013, 1832, 1613–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickard, M.R.; Williams, G.T. Regulation of Apoptosis by Long Non-Coding RNA GAS5 in Breast Cancer Cells: Implications for Chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 145, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickard, M.R.; Williams, G.T. The Hormone Response Element Mimic Sequence of GAS5 LncRNA Is Sufficient to Induce Apoptosis in Breast Cancer Cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 10104–10116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bledsoe, R.K.; Montana, V.G.; Stanley, T.B.; Delves, C.J.; Apolito, C.J.; McKee, D.D.; Consler, T.G.; Parks, D.J.; Stewart, E.L.; Willson, T.M.; et al. Crystal Structure of the Glucocorticoid Receptor Ligand Binding Domain Reveals a Novel Mode of Receptor Dimerization and Coactivator Recognition. Cell 2002, 110, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Lambert, M.H.; Xu, H.E. Activation of Nuclear Receptors: A Perspective from Structural Genomics. Structure 2003, 11, 741–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wurtz, J.-M.; Bourguet, W.; Renaud, J.-P.; Vivat, V.; Chambon, P.; Moras, D.; Gronemeyer, H. A Canonical Structure for the Ligand-Binding Domain of Nuclear Receptors. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 1996, 3, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suino-Powell, K.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Tao, Y.; Tolbert, W.D.; Simons, S.S.; Xu, H.E. Doubling the Size of the Glucocorticoid Receptor Ligand Binding Pocket by Deacylcortivazol. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 1915–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milhon, J.; Lee, S.; Kohli, K.; Chen, D.; Hong, H.; Stallcup, M.R. Identification of Amino Acids in the Τ2-Region of the Mouse Glucocorticoid Receptor That Contribute to Hormone Binding and Transcriptional Activation. Mol. Endocrinol. 1997, 11, 1795–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauppi, B.; Jakob, C.; Färnegårdh, M.; Yang, J.; Ahola, H.; Alarcon, M.; Calles, K.; Engström, O.; Harlan, J.; Muchmore, S.; et al. The Three-Dimensional Structures of Antagonistic and Agonistic Forms of the Glucocorticoid Receptor Ligand-Binding Domain: RU-486 Induces a Transconformation That Leads to Active Antagonism. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 22748–22754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biggadike, K.; Bledsoe, R.K.; Hassell, A.M.; Kirk, B.E.; McLay, I.M.; Shewchuk, L.M.; Stewart, E.L. X-Ray Crystal Structure of the Novel Enhanced-Affinity Glucocorticoid Agonist Fluticasone Furoate in the Glucocorticoid Receptor−Ligand Binding Domain. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 3349–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madauss, K.P.; Bledsoe, R.K.; Mclay, I.; Stewart, E.L.; Uings, I.J.; Weingarten, G.; Williams, S.P. The First X-Ray Crystal Structure of the Glucocorticoid Receptor Bound to a Non-Steroidal Agonist. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 6097–6099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridgham, J.T.; Ortlund, E.A.; Thornton, J.W. An Epistatic Ratchet Constrains the Direction of Glucocorticoid Receptor Evolution. Nature 2009, 461, 515–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoch, G.A.; D’Arcy, B.; Stihle, M.; Burger, D.; Bär, D.; Benz, J.; Thoma, R.; Ruf, A. Molecular Switch in the Glucocorticoid Receptor: Active and Passive Antagonist Conformations. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 395, 568–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggadike, K.; Bledsoe, R.K.; Coe, D.M.; Cooper, T.W.J.; House, D.; Iannone, M.A.; Macdonald, S.J.F.; Madauss, K.P.; McLay, I.M.; Shipley, T.J.; et al. Design and X-ray Crystal Structures of High-Potency Nonsteroidal Glucocorticoid Agonists Exploiting a Novel Binding Site on the Receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 18114–18119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, T.; Thoma, R.; Schoch, G.A.; Stihle, M.; Benz, J.; D’Arcy, B.; Wiget, A.; Ruf, A.; Hennig, M.; Sterner, R. Enhancing the Stability and Solubility of the Glucocorticoid Receptor Ligand-Binding Domain by High-Throughput Library Screening. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 403, 562–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edman, K.; Ahlgren, R.; Bengtsson, M.; Bladh, H.; Bäckström, S.; Dahmén, J.; Henriksson, K.; Hillertz, P.; Hulikal, V.; Jerre, A.; et al. The Discovery of Potent and Selective Non-Steroidal Glucocorticoid Receptor Modulators, Suitable for Inhalation. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 2571–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohn, J.A.; Deshpande, K.; Ortlund, E.A. Deciphering Modern Glucocorticoid Cross-Pharmacology Using Ancestral Corticosteroid Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 16267–16275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carson, M.W.; Luz, J.G.; Suen, C.; Montrose, C.; Zink, R.; Ruan, X.; Cheng, C.; Cole, H.; Adrian, M.D.; Kohlman, D.T.; et al. Glucocorticoid Receptor Modulators Informed by Crystallography Lead to a New Rationale for Receptor Selectivity, Function, and Implications for Structure-Based Design. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luz, J.G.; Carson, M.W.; Condon, B.; Clawson, D.; Pustilnik, A.; Kohlman, D.T.; Barr, R.J.; Bean, J.S.; Dill, M.J.; Sindelar, D.K.; et al. Indole Glucocorticoid Receptor Antagonists Active in a Model of Dyslipidemia Act via a Unique Association with an Agonist Binding Site. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 6607–6618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Yi, W.; Suino-Powell, K.; Zhou, X.E.; Tolbert, W.D.; Tang, X.; Yang, J.; Yang, H.; Shi, J.; Hou, L.; et al. Structures and Mechanism for the Design of Highly Potent Glucocorticoids. Cell Res. 2014, 24, 713–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edman, K.; Hosseini, A.; Bjursell, M.K.; Aagaard, A.; Wissler, L.; Gunnarsson, A.; Kaminski, T.; Köhler, C.; Bäckström, S.; Jensen, T.J.; et al. Ligand Binding Mechanism in Steroid Receptors: From Conserved Plasticity to Differential Evolutionary Constraints. Structure 2015, 23, 2280–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, M.; Rehwinkel, H.; Schmees, N.; Schäcke, H.; Edman, K.; Wissler, L.; Reichel, A.; Jaroch, S. Discovery of New Selective Glucocorticoid Receptor Agonist Leads. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmerling, M.; Edman, K.; Lepistö, M.; Eriksson, A.; Ivanova, S.; Dahmén, J.; Rehwinkel, H.; Berger, M.; Hendrickx, R.; Dearman, M.; et al. Discovery of Indazole Ethers as Novel, Potent, Non-Steroidal Glucocorticoid Receptor Modulators. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 5741–5748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmerling, M.; Nilsson, S.; Edman, K.; Eirefelt, S.; Russell, W.; Hendrickx, R.; Johnsson, E.; Kärrman Mårdh, C.; Berger, M.; Rehwinkel, H.; et al. Selective Nonsteroidal Glucocorticoid Receptor Modulators for the Inhaled Treatment of Pulmonary Diseases. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 8591–8605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, J.; Perera, L.; Krahn, J.M.; Jewell, C.M.; Moon, A.F.; Cidlowski, J.A.; Pedersen, L.C. Probing Dominant Negative Behavior of Glucocorticoid Receptor β through a Hybrid Structural and Biochemical Approach. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2018, 38, e00453-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rew, Y.; Du, X.; Eksterowicz, J.; Zhou, H.; Jahchan, N.; Zhu, L.; Yan, X.; Kawai, H.; McGee, L.R.; Medina, J.C.; et al. Discovery of a Potent and Selective Steroidal Glucocorticoid Receptor Antagonist (ORIC-101). J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 7767–7784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripa, L.; Edman, K.; Dearman, M.; Edenro, G.; Hendrickx, R.; Ullah, V.; Chang, H.-F.; Lepistö, M.; Chapman, D.; Geschwindner, S.; et al. Discovery of a Novel Oral Glucocorticoid Receptor Modulator (AZD9567) with Improved Side Effect Profile. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 1785–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Ortlund, E.A. First High-Resolution Crystal Structures of the Glucocorticoid Receptor Ligand-Binding Domain–Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated γ Coactivator 1-α Complex with Endogenous and Synthetic Glucocorticoids. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 96, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noddings, C.M.; Wang, R.Y.-R.; Johnson, J.L.; Agard, D.A. Structure of Hsp90–P23–GR Reveals the Hsp90 Client-Remodelling Mechanism. Nature 2022, 601, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.Y.-R.; Noddings, C.M.; Kirschke, E.; Myasnikov, A.G.; Johnson, J.L.; Agard, D.A. Structure of Hsp90–Hsp70–Hop–GR Reveals the Hsp90 Client-Loading Mechanism. Nature 2022, 601, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valotis, A.; Högger, P. Human Receptor Kinetics and Lung Tissue Retention of the Enhanced-Affinity Glucocorticoid Fluticasone Furoate. Respir. Res. 2007, 8, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadepond, F.; Ulmann, A.; Baulieu, E.-E. RU486 (Mifepristone): Mechanisms of Action and Clinical Uses. Annu. Rev. Med. 1997, 48, 129–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Panizo, A.; Alegre-Martí, A.; Tettey, T.T.; Fettweis, G.; Abella, M.; Antón, R.; Johnson, T.A.; Kim, S.; Schiltz, R.L.; Núñez-Barrios, I.; et al. The Multivalency of the Glucocorticoid Receptor Ligand-Binding Domain Explains Its Manifold Physiological Activities. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, 13063–13082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presman, D.M.; Ganguly, S.; Schiltz, R.L.; Johnson, T.A.; Karpova, T.S.; Hager, G.L. DNA Binding Triggers Tetramerization of the Glucocorticoid Receptor in Live Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 8236–8241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hörlein, A.J.; Näär, A.M.; Heinzel, T.; Torchia, J.; Gloss, B.; Kurokawa, R.; Ryan, A.; Kamei, Y.; Söderström, M.; Glass, C.K. Ligand-Independent Repression by the Thyroid Hormone Receptor Mediated by a Nuclear Receptor Co-Repressor. Nature 1995, 377, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.D.; Evans, R.M. A Transcriptional Co-Repressor That Interacts with Nuclear Hormone Receptors. Nature 1995, 377, 454–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oñate, S.A.; Tsai, S.Y.; Tsai, M.-J.; O’Malley, B.W. Sequence and Characterization of a Coactivator for the Steroid Hormone Receptor Superfamily. Science 1995, 270, 1354–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voegel, J.J.; Heine, M.J.; Zechel, C.; Chambon, P.; Gronemeyer, H. TIF2, a 160 KDa Transcriptional Mediator for the Ligand-Dependent Activation Function AF-2 of Nuclear Receptors. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 3667–3675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogatsky, I.; Luecke, H.F.; Leitman, D.C.; Yamamoto, K.R. Alternate Surfaces of Transcriptional Coregulator GRIP1 Function in Different Glucocorticoid Receptor Activation and Repression Contexts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 16701–16706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollins, D.A.; Kharlyngdoh, J.B.; Coppo, M.; Tharmalingam, B.; Mimouna, S.; Guo, Z.; Sacta, M.A.; Pufall, M.A.; Fisher, R.P.; Hu, X.; et al. Glucocorticoid-Induced Phosphorylation by CDK9 Modulates the Coactivator Functions of Transcriptional Cofactor GRIP1 in Macrophages. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heery, D.M.; Kalkhoven, E.; Hoare, S.; Parker, M.G. A Signature Motif in Transcriptional Co-Activators Mediates Binding to Nuclear Receptors. Nature 1997, 387, 733–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Lazar, M.A. The CoRNR Motif Controls the Recruitment of Corepressors by Nuclear Hormone Receptors. Nature 1999, 402, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picard, D.; Khursheed, B.; Garabedian, M.J.; Fortin, M.G.; Lindquist, S.; Yamamoto, K.R. Reduced Levels of Hsp90 Compromise Steroid Receptor Action in Vivo. Nature 1990, 348, 166–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschke, E.; Goswami, D.; Southworth, D.; Griffin, P.R.; Agard, D.A. Glucocorticoid Receptor Function Regulated by Coordinated Action of the Hsp90 and Hsp70 Chaperone Cycles. Cell 2014, 157, 1685–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cluning, C.; Ward, B.K.; Rea, S.L.; Arulpragasam, A.; Fuller, P.J.; Ratajczak, T. The Helix 1-3 Loop in the Glucocorticoid Receptor LBD Is a Regulatory Element for FKBP Cochaperones. Mol. Endocrinol. 2013, 27, 1020–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazaira, G.I.; Echeverría, P.C.; Ciucci, S.M.; Monte, M.; Gallo, L.I.; Erlejman, A.G.; Galigniana, M.D. Differential Regulation of the Glucocorticoid Receptor Nucleocytoplasmic Shuttling by TPR-Domain Proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Res. 2021, 1868, 119000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denny, W.B.; Prapapanich, V.; Smith, D.F.; Scammell, J.G. Structure-Function Analysis of Squirrel Monkey FK506-Binding Protein 51, a Potent Inhibitor of Glucocorticoid Receptor Activity. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 3194–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galigniana, M.D.; Erlejman, A.G.; Monte, M.; Gomez-Sanchez, C.; Piwien-Pilipuk, G. The Hsp90-FKBP52 Complex Links the Mineralocorticoid Receptor to Motor Proteins and Persists Bound to the Receptor in Early Nuclear Events. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2010, 30, 1285–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, T.H.; Ning, Y.-M.; Sánchez, E.R. A New First Step in Activation of Steroid Receptors: Hormone-Induced Switching of FKBP51 and FKBP52 Immunophilins. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 4597–4600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrell, J.M.; Murphy, P.J.M.; Morishima, Y.; Chen, H.; Mansfield, J.F.; Galigniana, M.D.; Pratt, W.B. Evidence for Glucocorticoid Receptor Transport on Microtubules by Dynein. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 54647–54654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picard, D.; Yamamoto, K.R. Two Signals Mediate Hormone-Dependent Nuclear Localization of the Glucocorticoid Receptor. EMBO J. 1987, 6, 3333–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Nishi, M.; Morimoto, M.; Sugimoto, T.; Kawata, M. Yellow Fluorescent Protein-Tagged and Cyan Fluorescent Protein-Tagged Imaging Analysis of Glucocorticoid Receptor and Importins in Single Living Cells. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 4070–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazaira, G.I.; Echeverria, P.C.; Galigniana, M.D. Nucleocytoplasmic Shuttling of the Glucocorticoid Receptor Is Influenced by Tetratricopeptide Repeat-Containing Proteins. J. Cell Sci. 2020, 133, jcs238873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echeverría, P.C.; Mazaira, G.; Erlejman, A.; Gomez-Sanchez, C.; Pilipuk, G.P.; Galigniana, M.D. Nuclear Import of the Glucocorticoid Receptor-Hsp90 Complex through the Nuclear Pore Complex Is Mediated by Its Interaction with Nup62 and Importin β. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009, 29, 4788–4797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrigan, A.; Walther, R.F.; Salem, H.A.; Wu, D.; Atlas, E.; Lefebvre, Y.A.; Haché, R.J.G. An Active Nuclear Retention Signal in the Glucocorticoid Receptor Functions as a Strong Inducer of Transcriptional Activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 10963–10971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stade, K.; Ford, C.S.; Guthrie, C.; Weis, K. Exportin 1 (Crm1p) Is an Essential Nuclear Export Factor. Cell 1997, 90, 1041–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holaska, J.M.; Black, B.E.; Rastinejad, F.; Paschal, B.M. Ca2+-Dependent Nuclear Export Mediated by Calreticulin. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 22, 6286–6297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, B.E.; Holaska, J.M.; Rastinejad, F.; Paschal, B.M. DNA Binding Domains in Diverse Nuclear Receptors Function as Nuclear Export Signals. Curr. Biol. 2001, 11, 1749–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFranco, D.B.; Ramakrishnan, C.; Tang, Y. Molecular Chaperones and Subcellular Trafficking of Steroid Receptors. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1998, 65, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payvar, F.; DeFranco, D.; Firestone, G.L.; Edgar, B.; Wrange, Ö.; Okret, S.; Gustafsson, J.-Å.; Yamamoto, K.R. Sequence-Specific Binding of Glucocorticoid Receptor to MTV DNA at Sites within and Upstream of the Transcribed Region. Cell 1983, 35, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlman-Wright, K.; Wright, A.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Carlstedt-Duke, J. Interaction of the Glucocorticoid Receptor DNA-Binding Domain with DNA as a Dimer Is Mediated by a Short Segment of Five Amino Acids. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 3107–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäcke, H.; Schottelius, A.; Döcke, W.-D.; Strehlke, P.; Jaroch, S.; Schmees, N.; Rehwinkel, H.; Hennekes, H.; Asadullah, K. Dissociation of Transactivation from Transrepression by a Selective Glucocorticoid Receptor Agonist Leads to Separation of Therapeutic Effects from Side Effects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.; Scanlan, T.S. Design and Evaluation of Novel Nonsteroidal Dissociating Glucocorticoid Receptor Ligands. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 5199–5203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundahl, N.; Bridelance, J.; Libert, C.; De Bosscher, K.; Beck, I.M. Selective Glucocorticoid Receptor Modulation: New Directions with Non-Steroidal Scaffolds. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 152, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, A.R.; Belvisi, M.G. Maps and Legends: The Quest for Dissociated Ligands of the Glucocorticoid Receptor. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 134, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianchetti, L.; Wassmer, B.; Defosset, A.; Smertina, A.; Tiberti, M.L.; Stote, R.H.; Dejaegere, A. Alternative Dimerization Interfaces in the Glucocorticoid Receptor-α Ligand Binding Domain. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gen. Subj. 2018, 1862, 1810–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paakinaho, V.; Johnson, T.A.; Presman, D.M.; Hager, G.L. Glucocorticoid Receptor Quaternary Structure Drives Chromatin Occupancy and Transcriptional Outcome. Genome Res. 2019, 29, 1223–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurley, D.M.; Accili, D.; Stratakis, C.A.; Karl, M.; Vamvakopoulos, N.; Rorer, E.; Constantine, K.; Taylor, S.I.; Chrousos, G.P. Point Mutation Causing a Single Amino Acid Substitution in the Hormone Binding Domain of the Glucocorticoid Receptor in Familial Glucocorticoid Resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 1991, 87, 680–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wang, J.; Sauter, N.K.; Pearce, D. Steroid Receptor Heterodimerization Demonstrated in vitro and in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 12480–12484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mifsud, K.R.; Reul, J.M.H.M. Acute Stress Enhances Heterodimerization and Binding of Corticosteroid Receptors at Glucocorticoid Target Genes in the Hippocampus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 11336–11341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mifsud, K.R.; Reul, J.M.H.M. Mineralocorticoid and Glucocorticoid Receptor-Mediated Control of Genomic Responses to Stress in the Brain. Stress 2018, 21, 389–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivers, C.A.; Rogers, M.F.; Stubbs, F.E.; Conway-Campbell, B.L.; Lightman, S.L.; Pooley, J.R. Glucocorticoid Receptor–Tethered Mineralocorticoid Receptors Increase Glucocorticoid-Induced Transcriptional Responses. Endocrinology 2019, 160, 1044–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Meng, E.C.; Couch, G.S.; Croll, T.I.; Morris, J.H.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF ChimeraX: Structure Visualization for Researchers, Educators, and Developers. Protein Sci. 2021, 30, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| PDB ID | GR Region + Mutations | Species | GRE Sequence | Method | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1GDC | 439–510 / | R. norvegicus | / | Solution NMR | [96] |
| 1GLU | 440–525 / | R. norvegicus | CCAGAACATCGATGTTCTG (Consensus GRE with 4 nt spacer) | XRD | [93] |
| 1LAT | 440–515 G458E, S459G, V462A, A477K, G478Y, R479E, N480G, D481K | R. norvegicus | TTCCAGAACATGTTCTGGA | XRD | [99] |
| 1R4O | 440–525 / | R. norvegicus | CCAGAACATCGATGTTCTG (Consensus GRE with 4 nt spacer) | XRD | [93] |
| 1R4R | 440–525 / | R. norvegicus | TCAGAACATGATGTTCTCA | XRD | [93] |
| 1RGD | 440–510 / | R. norvegicus | / | Solution NMR | [97] |
| 2GDA | / | R. norvegicus | / | Solution NMR | [96] |
| 3FYL | 440–525 / | R. norvegicus | AAGAACATTTTGTCCG | XRD | [54] |
| 3G6P | 440–525 / | R. norvegicus | CCAGAACACCCTGTTCTG (FKBP5 18 bp) | XRD | [54] |
| 3G6Q | 440–525 / | R. norvegicus | TAGAACAGGGTGTTCT (FKBP5 binding site complex 9) | XRD | [54] |
| 3G6R | 440–525 / | R. norvegicus | CCAGAACAGGGTGTTCTG (FKBP5 complex-52 18 bp) | XRD | [54] |
| 3G6T | 440–525 G470^Q471insR (GRγ) | R. norvegicus | AAGAACAGGGTGTTCT (FKBP5 16 bp complex-34) | XRD | [54] |
| 3G6U | 440–525 / | R. norvegicus | AAGAACACCCTGTTCT (FKBP5 16 bp complex-49) | XRD | [54] |
| 3G8U | 440–525 | R. norvegicus | AAGAACATTGGGTTCC (GILZ 16 bp complex-5) | XRD | [54] |
| 3G8X | 440–525 | R. norvegicus | AAGAACATTGGGTTCC (GILZ 16 bp complex-65) | XRD | [54] |
| 3G97 | 440–525 | R. norvegicus | TGGAACCCAATGTTCT (GILZ 16 bp complex-9) | XRD | [54] |
| 3G99 | 440–525 | R. norvegicus | AAGAACATTTTGTTCT (Pal complex-9) | XRD | [54] |
| 3G9I | 440–525 | R. norvegicus | AAGAACATTTTGTTCT (Pal complex-35) | XRD | [54] |
