Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury in Lung Transplantation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Clinical Dilemma in Lung Transplantation
3. Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury
3.1. Changes in Ischemic Storage
3.2. Consequences of Ischemia–Reperfusion
4. Strategies to Prevent Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury
4.1. Donor and Recipient Factors
4.2. Procurement and Preservation
4.3. Protection in Reperfusion and Ventilation
4.4. Donation after Cardiac Death and Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury
5. Current Therapies and Promising Future Possibilities
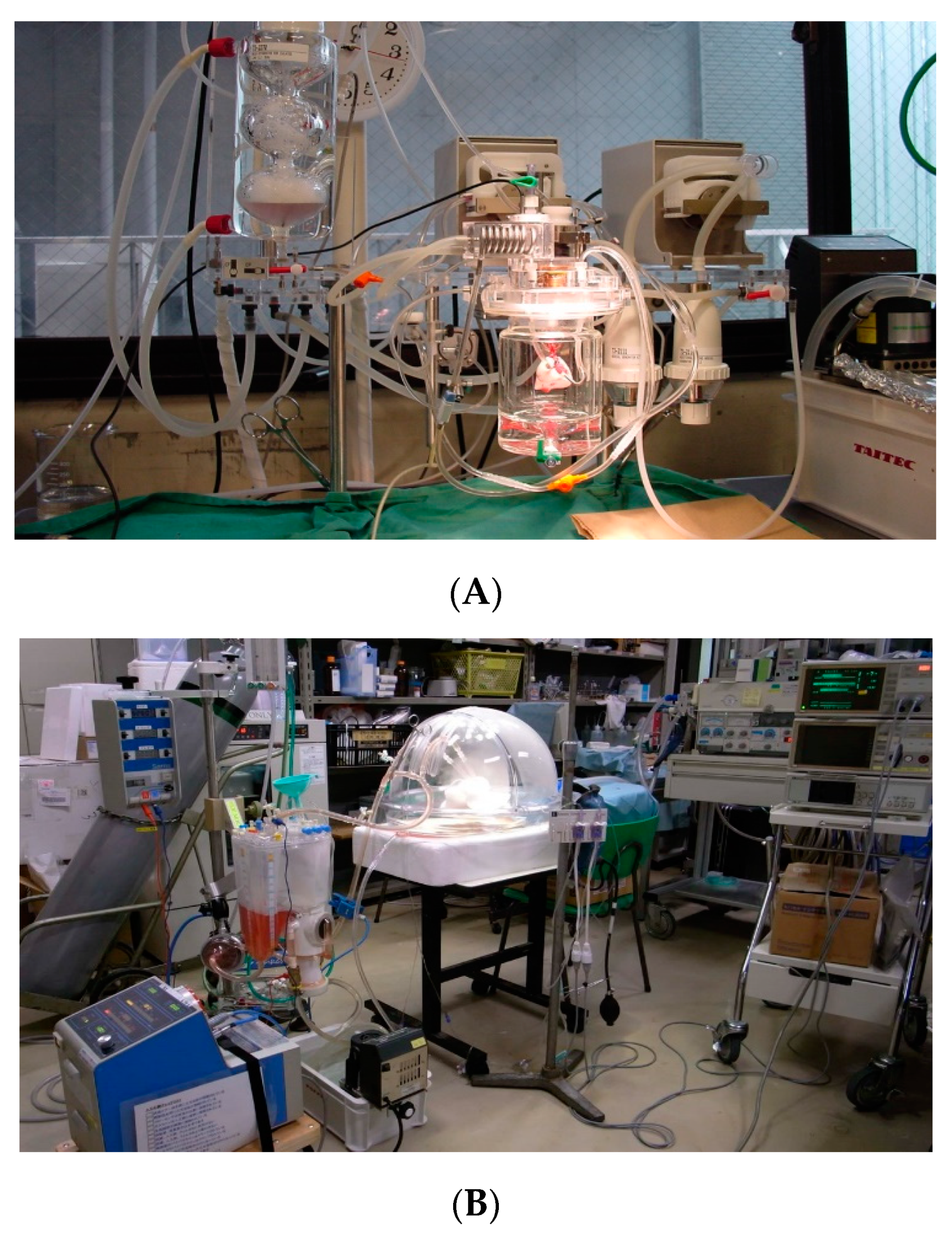
5.1. Ex Vivo Lung Perfusion
5.2. Novel Strategies for Endothelial Protection
5.3. Surfactants
5.4. Inhaled Beta-2 Adrenoreceptor Agonists
5.5. Therapeutic Gases
5.6. Fibrinolytic Treatment
5.7. Mesenchymal Stem Cells
6. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen-Yoshikawa, T.F.; Fukui, T.; Nakamura, S.; Ito, T.; Kadomatsu, Y.; Tsubouchi, H.; Ueno, H.; Sugiyama, T.; Goto, M.; Mori, S.; et al. Current trends in thoracic surgery. Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 2020, 82, 161–174. [Google Scholar]
- Cypel, M.; Yeung, J.; Liu, M.; Anraku, M.; Chen, F.; Karolak, W.; Sato, M.; Laratta, J.; Azad, S.; Madonik, M.; et al. Normothermic Ex Vivo Lung Perfusion in Clinical Lung Transplantation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1431–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Perrot, M.; Liu, M.; Waddell, T.K.; Keshavjee, S. Ischemia-reperfusion-induced lung injury. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 167, 490–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Date, H. Update on ischemia-reperfusion injury in lung transplantation. Curr. Opin. Organ. Transplant. 2015, 20, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gielis, J.F.; Boulet, G.A.; Briedé, J.J.; Horemans, T.; DeBergh, T.; Kussé, M.; Cos, P.; Van Schil, P.E. Longitudinal quantification of radical bursts during pulmonary ischaemia and reperfusion. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2015, 48, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Christie, J.; Keshavjee, S. Primary Graft Dysfunction: Definition, Risk Factors, Short-and Long-Term Outcomes. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 31, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toronto Lung Transplant Group: Unilateral lung transplantation for pulmonary fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1986, 314, 1140–1145. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, D.C.; Cherikh, W.S.; Harhay, M.O.; Hayes, D.; Hsich, E.; Khush, K.K.; Meiser, B.; Potena, L.; Rossano, J.W.; Toll, A.E.; et al. The International Thoracic Organ Transplant Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: Thirty-sixth adult lung and heart–lung transplantation Report—2019; Focus theme: Donor and recipient size match. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2019, 38, 1042–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, S.D. The Future of Lung Transplantation. Chest 2015, 147, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Suen, K.C.; Wang, Z.; Ma, D. Review 2: Primary graft dysfunction after lung transplant—pathophysiology, clinical considerations and therapeutic targets. J. Anesthesia 2020, 34, 729–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Cao, H.; Li, J.; Wang, B.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, X.D.; Liu, Z.; Yuan, H.; Zhan, Z. Autophagy induced by DAMPs facilitates the inflammation response in lungs undergoing ischemia-reperfusion injury through promoting TRAF6 ubiquitination. Cell Death Differ. 2017, 24, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Zhao, X.; Bi, S.; Cao, Y. Pretreatment with erythropoietin attenuates lung ischemia/reperfusion injury via toll-like receptor-4/nuclear factor-kappaB (TLR4/NF-kappaB) pathway. Med. Sci. Moint. 2018, 24, 1251–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Nieman, G.F.; Christie, J.D.; Fisher, A.B. Shear stress-related mechanosignaling with lung ischemia: Lessons from basic research can inform lung transplantation. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2014, 307, L668–L680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, M.A.; Sarathchandra, P.; Fryer, P.R.; Fuller, B.J.; Green, C.J. Scanning electron microscopic changes in morphology of pulmonary endothelium in rat lung isografts following hypothermic ischaemic storage and transplantation. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 1995, 76, 339–351. [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo, M.A.; Shah, K.A.; Fuller, B.J.; Green, C.J. Cold ischemia-induced damage to vascular endothelium results in permeability alternations in transplanted lungs. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 1996, 112, 1027–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fullerton, D.A.; Mitchell, M.B.; McIntyre, R.C.; Banerjee, A.; Campbell, D.N.; Harken, A.H.; Grover, F.L. Cold ischemia and reperfusion each produce pulmonary vasomotor dysfunction in the transplanted lung. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 1993, 106, 1213–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rancan, L.; Paredes, S.D.; Huerta, L.; Casanova, J.; Guzman, J.; Garutti, I.; Gonzalez-Aragoneses, F.; Simon, C.; Vara, E. Chemokine involvement in lung injury secondary to ischemia/reperfusion. Lung 2017, 195, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abela, C.B.; Homer-Vanniasinkham, S. Clinical implications of ischaemia-reperfusion injury. Pathophysiology 2003, 9, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Nakamura, T.; Wada, H. Development of New Organ Preservation Solutions in Kyoto University. Yonsei Med. J. 2004, 45, 1107–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyker, P.D.; Webb, C.A.J.; Kiamanesh, D.; Flynn, B.C. Lung ischemia reperfusion injury: A bench-to-beside review. Semin. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2012, 17, 28–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panday, A.; Sahoo, M.; Osorio, D.; Batra, S. NADPH oxidases: An overview from structure to innate immunity-associated pathologies. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 12, 5–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malczyk, M.; Veith, C.; Schermuly, R.T.; Gudermann, T.; Dietrich, A.; Sommer, N.; Weissmann, N.; Pak, O. NADPH oxidases-do they play a role in TRPC regulation under hypoxia? Pflugers Arch. 2016, 468, 23–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.; Dodia, C.; Chatterjee, S.; Feinstein, S.I.; Fisher, A.B. Protection against LPS-induced acute lung injury by a mechanism-based inhibitor of NADPH oxidase (type 2). Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2014, 306, L635–L644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ware, L.B.; Wang, Y.; Fang, X.; Warnock, M.; Sakuma, T.; Hall, T.S.; Matthay, M. Assessment of lungs rejected for transplantation and implications for donor selection. Lancet 2002, 360, 619–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayah, D.M.; Mallavia, B.; Liu, F.; Ortiz-Muñoz, G.; Caudrillier, A.; Derhovanessian, A.; Ross, D.J.; Iii, J.P.L.; Saggar, R.; Ardehali, A.; et al. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Are Pathogenic in Primary Graft Dysfunction after Lung Transplantation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 191, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fard, N.; Saffari, A.; Emami, G.; Hofer, S.; Kauczor, H.-U.; Mehrabi, A. Acute respiratory distress syndrome induction by pulmonary ischemia–reperfusion injury in large animal models. J. Surg. Res. 2014, 189, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laubach, V.E.; Sharma, A.K. Mechanisms of lung ischemia-reperfusion injury. Curr. Opin. Organ. Transplant. 2016, 21, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, M.; Chen-Yoshikawa, T.F.; Menju, T.; Ohata, K.; Kondo, T.; Motoyama, H.; Hijiya, K.; Aoyama, A.; Date, H. Inhibition of Toll-like receptor 4 signaling ameliorates lung ischemia–reperfusion injury in acute hyperglycemic conditions. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2016, 35, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, J.S.; Zhang, Z.K.; Tang, J.; Fan, K.; Guo, H.; Wang, J.J. Participation of autophagy in lung ischemia-reperfusion injury in vivo. J. Surg. Res. 2013, 182, e79–e87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.C.; Chen, S.B.; Liu, S.; Ling, X.; Xu, Q.R.; Yu, B.T.; Tang, J. Inhibition of mitochondrial autophagy protects donor lungs for lung transplantation against ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats via the mTOR pathway. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 3190–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christie, J.D.; Kotloff, R.M.; Ahya, V.N.; Tino, G.; Pochettino, A.; Gaughan, C.; DeMissie, E.; Kimmel, S.E. The effect of primary graft dysfunction on survival after lung transplantation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 171, 1312–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreisel, D.; Krupnick, A.S.; Puri, V.; Guthrie, T.J.; Trulock, E.P.; Meyers, B.F.; Patterson, G.A. Short-and long-term outcomes of 1000 adult lung transplant recipients at a single center. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2011, 141, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitson, B.A.; Prekker, M.E.; Herrington, C.S.; Whelan, T.P.; Radosevich, D.M.; Hertz, M.I.; Dahlberg, P.S. Primary Graft Dysfunction and Long-term Pulmonary Function After Lung Transplantation. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2007, 26, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Wang, Y.; Shiiya, H.; Sun, C.