The Pathogenic and Therapeutic Implications of Ceramide Abnormalities in Atopic Dermatitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
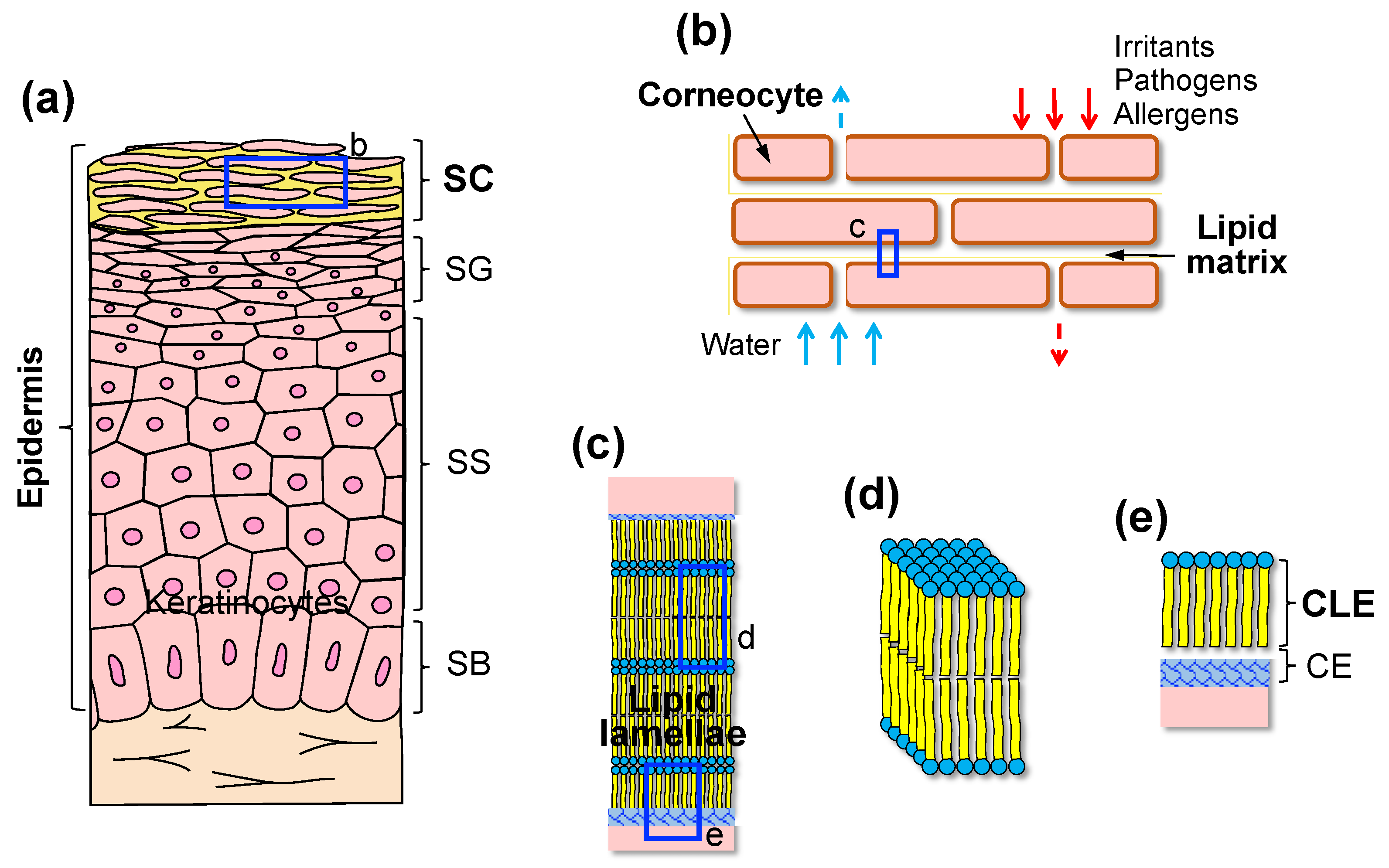
2. SC as a Permeability Barrier
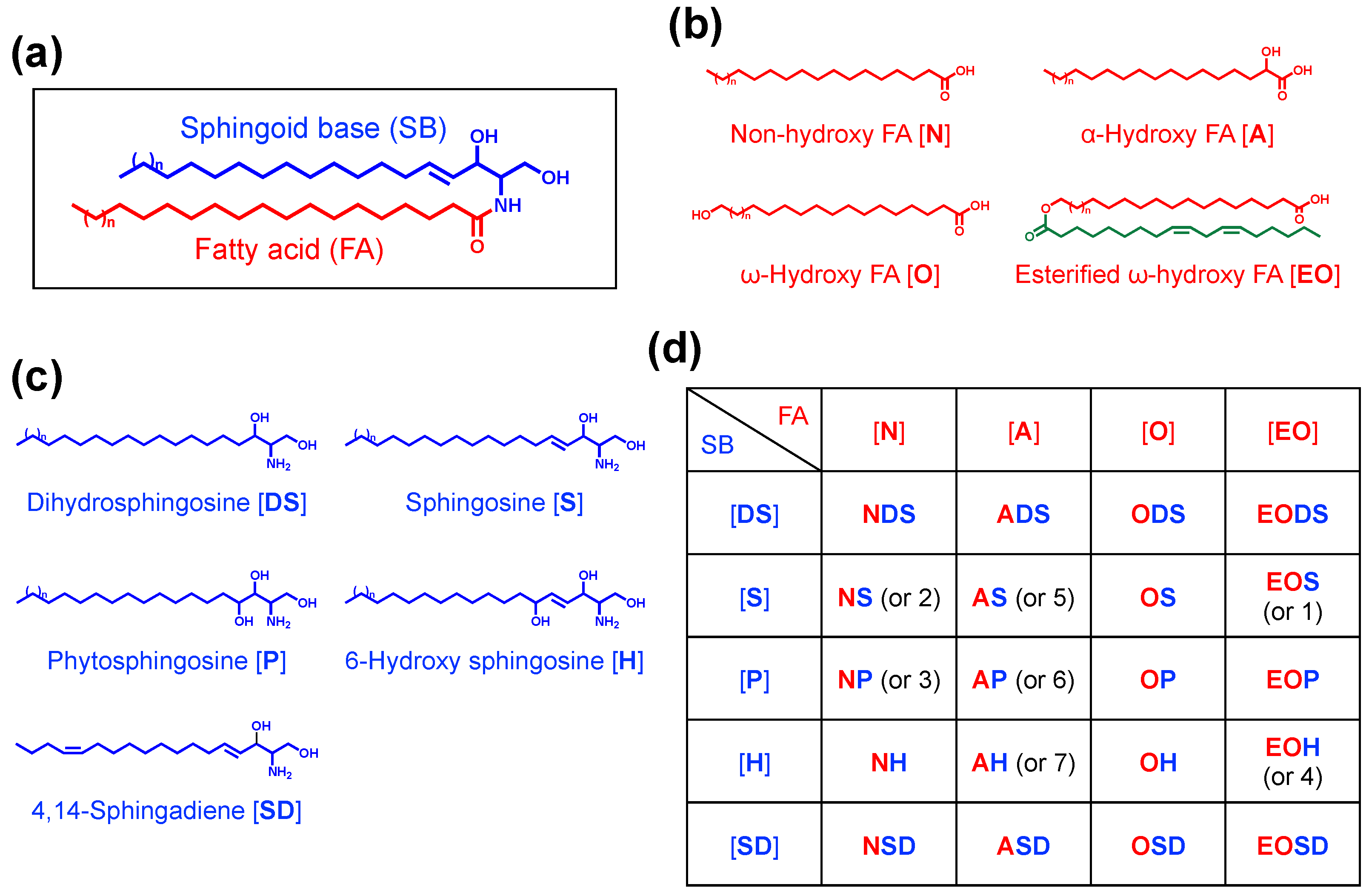
3. Diversity and Specificity of Epidermal Ceramides
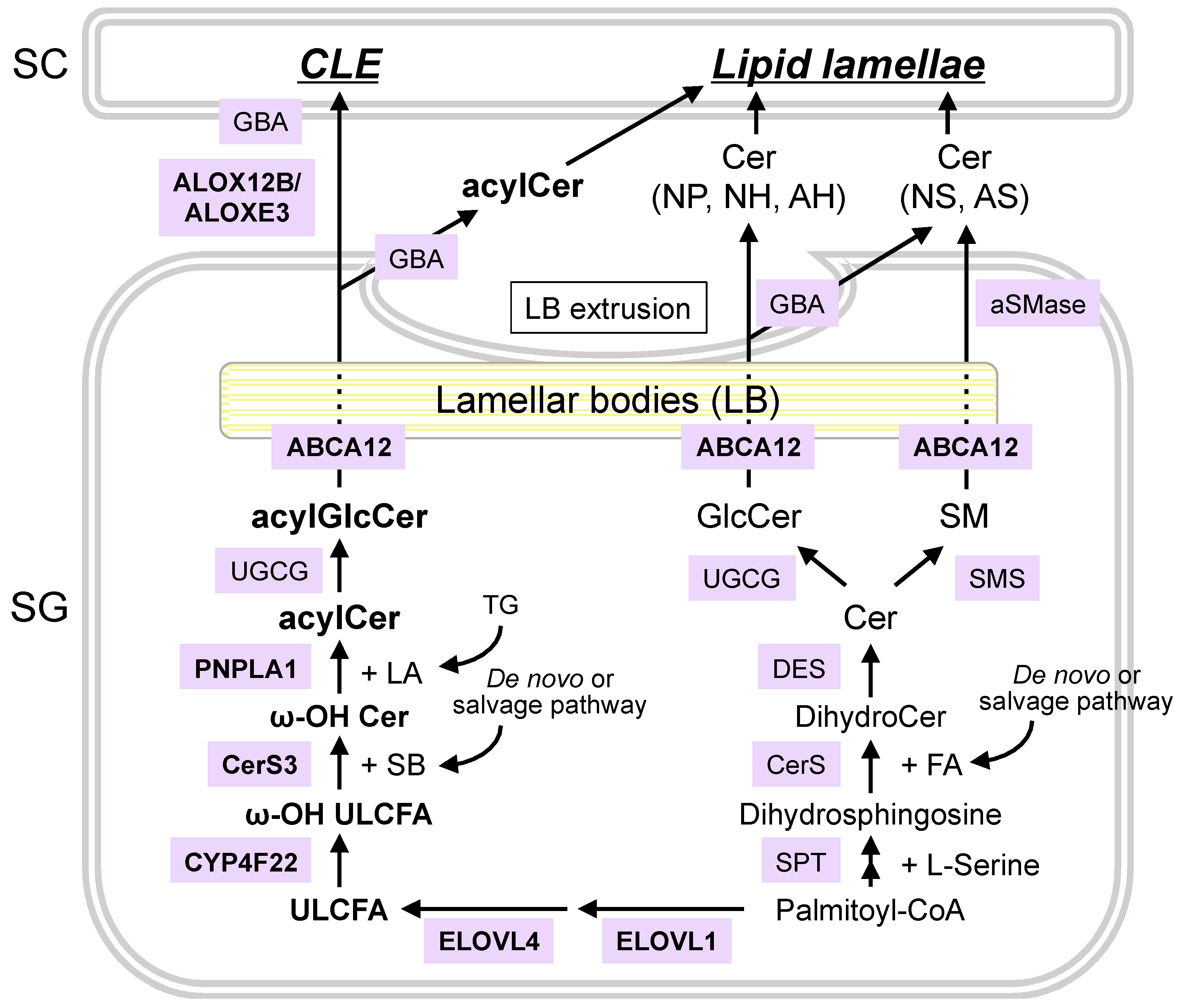
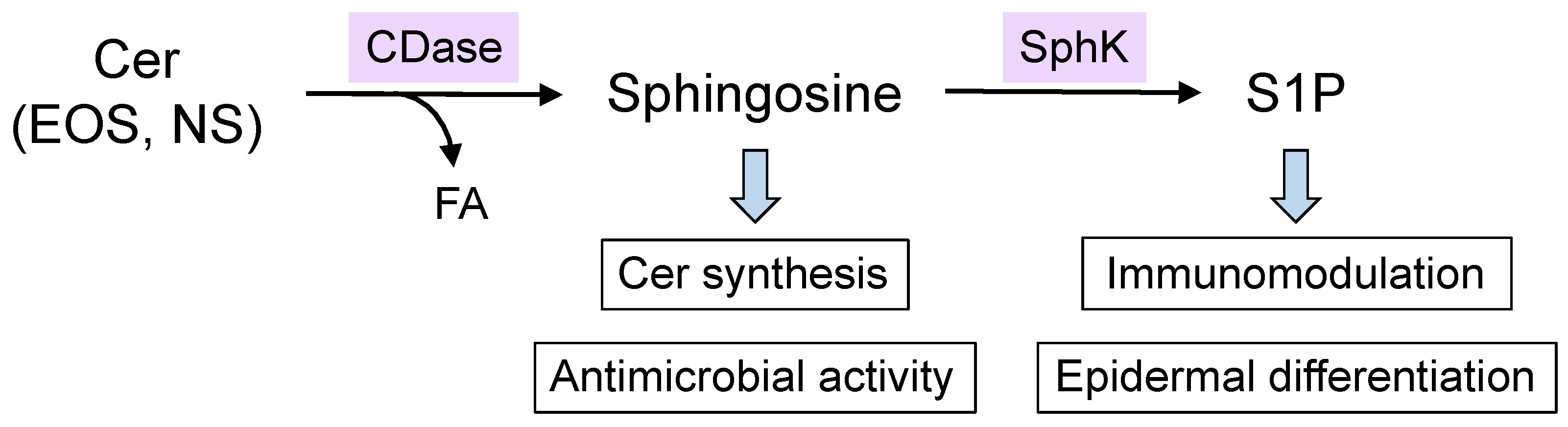
4. Synthetic and Degradation Pathways of Epidermal Ceramides
5. Altered Amount and Composition of Ceramides and Other Lipids in the Skin of Patients with AD
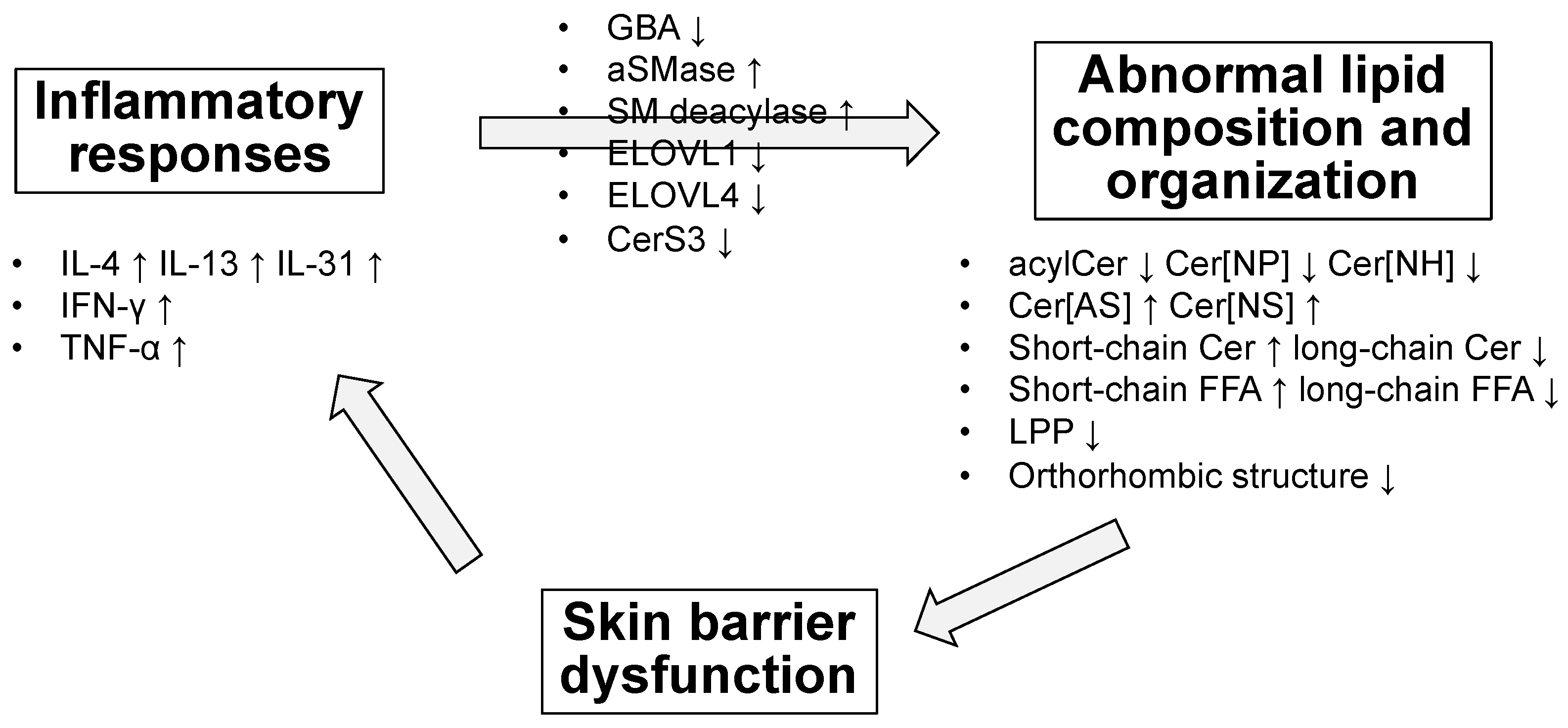
6. Possible Causes and Mechanisms of Lipid Abnormalities in AD
7. Potential Therapeutic Approaches to Correct Lipid Abnormalities in Patients with AD
8. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Elias, P.M. Stratum corneum defensive functions: An integrated view. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2005, 125, 183–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, N. Immune mechanisms leading to atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 112, S128–S139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cork, M.J.; Robinson, D.A.; Vasilopoulos, Y.; Ferguson, A.; Moustafa, M.; MacGowan, A.; Duff, G.W.; Ward, S.J.; Tazi-Ahnini, R. New perspectives on epidermal barrier dysfunction in atopic dermatitis: Gene-environment interactions. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2006, 118, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madaan, A. Epiceram for the treatment of atopic dermatitis. Drugs Today (Barc.) 2008, 44, 751–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elias, P.M. Epidermal lipids, barrier function, and desquamation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1983, 80, 44s–49s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wertz, P.W. Biochemistry of human stratum corneum lipids. In Skin Barrier; Elias, P., Feingold, K., Eds.; Taylor & Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Schreiner, V.; Gooris, G.S.; Pfeiffer, S.; Lanzendörfer, G.; Wenck, H.; Diembeck, W.; Proksch, E.; Bouwstra, J. Barrier characteristics of different human skin types investigated with X-ray diffraction, lipid analysis, and electron microscopy imaging. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2000, 114, 654–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Smeden, J.; Janssens, M.; Gooris, G.S.; Bouwstra, J.A. The important role of stratum corneum lipids for the cutaneous barrier function. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1841, 295–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwai, I.; Han, H.; Hollander, L.D.; Svensson, S.; Öfverstedt, L.G.; Anwar, J.; Brewer, J.; Bloksgaard, M.; Laloeuf, A.; Nosek, D.; et al. The Human Skin Barrier Is Organized as Stacked Bilayers of Fully Extended Ceramides with Cholesterol Molecules Associated with the Ceramide Sphingoid Moiety. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 2215–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sochorová, M.; Audrlická, P.; Červená, M.; Kováčik, A.; Kopečná, M.; Opálka, L.; Pullmannová, P.; Vávrová, K. Permeability and microstructure of cholesterol-depleted skin lipid membranes and human stratum corneum. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 535, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wertz, P.W.; Madison, K.C.; Downing, D.T. Covalently bound lipids of human stratum corneum. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1989, 92, 109–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wertz, P.W.; Swartzendruber, D.C.; Kitko, D.J.; Madison, K.C.; Downing, D.T. The role of the corneocyte lipid envelopes in cohesion of the stratum corneum. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1989, 93, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elias, P.M.; Gruber, R.; Crumrine, D.; Menon, G.; Williams, M.L.; Wakefield, J.S.; Holleran, W.M.; Uchida, Y. Formation and functions of the corneocyte lipid envelope (CLE). Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1841, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feingold, K.R. Thematic review series: Skin lipids. The role of epidermal lipids in cutaneous permeability barrier homeostasis. J. Lipid Res. 2007, 48, 2531–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, Y.; Holleran, W.M. Omega-O-acylceramide, a lipid essential for mammalian survival. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2008, 51, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robson, K.J.; Stewart, M.E.; Michelsen, S.; Lazo, N.D.; Downing, D.T. 6-Hydroxy-4-sphingenine in human epidermal ceramides. J. Lipid Res. 1994, 35, 2060–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vietzke, J.P.; Brandt, O.; Abeck, D.; Rapp, C.; Strassner, M.; Schreiner, V.; Hintze, U. Comparative investigation of human stratum corneum ceramides. Lipids 2001, 36, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponec, M.; Weerheim, A.; Lankhorst, P.; Wertz, P. New acylceramide in native and reconstructed epidermis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2003, 120, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farwanah, H.; Wohlrab, J.; Neubert, R.H.; Raith, K. Profiling of human stratum corneum ceramides by means of normal phase LC/APCI-MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2005, 383, 632–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masukawa, Y.; Narita, H.; Shimizu, E.; Kondo, N.; Sugai, Y.; Oba, T.; Homma, R.; Ishikawa, J.; Takagi, Y.; Kitahara, T.; et al. Characterization of overall ceramide species in human stratum corneum. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 1466–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, S.; Monti, M.; Sesana, S.; Caputo, R.; Carelli, S.; Ghidoni, R. Ceramide composition of the psoriatic scale. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1993, 1182, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawana, M.; Miyamoto, M.; Ohno, Y.; Kihara, A. Comparative profiling and comprehensive quantification of stratum corneum ceramides in humans and mice by LC/MS/MS. J. Lipid Res. 2020, 61, 884–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- t’Kindt, R.; Jorge, L.; Dumont, E.; Couturon, P.; David, F.; Sandra, P.; Sandra, K. Profiling and characterizing skin ceramides using reversed-phase liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabionet, M.; Bayerle, A.; Marsching, C.; Jennemann, R.; Gröne, H.J.; Yildiz, Y.; Wachten, D.; Shaw, W.; Shayman, J.A.; Sandhoff, R. 1-O-acylceramides are natural components of human and mouse epidermis. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 3312–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kováčik, A.; Roh, J.; Vávrová, K. The chemistry and biology of 6-hydroxyceramide, the youngest member of the human sphingolipid family. ChemBioChem 2014, 15, 1555–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Smeden, J.; Boiten, W.A.; Hankemeier, T.; Rissmann, R.; Bouwstra, J.A.; Vreeken, R.J. Combined LC/MS-platform for analysis of all major stratum corneum lipids, and the profiling of skin substitutes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1841, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kihara, A. Synthesis and degradation pathways, functions, and pathology of ceramides and epidermal acylceramides. Prog. Lipid Res. 2016, 63, 50–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwstra, J.A.; Gooris, G.S.; Dubbelaar, F.E.; Weerheim, A.M.; Ijzerman, A.P.; Ponec, M. Role of ceramide 1 in the molecular organization of the stratum corneum lipids. J. Lipid Res. 1998, 39, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wertz, P.W.; Cho, E.S.; Downing, D.T. Effect of essential fatty acid deficiency on the epidermal sphingolipids of the rat. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1983, 753, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melton, J.L.; Wertz, P.W.; Swartzendruber, D.C.; Downing, D.T. Effects of essential fatty acid deficiency on epidermal O-acylsphingolipids and transepidermal water loss in young pigs. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1987, 921, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Yin, H.; Boeglin, W.E.; Elias, P.M.; Crumrine, D.; Beier, D.R.; Brash, A.R. Lipoxygenases mediate the effect of essential fatty acid in skin barrier formation: A proposed role in releasing omega-hydroxyceramide for construction of the corneocyte lipid envelope. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 24046–24056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holleran, W.M.; Takagi, Y.; Uchida, Y. Epidermal sphingolipids: Metabolism, function, and roles in skin disorders. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 5456–5466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizutani, Y.; Mitsutake, S.; Tsuji, K.; Kihara, A.; Igarashi, Y. Ceramide biosynthesis in keratinocyte and its role in skin function. Biochimie 2009, 91, 784–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alderson, N.L.; Rembiesa, B.M.; Walla, M.D.; Bielawska, A.; Bielawski, J.; Hama, H. The human FA2H gene encodes a fatty acid 2-hydroxylase. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 48562–48568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ternes, P.; Franke, S.; Zähringer, U.; Sperling, P.; Heinz, E. Identification and characterization of a sphingolipid delta 4-desaturase family. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 25512–25518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akiyama, M. The roles of ABCA12 in epidermal lipid barrier formation and keratinocyte differentiation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1841, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, Y.; Hara, M.; Nishio, H.; Sidransky, E.; Inoue, S.; Otsuka, F.; Suzuki, A.; Elias, P.M.; Holleran, W.M.; Hamanaka, S. Epidermal sphingomyelins are precursors for selected stratum corneum ceramides. J. Lipid Res. 2000, 41, 2071–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamanaka, S.; Hara, M.; Nishio, H.; Otsuka, F.; Suzuki, A.; Uchida, Y. Human epidermal glucosylceramides are major precursors of stratum corneum ceramides. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2002, 119, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houben, E.; Holleran, W.M.; Yaginuma, T.; Mao, C.; Obeid, L.M.; Rogiers, V.; Takagi, Y.; Elias, P.M.; Uchida, Y. Differentiation-associated expression of ceramidase isoforms in cultured keratinocytes and epidermis. J. Lipid Res. 2006, 47, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, Y.; Nakamichi, S.; Ohkuni, A.; Kamiyama, N.; Naoe, A.; Tsujimura, H.; Yokose, U.; Sugiura, K.; Ishikawa, J.; Akiyama, M.; et al. Essential role of the cytochrome P450 CYP4F22 in the production of acylceramide, the key lipid for skin permeability barrier formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 7707–7712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, Y.; Kamiyama, N.; Nakamichi, S.; Kihara, A. PNPLA1 is a transacylase essential for the generation of the skin barrier lipid ω-O-acylceramide. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kien, B.; Grond, S.; Haemmerle, G.; Lass, A.; Eichmann, T.O.; Radner, F.P.W. ABHD5 stimulates PNPLA1-mediated ω-O-acylceramide biosynthesis essential for a functional skin permeability barrier. J. Lipid Res. 2018, 59, 2360–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-Garcia, A.; Thomas, C.P.; Keeney, D.S.; Zheng, Y.; Brash, A.R. The importance of the lipoxygenase-hepoxilin pathway in the mammalian epidermal barrier. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1841, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassa, T.; Ohno, Y.; Suzuki, S.; Nomura, T.; Nishioka, C.; Kashiwagi, T.; Hirayama, T.; Akiyama, M.; Taguchi, R.; Shimizu, H.; et al. Impaired epidermal permeability barrier in mice lacking elovl1, the gene responsible for very-long-chain fatty acid production. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 33, 2787–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldahmesh, M.A.; Mohamed, J.Y.; Alkuraya, H.S.; Verma, I.C.; Puri, R.D.; Alaiya, A.A.; Rizzo, W.B.; Alkuraya, F.S. Recessive mutations in ELOVL4 cause ichthyosis, intellectual disability, and spastic quadriplegia. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 89, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasireddy, V.; Uchida, Y.; Salem, N.; Kim, S.Y.; Mandal, M.N.; Reddy, G.B.; Bodepudi, R.; Alderson, N.L.; Brown, J.C.; Hama, H.; et al. Loss of functional ELOVL4 depletes very long-chain fatty acids (> or =C28) and the unique omega-O-acylceramides in skin leading to neonatal death. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2007, 16, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckl, K.M.; Tidhar, R.; Thiele, H.; Oji, V.; Hausser, I.; Brodesser, S.; Preil, M.L.; Onal-Akan, A.; Stock, F.; Müller, D.; et al. Impaired epidermal ceramide synthesis causes autosomal recessive congenital ichthyosis and reveals the importance of ceramide acyl chain length. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 2202–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennemann, R.; Rabionet, M.; Gorgas, K.; Epstein, S.; Dalpke, A.; Rothermel, U.; Bayerle, A.; van der Hoeven, F.; Imgrund, S.; Kirsch, J.; et al. Loss of ceramide synthase 3 causes lethal skin barrier disruption. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, 586–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grall, A.; Guaguère, E.; Planchais, S.; Grond, S.; Bourrat, E.; Hausser, I.; Hitte, C.; Le Gallo, M.; Derbois, C.; Kim, G.J.; et al. PNPLA1 mutations cause autosomal recessive congenital ichthyosis in golden retriever dogs and humans. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epp, N.; Fürstenberger, G.; Müller, K.; de Juanes, S.; Leitges, M.; Hausser, I.; Thieme, F.; Liebisch, G.; Schmitz, G.; Krieg, P. 12R-lipoxygenase deficiency disrupts epidermal barrier function. J. Cell Biol. 2007, 177, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, J.L.; Qiu, H.; Turbe-Doan, A.; Yun, Y.; Boeglin, W.E.; Brash, A.R.; Beier, D.R. A mouse mutation in the 12R-lipoxygenase, Alox12b, disrupts formation of the epidermal permeability barrier. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 1893–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieg, P.; Rosenberger, S.; de Juanes, S.; Latzko, S.; Hou, J.; Dick, A.; Kloz, U.; van der Hoeven, F.; Hausser, I.; Esposito, I.; et al. Aloxe3 knockout mice reveal a function of epidermal lipoxygenase-3 as hepoxilin synthase and its pivotal role in barrier formation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibel, D.J.; Aly, R.; Shah, S.; Shinefield, H.R. Sphingosines: Antimicrobial barriers of the skin. Acta Derm. Venereol. 1993, 73, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Japtok, L.; Bäumer, W.; Kleuser, B. Sphingosine-1-phosphate as signaling molecule in the skin: Relevance in atopic dermatitis. Allergo J. Int. 2014, 23, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidinger, S.; Beck, L.A.; Bieber, T.; Kabashima, K.; Irvine, A.D. Atopic dermatitis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2018, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flohr, C.; Mann, J. New insights into the epidemiology of childhood atopic dermatitis. Allergy 2014, 69, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imokawa, G.; Abe, A.; Jin, K.; Higaki, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Hidano, A. Decreased level of ceramides in stratum corneum of atopic dermatitis: An etiologic factor in atopic dry skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1991, 96, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, M.; Umemoto, N.; Sugiura, H.; Uehara, M. Difference in ceramide composition between “dry” and “normal” skin in patients with atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm. Venereol. 1999, 79, 246–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Nardo, A.; Wertz, P.; Giannetti, A.; Seidenari, S. Ceramide and cholesterol composition of the skin of patients with atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm. Venereol. 1998, 78, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, A.; Serizawa, S.; Ito, M.; Sato, Y. Stratum corneum lipid abnormalities in atopic dermatitis. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 1991, 283, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bleck, O.; Abeck, D.; Ring, J.; Hoppe, U.; Vietzke, J.P.; Wolber, R.; Brandt, O.; Schreiner, V. Two ceramide subfractions detectable in Cer(AS) position by HPTLC in skin surface lipids of non-lesional skin of atopic eczema. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1999, 113, 894–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, J.; Narita, H.; Kondo, N.; Hotta, M.; Takagi, Y.; Masukawa, Y.; Kitahara, T.; Takema, Y.; Koyano, S.; Yamazaki, S.; et al. Changes in the ceramide profile of atopic dermatitis patients. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 2511–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssens, M.; van Smeden, J.; Gooris, G.S.; Bras, W.; Portale, G.; Caspers, P.J.; Vreeken, R.J.; Hankemeier, T.; Kezic, S.; Wolterbeek, R.; et al. Increase in short-chain ceramides correlates with an altered lipid organization and decreased barrier function in atopic eczema patients. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 53, 2755–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Smeden, J.; Janssens, M.; Kaye, E.C.; Caspers, P.J.; Lavrijsen, A.P.; Vreeken, R.J.; Bouwstra, J.A. The importance of free fatty acid chain length for the skin barrier function in atopic eczema patients. Exp. Dermatol. 2014, 23, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danso, M.; Boiten, W.; van Drongelen, V.; Gmelig Meijling, K.; Gooris, G.; El Ghalbzouri, A.; Absalah, S.; Vreeken, R.; Kezic, S.; van Smeden, J.; et al. Altered expression of epidermal lipid bio-synthesis enzymes in atopic dermatitis skin is accompanied by changes in stratum corneum lipid composition. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2017, 88, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joo, K.M.; Hwang, J.H.; Bae, S.; Nahm, D.H.; Park, H.S.; Ye, Y.M.; Lim, K.M. Relationship of ceramide-, and free fatty acid-cholesterol ratios in the stratum corneum with skin barrier function of normal, atopic dermatitis lesional and non-lesional skins. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2015, 77, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Lee, N.R.; Park, S.Y.; Jun, M.; Lee, K.; Kim, S.; Park, C.S.; Liu, K.H.; Choi, E.H. As in Atopic Dermatitis, Nonlesional Skin in Allergic Contact Dermatitis Displays Abnormalities in Barrier Function and Ceramide Content. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 748–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokose, U.; Ishikawa, J.; Morokuma, Y.; Naoe, A.; Inoue, Y.; Yasuda, Y.; Tsujimura, H.; Fujimura, T.; Murase, T.; Hatamochi, A. The ceramide [NP]/[NS] ratio in the stratum corneum is a potential marker for skin properties and epidermal differentiation. BMC Dermatol. 2020, 20, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macheleidt, O.; Kaiser, H.W.; Sandhoff, K. Deficiency of epidermal protein-bound omega-hydroxyceramides in atopic dermatitis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2002, 119, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boiten, W.; van Smeden, J.; Bouwstra, J. The Cornified Envelope-Bound Ceramide Fraction Is Altered in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2020, 140, 1097–1100.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens, M.; van Smeden, J.; Gooris, G.S.; Bras, W.; Portale, G.; Caspers, P.J.; Vreeken, R.J.; Kezic, S.; Lavrijsen, A.P.; Bouwstra, J.A. Lamellar lipid organization and ceramide composition in the stratum corneum of patients with atopic eczema. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 2136–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.Y.; Kusuda, S.; Seguchi, T.; Takahashi, M.; Aisu, K.; Tezuka, T. Decreased level of prosaposin in atopic skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1997, 109, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jin, K.; Higaki, Y.; Takagi, Y.; Higuchi, K.; Yada, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Imokawa, G. Analysis of beta-glucocerebrosidase and ceramidase activities in atopic and aged dry skin. Acta Derm. Venereol. 1994, 74, 337–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boer, D.E.C.; van Smeden, J.; Al-Khakany, H.; Melnik, E.; van Dijk, R.; Absalah, S.; Vreeken, R.J.; Haenen, C.C.P.; Lavrijsen, A.P.M.; Overkleeft, H.S.; et al. Skin of atopic dermatitis patients shows disturbed β-glucocerebrosidase and acid sphingomyelinase activity that relates to changes in stratum corneum lipid composition. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2020, 1865, 158673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusuda, S.; Cui, C.Y.; Takahashi, M.; Tezuka, T. Localization of sphingomyelinase in lesional skin of atopic dermatitis patients. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1998, 111, 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jensen, J.M.; Fölster-Holst, R.; Baranowsky, A.; Schunck, M.; Winoto-Morbach, S.; Neumann, C.; Schütze, S.; Proksch, E. Impaired sphingomyelinase activity and epidermal differentiation in atopic dermatitis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2004, 122, 1423–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, J.; Higuchi, K.; Okamoto, R.; Kawashima, M.; Imokawa, G. High-expression of sphingomyelin deacylase is an important determinant of ceramide deficiency leading to barrier disruption in atopic dermatitis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2000, 115, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arikawa, J.; Ishibashi, M.; Kawashima, M.; Takagi, Y.; Ichikawa, Y.; Imokawa, G. Decreased levels of sphingosine, a natural antimicrobial agent, may be associated with vulnerability of the stratum corneum from patients with atopic dermatitis to colonization by Staphylococcus aureus. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2002, 119, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnishi, Y.; Okino, N.; Ito, M.; Imayama, S. Ceramidase activity in bacterial skin flora as a possible cause of ceramide deficiency in atopic dermatitis. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 1999, 6, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imokawa, G. A possible mechanism underlying the ceramide deficiency in atopic dermatitis: Expression of a deacylase enzyme that cleaves the N-acyl linkage of sphingomyelin and glucosylceramide. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2009, 55, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, Y.; Ogata, J.; Higaki, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Yada, Y.; Higuchi, K.; Tsuchiya, T.; Kawainami, S.; Imokawa, G. Abnormal expression of sphingomyelin acylase in atopic dermatitis: An etiologic factor for ceramide deficiency. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1996, 106, 1242–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teranishi, Y.; Kuwahara, H.; Ueda, M.; Takemura, T.; Kusumoto, M.; Nakamura, K.; Sakai, J.; Kimura, T.; Furutani, Y.; Kawashima, M.; et al. Sphingomyelin Deacylase, the Enzyme Involved in the Pathogenesis of Atopic Dermatitis, Is Identical to the β-Subunit of Acid Ceramidase. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatano, Y.; Terashi, H.; Arakawa, S.; Katagiri, K. Interleukin-4 suppresses the enhancement of ceramide synthesis and cutaneous permeability barrier functions induced by tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gamma in human epidermis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2005, 124, 786–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurahashi, R.; Hatano, Y.; Katagiri, K. IL-4 suppresses the recovery of cutaneous permeability barrier functions in vivo. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 1329–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.H.; Jang, W.H.; Seo, J.A.; Park, M.; Lee, T.R.; Park, Y.H.; Kim, D.K.; Lim, K.M. Decrease of ceramides with very long-chain fatty acids and downregulation of elongases in a murine atopic dermatitis model. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 476–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danso, M.O.; van Drongelen, V.; Mulder, A.; van Esch, J.; Scott, H.; van Smeden, J.; El Ghalbzouri, A.; Bouwstra, J.A. TNF-α and Th2 cytokines induce atopic dermatitis-like features on epidermal differentiation proteins and stratum corneum lipids in human skin equivalents. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 1941–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berdyshev, E.; Goleva, E.; Bronova, I.; Dyjack, N.; Rios, C.; Jung, J.; Taylor, P.; Jeong, M.; Hall, C.F.; Richers, B.N.; et al. Lipid abnormalities in atopic skin are driven by type 2 cytokines. JCI Insight 2018, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, E.; Yoshida, N.; Sugiura, A.; Imokawa, G. Th1 cytokines accentuate but Th2 cytokines attenuate ceramide production in the stratum corneum of human epidermal equivalents: An implication for the disrupted barrier mechanism in atopic dermatitis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2012, 68, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawada, C.; Kanoh, H.; Nakamura, M.; Mizutani, Y.; Fujisawa, T.; Banno, Y.; Seishima, M. Interferon-γ decreases ceramides with long-chain fatty acids: Possible involvement in atopic dermatitis and psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 712–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanoh, H.; Ishitsuka, A.; Fujine, E.; Matsuhaba, S.; Nakamura, M.; Ito, H.; Inagaki, N.; Banno, Y.; Seishima, M. IFN-γ Reduces Epidermal Barrier Function by Affecting Fatty Acid Composition of Ceramide in a Mouse Atopic Dermatitis Model. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 2019, 3030268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, C.N.; Irvine, A.D.; Terron-Kwiatkowski, A.; Zhao, Y.; Liao, H.; Lee, S.P.; Goudie, D.R.; Sandilands, A.; Campbell, L.E.; Smith, F.J.; et al. Common loss-of-function variants of the epidermal barrier protein filaggrin are a major predisposing factor for atopic dermatitis. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelova-Fischer, I.; Mannheimer, A.C.; Hinder, A.; Ruether, A.; Franke, A.; Neubert, R.H.; Fischer, T.W.; Zillikens, D. Distinct barrier integrity phenotypes in filaggrin-related atopic eczema following sequential tape stripping and lipid profiling. Exp. Dermatol. 2011, 20, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungersted, J.M.; Scheer, H.; Mempel, M.; Baurecht, H.; Cifuentes, L.; Høgh, J.K.; Hellgren, L.I.; Jemec, G.B.E.; Agner, T.; Weidinger, S. Stratum corneum lipids, skin barrier function and filaggrin mutations in patients with atopic eczema. Allergy 2010, 65, 911–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thyssen, J.P.; Kezic, S. Causes of epidermal filaggrin reduction and their role in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 792–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, J.S.; Fluhr, J.W.; Man, M.Q.; Fowler, A.J.; Hachem, J.P.; Crumrine, D.; Ahn, S.K.; Brown, B.E.; Elias, P.M.; Feingold, K.R. Short-term glucocorticoid treatment compromises both permeability barrier homeostasis and stratum corneum integrity: Inhibition of epidermal lipid synthesis accounts for functional abnormalities. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2003, 120, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Jung, M.; Hong, S.P.; Jeon, H.; Kim, M.J.; Cho, M.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Man, M.Q.; Elias, P.M.; Choi, E.H. Topical calcineurin inhibitors compromise stratum corneum integrity, epidermal permeability and antimicrobial barrier function. Exp. Dermatol. 