Pharmacological Profile of MP-101, a Novel Non-racemic Mixture of R- and S-dimiracetam with Increased Potency in Rat Models of Cognition, Depression and Neuropathic Pain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Materials
2.3. Synaptosome Purification
2.4. Release Experiments
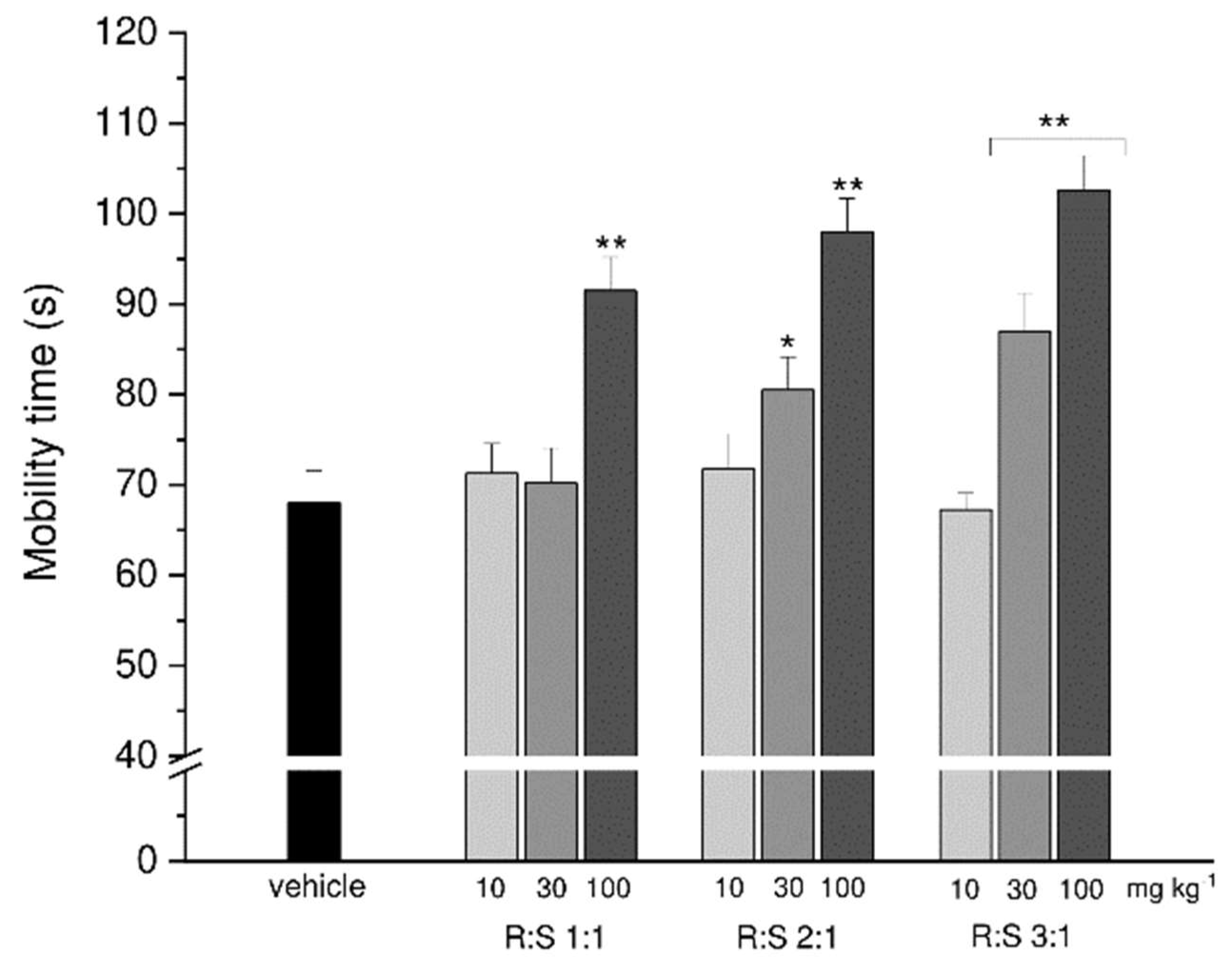
2.5. Sodium Monoiodoacetate-Induced Osteoarthritis Model
2.6. Oxaliplatin-Induced Neuropathic Pain Model
2.7. Assessment of Mechanical Hyperalgesia (Paw Pressure Test)
2.8. Assessment of Mechanical Allodynia (Von Frey Test)
2.9. Assessment of Thermal Allodynia (Cold Plate Test)
2.10. Assessment of Amnesic-like Behavior in Mice (Passive Avoidance Test)
2.11. Assessment of Depressive-like Behavior in Mice (Forced Swimming Test)
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
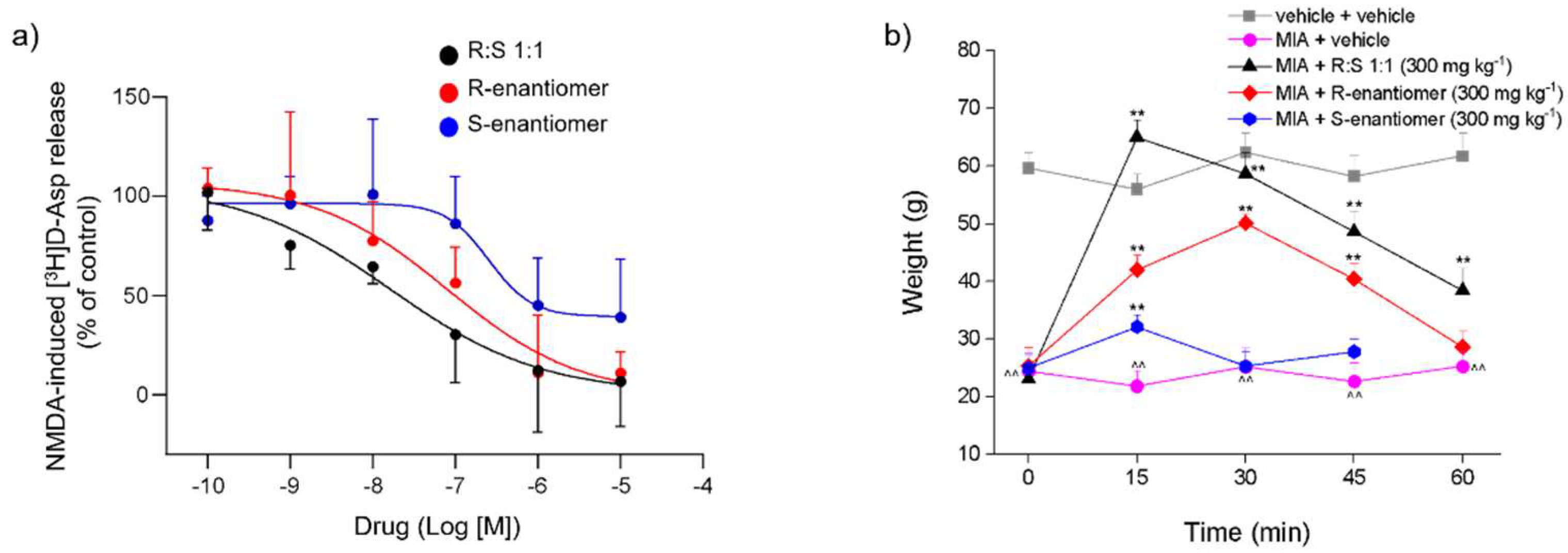
3.1. Effects of Dimiracetam (R:S 1:1) and Its Individual R- and S-enantiomers on the NMDA-Evoked Release of [3H]D-Asp from Rat Spinal Cord Synaptosomes
3.2. Effect of a Single Administration of Racemic Dimiracetam (R:S 1:1) and Its Isolated R- and S-enantiomers in an MIA-Induced Osteoarthritis Model
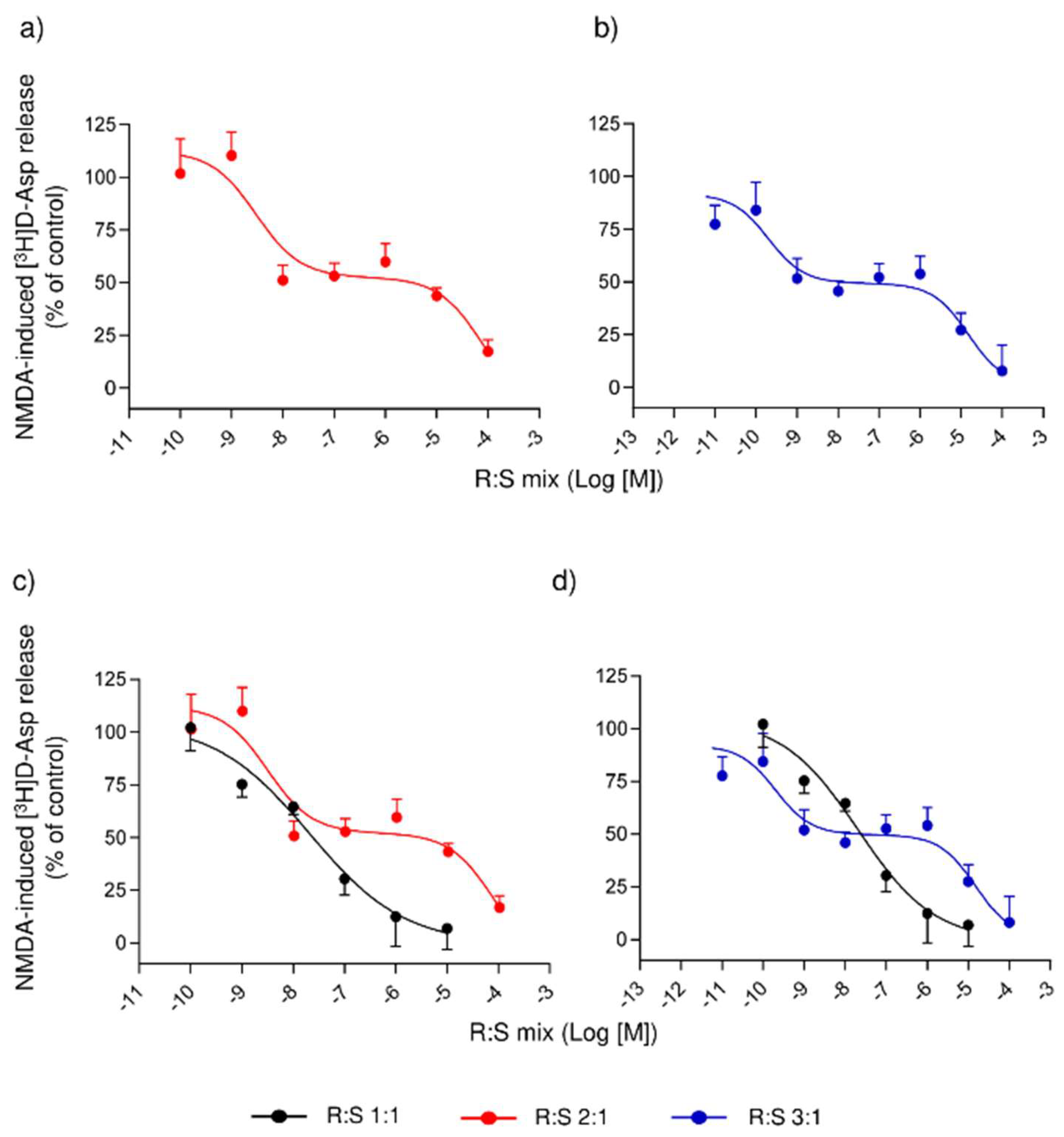
3.3. Comparison of Several Enantiomeric Mixtures in a Ratio of R- to S- Varying from 2:1 to 19:1, in Inhibiting the NMDA-Evoked Release of [3H]D-Asp from Rat Spinal Cord Synaptosomes
3.4. Effect of a Single Administration of R:S 3:1 and R:S 1:3 Enantiomeric Mixtures of Dimiracetam in the Rat Model of MIA-Induced Osteoarthritis
3.5. Effect of a Repeated Treatment with R:S 1:1 and R:S 3:1 (MP-101) Enantiomeric Mixtures of Dimiracetam in the Rat Oxaliplatin-Induced Neuropathic Pain Model
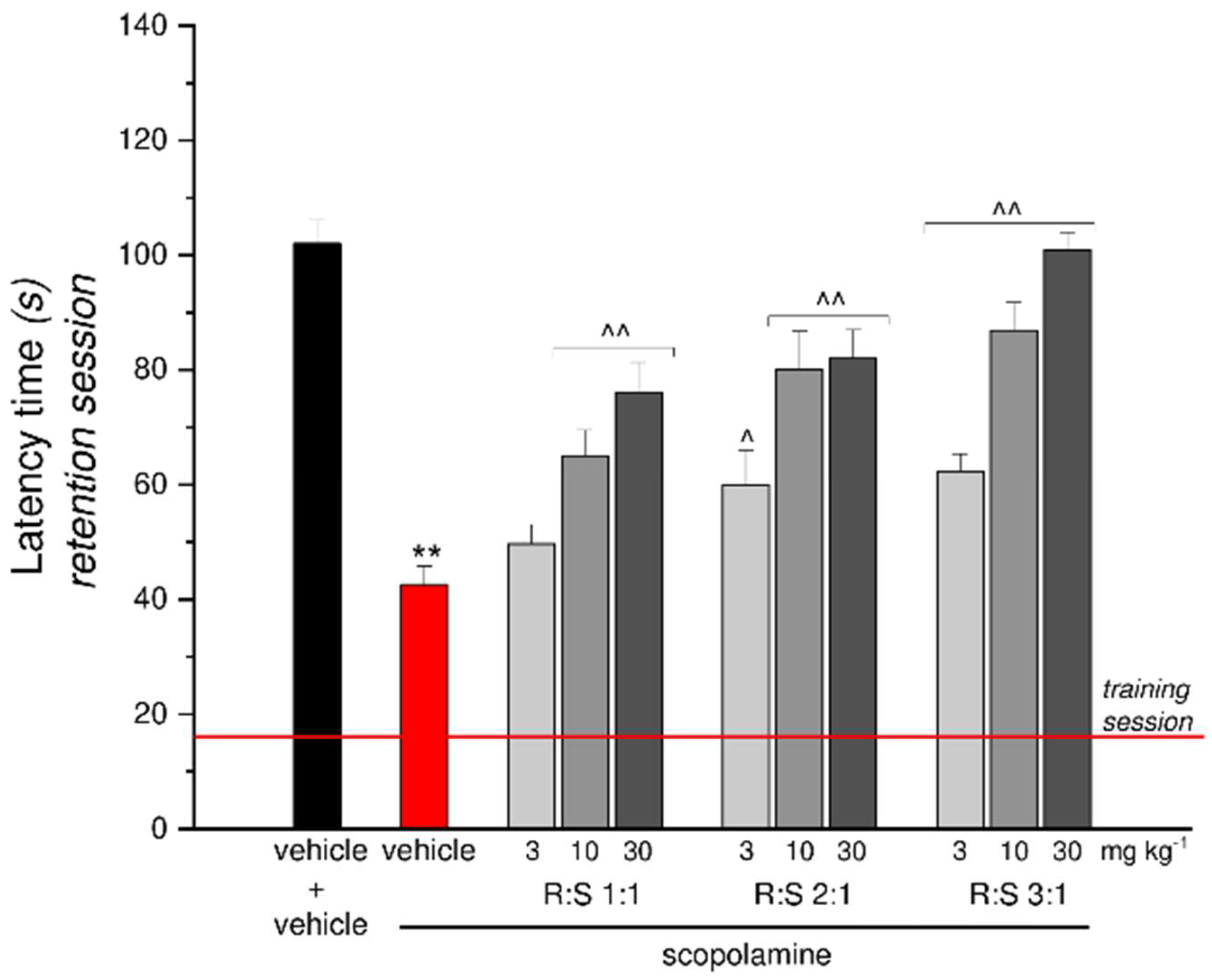
3.6. Effect of a Single Administration of R:S 1:1, 2:1 and 3:1 Mixtures against Scopolamine-Induced Amnesia
3.7. Effect of Single Administration of R:S 1:1, 2:1 and 3:1 Mixtures in a Depression Mouse Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Pinza, M.; Farina, C.; Cerri, A.; Pfeiffer, U.; Riccaboni, M.T.; Banfi, S.; Biagetti, R.; Pozzi, O.; Magnani, M.; Dorigotti, L. Synthesis and Pharmacological Activity of a Series of Dihydro-1H-Pyrrolo[1,2-a]Imidazole-2,5(3H,6H)-Diones, a Novel Class of Potent Cognition Enhancers. J. Med. Chem. 1993, 36, 4214–4220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fariello, R.G.; Ghelardini, C.; Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Zanardelli, M.; Farina, C. Antidepressant-like Activity of Dimiracetam (NT-11624) in the Rat Forced Swimming Test. In Proceedings of the Neuroscience Annual Meeting, Washington, DC, USA, 12–16 November 2011; p. Program n 789.08/EE25. [Google Scholar]
