Potential Therapeutic Effects of PPAR Ligands in Glioblastoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors
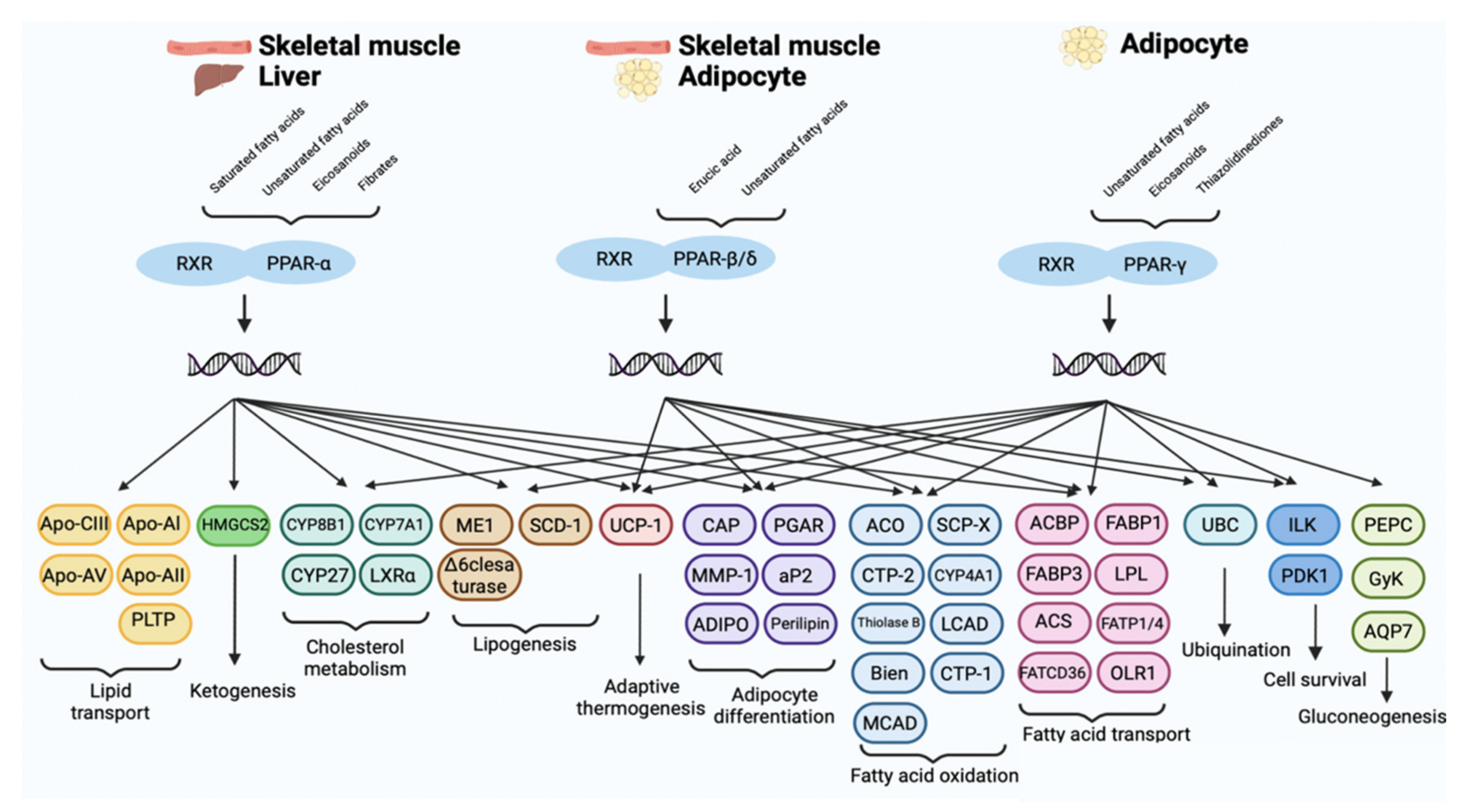
PPARs Isoforms: Tissue Distribution and Biological Activity
3. Role of PPARs in Tumors
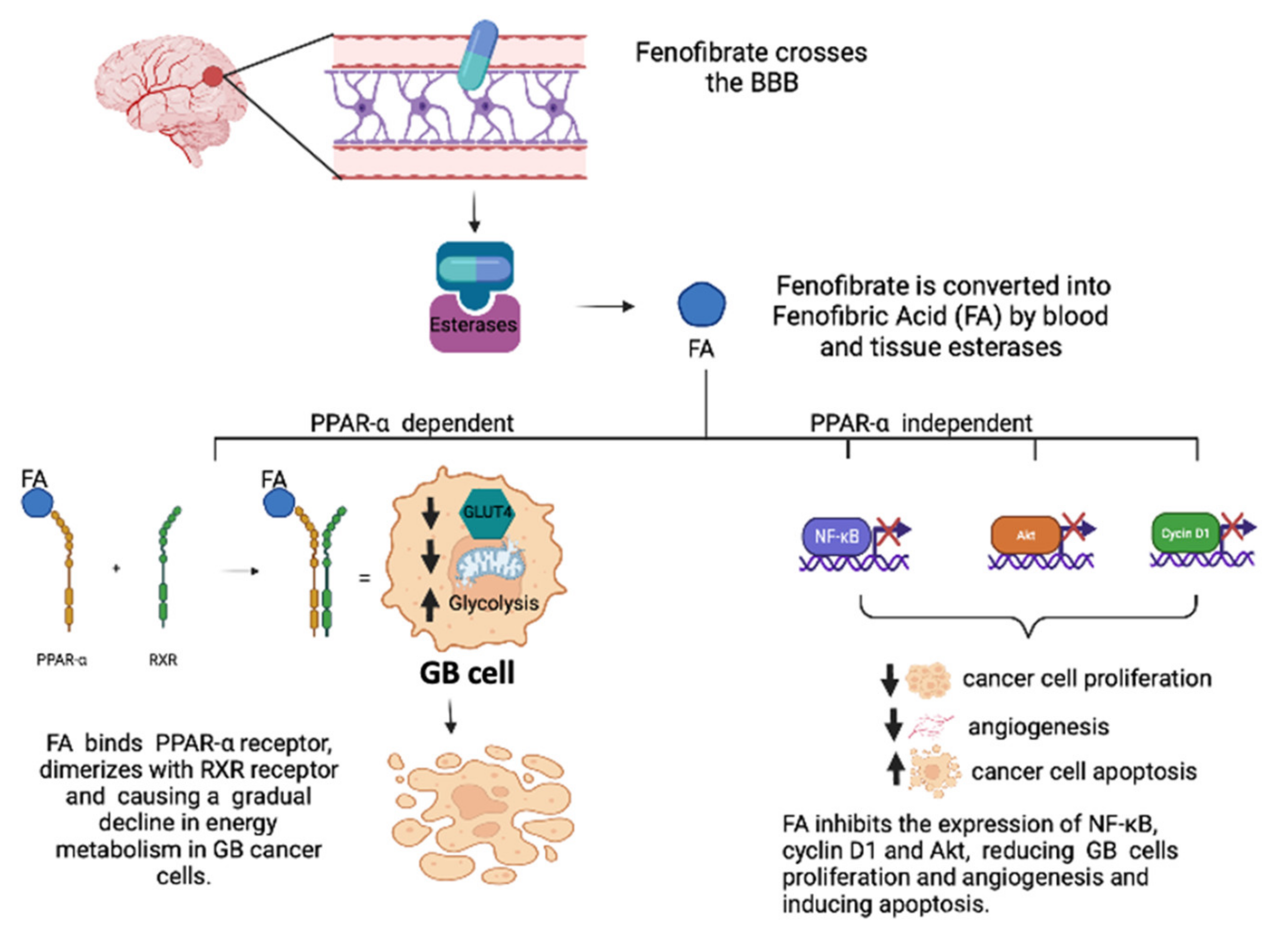
3.1. Role of PPAR-α Agonists in GB
3.2. Role of PPAR-β/δ in GB
3.3. Role of PPAR-γ Agonists in GB
4. Conclusions and Future Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kapoor, M.; Gupta, V. Astrocytoma; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Le Rhun, E.; Preusser, M.; Roth, P.; Reardon, D.A.; Van den Bent, M.; Wen, P.; Reifenberger, G.; Weller, M. Molecular targeted therapy of glioblastoma. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2019, 80, 101896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajaraman, P.; Melin, B.S.; Wang, Z.; McKean-Cowdin, R.; Michaud, D.S.; Wang, S.S.; Bondy, M.; Houlston, R.; Jenkins, R.B.; Wrensch, M.; et al. Genome-wide association study of glioma and meta-analysis. Hum. Genet. 2012, 131, 1877–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wrensch, M.; Jenkins, R.B.; Chang, J.S.; Yeh, R.F.; Xiao, Y.; Decker, P.A.; Ballman, K.V.; Berger, M.; Buckner, J.C.; Chang, S.; et al. Variants in the CDKN2B and RTEL1 regions are associated with high-grade glioma susceptibility. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 905–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardizzone, A.; Scuderi, S.A.; Giuffrida, D.; Colarossi, C.; Puglisi, C.; Campolo, M.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Esposito, E.; Paterniti, I. Role of Fibroblast Growth Factors Receptors (FGFRs) in Brain Tumors, Focus on Astrocytoma and Glioblastoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 3825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoyanov, G.S.; Dzhenkov, D.L. On the Concepts and History of Glioblastoma Multiforme-Morphology, Genetics and Epigenetics. Folia Med. 2018, 60, 48–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sasmita, A.O.; Wong, Y.P.; Ling, A.P.K. Biomarkers and therapeutic advances in glioblastoma multiforme. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 14, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patel, A.P.; Tirosh, I.; Trombetta, J.J.; Shalek, A.K.; Gillespie, S.M.; Wakimoto, H.; Cahill, D.P.; Nahed, B.V.; Curry, W.T.; Martuza, R.L.; et al. Single-cell RNA-seq highlights intratumoral heterogeneity in primary glioblastoma. Science 2014, 344, 1396–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stupp, R.; Mason, W.P.; Van den Bent, M.J.; Weller, M.; Fisher, B.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Belanger, K.; Brandes, A.A.; Marosi, C.; Bogdahn, U.; et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N. Eng. J. Med. 2005, 352, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupp, R.; Hegi, M.E.; Mason, W.P.; Van den Bent, M.J.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Janzer, R.C.; Ludwin, S.K.; Allgeier, A.; Fisher, B.; Belanger, K.; et al. