HCV-Induced Immunometabolic Crosstalk in a Triple-Cell Co-Culture Model Capable of Simulating Systemic Iron Homeostasis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cellular Systems and Viral Infections
2.2. Expression Analyses
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
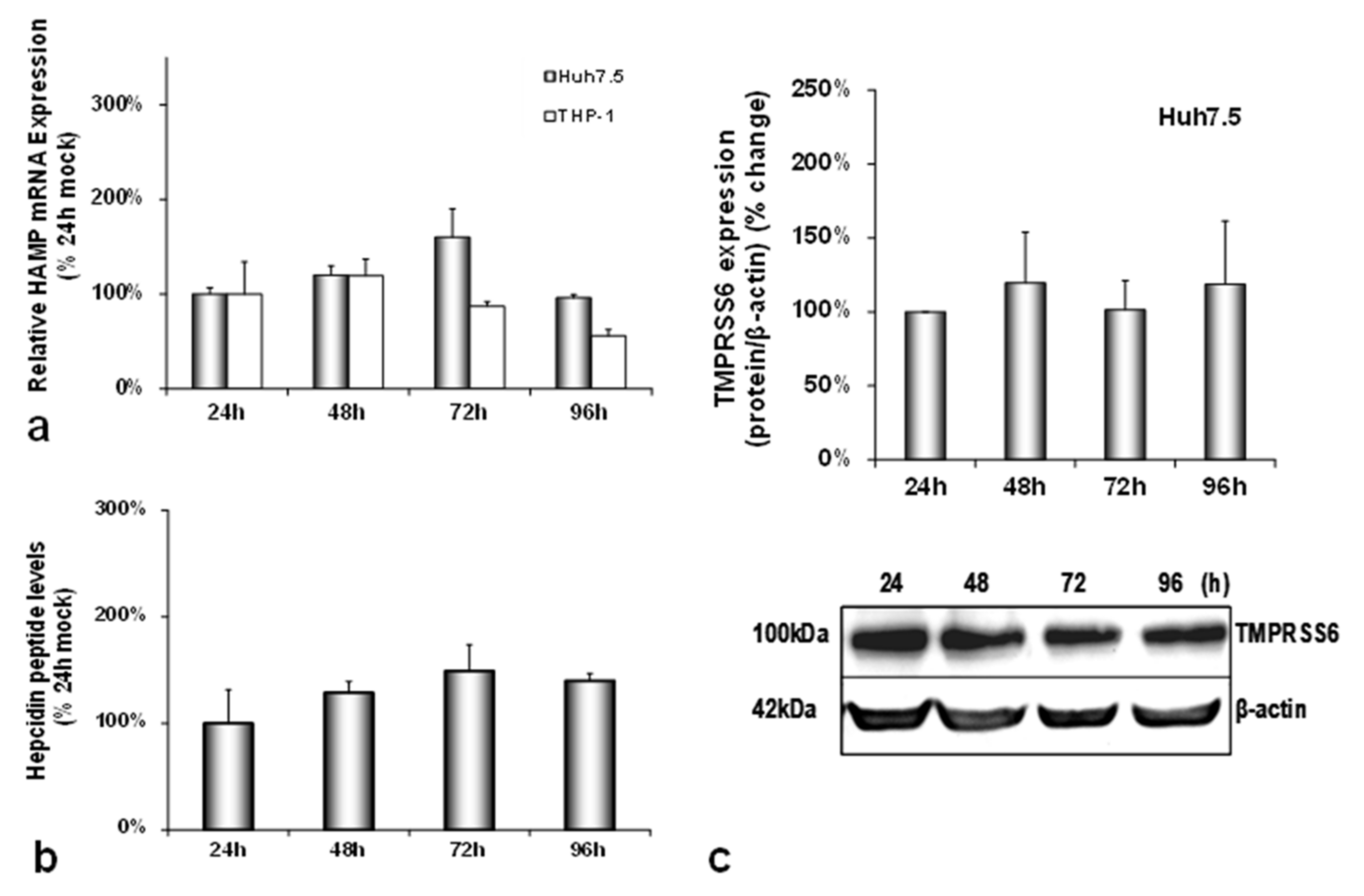
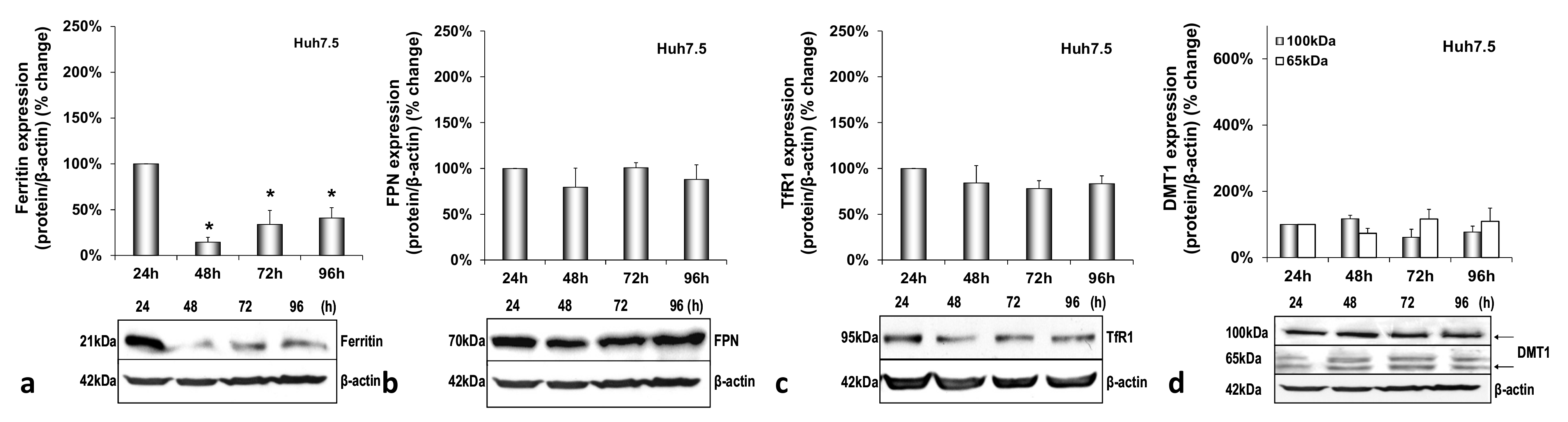
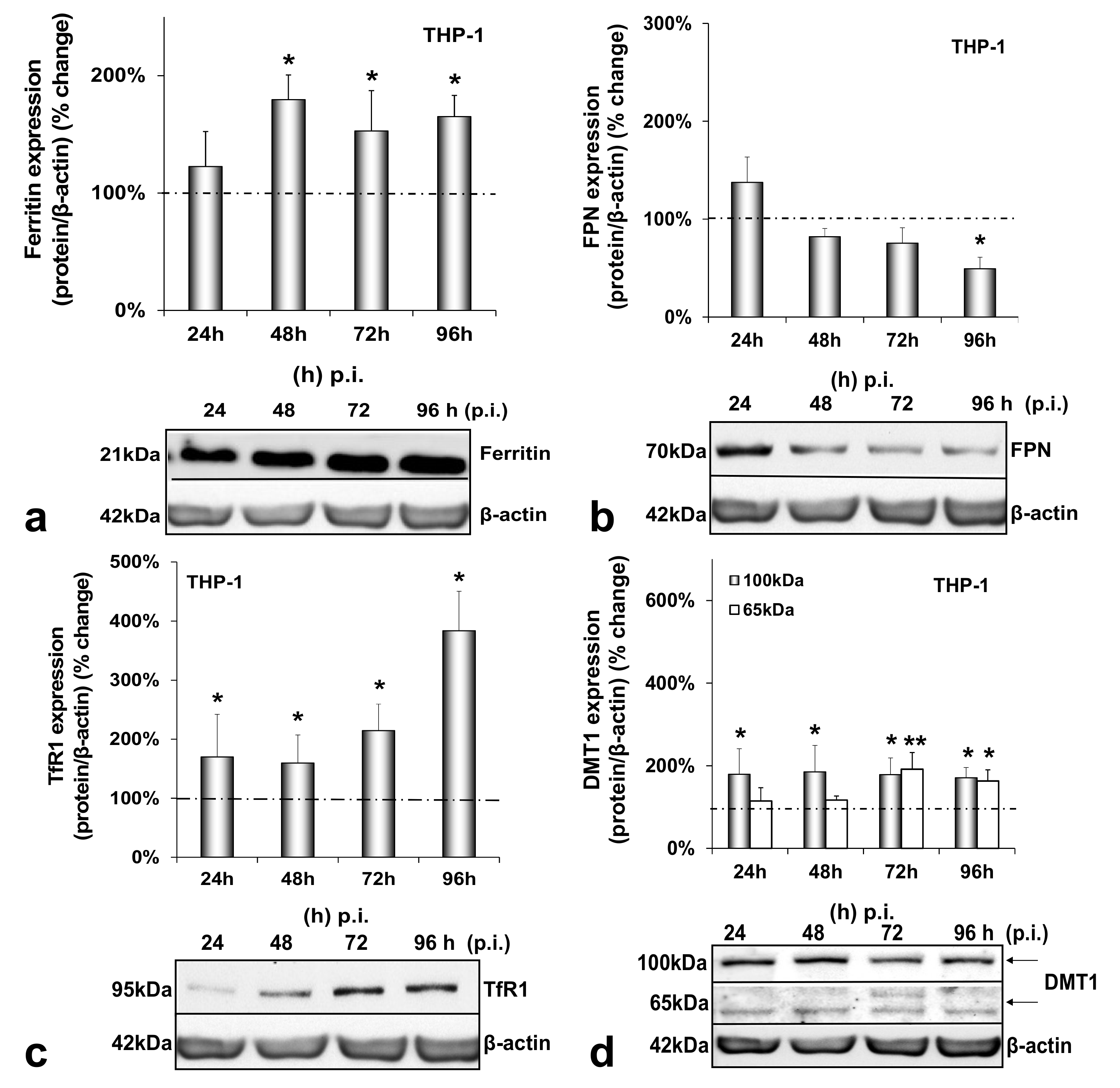
3.1. HCV Infection Modulates Systemic Iron Homeostasis in a Physiologically Relevant In Vitro Environment
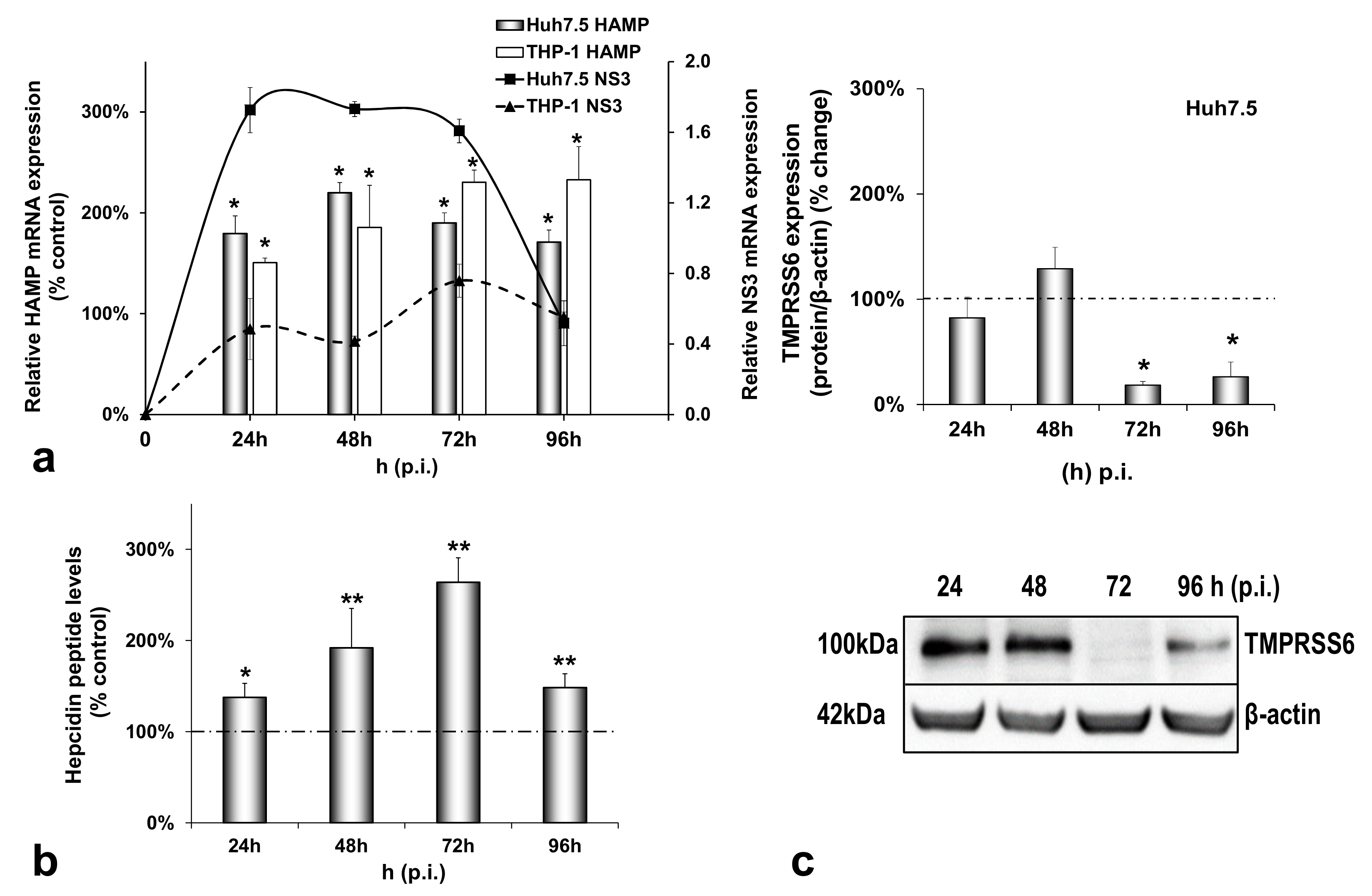
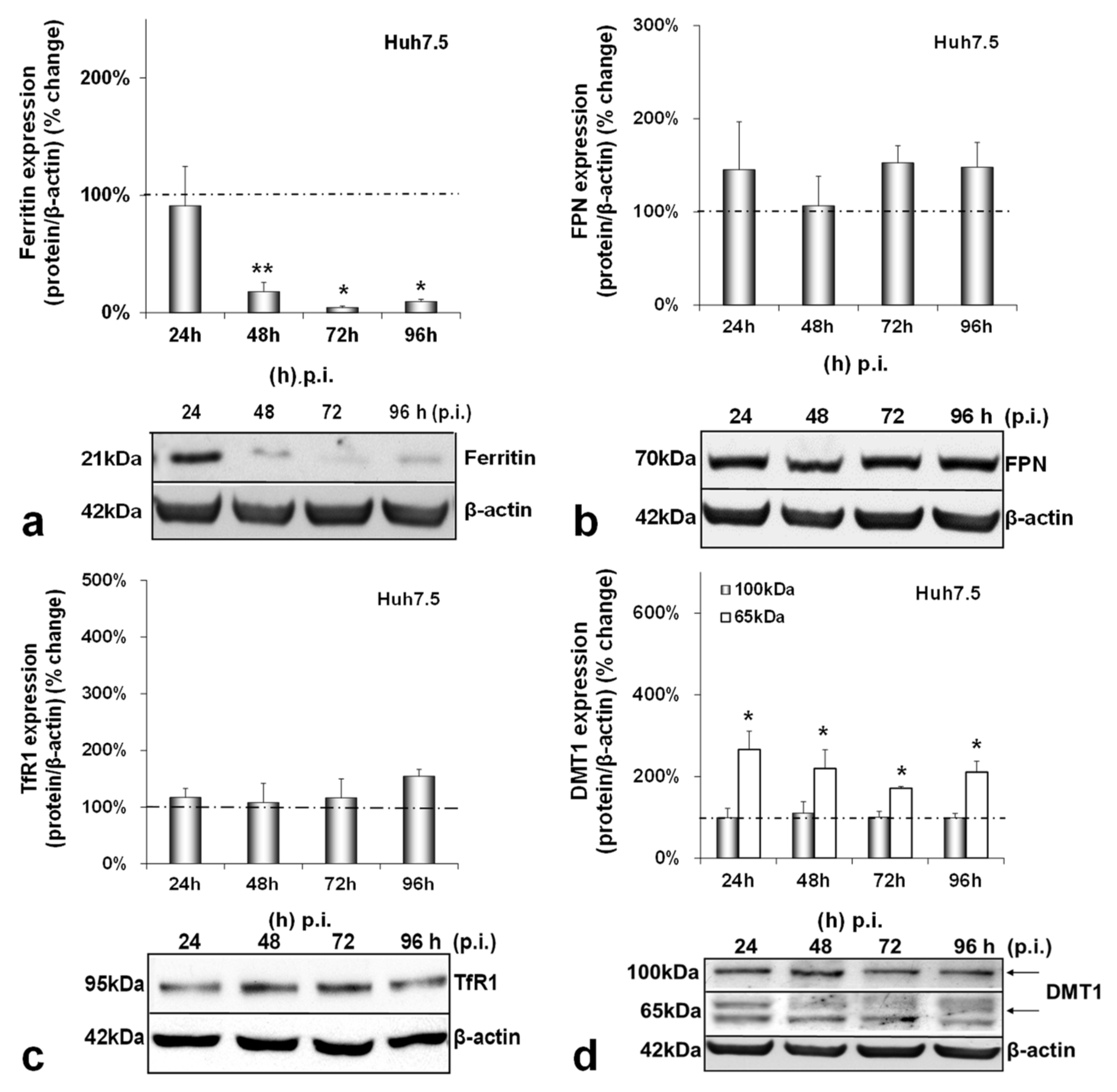
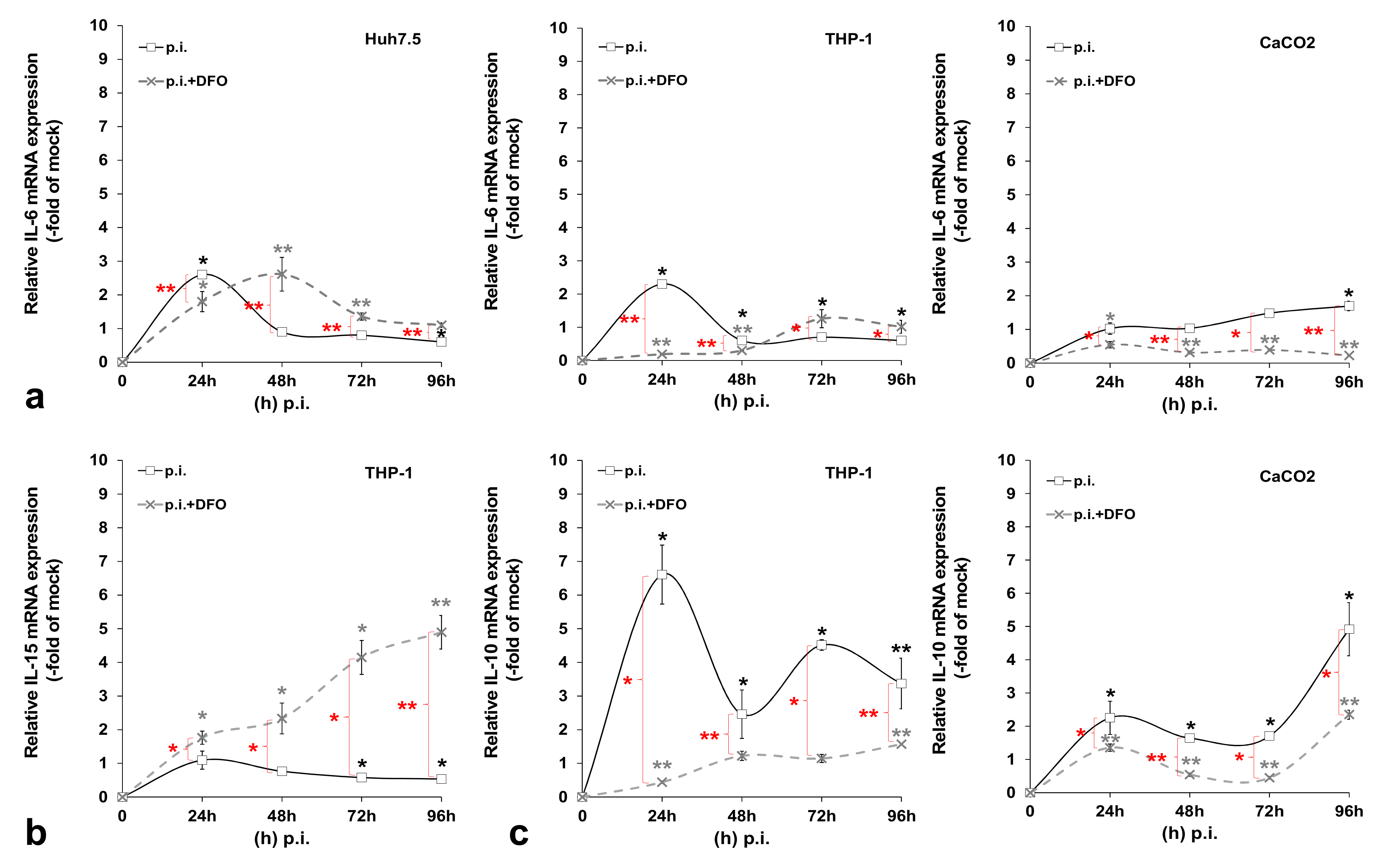
3.2. HCV-Mediated Changes on Iron Homeostasis Bestow an Anti-Inflammatory Phenotype on HCV-Infected Cells
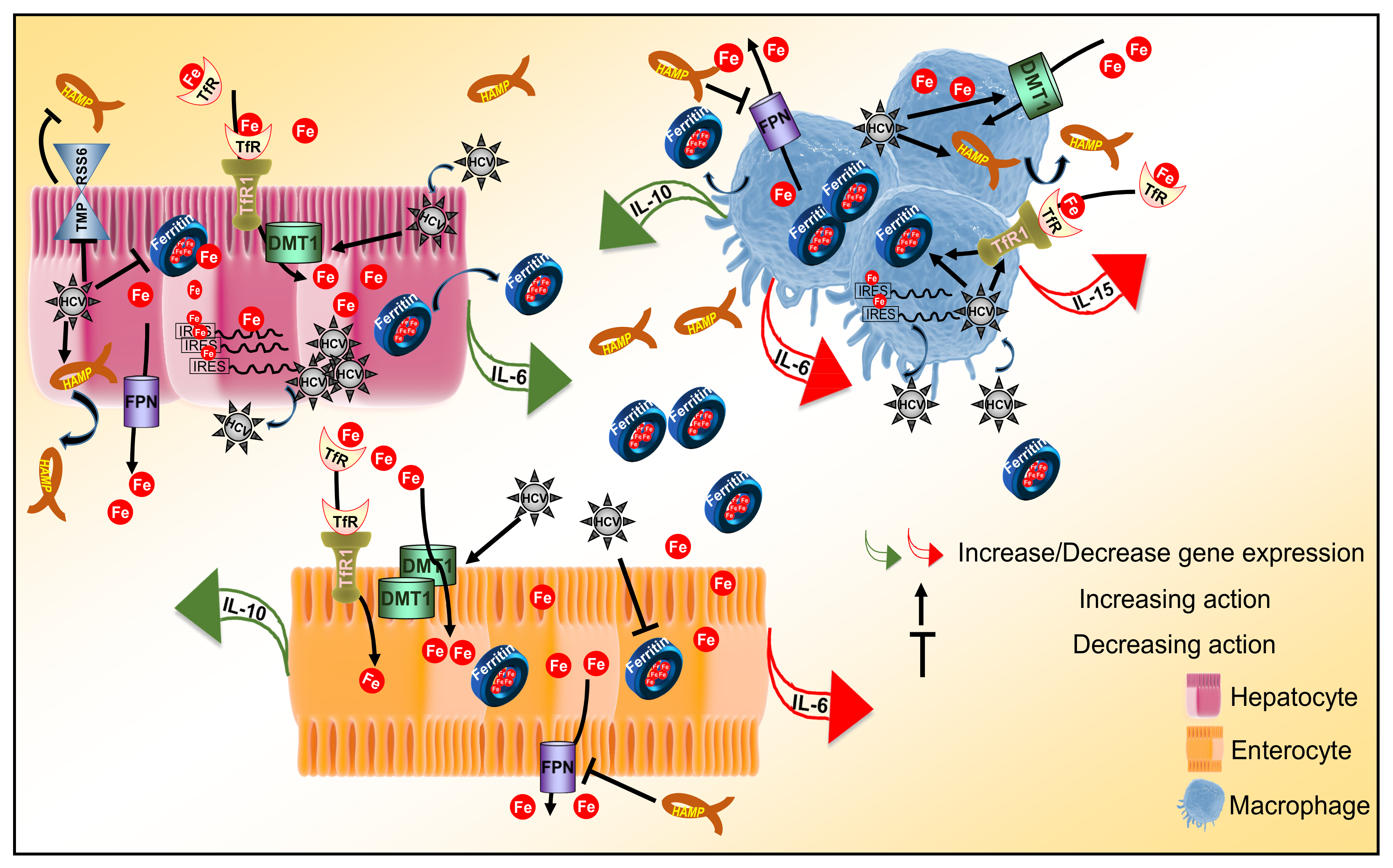
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A



References
- Nairz, M.; Dichtl, S.; Schroll, A.; Haschka, D.; Tymoszuk, P.; Theurl, I.; Weiss, G. Iron and innate antimicrobial immunity-Depriving the pathogen, defending the host. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. Organ. Soc. Miner. Trace Elem. 2018, 48, 118–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgopoulou, U.; Dimitriadis, A.; Foka, P.; Karamichali, E.; Mamalaki, A. Hepcidin and the iron enigma in HCV infection. Virulence 2014, 5, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessling-Resnick, M. Nramp1 and Other Transporters Involved in Metal Withholding during Infection. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 18984–18990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganz, T.; Nemeth, E. Iron homeostasis in host defence and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; She, E.; Gelbart, T.; Truksa, J.; Lee, P.; Xia, Y.; Khovananth, K.; Mudd, S.; Mann, N.; Moresco, E.M.; et al. The serine protease TMPRSS6 is required to sense iron deficiency. Science 2008, 320, 1088–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.S.; Anderson, S.A.; Wang, J.; Yang, F.; DeMaster, K.; Ahmed, R.; Nizzi, C.P.; Eisenstein, R.S.; Tsukamoto, H.; Enns, C.A. Suppression of hepatic hepcidin expression in response to acute iron deprivation is associated with an increase of matriptase-2 protein. Blood 2011, 117, 1687–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganz, T. Systemic iron homeostasis. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 1721–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsarou, A.; Pantopoulos, K. Basics and principles of cellular and systemic iron homeostasis. Mol. Asp. Med. 2020, 75, 100866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haschka, D.; Hoffmann, A.; Weiss, G. Iron in immune cell function and host defense. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 115, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanamori, Y.; Murakami, M.; Sugiyama, M.; Hashimoto, O.; Matsui, T.; Funaba, M. Interleukin-1β (IL-1β) transcriptionally activates hepcidin by inducing CCAAT enhancer-binding protein δ (C/EBPδ) expression in hepatocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 10275–10287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Xu, M.J.; Gao, B. Hepatocytes: A key cell type for innate immunity. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2016, 13, 301–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, G.; Schaible, U.E. Macrophage defense mechanisms against intracellular bacteria. Immunol. Rev. 2015, 264, 182–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golonka, R.; Yeoh, B.S.; Vijay-Kumar, M. The Iron Tug-of-War between Bacterial Siderophores and Innate Immunity. J. Innate Immun. 2019, 11, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Cherayil, B.J. Ironing out the wrinkles in host defense: Interactions between iron homeostasis and innate immunity. J. Innate Immun. 2009, 1, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villani, R.; Vendemiale, G.; Serviddio, G. Molecular Mechanisms Involved in HCC Recurrence after Direct-Acting Antiviral Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 20, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, M.Y.; Mina, E.; Roetto, A.; Porporato, P.E. Iron: An Essential Element of Cancer Metabolism. Cells 2020, 9, 2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastiani, G.; Vario, A.; Ferrari, A.; Pistis, R.; Noventa, F.; Alberti, A. Hepatic iron, liver steatosis and viral genotypes in patients with chronic hepatitis C. J. Viral Hepat. 2006, 13, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metwally, M.A.; Zein, C.O.; Zein, N.N. Clinical significance of hepatic iron deposition and serum iron values in patients with chronic hepatitis C infection. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 99, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kew, M.C. Hepatic iron overload and hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Cancer 2014, 3, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, C.; Siddaiah, N.; Berger, J.; Gish, R.; Brandhagen, D.; Sterling, R.K.; Cotler, S.J.; Fontana, R.J.; McCashland, T.M.; Han, S.H.; et al. Prevalence of hepatic iron overload and association with hepatocellular cancer in end-stage liver disease: Results from the National Hemochromatosis Transplant Registry. Liver Int. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Liver 2007, 27, 1394–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Lee, H.C.; Jang, S.K.; Kim, Y.K. Iron increases translation initiation directed by internal ribosome entry site of hepatitis C virus. Virus Genes 2008, 37, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foka, P.; Dimitriadis, A.; Karamichali, E.; Kyratzopoulou, E.; Giannimaras, D.; Koskinas, J.; Varaklioti, A.; Mamalaki, A.; Georgopoulou, U. Alterations in the iron homeostasis network: A driving force for macrophage-mediated hepatitis C virus persistency. Virulence 2016, 7, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lea, T. Caco-2 Cell Line. In The Impact of Food Bio-Actives on Gut Health; Verhoeckx, K., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 103–111. [Google Scholar]
