Depletion of HIF-1α by Inducible Cre/loxP Increases the Sensitivity of Cultured Murine Hepatocytes to Ionizing Radiation in Hypoxia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mice, Cell Culture, and Tamoxifen Administration
2.2. Antibodies and Reagents
2.3. SDS PAGE and Western Blot
2.4. Cell Viability and Colony Formation Assays
2.5. Quantitative PCR
2.6. Radiation
2.7. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.8. Apoptosis Assays
2.9. Neutral Comet Assay
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
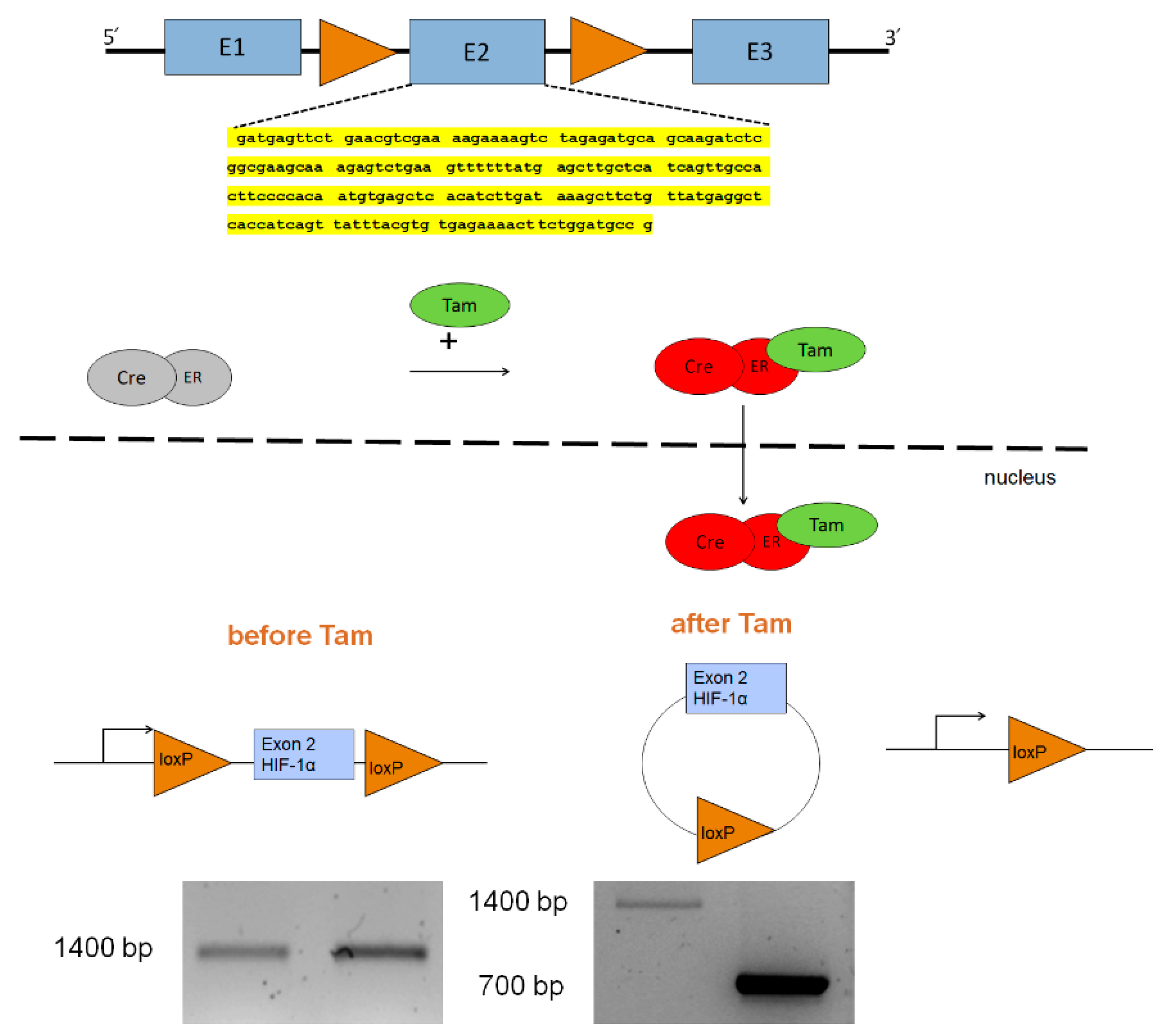
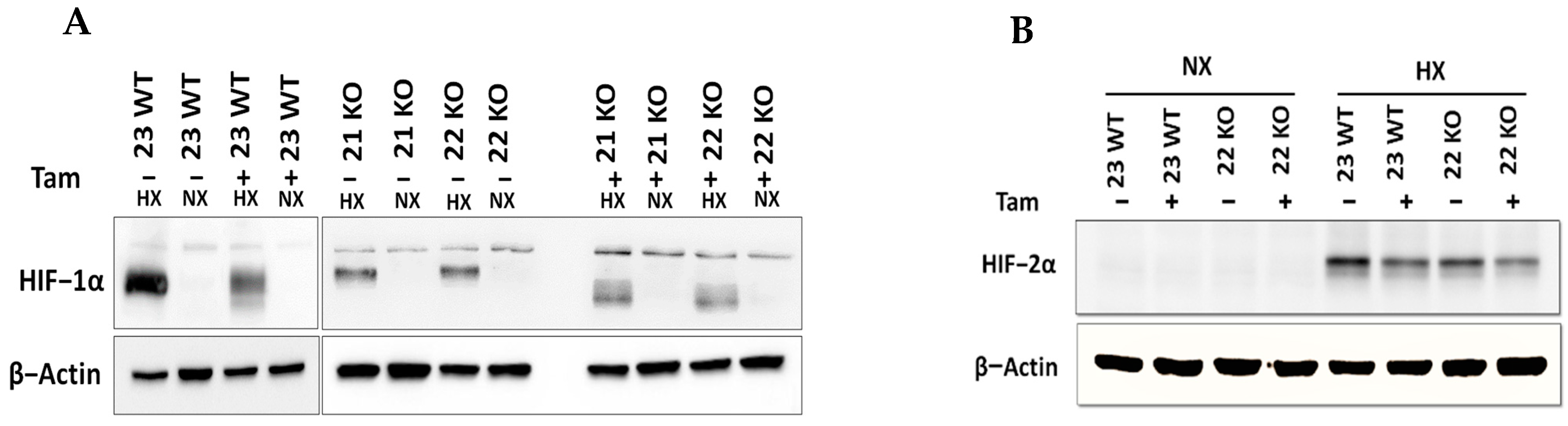
3.1. Generation of a Mouse Model with Tamoxifen-Inducible HIF-1α Knockout
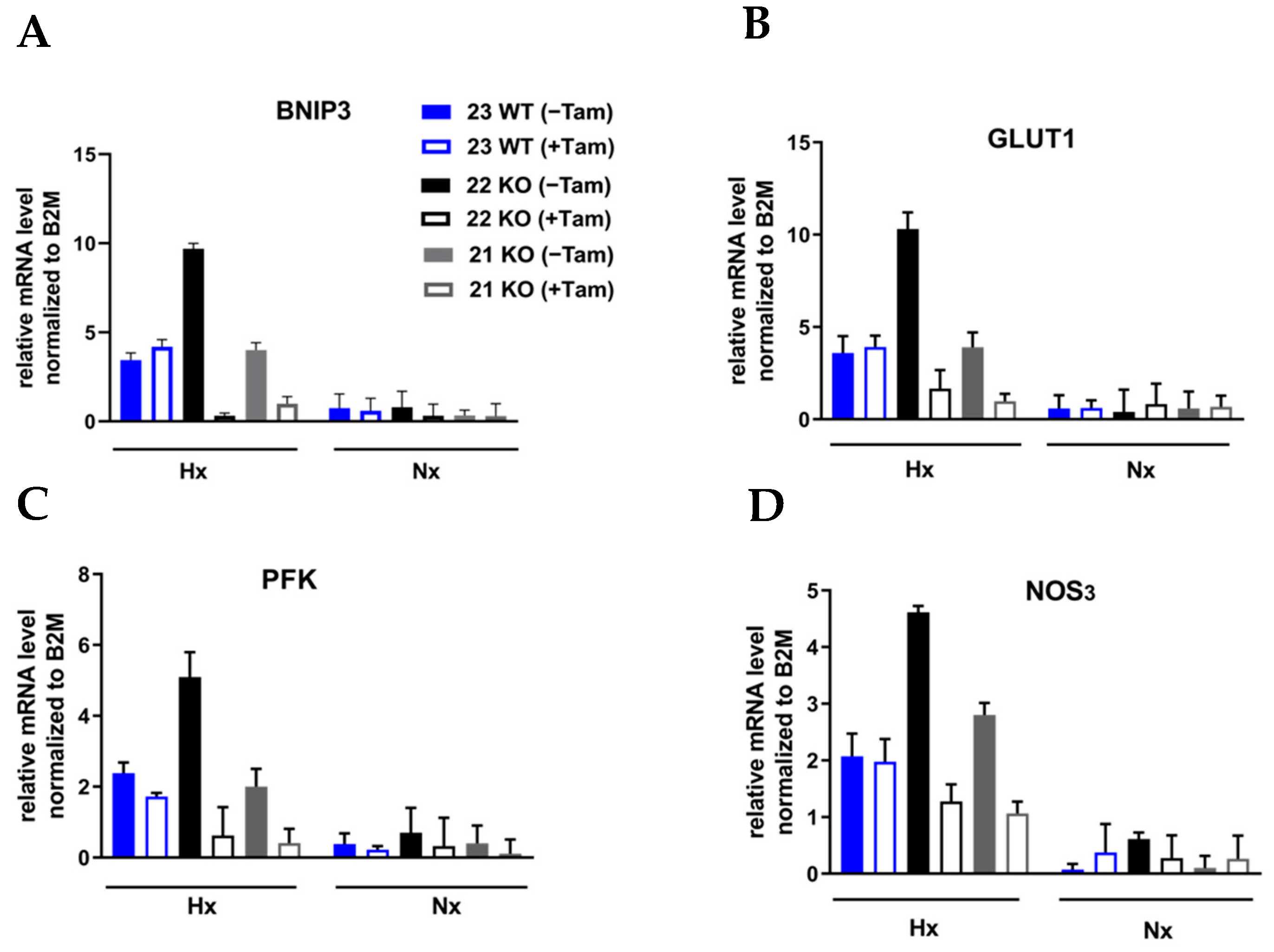
3.2. Characterization of mHDC Morphology and Function
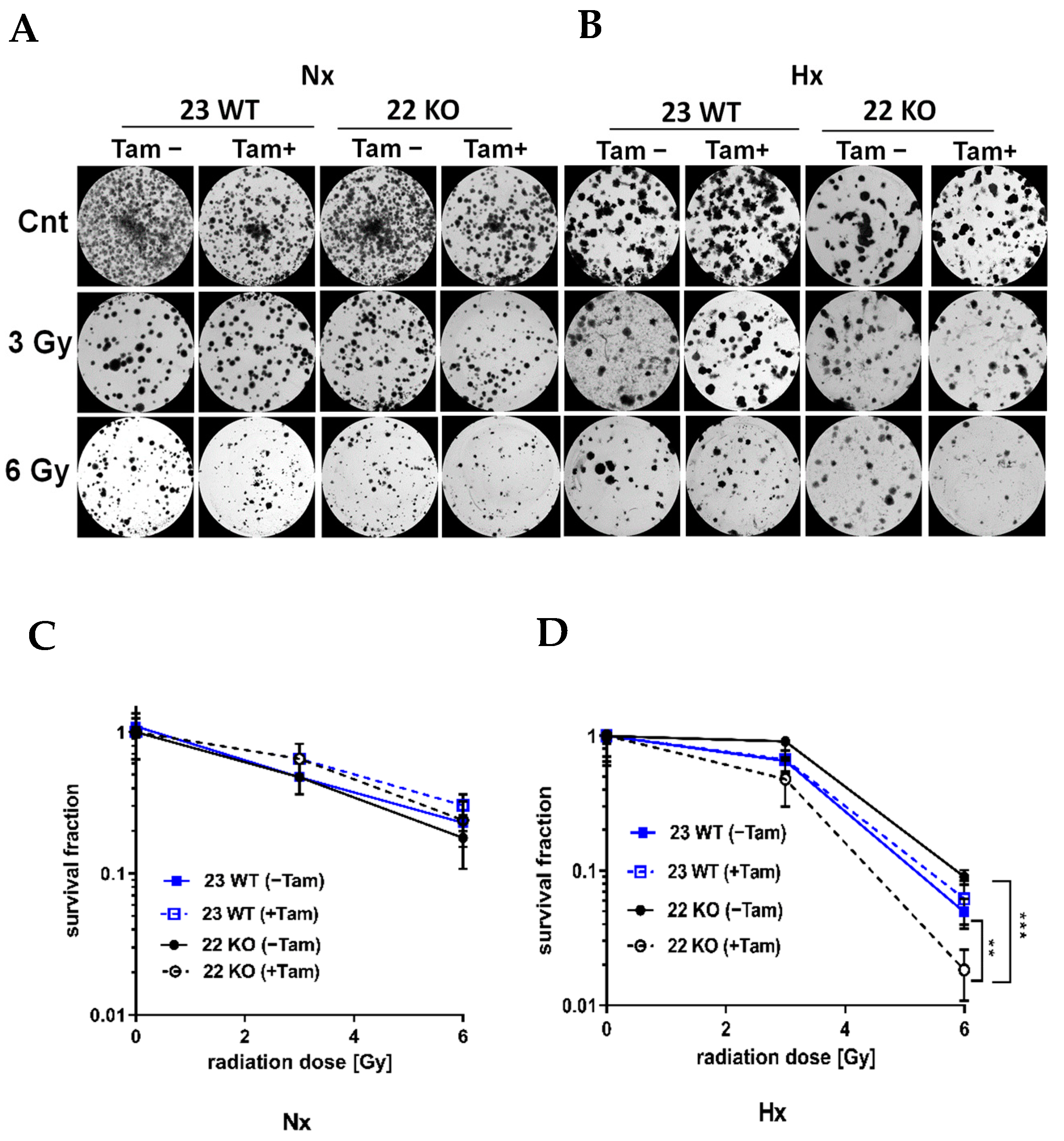
3.3. HIF-1α Knockout Promotes Cell Death and Increases Radiation Sensitivity
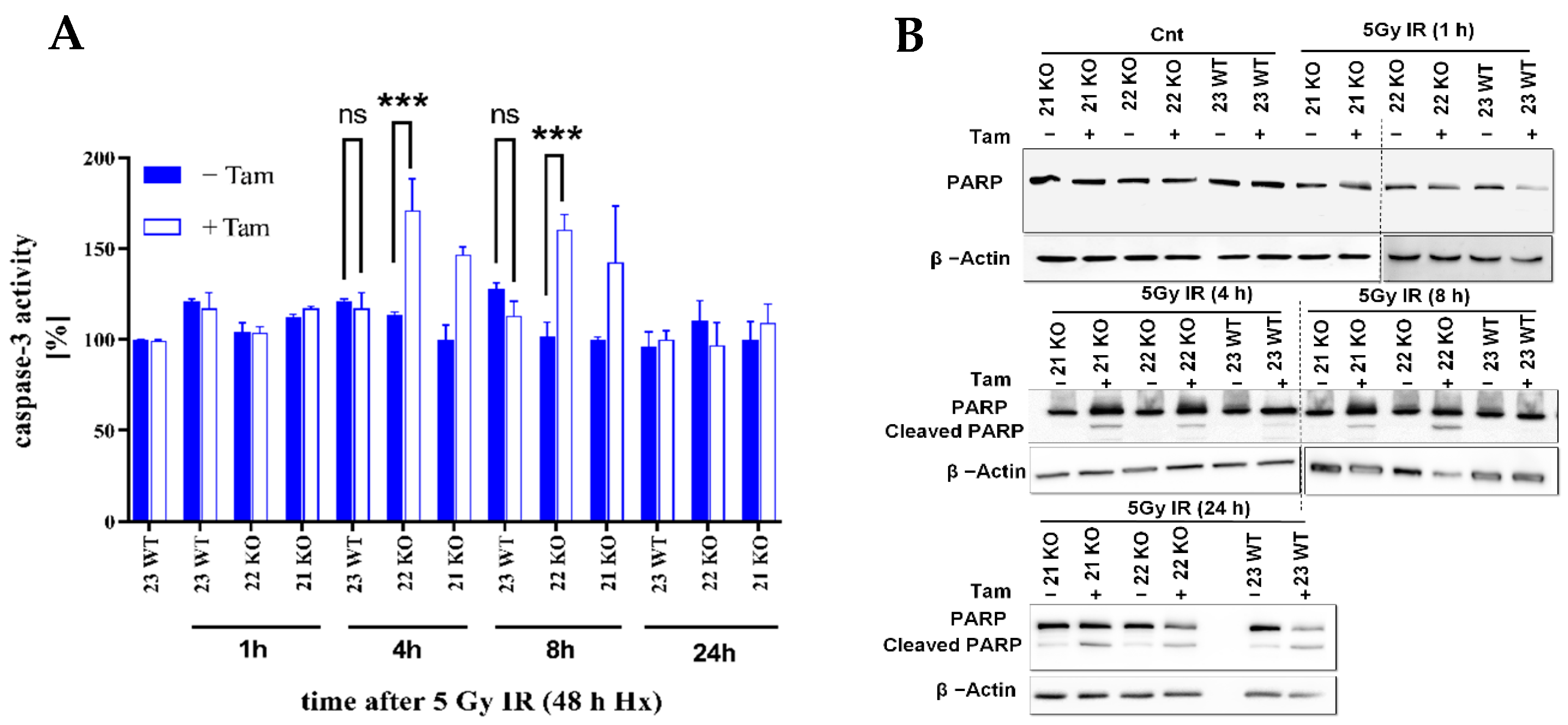
3.4. HIF-1α Knockout Modulates Apoptosis in Response to Radiation
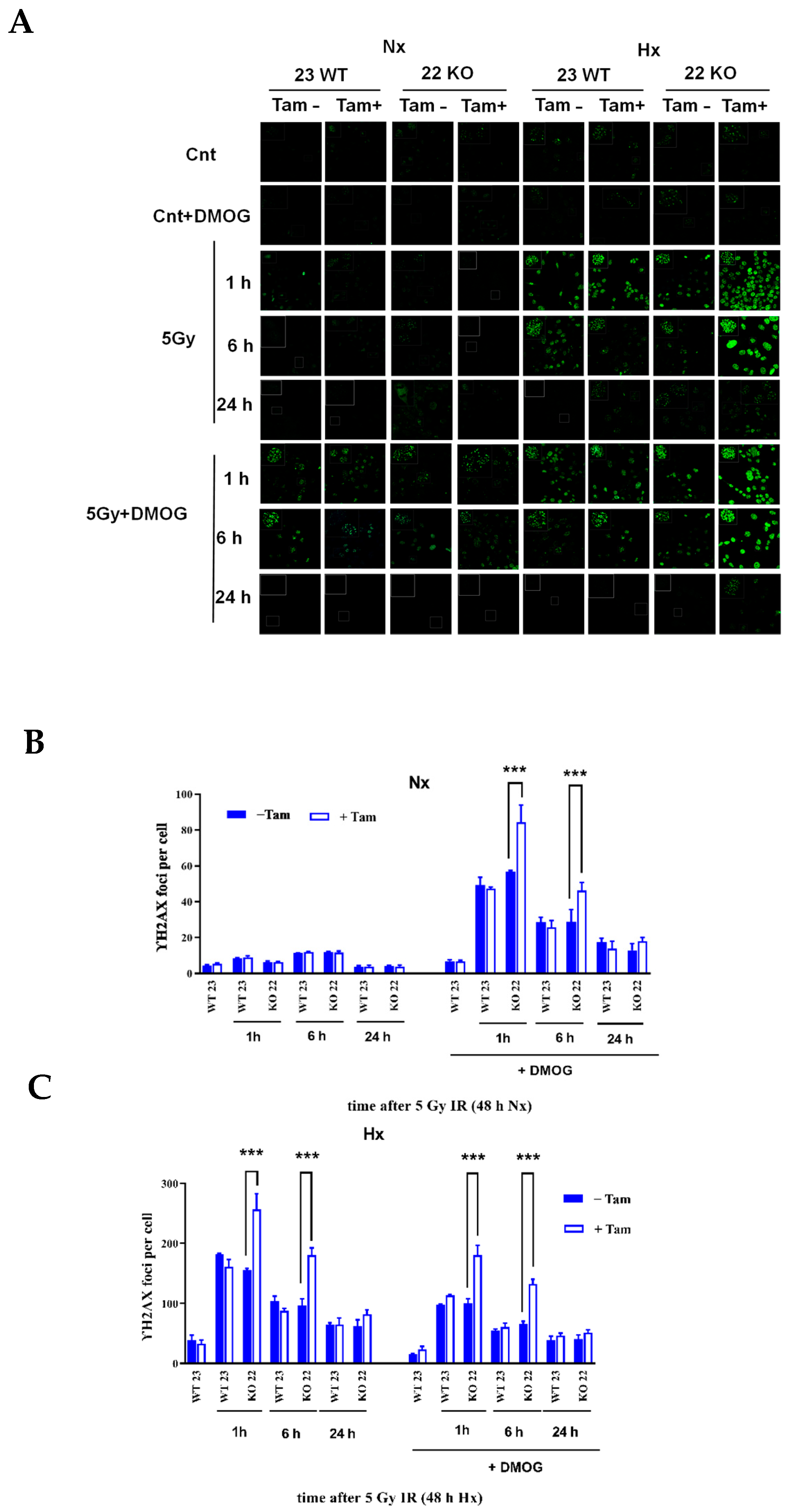
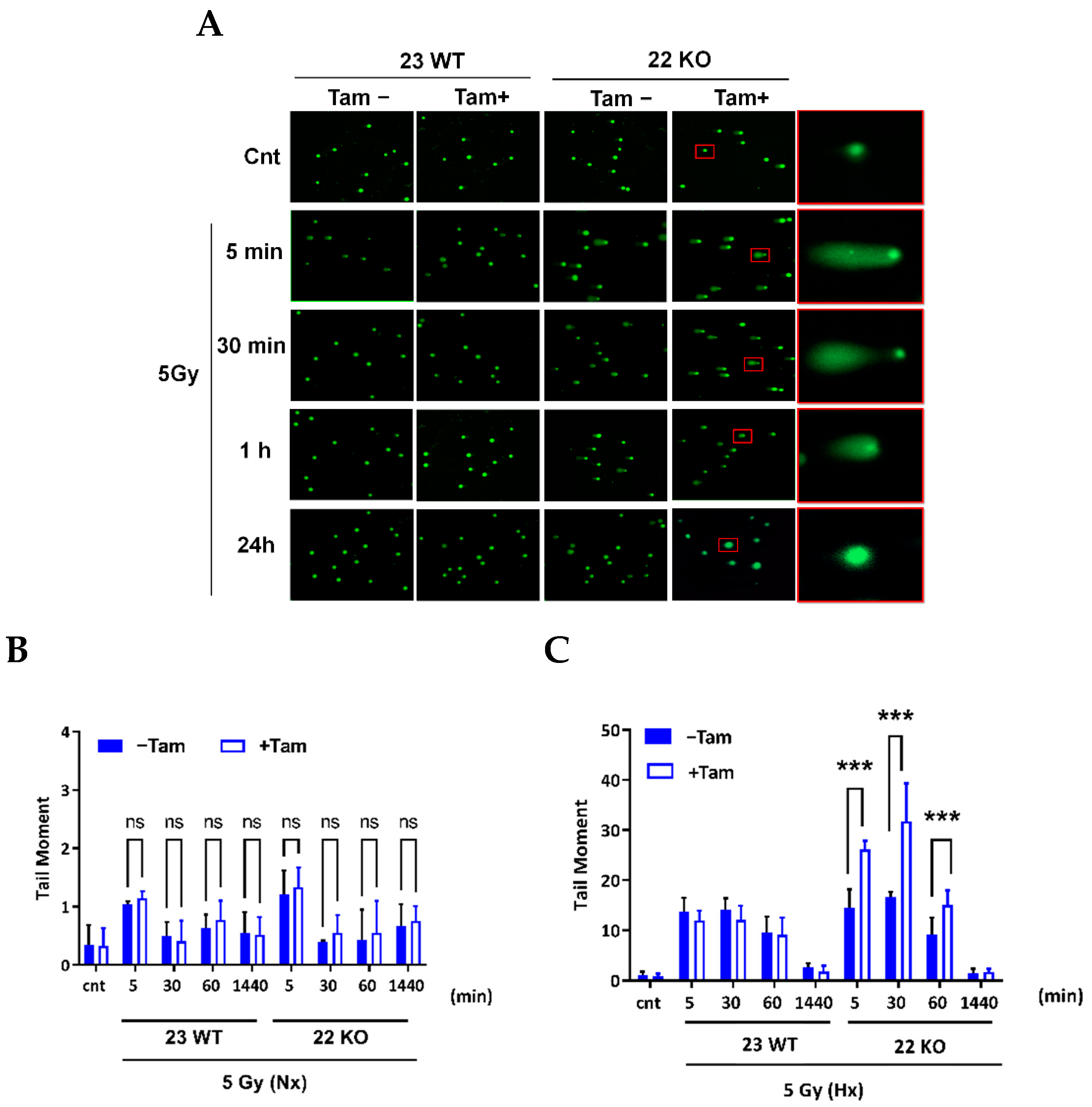
3.5. HIF-1α Deficiency Leads to Increased DNA Damage and Delay in DNA Repair
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wakim, K.G. Physiology of the Liver. Am. J. Med. 1954, 16, 256–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, H.; Yamaguchi, J.I.; Kato, S.; Hamada, M.; Tada, M.; Endo, H. Downregulation of CYP1A2, CYP2B6, and CYP3A4 in Human Hepatocytes by Prolyl Hydroxylase Domain 2 Inhibitors via Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-α Stabilization. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2021, 49, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duret, C.; Gerbal-Chaloin, S.; Ramos, J.; Fabre, J.-M.; Jacquet, E.; Navarro, F.; Blanc, P.; Sa-Cunha, A.; Maurel, P.; Daujat-Chavanieu, M. Isolation, Characterization, and Differentiation to Hepatocyte-Like Cells of Nonparenchymal Epithelial Cells from Adult Human Liver. Stem Cells 2007, 25, 1779–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ma, Y.; Yang, L.Y.; Zhao, D. MicroRNA-20a-5p Ameliorates Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease via Inhibiting the Expression of CD36. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 596329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzen, E.; Ratcliffe, P.J. HIF Hydroxylation and Cellular Oxygen Sensing. Biol. Chem. 2004, 385, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesener, M.S.; Jürgensen, J.S.; Rosenberger, C.; Scholze, C.K.; Hörstrup, J.H.; Warnecke, C.; Mandriota, S.; Bechmann, I.; Frei, U.A.; Pugh, C.W.; et al. Widespread Hypoxia-Inducible Expression of HIF-2alpha in Distinct Cell Populations of Different Organs. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 271–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Makino, Y.; Kanopka, A.; Wilson, W.J.; Tanaka, H.; Poellinger, L. Inhibitory PAS Domain Protein (IPAS) Is a Hypoxia-Inducible Splicing Variant of the Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-3α Locus. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 32405–32408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Epstein, A.C.R.; Gleadle, J.M.; McNeill, L.A.; Hewitson, K.S.; O’Rourke, J.; Mole, D.R.; Mukherji, M.; Metzen, E.; Wilson, M.I.; Dhanda, A.; et al. C. elegans EGL-9 and Mammalian Homologs Define a Family of Dioxygenases That Regulate HIF by Prolyl Hydroxylation. Cell 2001, 107, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaelin, W.G.; Ratcliffe, P.J. Oxygen Sensing by Metazoans: The Central Role of the HIF Hydroxylase Pathway. Mol. Cell 2008, 30, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenger, R.H.; Stiehl, D.P.; Camenisch, G. Integration of Oxygen Signaling at the Consensus HRE. Sci. STKE 2005, 2005, re12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.S.; Riopel, M.; Cabrales, P.; Bandyopadhyay, G.K. Hepatocyte-Specific HIF-1 Ablation Improves Obesity-Induced Glucose Intolerance by Reducing First-Pass GLP-1 Degradation. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaaw4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Jursa, T.; Aschner, M.; Smith, D.R.; Mukhopadhyay, S. Up-Regulation of the Manganese Transporter SLC30A10 by Hypoxia-Inducible Factors Defines a Homeostatic Response to Manganese Toxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2107673118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyssonnaux, C.; Zinkernagel, A.S.; Schuepbach, R.A.; Rankin, E.; Vaulont, S.; Haase, V.H.; Nizet, V.; Johnson, R.S. Regulation of Iron Homeostasis by the Hypoxia-Inducible Transcription Factors (HIFs). J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 1926–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alarcón, K.; Alba de, J.; Xu, X. Mechanisms of Radioresistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Oncol. Transl. Med. 2017, 3, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Huang, R.; Hu, H.; Yu, L.; Tang, Q.; Tao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, G. Integrative Analysis of Hypoxia-Associated Signature in Pan-Cancer. iScience 2020, 23, 101460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, A.L. Hypoxia—A Key Regulatory Factor in Tumour Growth. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bristow, R.G.; Hill, R.P. Hypoxia and Metabolism: Hypoxia, DNA Repair and Genetic Instability. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horsman, M.R.; Overgaard, J. The Impact of Hypoxia and Its Modification of the Outcome of Radiotherapy. J. Radiat. Res. 2016, 57, i90–i98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rofstad, E.K.; Sundfør, K.; Lyng, H.; Tropé, C.G. Hypoxia-Induced Treatment Failure in Advanced Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Uterine Cervix Is Primarily Due to Hypoxia-Induced Radiation Resistance Rather than Hypoxia-Induced Metastasis. Br. J. Cancer 2000, 83, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenza, G.L. HIF-1: Upstream and Downstream of Cancer Metabolism. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2010, 20, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vooijs, M.; Gort, E.; Groot, A.; der Wall, E.; van Diest, P. Hypoxic Regulation of Metastasis via Hypoxia-Inducible Factors. Curr. Mol. Med. 2008, 8, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, A.S.; Dawson, L.A. Current Understanding of Ablative Radiation Therapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2021, 8, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, W.P.; Kaina, B. DNA Damage-Induced Cell Death: From Specific DNA Lesions to the DNA Damage Response and Apoptosis. Cancer Lett. 2013, 332, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankenberg-Schwager, M.; Gebauer, A.; Koppe, C.; Wolf, H.; Pralle, E.; Frankenberg, D. Single-Strand Annealing, Conservative Homologous Recombination, Nonhomologous DNA End Joining, and the Cell Cycle-Dependent Repair of DNA Double-Strand Breaks Induced by Sparsely or Densely Ionizing Radiation. Radiat. Res. 2009, 171, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibler, J.; Zevnik, B.; Küter-Luks, B.; Andreas, S.; Kern, H.; Hennek, T.; Rode, A.; Heimann, C.; Faust, N.; Kauselmann, G.; et al. Rapid Generation of Inducible Mouse Mutants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, H.E.; Poloni, M.; McNulty, W.; Elson, D.; Gassmann, M.; Arbeit, J.M.; Johnson, R.S. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α Is a Positive Factor in Solid Tumor Growth. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 4010–4015. [Google Scholar]
- Levy, G.; Bomze, D.; Heinz, S.; Ramachandran, S.D.; Noerenberg, A.; Cohen, M.; Shibolet, O.; Sklan, E.; Braspenning, J.; Nahmias, Y. Long-Term Culture and Expansion of Primary Human Hepatocytes. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 1264–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pompsch, M.; Vogel, J.; Classen, F.; Kranz, P.; Iliakis, G.; Riffkin, H.; Brockmeier, U.; Metzen, E. The Presumed MTH1-Inhibitor TH588 Sensitizes Colorectal Carcinoma Cells to Ionizing Radiation in Hypoxia. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Classen, F.; Kranz, P.; Riffkin, H.; Pompsch, M.; Wolf, A.; Göpelt, K.; Baumann, M.; Baumann, J.; Brockmeier, U.; Metzen, E. Autophagy Induced by Ionizing Radiation Promotes Cell Death over Survival in Human Colorectal Cancer Cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2019, 374, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olive, P.L.; Banáth, J.P. The Comet Assay: A Method to Measure DNA Damage in Individual Cells. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelino-Camelia, G.; Ellis, J.; Mavromatos, N.E.; Nanopoulos, D.V.; Sarkar, S. Tests of Quantum Gravity from Observations of γ-Ray Bursts. Nature 1998, 393, 763–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ryan, H.E.; Lo, J.; Johnson, R.S. HIF-1α Is Required for Solid Tumor Formation and Embryonic Vascularization. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 3005–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Branco-Price, C.; Zhang, N.; Schnelle, M.; Evans, C.; Katschinski, D.M.; Liao, D.; Ellies, L.; Johnson, R.S. Endothelial Cell HIF-1α and HIF-2α Differentially Regulate Metastatic Success. Cancer Cell 2012, 21, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brown, M.; Bristow, R.; Glazer, P.; Hill, R.; McBride, W.; McKenna, G.; Muschel, R. Comment on “Tumor Response to Radiotherapy Regulated by Endothelial Cell Apoptosis” (II). Science 2003, 302, 1155–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rohwer, N.; Zasada, C.; Kempa, S.; Cramer, T. The Growing Complexity of HIF-1α’s Role in Tumorigenesis: DNA Repair and Beyond. Oncogene 2013, 32, 3569–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, N.P.; McCoy, M.T.; Tice, R.R.; Schneider, E.L. A Simple Technique for Quantitation of Low Levels of DNA Damage in Individual Cells. Exp. Cell Res. 1988, 175, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wen, P.; Locker, J. A Novel Hepatocytic Transcription Factor That Binds the Alpha-Fetoprotein Promoter-Linked Coupling Element. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1994, 14, 6616–6626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammerer, S. Three-Dimensional Liver Culture Systems to Maintain Primary Hepatic Properties for Toxicological Analysis In Vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkard, A.; Dähn, C.; Heinz, S.; Zutavern, A.; Sonntag-Buck, V.; Maltman, D.; Przyborski, S.; Hewitt, N.J.; Braspenning, J. Generation of Proliferating Human Hepatocytes Using Upcyte® Technology: Characterisation and Applications in Induction and Cytotoxicity Assays. Xenobiotica 2012, 42, 939–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolosa, L.; Gómez-Lechón, M.J.; López, S.; Guzmán, C.; Castell, J.V.; Donato, M.T.; Jover, R. Human Upcyte Hepatocytes: Characterization of the Hepatic Phenotype and Evaluation for Acute and Long-Term Hepatotoxicity Routine Testing. Toxicol. Sci. 2016, 152, 214–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Semenza, G.L. Oxygen Sensing, Homeostasis, and Disease. N Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaelin, W.G. The von Hippel-Lindau Tumour Suppressor Protein: O2 Sensing and Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 865–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semenza, G.L. HIF-1 Mediates Metabolic Responses to Intratumoral Hypoxia and Oncogenic Mutations. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 3664–3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Depping, R.; Steinhoff, A.; Schindler, S.G.; Friedrich, B.; Fagerlund, R.; Metzen, E.; Hartmann, E.; Köhler, M. Nuclear Translocation of Hypoxia-Inducible Factors (HIFs): Involvement of the Classical Importin α/β Pathway. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Cell Res. 2008, 1783, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, L.Q.; Zhang, B.L.; Chang, Q.; Zhu, F.P.; Li, Y.Y.; Wei, Y.Q.; Guan, Y.S. 3D Conformal Radiotherapy Combined with Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 17227–17234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.M.; Giaccia, A.J. The Unique Physiology of Solid Tumors: Opportunities (and Problems) for Cancer Therapy. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 1408–1416. [Google Scholar]