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Kim, L.J.; Wang, X.; Wu, Q.; Sanvoranart, T.; Hubert, C.G.; Prager, B.C.; Wallace, L.C.; Jin, X.; Mack, S.C.; et al. Nicotinamide metabolism regulates glioblastoma stem cell maintenance. JCI Insight 2017, 2, e90019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pozzi, V.; Salvolini, E.; Lucarini, G.; Salvucci, A.; Campagna, R.; Rubini, C.; Sartini, D.; Emanuelli, M. Cancer stem cell enrichment is associated with enhancement of nicotinamide N-methyltransferase expression. IUBMB Life 2020, 72, 1415–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegi, M.E.; Diserens, A.C.; Gorlia, T.; Hamou, M.F.; De Tribolet, N.; Weller, M.; Kros, J.M.; Hainfellner, J.A.; Mason, W.; Mariani, L.; et al. MGMT gene silencing and benefit from temozolomide in glioblastoma. N. Eng. J. Med. 2005, 352, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Riemenschneider, M.J.; Hegi, M.E.; Reifenberger, G. MGMT promoter methylation in malignant gliomas. Target. Oncol. 2010, 5, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, M.T.C.; Keni, S.; Vimalan, V.; Ip, C.; Smith, C.; Erridge, S.; Weir, C.J.; Brennan, P.M. Extent of MGMT promoter methylation modifies the effect of temozolomide on overall survival in patients with glioblastoma: A regional cohort study. Neurooncol. Adv. 2021, 3, vdab171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derosa, G.; Sahebkar, A.; Maffioli, P. The role of various peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors and their ligands in clinical practice. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtowicz, S.; Strosznajder, A.K.; Jezyna, M.; Strosznajder, J.B. The Novel Role of PPAR Alpha in the Brain: Promising Target in Therapy of Alzheimer’s Disease and Other Neurodegenerative Disorders. Neurochem. Res. 2020, 45, 972–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Villapol, S. Roles of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma on Brain and Peripheral Inflammation. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 38, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cimini, A.; Cristiano, L.; Colafarina, S.; Benedetti, E.; Di Loreto, S.; Festuccia, C.; Amicarelli, F.; Canuto, R.A.; Ceru, M.P. PPARgamma-dependent effects of conjugated linoleic acid on the human glioblastoma cell line (ADF). Int. J. Cancer 2005, 117, 923–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidoamore, A.; Cristiano, L.; Laezza, C.; Galzio, R.; Benedetti, E.; Cinque, B.; Antonosante, A.; d’Angelo, M.; Castelli, V.; Cifone, M.G.; et al. Energy metabolism in glioblastoma stem cells: PPARalpha a metabolic adaptor to intratumoral microenvironment. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 108430–108450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ellis, H.P.; Kurian, K.M. Biological Rationale for the Use of PPARgamma Agonists in Glioblastoma. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, L.S.; Wells, R.A. Cross-Talk between PPARs and the Partners of RXR: A Molecular Perspective. PPAR Res. 2009, 2009, 925309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yousefnia, S.; Momenzadeh, S.; Seyed Forootan, F.; Ghaedi, K.; Nasr Esfahani, M.H. The influence of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) ligands on cancer cell tumorigenicity. Gene 2018, 649, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, A.Z.; Althagafi, I.I.; Shamshad, H. Role of PPAR receptor in different diseases and their ligands: Physiological importance and clinical implications. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 166, 502–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasui, Y.; Kim, M.; Tanaka, T. PPAR Ligands for Cancer Chemoprevention. PPAR Res. 2008, 2008, 548919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lazennec, G.; Canaple, L.; Saugy, D.; Wahli, W. Activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) by their ligands and protein kinase A activators. Mol. Endocrinol. 2000, 14, 1962–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunmeir, R.; Xu, F. Functional Regulation of PPARs through Post-Translational Modifications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grygiel-Gorniak, B. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors and their ligands: Nutritional and clinical implications—A review. Nutr. J. 2014, 13, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takeyama, K.; Kodera, Y.; Suzawa, M.; Kato, S. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)—Structure, function, tissue distribution, gene expression. Nihon Rinsho 2000, 58, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mishra, A.; Chaudhary, A.; Sethi, S. Oxidized omega-3 fatty acids inhibit NF-kappaB activation via a PPARalpha-dependent pathway. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2004, 24, 1621–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, L.; Shen, W.J.; Bittner, S.; Kraemer, F.B.; Azhar, S. PPARs: Regulators of metabolism and as therapeutic targets in cardiovascular disease. Part I: PPAR-alpha. Future Cardiol. 2017, 13, 259–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, K.D.; Wagner, N. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor beta/delta (PPARbeta/delta) acts as regulator of metabolism linked to multiple cellular functions. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 125, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strosznajder, A.K.; Wojtowicz, S.; Jezyna, M.J.; Sun, G.Y.; Strosznajder, J.B. Recent Insights on the Role of PPAR-beta/delta in Neuroinflammation and Neurodegeneration, and Its Potential Target for Therapy. Neuromolecular. Med. 2021, 23, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Colby, J.K.; Zuo, X.; Jaoude, J.; Wei, D.; Shureiqi, I. The Role of PPAR-delta in Metabolism, Inflammation, and Cancer: Many Characters of a Critical Transcription Factor. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Altinoz, M.A.; Elmaci, I.; Hacimuftuoglu, A.; Ozpinar, A.; Hacker, E.; Ozpinar, A. PPARdelta and its ligand erucic acid may act anti-tumoral, neuroprotective, and myelin protective in neuroblastoma, glioblastoma, and Parkinson’s disease. Mol. Aspects Med. 2021, 78, 100871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marion-Letellier, R.; Savoye, G.; Ghosh, S. Fatty acids, eicosanoids and PPAR gamma. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 785, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takada, I.; Makishima, M. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor agonists and antagonists: A patent review (2014–present). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2020, 30, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.S.; Yip, Y.S.; Lim, E.K.Y.; Wahli, W.; Tan, N.S. PPARs and Tumor Microenvironment: The Emerging Roles of the Metabolic Master Regulators in Tumor Stromal-Epithelial Crosstalk and Carcinogenesis. Cancers 2021, 13, 2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandran, K.; Goswami, S.; Sharma-Walia, N. Implications of a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha) ligand clofibrate in breast cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 15577–15599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigeto, T.; Yokoyama, Y.; Xin, B.; Mizunuma, H. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha and gamma ligands inhibit the growth of human ovarian cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2007, 18, 833–840. [Google Scholar]
- Castelli, V.; Catanesi, M.; Alfonsetti, M.; Laezza, C.; Lombardi, F.; Cinque, B.; Cifone, M.G.; Ippoliti, R.; Benedetti, E.; Cimini, A.; et al. PPARalpha-Selective Antagonist GW6471 Inhibits Cell Growth in Breast Cancer Stem Cells Inducing Energy Imbalance and Metabolic Stress. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, N.; Wagner, K.D. PPAR Beta/Delta and the Hallmarks of Cancer. Cells 2020, 9, 1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, S.; Wagner, N.; Wagner, K.D. The Emerging Role of PPAR Beta/Delta in Tumor Angiogenesis. PPAR Res. 2020, 2020, 3608315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.C.; Chan, T.A.; Vogelstein, B.; Kinzler, K.W. PPARdelta is an APC-regulated target of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Cell 1999, 99, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Deguchi, Y.; Tian, R.; Wei, D.; Wu, L.; Chen, W.; Xu, W.; Xu, M.; Liu, F.; Gao, S.; et al. Pleiotropic Effects of PPARD Accelerate Colorectal Tumorigenesis, Progression, and Invasion. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 954–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wagner, K.D.; Benchetrit, M.; Bianchini, L.; Michiels, J.F.; Wagner, N. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor beta/delta (PPARbeta/delta) is highly expressed in liposarcoma and promotes migration and proliferation. J. Pathol. 2011, 224, 575–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, G.; Shi, Y.; Sun, L.; Gorczynski, R.; Li, Y.J.; Xu, Z.; Spaner, D.E. PPAR-delta promotes survival of breast cancer cells in harsh metabolic conditions. Oncogenesis 2016, 5, e232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elix, C.; Pal, S.K.; Jones, J.O. The role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma in prostate cancer. Asian J. Androl. 2018, 20, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, S.M.; Materazzi, G.; Baldini, E.; Ulisse, S.; Miccoli, P.; Antonelli, A.; Fallahi, P. Antineoplastic Effects of PPARgamma Agonists, with a Special Focus on Thyroid Cancer. Curr. Med. Chem. 2016, 23, 636–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammu, R.K.; Garikapati, K.K.; Krishnamurthy, P.T.; Chintamaneni, P.K.; Pindiprolu, S.K.S. Possible role of PPAR-gamma and COX-2 receptor modulators in the treatment of Non-Small Cell lung carcinoma. Med. Hypotheses 2019, 124, 98–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatino, L.; Pancione, M.; Votino, C.; Colangelo, T.; Lupo, A.; Novellino, E.; Lavecchia, A.; Colantuoni, V. Emerging