- Lohmann, V. HCV replicons: Overview and basic protocols. Methods Mol. Biol. 2009, 510, 145–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuiper, J.B.A.; Knook, D.L.; Van Berkel, T.J.C. Kupffer and Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells: In The Liver: Biology and Pathobiology; Raven Press: New York, NY, USA, 1994; pp. 791–818. [Google Scholar]
- Foka, P.; Dimitriadis, A.; Kyratzopoulou, E.; Giannimaras, D.A.; Sarno, S.; Simos, G.; Georgopoulou, U.; Mamalaki, A. A complex signaling network involving protein kinase CK2 is required for hepatitis C virus core protein-mediated modulation of the iron-regulatory hepcidin gene expression. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 71, 4243–4258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeuke, S.; Ulmer, A.J.; Kusumoto, S.; Katus, H.A.; Heine, H. TLR4-mediated inflammatory activation of human coronary artery endothelial cells by LPS. Cardiovasc. Res. 2002, 56, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foka, P.; Karamichali, E.; Dalagiorgou, G.; Serti, E.; Doumba, P.P.; Pissas, G.; Kakkanas, A.; Kazazi, D.; Kochlios, E.; Gaitanou, M.; et al. Hepatitis C virus modulates lipid regulatory factor Angiopoietin-like 3 gene expression by repressing HNF-1α activity. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koliaraki, V.; Marinou, M.; Vassilakopoulos, T.P.; Vavourakis, E.; Tsochatzis, E.; Pangalis, G.A.; Papatheodoridis, G.; Stamoulakatou, A.; Swinkels, D.W.; Papanikolaou, G.; et al. A novel immunological assay for hepcidin quantification in human serum. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mee, C.J.; Grove, J.; Harris, H.J.; Hu, K.; Balfe, P.; McKeating, J.A. Effect of cell polarization on hepatitis C virus entry. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanatori, I.; Kishi, F. DMT1 and iron transport. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 133, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molyvdas, A.; Georgopoulou, U.; Lazaridis, N.; Hytiroglou, P.; Dimitriadis, A.; Foka, P.; Vassiliadis, T.; Loli, G.; Phillipidis, A.; Zebekakis, P.; et al. The role of the NLRP3 inflammasome and the activation of IL-1β in the pathogenesis of chronic viral hepatic inflammation. Cytokine 2018, 110, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacey, A.R.; Norris, P.J.; Qin, L.; Haygreen, E.A.; Taylor, E.; Heitman, J.; Lebedeva, M.; DeCamp, A.; Li, D.; Grove, D.; et al. Induction of a striking systemic cytokine cascade prior to peak viremia in acute human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection, in contrast to more modest and delayed responses in acute hepatitis B and C virus infections. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 3719–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osburn, W.O.; Levine, J.S.; Chattergoon, M.A.; Thomas, D.L.; Cox, A.L. Anti-inflammatory cytokines, pro-fibrogenic chemokines and persistence of acute HCV infection. J. Viral Hepat. 2013, 20, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevvana, M.; Keck, Z.; Foung, S.K.; Kuhn, R.J. Structural perspectives on HCV humoral immune evasion mechanisms. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2021, 49, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halleux, C.; Schneider, Y.J. Iron absorption by intestinal epithelial cells: 1. CaCo2 cells cultivated in serum-free medium, on polyethyleneterephthalate microporous membranes, as an in vitro model. In Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. J. Tissue Cult. Assoc. 1991, 27A, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, N.; Nizzi, C.P.; Anderson, S.A.; Wang, J.; Ueno, A.; Tsukamoto, H.; Eisenstein, R.S.; Enns, C.A.; Zhang, A.S. Low intracellular iron increases the stability of matriptase-2. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 4432–4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meynard, D.; Sun, C.C.; Wu, Q.; Chen, W.; Chen, S.; Nelson, C.N.; Waters, M.J.; Babitt, J.L.; Lin, H.Y. Inflammation regulates TMPRSS6 expression via STAT5. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidane, T.Z.; Sauble, E.; Linder, M.C. Release of iron from ferritin requires lysosomal activity. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2006, 291, C445–C455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truty, J.; Malpe, R.; Linder, M.C. Iron prevents ferritin turnover in hepatic cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 48775–48780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philpott, C.C. Coming into view: Eukaryotic iron chaperones and intracellular iron delivery. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 13518–13523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sp Ngberg, K.; Schwartz, S. Poly(C)-binding protein interacts with the hepatitis C virus 5′ untranslated region. J. Gen. Virol. 1999, 80 Pt 6, 1371–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, J.A.; Howie, H.L.; So, M. Neisseria meningitidis accelerates ferritin degradation in host epithelial cells to yield an essential iron source. Mol. Microbiol. 