The Role of Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 (IGF-1) in the Control of Neuroendocrine Regulation of Growth
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland Axis
2.1. The Anterior Pituitary
2.2. The Posterior Pituitary
3. IGF-1 and the IGF-1 Receptor
4. IGF-1 and IGF-1R Expression in Neuroendocrine Tissues
5. The Role of IGF-1 in the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Somatotroph Axis (HPS Axis)
6. Transgenic Mouse Models with Alterations in the IGF-1 Signaling System
6.1. Somatotroph IGF-1 Receptor Knockout Mouse Model (SIGFRKO)
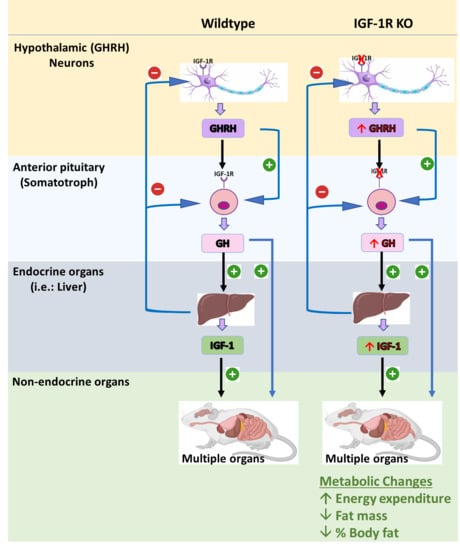
6.2. Mouse Models Deleting the IGF-1R from GHRH Neurons (GIGFRKO) and the Pituitary Somatotrophs and GHRH Neurons (S-GIGFRKO)
7. Transgenic Mouse Models with Altered GH Expression
7.1. GH −/− Mouse Model
7.2. GHR−/− Mouse Model
7.3. Mouse Model Overexpressing GH
7.4. Mouse Models of Altered IGF-1 Signaling
7.5. Mouse Model with a Whole-Body Deletion of IGF-1 and the IGF-1R
7.6. Brain-Specific IGF-1 R−/+ Knockout Mouse Model
8. The Role of the IGF-1 Signaling System in Glucose Metabolism
9. The Role of the IGF-1 Signaling System in Obesity
10. The Role of the IGF-1 Signaling System in Modulating Aging and Longevity
11. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alvarez-Bolado, G. Development of neuroendocrine neurons in the mammalian hypothalamus. Cell Tissue Res. 2019, 375, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, J.E. Chapter 1-An Introduction to Neuroendocrine Systems. In Handbook of Neuroendocrinology; Fink, G., Pfaff, D.W., Levine, J.E., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, C.J.; Ng, Y.; Luque, R.M.; Kineman, R.D.; Koch, L.; Bruning, J.C.; Radovick, S. Targeted Deletion of Somatotroph Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I Signaling in a Cell-Specific Knockout Mouse Model. Mol. Endocrinol. 2010, 24, 1077–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Domené, S.; Domené, H.M. Genetic Mutations in the GH/IGF Axis. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2018, 16, 39–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakuno, F.; Takahashi, S.I. IGF1 receptor signaling pathways. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2018, 61, T69–t86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vitale, G.; Pellegrino, G.; Vollery, M.; Hofland, L.J. ROLE of IGF-1 System in the Modulation of Longevity: Controversies and New Insights From a Centenarians’ Perspective. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Junnila, R.K.; List, E.O.; Berryman, D.E.; Murrey, J.W.; Kopchick, J.J. The GH/IGF-1 axis in ageing and longevity. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2013, 9, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, Y. The Role of Growth Hormone and Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I in the Liver. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Dong, L.; Zhang, H.; Teng, Z.; Wang, X.; Yan, Z.; She, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. Review of Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 Signaling Pathway and Its Role in Protection against Brain Diseases. Transl. Neurosci. Clin. 2017, 3, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wrigley, S.; Arafa, D.; Tropea, D. Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1: At the Crossroads of Brain Development and Aging. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maglio, L.E.; Noriega-Prieto, J.A.; Maroto, I.B.; Martin-Cortecero, J.; Muñoz-Callejas, A.; Callejo-Móstoles, M.; Fernández de Sevilla, D. IGF-1 facilitates extinction of conditioned fear. Elife 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gahete, M.D.; Córdoba-Chacón, J.; Lin, Q.; Brüning, J.C.; Kahn, C.R.; Castaño, J.P.; Christian, H.; Luque, R.M.; Kineman, R.D. Insulin and IGF-I inhibit GH synthesis and release in vitro and in vivo by separate mechanisms. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 2410–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fink, G.; Pfaff, D.W.; Levine, J. Handbook of Neuroendocrinology; Elsevier Science & Technology: San Diego, CA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lechan, R.M.; Toni, R. Functional Anatomy of the Hypothalamus and Pituitary. In Endotext; Feingold, K.R., Anawalt, B., Boyce, A., Chrousos, G., de Herder, W.W., Dungan, K., Grossman, A., Hershman, J.M., Hofland, J., Kaltsas, G., et al., Eds.; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Lechan RM, T.R. Functional Anatomy of the Hypothalamus and Pituitary. 2016. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279126/ (accessed on 12 June 2021).