role of the beta-catenin-PPARgamma axis in the pathogenesis of colorectal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 7137–7151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalano, S.; Mauro, L.; Bonofiglio, D.; Pellegrino, M.; Qi, H.; Rizza, P.; Vizza, D.; Bossi, G.; Ando, S. In vivo and in vitro evidence that PPARgamma ligands are antagonists of leptin signaling in breast cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 179, 1030–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawayama, H.; Ishimoto, T.; Watanabe, M.; Yoshida, N.; Sugihara, H.; Kurashige, J.; Hirashima, K.; Iwatsuki, M.; Baba, Y.; Oki, E.; et al. Small molecule agonists of PPAR-gamma exert therapeutic effects in esophageal cancer. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keshamouni, V.G.; Reddy, R.C.; Arenberg, D.A.; Joel, B.; Thannickal, V.J.; Kalemkerian, G.P.; Standiford, T.J. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma activation inhibits tumor progression in non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncogene 2004, 23, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galbraith, L.C.A.; Mui, E.; Nixon, C.; Hedley, A.; Strachan, D.; MacKay, G.; Sumpton, D.; Sansom, O.J.; Leung, H.Y.; Ahmad, I. PPAR-gamma induced AKT3 expression increases levels of mitochondrial biogenesis driving prostate cancer. Oncogene 2021, 40, 2355–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meylan, P.; Pich, C.; Winkler, C.; Ginster, S.; Mury, L.; Sgandurra, M.; Dreos, R.; Frederick, D.T.; Hammond, M.; Boland, G.M.; et al. Low expression of the PPARgamma-regulated gene thioredoxin-interacting protein accompanies human melanoma progression and promotes experimental lung metastases. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, H.R.; White, P.; Hares, K.M.; Redondo, J.; Kemp, K.C.; Singleton, W.G.B.; Killick-Cole, C.L.; Stevens, J.R.; Garadi, K.; Guglani, S.; et al. The transcription factor PPARalpha is overexpressed and is associated with a favourable prognosis in IDH-wildtype primary glioblastoma. Histopathology 2017, 70, 1030–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, E.; d’Angelo, M.; Ammazzalorso, A.; Gravina, G.L.; Laezza, C.; Antonosante, A.; Panella, G.; Cinque, B.; Cristiano, L.; Dhez, A.C.; et al. PPARalpha Antagonist AA452 Triggers Metabolic Reprogramming and Increases Sensitivity to Radiation Therapy in Human Glioblastoma Primary Cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2017, 232, 1458–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Han, D.; Sun, L.; Huang, Q.; Gai, G.; Wu, Z.; Meng, W.; Chen, X. PPARalpha Regulates the Proliferation of Human Glioma Cells through miR-214 and E2F2. Biomed. Res. Int 2018, 2018, 3842753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, Y.; Luan, W.; Tao, T.; Wang, J.; Qian, J.; Dong, Q.; Liu, N.; You, Y. Expression of peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor in glioma and its effect on the growth of human glioma cells. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi 2014, 31, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabacka, M.; Plonka, P.M.; Urbanska, K.; Reiss, K. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha activation decreases metastatic potential of melanoma cells in vitro via down-regulation of Akt. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 3028–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Urbanska, K.; Pannizzo, P.; Grabacka, M.; Croul, S.; Del Valle, L.; Khalili, K.; Reiss, K. Activation of PPARalpha inhibits IGF-I-mediated growth and survival responses in medulloblastoma cell lines. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 123, 1015–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stalinska, J.; Zimolag, E.; Pianovich, N.A.; Zapata, A.; Lassak, A.; Rak, M.; Dean, M.; Ucar-Bilyeu, D.; Wyczechowska, D.; Culicchia, F.; et al. Chemically Modified Variants of Fenofibrate with Antiglioblastoma Potential. Transl. Oncol. 2019, 12, 895–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilk, A.; Wyczechowska, D.; Zapata, A.; Dean, M.; Mullinax, J.; Marrero, L.; Parsons, C.; Peruzzi, F.; Culicchia, F.; Ochoa, A.; et al. Molecular mechanisms of fenofibrate-induced metabolic catastrophe and glioblastoma cell death. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2015, 35, 182–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Binello, E.; Mormone, E.; Emdad, L.; Kothari, H.; Germano, I.M. Characterization of fenofibrate-mediated anti-proliferative pro-apoptotic effects on high-grade gliomas and anti-invasive effects on glioma stem cells. J. Neurooncol. 2014, 117, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.F.; Zhang, J.X.; Wei, W.J.; Tao, T.; Hu, Q.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wang, X.F.; Liu, N.; You, Y.P. Fenofibrate induces G0/G1 phase arrest by modulating the PPARalpha/FoxO1/p27 kip pathway in human glioblastoma cells. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 3823–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drukala, J.; Urbanska, K.; Wilk, A.; Grabacka, M.; Wybieralska, E.; Del Valle, L.; Madeja, Z.; Reiss, K. ROS accumulation and IGF-IR inhibition contribute to fenofibrate/PPARalpha-mediated inhibition of glioma cell motility in vitro. Mol. Cancer 2010, 9, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, C.; Lai, S.W.; Shen, C.K.; Chen, C.W.; Tsai, C.F.; Liu, Y.S.; Lu, D.Y.; Huang, B.R. Fenofibrate inhibits hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha and carbonic anhydrase expression through activation of AMP-activated protein kinase/HO-1/Sirt1 pathway in glioblastoma cells. Environ. Toxicol. 2021, 36, 2551–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.C.; Zang, C.B.; Liu, H.Y.; Possinger, K.; Fan, S.G.; Elstner, E. A novel PPAR alpha/gamma dual agonist inhibits cell growth and induces apoptosis in human glioblastoma T98G cells. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2004, 25, 1312–1319. [Google Scholar]