- Fariello, R.G.; Ghelardini, C.; Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Bonanno, G.; Pittaluga, A.; Milanese, M.; Misiano, P.; Farina, C. Broad Spectrum and Prolonged Efficacy of Dimiracetam in Models of Neuropathic Pain. Neuropharmacology 2014, 81, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flicker, L.; Grimley Evans, G. Piracetam for Dementia or Cognitive Impairment. Cochrane database Syst. Rev. 2001, CD001011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schifano, F.; Catalani, V.; Sharif, S.; Napoletano, F.; Corkery, J.M.; Arillotta, D.; Fergus, S.; Vento, A.; Guirguis, A. Benefits and Harms of “Smart Drugs” (Nootropics) in Healthy Individuals. Drugs 2022, 82, 633–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gower, A.J.; Noyer, M.; Verloes, R.; Gobert, J.; Wülfert, E. Ucb L059, a Novel Anti-Convulsant Drug: Pharmacological Profile in Animals. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1992, 222, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beran, R.G.; Spira, P.J. Levetiracetam in Chronic Daily Headache: A Double-Blind, Randomised Placebo-Controlled Study. (The Australian KEPPRA Headache Trial [AUS-KHT]). Cephalalgia 2011, 31, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capuano, A.; Vollono, C.; Mei, D.; Pierguidi, L.; Ferraro, D.; Di Trapani, G. Antiepileptic Drugs in Migraine Prophylaxis: State of the Art. Clin. Ter. 2004, 155, 79–87. [Google Scholar]
- Krusz, J.C. Levetiracetam as Prophylaxis for Resistant Headaches. Cephalalgia 2001, 21, 373. [Google Scholar]
- Holbech, J.V.; Otto, M.; Bach, F.W.; Jensen, T.S.; Sindrup, S.H. The Anticonvulsant Levetiracetam for the Treatment of Pain in Polyneuropathy: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Cross-over Trial. Eur. J. Pain 2011, 15, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsikostas, D.D.; Pantes, G.V.; Avramidis, T.G.; Karageorgiou, K.E.; Gatzonis, S.D.; Stathis, P.G.; Fili, V.A.; Siatouni, A.D.; Vikelis, M. An Observational Trial to Investigate the Efficacy and Tolerability of Levetiracetam in Trigeminal Neuralgia. Headache 2010, 50, 1371–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, M.H.; Ueda, H. Nonopioid and Neuropathy-Specific Analgesic Action of the Nootropic Drug Nefiracetam in Mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2002, 303, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malykh, A.G.; Sadaie, M.R. Piracetam and Piracetam-like Drugs: From Basic Science to Novel Clinical Applications to CNS Disorders. Drugs 2010, 70, 287–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischer, S.; Paulus, W.; Sommer, M.; Tergau, F. Piracetam Affects Facilitatory I-Wave Interaction in the Human Motor Cortex. Clin. Neurophysiol. Off. J. Int. Fed. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2001, 112, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horvath, B.; Marton, Z.; Halmosi, R.; Alexy, T.; Szapary, L.; Vekasi, J.; Biro, Z.; Habon, T.; Kesmarky, G.; Toth, K. In Vitro Antioxidant Properties of Pentoxifylline, Piracetam, and Vinpocetine. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 2002, 25, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepeu, G.; Spignoli, G. Nootropic Drugs and Brain Cholinergic Mechanisms. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 1989, 13, S77–S88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilch, H.; Müller, W.E. Piracetam Elevates Muscarinic Cholinergic Receptor Density in the Frontal Cortex of Aged but Not of Young Mice. Psychopharmacology 1988, 94, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musante, V.; Summa, M.; Cunha, R.A.; Raiteri, M.; Pittaluga, A. Pre-Synaptic Glycine GlyT1 Transporter--NMDA Receptor Interaction: Relevance to NMDA Autoreceptor Activation in the Presence of Mg2+ Ions. J. Neurochem. 2011, 117, 516–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raiteri, M.; Costa, R.; Marchi, M. Effects of Oxiracetam on Neurotransmitter Release from Rat Hippocampus Slices and Synaptosomes. Neurosci. Lett. 1992, 145, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittaluga, A.; Pattarini, R.; Raiteri, M. Putative Cognition Enhancers Reverse Kynurenic Acid Antagonism at Hippocampal NMDA Receptors. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1995, 272, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanno, G.; Misiano, P.; Bonifacino, T.; Pittaluga, A.; Fariello, R.G.; Farina, C. Effects of Dimiracetam at Ionotropic and Metabotropic Glutamatergic Receptors Regulating Neurotransmitter Release in the Rat CNS. In Proceedings of the Neuroscience Annual Meeting; 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, M.; Liu, H.; Tepp, W.H.; Johnson, E.A.; Janz, R.; Chapman, E.R. Glycosylated SV2A and SV2B Mediate the Entry of Botulinum Neurotoxin E into Neurons. Mol. Biol. Cell 2008, 19, 5226–5237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carunchio, I.; Pieri, M.; Ciotti, M.T.; Albo, F.; Zona, C. Modulation of AMPA Receptors in Cultured Cortical Neurons Induced by the Antiepileptic Drug Levetiracetam. Epilepsia 2007, 48, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrero, J.F.; Laird, J.M.; López-García, J.A. Wind-up of Spinal Cord Neurones and Pain Sensation: Much Ado about Something? Prog. Neurobiol. 