Chronic Alcohol Exposure of Cells Using Controlled Alcohol-Releasing Capillaries
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
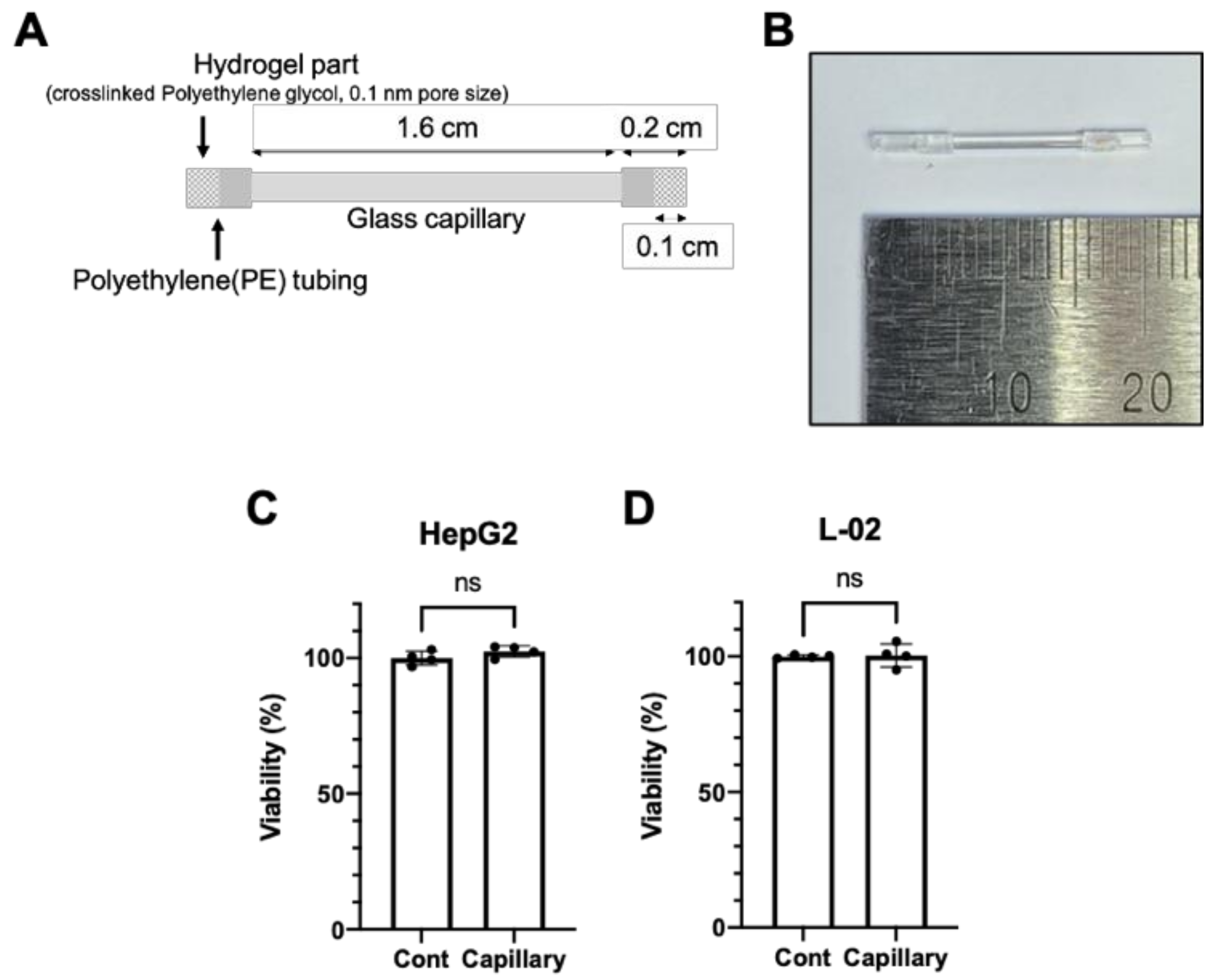
2.1. Fabrication of Glass Capillary Device
2.2. Cell Culture and Ethanol Treatment
2.3. RNA Quantification
2.4. Cell Viability and Ethanol Measurement
2.5. Oil Red O Staining