- Khoo, N.K.; Hebbar, S.; Zhao, W.; Moore, S.A.; Domann, F.E.; Robbins, M.E. Differential activation of catalase expression and activity by PPAR agonists: Implications for astrocyte protection in anti-glioma therapy. Redox Biol. 2013, 1, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schnegg, C.I.; Kooshki, M.; Hsu, F.C.; Sui, G.; Robbins, M.E. PPARdelta prevents radiation-induced proinflammatory responses in microglia via transrepression of NF-kappaB and inhibition of the PKCalpha/MEK1/2/ERK1/2/AP-1 pathway. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 52, 1734–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Altinoz, M.A.; Bilir, A.; Elmaci, I. Erucic acid, a component of Lorenzo’s oil and PPAR-delta ligand modifies C6 glioma growth and toxicity of doxorubicin. Experimental data and a comprehensive literature analysis. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2018, 294, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagnolo, A.; Grant, E.N.; Glick, R.; Lichtor, T.; Feinstein, D.L. Differential effects of PPARgamma agonists on the metabolic properties of gliomas and astrocytes. Neurosci. Lett. 2007, 417, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morosetti, R.; Servidei, T.; Mirabella, M.; Rutella, S.; Mangiola, A.; Maira, G.; Mastrangelo, R.; Koeffler, H.P. The PPARgamma ligands PGJ2 and rosiglitazone show a differential ability to inhibit proliferation and to induce apoptosis and differentiation of human glioblastoma cell lines. Int. J. Oncol. 2004, 25, 493–502. [Google Scholar]
- Strakova, N.; Ehrmann, J.; Dzubak, P.; Bouchal, J.; Kolar, Z. The synthetic ligand of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma ciglitazone affects human glioblastoma cell lines. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2004, 309, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, M.W.; Kim, D.S.; Kim, H.R.; Kim, H.J.; Yang, J.M.; Ryu, S.; Noh, Y.H.; Lee, S.H.; Son, M.H.; Jung, H.L.; et al. Cell death is induced by ciglitazone, a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) agonist, independently of PPARgamma in human glioma cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 417, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, A.; Mondal, P.; Ghosh, S.; Mehta, V.S.; Sen, E. PPARgamma regulated CIDEA affects pro-apoptotic responses in glioblastoma. Cell Death Discov. 2015, 1, 15038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wan, Z.; Shi, W.; Shao, B.; Shi, J.; Shen, A.; Ma, Y.; Chen, J.; Lan, Q. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma agonist pioglitazone inhibits beta-catenin-mediated glioma cell growth and invasion. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2011, 349, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ching, J.; Amiridis, S.; Stylli, S.S.; Bjorksten, A.R.; Kountouri, N.; Zheng, T.; Paradiso, L.; Luwor, R.B.; Morokoff, A.P.; O’Brien, T.J.; et al. The peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma agonist pioglitazone increases functional expression of the glutamate transporter excitatory amino acid transporter 2 (EAAT2) in human glioblastoma cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 21301–21314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grommes, C.; Karlo, J.C.; Caprariello, A.; Blankenship, D.; Dechant, A.; Landreth, G.E. The PPARgamma agonist pioglitazone crosses the blood-brain barrier and reduces tumor growth in a human xenograft model. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2013, 71, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grommes, C.; Conway, D.S.; Alshekhlee, A.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. Inverse association of PPARgamma agonists use and high grade glioma development. J. Neurooncol. 