Lessons Learned from Targeting IGF-I Receptor in Thyroid-Associated Ophthalmopathy
Abstract
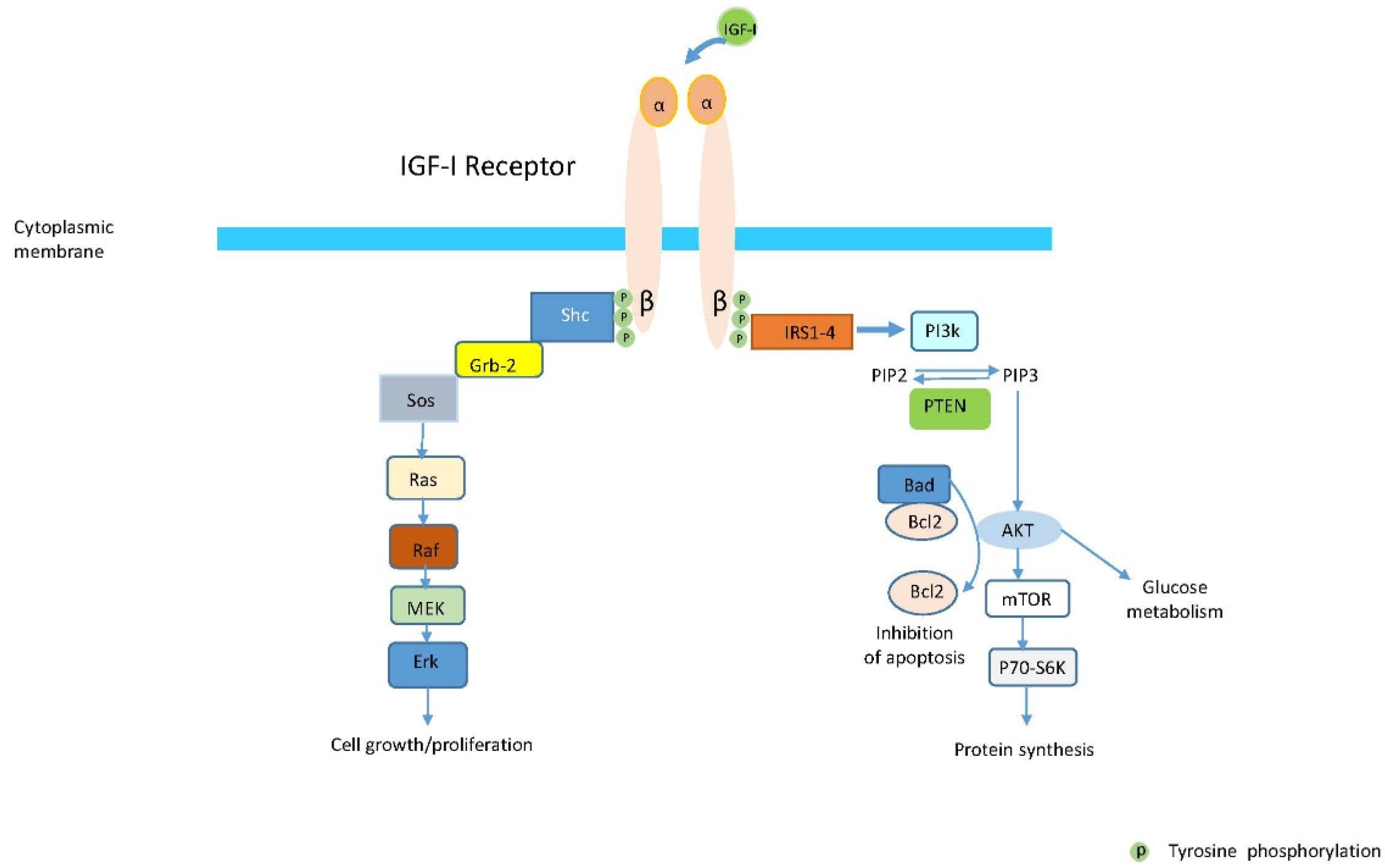
:1. Biology of Insulin-Like Growth Factor (IGF) Family and Their Receptors and Associated Proteins
2. Role of IGFs and IGF-IR in Regulating Growth and Development
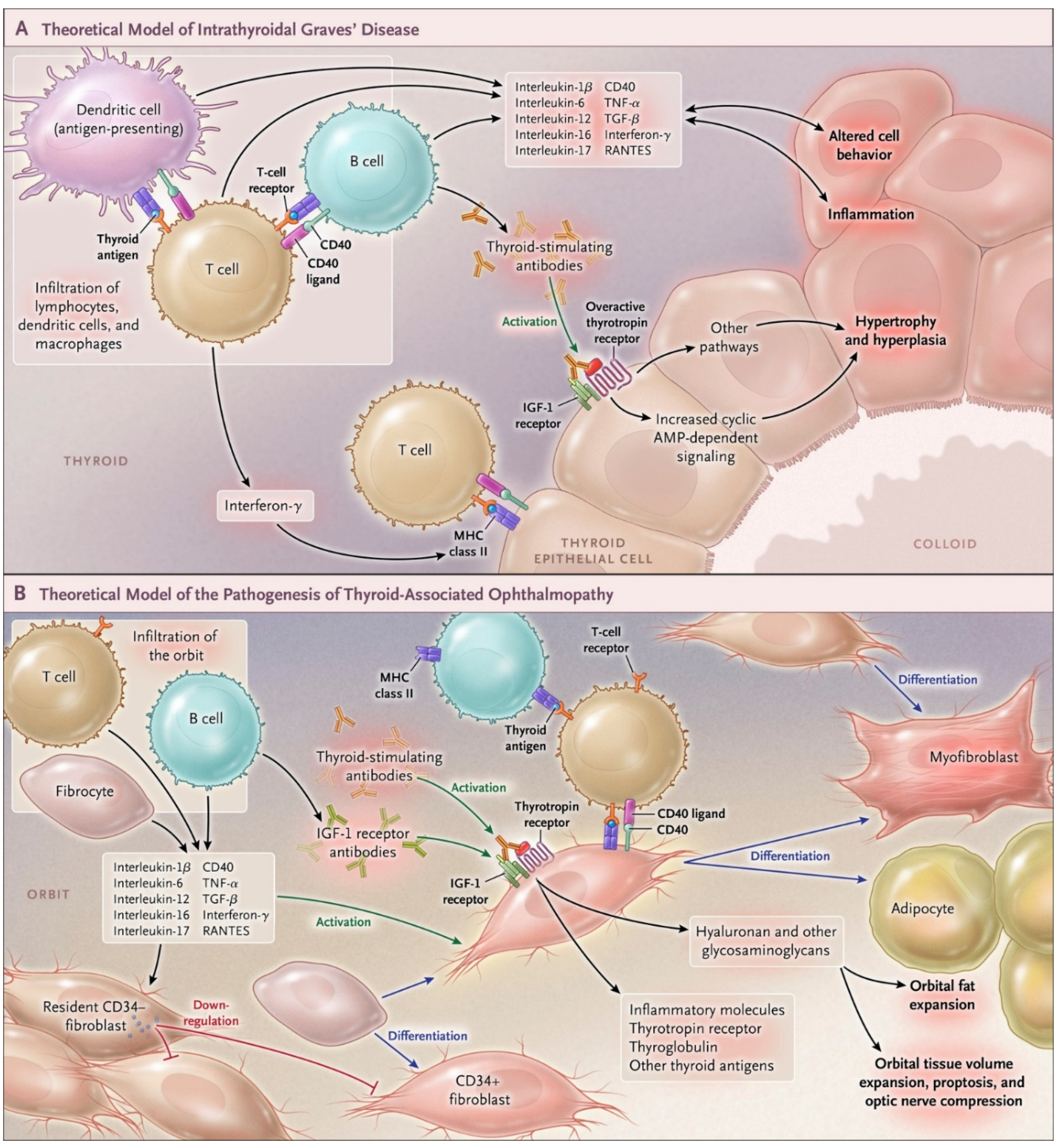
3. Role of the IGF-I Pathway in Regulating Immune Function
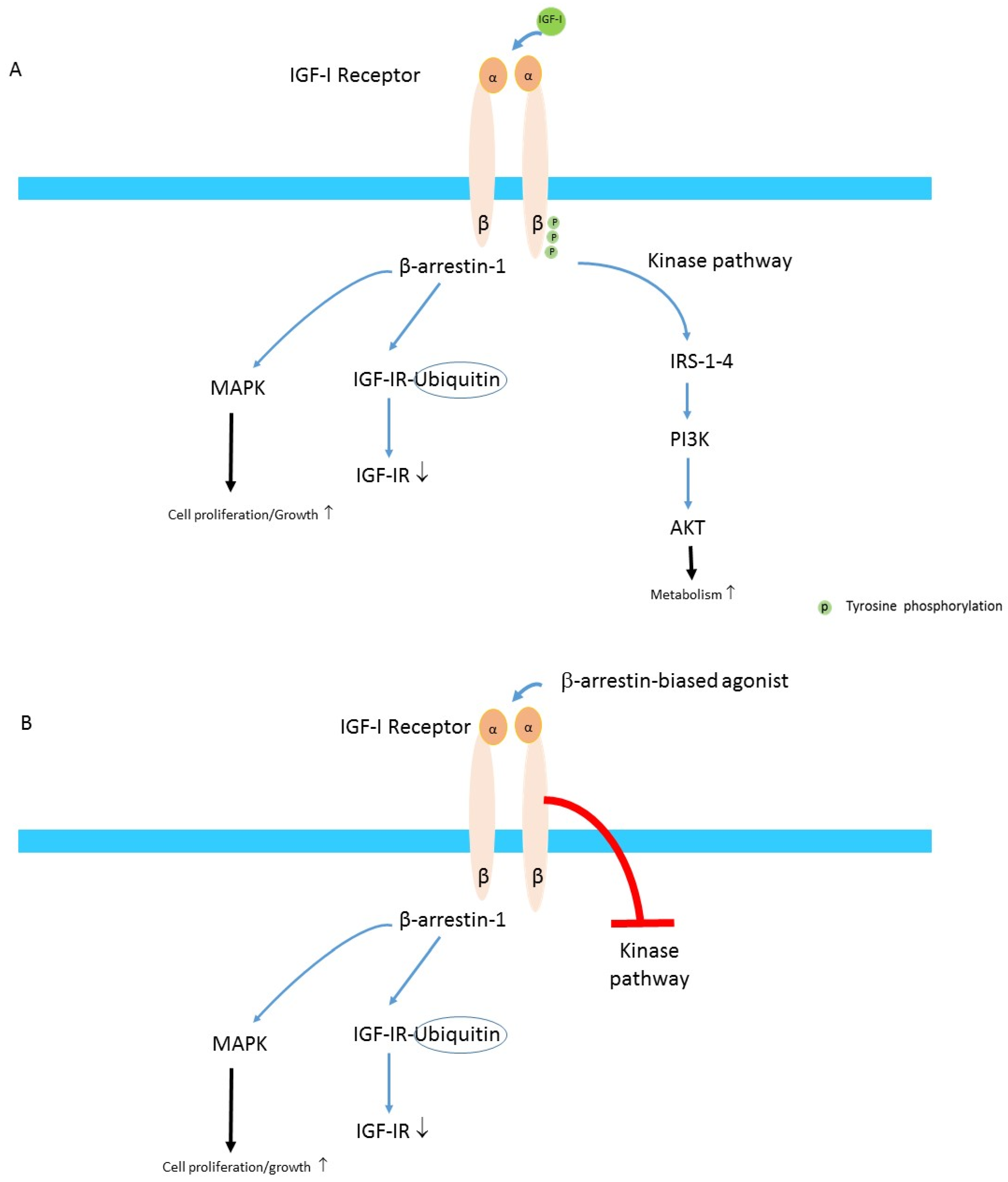
4. IGF-IR and TAO
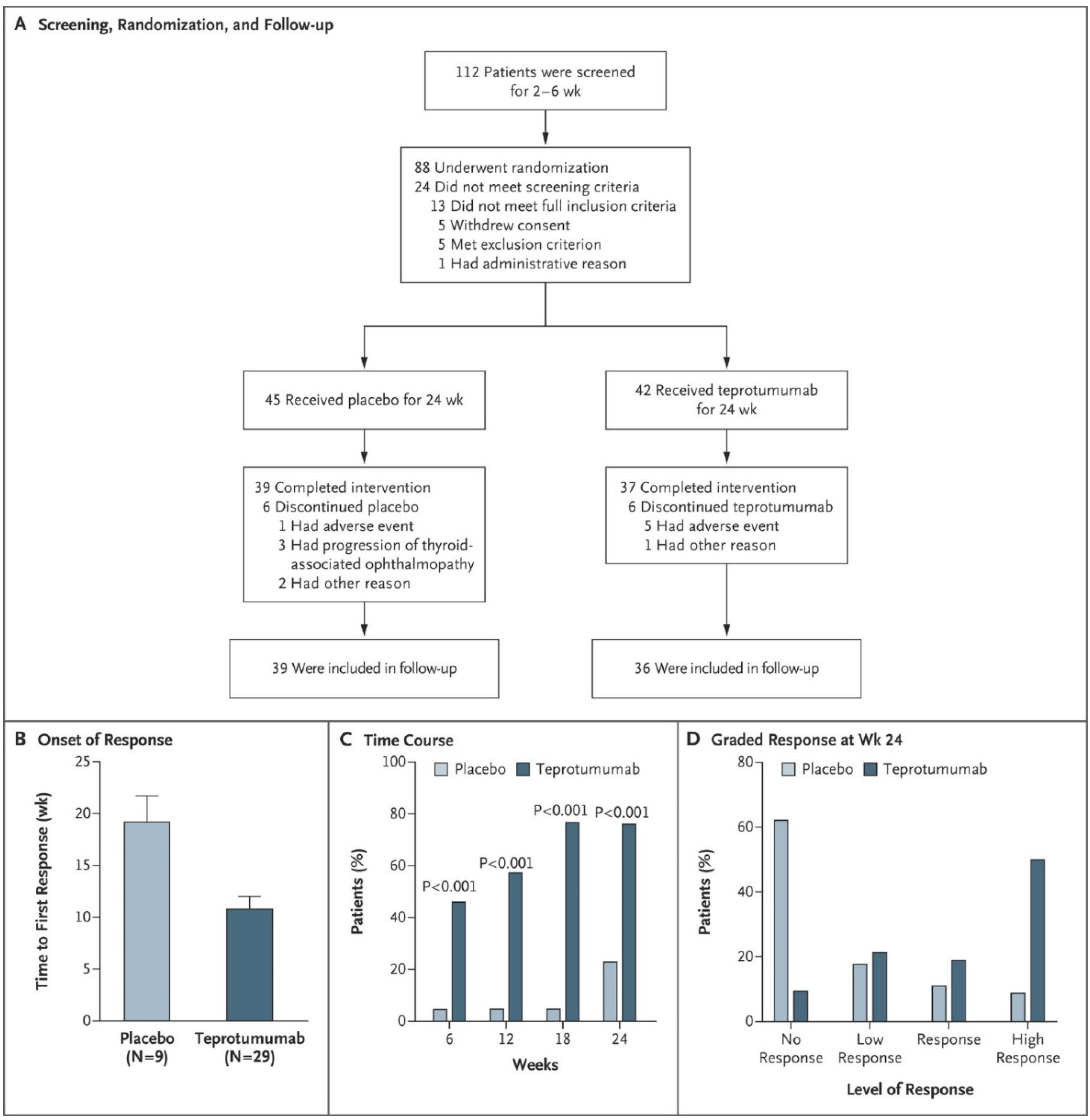
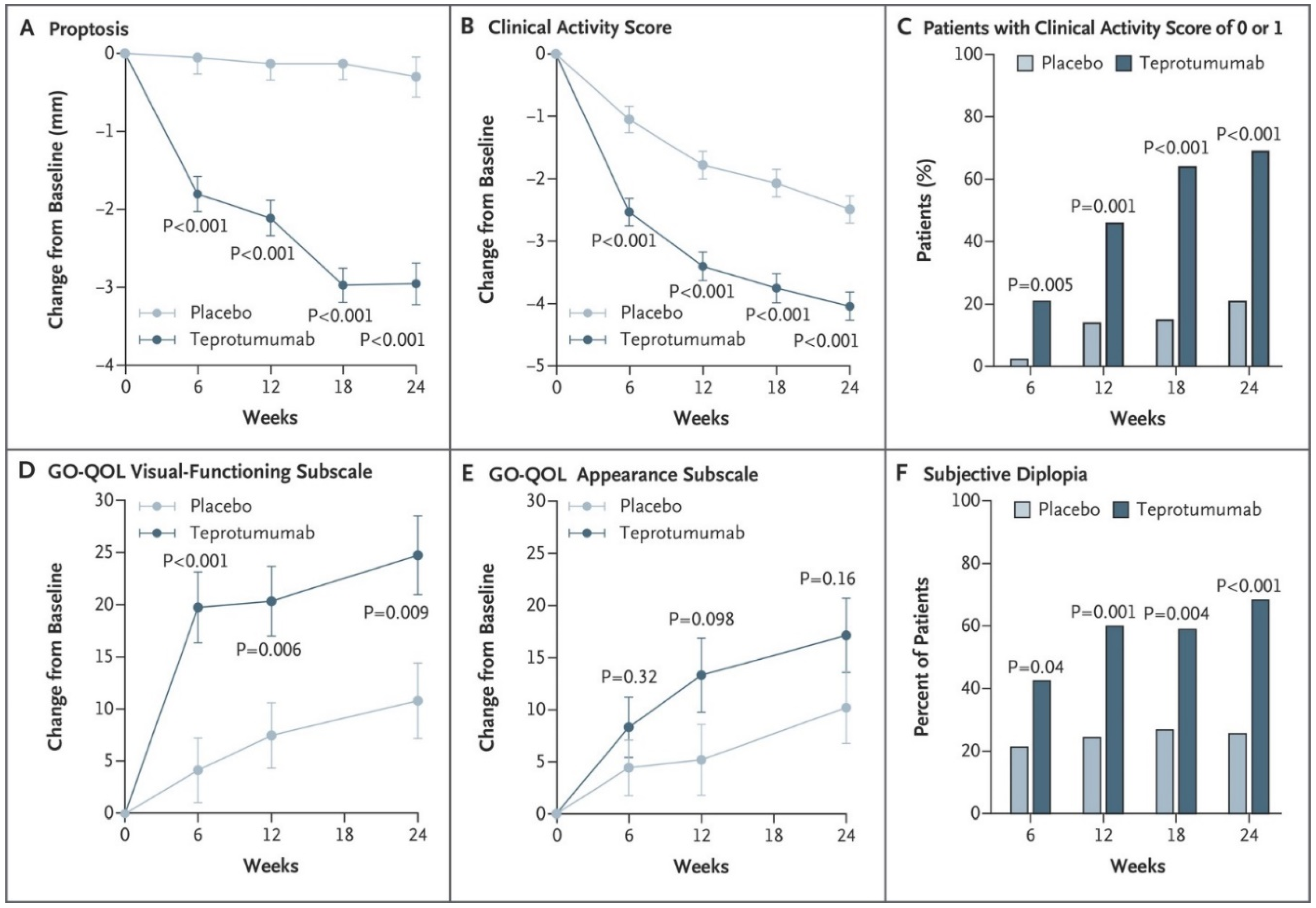
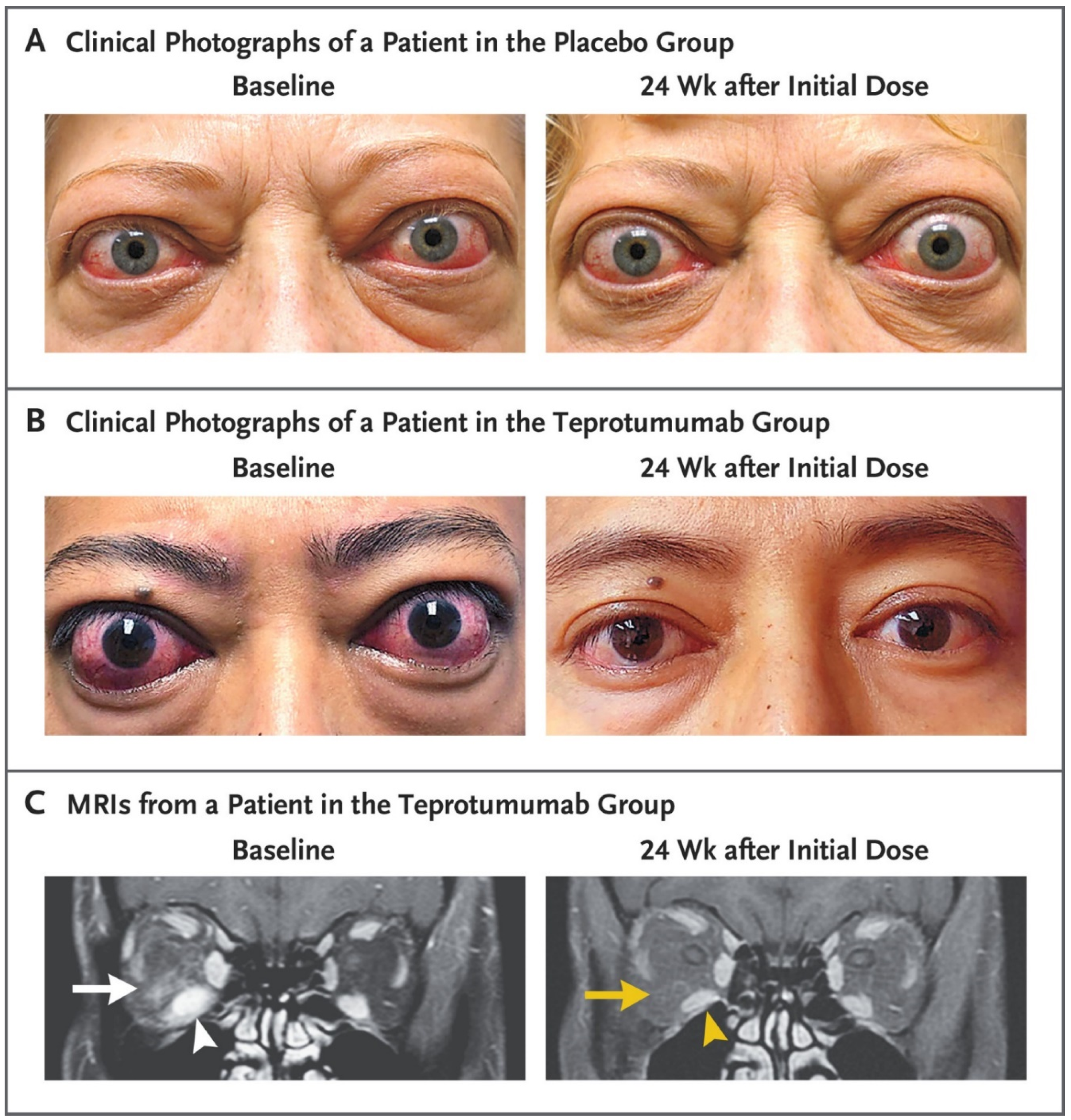
5. Teprotumumab Has Proven Effective and Safe in Moderate to Severe, Active TAO in Two Clinical Trials
5.1. Phase 2 Trial
5.2. Phase 3 Trial
6. Adverse Events
7. The Future
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EGF | Epidermal Growth Factor |
| EGFR | Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor |
| ERK | Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase |
| GH | Growth Hormone |
| GPCR | G-protein coupled receptor |
| IR | Insulin Receptor |
| IR-A | Insulin Receptor A |
| IR-B | Insulin Receptor B |
| IGF | Insulin-like Growth Factor |
| IGFBP | Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Proteins |
| IGFBP-rp | IGFBP-related proteins |
| IGF-IR | Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor |
| IGF-IRβ | Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor beta subunit |
| IGF-II | Insulin-like growth factor-II receptor |
| Kd | Equilibrium dissociation constant |
| MAPK/MEK | Mitogen-Activated Protein/Extracellular Kinase |
| MTor | Mammalian Target of rapamycin |
| PI3K | Phosphatidylnositol-3- Kinase |
| Raf | Rapidly Accelerated Fibrosarcoma |
| Ras | Rat Sarcoma |
| RTK | Receptor Tyrosine Kinase |
| TAO | Thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy |
| TCF | T-Cell Factor |
| TSH | Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone |
| TSHR | Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone Receptor |
References
- Collett-Solberg, P.F.; Cohen, P. Genetics, chemistry, and function of the IGF/IGFBP system. Endocrine 2000, 12, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinderknecht, E.; Humbel, R.E. The amino acid sequence of human insulin-like growth factor I and its structural homology with proinsulin. J. Biol. Chem. 1978, 253, 2769–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froesch, E.R.; Schmid, C.; Schwander, J.; Zapf, J. Actions of insulin-like growth factors. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1985, 47, 443–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O′Dell, S.D.; Day, I.N. Insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II). Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1998, 30, 767–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holly, J.M.P.; Biernacka, K.; Perks, C.M. The Neglected Insulin: IGF-II, a Metabolic Regulator with Implications for Diabetes, Obesity, and Cancer. Cells 2019, 8, 1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siddle, K. Molecular basis of signaling specificity of insulin and IGF receptors: Neglected corners and recent advances. Front. Endocrinol. 2012, 3, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ullrich, A.; Gray, A.; Tam, A.W.; Yang-Feng, T.; Tsubokawa, M.; Collins, C.; Henzel, W.; Le Bon, T.; Kathuria, S.; Chen, E. Insulin-like growth factor I receptor primary structure: Comparison with insulin receptor suggests structural determinants that define functional specificity. EMBO J. 1986, 5, 2503–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massague, J.; Czech, M.P. The subunit structures of two distinct receptors for insulin-like growth factors I and II and their relationship to the insulin receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1982, 257, 5038–5045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakesley, V.A.; Scrimgeour, A.; Esposito, D.; Le Roith, D. Signaling via the insulin-like growth factor-I receptor: Does it differ from insulin receptor signaling? Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 1996, 7, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belfiore, A.; Frasca, F.; Pandini, G.; Sciacca, L.; Vigneri, R. Insulin receptor isoforms and insulin receptor/insulin-like growth factor receptor hybrids in physiology and disease. Endocr. Rev. 2009, 30, 586–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frasca, F.; Pandini, G.; Scalia, P.; Sciacca, L.; Mineo, R.; Costantino, A.; Goldfine, I.D.; Belfiore, A.; Vigneri, R. Insulin receptor isoform A, a newly recognized, high-affinity insulin-like growth factor II receptor in fetal and cancer cells. Mol. Cell Biol. 1999, 19, 3278–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janssen, J.A.; Hofland, L.J.; Strasburger, C.J.; van den Dungen, E.S.; Thevis, M. Potency of Full-Length MGF to Induce Maximal Activation of the IGF-I R Is Similar to Recombinant Human IGF-I at High Equimolar Concentrations. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arnaldez, F.I.; Helman, L.J. Targeting the insulin growth factor receptor 1. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 26, 527–542, vii–viii. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Worrall, C.; Nedelcu, D.; Serly, J.; Suleymanova, N.; Oprea, I.; Girnita, A.; Girnita, L. Novel mechanisms of regulation of IGF-1R action: Functional and therapeutic implications. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Rev. 2013, 10, 473–484. [Google Scholar]
- Janssen, J.A.M.J.L. New Insights from IGF-IR Stimulating Activity Analyses: Pathological Considerations. Cells 2020, 9, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boucher, J.; Tseng, Y.H.; Kahn, C.R. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor-1 receptors act as ligand-specific amplitude modulators of a common pathway regulating gene transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 17235–17245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jamwal, G.; Singh, G.; Dar, M.S.; Singh, P.; Bano, N.; Syed, S.H.; Sandhu, P.; Akhter, Y.; Monga, S.P.; Dar, M.J. Identification of a unique loss-of-function mutation in IGF1R and a crosstalk between IGF1R and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathways. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2018, 1865, 920–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoa, N.; Tsui, S.; Afifiyan, N.F.; Hikim, A.S.; Li, B.; Douglas, R.S.; Smith, T.J. Nuclear targeting of IGF-1 receptor in orbital fibroblasts from Graves′ disease: Apparent role of ADAM17. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarfstein, R.; Pasmanik-Chor, M.; Yeheskel, A.; Edry, L.; Shomron, N.; Warman, N.; Wertheimer, E.; Maor, S.; Shochat, L.; Werner, H. Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor (IGF-IR) translocates to nucleus and autoregulates IGF-IR gene expression in breast cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 2766–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valenta, T.; Hausmann, G.; Basler, K. The many faces and functions of beta-catenin. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 2714–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aleksic, T.; Chitnis, M.M.; Perestenko, O.V.; Gao, S.; Thomas, P.H.; Turner, G.D.; Protheroe, A.S.; Howarth, M.; Macaulay, V.M. Type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor translocates to the nucleus of human tumor cells. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 6412–6419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sehat, B.; Tofigh, A.; Lin, Y.; Trocmé, E.; Liljedahl, U.; Lagergren, J.; Larsson, O. SUMOylation mediates the nuclear translocation and signaling of the IGF-1 receptor. Sci. Signal. 2010, 3, ra10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girnita, L.; Worrall, C.; Takahashi, S.; Seregard, S.; Girnita, A. Something old, something new and something borrowed: Emerging paradigm of insulin-like growth factor type 1 receptor (IGF-1R) signaling regulation. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 71, 2403–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crudden, C.; Ilic, M.; Suleymanova, N.; Worrall, C.; Girnita, A.; Girnita, L. The dichotomy of the Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor: RTK and GPCR: Friend or foe for cancer treatment? Growth Horm. IGF Res. 2015, 25, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Shen, H.; Oprea, I.; Worrall, C.; Stefanescu, R.; Girnita, A.; Girnita, L. beta-Arrestin-biased agonism as the central mechanism of action for insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor-targeting antibodies in Ewing′s sarcoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 20620–20625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salisbury, T.B.; Tomblin, J.K. Insulin/Insulin-like growth factors in cancer: New roles for the aryl hydrocarbon receptor, tumor resistance mechanisms, and new blocking strategies. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2015, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Slaaby, R. Specific insulin/IGF1 hybrid receptor activation assay reveals IGF1 as a more potent ligand than insulin. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 7911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Nagle, A.M.; Wang, Y.F.; Boone, D.N.; Lee, A.V. Controlled dimerization of insulin-like growth factor-1 and insulin receptors reveals shared and distinct activities of holo and hybrid receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 3700–3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soos, M.A.; Field, C.E.; Siddle, K. Purified hybrid insulin/insulin-like growth factor-I receptors bind insulin-like growth factor-I, but not insulin, with high affinity. Biochem. J. 1993, 290, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morgillo, F.; Woo, J.K.; Kim, E.S.; Hong, W.K.; Lee, H.Y. Heterodimerization of insulin-like growth factor receptor/epidermal growth factor receptor and induction of survivin expression counteract the antitumor action of erlotinib. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 10100–10111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- King, E.R.; Wong, K.K. Insulin-like growth factor: Current concepts and new developments in cancer therapy. Recent Pat. Anti-Cancer Drug Discov. 2012, 7, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van der Veeken, J.; Oliveira, S.; Schiffelers, R.M.; Storm, G.; van Bergen En Henegouwen, P.M.; Roovers, R.C. Crosstalk between epidermal growth factor receptor- and insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor signaling: Implications for cancer therapy. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2009, 9, 748–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.J.; Janssen, J.A. Building the Case for Insulin-Like Growth Factor Receptor-I Involvement in Thyroid-Associated Ophthalmopathy. Front. Endocrinol. 2016, 7, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsui, S.; Naik, V.; Hoa, N.; Hwang, C.J.; Afifiyan, N.F.; Sinha Hikim, A.; Gianoukakis, A.G.; Douglas, R.S.; Smith, T.J. Evidence for an association between thyroid-stimulating hormone and insulin-like growth factor 1 receptors: A tale of two antigens implicated in Graves′ disease. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 4397–4405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ock, S.; Ahn, J.; Lee, S.H.; Kang, H.; Offermanns, S.; Ahn, H.Y.; Jo, Y.S.; Shong, M.; Cho, B.Y.; Jo, D.; et al. IGF-1 receptor deficiency in thyrocytes impairs thyroid hormone secretion and completely inhibits TSH-stimulated goiter. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 4899–4908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krieger, C.C.; Perry, J.D.; Morgan, S.J.; Kahaly, G.J.; Gershengorn, M.C. TSH/IGF-1 Receptor Cross-Talk Rapidly Activates Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinases in Multiple Cell Types. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 3676–3783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, J.I.; Clemmons, D.R. Insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins: Biological actions. Endocr. Rev. 1995, 16, 3–34. [Google Scholar]
- Firth, S.M.; Baxter, R.C. Cellular actions of the insulin-like growth factor binding proteins. Endocr. Rev. 2002, 23, 824–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, C.; Xu, Q. Roles of insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding proteins in regulating IGF actions. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2005, 142, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, J.A.; van der Lely, A.J.; Lamberts, S.W. Circulating free insulin-like growth-factor-I (IGF-I) levels should also be measured to estimate the IGF-I bioactivity. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2003, 26, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holly, J.; Perks, C. The role of insulin-like growth factor binding proteins. Neuroendocrinology 2006, 83, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bach, L.A. IGF-binding proteins. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2018, 61, T11–T28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clemmons, D.R. Role of IGF-binding proteins in regulating IGF responses to changes in metabolism. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2018, 61, T139–T69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maile, L.A.; Xu, S.; Cwyfan-Hughes, S.C.; Fernihough, J.K.; Pell, J.M.; Holly, J.M. Active and inhibitory components of the insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 protease system in adult serum, interstitial, and synovial fluid. Endocrinology 1998, 139, 4772–4781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, J.; Varewijck, A.J.; Brugts, M.P. The insulin-like growth factor-I receptor stimulating activity (IRSA) in health and disease. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 2019, 48–49, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clemmons, D.R. Modifying IGF1 activity: An approach to treat endocrine disorders, atherosclerosis and cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007, 6, 821–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, W. Insulin-like growth factors and igf-binding proteins: Their use for diagnosis of growth hormone deficiency. In Growth Hormone Adults; Juul, A., Jorgensen, J., Eds.; Press Syndicate of the University of Cambridge: Cambridge, UK, 1996; pp. 48–74. [Google Scholar]
- Thissen, J.P.; Ketelslegers, J.M.; Underwood, L.E. Nutritional regulation of the insulin-like growth factors. Endocr. Rev. 1994, 15, 80–101. [Google Scholar]