-B.; Uemura, Y.; Sato, M.; Nakajima, J. Outcomes of marginal donors for lung transplantation after ex vivo lung perfusion: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2020, 159, 720–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valapour, M.; Paulson, K.; Smith, J.M.; Hertz, M.I.; Skeans, M.A.; Heubner, B.M.; Edwards, L.B.; Snyder, J.J.; Israni, A.K.; Kasiske, B.L. OPTN/SRTR 2011 Annual Data Report: Lung. Arab. Archaeol. Epigr. 2012, 13, 149–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cypel, M.; Yeung, J.C.; Machuca, T.; Chen, M.; Singer, L.G.; Yasufuku, K.; De Perrot, M.; Pierre, A.; Waddell, T.K.; Keshavjee, S. Experience with the first 50 ex vivo lung perfusions in clinical transplantation. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2012, 144, 1200–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruttens, D.; Martens, A.; Ordies, S.; Verlede, S.E.; Neyrinck, A.P.; Vos, R.; Boada, M.C.; Vanaudenaerde, B.M.; Verleden, G.M.; Van Raemdonck, D. Short-and long-term outcomes after lung transplantation from circulatory-dead donors: A single-center experience. Transplantation 2017, 101, 2691–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Raemdonck, D.; Hartwig, M.G.; Hertz, M.I.; Davis, R.D.; Cypel, M.; Hayes, D.; Ivulich, S.; Kukreja, J.; Lease, E.D.; Loor, G.; et al. Report of the ISHLT Working Group on primary lung graft dysfunction Part IV: Prevention and treatment: A 2016 Consensus Group statement of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2017, 36, 1121–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porteous, M.K.; Diamond, J.M.; Christie, J.D. Primary graft dysfunction: Lessons learned about the first 72 hours after lung transplantation. Curr. Opin. Organ. Transplant. 2015, 20, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaver, C.M.; Ware, L.B. Primary graft dysfunction: Pathophysiology to guide new preventive therapies. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2017, 11, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledere, D.J.; Kawut, S.M.; Wickersham, N.; Winterbottom, C.; Bhorade, S.; Palmer, S.M.; Lee, J.; Diamond, J.M.; Wille, K.M.; Weinacker, A.; et al. Obesity and primary graft dysfunction after lung transplantation: The Lung Transplant Outcomes Group Obesity Study. Am. J. Respir Crit. Care Med. 2011, 184, 1055–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eberlein, M.; Reed, R.M.; Bölükbas, S.; Diamond, J.M.; Wille, K.M.; Orens, J.B.; Brower, R.G.; Christie, J.D. Lung Transplant Outcomes Group Lung size mismatch and primary graft dysfunction after bilateral lung transplantation. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2015, 34, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latchana, N.; Peck, J.R.; Whitson, B.; Black, S.M. Preservation solutions for cardiac and pulmonary donor grafts: A review of the current literature. J. Thorac. Dis. 2014, 6, 1143–1149. [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda, M.; Bando, T.; Yamada, T.; Sato, M.; Menjyu, T.; Aoyama, A.; Sato, T.; Chen, F.; Sonobe, M.; Omasa, M.; et al. Clinical application of ET-K solution for lung transplantation. Surg. Today 2015, 45, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohrbandt, B.; Simon, A.R.; Warnecke, G.; Fischer, S.; Hagl, C.; Niehaus, A.; Gorrlieb, J.; Welte, T.; Haverich, A.; Strueber, M. Lung preservation with Perfadex or Celsior in clinical transplantation: A retrospective single-center analysis of outcomes. Transplantation 2015, 99, 1933–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van De Wauwer, C.; Neyrinck, A.P.; Rega, F.R.; Verbeken, E.; Van Raemdonck, D.E. Retrograde flush is more protective than heparin in the uncontrolled donation after circulatory death lung donor. J. Surg. Res. 2014, 187, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungraithmayr, W. Novel strategies for endothelial preservation in lung transplant ischemia-reperfusion injury. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 581240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mrazkova, H.; Lischke, R.; Hodyc, D.; Herget, J. The protective effect of hypercapnia on ischemia-reperfusion injury in lungs. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2015, 205, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beer, A.; Reed, R.M.; Bolukbas, S.; Budev, M.; Chaux, G.; Zamore, M.R.; Snell, G.; Orens, J.B.; Klesney-Tait, J.A.; Schmidt, G.A.; et al. Mechanical ventilation after lung transplantation: An international survey of practices and preferences. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2014, 11, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, J.M.; Ahya, V.N. Mechanical ventilation after lung transplantation. It’s time for a trial. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2014, 11, 598–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, S.; Benazzo, A.; Dunkler, D.; Muckenhuber, M.; Del Sorbo, L.; Di Nardo, M.; Sinn, K.; Moser, B.; Matilla, J.R.; Lang, G.; et al. Ventilation parameters and early graft function in double lung transplantation. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2021, 40, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ius, F.; Sommer, W.; Tudorache, I.; Avsar, M.; Siemeni, T.; Salman, J.; Molitoris, U.; Gras, C.; Juettner, B.; Puntigam, J.; et al. Five-year experience with intraoperative extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in lung transplantation: Indications and midterm results. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2016, 35, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoechter, D.J.; Shen, Y.-M.; Kammerer, T.; Günther, S.; Weig, T.; Schramm, R.; Hagl, C.; Born, F.; Meiser, B.; Preissler, G.; et al. Extracorporeal Circulation During Lung Transplantation Procedures: A Meta-Analysis. ASAIO J. 2017, 63, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoetzenecker, K.; Benazzo, A.; Stork, T.; Sinn, K.; Schwarz, S.; Schweiger, T.; Klepetko, W.; Vienna Lung Transplant Group. Bilateral lung transplantation on intraoperative extracorporeal membrane oxygenator: An observational study. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2020, 160, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Raemdonck, D.; Keshavjee, S.; Levvey, B.; Cherikh, W.S.; Snell, G.; Erasmus, M.; Simon, A.; Glanville, A.R.; Clark, S.; D’Ovidio, F.; et al. Donation after circulatory death in lung transplantation-five-year follow-up from ISHLT Registry. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2019, 38, 1235–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villavicencio, M.A.; Axtell, A.L.; Spencer, P.J.; Heng, E.E.; Kilmarx, S.; Dalpozzal, N.; Funamoto, M.; Roy, N.; Osho, A.; Melnitchouk, S.; et al. Lung Transplantation From Donation After Circulatory Death: United States and Single-Center Experience. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2018, 106, 1619–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Nakamura, T.; Fujinaga, T.; Zhang, J.; Hamakawa, H.; Omasa, M.; Sakai, H.; Hanaoka, N.; Bando, T.; Wada, H.; et al. Protective Effect of a Nebulized β2-Adrenoreceptor Agonist in Warm Ischemic–Reperfused Rat Lungs. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2006, 82, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munshi, L.; Keshavjee, S.; Cypel, M. Donor management and lung preservation for lung transplantation. Lancet Respir. Med. 2013, 1, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steen, S.; Sjöberg, T.; Pierre, L.; Liao, Q.; Eriksson, L.; Algotsson, L. Transplantation of lungs from a non-heart-beating donor. Lancet 2001, 357, 825–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingemansson, R.; Eyjolfsson, A.; Mared, L.; Pierre, L.; Algotsson, L.; Ekmehag, B.; Gustafsson, R.; Johnsson, P.; Koul, B.; Lindstedt, S.; et al. Clinical Transplantation of Initially Rejected Donor Lungs After Reconditioning Ex Vivo. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2009, 87, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cypel, M.; Yeung, J.; Donahoe, L.; Chen, M.; Zamel, R.; Hoetzenecker, K.; Yasufuku, K.; de Perrot, M.; Pierre, A.F.; Waddell, T.K.; et al. Normothermic ex vivo lung perfusion: Does the indication impact organ utilization and patient outcomes after transplantation? J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2020, 159, 346–355.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warnecke, G.; Moradiellos, J.; Tudorache, I.; Kuhn, C.; Avsar, M.; Wiegmann, B.; Sommer, W.; Ius, F.; Kunze, C.; Gottlieb, J.; et al. Normothermic perfusion of donor lungs for preservation and assessment with the Organ Care System Lung before bilateral transplantation: A pilot study of 12 patients. Lancet 2012, 380, 1851–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Lv, W.; Hu, J. The Conversional Efficacy of Ex Vivo Lung Perfusion and Clinical Outcomes in Patients Undergoing Transplantation of Donor Lungs by Ex Vivo Lung Perfusion: A Meta-Analysis. Ann. Transplant. 2019, 24, 647–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, D.; Chen, F.; Yamada, T.; Sakamoto, J.; Ohsumi, A.; Bando, T.; Date, H. Reconditioning of lungs donated after circulatory death with normothermic ex vivo lung perfusion. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2012, 31, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weymann, A.; Popov, A.