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Glass Capillary Device Led to a Controlled Release of Ethanol
3.2. Glass Capillary System for the Controlled Release of Ethanol
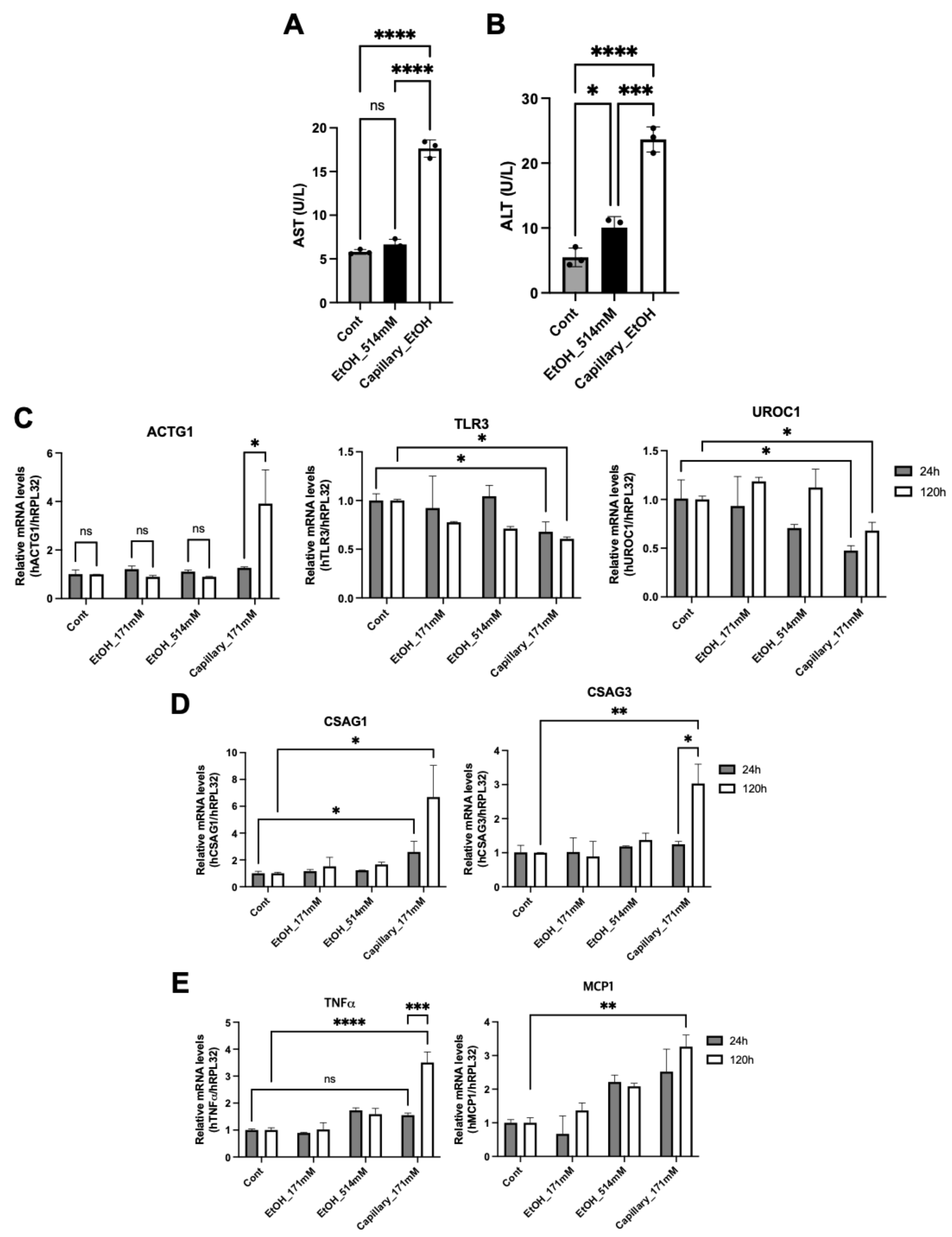
3.3. Long-Term Exposure of Ethanol Induces Hepatic Cytotoxicity
3.4. Ethanol Capillary System Shows a Different Hepatic Physiology
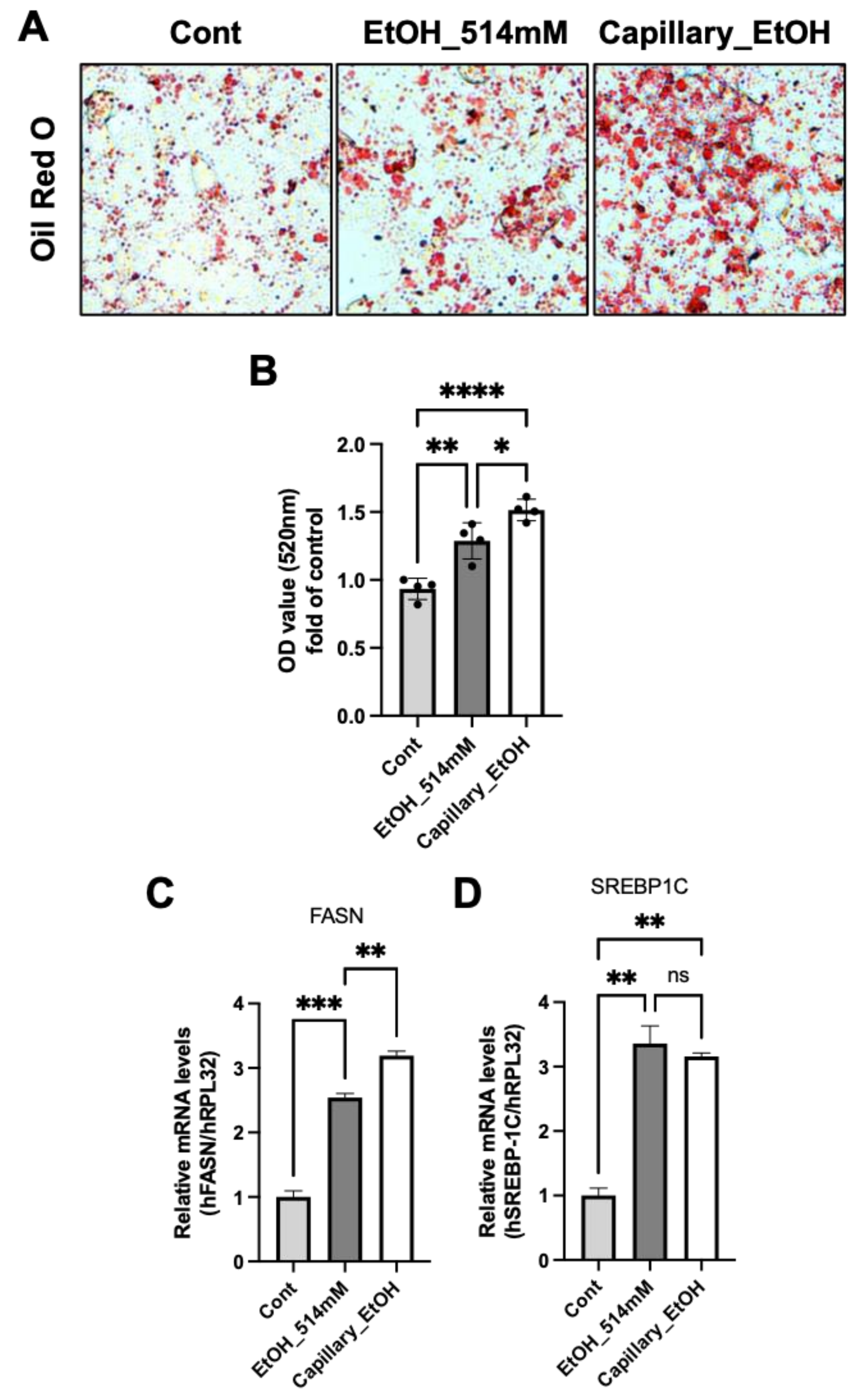
3.5. A Long-Term Exposure to Ethanol Induces Cellular Lipid Accumulation
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- SAMHSA. Table 2.1B—Tobacco Product and Alcohol Use in Lifetime, Past Year, and Past Month among Persons Aged 12 or Older, by Age Group: Percentages, 2018 and 2019. Available online: https://www.samhsa.gov/data/sites/default/files/reports/rpt29394/NSDUHDetailedTabs2019/NSDUHDetTabsSect2pe2019.htm (accessed on 6 May 2021).