- Yakar, S.; Liu, J.-L.; Stannard, B.; Butler, A.; Accili, D.; Sauer, B.; Leroith, D. Normal growth and development in the absence of hepatic insulin-like growth factor I. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 7324–7329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Roith, D.; Bondy, C.; Yakar, S.; Liu, J.L.; Butler, A. The somatomedin hypothesis: 2001. Endocr. Rev. 2001, 22, 53–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjogren, K.; Jansson, J.O.; Isaksson, O.G.; Ohlsson, C. A model for tissue-specific inducible insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) inactivation to determine the physiological role of liver-derived IGF-I. Endocrine 2002, 19, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, V.K.; D′Ercole, A.J.; Lund, P.K. Cellular localization of somatomedin (insulin-like growth factor) messenger RNA in the human fetus. Science 1987, 236, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, J.A. Advantages and disadvantages of GH/IGF-I combination treatment. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2009, 10, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Schulz, T.C.; Sherrer, E.S.; Dauphin, D.S.; Shin, S.; Nelson, A.M.; Ware, C.B.; Zhan, M.; Song, C.-Z.; Chen, X.; et al. Self-renewal of human embryonic stem cells requires insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor and ERBB2 receptor signaling. Blood 2007, 110, 4111–4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Sheppard, A.M.; Kaye, P.L.; Noakes, P.G. IGF-I and insulin activate mitogen-activated protein kinase via the type 1 IGF receptor in mouse embryonic stem cells. Reproduction 2007, 134, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brooker, G.J.; Kalloniatis, M.; Russo, V.C.; Murphy, M.; Werther, G.A.; Bartlett, P.F. Endogenous IGF-1 regulates the neuronal differentiation of adult stem cells. J. Neurosci. Res. 2000, 59, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourkioti, F.; Rosenthal, N. IGF-1, inflammation and stem cells: Interactions during muscle regeneration. Trends Immunol. 2005, 26, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakuno, F.; Takahashi, S.I. IGF1 receptor signaling pathways. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2018, 61, T69–T86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conover, C.A. The IGF-p53 connection in cancer. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 2018, 39, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, J.A. IGF-I and the endocrinology of aging. Curr. Opin. Endocr. Metab. Res. 2019, 5, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornreich, L.; Konen, O.; Lilos, P.; Laron, Z. The globe and orbit in Laron syndrome. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2011, 32, 1560–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bourla, D.H.; Laron, Z.; Snir, M.; Lilos, P.; Weinberger, D.; Axer-Siegel, R. Insulinlike growth factor I affects ocular development: A study of untreated and treated patients with Laron syndrome. Ophthalmology 2006, 113, 1197-e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, K.; Lust, K.; Wittbrodt, J. Igf Signalling Uncouples Retina Growth from Body Size by Modulating Progenitor Cell Division. bioRxiv 2020. Available online: https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.06.10.144360v1 (accessed on 10 June 2020). [CrossRef]