- Hubbi, M.E.; Semenza, G.L. Regulation of Cell Proliferation by Hypoxia-Inducible Factors. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2015, 309, C775–C782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abend, M. Reasons to Reconsider the Significance of Apoptosis for Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2003, 79, 927–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravind, L.; Koonin, E.V. The DNA-repair protein AlkB, EGL-9, and leprecan define new families of 2-oxoglutarate- and iron dependent dioxygenases. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 10, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Wirthner, R.; Wrann, S.; Balamurugan, K.; Wenger, R.H.; Stiehl, D.P. Impaired DNA Double-Strand Break Repair Contributes to Chemoresistance in HIF-1α-Deficient Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts. Carcinogenesis 2008, 29, 2306–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marampon, F.; Gravina, G.L.; Zani, B.M.; Popov, V.M.; Fratticci, A.; Cerasani, M.; Di Genova, D.; Mancini, M.; Ciccarelli, C.; Ficorella, C.; et al. Hypoxia Sustains Glioblastoma Radioresistance through ERKs/DNA-PKcs/HIF- 1α Functional Interplay. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 45, 2121–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wozny, A.S.; Gauthier, A.; Alphonse, G.; Malésys, C.; Varoclier, V.; Beuve, M.; Brichart-Vernos, D.; Magné, N.; Vial, N.; Ardail, D.; et al. Involvement of Hif-1α in the Detection, Signaling, and Repair of Dna Double-Strand Breaks after Photon and Carbon-Ion Irradiation. Cancers 2021, 13, 3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrann, S.; Kaufmann, M.R.; Wirthner, R.; Stiehl, D.P.; Wenger, R.H. HIF Mediated and DNA Damage Independent Histone H2AX