2000, 61, 169–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.R.; Urits, I.; Wolf, J.; Corrigan, D.; Colburn, L.; Peterson, E.; Williamson, A.; Viswanath, O. Drug-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy: A Narrative Review. Curr. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 15, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attal, N. Pharmacological Treatments of Neuropathic Pain: The Latest Recommendations. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 175, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Maresca, M.; Farina, C.; Scherz, M.W.; Ghelardini, C. A Model of Neuropathic Pain Induced by Sorafenib in the Rat: Effect of Dimiracetam. Neurotoxicology 2015, 50, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Maresca, M.; Micheli, L.; Farina, C.; Scherz, M.W.; Ghelardini, C. A Rat Model of FOLFOX-Induced Neuropathy: Effects of Oral Dimiracetam in Comparison with Duloxetine and Pregabalin. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2017, 80, 1091–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farina, C.; Gagliardi, S.; Ghelardini, C.; Martinelli, M.; Norcini, M.; Parini, C.; Petrillo, P.; Ronzoni, S. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel Dimiracetam Derivatives Useful for the Treatment of Neuropathic Pain. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 3224–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGrath, J.C.; Lilley, E. Implementing Guidelines on Reporting Research Using Animals (ARRIVE Etc.): New Requirements for Publication in BJP. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 3189–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stigliani, S.; Zappettini, S.; Raiteri, L.; Passalacqua, M.; Melloni, E.; Venturi, C.; Tacchetti, C.; Diaspro, A.; Usai, C.; Bonanno, G. Glia Re-Sealed Particles Freshly Prepared from Adult Rat Brain Are Competent for Exocytotic Release of Glutamate. J. Neurochem. 2006, 96, 656–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleck, M.W.; Barrionuevo, G.; Palmer, A.M. Synaptosomal and Vesicular Accumulation of L-Glutamate, L-Aspartate and D-Aspartate. Neurochem. Int. 2001, 39, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raiteri, M.; Sala, R.; Fassio, A.; Rossetto, O.; Bonanno, G. Entrapping of Impermeant Probes of Different Size into Nonpermeabilized Synaptosomes as a Method to Study Presynaptic Mechanisms. J. Neurochem. 