Affinity Tag Coating Enables Reliable Detection of Antigen-Specific B Cells in Immunospot Assays
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Human Subjects
2.2. Polyclonal Human B-Cell Stimulation
2.3. Recombinant Proteins
2.4. Total (IgA/IgG/IgM) Human B-Cell ImmunoSpot® Assays
2.5. Antigen-Specific Human B-Cell ImmunoSpot® Assays
2.6. Murine B-Cell Hybridomas
2.7. Murine B-Cell ImmunoSpot® Assays
2.8. ImmunoSpot® Image Acquisition and Counting
2.9. Bivariate Visualization of FluoroSpots
2.10. Statistical Methods
3. Results
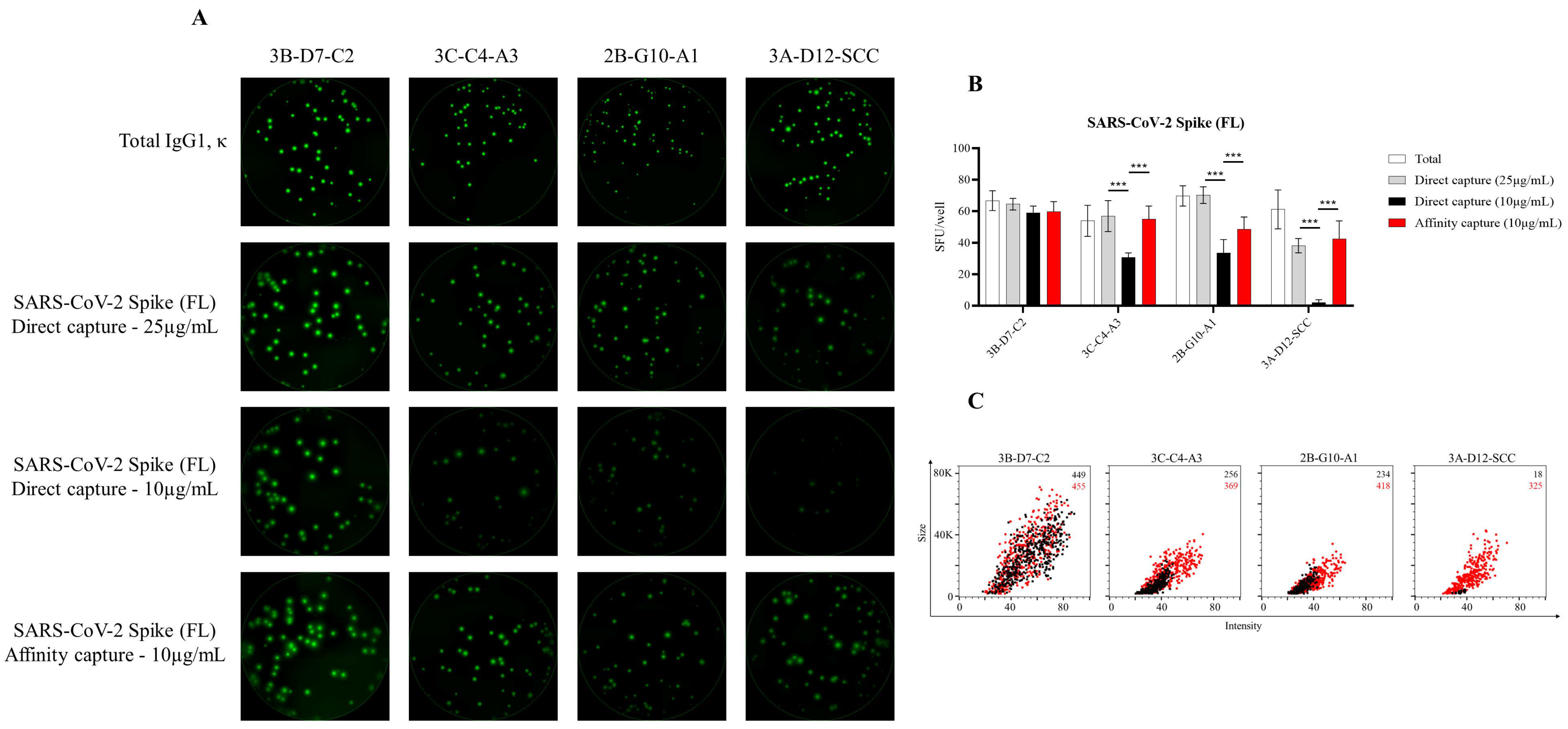
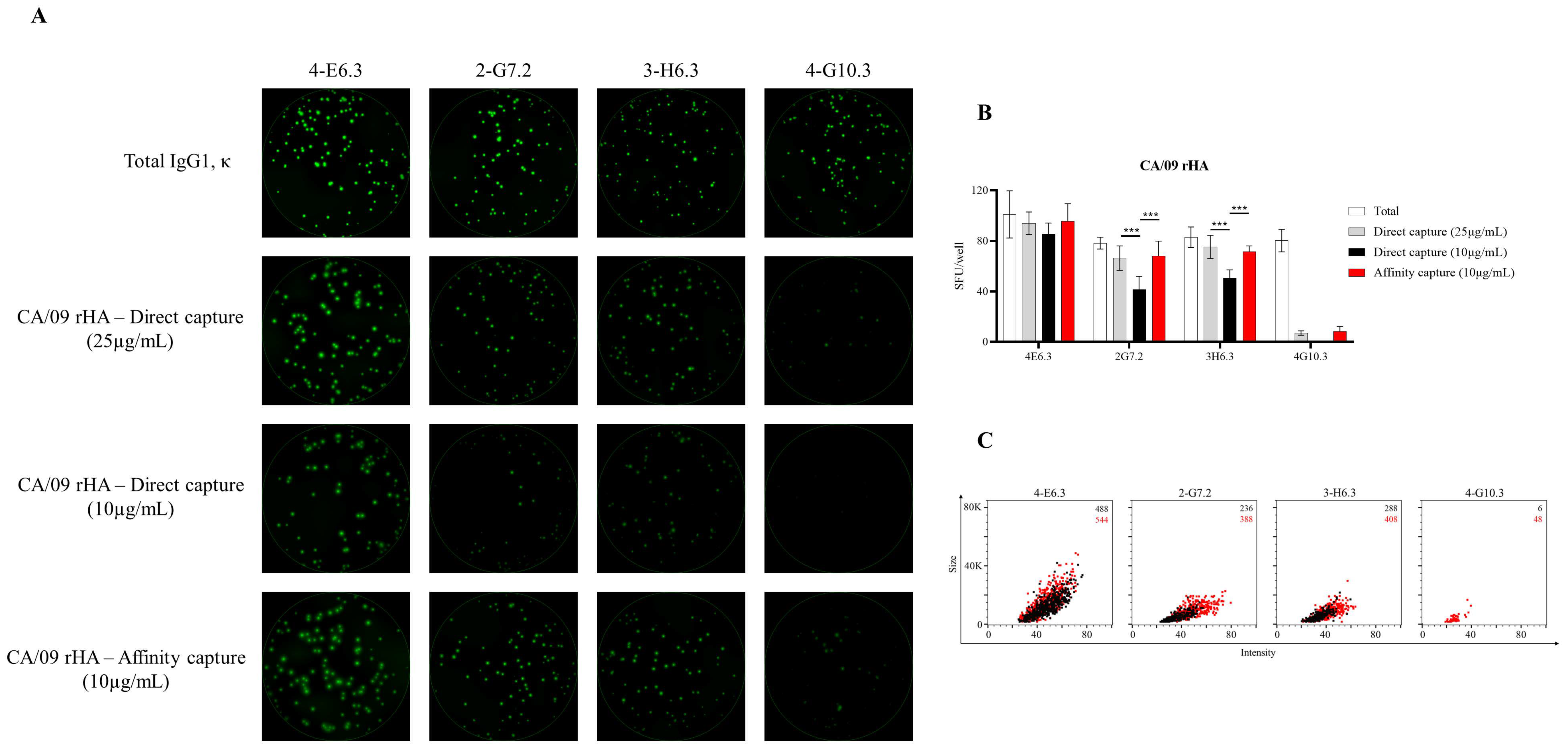
3.1. Affinity Tag Capture of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Proteins Improves Antigen-Specific FluoroSpot Assays
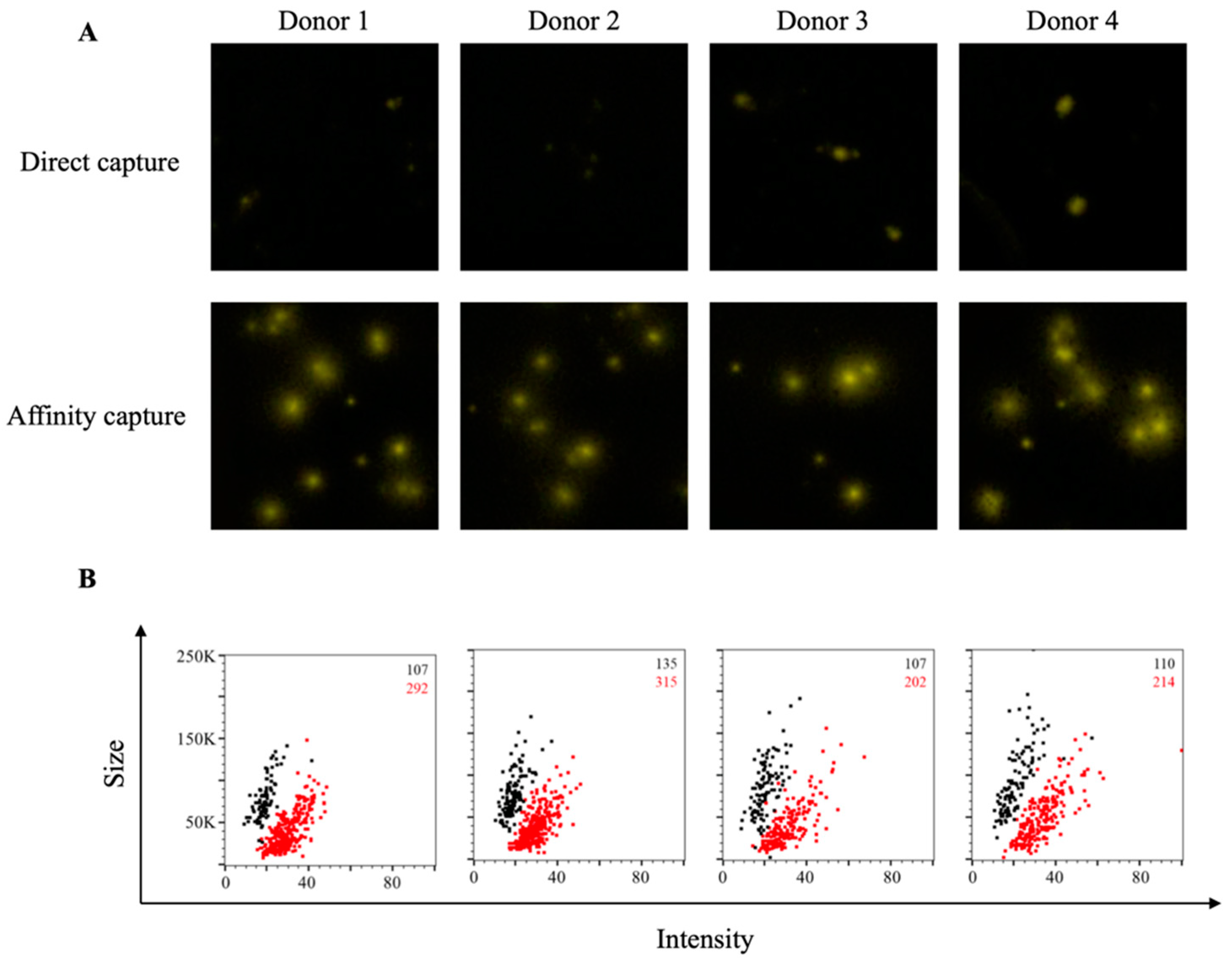
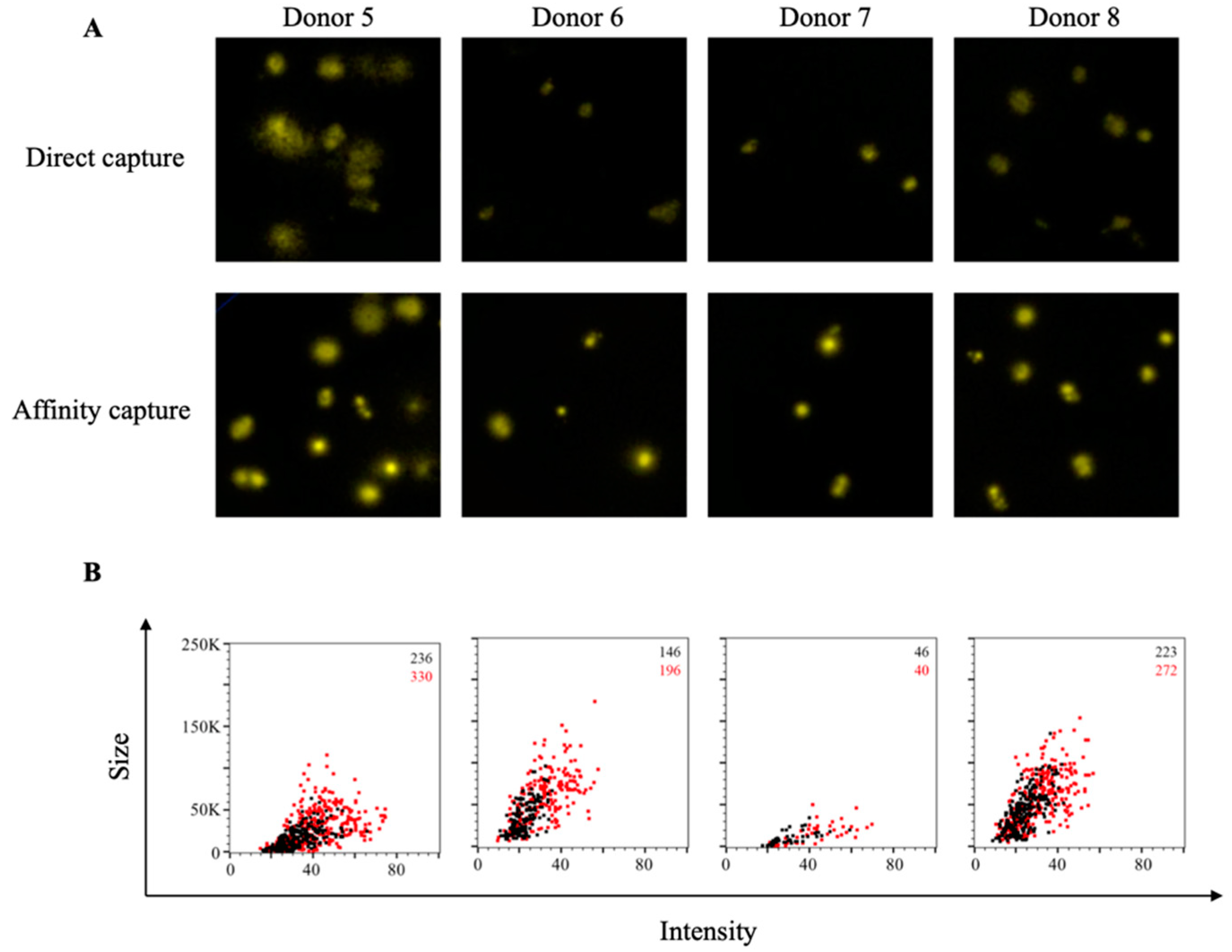
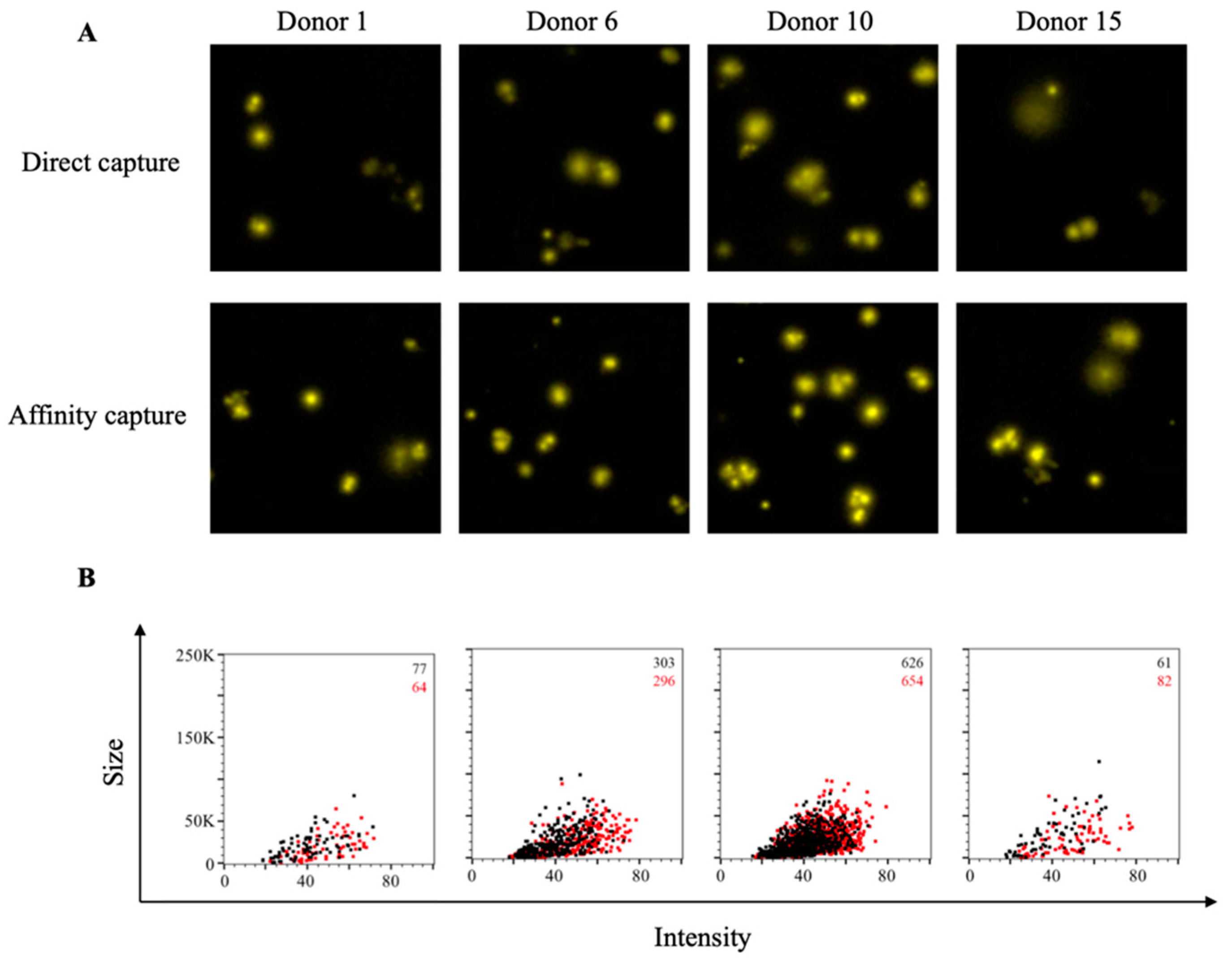
3.2. Affinity Tag Capture of EBV EBNA1 Protein Improves Detection of Antigen-Specific Memory B Cells
3.3. Affinity Tag Capture of HCMV gH Protein Improves Detection of Antigen-Specific Memory B Cells
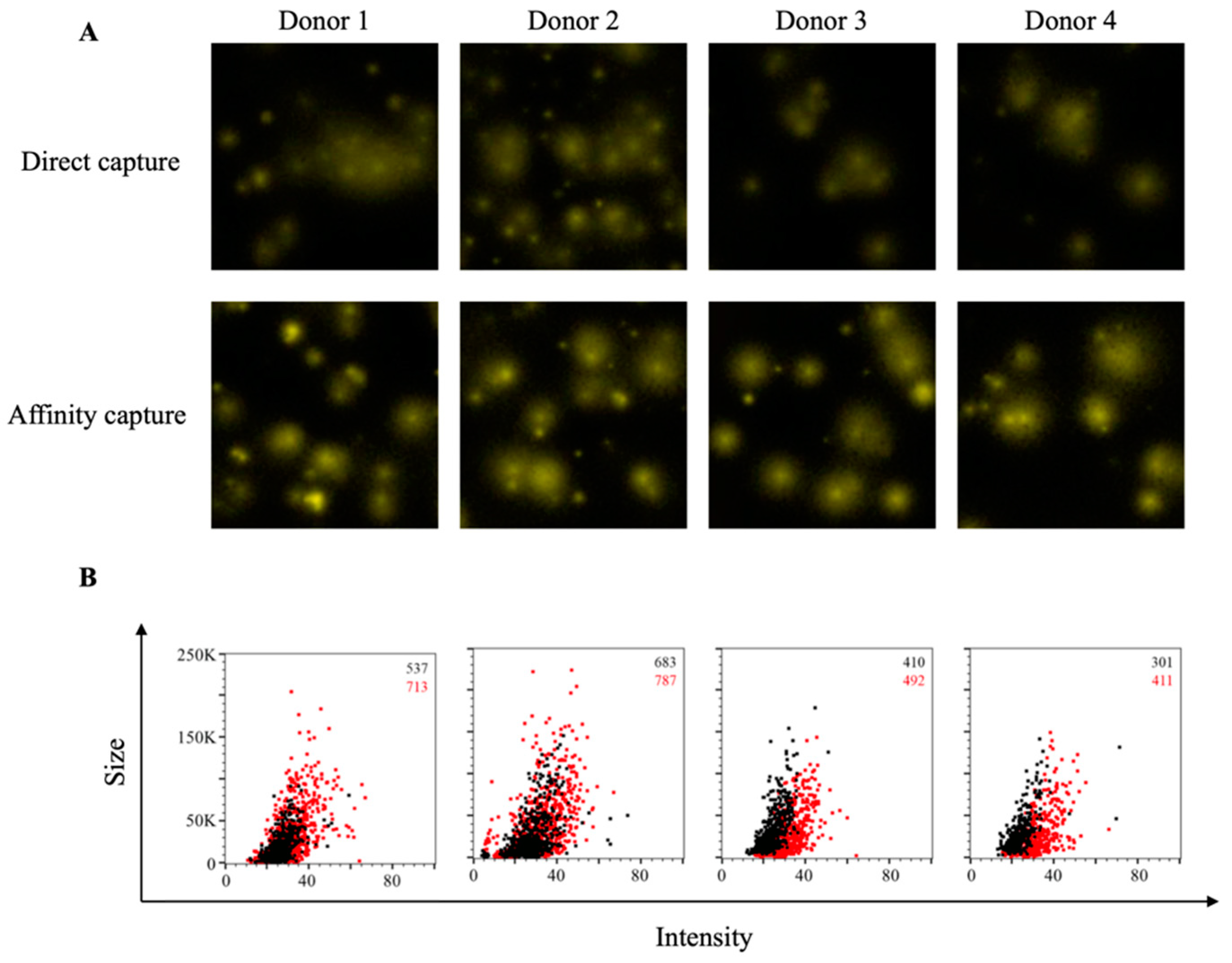
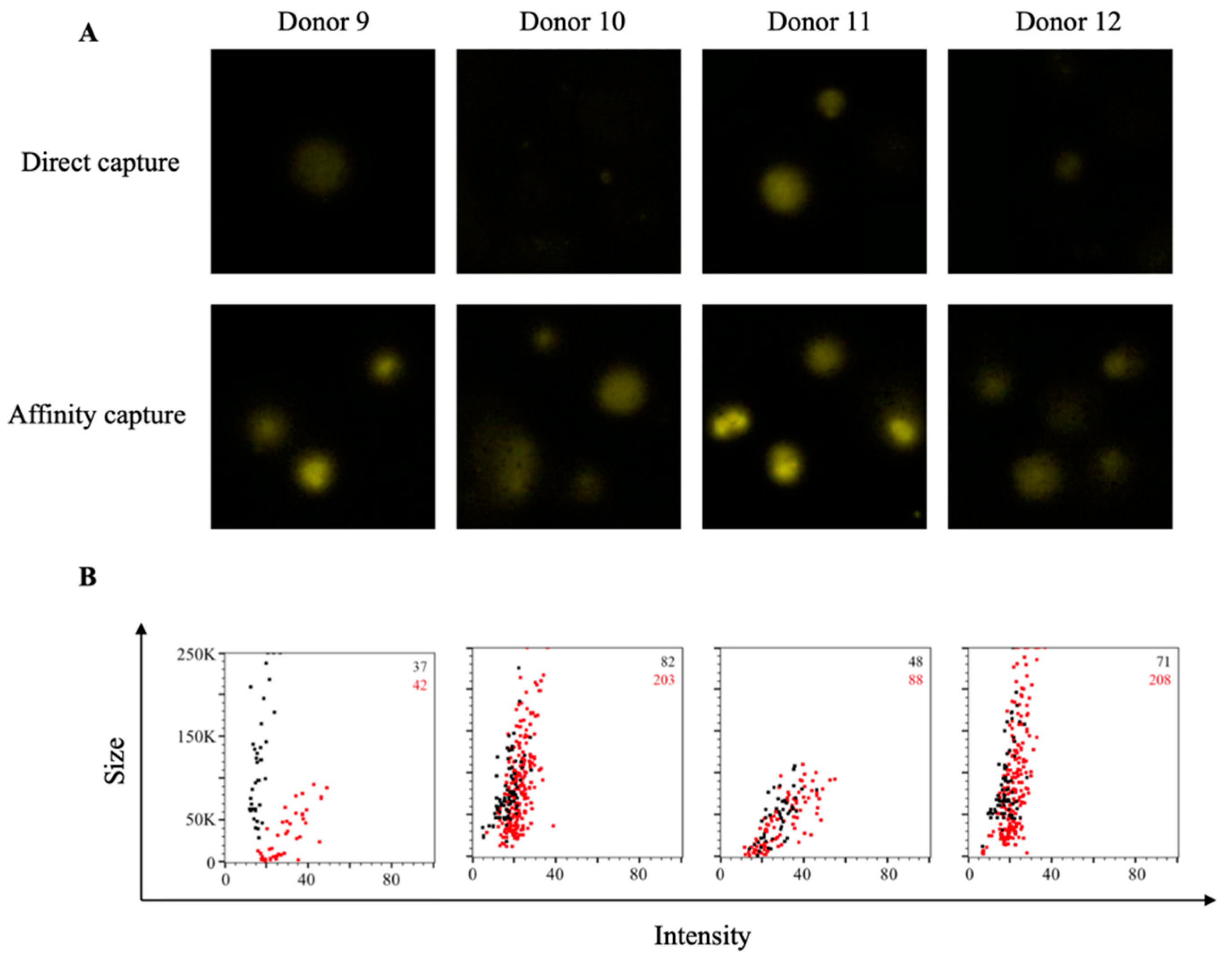
3.4. Affinity Tag Capture of Influenza Hemagglutinin Improves Antigen-Specific FluoroSpot Assays
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morell, A.; Terry, W.D.; Waldmann, T.A. Metabolic properties of IgG subclasses in man. J. Clin. Investig. 1970, 49, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vieira, P.; Rajewsky, K. The half-lives of serum immunoglobulins in adult mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 1988, 18, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrammert, J.; Onlamoon, N.; Akondy, R.S.; Perng, G.C.; Polsrila, K.; Chandele, A.; Kwissa, M.; Pulendran, B.; Wilson, P.C.; Wittawatmongkol, O.; et al. Rapid and Massive Virus-Specific Plasmablast Responses during Acute Dengue Virus Infection in Humans. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 2911–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wrammert, J.; Smith, K.; Miller, J.; Langley, W.A.; Kokko, K.; Larsen, C.; Zheng, N.-Y.; Mays, I.; Garman, L.; Helms, C.; et al. Rapid cloning of high-affinity human monoclonal antibodies against influenza virus. Nature 2008, 453, 667–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thevarajan, I.; Nguyen, T.H.O.; Koutsakos, M.; Druce, J.; Caly, L.; van de Sandt, C.E.; Jia, X.; Nicholson, S.; Catton, M.; Cowie, B.; et al. Breadth of concomitant immune responses prior to patient recovery: A case report of non-severe COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 453–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manz, R.A.; Hauser, A.E.; Hiepe, F.; Radbruch, A. Maintenance of serum antibody levels. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 23, 367–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.G.C.; Light, A.; O’Reilly, L.A.; Ang, S.-M.; Strasser, A.; Tarlinton, D. bcl-2 Transgene Expression Inhibits Apoptosis in the Germinal Center and Reveals Differences in the Selection of Memory B Cells and Bone Marrow Antibody-Forming Cells. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 191, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phan, T.G.; Paus, D.; Chan, T.D.; Turner, M.L.; Nutt, S.L.; Basten, A.; Brink, R. High affinity germinal center B cells are actively selected into the plasma cell compartment. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 2419–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lightman, S.M.; Utley, A.; Lee, K.P. Survival of Long-Lived Plasma Cells (LLPC): Piecing Together the Puzzle. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro-Shelef, M.; Calame, K. Regulation of plasma-cell development. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, K.; Tokoyoda, K.; Radbruch, A.; MacLennan, I.; Manz, R.A. Stromal niches, plasma cell differentiation and survival. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2006, 18, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, C.W.; Jackson, K.J.L.; McCausland, M.M.; Darce, J.; Chang, C.; Linderman, S.L.; Chennareddy, C.; Gerkin, R.; Brown, S.J.; Wrammert, J.; et al. Influenza vaccine–induced human bone marrow plasma cells decline within a year after vaccination. Science 2020, 370, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, C.W.; Jackson, K.J.L.; McElroy, A.K.; Halfmann, P.; Huang, J.; Chennareddy, C.; Piper, A.E.; Leung, Y.; Albariño, C.G.; Crozier, I.; et al. Longitudinal Analysis of the Human B Cell Response to Ebola Virus Infection. Cell 2019, 177, 1566–1582.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nivarthi, U.K.; Tu, H.A.; Delacruz, M.J.; Swanstrom, J.; Patel, B.; Durbin, A.P.; Whitehead, S.S.; Pierce, K.K.; Kirkpatrick, B.D.; Baric, R.S.; et al. Longitudinal analysis of acute and convalescent B cell responses in a human primary dengue serotype 2 infection model. EBioMedicine 2019, 41, 465–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Turner, J.S.; Kim, W.; Kalaidina, E.; Goss, C.W.; Rauseo, A.M.; Schmitz, A.J.; Hansen, L.; Haile, A.; Klebert, M.K.; Pusic, I.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection induces long-lived bone marrow plasma cells in humans. Res. Sq. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, W.; Hayes, G.M.; Liu, H.; Gemmell, L.; Schmeling, D.O.; Radecki, P.; Aguilar, F.; Burbelo, P.D.; Woo, J.; Balfour, H.H.; et al. Kinetics of Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) Neutralizing and Virus-Specific Antibodies after Primary Infection with EBV. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2016, 23, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shibamura, M.; Yoshikawa, T.; Yamada, S.; Inagaki, T.; Nguyen, P.H.A.; Fujii, H.; Harada, S.; Fukushi, S.; Oka, A.; Mizuguchi, M.; et al. Association of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) neutralizing antibodies with antibodies to the HCMV glycoprotein complexes. Virol. J. 2020, 17, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimamura, M.; Mach, M.; Britt, W.J. Human Cytomegalovirus Infection Elicits a Glycoprotein M (gM)/gN-Specific Virus-Neutralizing Antibody Response. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 4591–4600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tarlinton, D.; Radbruch, A.; Hiepe, F.; Dörner, T. Plasma cell differentiation and survival. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2008, 20, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammarlund, E.; Thomas, A.; Poore, E.A.; Amanna, I.J.; Rynko, A.E.; Mori, M.; Chen, Z.; Slifka, M.K. Durability of Vaccine-Induced Immunity Against Tetanus and Diphtheria Toxins: A Cross-sectional Analysis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 62, 1111–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antia, A.; Ahmed, H.; Handel, A.; Carlson, N.E.; Amanna, I.J.; Antia, R.; Slifka, M. Heterogeneity and longevity of antibody memory to viruses and vaccines. PLoS Biol. 2018, 16, e2006601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, Q.-X.; Tang, X.-J.; Shi, Q.-L.; Li, Q.; Deng, H.-J.; Yuan, J.; Hu, J.-L.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, F.-J.; et al. Clinical and immunological assessment of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infections. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1200–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seow, J.; Graham, C.; Merrick, B.; Acors, S.; Pickering, S.; Steel, K.J.A.; Hemmings, O.; O’Byrne, A.; Kouphou, N.; Galao, R.P.; et al. Longitudinal observation and decline of neutralizing antibody responses in the three months following SARS-CoV-2 infection in humans. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 1598–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, J.M.; Mateus, J.; Kato, Y.; Hastie, K.M.; Yu, E.D.; Faliti, C.E.; Grifoni, A.; Ramirez, S.I.; Haupt, S.; Frazier, A.; et al. Immunological memory to SARS-CoV-2 assessed for up to 8 months after infection. Science 2021, 371, eabf4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkaya, M.; Kwak, K.; Pierce, S.K. B cell memory: Building two walls of protection against pathogens. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engels, N.; Wienands, J. Memory control by the B cell antigen receptor. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 283, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palm, A.-K.E.; Henry, C. Remembrance of Things Past: Long-Term B Cell Memory After Infection and Vaccination. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanz, I.; Wei, C.; Jenks, S.A.; Cashman, K.S.; Tipton, C.; Woodruff, M.C.; Hom, J.; Lee, F.E.-H. Challenges and Opportunities for Consistent Classification of Human B Cell and Plasma Cell Populations. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boonyaratanakornkit, J.; Taylor, J.J. Techniques to Study Antigen-Specific B Cell Responses. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittle, J.R.R.; Wheatley, A.K.; Wu, L.; Lingwood, D.; Kanekiyo, M.; Ma, S.S.; Narpala, S.R.; Yassine, H.M.; Frank, G.M.; Yewdell, J.W.; et al. Flow Cytometry Reveals that H5N1 Vaccination Elicits Cross-Reactive Stem-Directed Antibodies from Multiple Ig Heavy-Chain Lineages. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 4047–4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scheid, J.F.; Mouquet, H.; Feldhahn, N.; Walker, B.D.; Pereyra, F.; Cutrell, E.; Seaman, M.S.; Mascola, J.R.; Wyatt, R.T.; Wardemann, H.; et al. A method for identification of HIV gp140 binding memory B cells in human blood. J. Immunol. Methods 2009, 343, 65–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodda, L.B.; Netland, J.; Shehata, L.; Pruner, K.B.; Morawski, P.A.; Thouvenel, C.D.; Takehara, K.K.; Eggenberger, J.; Hemann, E.A.; Waterman, H.R.; et al. Functional SARS-CoV-2-Specific Immune Memory Persists after Mild COVID-19. Cell 2021, 184, 169–183.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartley, G.E.; Edwards, E.S.J.; Aui, P.M.; Varese, N.; Stojanovic, S.; McMahon, J.; Peleg, A.Y.; Boo, I.; Drummer, H.E.; Hogarth, P.M.; et al. Rapid generation of durable B cell memory to SARS-CoV-2 spike and nucleocapsid proteins in COVID-19 and convalescence. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5, eabf8891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setliff, I.; Shiakolas, A.R.; Pilewski, K.A.; Murji, A.A.; Mapengo, R.E.; Janowska, K.; Richardson, S.; Oosthuysen, C.; Raju, N.; Ronsard, L.; et al. High-Throughput Mapping of B Cell Receptor Sequences to Antigen Specificity. Cell 2019, 179, 1636–1646.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, P.D.; DeKosky, B.J.; Ulmer, J.B. Antibody-guided structure-based vaccines. Semin. Immunol. 2020, 50, 101428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, J.A.; Dong, J.; Sevy, A.M.; Parrish, E.; Gilchuk, I.; Nargi, R.; Scarlett-Jones, M.; Reichard, W.; Bombardi, R.; Voss, T.G.; et al. Identification of Structurally Related Antibodies in Antibody Sequence Databases Using Rosetta-Derived Position-Specific Scoring. Structure 2020, 28, 1124–1130.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franke, F.; Kirchenbaum, G.A.; Kuerten, S.; Lehmann, P.V. IL-21 in Conjunction with Anti-CD40 and IL-4 Constitutes a Potent Polyclonal B Cell Stimulator for Monitoring Antigen-Specific Memory B Cells. Cells 2020, 9, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crotty, S.; Aubert, R.D.; Glidewell, J.; Ahmed, R. Tracking human antigen-specific memory B cells: A sensitive and generalized ELISPOT system. J. Immunol. Methods 2004, 286, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Gordic, M.; Kobold, S.; Lajmi, N.; Meyer, S.; Bartels, K.; Hildebrandt, Y.; Luetkens, T.; Ihloff, A.S.; Kröger, N.; et al. An optimized assay for the enumeration of antigen-specific memory B cells in different compartments of the human body. J. Immunol. Methods 2010, 358, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinna, D.; Corti, D.; Jarrossay, D.; Sallusto, F.; Lanzavecchia, A. Clonal dissection of the human memory B-cell repertoire following infection and vaccination. Eur. J. Immunol. 2009, 39, 1260–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, P.N.; Friedrich, D.P.; Williams, J.A.; Smith, R.J.; Stewart, T.L.; Carter, D.K.; Liao, H.-X.; McElrath, M.J.; Frahm, N. Optimization and qualification of a memory B-cell ELISpot for the detection of vaccine-induced memory responses in HIV vaccine trials. J. Immunol. Methods 2013, 394, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jahnmatz, M.; Kesa, G.; Netterlid, E.; Buisman, A.