-F.; Sabashnikov, A.; Patil, N.P.; Zeriouh, M.; Mohite, P.N.; Zych, B.; Sáez, D.G.; Schmack, B.; Ruhparwar, A.; et al. Ex Vivo Lung Perfusion—State of the Art in Lung Donor Pool Expansion. Med. Sci. Monit. Basic Res. 2015, 21, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cypel, M.; Keshavjee, S. Extending the donor pool: Rehabilitation of poor organs. Thorac. Surg. Clin. 2015, 25, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohata, K.; Chen-Yoshikawa, T.F.; Menju, T.; Miyamoto, E.; Tanaka, S.; Takahashi, M.; Motoyama, H.; Hijiya, K.; Aoyama, A.; Date, H. Protective Effect of Inhaled Rho-Kinase Inhibitor on Lung Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2017, 103, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nakajima, D.; Chen, F.; Yamada, T.; Sakamoto, J.; Osumi, A.; Fujinaga, T.; Shoji, T.; Sakai, H.; Bando, T.; Date, H. Hypothermic Machine Perfusion Ameliorates Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Rat Lungs From Non-Heart-Beating Donors. Transplantation 2011, 92, 858–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Ali, A.; Keshavjee, S.; Liu, M.; Cypel, M. Ex vivo lung perfusion for donor lung assessment and repair: A review of translational interspecies models. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2020, 319, L932–L940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cypel, M.; Yeung, J.; Hirayama, S.; Rubacha, M.; Fischer, S.; Anraku, M.; Sato, M.; Harwood, S.; Pierre, A.; Waddell, T.K.; et al. Technique for Prolonged Normothermic Ex Vivo Lung Perfusion. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2008, 27, 1319–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liersch-Nordqvist, A.; Ingemansson, R.; Pierre, L.; Hlebowicz, J.; Lindstedt, S. Lungs exposed to 1 hour warm ischemia without heparin before harvesting might be suitable candidates for transplantation. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2015, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenza, F.; Rosso, L.; Coppola, S.; Froio, S.; Colombo, J.; Dossi, R.; Fumagalli, J.; Salice, V.; Pizzocri, M.; Conte, G.; et al. Beta-adrenergic agonist infusion during extracorporeal lung perfusion: Effects on glucose concentration in the perfusion fluid and on lung function. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2012, 31, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalife-Hocquemiller, T.; Sage, E.; Dorfmuller, P.; Mussot, S.; Houerou, D.L.; Eddahibi, S.; Fadel, E. Exogenous surfactant sttenuates lung injury from gastric-acid aspiration during ex vivo reconditioning in pigs. Transplantation 2014, 97, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommer, W.; Salman, J.; Avsar, M.; Hoeffler, K.; Jansson, K.; Siemeni, T.N.; Knoefel, A.-K.; Ahrens, L.; Poyanmehr, R.; Tudorache, I.; et al. Prediction of transplant outcome after 24-hour ex vivo lung perfusion using the Organ Care System in a porcine lung transplantation model. Arab. Archaeol. Epigr. 2019, 19, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonati, C.; Bassani, G.A.; Brambilla, D.; Leonardi, P.; Carlin, A.; Faversani, A.; Gatti, S.; Valenza, F. Influence of ex vivo perfusion on the biomolecular profile of rat lungs. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 5532–5549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, K.; Shigemura, N.; Tanaka, Y.; Bhama, J.; D’Cunha, J.; Kobayashi, H.; Luketich, J.D.; Bermudez, C.A. Hydrogen Preconditioning During Ex Vivo Lung Perfusion Improves the Quality of Lung Grafts in Rats. Transplantation 2014, 98, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.; Zamel, R.; Yeung, J.; Bader, G.D.; Dos Santos, C.C.; Bai, X.; Wang, Y.; Keshavjee, S.; Liu, M. Potential therapeutic targets for lung repair during human ex vivo lung perfusion. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1902222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abassi, Z.; Armaly, Z.; Heyman, S.N. Glycocalyx Degradation in Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Am. J. Pathol. 2020, 190, 752–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, F.W.; Da, Q.; Guillory, B.; Cruz, M.A. Recombinant Human Vimentin Binds to P-Selectin and Blocks Neutrophil Capture and Rolling on Platelets and Endothelium. J. Immunol. 2018, 200, 1718–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, K.; Kölbel, H.C.; Metzger, R.P.; Hanusch, C.; Frohnmeyer, M.; Hohenberger, P.; Danilov, S.M. Immunotargeting of the Pulmonary Endothelium via Angiotensin-Converting-Enzyme in Isolated Ventilated and Perfused Human Lung. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2013, 756, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Chen, F.; Sakamoto, J.; Nakajima, D.; Ohsumi, A.; Bando, T.; Date, H. Impact of the cardiac arrest mode on cardiac death donor lungs. J. Surg. Res. 2015, 195, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struber, M.; Cremer, J.; Harringer, W.; Hirt, S.W.; Costard Jackle, A.; Haverich, A. Nebulized systemic surfactant in reperfusion injury after single lung transplantation. J. Thorac. Cadriovasc. Surg. 1995, 110, 563–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kermeen, F.; McNeil, K.; Fraser, J.; McCarthy, J.; Ziegenfuss, M.; Mullany, D.; Dunning, J.; Hopkins, P. Resolution of Severe Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury Post–Lung Transplantation After Administration of Endobronchial Surfactant. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2007, 26, 850–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struber, M.; Fischer, S.; Niedermeyer, J.; Warnecke, G.; Gohrbandt, B.; Görler, A.; Simon, A.R.; Haverich, A.; Hohlfeld, J.M. Effects of exogenous surfactant instillation in clinical lung transplantation: A prospective, randomized trial. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2007, 133, 1620–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, G.; Knudsen, L.; Madershahian, N.; Mühlfeld, C.; Frank, K.; Rahmanian, P.; Wahlers, T.; Wittwer, T.; Ochs, M. Effects of exogenous surfactant on the non-heart-beating donor lung graft in experimental lung transplantation-a stereological study. J. Anat. 2014, 224, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohsumi, A.; Chen, F.; Sakamoto, J.; Nakajima, D.; Hijiya, K.; Motoyama, H.; Okita, K.; Horita, K.; Kikuchi, R.; Yamada, T.; et al. Protective effect of pre-recovery surfactant inhalation on lungs donated after cardiac death in a canine lung transplantation model. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2012, 31, 1136–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Nakajima, D.; Liu, M.; Ohsumi, A.; Kalaf, R.; Iskender, I.; Hsin, M.; Kanou, T.; Chen, M.; Baer, B.; Coutinho, R.; et al. Lung Lavage and Surfactant Replacement During Ex Vivo Lung Perfusion for Treatment of Gastric Acid Aspiration–Induced Donor Lung Injury. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2017, 36, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’ Ovido, F.; Floros, J.; Aramini, B.; Lederer, D.; DiAngelo, S.L.; Arcasoy, S.; Sonett, J.R.; Robbins, H.; Shah, L.; Costa, J.; et al. Donor surfactant protein A2 polymorphism and lung transplant survival. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1900618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belhaj, A.; Boven, C.; Dewachter, L.; Patino, M.R.; Sokolow, Y.; Rondelet, B. Influence of Donor Lung Surfactant-A and-B Protein Expression on the Development of Primary Graft Dysfunction After Lung Transplantation: A Pilot Study. Ann. Transplant. 2017, 22, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ware, L.B.; Landeck, M.; Koyama, T.; Zhao, Z.; Singer, J.; Kern, R.; Neidlinger, N.; Nguyen, J.; Johnson, E.; Janz, D.R.; et al. A Randomized Trial of the Effects of Nebulized Albuterol on Pulmonary Edema in Brain-Dead Organ Donors. Arab. Archaeol. Epigr. 2014, 14, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, J.C.; Nishikawa, M.; Haddad, E.B.; Kwon, O.J.; Hirst, S.J.; Twort, C.H.; Barnes, P.J. Localisation and expression of beta-adrenoreceptor subtype mRNAs in human lung. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1996, 302, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, J.; Chen, F.; Nakajima, D.; Yamada, T.; Ohsumi, A.; Sakai, H.; Bando, T.; Date, H. 418 The Effect of beta-2 Adrenoreceptor Agonist Inhalation on Lungs Donated after Cardiac Death in a Canine Lung Transplantation Model. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2012, 31, S148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijiya, K.; Chen-Yoshikawa, T.F.; Kondo, T.; Motoyama, H.; Ohsumi, A.; Nakajima, D.; Sakamoto, J.; Ohata, K.; Takahashi, M.; Tanaka, S.; et al. Bronchodilator inhalation during EVLP improves post-transplant graft dysfunction following warm ischemia. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2017, 103, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, T.; Chen, F.; Ohsumi, A.; Hijiya, K.; Motoyama, H.; Sowa, T.; Ohata, K.; Takahashi, M.; Yamada, T.; Sato, M.; et al. Beta-2 adrenoreceptor agonist inhalation during ex vivo lung perfusion attenuates lung injury. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2015, 100, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.-X.; Zhu, H.-W.; Chen, X.; Wei, J.-L.; Zhang, X.-F.; Xu, M.-Y. Inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibition reverses pulmonary arterial dysfunction in lung transplantation. Inflamm. Res. 2014, 63, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meade, M.O.; Granton, J.T.; Matte-Martyn, A.; McRae, K.; Weaver, B.; Cripps, P.; Keshavjee, S. A Randomized Trial of Inhaled Nitric Oxide to Prevent Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury after Lung Transplantation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 167, 1483–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryter, S.W.; Choi, A.M.K. Carbon monoxide: Present and future indications for a medical gas. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2013, 28, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, M.Z.; Sutherland, A.I.; Huang, H.; Ploeg, R.J.; Pugh, C.W. The Role of Hypoxia-Inducible Factors in Organ Donation and Transplantation: The Current Perspective and Future Opportunities. Arab. Archaeol. Epigr. 2014, 14, 1481–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohsawa, I.; Ishikawa, M.; Takahashi, K.; Watanabe, M.; Nishimaki, K.; Yamagata, K.; Katsura, K.