2010, 19, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.M.; Pfeiffer, S.; Witt, M.; Bräutigam, M.; Neumann, C.; Weichenthal, M.; Schwarz, T.; Fölster-Holst, R.; Proksch, E. Different effects of pimecrolimus and betamethasone on the skin barrier in patients with atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 123, 1124–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dähnhardt, D.; Bastian, M.; Dähnhardt-Pfeiffer, S.; Buchner, M.; Fölster-Holst, R. Comparing the effects of proactive treatment with tacrolimus ointment and mometasone furoate on the epidermal barrier structure and ceramide levels of patients with atopic dermatitis. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohner, M.H.; Thormann, K.; Cazzaniga, S.; Yousefi, S.; Simon, H.U.; Schlapbach, C.; Simon, D. Dupilumab reduces inflammation and restores the skin barrier in patients with atopic dermatitis. Allergy 2021, 76, 1268–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagawa-Nakamura, A.; Ryoke, K.; Yasui, Y.; Shoda, T.; Sugai, S. Effects of Delgocitinib Ointment 0.5% on the Normal Mouse Skin and Epidermal Tight Junction Proteins in Comparison With Topical Corticosteroids. Toxicol. Pathol. 2020, 48, 1008–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man MQ, M.; Feingold, K.R.; Thornfeldt, C.R.; Elias, P.M. Optimization of physiological lipid mixtures for barrier repair. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1996, 106, 1096–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamlin, S.L.; Kao, J.; Frieden, I.J.; Sheu, M.Y.; Fowler, A.J.; Fluhr, J.W.; Williams, M.L.; Elias, P.M. Ceramide-dominant barrier repair lipids alleviate childhood atopic dermatitis: Changes in barrier function provide a sensitive indicator of disease activity. J. Am. Acad Dermatol. 2002, 47, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugarman, J.L.; Parish, L.C. Efficacy of a lipid-based barrier repair formulation in moderate-to-severe pediatric atopic dermatitis. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2009, 8, 1106–1111. [Google Scholar]
- Draelos, Z.D. The effect of ceramide-containing skin care products on eczema resolution duration. Cutis 2008, 81, 87–91. [Google Scholar]
- Hon, K.L.; Leung, A.K.; Barankin, B. Barrier repair therapy in atopic dermatitis: An overview. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2013, 14, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynde, C.W.; Andriessen, A. A cohort study on a ceramide-containing cleanser and moisturizer used for atopic dermatitis. Cutis 2014, 93, 207–213. [Google Scholar]
- Seghers, A.C.; Cai, S.C.; Ho, M.S.; Giam, Y.C.; Tan, L.; Grönhagen, C.M.; Tang, M.B. Evaluation of a Pseudoceramide Moisturizer in Patients with Mild-to-Moderate Atopic Dermatitis. Dermatol. Ther. 2014, 4, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Draelos, Z.D.; Raymond, I. The Efficacy of a Ceramide-based Cream in Mild-to-moderate Atopic Dermatitis. J. Clin. Aesthet. Dermatol. 2018, 11, 30–32. [Google Scholar]
- Ishida, K.; Takahashi, A.; Bito, K.; Draelos, Z.; Imokawa, G. Treatment with Synthetic Pseudoceramide Improves Atopic Skin, Switching the Ceramide Profile to a Healthy Skin Phenotype. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2020, 140, 1762–1770.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danby, S.G.; Andrew, P.V.; Brown, K.; Chittock, J.; Kay, L.J.; Cork, M.J. An Investigation of the Skin Barrier Restoring Effects of a Cream and Lotion Containing Ceramides in a Multi-vesicular Emulsion in People with Dry, Eczema-Prone, Skin: The RESTORE Study Phase 1. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 10, 1031–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, O.; Ogura, R.; Hayashi, K.; Okuda, M.; Yoshimura, K. Safety studies of pseudo-ceramide SLE66: Acute and short-term toxicity. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.D.; Youm, J.K.; Jeong, S.K.; Choi, E.H.; Ahn, S.K.; Lee, S.H. The characterization of molecular organization of multilamellar emulsions containing pseudoceramide and type III synthetic ceramide. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2003, 121, 794–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
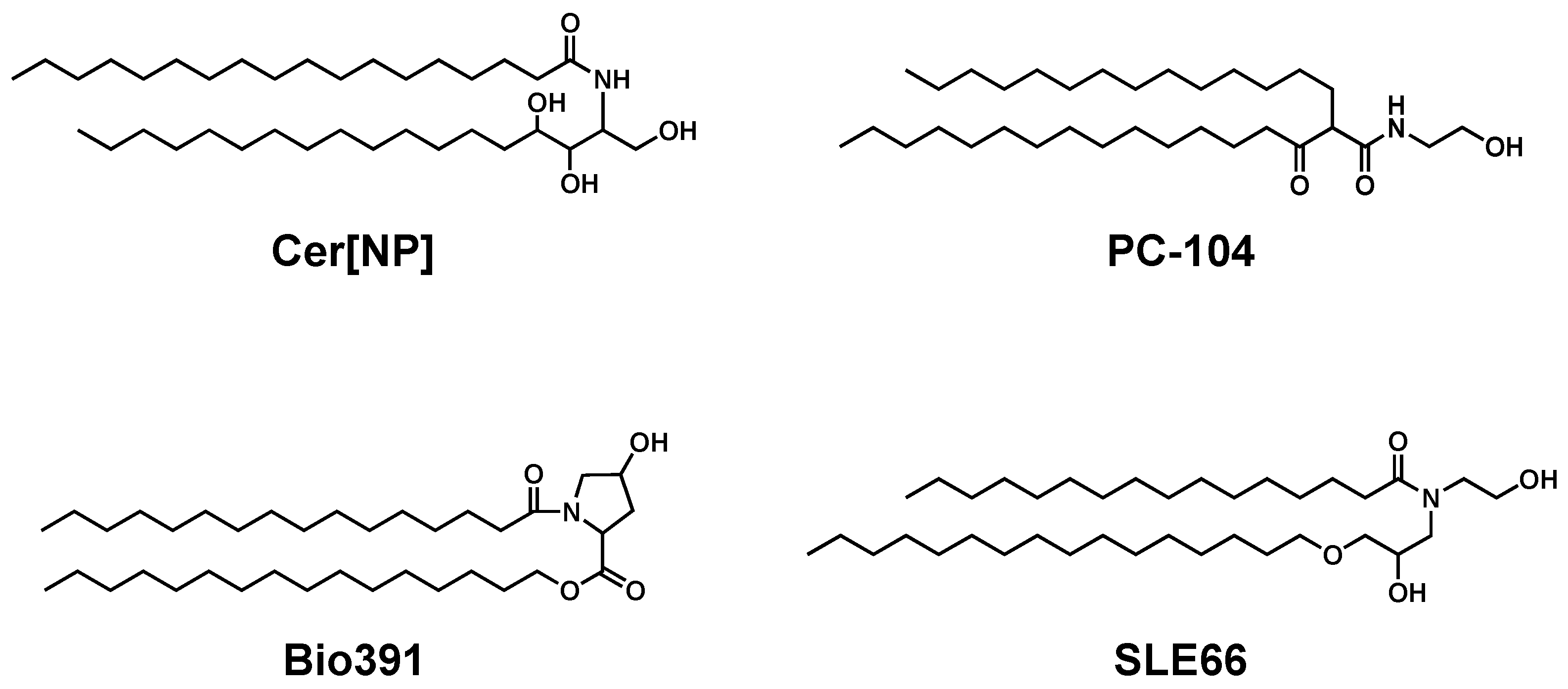