- CDC. Annual Average for United States 2011–2015 Alcohol-Attributable Deaths Due to Excessive Alcohol Use, All Ages, 2020. Alcohol and Public Health: Alcohol-Relat. Related Disease Impact (ARDI). Available online: https://nccd.cdc.gov/DPH_ARDI/Default/Report.aspx?T=AAM&P=1A04A664-0244-42C1-91DE-316F3AF6B447&R=B885BD06-13DF-45CD-8DD8-AA6B178C4ECE&M=32B5FFE7-81D2-43C5-A892-9B9B3C4246C7&L=&F=AAMCauseAgeGroupAllNew&D=H (accessed on 6 May 2021).
- National Highway Traffic Safety Administration. 2014 Crash Data Key Findings, 2015. Traffic Safety Facts Crash Stats. Available online: https://crashstats.nhtsa.dot.gov/Api/Public/ViewPublication/812219 (accessed on 6 May 2021).
- Shield, K.D.; Parry, C.; Rehm, J. Chronic diseases and conditions related to alcohol use. Alcohol Res. 2013, 35, 155–173. [Google Scholar]
- Dusak, A.; Onur, M.R.; Cicek, M.; Firat, U.; Ren, T.; Dogra, V.S. Radiological Imaging Features of Fasciola hepatica Infection–A Pictorial Review. J. Clin. Imaging Sci. 2012, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanaway, J.D.; Flaxman, A.D.; Naghavi, M.; Fitzmaurice, C.; Vos, T.; Abubakar, I.; Abu-Raddad, L.J.; Assadi, R.; Bhala, N.; Cowie, B.; et al. The global burden of viral hepatitis from 1990 to 2013: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2016, 388, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, G.Y. Acute Alcoholic Hepatitis. Clin. Liver Dis. 2019, 23, 81–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuppalanchi, R.; Noureddin, M.; Alkhouri, N.; Sanyal, A.J. Therapeutic pipeline in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisseleva, T.; Brenner, D. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of liver fibrosis and its regression. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, J.S. Alcohol, liver disease and the gut microbiota. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathurin, P.; Bataller, R. Trends in the management and burden of alcoholic liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, S38–S46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massey, V.L.; Arteel, G.E. Acute alcohol-induced liver injury. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieber, C.S. Alcoholic fatty liver: Its pathogenesis and mechanism of progression to inflammation and fibrosis. Alcohol 2004, 34, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucey, M.R.; Mathurin, P.; Morgan, T.R. Alcoholic hepatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 2758–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegmund, S.V.; Dooley, S.; Brenner, D.A. Molecular mechanisms of alcohol-induced hepatic fibrosis. Dig. Dis. 2005, 23, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osna, N.A.; Donohue, T.M., Jr.; Kharbanda, K.K. Alcoholic Liver Disease: Pathogenesis and Current Management. Alcohol Res. 2017, 38, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Iida-Ueno, A.; Enomoto, M.; Tamori, A.; Kawada, N. Hepatitis B virus infection and alcohol consumption. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 2651–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cromie, S.L.; Jenkins, P.J.; Bowden, D.S.; Dudley, F.J. Chronic hepatitis C: Effect of alcohol on hepatitic activity and viral titre. J. Hepatol. 1996, 25, 821–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beier, J.I.; McClain, C.J. Mechanisms and cell signaling in alcoholic liver disease. Biol. Chem. 2010, 391, 1249–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louvet, A.; Mathurin, P. Alcoholic liver disease: Mechanisms of injury and targeted treatment. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 12, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stickel, F.; Hampe, J. Genetic determinants of alcoholic liver disease. Gut 2012, 61, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Chang, B.; Li, X.; Zou, Z. Role of ALDH2 in Hepatic Disorders: Gene Polymorphism and Disease Pathogenesis. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2021, 9, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Cederbaum, A.I. Cytochrome P450s and Alcoholic Liver Disease. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 1502–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Fu, J.; Li, L.; Chen, C.; Wang, H.; Hou, Y.; Xu, Y.; Pi, J. Nrf2 in alcoholic liver disease. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2018, 357, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolganiuc, A.; Szabo, G. In vitro and in vivo models of acute alcohol exposure. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 1168–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eysseric, H.; Gonthier, B.; Soubeyran, A.; Bessard, G.; Saxod, R.; Barret, L. There is not simple method to maintain a constant ethanol concentration in long-term cell culture: Keys to a solution applied to the survey of astrocytic ethanol absorption. Alcohol 1997, 14, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, V.; Reneau, J.C.; Dertien, J.S.; Agrawal, R.G.; Guerra, I.; Bhakta, Y.; Busari, K.; Neumann, M.K.; Bergeson, S.E.; Popp, R.L. An in vitro model for studying the effects of continuous ethanol exposure on N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor function. Alcohol 2012, 46, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrasekaran, K.; Swaminathan, K.; Mathan Kumar, S.; Clemens, D.L.; Dey, A. In vitro evidence for chronic alcohol and high glucose mediated increased oxidative stress and hepatotoxicity. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2012, 36, 1004–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Wang, S.; Ren, Z.; Frank, J.A.; Yang, X.H.; Zhang, Z.; Ke, Z.J.; Shi, X.; Luo, J. Chronic ethanol exposure enhances the aggressiveness of breast cancer: The role of p38gamma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 3489–3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, K.P.; Lieberman, R.; Kranzler, H.R.; Gelernter, J.; Clinton, K.; Covault, J. Alcohol-responsive genes identified in human iPSC-derived neural cultures. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Meng, X.; Xu, J.; Huang, X.; Li, H.; Li, G.; Wang, S.; Man, Y.; Tang, W.; Li, J. GPR40 agonist ameliorates liver X receptor-induced lipid accumulation in liver by activating AMPK pathway. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellott, M.B.; Searcy, K.; Pishko, M.V. Release of protein from highly cross-linked hydrogels of poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate fabricated by UV polymerization. Biomaterials 2001, 22, 929–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pochareddy, S.; Edenberg, H.J. Chronic alcohol exposure alters gene expression in HepG2 cells. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2012, 36, 1021–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.H.; Li, W.L.; Jin, M.H.; Jin, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Kong, L.Z.; Yu, L.Y.; Hyun, J.W.; Kwon, J.; Sun, H.N.; et al. Peroxiredoxin II Inhibits Alcohol-induced Apoptosis in L02 Hepatocytes Through AKT/beta-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Anticancer Res. 2020, 40, 4491–4504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tong, J.; Chang, B.; Wang, B.F.; Zhang, D.; Wang, B.Y. Effects of ethanol on the expression of caveolin-1 in HepG2 cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 11, 4409–4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Neuman, M.G.; Koren, G.; Tiribelli, C. In vitro assessment of the ethanol-induced hepatotoxicity on HepG2 cell line. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1993, 197, 932–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannini, E.G.; Testa, R.; Savarino, V. Liver enzyme alteration: A guide for clinicians. CMAJ 2005, 172, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, B.; Li, S.; Tan, Z.; Ma, L.; Liu, J. ACTG1 and TLR3 are biomarkers for alcohol-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 1714–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Kang, C.; Li, N.