2004, 53, 807–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabuchi, M.; Tanaka, N.; Nishida-Kitayama, J.; Ohno, H.; Kishi, F. Alternative splicing regulates the subcellular localization of divalent metal transporter 1 isoforms. Mol. Biol. Cell 2002, 13, 4371–4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La, A.; Nguyen, T.; Tran, K.; Sauble, E.; Tu, D.; Gonzalez, A.; Kidane, T.Z.; Soriano, C.; Morgan, J.; Doan, M.; et al. Mobilization of iron from ferritin: New steps and details. Met. Integr. Biometal. Sci. 2018, 10, 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mühlenhoff, U.; Hoffmann, B.; Richter, N.; Rietzschel, N.; Spantgar, F.; Stehling, O.; Uzarska, M.A.; Lill, R. Compartmentalization of iron between mitochondria and the cytosol and its regulation. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2015, 94, 292–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.N.; Uprichard, S.L. Identification of transferrin receptor 1 as a hepatitis C virus entry factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 10777–10782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, F.; Guo, X.; An, P.; Tao, Y.; Wang, F. Ferroportin1 in hepatocytes and macrophages is required for the efficient mobilization of body iron stores in mice. Hepatology 2012, 56, 961–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, B.; Chaston, T.; Marks, J.; Srai, S.K.; Sharp, P.A. Hepcidin decreases iron transporter expression in vivo in mouse duodenum and spleen and in vitro in THP-1 macrophages and intestinal Caco-2 cells. J. Nutr. 2009, 139, 1457–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.; Miyanishi, K.; Tanaka, S.; Sakurada, A.; Sakamoto, H.; Kawano, Y.; Takada, K.; Kobune, M.; Kato, J. Increased Duodenal Iron Absorption through Upregulation of Ferroportin 1 due to the Decrement in Serum Hepcidin in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 2018, 2154361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brasse-Lagnel, C.; Karim, Z.; Letteron, P.; Bekri, S.; Bado, A.; Beaumont, C. Intestinal DMT1 cotransporter is down-regulated by hepcidin via proteasome internalization and degradation. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 1261–1271.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mena, N.P.; Esparza, A.; Tapia, V.; Valdés, P.; Núñez, M.T. Hepcidin inhibits apical iron uptake in intestinal cells. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2008, 294, G192–G198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaston, T.; Chung, B.; Mascarenhas, M.; Marks, J.; Patel, B.; Srai, S.K.; Sharp, P. Evidence for differential effects of hepcidin in macrophages and intestinal epithelial cells. Gut 2008, 57, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiabrando, D.; Fiorito, V.; Marro, S.; Silengo, L.; Altruda, F.; Tolosano, E. Cell-specific regulation of Ferroportin transcription following experimentally-induced acute anemia in mice. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2013, 50, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Kashanchi, F.; Foster, A.; Rotimi, J.; Turner, W.; Gordeuk, V.R.; Nekhai, S. Hepcidin induces HIV-1 transcription inhibited by ferroportin. Retrovirology 2010, 7, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobune, M.; Kohgo, Y.; Kato, J.; Miyazaki, E.; Niitsu, Y. Interleukin-6 enhances hepatic transferrin uptake and ferritin expression in rats. Hepatology 1994, 19, 1468–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.N.; Eubanks, S.K.; Schaffer, K.J.; Zhou, C.Y.; Linder, M.C. Secretion of ferritin by rat hepatoma cells and its regulation by inflammatory cytokines and iron. Blood 1997, 90, 4979–4986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Hevi, S.; Chuck, S.L. Regulated secretion of glycosylated human ferritin from hepatocytes. Blood 2004, 103, 2369–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawabata, H. Transferrin and transferrin receptors update. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 133, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, S.; Kawabata, H.; Masuda, T.; Uchiyama, T.; Mizumoto, C.; Ohmori, K.; Koeffler, H.P.; Kadowaki, N.; Takaori-Kondo, A. H-Ferritin Is Preferentially Incorporated by Human Erythroid Cells through Transferrin Receptor 1 in a Threshold-Dependent Manner. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwiczek, S.; Aigner, E.; Theurl, I.; Weiss, G. Cytokine-mediated regulation of iron transport in human monocytic cells. Blood 2003, 101, 4148–4154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.B.; Callaghan, K.D.; Ghio, A.J.; Haile, D.J.; Yang, F. Hepcidin expression and iron transport in alveolar macrophages. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2006, 291, L417–L425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owusu-Boaitey, N.; Bauckman, K.A.; Zhang, T.; Mysorekar, I.U. Macrophagic control of the response to uropathogenic E. coli infection by regulation of iron retention in an IL-6-dependent manner. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2016, 4, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakita, T.; Pietschmann, T.; Kato, T.; Date, T.; Miyamoto, M.; Zhao, Z.; Murthy, K.; Habermann, A.; Kräusslich, H.G.; Mizokami, M.; et al. Production of infectious hepatitis C virus in tissue culture from a cloned viral genome. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Domenico, I.; Zhang, T.Y.; Koening, C.L.; Branch, R.W.; London, N.; Lo, E.; Daynes, R.A.; Kushner, J.P.; Li, D.; Ward, D.M.; et al. Hepcidin mediates transcriptional changes that modulate acute cytokine-induced inflammatory responses in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 2395–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, C.P.; Franco, A.V.; Arosio, P.; Hersey, P. Immunosuppressive effects of melanoma-derived heavy-chain ferritin are