- Abboud, S.L.; Bethel, C.R.; Aron, D.C. Secretion of insulinlike growth factor I and insulinlike growth factor-binding proteins by murine bone marrow stromal cells. J. Clin. Investig. 1991, 88, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigent, D.A. Lymphocyte GH-axis hormones in immunity. Cell Immunol. 2013, 285, 118–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heemskerk, V.H.; Daemen, M.A.; Buurman, W.A. Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) and growth hormone (GH) in immunity and inflammation. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 1999, 10, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardieu, P.; Clark, R.; Mortensen, D.; Dorshkind, K. In vivo administration of insulin-like growth factor-I stimulates primary B lymphopoiesis and enhances lymphocyte recovery after bone marrow transplantation. J. Immunol. 1994, 152, 4320–4327. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Clark, R.; Strasser, J.; McCabe, S.; Robbins, K.; Jardieu, P. Insulin-like growth factor-1 stimulation of lymphopoiesis. J. Clin. Investig. 1993, 92, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimata, H.; Yoshida, A. Effect of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor-I on immunoglobulin production by and growth of human B cells. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1994, 78, 635–641. [Google Scholar]
- Kooijman, R.; Willems, M.; De Haas, C.J.; Rijkers, G.T.; Schuurmans, A.L.; Van Buul-Offers, S.C.; Heijnen, C.J.; Zegers, B.J. Expression of type I insulin-like growth factor receptors on human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Endocrinology 1992, 131, 2244–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X.; McBride, B.W.; Trouten-Radford, L.M.; Burton, J.H. Specific insulin-like growth factor-I receptors on circulating bovine mononuclear cells. J. Recept. Res. 1992, 12, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, J.A.; Hoogerbrugge, N.; van Neck, J.W.; Uitterlinden, P.; Lamberts, S.W. The IGF-I/IGFBP system in congenital partial lipodystrophy. Clin. Endocrinol. 1998, 49, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verland, S.; Gammeltoft, S. Functional receptors for insulin-like growth factors I and II in rat thymocytes and mouse thymoma cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1989, 67, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, C.A.; Meehan, R.T.; Neale, L.S.; Cintron, N.M.; Furlanetto, R.W. Insulin-like growth factor-I binds selectively to human peripheral blood monocytes and B-lymphocytes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1991, 72, 1117–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooijman, R.; Scholtens, L.E.; Rijkers, G.T.; Zegers, B.J. Type I insulin-like growth factor receptor expression in different developmental stages of human thymocytes. J. Endocrinol. 1995, 147, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kooijman, R.; van Buul-Offers, S.C.; Scholtens, L.E.; Schuurman, H.J.; Van den Brande, L.J.; Zegers, B.J. T cell development in insulin-like growth factor-II transgenic mice. J. Immunol. 1995, 154, 5736–5745. [Google Scholar]
- Kooijman, R.; Scholtens, L.E.; Rijkers, G.T.; Zegers, B.J. Differential expression of type I insulin-like growth factor receptors in different stages of human T cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 1995, 25, 931–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schillaci, R.; Brocardo, M.G.; Galeano, A.; Roldán, A. Downregulation of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R) expression in human T lymphocyte activation. Cell. Immunol. 1998, 183, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapson, V.F.; Boni-Schnetzler, M.; Pilch, P.F.; Center, D.M.; Berman, J.S. Structural and functional characterization of the human T lymphocyte receptor for insulin-like growth factor I in vitro. J. Clin. Investig. 1988, 82, 950–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Mardell, C.; Xian, C.J.; Zola, H.; Read, L.C. Expression of functional insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor on lymphoid cell subsets of rats. Immunology 1995, 85, 394–399. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, E.W.; Jones, L.A.; Kozak, R.W. Expression and function of insulin-like growth factor receptors on anti-CD3-activated human T lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 1992, 148, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gjerset, R.A.; Yeargin, J.; Volkman, S.K.; Vila, V.; Arya, J.; Haas, M. Insulin-like growth factor-I supports proliferation of autocrine thymic lymphoma cells with a pre-T cell phenotype. J. Immunol. 1990, 145, 3497–3501. [Google Scholar]