Phosphorylation in Chronic Hypoxia. Biol. Chem. 2013, 394, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mladenov, E.; Magin, S.; Soni, A.; Iliakis, G. DNA Double-Strand-Break Repair in Higher Eukaryotes and Its Role in Genomic Instability and Cancer: Cell Cycle and Proliferation-Dependent Regulation. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2016, 37–38, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindra, R.S.; Schaffer, P.J.; Meng, A.; Woo, J.; Måseide, K.; Roth, M.E.; Lizardi, P.; Hedley, D.W.; Bristow, R.G.; Glazer, P.M. Down-Regulation of Rad51 and Decreased Homologous Recombination in Hypoxic Cancer Cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 8504–8518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hamidi, A.; Wolf, A.; Dueva, R.; Kaufmann, M.; Göpelt, K.; Iliakis, G.; Metzen, E. Depletion of HIF-1α by Inducible Cre/loxP Increases the Sensitivity of Cultured Murine Hepatocytes to Ionizing Radiation in Hypoxia. Cells 2022, 11, 1671. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11101671
Hamidi A, Wolf A, Dueva R, Kaufmann M, Göpelt K, Iliakis G, Metzen E. Depletion of HIF-1α by Inducible Cre/loxP Increases the Sensitivity of Cultured Murine Hepatocytes to Ionizing Radiation in Hypoxia. Cells. 2022; 11(10):1671. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11101671
Chicago/Turabian StyleHamidi, Akram, Alexandra Wolf, Rositsa Dueva, Melanie Kaufmann, Kirsten Göpelt, George Iliakis, and Eric Metzen. 2022. "Depletion of HIF-1α by Inducible Cre/loxP Increases the Sensitivity of Cultured Murine Hepatocytes to Ionizing Radiation in Hypoxia" Cells 11, no. 10: 1671. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11101671
APA StyleHamidi, A., Wolf, A., Dueva, R., Kaufmann, M., Göpelt, K., Iliakis, G., & Metzen, E. (2022). Depletion of HIF-1α by Inducible Cre/loxP Increases the Sensitivity of Cultured Murine Hepatocytes to Ionizing Radiation in Hypoxia. Cells, 11(10), 1671. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11101671