| 3G9J | 440–525 | R. norvegicus | CCAGAACAAAATGTTCTG (Pal, 18 bp complex-36) | XRD | [54] |
| 3G9M | 440–525 | R. norvegicus | AAGAACATTTTGTCCG (Sgk, 16 bp complex-44) | XRD | [54] |
| 3G9O | 440–525 | R. norvegicus | AAGAACATTTTGTCCG (Sgk, 16 bp complex-9) | XRD | [54] |
| 3G9P | 440–525 / | R. norvegicus | AAGAACATTTTGTCCG (Sgk 16 bp complex 7) | XRD | [54] |
| 4HN5 | 417–506 | Homo sapiens | CGCCTCCGGGAGAGCT (TSLP IR-nGRE) | XRD | [100] |
| 4HN6 | 417–506 R460D, D462R | H. sapiens | CGCCTCCGGGAGAGCT (TSLP IR-nGRE) | XRD | [100] |
| 5CBX | 412–495 | Ancestral | CCAGAACAGAGTGTTCTG | XRD | [101] |
| 5CBY | 412–495 | Ancestral | CCAGAACAGAGTGTTCTG | XRD | [101] |
| 5CC1 | 412–495 S425G | Ancestral | CCAGAACAGAGTGTTCTG | XRD | [101] |
| 5E69 | 417–506 | H. sapiens | ATCGTGGAATTTCCTC (IL-8 ĸB-RE) | XRD | [102] |
| 5E6A | 417–506 | H. sapiens | ATCAGGAAATTCCCAG (PLAU ĸB-RE) | XRD | [102] |
| 5E6B | 417–506 | H. sapiens | CCGGGGAATTCCGCCG (RelB ĸB-RE) | XRD | [102] |
| 5E6C | 417–506 | H. sapiens | AGTGGAAATTCCCACT (CCL2 ĸB-RE) | XRD | [102] |
| 5E6D | 417–506 | H. sapiens | GCTCCGGAATTTCCAA (ICAM-1 ĸB-RE) | XRD | [102] |
| 5EMC | 411–500 | H. sapiens | CCAGAA(methyl)CATCATGTTCTG | XRD | [103] |
| 5EMP | 411–500 | H. sapiens | CCAGAACATGATGTTCTG | XRD | [103] |
| 5EMQ | 411–500 | H. sapiens | CCAGAACATCATGTTCTG | XRD | [103] |
| 5VA0 | 419–490 | H. sapiens | CGGCTGACTCATCAAG (VCAM-1 TRE) | XRD | [104] |
| 5VA7 | 419–488 | H. sapiens | AGGGTGAGTCAGGATG (IL-11 TRE) | XRD | [104] |
| 6BQU | 421–490 | H. sapiens | AAGCTAGTACATTTGC (monomeric DNA binding site) | XRD | / |
| 6BSE | 420–505 | S. oedipus | ACCACGTGTACTTTTT | XRD | / |
| 6BSF | 418–507 | H. sapiens | AAGCTAGTACATTTGC | XRD | / |
| 6CFN | 418–506 | H. sapiens | / | XRD | [98] |
| 6 × 6D | 417–490 | H. sapiens | CCAGAACGGAGCGTTCTG (pre-GRE) | XRD | [105] |
| 6X6E | 417–491 | H. sapiens | CCAGAACGGAG(methyl)CGTTCTG (methylated pre-GRE) | XRD | [105] |
| PDB ID | Ligand | GR Region + Mutations | Species | Cofactor Peptide | GRE Sequence | Method | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1M2Z | Dex | 521–777 F602S | H. sapiens | PVSPKKKENALLRYLLDKDDT (NCOA2) | / | XRD | [142] |
| 1NHZ | RU-486 | 500–777 N517D, F602S, C638D | H. sapiens | / | / | XRD | [147] |
| 1P93 | Dex | 500–777 N517D, F602S, C638D | H. sapiens | KENALLRYLLDK (NCOA2) | / | XRD | [147] |
| 3BQD | Deacyl-cortivazol (DAC) | 525–777 F602S | H. sapiens | AQQKSLLQQLLTE (NCOA1) | / | XRD | [145] |
| 3CLD | Fluticasone furoate (GW6) | 521–777 F602Y, C638G | H. sapiens | KENALLRYLLDK (NCOA2) | / | XRD | [148] |
| 3E7C | GSK866 | 521–777 F602Y, C638G | H. sapiens | ENALLRYLLDK (NCOA2) | / | XRD | [149] |
| 3GN8 | Dex | 529–777 N.A. | Ancestral | PVSPKKKENARYLLDKDDT (NCOA2) | / | XRD | [150] |
| 3H52 | RU-486 | 528–777 F602S, C638D, E684A, E688A, W712S | H. sapiens | ASNLGLEDIIRKALMGSFD (NCOR1) | / | XRD | [151] |
| 3K22 | alaninamide 10 | 521–777 F602Y, C638G | H. sapiens | KENALLRYLLDK (NCOA2) | / | XRD | [152] |
| 3K23 | D-prolinamide 11 | 521–777 F602Y, C638G | H. sapiens | KENALLRYLLDK (NCOA2) | / | XRD | [152] |
| 3MNE | Dex | 527–783 F617S | M. musculus | KENALLRYLLDKD (NCOA2) | / | XRD | [153] |
| 3MNO | Dex | 527–783 F608S, A611V | M. musculus | KENALLRYLLDKD (NCOA2) | / | XRD | [153] |
| 3MNP | Dex | 527–783 A611V, V708A, E711G | M. musculus | KENALLRYLLDKD (NCOA2) | / | XRD | [153] |
| 4CSJ | Compound 30 (NN7) | 500–777 N517D, V571M, F602S, C638D | H. sapiens | ENALLRYLLDKDD (NCOA2) | / | XRD | [154] |
| 4E2J | mometasone furoate | Synthetic 250AA fragment, ancestral GR | Ancestral | NCOA2 (741–752) | / | [155] | |
| 4LSJ | Compound 10 (LSJ) | 522–777 F602Y, C638G | H. sapiens | HSSRLWELLMEAT (Synthetic D30 peptide) | / | XRD | [156] |