-M.; Thorstensson, R.; Ahlborg, N. Optimization of a human IgG B-cell ELISpot assay for the analysis of vaccine-induced B-cell responses. J. Immunol. Methods 2013, 391, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muir, L.; McKay, P.F.; Petrova, V.N.; Klymenko, O.V.; Kratochvil, S.; Pinder, C.L.; Kellam, P.; Shattock, R.J. Optimisation of ex vivo memory B cell expansion/differentiation for interrogation of rare peripheral memory B cell subset responses. Wellcome Open Res. 2017, 2, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czerkinsky, C.C.; Nilsson, L.-Å.; Nygren, H.; Ouchterlony, Ö.; Tarkowski, A. A solid-phase enzyme-linked immunospot (ELISPOT) assay for enumeration of specific antibody-secreting cells. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundararaman, S.; Karulin, A.Y.; Ansari, T.; BenHamouda, N.; Gottwein, J.; Laxmanan, S.; Levine, S.M.; Loffredo, J.T.; McArdle, S.; Neudoerfl, C.; et al. High Reproducibility of ELISPOT Counts from Nine Different Laboratories. Cells 2015, 4, 21–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, M.J.; Mitchell, R.M.; Meyer Sauteur, P.M.; Kelly, D.F.; Trück, J. The Antibody-Secreting Cell Response to Infection: Kinetics and Clinical Applications. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrammert, J.; Koutsonanos, D.; Li, G.-M.; Edupuganti, S.; Sui, J.; Morrissey, M.; McCausland, M.; Skountzou, I.; Hornig, M.; Lipkin, W.I.; et al. Broadly cross-reactive antibodies dominate the human B cell response against 2009 pandemic H1N1 influenza virus infection. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellebedy, A.H.; Krammer, F.; Li, G.-M.; Miller, M.S.; Chiu, C.; Wrammert, J.; Chang, C.Y.; Davis, C.W.; McCausland, M.; Elbein, R.; et al. Induction of broadly cross-reactive antibody responses to the influenza HA stem region following H5N1 vaccination in humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 13133–13138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhaumik, S.K.; Priyamvada, L.; Kauffman, R.C.; Lai, L.; Natrajan, M.S.; Cho, A.; Rouphael, N.; Suthar, M.S.; Mulligan, M.J.; Wrammert, J. Pre-Existing Dengue Immunity Drives a DENV-Biased Plasmablast Response in ZIKV-Infected Patient. Viruses 2019, 11, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verheul, A.M.; Versteeg, A.A.; Westerdaal, N.A.C.; Van Dam, G.J.; Jansze, M.; Snippe, H. Measurement of the humoral immune response against streptococcus pneumoniae type 14-derived antigens by an ELISA and ELISPOT assay based on biotin-avidin technology. J. Immunol. Methods 1990, 126, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaultier, G.N.; McCready, W.; Ulanova, M. The effect of pneumococcal immunization on total and antigen-specific B cells in patients with severe chronic kidney disease. BMC Immunol. 2019, 20, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, G.; Xia, J.; Zhao, X.-A.; Huang, R.; Lu, S.; et al. Use of ELISpot assay to study HBs-specific B cell responses in vaccinated and HBV infected humans. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuerten, S.; Pommerschein, G.; Barth, S.K.; Hohmann, C.; Milles, B.; Sammer, F.W.; Duffy, C.E.; Wunsch, M.; Rovituso, D.M.; Schroeter, M.; et al. Identification of a B cell-dependent subpopulation of multiple sclerosis by measurements of brain-reactive B cells in the blood. Clin. Immunol. 2014, 152, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taddeo, A.; Khodadadi, L.; Voigt, C.; Mumtaz, I.M.; Cheng, Q.; Moser, K.; Alexander, T.; Manz, R.A.; Radbruch, A.; Hiepe, F.; et al. Long-lived plasma cells are early and constantly generated in New Zealand Black/New Zealand White F1 mice and their therapeutic depletion requires a combined targeting of autoreactive plasma cells and their precursors. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Rangel-Moreno, J.; Owen, T.; Barnard, J.; Nevarez, S.; Ichikawa, H.T.; Anolik, J.H. Long-Term B Cell Depletion in Murine Lupus Eliminates Autoantibody-Secreting Cells and Is Associated with Alterations in the Kidney Plasma Cell Niche. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 3011–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sasaki, S.; Sullivan, M.; Narvaez, C.F.; Holmes, T.H.; Furman, D.; Zheng, N.-Y.; Nishtala, M.; Wrammert, J.; Smith, K.; James, J.A.; et al. Limited efficacy of inactivated influenza vaccine in elderly individuals is associated with decreased production of vaccine-specific antibodies. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 3109–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Painter, S.D.; Haralambieva, I.H.; Ovsyannikova, I.G.; Grill, D.E.; Poland, G.A. Detection of Influenza A/H1N1-Specific Human IgG-Secreting B Cells in Older Adults by ELISPOT Assay. Viral Immunol. 2014, 27, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caspell, R.; Lehmann, P.V. Detecting all Immunoglobulin Classes and Subclasses in a Multiplex 7 Color ImmunoSpot® Assay. In Handbook of ELISPOT: Methods and Protocols; Kalyuzhny, A.E., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 85–94. [Google Scholar]
- Megyesi, Z.; Lehmann, P.V.; Karulin, A.Y. Multi-Color FLUOROSPOT Counting Using ImmunoSpot® Fluoro-X™ Suite. In Handbook of ELISPOT: Methods and Protocols; Kalyuzhny, A.E., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 115–131. [Google Scholar]
- Karulin, A.Y.; Lehmann, P.V. How ELISPOT Morphology Reflects on the Productivity and Kinetics of Cells’ Secretory Activity. In Handbook of ELISPOT: Methods and Protocols; Kalyuzhny, A.E., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 125–143. [Google Scholar]
- Priyamvada, L.; Cho, A.; Onlamoon, N.; Zheng, N.-Y.; Huang, M.; Kovalenkov, Y.; Chokephaibulkit, K.; Angkasekwinai, N.; Pattanapanyasat, K.; Ahmed, R.; et al. B Cell Responses during Secondary Dengue Virus Infection Are Dominated by Highly Cross-Reactive, Memory-Derived Plasmablasts. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 5574–5585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kirchenbaum, G.A.; Allen, J.D.; Layman, T.S.; Sautto, G.A.; Ross, T.M. Infection of Ferrets with Influenza Virus Elicits a Light Chain–Biased Antibody Response against Hemagglutinin. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 3798–3807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromage, E.; Stephens, R.; Hassoun, L. The third dimension of ELISPOTs: Quantifying antibody secretion from individual plasma cells. J. Immunol. Methods 2009, 346, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyuzhny, A.E. Membrane Microplates for One- and Two-Color ELISPOT and FLUOROSPOT Assays. In Western Blotting: Methods and Protocols; Kurien, B.T., Scofield, R.H., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 435–447. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, A.J. Overview of Membranes and Membrane Plates Used in Research and Diagnostic ELISPOT Assays. In Handbook of ELISPOT: Methods and Protocols; Kalyuzhny, A.E., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 243–256. [Google Scholar]
- Ramachandran, H.; Laux, J.; Moldovan, I.; Caspell, R.; Lehmann, P.V.; Subbramanian, R.A. Optimal Thawing of Cryopreserved Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells for Use in High-Throughput Human Immune Monitoring Studies. Cells 2012, 1, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fecher, P.; Caspell, R.; Naeem, V.; Karulin, A.Y.; Kuerten, S.; Lehmann, P.V. B Cells and B Cell Blasts Withstand Cryopreservation While Retaining Their Functionality for Producing Antibody. Cells 2018, 7, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ecker, J.W.; Kirchenbaum, G.A.; Pierce, S.R.; Skarlupka, A.L.; Abreu, R.B.; Cooper, R.E.; Taylor-Mulneix, D.; Ross, T.M.; Sautto, G.A. High-Yield Expression and Purification of Recombinant Influenza Virus Proteins from Stably-Transfected Mammalian Cell Lines. Vaccines 2020, 8, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.-L.; Goldsmith, J.A.; Schaub, J.M.; DiVenere, A.M.; Kuo, H.-C.; Javanmardi, K.; Le, K.C.; Wrapp, D.; Lee, A.G.; Liu, Y.; et al. Structure-based design of prefusion-stabilized SARS-CoV-2 spikes. Science 2020, 369, 1501–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Following Reagent was Produced under HHSN272201400008C and Obtained through BEI Resources, N., NIH: Vector pCAGGS Containing the SARS-Related Coronavirus 2, Wuhan-Hu-1 Spike Glycoprotein Receptor Binding Domain (RBD), NR-52309. Available online: https://www.beiresources.org/Catalog/BEIPlasmidVectors/NR-52309.aspx (accessed on 30 May 2021).
- Sautto, G.A.; Kirchenbaum, G.A.; Abreu, R.B.; Ecker, J.W.; Pierce, S.R.; Kleanthous, H.; Ross, T.M. A Computationally Optimized Broadly Reactive Antigen Subtype–Specific Influenza Vaccine Strategy Elicits Unique Potent Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies against Hemagglutinin. J. Immunol. 2020, 204, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Following Reagent was Deposited by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and Obtained through BEI Resources, N., NIH: SARS-Related Coronavirus 2, Isolate USA-WA1/2020, Heat Inactivated, NR-52286. Available online: https://www.beiresources.org/Catalog/antigen/NR-52286.aspx (accessed on 30 May 2021).