2000, 74, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raiteri, L.; Stigliani, S.; Usai, C.; Diaspro, A.; Paluzzi, S.; Milanese, M.; Raiteri, M.; Bonanno, G. Functional Expression of Release-Regulating Glycine Transporters GLYT1 on GABAergic Neurons and GLYT2 on Astrocytes in Mouse Spinal Cord. Neurochem. Int. 2008, 52, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Bani, D.; Bencini, A.; Brandi, M.L.; Calosi, L.; Cantore, M.; Carossino, A.M.; Ghelardini, C.; Valtancoli, B.; Failli, P. Therapeutic Effects of the Superoxide Dismutase Mimetic Compound MnIIMe2DO2A on Experimental Articular Pain in Rats. Mediators Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 905360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guingamp, C.; Gegout-Pottie, P.; Philippe, L.; Terlain, B.; Netter, P.; Gillet, P. Mono-Iodoacetate-Induced Experimental Osteoarthritis: A Dose-Response Study of Loss of Mobility, Morphology, and Biochemistry. Arthritis Rheum. 1997, 40, 1670–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaletti, G.; Tredici, G.; Petruccioli, M.G.; Dondè, E.; Tredici, P.; Marmiroli, P.; Minoia, C.; Ronchi, A.; Bayssas, M.; Etienne, G.G. Effects of Different Schedules of Oxaliplatin Treatment on the Peripheral Nervous System of the Rat. Eur. J. Cancer 2001, 37, 2457–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resta, F.; Micheli, L.; Laurino, A.; Spinelli, V.; Mello, T.; Sartiani, L.; Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Cerbai, E.; Ghelardini, C.; Romanelli, M.N.; et al. Selective HCN1 Block as a Strategy to Control Oxaliplatin-Induced Neuropathy. Neuropharmacology 2018, 131, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Pacini, A.; Bonaccini, L.; Zanardelli, M.; Mello, T.; Ghelardini, C. Morphologic Features and Glial Activation in Rat Oxaliplatin-Dependent Neuropathic Pain. J. pain 2013, 14, 1585–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Micheli, L.; Zanardelli, M.; Ghelardini, C. Low Dose Native Type II Collagen Prevents Pain in a Rat Osteoarthritis Model. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2013, 14, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, M.; Egashira, N.; Kawashiri, T.; Yano, T.; Ikesue, H.; Oishi, R. Oxaliplatin-Induced Neuropathy in the Rat: Involvement of Oxalate in Cold Hyperalgesia but Not Mechanical Allodynia. Pain 2009, 147, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptista-de-Souza, D.; Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Zanardelli, M.; Micheli, L.; Nunes-de-Souza, R.L.; Canto-de-Souza, A.; Ghelardini, C. Serotonergic Modulation in Neuropathy Induced by Oxaliplatin: Effect on the 5HT2C Receptor. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 735, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvik, M.E.; Kopp, R. An Improved One-Trial Passive Avoidance Learning Situation. Psychol. Rep. 1967, 21, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porsolt, R.D.; Bertin, A.; Jalfre, M. Behavioral Despair in Mice: A Primary Screening Test for Antidepressants. Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. Ther. 1977, 229, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luccini, E.; Musante, V.; Neri, E.; Raiteri, M.; Pittaluga, A. N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Autoreceptors Respond to Low and High Agonist Concentrations by Facilitating, Respectively, Exocytosis and Carrier-Mediated Release of Glutamate in Rat Hippocampus. J. Neurosci. Res. 2007, 85, 3657–3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittaluga, A. Presynaptic Release-Regulating NMDA Receptors in Isolated Nerve Terminals: A Narrative Review. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 178, 1001–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safety and Preliminary Evidence of Efficacy of Escalating Doses of Dimiracetam in AIDS Patients with Painful Neuropathy. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01135251 (accessed on 9 November 2022).
- Bonanno, G.; Fassio, A.; Sala, R.; Schmid, G.; Raiteri, M. GABA(B) Receptors as Potential Targets for Drugs Able to Prevent Excessive Excitatory Amino Acid Transmission in the Spinal Cord. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 362, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittaluga, A.; Vaccari, D.; Raiteri, M. The “Kynurenate Test”, a Biochemical Assay for Putative Cognition Enhancers. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1997, 283, 82–90. [Google Scholar]
- Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Marcoli, M.; Micheli, L.; Zanardelli, M.; Maura, G.; Ghelardini, C.; Cervetto, C. Oxaliplatin Evokes P2X7-Dependent Glutamate Release in the Cerebral Cortex: A Pain Mechanism Mediated by Pannexin 1. Neuropharmacology 2015, 97, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobert, J.A.; Cirillo, V.J.; Hitzenberger, G.; James, I.; Pryor, J.; Cook, T.; Buntinx, A.; Holmes, I.B.; Lutterbeck, P.M. Enhancement of Uricosuric Properties of Indacrinone by Manipulation of the Enantiomer Ratio. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1981, 29, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudo, R.T.; Russo, V.F.; Russo, E.M. Use of a Non-Racemic Mixture of Bupivacaina Enantiomenrs, for Improving the Anesthesia Profile. U.S. Patent 7700629 B2, 20 April 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Trachez, M.M.; Zapata-Sudo, G.; Moreira, O.R.; Chedid, N.G.B.; Russo, V.F.T.; Russo, E.M.S.; Sudo, R.T. Motor Nerve Blockade Potency and Toxicity of Non-Racemic Bupivacaine in Rats. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2005, 49, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Froestl, W.; Muhs, A.; Pfeifer, A. Cognitive Enhancers (Nootropics). Part 1: Drugs Interacting with Receptors. J. Alzheimers. Dis. 2012, 32, 793–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copani, A.; Genazzani, A.A.; Aleppo, G.; Casabona, G.; Canonico, P.L.; Scapagnini, U.; Nicoletti, F. Nootropic Drugs Positively Modulate Alpha-Amino-3-Hydroxy-5-Methyl-4-Isoxazolepropionic Acid-Sensitive Glutamate Receptors in Neuronal Cultures. J. Neurochem. 1992, 58, 1199–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, M.J.; Witkin, J.M. AMPA Receptor Potentiators: Application for Depression and Parkinson’s Disease. Curr. Drug Targets 2007, 8, 603–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partin, K.M.; Fleck, M.W.; Mayer, M.L. AMPA Receptor Flip/Flop Mutants Affecting Deactivation, Desensitization, and Modulation by Cyclothiazide, Aniracetam, and Thiocyanate. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 6634–6647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.; Clark, S.; Weeks, A.M.; Dudman, J.T.; Gouaux, E.; Partin, K.M. Mechanism of Positive Allosteric Modulators Acting on AMPA Receptors. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 9027–9036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaglenova, J.; Pandiella, N.; Wijayawardhane, N.; Vaithianathan, T.; Birru, S.; Breese, C.; Suppiramaniam, V.; Randal, C. Aniracetam Reversed Learning and Memory Deficits Following Prenatal Ethanol Exposure by Modulating Functions of Synaptic AMPA Receptors. Neuropsychopharmacol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2008, 33, 1071–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, A.; Lynch, G. Factors Regulating the Magnitude of Long-Term Potentiation Induced by Theta Pattern Stimulation. Brain Res. 1992, 598, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.H.; Oswald, R.E. Piracetam Defines a New Binding Site for Allosteric Modulators of Alpha-Amino-3-Hydroxy-5-Methyl-4-Isoxazole-Propionic Acid (AMPA) Receptors. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 2197–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Olson, R.; Horning, M.; Armstrong, N.; Mayer, M.; Gouaux, E. Mechanism of Glutamate Receptor Desensitization. Nature 2002, 417, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, B.A.; Lambeng, N.; Nocka, K.; Kensel-Hammes, P.; Bajjalieh, S.M.; Matagne, A.; Fuks, B. The Synaptic Vesicle Protein SV2A Is the Binding Site for the Antiepileptic Drug Levetiracetam. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 9861–9866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Rosenstiel, P. Brivaracetam (UCB 34714). Neurother. J. Am. Soc. Exp. Neurother. 2007, 4, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elia, J.; Ungal, G.; Kao, C.; Ambrosini, A.; De Jesus-Rosario, N.; Larsen, L.; Chiavacci, R.; Wang, T.; Kurian, C.; Titchen, K.; et al. Fasoracetam in Adolescents with ADHD and Glutamatergic Gene Network Variants Disrupting MGluR Neurotransmitter Signaling. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zvejniece, L.; Svalbe, B.; Veinberg, G.; Grinberga, S.; Vorona, M.; Kalvinsh, I.; Dambrova, M. Investigation into Stereoselective Pharmacological Activity of Phenotropil. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2011, 109, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bonifacino, T.; Micheli, L.; Torazza, C.; Ghelardini, C.; Farina, C.; Bonanno, G.; Milanese, M.; Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Scherz, M.W. Pharmacological Profile of MP-101, a Novel Non-racemic Mixture of R- and S-dimiracetam with Increased Potency in Rat Models of Cognition, Depression and Neuropathic Pain. Cells 2022, 11, 4027. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11244027
Bonifacino T, Micheli L, Torazza C, Ghelardini C, Farina C, Bonanno G, Milanese M, Di Cesare Mannelli L, Scherz MW. Pharmacological Profile of MP-101, a Novel Non-racemic Mixture of R- and S-dimiracetam with Increased Potency in Rat Models of Cognition, Depression and Neuropathic Pain. Cells. 2022; 11(24):4027. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11244027
Chicago/Turabian StyleBonifacino, Tiziana, Laura Micheli, Carola Torazza, Carla Ghelardini, Carlo Farina, Giambattista Bonanno, Marco Milanese, Lorenzo Di Cesare Mannelli, and Michael W. Scherz. 2022. "Pharmacological Profile of MP-101, a Novel Non-racemic Mixture of R- and S-dimiracetam with Increased Potency in Rat Models of Cognition, Depression and Neuropathic Pain" Cells 11, no. 24: 4027. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11244027
APA StyleBonifacino, T., Micheli, L., Torazza, C., Ghelardini, C., Farina, C., Bonanno, G., Milanese, M., Di Cesare Mannelli, L., & Scherz, M. W. (2022). Pharmacological Profile of MP-101, a Novel Non-racemic Mixture of R- and S-dimiracetam with Increased Potency in Rat Models of Cognition, Depression and Neuropathic Pain. Cells, 11(24), 4027. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11244027









