Validation of AAC-11-Derived Peptide Anti-Tumor Activity in a Single Graft Sézary Patient-Derived Xenograft Mouse Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Peptides Synthesis
2.2. Patients
2.3. Flow Cytometry
2.4. Generation of PDX Mice and Peptide Treatment
2.5. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) and Immunofluorescence (IF)
3. Results
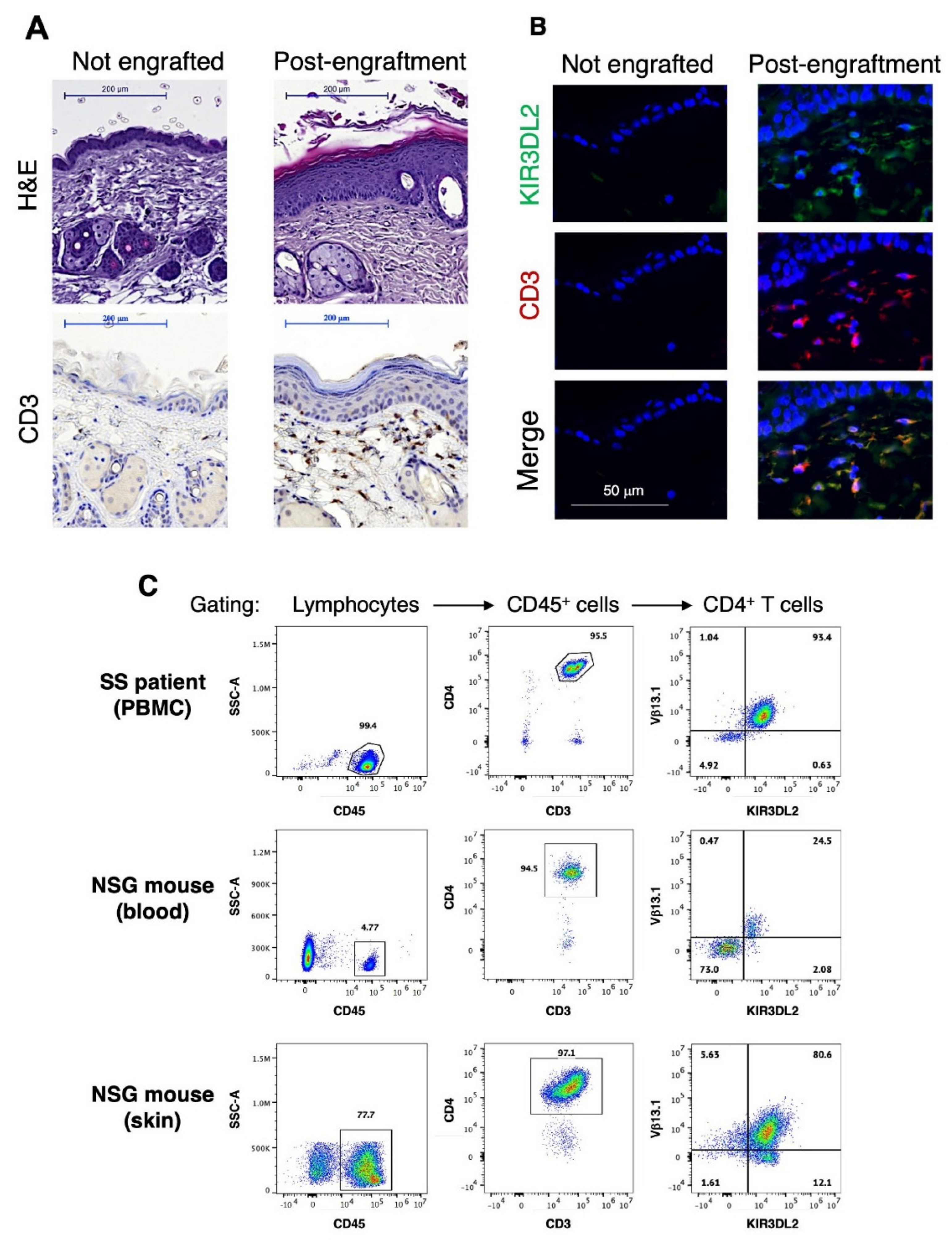
3.1. Generation and Characterization of a Novel Single Graft Sézary PDX Mouse Model
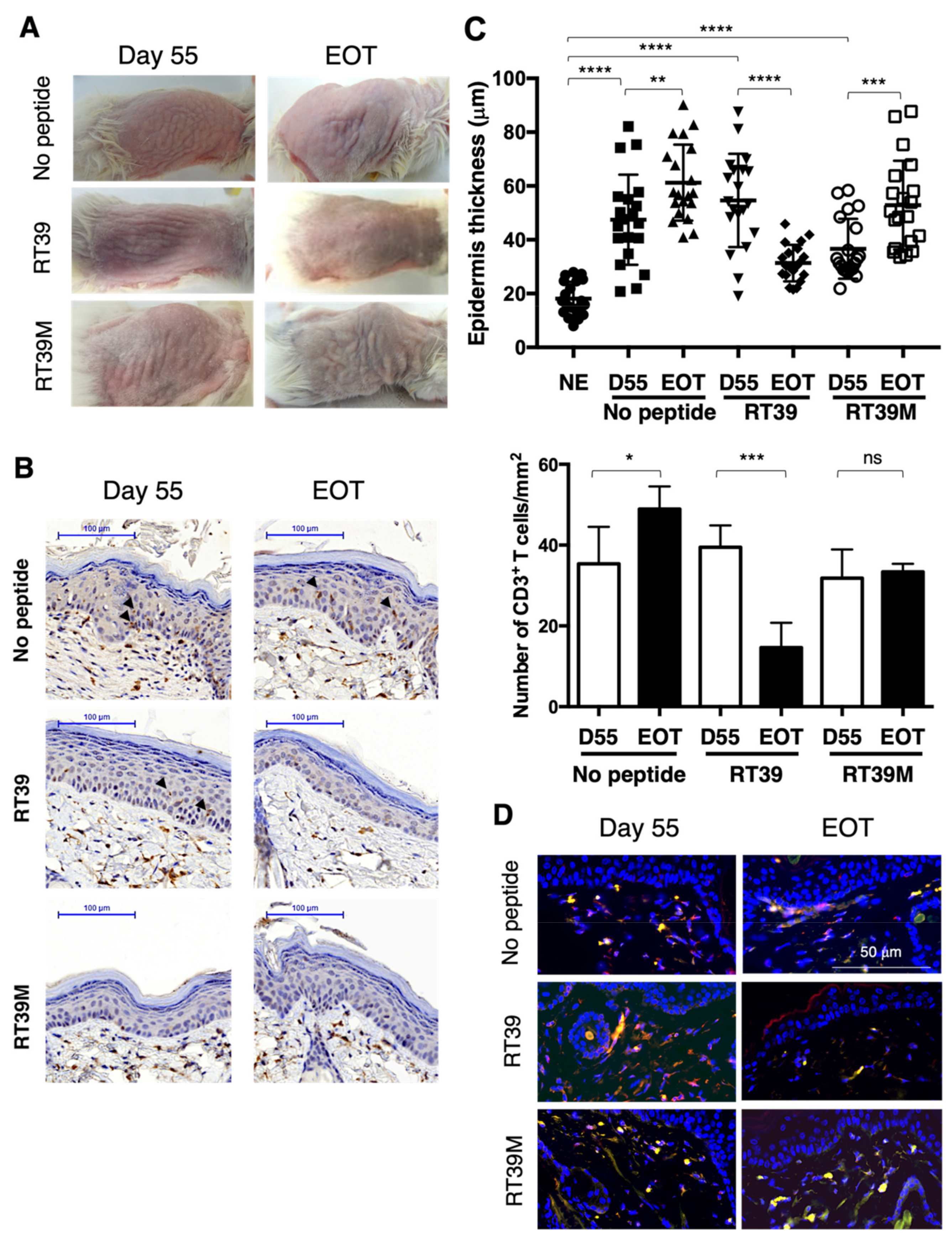
3.2. RT39 Treatment Promotes Depletion of the Tumor T Cell Clone in SS PDX Mouse Dermis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Fujii, K. New Therapies and Immunological Findings in Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Zou, X.; Cheng, K.; Zhong, S.; Su, Y.; Wu, T.; Tao, Y.; Cong, L.; Yan, B.; Jiang, Y. The role of cell-penetrating peptides in potential anti-cancer therapy. Clin. Transl. Med. 2022, 12, e822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tewari, M.; Yu, M.; Ross, B.; Dean, C.; Giordano, A.; Rubin, R. AAC-11, a novel cDNA that inhibits apoptosis after growth factor withdrawal. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 4063–4069. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.W.; Cho, H.S.; Kim, J.H.; Hur, S.Y.; Kim, T.E.; Lee, J.M.; Kim, I.K.; Namkoong, S.E. AAC-11 overexpression induces invasion and protects cervical cancer cells from apoptosis. Lab. Investig. 2000, 80, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sasaki, H.; Moriyama, S.; Yukiue, H.; Kobayashi, Y.; Nakashima, Y.; Kaji, M.; Fukai, I.; Kiriyama, M.; Yamakawa, Y.; Fujii, Y. Expression of the antiapoptosis gene, AAC-11, as a prognosis marker in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung. Cancer 2001, 34, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.H.; Kim, S.H.; Noh, K.H.; Bae, H.C.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, H.J.; Song, J.; Kang, T.H.; Kim, D.W.; Oh, S.J.; et al. Apoptosis Inhibitor 5 Increases Metastasis via Erk-mediated MMP expression. BMB Rep. 2015, 48, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertero, T.; Bourget-Ponzio, I.; Puissant, A.; Loubat, A.; Mari, B.; Meneguzzi, G.; Auberger, P.; Barbry, P.; Ponzio, G.; Rezzonico, R. Tumor suppressor function of miR-483-3p on squamous cell carcinomas due to its pro-apoptotic properties. Cell Cycle 2013, 12, 2183–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekow, J.; Meckel, K.; Dougherty, U.; Butun, F.; Mustafi, R.; Lim, J.; Crofton, C.; Chen, X.; Joseph, L.; Bissonnette, M. Tumor suppressors miR-143 and miR-145 and predicted target proteins API5, ERK5, K-RAS, and IRS-1 are differentially expressed in proximal and distal colon. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2015, 308, G179–G187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siu, M.K.; Abou-Kheir, W.; Yin, J.J.; Chang, Y.S.; Barrett, B.; Suau, F.; Casey, O.; Chen, W.Y.; Fang, L.; Hynes, P.; et al. Loss of EGFR signaling regulated miR-203 promotes prostate cancer bone metastasis and tyrosine kinase inhibitors resistance. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 3770–3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lee, A.T.; Ma, J.Z.; Wang, J.; Ren, J.; Yang, Y.; Tantoso, E.; Li, K.B.; Ooi, L.L.; Tan, P.; et al. Profiling microRNA expression in hepatocellular carcinoma reveals microRNA-224 up-regulation and apoptosis inhibitor-5 as a microRNA-224-specific target. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 13205–13215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagot-Lacoussiere, L.; Kotula, E.; Villoutreix, B.O.; Bruzzoni-Giovanelli, H.; Poyet, J.L. A Cell-Penetrating Peptide Targeting AAC-11 Specifically Induces Cancer Cells Death. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 5479–5490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, H.S.; Woo, S.R.; Song, K.H.; Cho, H.; Chay, D.B.; Hong, S.O.; Lee, H.J.; Oh, S.J.; Chung, J.Y.; Kim, J.H.; et al. API5 induces cisplatin resistance through FGFR signaling in human cancer cells. Exp. Mol. Med. 2017, 49, e374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigou, P.; Piddubnyak, V.; Faye, A.; Rain, J.C.; Michel, L.; Calvo, F.; Poyet, J.L. The antiapoptotic protein AAC-11 interacts with and regulates Acinus-mediated DNA fragmentation. EMBO J. 2009, 28, 1576–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Wu, W.; Liu, D.; Lv, Y.; Deng, H.; Gao, S.; Gu, Y.; Huang, M.; Guo, X.; Liu, B.; et al. Evolution and Structure of API5 and Its Roles in Anti-Apoptosis. Protein Pept. Lett. 2021, 28, 612–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, B.G.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, S.J.; Jeong, K.C.; Cho, J.W.; Noh, K.H.; Kim, T.W.; Kim, S.J.; Yoon, H.J.; Suh, S.W.; et al. Helical repeat structure of apoptosis inhibitor 5 reveals protein-protein interaction modules. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 10727–10737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habault, J.; Thonnart, N.; Pasquereau-Kotula, E.; Bagot, M.; Bensussan, A.; Villoutreix, B.O.; Marie-Cardine, A.; Poyet, J.L. PAK1-Dependent Antitumor Effect of AAC-11Derived Peptides on Sezary Syndrome Malignant CD4(+) T Lymphocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 141, 2261–2271.e2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Sugihara, E.; Yamada, T.; Ikuta, K.; Pittaluga, S.; Saya, H.; Amagai, M.; Nagao, K. Hair follicle-derived IL-7 and IL-15 mediate skin-resident memory T cell homeostasis and lymphoma. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 1272–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrique, L.; Poglio, S.; Prochazkova-Carlotti, M.; Kadin, M.E.; Giese, A.; Idrissi, Y.; Beylot-Barry, M.; Merlio, J.P.; Chevret, E. Intrahepatic Xenograft of Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma Cell Lines: A Useful Model for Rapid Biological and Therapeutic Evaluation. Am. J. Pathol. 2016, 186, 1775–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornejo, M.G.; Kharas, M.G.; Werneck, M.B.; Le Bras, S.; Moore, S.A.; Ball, B.; Beylot-Barry, M.; Rodig, S.J.; Aster, J.C.; Lee, B.H.; et al. Constitutive JAK3 activation induces lymphoproliferative syndromes in murine bone marrow transplantation models. Blood 2009, 113, 2746–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Su, M.W.; Jiang, X.; Zhou, Y. Evidence of an oncogenic role of aberrant TOX activation in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Blood 2015, 125, 1435–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, A.; Ishida, T.; Yano, H.; Inagaki, A.; Suzuki, S.; Sato, F.; Takino, H.; Mori, F.; Ri, M.; Kusumoto, S.; et al. Defucosylated anti-CCR4 monoclonal antibody exercises potent ADCC-mediated antitumor effect in the novel tumor-bearing humanized NOD/Shi-scid, IL-2Rgamma(null) mouse model. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2009, 58, 1195–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, S.; Stroopinsky, D.; Yin, L.; Rosenblatt, J.; Alam, M.; Bhargava, P.; Clark, R.A.; Kupper, T.S.; Palmer, K.; Coll, M.D.; et al. Mucin 1 is a potential therapeutic target in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Blood 2015, 126, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krejsgaard, T.; Kopp, K.; Ralfkiaer, E.; Willumsgaard, A.E.; Eriksen, K.W.; Labuda, T.; Rasmussen, S.; Mathiesen, A.M.; Geisler, C.; Lauenborg, B.; et al. A novel xenograft model of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Exp. Dermatol. 2010, 19, 1096–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; La Perle, K.; Kwiatkowski, S.; Sullivan, L.A.; Sams, G.H.; Johns, J.; Curphey, D.P.; Wen, J.; McConnell, K.; Qi, J.; et al. Mechanism, Consequences, and Therapeutic Targeting of Abnormal IL15 Signaling in Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 986–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblatt-Velin, N.; Arrighi, J.F.; Dietrich, P.Y.; Schnuriger, V.; Masouye, I.; Hauser, C. Transformed and nontransformed human T lymphocytes migrate to skin in a chimeric human skin/SCID mouse model. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1997, 109, 744–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Thaler, S.; Burger, A.M.; Schulz, T.; Brill, B.; Bittner, A.; Oberholzer, P.A.; Dummer, R.; Schnierle, B.S. Establishment of a mouse xenograft model for mycosis fungoides. Exp. Dermatol. 