The Inflammatory Profile of CTEPH-Derived Endothelial Cells Is a Possible Driver of Disease Progression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population and Samples Collected
2.2. Pulmonary Endothelial Cell Isolation and Culture
2.3. Gene Expression Analysis
2.4. Immunostaining
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
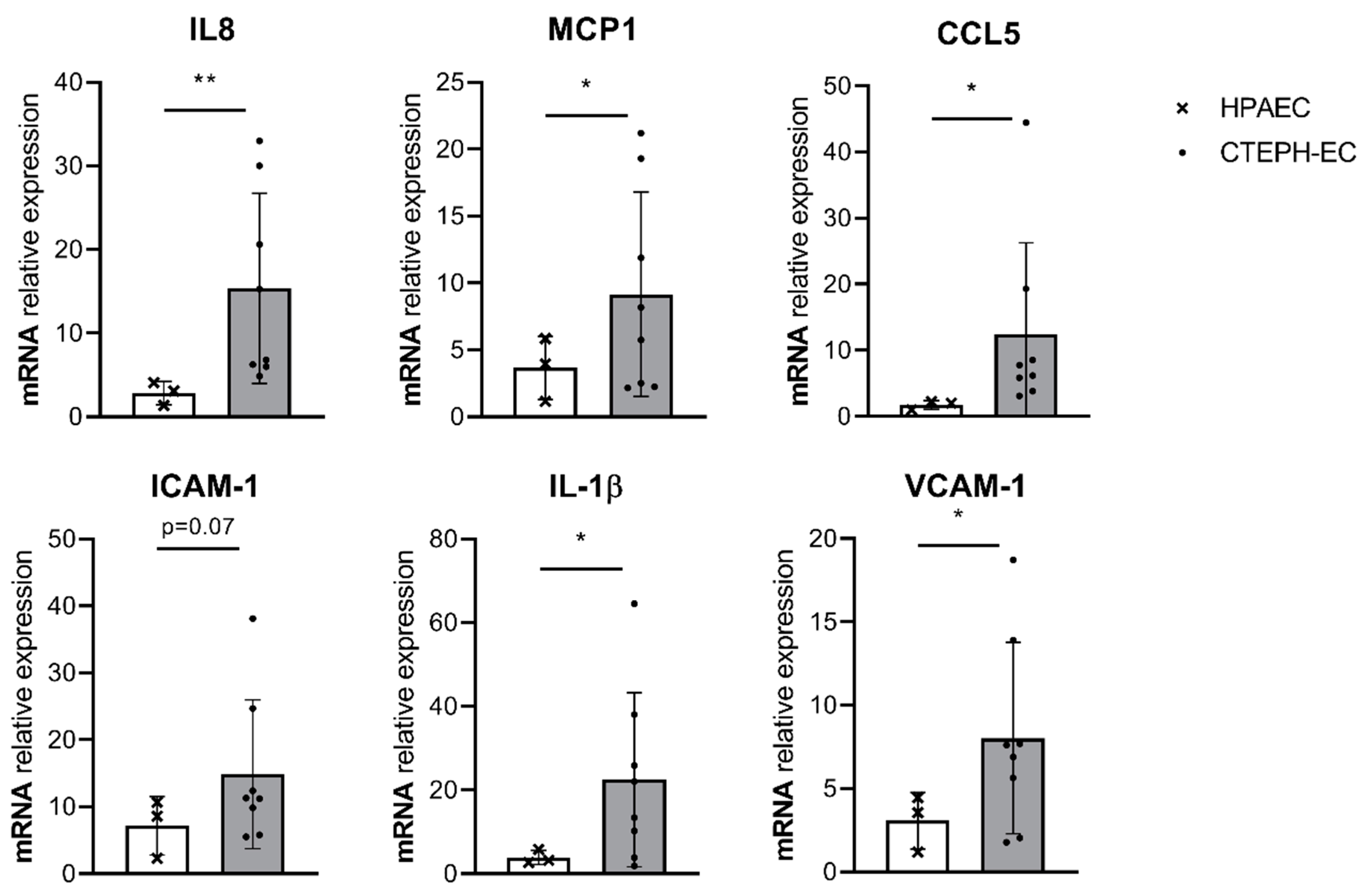
3.1. Basal Inflammatory Gene Expression in CTEPH-ECs and PAH-ECs
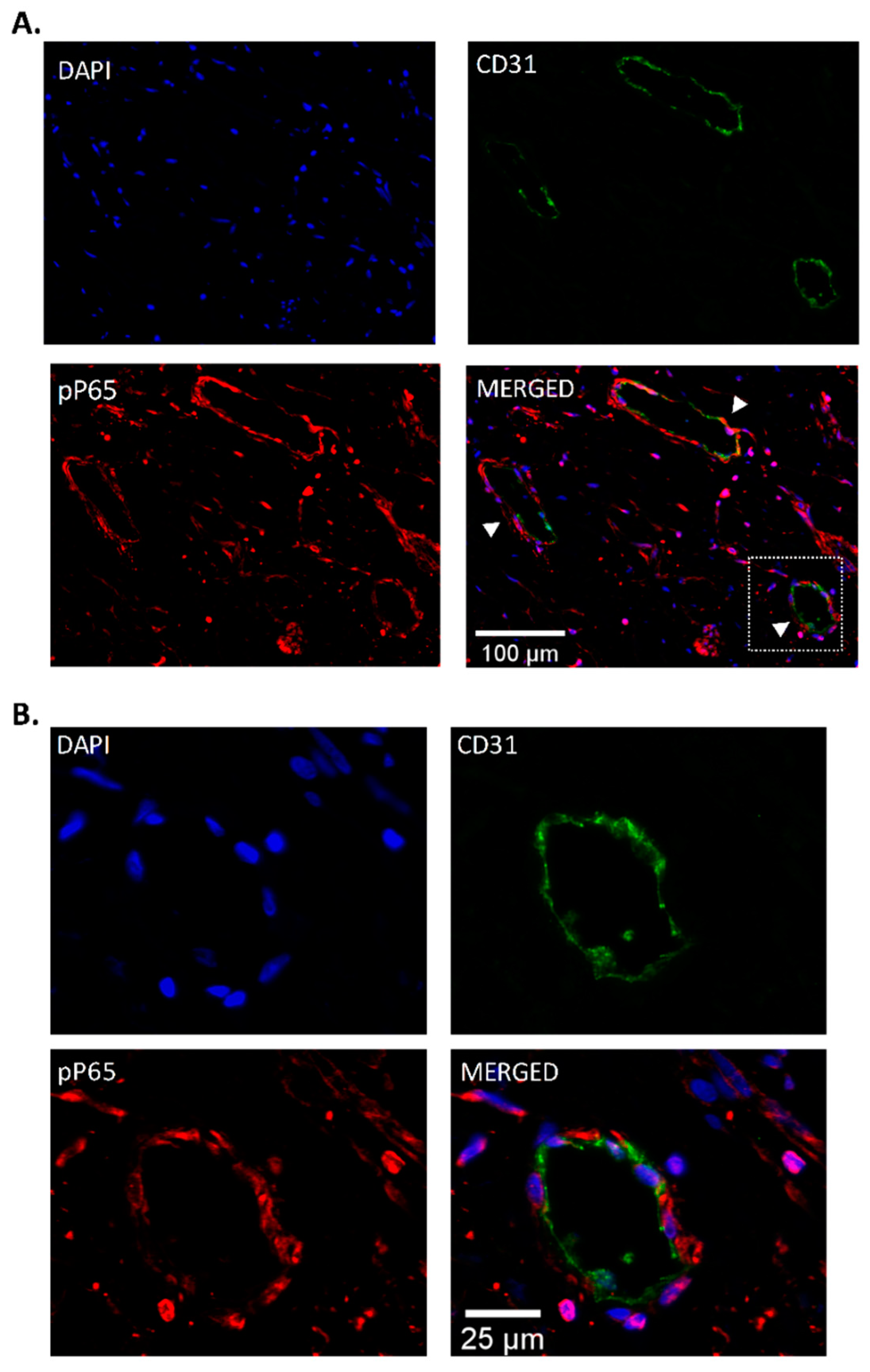
3.2. Fluorescence Staining of Phospho-P65 in CTEPH-Ecs
3.3. Endothelial Localization of Phospho-P65 in CTEPH Specimen
3.4. Effect of NF-κB Inhibition in CTEPH-ECs
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simonneau, G.; Montani, D.; Celermajer, D.S.; Denton, C.P.; Gatzoulis, M.A.; Krowka, M.; Williams, P.G.; Souza, R. Haemodynamic definitions and updated clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonneau, G.; Torbicki, A.; Dorfmuller, P.; Kim, N. The pathophysiology of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. Rev. Off. J. Eur. Respir. Soc. 2017, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, G.; Azzam, Z.S.; Hardak, E.; Tavor, Y.; Yigla, M. Idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension or chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: Can we be certain? Isr. Med Assoc. J. IMAJ 2011, 13, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Madani, M.; Ogo, T.; Simonneau, G. The changing landscape of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension management. Eur. Respir. Rev. Off. J. Eur. Respir. Soc. 2017, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, E.; Jenkins, D.; Lindner, J.; D’Armini, A.; Kloek, J.; Meyns, B.; Ilkjaer, L.B.; Klepetko, W.; Delcroix, M.; Lang, I.; et al. Surgical management and outcome of patients with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: Results from an international prospective registry. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2011, 141, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, I.; Meyer, B.C.; Ogo, T.; Matsubara, H.; Kurzyna, M.; Ghofrani, H.A.; Mayer, E.; Brenot, P. Balloon pulmonary angioplasty in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. Rev. Off. J. Eur. Respir. Soc. 2017, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, I.M.; Pesavento, R.; Bonderman, D.; Yuan, J.X. Risk factors and basic mechanisms of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: A current understanding. Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 41, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alias, S.; Redwan, B.; Panzenboeck, A.; Winter, M.P.; Schubert, U.; Voswinckel, R.; Frey, M.K.; Jakowitsch, J.; Alimohammadi, A.; Hobohm, L.; et al. Defective angiogenesis delays thrombus resolution: A potential pathogenetic mechanism underlying chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 810–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quarck, R.; Wynants, M.; Verbeken, E.; Meyns, B.; Delcroix, M. Contribution of inflammation and impaired angiogenesis to the pathobiology of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 46, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakao, S.; Hao, H.; Tanabe, N.; Kasahara, Y.; Kurosu, K.; Tatsumi, K. Endothelial-like cells in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: Crosstalk with myofibroblast-like cells. Respir. Res. 2011, 12, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercier, O.; Arthur Ataam, J.; Langer, N.B.; Dorfmuller, P.; Lamrani, L.; Lecerf, F.; Decante, B.; Dartevelle, P.; Eddahibi, S.; Fadel, E. Abnormal pulmonary endothelial cells may underlie the enigmatic pathogenesis of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. J. heart Lung Transplant. Off. Publ. Int. Soc. Heart Transplant. 2017, 36, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur Ataam, J.; Mercier, O.; Lamrani, L.; Amsallem, M.; Arthur Ataam, J.; Arthur Ataam, S.; Guihaire, J.; Lecerf, F.; Capuano, V.; Ghigna, M.R.; et al. ICAM-1 promotes the abnormal endothelial cell phenotype in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. J. heart Lung Transplant. Off. Publ. Int. Soc. Heart Transplant. 2019, 38, 982–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolders, V.F.E.D.; Rodríguez, C.; Morén, C.; Blanco, I.; Osorio, J.; Piccari, L.; Bonjoch, C.; Quax, P.H.A.; Peinado, V.I.; Castellà, M.; et al. Decreased glycolysis as metabolic fingerprint of endothelial cells in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2020. accepted. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huertas, A.; Guignabert, C.; Barbera, J.A.; Bartsch, P.; Bhattacharya, J.; Bhattacharya, S.; Bonsignore, M.R.; Dewachter, L.; Dinh-Xuan, A.T.; Dorfmuller, P.; et al. Pulmonary vascular endothelium: The orchestra conductor in respiratory diseases: Highlights from basic research to therapy. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, N. New paradigms in inflammatory signaling in vascular endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2014, 306, H317–H325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanaji, N.; Sato, T.; Nelson, A.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Kim, M.; Nakanishi, M.; Basma, H.; Michalski, J.; Farid, M.; et al. Inflammatory cytokines regulate endothelial cell survival and tissue repair functions via NF-kappaB signaling. J. Inflamm. Res. 2011, 4, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farkas, D.; Alhussaini, A.A.; Kraskauskas, D.; Kraskauskiene, V.; Cool, C.D.; Nicolls, M.R.; Natarajan, R.; Farkas, L. Nuclear factor kappaB inhibition reduces lung vascular lumen obliteration in severe pulmonary hypertension in rats. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2014, 51, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Q.; Liu, Z.; Song, Y.; Gan, H.; Huang, Z.; Luo, Q.; Zhao, Z. Proteomic Analyses of Endarterectomized Tissues from Patients with Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension. Cardiology 2020, 145, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzales, J.N.; Verin, A.D. Pulmonary Vascular Endothelial Cells. In Endothelial Dysfunction: Old Concepts and New Challenges; Lenasa, H., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coker, R.K.; Laurent, G.J. Pulmonary fibrosis: Cytokines in the balance. Eur. Respir. J. 1998, 11, 1218–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynants, M.; Vengethasamy, L.; Ronisz, A.; Meyns, B.; Delcroix, M.; Quarck, R. NF-κB pathway is involved in CRP-induced effects on pulmonary arterial endothelial cells in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2013, 305, L934–L942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabini, D.; Heinemann, A.; Foris, V.; Nagaraj, C.; Nierlich, P.; Balint, Z.; Kwapiszewska, G.; Lang, I.M.; Klepetko, W.; Olschewski, H.; et al. Comprehensive analysis of inflammatory markers in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension patients. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 44, 951–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Deng, C.; Wu, D.; Zhong, Z.; Lv, X.; Huang, Z.; Lian, N.; Liu, K.; Zhang, Q. The role of mononuclear cell tissue factor and inflammatory cytokines in patients with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2016, 42, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsh, L.M.; Jandl, K.; Grunig, G.; Foris, V.; Bashir, M.; Ghanim, B.; Klepetko, W.; Olschewski, H.; Olschewski, A.; Kwapiszewska, G. The inflammatory cell landscape in the lungs of patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dummer, A.; Rol, N.; Szulcek, R.; Kurakula, K.; Pan, X.; Visser, B.I.; Bogaard, H.J.; DeRuiter, M.C.; Goumans, M.J.; Hierck, B.P. Endothelial dysfunction in pulmonary arterial hypertension: Loss of cilia length regulation upon cytokine stimulation. Pulm. Circ. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, J.W.; Schoenleber, R.; Jesmok, G.; Best, J.; Moore, S.A.; Collins, T.; Gerritsen, M.E. Novel inhibitors of cytokine-induced IkappaBalpha phosphorylation and endothelial cell adhesion molecule expression show anti-inflammatory effects in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 21096–21103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galiè, N.; Humbert, M.; Vachiery, J.L.; Gibbs, S.; Lang, I.; Torbicki, A.; Simonneau, G.; Peacock, A.; Vonk Noordegraaf, A.; Beghetti, M.; et al. 2015 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: The Joint Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS): Endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT). Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 46, 903–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tura-Ceide, O.; Aventín-Beamonte, N.; Chamorro-Tort, N.; García-Lucio, J.; Coll-Bonfill, N.; Blanco-Vich, I.; Peinado Cabré, V.I.; Pomar, J.L.; Catesllà Pericàs, M.; Barberà Mir, J.A. Derivation and characterisation of endothelial cells from patients with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 44, P2327. [Google Scholar]
- Bolte, S.; Cordelières, F.P. A guided tour into subcellular colocalization analysis in light microscopy. J. Microsc. 2006, 224, 213–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bijli, K.M.; Fazal, F.; Rahman, A. Regulation of Rela/p65 and endothelial cell inflammation by proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2012, 47, 660–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, D.C.; Beers, C.; Cameron, V.; Thomson, L.; Flitney, F.W.; Hay, R.T. Activation of NF-kappaB nuclear transcription factor by flow in human endothelial cells. Biochim. Biophys Acta 2003, 1642, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, T.; Read, M.A.; Neish, A.S.; Whitley, M.Z.; Thanos, D.; Maniatis, T. Transcriptional regulation of endothelial cell adhesion molecules: NF-kappa B and cytokine-inducible enhancers. FASEB J. 1995, 9, 899–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, L.; Tan, S.; Zhou, Y.; Lin, J.; Wang, H.; Oyang, L.; Tian, Y.; Liu, L.; Su, M.; Wang, H.; et al. Role of the NFkappaB-signaling pathway in cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2018, 11, 2063–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gareus, R.; Kotsaki, E.; Xanthoulea, S.; van der Made, I.; Gijbels, M.J.; Kardakaris, R.; Polykratis, A.; Kollias, G.; de Winther, M.P.; Pasparakis, M. Endothelial cell-specific NF-kappaB inhibition protects mice from atherosclerosis. Cell Metab. 2008, 8, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuliga, M. NF-kappaB Signaling in Chronic Inflammatory Airway Disease. Biomolecules 2015, 5, 1266–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurakula, K.; Hamers, A.A.; van Loenen, P.; de Vries, C.J. 6-Mercaptopurine reduces cytokine and Muc5ac expression involving inhibition of NFκB activation in airway epithelial cells. Respir. Res. 2015, 16, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Pol, V.; Vos, M.; DeRuiter, M.C.; Goumans, M.J.; de Vries, C.J.M.; Kurakula, K. LIM-only protein FHL2 attenuates inflammation in vascular smooth muscle cells through inhibition of the NFκB pathway. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2020, 125–126, 106634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrábel, D.; Pour, L.; Ševčíková, S. The impact of NF-κB signaling on pathogenesis and current treatment strategies in multiple myeloma. Blood Rev. 2019, 34, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| CTEPH (n = 8) | |