2010, 100, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, C.K.; Alphonse-Sullivan, N.; Isom, S.; Metheny-Barlow, L.J.; Cummings, T.L.; Page, B.R.; Brown, D.R.; Blackstock, A.W., Jr.; Peiffer, A.M.; Strowd, R.E.; et al. Safety of pioglitazone during and after radiation therapy in patients with brain tumors: A phase I clinical trial. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 145, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korbecki, J.; Bobinski, R.; Dutka, M. Self-regulation of the inflammatory response by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors. Inflamm. Res. 2019, 68, 443–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bundscherer, A.; Reichle, A.; Hafner, C.; Meyer, S.; Vogt, T. Targeting the tumor stroma with peroxisome proliferator activated receptor (PPAR) agonists. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2009, 9, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, A.; Macaluso, M. Fenofibrate triggers apoptosis of glioblastoma cells in vitro: New insights for therapy. Cell Cycle 2012, 11, 3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tapia-Perez, J.H.; Kirches, E.; Mawrin, C.; Firsching, R.; Schneider, T. Cytotoxic effect of different statins and thiazolidinediones on malignant glioma cells. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2011, 67, 1193–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Drug | Target | Effects | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fenofibrate | PPAR-α | -Repression of GLUT4 -Inhibition of NF-κB, cyclin D1 and Akt expression | [63,64,65,66,67,68] |
| TZD18 | PPAR-α/PPAR-γ | -Activation of caspase-3 -Reduction of Bcl-2 expression | [69] |
| PGJ2 Rosiglitazone | PPAR-γ | -Induction of G2/M arrest | [74] |
| Ciglitazone | PPAR-γ | -Reduction of telomerase activity -Reduction Akt and Bcl-2 expression | [75,76] |
| Pioglitazone | PPAR-γ | -Reduction β-catenin expression -Increase EAAT2 expression | [78,79,80] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Basilotta, R.; Lanza, M.; Casili, G.; Chisari, G.; Munao, S.; Colarossi, L.; Cucinotta, L.; Campolo, M.; Esposito, E.; Paterniti, I. Potential Therapeutic Effects of PPAR Ligands in Glioblastoma. Cells 2022, 11, 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11040621
Basilotta R, Lanza M, Casili G, Chisari G, Munao S, Colarossi L, Cucinotta L, Campolo M, Esposito E, Paterniti I. Potential Therapeutic Effects of PPAR Ligands in Glioblastoma. Cells. 2022; 11(4):621. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11040621
Chicago/Turabian StyleBasilotta, Rossella, Marika Lanza, Giovanna Casili, Giulia Chisari, Stefania Munao, Lorenzo Colarossi, Laura Cucinotta, Michela Campolo, Emanuela Esposito, and Irene Paterniti. 2022. "Potential Therapeutic Effects of PPAR Ligands in Glioblastoma" Cells 11, no. 4: 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11040621
APA StyleBasilotta, R., Lanza, M., Casili, G., Chisari, G., Munao, S., Colarossi, L., Cucinotta, L., Campolo, M., Esposito, E., & Paterniti, I. (2022). Potential Therapeutic Effects of PPAR Ligands in Glioblastoma. Cells, 11(4), 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11040621









