Low-Dose rIL-15 Protects from Nephrotoxic Serum Nephritis via CD8+ T Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Studies
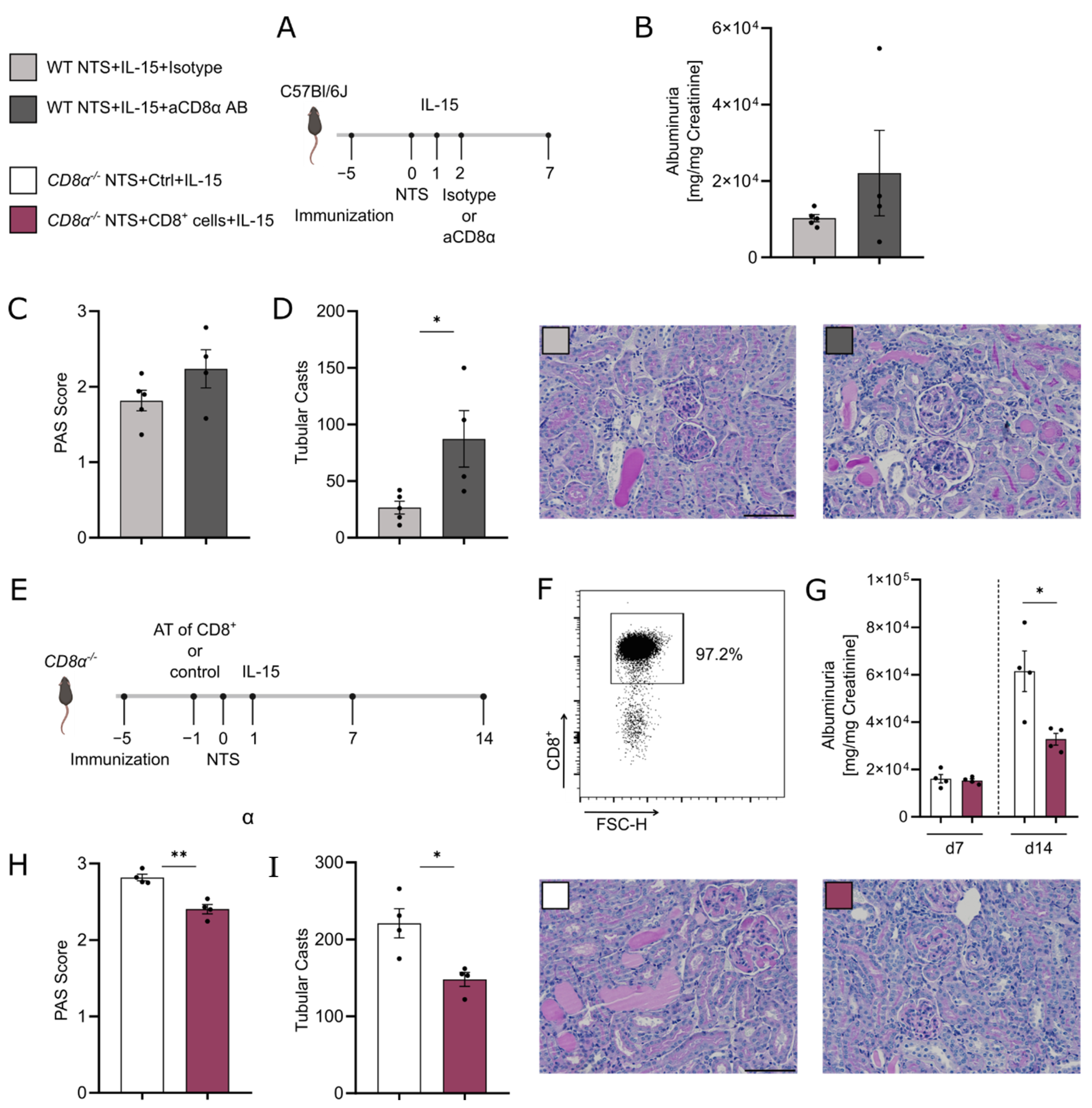
2.2. In Vivo Interventions
2.3. Assessment of Renal Injury
2.4. Multicolor Flow Cytometry Analysis
2.5. TEC Isolation and Gene Expression Analysis
2.6. Negative MACS Sort of CD8α+ Cells
2.7. Cell Culture
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
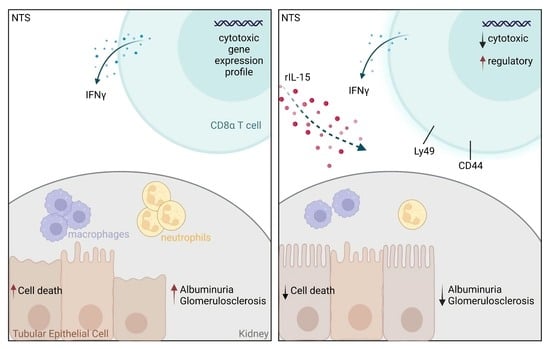
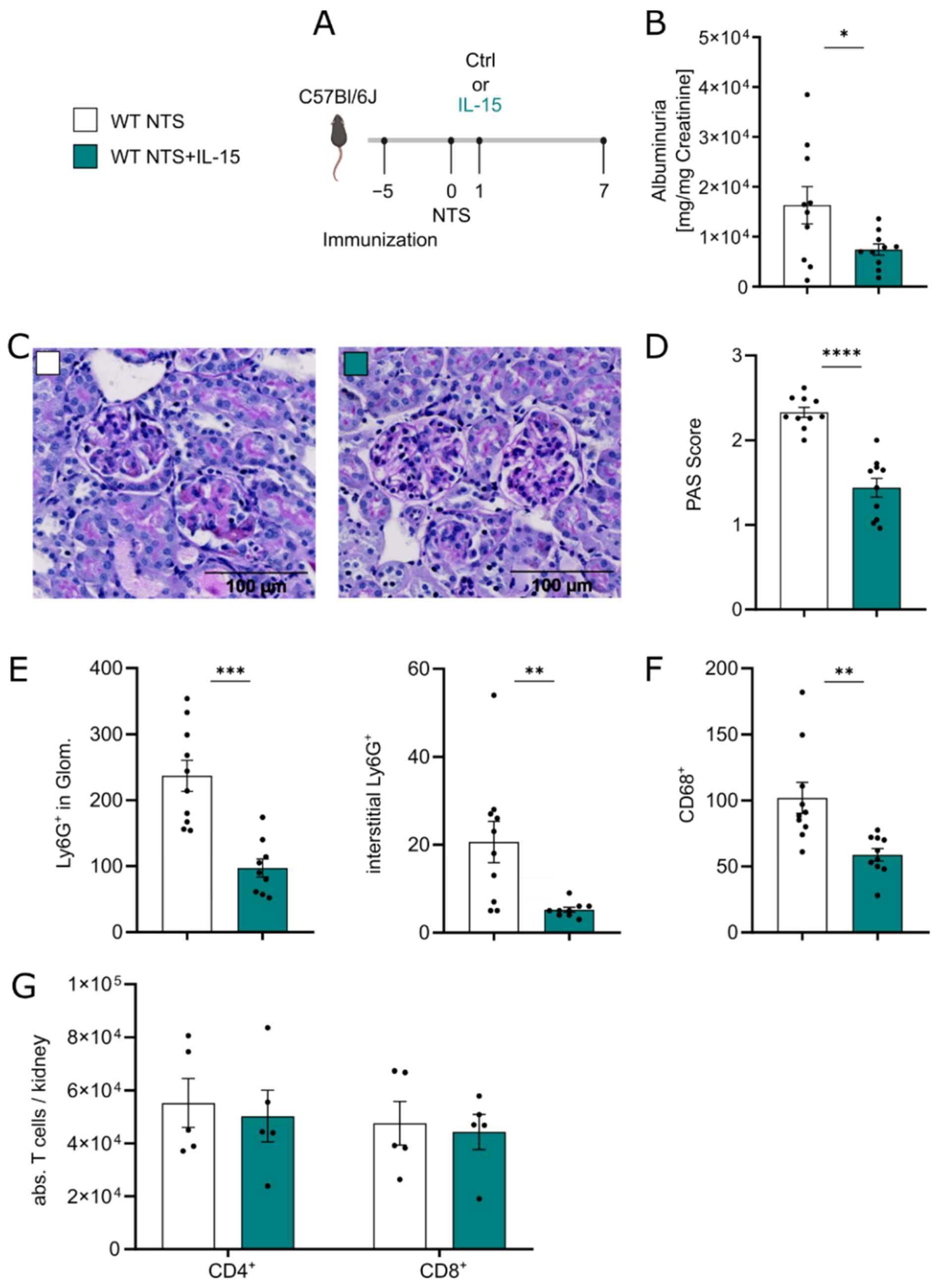
3.1. Low-Dose rIL-15 Treatment Ameliorates NTS
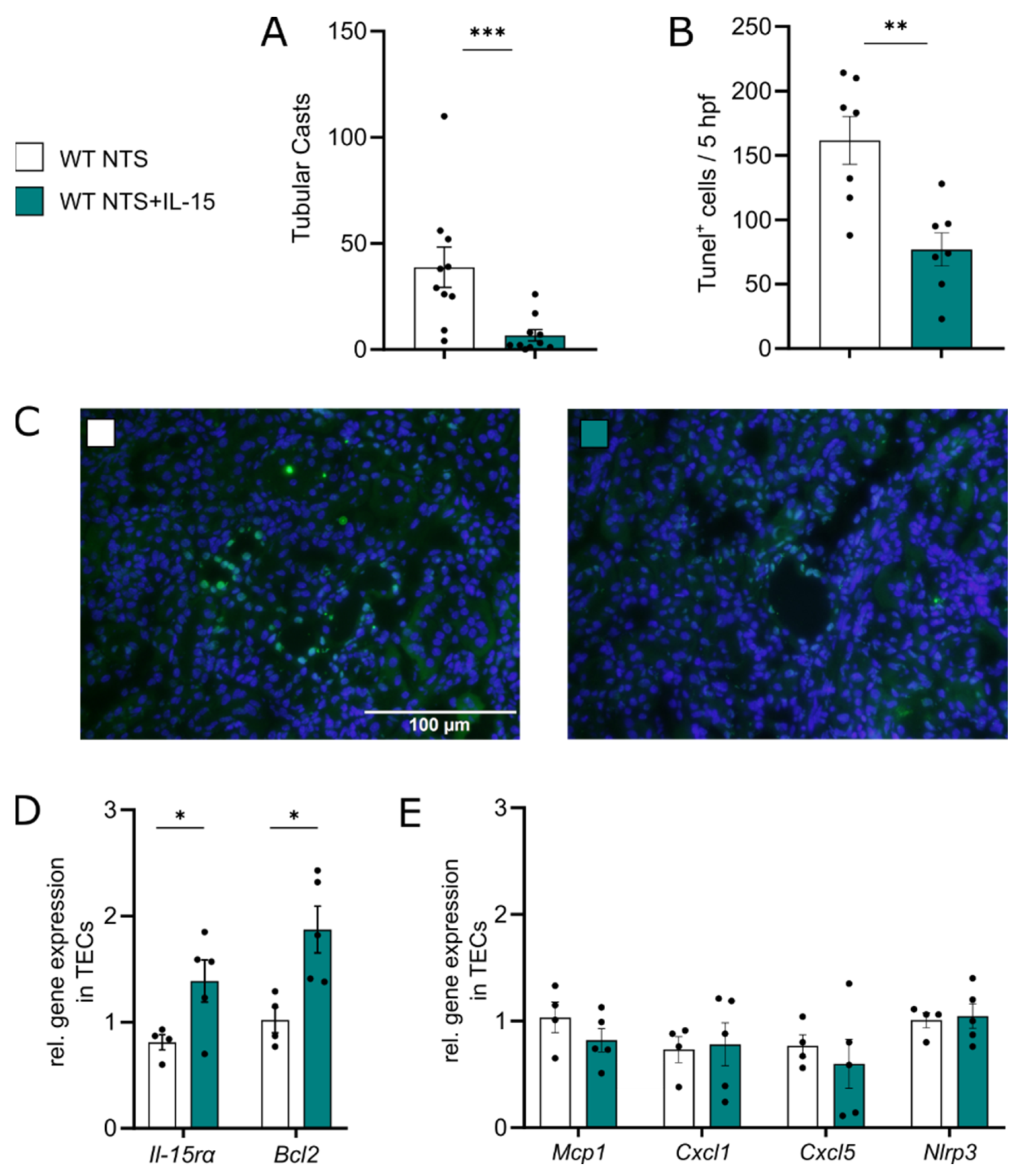
3.2. rIL-15 Protects TECs from Cell Death in NTS
3.3. Administration of rIL-15 in NTS Alters CD8+ T Cell Gene Expression Profile and Function
3.4. rIL-15 Does Not Increase CD4+ Tregs but Induces Higher Rates of IFNγ+CD4+ T Cells
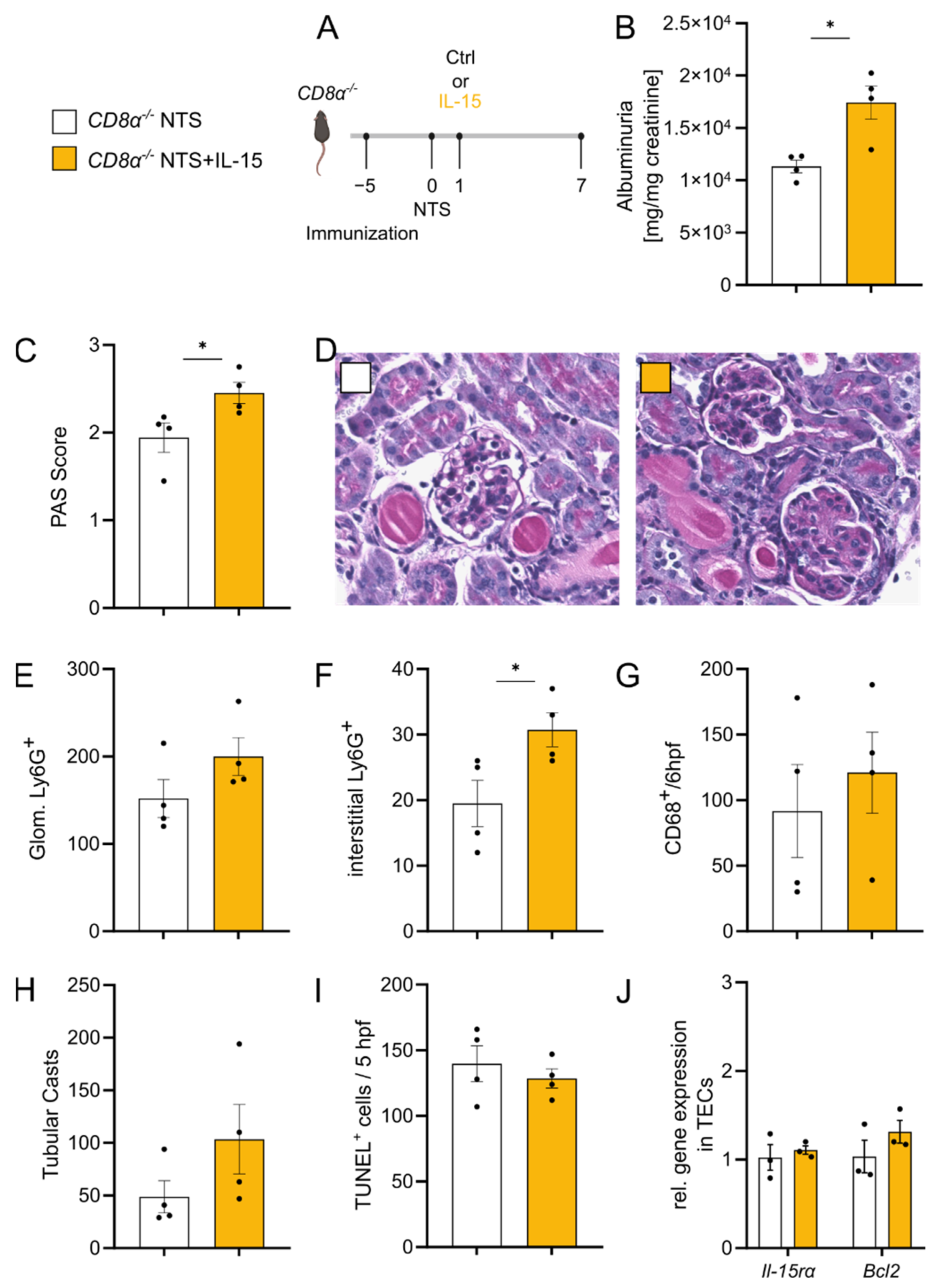
3.5. rIL-15-Mediated Protection of TECs from Cell Death Is Dependent on CD8+ Cells
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pyart, R.; Evans, K.M.; Steenkamp, R.; Casula, A.; Wong, E.; Magadi, W.; Medcalf, J. The 21st UK Renal Registry Annual Report: A Summary of Analyses of Adult Data in 2017. Nephron 2020, 144, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bikbov, B.; Purcell, C.A.; Levey, A.S.; Smith, M.; Abdoli, A.; Abebe, M.; Adebayo, O.M.; Afarideh, M.; Agarwal, S.K.; Agudelo-Botero, M.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Chronic Kidney Disease, 1990–2017: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2020, 395, 709–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, S.; Haas, M.; Markowitz, G.S.; D’Agati, V.D.; Rennke, H.G.; Jennette, J.C.; Bajema, I.M.; Alpers, C.E.; Chang, A.; Cornell, L.D.; et al. Mayo Clinic/Renal Pathology Society Consensus Report on Pathologic Classification, Diagnosis, and Reporting of GN. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2016, 27, 1278–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsuwaida, A.O. Interstitial Inflammation and Long-Term Renal Outcomes in Lupus Nephritis. Lupus 2013, 22, 1446–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berden, A.E.; Ferrario, F.; Hagen, E.C.; Jayne, D.R.; Jennette, J.C.; Joh, K.; Neumann, I.; Noël, L.H.; Pusey, C.D.; Waldherr, R.; et al. Histopathologic Classification of ANCA-Associated Glomerulonephritis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2010, 21, 1628–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, S.A. IL-2: The First Effective Immunotherapy for Human Cancer. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 5451–5458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graßhoff, H.; Comdühr, S.; Monne, L.R.; Müller, A.; Lamprecht, P.; Riemekasten, G.; Humrich, J.Y. Low-Dose IL-2 Therapy in Autoimmune and Rheumatic Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhang, X.; Wei, Y.; Sun, X.; Chen, Y.; Deng, J.; Jin, Y.; Gan, Y.; Hu, X.; Jia, R.; et al. Low-Dose Interleukin-2 Treatment Selectively Modulates CD4+ T Cell Subsets in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 991–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humrich, J.Y.; Von Spee-Mayer, C.; Siegert, E.; Alexander, T.; Hiepe, F.; Radbruch, A.; Burmester, G.R.; Riemekasten, G. Rapid Induction of Clinical Remission by Low-Dose Interleukin-2 in a Patient with Refractory SLE. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 791–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenzwajg, M.; Churlaud, G.; Mallone, R.; Six, A.; Dérian, N.; Chaara, W.; Lorenzon, R.; Long, S.A.; Buckner, J.H.; Afonso, G.; et al. Low-Dose Interleukin-2 Fosters a Dose-Dependent Regulatory T Cell Tuned Milieu in T1D Patients. J. Autoimmun. 2015, 58, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.A.; Rieck, M.; Sanda, S.; Bollyky, J.B.; Samuels, P.L.; Goland, R.; Ahmann, A.; Rabinovitch, A.; Aggarwal, S.; Phippard, D.; et al. Rapamycin/IL-2 Combination Therapy in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Augments Tregs yet Transiently Impairs β-Cell Function. Diabetes 2012, 61, 2340–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldmann, T.A. The Biology of Interleukin-2 and Interleukin-15: Implications for Cancer Therapy and Vaccine Design. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldmann, T.A.; Dubois, S.; Miljkovic, M.D.; Conlon, K.C. IL-15 in the Combination Immunotherapy of Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiler, M.; Rogashev, B.; Einbinder, T.; Hausmann, M.J.; Kaneti, J.; Chaimovitz, C.; Douvdevani, A. Interleukin-15, a Leukocyte Activator and Growth Factor, Is Produced by Cortical Tubular Epithelial Cells. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1998, 9, 1194–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tejman-Yarden, N.; Zlotnik, M.; Lewis, E.; Etzion, O.; Chaimovitz, C.; Douvdevani, A. Renal Cells Express a Functional Interleukin-15 Receptor. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2005, 20, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giron-Michel, J.; Azzi, S.; Khawam, K.; Mortier, E.; Caignard, A.; Devocelle, A.; Ferrini, S.; Croce, M.; François, H.; Lecru, L.; et al. Interleukin-15 Plays a Central Role in Human Kidney Physiology and Cancer through the Γc Signaling Pathway. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinozaki, M.; Hirahashi, J.; Lebedeva, T.; Liew, F.Y.; Salant, D.J.; Maron, R.; Kelley, V.R. IL-15, a Survival Factor for Kidney Epithelial Cells, Counteracts Apoptosis and Inflammation during Nephritis. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 109, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devocelle, A.; Lecru, L.; Ferlicot, S.; Bessede, T.; Candelier, J.J.; Giron-michel, J.; François, H. IL-15 Prevents Renal Fibrosis by Inhibiting Collagen Synthesis: A New Pathway in Chronic Kidney Disease? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devocelle, A.; Lecru, L.; François, H.; Desterke, C.; Gallerne, C.; Eid, P.; Estelle, O.; Azzarone, B.; Giron-Michel, J. Inhibition of TGF- β 1 Signaling by IL-15: A Novel Role for IL-15 in the Control of Renal Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition: IL-15 Counteracts TGF- β 1-Induced EMT in Renal Fibrosis. Int. J. Cell Biol. 2019, 2019, 9151394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.R.; Holdsworth, S.R.; Tipping, P.G. Evidence for Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity Mechanisms in Glomerular Crescent Formation. Kidney Int. 1994, 46, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Holdsworth, S.R.; Tipping, P.G. Antibody Independent Crescentic Glomerulonephritis in μ Chain Deficient Mice. Kidney Int. 1997, 51, 672–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tipping, P.G.; Huang, X.R.; Qi, M.; Van, G.Y.; Tang, W.W. Crescentic Glomerulonephritis in CD4- and CD8-Deficient Mice. Requirement for CD4 but Not CD8 Cells. Am. J. Pathol. 1998, 152, 1541–1548. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wolf, D.; Hochegger, K.; Wolf, A.M.; Rumpold, H.F.; Gastl, G.; Tilg, H.; Mayer, G.; Gunsilius, E.; Rosenkranz, A.R. CD4+CD25+ Regulatory T Cells Inhibit Experimental Anti-Glomerular Basement Membrane Glomerulonephritis in Mice. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 1360–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eller, K.; Weber, T.; Pruenster, M.; Wolf, A.M.; Mayer, G.; Rosenkranz, A.R.; Rot, A. CCR7 Deficiency Exacerbates Injury in Acute Nephritis Due to Aberrant Localization of Regulatory T Cells. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paust, H.-J.; Ostmann, A.; Erhardt, A.; Turner, J.-E.; Velden, J.; Mittrü Cker, H.-W.; Sparwasser, T.; Panzer, U.; Tiegs, G. Regulatory T Cells Control the Th1 Immune Response in Murine Crescentic Glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 2011, 80, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ooi, J.D.; Snelgrove, S.L.; Engel, D.R.; Hochheiser, K.; Ludwig-Portugall, I.; Nozaki, Y.; O’Sullivan, K.M.; Hickey, M.J.; Holdsworth, S.R.; Kurts, C.; et al. Endogenous Foxp3+ T-Regulatory Cells Suppress Anti-Glomerular Basement Membrane Nephritis. Kidney Int. 2011, 79, 977–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linke, A.; Tiegs, G.; Neumann, K. Pathogenic T-Cell Responses in Immune-Mediated Glomerulonephritis. Cells 2022, 11, 1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInnes, I.B.; Leung, B.P.; Sturrock, R.D.; Field, M.; Liew, F.Y. Interleukin-15 Mediates T Cell-Dependent Regulation of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Production in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nat Med 1997, 3, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, C.; Deblois, G.; Clénet, M.-L.; Moratalla, A.C.; Farzam-kia, N.; Girard, M.; Duquette, P.; Prat, A.; Larochelle, C.; Arbour, N. Interleukin-15 Enhances Proinflammatory T-Cell Responses in Patients with MS and EAE. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 8, e931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenkranz, A.R.; Mendrick, D.L.; Cotran, R.S.; Mayadas, T.N. P-Selectin Deficiency Exacerbates Experimental Glomerulonephritis: A Protective Role for Endothelial P-Selectin in Inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 103, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, S.; Hwang, I.; Tough, D.F.; Sprent, J. Potent and Selective Stimulation of Memory-Phenotype CD8+ T Cells in Vivo by IL-15. Immunity 1998, 8, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodolce, J.P.; Burkett, P.R.; Boone, D.L.; Chien, M.; Ma, A. T Cell-Independent Interleukin 15Rα Signals Are Required for Bystander Proliferation. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 194, 1187–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berard, M.; Brandt, K.; Paus, S.B.; Tough, D.F. IL-15 Promotes the Survival of Naive and Memory Phenotype CD8 + T Cells. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 5018–5026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, N.; Paltser, G.; Ashkar, A.A. Interleukin-15 Expression Affects Homeostasis and Function of B Cells through NK Cell-Derived Interferon-Gamma. Cell. Immunol. 2009, 258, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armitage, R.J.; Macduff, B.M.; Eisenman, J.; Paxton, R.; Grabstein, K.H. IL-15 Has Stimulatory Activity for the Induction of B Cell Proliferation and Differentiation. J. Immunol. 1995, 154, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aringer, I.; Artinger, K.; Kirsch, A.H.; Schabhüttl, C.; Jandl, K.; Bärnthaler, T.; Mooslechner, A.A.; Herzog, S.A.; Uhlig, M.; Kirsch, A.; et al. Blockade of Prostaglandin E2 Receptor 4 Ameliorates Nephrotoxic Serum Nephritis. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2018, 315, F1869–F1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, G.; Jocks, T.; Zahner, G.; Panzer, U.; Stahl, R.A.K. Existence of a Regulatory Loop between MCP-1 and TGF-β in Glomerular Immune Injury. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2002, 283, F1075–F1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Guo, J.; Moledina, D.G.; Cantley, L.G. Immune-Mediated Tubule Atrophy Promotes Acute Kidney Injury to Chronic Kidney Disease Transition. Nat Commun 2022, 13, 4892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassatella, M.A.; McDonald, P.P. Interleukin-15 and Its Impact on Neutrophil Function. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2000, 7, 174–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linke, A.; Cicek, H.; Müller, A.; Meyer-Schwesinger, C.; Melderis, S.; Wiech, T.; Wegscheid, C.; Ridder, J.; Steinmetz, O.M.; Diehl, L.; et al. Antigen Cross-Presentation by Murine Proximal Tubular Epithelial Cells Induces Cytotoxic and Inflammatory CD8 + T Cells. Cells 2022, 11, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whangbo, J.S.; Kim, H.T.; Mirkovic, N.; Leonard, L.; Poryanda, S.; Silverstein, S.; Kim, S.; Reynolds, C.G.; Rai, S.C.; Verrill, K.; et al. Dose-Escalated Interleukin-2 Therapy for Refractory Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease in Adults and Children. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 2550–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuoka, K.I.; Koreth, J.; Kim, H.T.; Bascug, G.; McDonough, S.; Kawano, Y.; Murase, K.; Cutler, C.; Ho, V.T.; Alyea, E.P.; et al. Low-Dose Interleukin-2 Therapy Restores Regulatory T Cell Homeostasis in Patients with Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 179ra43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldmann, T.A. The Shared and Contrasting Roles of IL2 and IL15 in the Life and Death of Normal and Neoplastic Lymphocytes: Implications for Cancer Therapy. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2015, 3, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, A.; Von Spee-Mayer, C.; Kloke, L.; Wu, K.; Kühl, A.; Enghard, P.; Burmester, G.R.; Riemekasten, G.; Humrich, J.Y. IL-2 Therapy Diminishes Renal Inflammation and the Activity of Kidney-Infiltrating CD4+ T Cells in Murine Lupus Nephritis. Cells 2019, 8, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, J.; Norgan, V.A.; Bhambra, U.; Smith, J.; Cook, H.T.; Pusey, C.D. Anti-CD8 Monoclonal Antibody Therapy Is Effective in the Prevention and Treatment of Experimental Autoimmune Glomerulonephritis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.; Eggenhuizen, P.; O’Sullivan, K.M.; Alikhan, M.A.; Holdsworth, S.R.; Ooi, J.D.; Kitching, A.R. CD8+ T Cells Effect Glomerular Injury in Experimental Anti-Myeloperoxidase GN. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, K.; Yaoita, E.; Yamamoto, T.; Kihara, I. Depletion of CD8 Positive Cells in Nephrotoxic Serum Nephritis of WKY Rats. Kidney Int. 1992, 41, 1517–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, S.; Holdsworth, S.R.; Tipping, P.G. MHC Class I Pathway Is Not Required for the Development of Crescentic Glomerulonephritis in Mice. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2000, 122, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-J.; Barnitz, R.A.; Kreslavsky, T.; Brown, F.D.; Moffett, H.; Lemieux, M.E.; Kaygusuz, Y.; Meissner, T.; Holderried, T.A.W.; Chan, S.; et al. Stable Inhibitory Activity of Regulatory T Cells Requires the Transcription Factor Helios. Science 2015, 350, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zaslavsky, M.; Su, Y.; Guo, J.; Sikora, M.J.; van Unen, V.; Christophersen, A.; Chiou, S.-H.; Chen, L.; Li, J.; et al. KIR+CD8+ T Cells Suppress Pathogenic T Cells and Are Active in Autoimmune Diseases and COVID-19. Science 2022, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holderried, T.A.W.; Kruse, M.; Serries, M.; Brossart, P.; Wolf, D.; Wolf, A.M. Helios-Expressing CD8+ T Cells Are Decreased in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Lupus 2021, 30, 1022–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-H.; Ishida, Y.; Rifa’i, M.; Shi, Z.; Isobe, K.; Suzuki, H. Essential Role of CD8+CD122+ Regulatory T Cells in the Recovery from Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endharti, A.T.; Rifa’, M.; Shi, Z.; Fukuoka, Y.; Nakahara, Y.; Kawamoto, Y.; Takeda, K.; Isobe, K.-i.; Suzuki, H. Cutting Edge: CD8+CD122+ Regulatory T Cells Produce IL-10 to Suppress IFN- Production and Proliferation of CD8+ T Cells. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 7093–7097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Wang, X.; Radfar, S.; Sproule, T.J.; Roopenian, D.C.; Cantor, H. CD8+ T Regulatory Cells Express the Ly49 Class I MHC Receptor and Are Defective in Autoimmune Prone B6-Yaa Mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 2010–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saligrama, N.; Zhao, F.; Sikora, M.J.; Serratelli, W.S.; Fernandes, R.A.; Louis, D.M.; Yao, W.; Ji, X.; Idoyaga, J.; Mahajan, V.B.; et al. Opposing T Cell Responses in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. Nature 2019, 572, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.E.; Becker, M.; Mittrücker, H.W.; Panzer, U. Tissue-Resident Lymphocytes in the Kidney. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehniger, T.A.; Caligiuri, M.A. Interleukin 15: Biology and Relevance to Human Disease. Blood 2001, 97, 14–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rickassel, C.; Gnirck, A.-C.; Shaikh, N.; Adamiak, V.; Waterhölter, A.; Tanriver, Y.; Neumann, K.; Huber, T.B.; Gasteiger, G.; Panzer, U.; et al. Conventional NK Cells and Type 1 Innate Lymphoid Cells Do Not Influence Pathogenesis of Experimental Glomerulonephritis. J. Immunol. 2022, 208, 1585–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesnard, L.; Keller, A.D.C.; Michel, M.L.; Vandermeersch, S.; Rafat, C.; Letavernier, E.; Tillet, Y.; Rondeau, E.; Leite-de-Moraes, M.C. Invariant Natural Killer T Cells and TGF-β Attenuate Anti-GBM Glomerulonephritis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 1282–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krebs, C.F.; Steinmetz, O.M. CD4+ T Cell Fate in Glomerulonephritis: A Tale of Th1, Th17, and Novel Treg Subtypes. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosiek, M.J.; Fiette, L.; El Daker, S.; Eberl, G.; Freitas, A.A. IL-15-Dependent Balance between Foxp3 and RORγt Expression Impacts Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mooslechner, A.A.; Schuller, M.; Artinger, K.; Kirsch, A.H.; Schabhüttl, C.; Eller, P.; Rosenkranz, A.R.; Eller, K. Low-Dose rIL-15 Protects from Nephrotoxic Serum Nephritis via CD8+ T Cells. Cells 2022, 11, 3656. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11223656
Mooslechner AA, Schuller M, Artinger K, Kirsch AH, Schabhüttl C, Eller P, Rosenkranz AR, Eller K. Low-Dose rIL-15 Protects from Nephrotoxic Serum Nephritis via CD8+ T Cells. Cells. 2022; 11(22):3656. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11223656
Chicago/Turabian StyleMooslechner, Agnes A., Max Schuller, Katharina Artinger, Alexander H. Kirsch, Corinna Schabhüttl, Philipp Eller, Alexander R. Rosenkranz, and Kathrin Eller. 2022. "Low-Dose rIL-15 Protects from Nephrotoxic Serum Nephritis via CD8+ T Cells" Cells 11, no. 22: 3656. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11223656
APA StyleMooslechner, A. A., Schuller, M., Artinger, K., Kirsch, A. H., Schabhüttl, C., Eller, P., Rosenkranz, A. R., & Eller, K. (2022). Low-Dose rIL-15 Protects from Nephrotoxic Serum Nephritis via CD8+ T Cells. Cells, 11(22), 3656. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11223656