| 4MDD | Compound 8 Non-steroidal antagonist | 522–777 L525S, L528S, L535A, V538T, F602Y, C638D, E684A, E688A, W712S | H. sapiens | NLGLEDIIRKALMGS (NCOR1) | / | XRD | [157] |
| 4P6W | Mometasone Furoate | 526–777 F602A, C622Y, T668V, S674T, V675I, K699A, K703A | H. sapiens | ANALLRYLLDKD (NCOA2) | / | XRD | [158] |
| 4P6X | Cortisol | 523–777 F602A, C622Y, T668V, S674T, V675I, E684A, E688A | H. sapiens | KENALLRYLLDKDD (NCOA2) | / | XRD | [158] |
| 4UDC | Dex | 500–777 N517D, F602S, C638D | H. sapiens | KENALLRYLLDKDD (NCOA2) | / | XRD | [159] |
| 4UDD | Desisobutyryl-ciclesonide | 500–777 N517D, V571M, F602S, C638D | H. sapiens | KENALLRYLLDKDD (NCOA2) | / | XRD | [159] |
| 5G3J | Compound 15 (E7T) | 500–777 N517D, V571M, F602S, C638D | H. sapiens | KENALLRYLLDKDD (NCOA2) | / | XRD | [160] |
| 5G5W | Compound 8b (R8C) | 500–777 N517D, V571M, F602S, C638D | H. sapiens | KENALLRYLLDKDD (NCOA2) | / | XRD | [161] |
| 5NFP | Budesonide | 500–777 N517D, V571M, F602S, C638D, | H. sapiens | KENALLRYLLDKDD (NCOA2) | / | XRD | [162] |
| 5NFT | AZD5423 | 500–777 N517D, V571M, F602S, C638D, E638A, W712S | H. sapiens | KENALLRYLLDKDD (NCOA2) | / | XRD | [162] |
| 5UC1 | RU-486 | 519–727 (GRβ) F599S | H. glaber | / | / | XRD | [163] |
| 5UC3 | RU-486 | 522–777 L733K, N734P | H. sapiens | / | / | XRD | / |
| 6DXK | Compound 11 | 522–777 L525S, L528S, L535A, V538T, F602Y, C638D, E684A, E688A? W712S | H. sapiens | / | / | XRD | [164] |
| 6EL6 | Compound 4 | 500–777 N517D, V571M, F602S, C638D | H. sapiens | KENALLRYLLDKDD (NCOA2) | / | XRD | [165] |
| 6EL7 | Compound 31 | 500–777 N517D, V571M, F602S, C638D, E684A, W712S | H. sapiens | KENALLRYLLDKDD (NCOA2) | / | XRD | [165] |
| 6EL9 | AZD9567 | 500–777 N517D, V571M, F602S, C638D, E684A, W712S | H. sapiens | KENALLRYLLDKDD (NCOA2) | / | XRD | [165] |
| 6NWK | Dex | 529–777 N.A. | Ancestral | PSLLKKLLLAPA (PGC1α) | / | XRD | [166] |
| 6NWL | Cortisol | 529–777 N.A. | Ancestral | PSLLKKLLLAPA (PGC1α) | / | XRD | [166] |
| 7KRJ | Dex | 520–777 F602S | H. sapiens | Hsp90, p23 (full-length) | / | CEM | [167] |
| 7KW7 | / | Full-length (LBD structure) | H. sapiens | Hsp90, Hsp70, Hop (full-length) | / | CEM | [168] |
| 7PRV | Fluticasone furoate (GW6) | 385–777 S404A N517D V571M F602S C638D | H. sapiens | PPQEAEEPSLLKKLLLAPANT (PGC1α) | TACAGAACATTTTGTCCGTCGAC (Sgk1 23 bp; overhang) | XRD | [122] |
| 7PRW | Velsecorat | 385–777 S404A N517D V571M F602S C638D | H. sapiens | PPQEAEEPSLLKKLLLAPANT (PGC1α) | GTACAGAACATTTTGTCCGTCGA (Sgk1 23 bp; blunt) | XRD | [122] |
| 7PRX | Velsecorat | 529–777 | H. sapiens | PPQEAEEPSLLKKLLLAPANT (PGC1α) | / | XRD | [122] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deploey, N.; Van Moortel, L.; Rogatsky, I.; Peelman, F.; De Bosscher, K. The Biologist’s Guide to the Glucocorticoid Receptor’s Structure. Cells 2023, 12, 1636. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12121636
Deploey N, Van Moortel L, Rogatsky I, Peelman F, De Bosscher K. The Biologist’s Guide to the Glucocorticoid Receptor’s Structure. Cells. 2023; 12(12):1636. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12121636
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeploey, Nick, Laura Van Moortel, Inez Rogatsky, Frank Peelman, and Karolien De Bosscher. 2023. "The Biologist’s Guide to the Glucocorticoid Receptor’s Structure" Cells 12, no. 12: 1636. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12121636
APA StyleDeploey, N., Van Moortel, L., Rogatsky, I., Peelman, F., & De Bosscher, K. (2023). The Biologist’s Guide to the Glucocorticoid Receptor’s Structure. Cells, 12(12), 1636. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12121636