2004, 13, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Fits, L.; Rebel, H.G.; Out-Luiting, J.J.; Pouw, S.M.; Smit, F.; Vermeer, K.G.; van Zijl, L.; Tensen, C.P.; Weijer, K.; Vermeer, M.H. A novel mouse model for Sezary syndrome using xenotransplantation of Sezary cells into immunodeficient RAG2(-/-) gammac(-/-) mice. Exp. Dermatol. 2012, 21, 706–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Sells, R.E.; Hwang, S.T. Upregulation of inflammatory cytokines and oncogenic signal pathways preceding tumor formation in a murine model of T-cell lymphoma in skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 1727–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poglio, S.; Prochazkova-Carlotti, M.; Cherrier, F.; Gros, A.; Laharanne, E.; Pham-Ledard, A.; Beylot-Barry, M.; Merlio, J.P. Xenograft and cell culture models of Sezary syndrome reveal cell of origin diversity and subclonal heterogeneity. Leukemia 2021, 35, 1696–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.H.; Yang, C.Y.; Wang, L.; Gao, H.X.; Rakhshandehroo, T.; Afghani, S.; Pincus, L.; Balassanian, R.; Rubenstein, J.; Gill, R.; et al. Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma PDX Drug Screening Platform Identifies Cooperation between Inhibitions of PI3Kalpha/delta and HDAC. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 141, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagot, M.; Charue, D.; Boulland, M.L.; Gaulard, P.; Revuz, J.; Schmitt, C.; Wechsler, J. Interleukin-7 receptor expression in cutaneous T-cell lymphomas. Br. J. Dermatol. 1996, 135, 572–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marie-Cardine, A.; Huet, D.; Ortonne, N.; Remtoula, N.; Le Gouvello, S.; Bagot, M.; Bensussan, A. Killer cell Ig-like receptors CD158a and CD158b display a coactivatory function, involving the c-Jun NH2-terminal protein kinase signaling pathway, when expressed on malignant CD4+ T cells from a patient with Sezary syndrome. Blood 2007, 109, 5064–5065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poszepczynska, E.; Bagot, M.; Echchakir, H.; Martinvalet, D.; Ramez, M.; Charue, D.; Boumsell, L.; Bensussan, A. Functional characterization of an IL-7-dependent CD4(+)CD8alphaalpha(+) Th3-type malignant cell line derived from a patient with a cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Blood 2000, 96, 1056–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talpur, R.; Jones, D.M.; Alencar, A.J.; Apisarnthanarax, N.; Herne, K.L.; Yang, Y.; Duvic, M. CD25 expression is correlated with histological grade and response to denileukin diftitox in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2006, 126, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurabielle, C.; Thonnart, N.; Ram-Wolff, C.; Sicard, H.; Bensussan, A.; Bagot, M.; Marie-Cardine, A. Usefulness of KIR3DL2 to Diagnose, Follow-Up, and Manage the Treatment of Patients with Sezary Syndrome. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 3619–3627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marie-Cardine, A.; Viaud, N.; Thonnart, N.; Joly, R.; Chanteux, S.; Gauthier, L.; Bonnafous, C.; Rossi, B.; Blery, M.; Paturel, C.; et al. IPH4102, a humanized KIR3DL2 antibody with potent activity against cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 6060–6070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolay, J.P.; Felcht, M.; Schledzewski, K.; Goerdt, S.; Geraud, C. Sezary syndrome: Old enigmas, new targets. J. Dtsch Dermatol. Ges 2016, 14, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelens, M.; de Masson, A.; Andrillon, A.; Ram-Wolff, C.; Biard, L.; Boisson, M.; Mourah, S.; Battistella, M.; Toubert, A.; Bagot, M.; et al. Mogamulizumab induces long-term immune restoration and reshapes tumour heterogeneity in Sezary syndrome. Br. J. Dermatol. 2022, 186, 1010–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Experiment n° | Patient | % of Cell Subset in PBMC | % of Tumor Cells in CD4+ T Cells ** | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n° | Sex/Age | TNMB Classification | CD4+ T Cells | CD8+ T Cells | NK Cells | ||
| 1 | 1 | F/62 | T2bN0M0B2 | 74.1 | 1.7 | <1% | 93.7 |
| 2 | 2 | M/65 | T4N3M0B2 | 66.5 | 5.2 | <1% | 86.3 |
| 3 | 3 | F/89 | T2bNXM0B2 | 92.3 | 1.9 | 1.4 | 92.1 |
| 4 | 4 | M/82 | T4NXM0B2 | 97.1 | <1% | n.d | 99.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Habault, J.; Thonnart, N.; Ram-Wolff, C.; Bagot, M.; Bensussan, A.; Poyet, J.-L.; Marie-Cardine, A. Validation of AAC-11-Derived Peptide Anti-Tumor Activity in a Single Graft Sézary Patient-Derived Xenograft Mouse Model. Cells 2022, 11, 2933. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11192933
Habault J, Thonnart N, Ram-Wolff C, Bagot M, Bensussan A, Poyet J-L, Marie-Cardine A. Validation of AAC-11-Derived Peptide Anti-Tumor Activity in a Single Graft Sézary Patient-Derived Xenograft Mouse Model. Cells. 2022; 11(19):2933. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11192933
Chicago/Turabian StyleHabault, Justine, Nicolas Thonnart, Caroline Ram-Wolff, Martine Bagot, Armand Bensussan, Jean-Luc Poyet, and Anne Marie-Cardine. 2022. "Validation of AAC-11-Derived Peptide Anti-Tumor Activity in a Single Graft Sézary Patient-Derived Xenograft Mouse Model" Cells 11, no. 19: 2933. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11192933
APA StyleHabault, J., Thonnart, N., Ram-Wolff, C., Bagot, M., Bensussan, A., Poyet, J.-L., & Marie-Cardine, A. (2022). Validation of AAC-11-Derived Peptide Anti-Tumor Activity in a Single Graft Sézary Patient-Derived Xenograft Mouse Model. Cells, 11(19), 2933. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11192933