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Gao, F.; Dai, L. Identification of special key genes for alcohol-related hepatocellular carcinoma through bioinformatic analysis. PeerJ 2019, 7, e6375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Wheeler, M.D.; Kono, H.; Bradford, B.U.; Gallucci, R.M.; Luster, M.I.; Thurman, R.G. Essential role of tumor necrosis factor alpha in alcohol-induced liver injury in mice. Gastroenterology 1999, 117, 942–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandrekar, P.; Ambade, A.; Lim, A.; Szabo, G.; Catalano, D. An essential role for monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in alcoholic liver injury: Regulation of proinflammatory cytokines and hepatic steatosis in mice. Hepatology 2011, 54, 2185–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keegan, A.; Martini, R.; Batey, R. Ethanol-related liver injury in the rat: A model of steatosis, inflammation and pericentral fibrosis. J. Hepatol. 1995, 23, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altamirano, J.; Bataller, R. Alcoholic liver disease: Pathogenesis and new targets for therapy. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 8, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoist, F.; Grand-Perret, T. ApoB-100 secretion by HepG2 cells is regulated by the rate of triglyceride biosynthesis but not by intracellular lipid pools. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1996, 16, 1229–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meex, S.J.; Andreo, U.; Sparks, J.D.; Fisher, E.A. Huh-7 or HepG2 cells: Which is the better model for studying human apolipoprotein-B100 assembly and secretion? J. Lipid Res. 2011, 52, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allister, E.M.; Mulvihill, E.E.; Barrett, P.H.; Edwards, J.Y.; Carter, L.P.; Huff, M.W. Inhibition of apoB secretion from HepG2 cells by insulin is amplified by naringenin, independent of the insulin receptor. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 2218–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, O.; Kesselmeier, M.; Geffers, R.; Pellegrino, R.; Radlwimmer, B.; Hoffmann, K.; Ehemann, V.; Schemmer, P.; Schirmacher, P.; Lorenzo Bermejo, J.; et al. Methylome analysis and integrative profiling of human HCCs identify novel protumorigenic factors. Hepatology 2012, 56, 1817–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzoccoli, J.P.; Feke, D.L.; Baskaran, H.; Pintauro, P.N. Mechanical and cell viability properties of crosslinked low- and high-molecular weight poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate blends. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2010, 93, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolla, R.; Vay, D.; Mottaran, E.; Parodi, M.; Traverso, N.; Arico, S.; Sartori, M.; Bellomo, G.; Klassen, L.W.; Thiele, G.M.; et al. Detection of circulating antibodies against malondialdehyde-acetaldehyde adducts in patients with alcohol-induced liver disease. Hepatology 2000, 31, 878–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKillop, I.H.; Schrum, L.W.; Thompson, K.J. Role of alcohol in the development and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepat. Oncol. 2016, 3, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrasek, J.; Csak, T.; Ganz, M.; Szabo, G. Differences in innate immune signaling between alcoholic and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 28, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, G.; Petrasek, J.; Bala, S. Innate immunity and alcoholic liver disease. Dig. Dis. 2012, 30, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, W.; Jeong, H.-S.; Kim, S.-C.; Choi, C.-H.; Lee, K.-H. Chronic Alcohol Exposure of Cells Using Controlled Alcohol-Releasing Capillaries. Cells 2021, 10, 1120. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10051120
Kim W, Jeong H-S, Kim S-C, Choi C-H, Lee K-H. Chronic Alcohol Exposure of Cells Using Controlled Alcohol-Releasing Capillaries. Cells. 2021; 10(5):1120. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10051120
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Wanil, Hye-Seon Jeong, Sang-Chan Kim, Chang-Hyung Choi, and Kyung-Ha Lee. 2021. "Chronic Alcohol Exposure of Cells Using Controlled Alcohol-Releasing Capillaries" Cells 10, no. 5: 1120. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10051120
APA StyleKim, W., Jeong, H.-S., Kim, S.-C., Choi, C.-H., & Lee, K.-H. (2021). Chronic Alcohol Exposure of Cells Using Controlled Alcohol-Releasing Capillaries. Cells, 10(5), 1120. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10051120