- Kooijman, R.; Coppens, A.; Hooghe-Peters, E. Igf-I inhibits spontaneous apoptosis in human granulocytes. Endocrinology 2002, 143, 1206–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rom, W.N.; Pääkkö, P. Activated alveolar macrophages express the insulin-like growth factor-I receptor. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1991, 4, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kooijman, R.; Coppens, A.; Hooghe-Peters, E. IGF-I stimulates IL-8 production in the promyelocytic cell line HL-60 through activation of extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase. Cell Signal. 2003, 15, 1091–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooijman, R.; Rijkers, G.T.; Zegers, B.J. IGF-I potentiates interleukin-2 production in human peripheral T cells. J. Endocrinol. 1996, 149, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooijman, R.; Coppens, A. Insulin-like growth factor-I stimulates IL-10 production in human T cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2004, 76, 862–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohyi, M.; Smith, T.J. IGF1 receptor and thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2018, 61, T29–T43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, T.J.; Hegedus, L. Graves′ Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1552–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weightman, D.R.; Perros, P.; Sherif, I.H.; Kendall-Taylor, P. Autoantibodies to IGF-1 binding sites in thyroid associated ophthalmopathy. Autoimmunity 1993, 16, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, R.S.; Gianoukakis, A.G.; Kamat, S.; Smith, T.J. Aberrant expression of the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor by T cells from patients with Graves′ disease may carry functional consequences for disease pathogenesis. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 3281–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, R.S.; Naik, V.; Hwang, C.J.; Afifiyan, N.F.; Gianoukakis, A.G.; Sand, D.; Kamat, S.; Smith, T.J. B cells from patients with Graves′ disease aberrantly express the IGF-1 receptor: Implications for disease pathogenesis. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 5768–5774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strianese, D.; Rossi, F. Interruption of autoimmunity for thyroid eye disease: B-cell and T-cell strategy. Eye 2019, 33, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pritchard, J.; Han, R.; Horst, N.; Cruikshank, W.W.; Smith, T.J. Immunoglobulin activation of T cell chemoattractant expression in fibroblasts from patients with Graves′ disease is mediated through the insulin-like growth factor I receptor pathway. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 6348–6354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pritchard, J.; Horst, N.; Cruikshank, W.; Smith, T.J. Igs from patients with Graves′ disease induce the expression of T cell chemoattractants in their fibroblasts. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 942–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.J.; Hoa, N. Immunoglobulins from patients with Graves′ disease induce hyaluronan synthesis in their orbital fibroblasts through the self-antigen, insulin-like growth factor-I receptor. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 5076–5080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hansson, H.A.; Petruson, B.; Skottner, A. Somatomedin C in pathogenesis of malignant exophthalmos of endocrine origin. Lancet 1986, 1, 218–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, K.; Manso, P.G.; Marback, E.; Furlanetto, R.; Alberti, G.N.; Nosé, V. Protein expression of VEGF, IGF-1 and FGF in retroocular connective tissues and clinical correlation in Graves′ ophthalmopathy. Arq. Bras. Oftalmol. 2008, 71, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, T.J.; Kahaly, G.J.; Ezra, D.G.; Fleming, J.C.; Dailey, R.A.; Tang, R.A.; Harris, G.J.; Antonelli, A.; Salvi, M.; Goldberg, R.A.; et al. Teprotumumab for Thyroid-Associated Ophthalmopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1748–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terwee, C.B.; Gerding, M.N.; Dekker, F.W.; Prummel, M.F.; Wiersinga, W.M. Development of a disease specific quality of life questionnaire for patients with Graves′ ophthalmopathy: The GO-QOL. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1998, 82, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Douglas, R.S.; Kahaly, G.J.; Patel, A.; Sile, S.; Thompson, E.H.; Perdok, R.; Fleming, J.C.; Fowler, B.T.; Marcocci, C.; Marinò, M.; et al. Teprotumumab for the Treatment of Active Thyroid Eye Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sears, C.M.; Azad, A.D.; Dosiou, C.; Kossler, A.L. Teprotumumab for Dysthyroid Optic Neuropathy: Early Response to Therapy. Ophthalmic Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slentz, D.H.; Smith, T.J.; Kim, D.S.; Joseph, S.S. Teprotumumab for Optic Neuropathy in Thyroid Eye Disease. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozzello, D.J.; Kikkawa, D.O.; Korn, B.S. Early experience with teprotumumab for chronic thyroid eye disease. Am. J. Ophthalmol. Case Rep. 2020, 19, 100744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, A.; Rheeman, C.; Levitt, J. Resolution of pretibial myxedema with teprotumumab in a patient with Graves disease. JAAD Case Rep. 2020, 6, 1281–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, J.; Tsui, S.; Horst, N.; Cruikshank, W.W.; Smith, T.J. Synovial fibroblasts from patients with rheumatoid arthritis, like fibroblasts from Graves′ disease, express high levels of IL-16 when treated with Igs against insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 3564–3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.; Kim, S.R.; Oh, Y.; Cho, S.H.; Schleimer, R.P.; Lee, Y.C. Targeting insulin-like growth factor-I and insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 signaling pathways. A novel therapeutic approach for asthma. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2014, 50, 667–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Janssen, J.A.M.J.L.; Smith, T.J. Lessons Learned from Targeting IGF-I Receptor in Thyroid-Associated Ophthalmopathy. Cells 2021, 10, 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10020383
Janssen JAMJL, Smith TJ. Lessons Learned from Targeting IGF-I Receptor in Thyroid-Associated Ophthalmopathy. Cells. 2021; 10(2):383. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10020383
Chicago/Turabian StyleJanssen, Joseph A.M.J.L., and Terry J. Smith. 2021. "Lessons Learned from Targeting IGF-I Receptor in Thyroid-Associated Ophthalmopathy" Cells 10, no. 2: 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10020383
APA StyleJanssen, J. A. M. J. L., & Smith, T. J. (2021). Lessons Learned from Targeting IGF-I Receptor in Thyroid-Associated Ophthalmopathy. Cells, 10(2), 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10020383