|---|---|
| Female/male | 5/3 |
| Age years | 63.15 ± 10.88 |
| BMI kg·m−2 | 25.97 ± 4.35 |
| mPAP mmHg | 42.13 ± 9.52 |
| PVR dyn·s·m−5 | 706.75 ± 230.07 |
| PAOP mmHg | 10.25 ± 3.77 |
| Cardiac index L·min−1·m−2 | 2.23 ± 0.61 |
| Right atrial pressure mmHg | 9.38 ± 4.63 |
| SvO2 % | 59.50 ± 7.86 |
| 6MWD m | 398.13 ± 102.02 |
| BNP pg·mL−1 | 209.54 ± 360.12 |
| History of VTE | 1/7 |
| WHO FC | |
| I | 0 |
| II | 2 |
| III | 6 |
| Gene Name | Forward Primer (5′-3′) | Reverse Primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| IL-8 | CTGGCCGTGGCTCTCTTG | CTTGGCAAAACTGCACCTTCA |
| MCP-1 | CTGTGCCTGCTGCTCATAG | AGCTTCTTTGGGACACTTGC |
| CCL5 | GCATCTGCCTCCCCATATTC | AGTGGGCGGGCAATGTAG |
| IL-1β | CGAATCTCCGACCACCACTAC | TCCATGGCCACAACAACTGA |
| ICAM | CTGCAGACAGTGACCATC | GTCCAGTTTCCCGGACAA |
| VCAM | CAGGCTGGAAGAAGCAGA | GGCCTTTCGGATGGTATAGG |
| ARP | CACCATTGAAATCCTGAGTGATGT | TGACCAGCCGAAAGGAGAAG |
| TBP | TGGAAAAGTTGTATTAACAGGTGCT | GCAAGGGTACATGAGAGCCA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Smolders, V.F.E.D.; Lodder, K.; Rodríguez, C.; Tura-Ceide, O.; Barberà, J.A.; Jukema, J.W.; Quax, P.H.A.; Goumans, M.J.; Kurakula, K. The Inflammatory Profile of CTEPH-Derived Endothelial Cells Is a Possible Driver of Disease Progression. Cells 2021, 10, 737. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10040737
Smolders VFED, Lodder K, Rodríguez C, Tura-Ceide O, Barberà JA, Jukema JW, Quax PHA, Goumans MJ, Kurakula K. The Inflammatory Profile of CTEPH-Derived Endothelial Cells Is a Possible Driver of Disease Progression. Cells. 2021; 10(4):737. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10040737
Chicago/Turabian StyleSmolders, Valérie F. E. D., Kirsten Lodder, Cristina Rodríguez, Olga Tura-Ceide, Joan Albert Barberà, J. Wouter Jukema, Paul H. A. Quax, Marie José Goumans, and Kondababu Kurakula. 2021. "The Inflammatory Profile of CTEPH-Derived Endothelial Cells Is a Possible Driver of Disease Progression" Cells 10, no. 4: 737. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10040737
APA StyleSmolders, V. F. E. D., Lodder, K., Rodríguez, C., Tura-Ceide, O., Barberà, J. A., Jukema, J. W., Quax, P. H. A., Goumans, M. J., & Kurakula, K. (2021). The Inflammatory Profile of CTEPH-Derived Endothelial Cells Is a Possible Driver of Disease Progression. Cells, 10(4), 737. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10040737