-I.; Katayama, Y.; Asoh, S.; Ohata, S. Hydrogen acts as a therapeutic antioxidant by selectively reducing cytotoxic oxygen radicals. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dark, J. Hydrogen in lung conditioning—More than just inflation. Transplantation 2014, 98, 497–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, T.; Wakabayashi, N.; Shigemura, N.; Huang, C.-S.; Masutani, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Noda, K.; Peng, X.; Takahashi, T.; Billiar, T.R.; et al. Hydrogen gas reduces hyperoxic lung injury via the Nrf2 pathway in vivo. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2013, 304, L646–L656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haam, S.; Lee, S.; Paik, H.C.; Park, M.S.; Song, J.H.; Lim, B.J.; Nakao, A. The effects of hydrogen gas inhalation during ex vivo lung perfusion on donor lungs obtained after cardiac death. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2015, 48, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Liang, X.; Wang, D.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L.; Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Duan, Q.; Xie, K. Combination Therapy With Nitric Oxide and Molecular Hydrogen in a Murine Model of Acute Lung Injury. Shock 2015, 43, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayawake, H.; Chen-Yoshikawa, T.F.; Saito, M.; Yamagishi, H.; Yoshizawa, A.; Hirano, S.-I.; Kurokawa, R.; Date, H. Protective Effects of a Hydrogen-Rich Preservation Solution in a Canine Lung Transplantation Model. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2021, 111, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, M.; Chen-Yoshikawa, T.; Hirano, S.; Kayawake, H.; Ueda, S.; Tokuno, J.; Yamagishi, H.; Gochi, F.; Okabe, R.; Takahagi, A.; et al. Protective Effect of a Hydrogen-Rich Preservation Solution During Cold Ischemia in Rat Lung Transplantation. J. Heart. Lung Transplant. 2018, 37, S226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Chen-Yoshikawa, T.F.; Saito, M.; Tanaka, S.; Miyamoto, E.; Ohata, K.; Kondo, T.; Motoyama, H.; Hijiya, K.; Aoyama, A.; et al. Immersing lungs in hydrogen-rich saline attenuates lung ischemia-reperfusion injury. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2017, 51, 442–448. [Google Scholar]
- Inci, I.; Yamada, Y.; Hillinger, S.; Jungraithmayr, W.; Trinkwitz, M.; Weder, W. Successful Lung Transplantation After Donor Lung Reconditioning With Urokinase in Ex Vivo Lung Perfusion System. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2014, 98, 1837–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liersch-Nordqvist, A.; Fakhro, M.; Pierre, L.; Hlebowicz, J.; Malmsjo, M.; Ingemansson, R.; Lindstedt, S. The impact of alteplase on pulmonary graft function in donation after circulatory death—An experimental study. Ann. Med. Surg. 2017, 22, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luc, J.G.; Bozso, S.J.; Freed, D.H.; Nagendran, J. Successful Repair of Donation After Circulatory Death Lungs With Large Pulmonary Embolus Using the Lung Organ Care System for Ex Vivo Thrombolysis and Subsequent Clinical Transplantation. Transplantation 2015, 99, e1–e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motoyama, H.; Chen, F.; Ohsumi, A.; Hijiya, K.; Ohata, K.; Nakajima, D.; Sakamoto, J.; Yamada, T.; Sato, M.; Aoyama, A.; et al. Protective effect of plasmin in marginal donor lungs in an ex vivo lung erfusion model. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2013, 32, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motoyama, H.; Chen, F.; Hijiya, K.; Kondo, T.; Ohsumi, A.; Yamada, T.; Sato, M.; Aoyama, A.; Bando, T.; Date, H. Plasmin administration during ex vivo lung perfusion ameliorates lung ischemia–reperfusion injury. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2014, 33, 1093–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Rosso, L.; Zanella, A.; Righi, I.; Barilani, M.; Lazzari, L.; Scotti, E.; Gori, F.; Mendogni, P. Lung transplantation, ex-vivo reconditioning and regeneration: State of the art and perspectives. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, S2423–S2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souidi, N.; Stolk, M.; Seifert, M. Ischemia-reperfusion injury: Beneficial effects of mesenchymal stromal cells. Curr. Opin. Orgn. Transplant. 2013, 1, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Dai, X.; Li, G.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Du, C.; Wang, H. Infusion of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Protects Lung Transplants from Cold Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Mice. Lung 2014, 193, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruk, D.M.; Heijink, I.H.; Slebos, D.-J.; Timens, W.; Hacken, N.H.T. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells to Regenerate Emphysema: On the Horizon? Respiration 2018, 96, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, H. Extracellular Vesicles in Lung Disease. Chest 2018, 153, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallabhajosyula, P.; Korutla, L.; Habertheuer, A.; Reddy, S.; Schaufler, C.; Lasky, J.; Diamond, J.; Cantu, E.; Shaufler, C.; Iii, E.C. Ex Vivo Lung Perfusion Model to Study Pulmonary Tissue Extracellular Microvesicle Profiles. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2017, 103, 1758–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, M.L.; Zhao, Y.; Smith, R.; Weiss, M.L.; Kron, I.L.; Laubach, V.E.; Sharma, A.K. Mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles attenuate lung ischemia-reperfusion injury and enhance reconditioning of donor lungs after circulatory death. Respir. Res. 2017, 18, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonati, C.; Bassani, G.A.; Brambilla, D.; Leonardi, P.; Carlin, A.; Maggioni, M.; Zanella, A.; Dondossola, D.; Fonsato, V.; Grange, C.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cell–derived extracellular vesicles improve the molecular phenotype of isolated rat lungs during ischemia/reperfusion injury. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2019, 38, 1306–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yabuki, H.; Wakao, S.; Kushida, Y.; Dezawa, M.; Okada, Y. Human Multilineage-differentiating Stress-Enduring Cells Exert Pleiotropic Effects to Ameliorate Acute Lung Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury in a Rat Model. Cell Transplant. 2018, 27, 979–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, M.A.; Laffey, J.G.; Pelosi, P.; Rocco, P.R. Mesenchymal stem cell trials for pulmonary diseases. J. Cell. Biochem. 2014, 115, 1023–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, D.; Watanabe, Y.; Ohsumi, A.; Pipkin, M.; Chen, M.; Mordant, P.; Kanou, T.; Saito, T.; Lam, R.; Coutinho, R.; et al. Mesenchymal stromal cell therapy during ex vivo lung perfusion ameliorates ischemia-reperfusion injury in lung transplantation. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2019, 38, 1214–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Røsland, G.V.; Svendsen, A.; Torsvik, A.; Sobala, E.; McCormack, E.; Immervoll, H.; Mysliwietz, J.; Tonn, J.-C.; Goldbrunner, R.; Lønning, P.E.; et al. Long-term Cultures of Bone Marrow–Derived Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Frequently Undergo Spontaneous Malignant Transformation. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 5331–5339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthay, M.A.; Calfee, C.S.; Zhuo, H.; Thompson, B.T.; Wilson, J.G.; Levitt, J.E.; Rogers, A.J.; Gotts, J.E.; Wiener-Kronish, J.P.; Bajwa, E.K.; et al. Treatment with allogeneic mesenchymal stromal cells for moderate to severe acute respiratory distress syndrome (START study): A randomised phase 2a safety trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrell, C.R.; Sadikot, R.; Pascual, J.; Fellabaum, C.; Jankovic, M.G.; Jovicic, N.; Djonov, V.; Arsenijevic, N.; Volarevic, V. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Based Therapy of Inflammatory Lung Diseases: Current Understanding and Future Perspectives. Stem Cells Int. 2019, 2019, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talaie, T.; DiChiacchio, L.; Prasad, N.K.; Pasrija, C.; Julliard, W.; Kaczorowski, D.J.; Zhao, Y.; Lau, C.L. Ischemia-reperfusion Injury in the Transplanted Lung: A Literature Review. Transplant. Direct 2021, 7, e652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, D.C.; Enever, D.; Lawrence, S.; Sturm, M.J.; Herrmann, R.; Yerkovich, S.; Musk, M.; Hopkins, P.M. Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Therapy for Chronic Lung Allograft Dysfunction: Results of a First-in-Man Study. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2017, 6, 1152–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, C.A.; Gonwa, T.A.; Hodge, D.O.; Hei, D.J.; Centanni, J.M.; Zubair, A.C. Feasibility, Safety, and Tolerance of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for Obstructive Chronic Lung Allograft Dysfunction. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2018, 7, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen-Yoshikawa, T.F. Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury in Lung Transplantation. Cells 2021, 10, 1333. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061333
Chen-Yoshikawa TF. Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury in Lung Transplantation. Cells. 2021; 10(6):1333. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061333
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen-Yoshikawa, Toyofumi Fengshi. 2021. "Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury in Lung Transplantation" Cells 10, no. 6: 1333. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061333
APA StyleChen-Yoshikawa, T. F. (2021). Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury in Lung Transplantation. Cells, 10(6), 1333. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061333