- Kirchenbaum, G.A.; Ross, T.M. Generation of Monoclonal Antibodies against Immunoglobulin Proteins of the Domestic Ferret (Mustela putorius furo). J. Immunol. Res. 2017, 2017, 5874572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hicks, J.; Klumpp-Thomas, C.; Kalish, H.; Shunmugavel, A.; Mehalko, J.; Denson, J.-P.; Snead, K.R.; Drew, M.; Corbett, K.S.; Graham, B.S.; et al. Serologic Cross-Reactivity of SARS-CoV-2 with Endemic and Seasonal Betacoronaviruses. J. Clin. Immunol. 2021, 41, 906–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suthar, M.S.; Zimmerman, M.G.; Kauffman, R.C.; Mantus, G.; Linderman, S.L.; Hudson, W.H.; Vanderheiden, A.; Nyhoff, L.; Davis, C.W.; Adekunle, O.; et al. Rapid Generation of Neutralizing Antibody Responses in COVID-19 Patients. Cell Rep. Med. 2020, 1, 100040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantus, G.; Nyhoff, L.E.; Kauffman, R.C.; Edara, V.V.; Lai, L.; Floyd, K.; Shi, P.-Y.; Menachery, V.D.; Edupuganti, S.; Scherer, E.M.; et al. Evaluation of Cellular and Serological Responses to Acute SARS-CoV-2 Infection Demonstrates the Functional Importance of the Receptor-Binding Domain. J. Immunol. 2021, 206, 2605–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunmire, S.K.; Hogquist, K.A.; Balfour, H.H. Infectious Mononucleosis. In Epstein Barr Virus Volume 1: One Herpes Virus: Many Diseases; Münz, C., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 211–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kempkes, B.; Robertson, E.S. Epstein-Barr virus latency: Current and future perspectives. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2015, 14, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joseph, A.M.; Babcock, G.J.; Thorley-Lawson, D.A. EBV Persistence Involves Strict Selection of Latently Infected B Cells. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 2975–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frappier, L. The Epstein-Barr Virus EBNA1 Protein. Scientifica 2012, 2012, 438204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henle, W.; Henle, G.; Andersson, J.; Ernberg, I.; Klein, G.; Horwitz, C.A.; Marklund, G.; Rymo, L.; Wellinder, C.; Straus, S.E. Antibody responses to Epstein-Barr virus-determined nuclear antigen (EBNA)-1 and EBNA-2 in acute and chronic Epstein-Barr virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ha, S.; Li, F.; Troutman, M.C.; Freed, D.C.; Tang, A.; Loughney, J.W.; Wang, D.; Wang, I.-M.; Vlasak, J.; Nickle, D.C.; et al. Neutralization of Diverse Human Cytomegalovirus Strains Conferred by Antibodies Targeting Viral gH/gL/pUL128-131 Pentameric Complex. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e02033-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ezzell, C. AIDS envelope protein patent. Nature 1988, 331, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen-Contant, P.; Embong, A.K.; Kanagaiah, P.; Chaves, F.A.; Yang, H.; Branche, A.R.; Topham, D.J.; Sangster, M.Y.; Ellebedy, A.; Schultz-Cherry, S. S Protein-Reactive IgG and Memory B Cell Production after Human SARS-CoV-2 Infection Includes Broad Reactivity to the S2 Subunit. mBio 2020, 11, e01991-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byazrova, M.; Yusubalieva, G.; Spiridonova, A.; Efimov, G.; Mazurov, D.; Baranov, K.; Baklaushev, V.; Filatov, A. Pattern of circulating SARS-CoV-2-specific antibody-secreting and memory B-cell generation in patients with acute COVID-19. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2021, 10, e1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, L.; Wang, G.-L.; Shen, Y.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Zhan, B.-D.; Duan, L.-J.; Lu, B.; Shi, C.; Gao, Y.-M.; Peng, H.-H.; et al. Persistence of Antibody and Cellular Immune Responses in COVID-19 patients over Nine Months after Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherina, N.; Piralla, A.; Du, L.; Wan, H.; Kumagai-Braesch, M.; Andréll, J.; Braesch-Andersen, S.; Cassaniti, I.; Percivalle, E.; Sarasini, A.; et al. Persistence of SARS-CoV-2-specific B and T cell responses in convalescent COVID-19 patients 6–8 months after the infection. Med 2021, 2, 281–295.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, A.; Arya, R.; Sachan, S.; Jha, S.N.; Kalia, A.; Lall, A.; Sette, A.; Grifoni, A.; Weiskopf, D.; Coshic, P.; et al. Immune Memory in Mild COVID-19 Patients and Unexposed Donors Reveals Persistent T Cell Responses After SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornhorst, J.A.; Falke, J.J. Purification of proteins using polyhistidine affinity tags. Methods Enzymol. 2000, 326, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X.; Li, G.; Liang, S. Several affinity tags commonly used in chromatographic purification. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2013, 2013, 581093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Einhauer, A.; Jungbauer, A. The FLAG™ peptide, a versatile fusion tag for the purification of recombinant proteins. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2001, 49, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.-M.; Kim, G.-Y.; Rhim, H. A new idea for simple and rapid monitoring of gene expression: Requirement of nucleotide sequences encoding an N-terminal HA tag in the T7 promoter-driven expression in E. coli. Biotechnol. Lett. 2012, 34, 1841–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillman, M.C.; Yang, L.S.; Sun, S.; Duke, J.L.; O’Neil, K.T.; Kochie, J.E.; Karjoo, A.; Nath, P.; Breth, L.A.; Murphy, K.; et al. A Comprehensive System for Protein Purification and Biochemical Analysis Based on Antibodies to c-myc Peptide. Protein Expr. Purif. 2001, 23, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, T.G.M.; Koepke, J.; Frank, R.; Skerra, A. Molecular Interaction Between the Strep-tag Affinity Peptide and its Cognate Target, Streptavidin. J. Mol. Biol. 1996, 255, 753–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, J. Oriented immobilization of proteins on solid supports for use in biosensors and biochips: A review. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuñez, I.A.; Carlock, M.A.; Allen, J.D.; Owino, S.O.; Moehling, K.K.; Nowalk, P.; Susick, M.; Diagle, K.; Sweeney, K.; Mundle, S.; et al. Impact of age and pre-existing influenza immune responses in humans receiving split inactivated influenza vaccine on the induction of the breadth of antibodies to influenza A strains. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McCarthy, K.R.; Raymond, D.D.; Do, K.T.; Schmidt, A.G.; Harrison, S.C. Affinity maturation in a human humoral response to influenza hemagglutinin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 26745–26751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kyu, S.Y.; Kobie, J.; Yang, H.; Zand, M.S.; Topham, D.J.; Quataert, S.A.; Sanz, I.; Lee, F.E.-H. Frequencies of human influenza-specific antibody secreting cells or plasmablasts post vaccination from fresh and frozen peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J. Immunol. Methods 2009, 340, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Varnaitė, R.; García, M.; Glans, H.; Maleki, K.T.; Sandberg, J.T.; Tynell, J.; Christ, W.; Lagerqvist, N.; Asgeirsson, H.; Ljunggren, H.-G.; et al. Expansion of SARS-CoV-2–Specific Antibody-Secreting Cells and Generation of Neutralizing Antibodies in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients. J. Immunol. 2020, 205, 2437–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demonbreun, A.R.; McDade, T.W.; Pesce, L.; Vaught, L.A.; Reiser, N.L.; Bogdanovic, E.; Velez, M.P.; Hsieh, R.R.; Simons, L.M.; Saber, R.; et al. Patterns and persistence of SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibodies in Chicago to monitor COVID-19 exposure. JCI Insight 2021, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Köppert, S.; Wolf, C.; Becza, N.; Sautto, G.A.; Franke, F.; Kuerten, S.; Ross, T.M.; Lehmann, P.V.; Kirchenbaum, G.A. Affinity Tag Coating Enables Reliable Detection of Antigen-Specific B Cells in Immunospot Assays. Cells 2021, 10, 1843. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10081843
Köppert S, Wolf C, Becza N, Sautto GA, Franke F, Kuerten S, Ross TM, Lehmann PV, Kirchenbaum GA. Affinity Tag Coating Enables Reliable Detection of Antigen-Specific B Cells in Immunospot Assays. Cells. 2021; 10(8):1843. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10081843
Chicago/Turabian StyleKöppert, Sebastian, Carla Wolf, Noémi Becza, Giuseppe A. Sautto, Fridolin Franke, Stefanie Kuerten, Ted M. Ross, Paul V. Lehmann, and Greg A. Kirchenbaum. 2021. "Affinity Tag Coating Enables Reliable Detection of Antigen-Specific B Cells in Immunospot Assays" Cells 10, no. 8: 1843. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10081843
APA StyleKöppert, S., Wolf, C., Becza, N., Sautto, G. A., Franke, F., Kuerten, S., Ross, T. M., Lehmann, P. V., & Kirchenbaum, G. A. (2021). Affinity Tag Coating Enables Reliable Detection of Antigen-Specific B Cells in Immunospot Assays. Cells, 10(8), 1843. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10081843