dependent on stimulation of IL-10 production. Int. J. Cancer 2001, 92, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Zhan, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Han, Y.; Hu, W.; Hou, J. Up-regulated ferritin in periodontitis promotes inflammatory cytokine expression in human periodontal ligament cells through transferrin receptor via ERK/P38 MAPK pathways. Clin. Sci. 2019, 133, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, H.; Xiong, S.; Lin, M.; Zandi, E.; Giulivi, C.; Tsukamoto, H. Iron activates NF-kappaB in Kupffer cells. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2002, 283, G719–G726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higuchi, T.; Moriyama, M.; Fukushima, A.; Matsumura, H.; Matsuoka, S.; Kanda, T.; Sugitani, M.; Tsunemi, A.; Ueno, T.; Fukuda, N. Association of mRNA expression of iron metabolism-associated genes and progression of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in rats. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 26183–26194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porto, G.; De Sousa, M. Iron overload and immunity. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 4707–4715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, R.; Yu, Q.; Dong, L.; Bi, Y.; Liu, G. Metabolic reprogramming of macrophages during infections and cancer. Cancer Lett. 2019, 452, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maliken, B.D.; Nelson, J.E.; Kowdley, K.V. The hepcidin circuits act: Balancing iron and inflammation. Hepatology 2011, 53, 1764–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira Fulco, T.; Andrade, P.R.; de Mattos Barbosa, M.G.; Pinto, T.G.; Ferreira, P.F.; Ferreira, H.; da Costa Nery, J.A.; Real, S.C.; Borges, V.M.; Moraes, M.O.; et al. Effect of apoptotic cell recognition on macrophage polarization and mycobacterial persistence. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 3968–3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handa, P.; Thomas, S.; Morgan-Stevenson, V.; Maliken, B.D.; Gochanour, E.; Boukhar, S.; Yeh, M.M.; Kowdley, K.V. Iron alters macrophage polarization status and leads to steatohepatitis and fibrogenesis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2019, 105, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momtazi-Borojeni, A.A.; Abdollahi, E.; Nikfar, B.; Chaichian, S.; Ekhlasi-Hundrieser, M. Curcumin as a potential modulator of M1 and M2 macrophages: New insights in atherosclerosis therapy. Heart Fail. Rev. 2019, 24, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, J.K.; Wang, S.C.; Ho, L.W.; Huang, S.W.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, M.S.; Yang, R.C.; Shieh, J.J. M2-like polarization of THP-1 monocyte-derived macrophages under chronic iron overload. Ann. Hematol. 