- Uchida, Y.; Holleran, W.M.; Elias, P.M. On the effects of topical synthetic pseudoceramides: Comparison of possible keratinocyte toxicities provoked by the pseudoceramides, PC104 and BIO391, and natural ceramides. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2008, 51, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokudome, Y.; Endo, M.; Hashimoto, F. Application of glucosylceramide-based liposomes increased the ceramide content in a three-dimensional cultured skin epidermis. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2014, 27, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vovesná, A.; Zhigunov, A.; Balouch, M.; Zbytovská, J. Ceramide liposomes for skin barrier recovery: A novel formulation based on natural skin lipids. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 120264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, A.; Su, J.; Tang, M.; Lodge, C.J.; Matheson, M.; Allen, K.J.; Varigos, G.; Sasi, A.; Cranswick, N.; Hamilton, S.; et al. PEBBLES study protocol: A randomised controlled trial to prevent atopic dermatitis, food allergy and sensitisation in infants with a family history of allergic disease using a skin barrier improvement strategy. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e024594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, M.; Tomozawa, J.; Mizutani, N.; Nabe, T.; Danno, K.; Kohno, S. Atopic dermatitis-like pruritic skin inflammation caused by feeding a special diet to HR-1 hairless mice. Exp. Dermatol. 2005, 14, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, M.; Shimazaki, Y.; Muto, Y.; Kohno, S.; Ohya, S.; Nabe, T. Dietary deficiencies of unsaturated fatty acids and starch cause atopic dermatitis-like pruritus in hairless mice. Exp. Dermatol. 2015, 24, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, M.; Nakashima, H.; Tomozawa, J.; Shimazaki, Y.; Ohyanagi, C.; Kawaguchi, N.; Ohya, S.; Kohno, S.; Nabe, T. Deficiency of n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids is mainly responsible for atopic dermatitis-like pruritic skin inflammation in special diet-fed hairless mice. Exp. Dermatol. 2013, 22, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, M.; Ohyanagi, C.; Kawaguchi, N.; Matsuda, H.; Miyamoto, Y.; Ohya, S.; Nabe, T. Eicosapentaenoic acid ethyl ester ameliorates atopic dermatitis-like symptoms in special diet-fed hairless mice, partly by restoring covalently bound ceramides in the stratum corneum. Exp. Dermatol. 2018, 27, 837–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| NDS | NS | NP | NH | NSD | NT | ADS | AS | AP | AH | ASD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Masukawa et al. [20] | 5.9 | 6.3 | 21.3 | 22.6 | n.d. | n.d. | 0.8 | 3.6 | 16.1 | 15.7 | n.d. |
| t’Kindt et al. [23] | 9.8 | 7.4 | 22.1 | 14.5 | n.d. | 1.7 | 1.6 | 9.6 | 8.8 | 10.8 | n.d. |
| van Smeden et al. [26] | 8.6 | 6.7 | 25.8 | 12.4 | n.d. | n.d. | 1.9 | 3.8 | 13.4 | 12.4 | n.d. |
| Kawana et al. [22] | 6.2 | 5.2 | 24.2 | 23.7 | 0.1 | n.d. | 0.9 | 4.3 | 9.2 | 18.0 | 0.2 |
| ODS | OS | OP | OH | OSD | BS | EODS | EOS | EOP | EOH | EOSD | |
| Masukawa et al. [20] | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 4.3 | 0.9 | 2.5 | n.d. |
| t’Kindt et al. [23] | n.d. | 0.7 | 0.2 | 0.4 | n.d. | n.d. | 0.4 | 6.5 | 1.1 | 4.3 | n.d. |
| van Smeden et al. [26] | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 1.3 | 5.4 | 2.7 | 5.4 | n.d. |
| Kawana et al. [22] | 0.1 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 2.1 | 1.0 | 3.1 | 0.0 |
| Ceramide Species (Compound Name) | Formulation (Brand Name) | Outcome | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-ceramide (PC-104) | Cream (Triceram®) | Disease severity ↓ TEWL ↓ SC hydration ↑ Extracellular lipid lamellae ↑ | Chamlin et al. [98] |
| Pseudo-ceramide (PC-104) | Cream (Epiceram®) | Disease severity ↓ pruritus ↓ sleep ↑ | Sugarman et al. [99] |
| Pseudo-ceramide (SLE66) | Cream (Curel®) | Disease severity ↓ TEWL → SC hydration ↑ | Seghers et al. [103] |
| Pseudo-ceramide (PC-104) | Cream (NeoCera™) | Disease severity ↓ TEWL → SC hydration ↑ | Draelos et al. [107] |
| Pseudo-ceramide (SLE66) | Oil-in-water lotion | Disease severity ↓ TEWL ↓ SC hydration ↑ Cer[NH], Cer[NP] ↑ Cer[NS], Cer[AS] ↓ | Ishida et al. [108] |
| Cer[NP], Cer[AP], Cer[EOS] | Multivesicular emulsion (CeraVe®) | SC hydration ↑ Skin dryness ↓ | Danby et al. [109] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fujii, M. The Pathogenic and Therapeutic Implications of Ceramide Abnormalities in Atopic Dermatitis. Cells 2021, 10, 2386. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10092386
Fujii M. The Pathogenic and Therapeutic Implications of Ceramide Abnormalities in Atopic Dermatitis. Cells. 2021; 10(9):2386. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10092386
Chicago/Turabian StyleFujii, Masanori. 2021. "The Pathogenic and Therapeutic Implications of Ceramide Abnormalities in Atopic Dermatitis" Cells 10, no. 9: 2386. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10092386
APA StyleFujii, M. (2021). The Pathogenic and Therapeutic Implications of Ceramide Abnormalities in Atopic Dermatitis. Cells, 10(9), 2386. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10092386