2020, 99, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allaire, J.M.; Crowley, S.M.; Law, H.T.; Chang, S.Y.; Ko, H.J.; Vallance, B.A. The Intestinal Epithelium: Central Coordinator of Mucosal Immunity. Trends Immunol. 2018, 39, 677–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markel, T.A.; Crisostomo, P.R.; Wang, M.; Herring, C.M.; Lahm, T.; Meldrum, K.K.; Lillemoe, K.D.; Rescorla, F.J.; Meldrum, D.R. Iron chelation acutely stimulates fetal human intestinal cell production of IL-6 and VEGF while decreasing HGF: The roles of p38, ERK, and JNK MAPK signaling. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2007, 292, G958–G963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Robinson, M.W.; Harmon, C.; O’Farrelly, C. Liver immunology and its role in inflammation and homeostasis. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2016, 13, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corna, G.; Campana, L.; Pignatti, E.; Castiglioni, A.; Tagliafico, E.; Bosurgi, L.; Campanella, A.; Brunelli, S.; Manfredi, A.A.; Apostoli, P.; et al. Polarization dictates iron handling by inflammatory and alternatively activated macrophages. Haematologica 2010, 95, 1814–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldmann, T.A. Interleukin-15. In Encyclopedia of Hormones; Henry, H.L., Norman, A.W., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2003; pp. 478–484. [Google Scholar]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Foka, P.; Dimitriadis, A.; Karamichali, E.; Kochlios, E.; Eliadis, P.; Valiakou, V.; Koskinas, J.; Mamalaki, A.; Georgopoulou, U. HCV-Induced Immunometabolic Crosstalk in a Triple-Cell Co-Culture Model Capable of Simulating Systemic Iron Homeostasis. Cells 2021, 10, 2251. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10092251
Foka P, Dimitriadis A, Karamichali E, Kochlios E, Eliadis P, Valiakou V, Koskinas J, Mamalaki A, Georgopoulou U. HCV-Induced Immunometabolic Crosstalk in a Triple-Cell Co-Culture Model Capable of Simulating Systemic Iron Homeostasis. Cells. 2021; 10(9):2251. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10092251
Chicago/Turabian StyleFoka, Pelagia, Alexios Dimitriadis, Eirini Karamichali, Emmanouil Kochlios, Petros Eliadis, Vaia Valiakou, John Koskinas, Avgi Mamalaki, and Urania Georgopoulou. 2021. "HCV-Induced Immunometabolic Crosstalk in a Triple-Cell Co-Culture Model Capable of Simulating Systemic Iron Homeostasis" Cells 10, no. 9: 2251. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10092251
APA StyleFoka, P., Dimitriadis, A., Karamichali, E., Kochlios, E., Eliadis, P., Valiakou, V., Koskinas, J., Mamalaki, A., & Georgopoulou, U. (2021). HCV-Induced Immunometabolic Crosstalk in a Triple-Cell Co-Culture Model Capable of Simulating Systemic Iron Homeostasis. Cells, 10(9), 2251. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10092251