- Pituitary Gland Physiology. In StatPearls, StatPearls Publishing; El Sayed, S.A.; Fahmy, M.W.; Schwartz, J. (Eds.) StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gjerstad, J.K.; Lightman, S.L.; Spiga, F. Role of glucocorticoid negative feedback in the regulation of HPA axis pulsatility. Stress 2018, 21, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hiller-Sturmhöfel, S.; Bartke, A. The endocrine system: An overview. Alcohol Health Res. World 1998, 22, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Physiology, Pituitary Hormones. In StatPearls; Sadiq, N.M.; Tadi, P. (Eds.) StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht, E.; Humbel, R.E. Primary structure of human insulin-like growth factor II. Febs Lett. 1978, 89, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- AsghariHanjani, N.; Vafa, M. The role of IGF-1 in obesity, cardiovascular disease, and cancer. Med. J. Islam Repub Iran. 2019, 33, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annunziata, M.; Granata, R.; Ghigo, E. The IGF system. Acta Diabetol. 2011, 48, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.P.; Baker, J.; Perkins, A.S.; Robertson, E.J.; Efstratiadis, A. Mice carrying null mutations of the genes encoding insulin-like growth factor I (Igf-1) and type 1 IGF receptor (Igf1r). Cell 1993, 75, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulik, G.; Klippel, A.; Weber, M.J. Antiapoptotic signalling by the insulin-like growth factor I receptor, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, and Akt. Mol. Cell Biol. 1997, 17, 1595–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- LeRoith, D. Insulin-like growth factor I receptor signaling--overlapping or redundant pathways? Endocrinology 2000, 141, 1287–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baxter, R.C.; Martin, J.L.; Beniac, V.A. High molecular weight insulin-like growth factor binding protein complex. Purification and properties of the acid-labile subunit from human serum. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 11843–11848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, L.A. IGF-binding proteins. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2018, 61, T11–t28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clemmons, D.R. Modifying IGF1 activity: An approach to treat endocrine disorders, atherosclerosis and cancer. Nat. Reviews. Drug Discov. 2007, 6, 821–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guler, H.P.; Zapf, J.; Schmid, C.; Froesch, E.R. Insulin-like growth factors I and II in healthy man. Estimations of half-lives and production rates. Acta Endocrinol. 1989, 121, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaram, S.; Baylink, D.J.; Mohan, S. Insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins in serum and other biological fluids: Regulation and functions. Endocr. Rev. 1997, 18, 801–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Firth, S.M.; Baxter, R.C. Cellular Actions of the Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Proteins. Endocr. Rev. 2002, 23, 824–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kappeler, L.; De Magalhaes Filho, C.; Leneuve, P.; Xu, J.; Brunel, N.; Chatziantoniou, C.; Le Bouc, Y.; Holzenberger, M. Early postnatal nutrition determines somatotropic function in mice. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Decourtye, L.; Mire, E.; Clemessy, M.; Heurtier, V.; Ledent, T.; Robinson, I.C.; Mollard, P.; Epelbaum, J.; Meaney, M.J.; Garel, S.; et al. IGF-1 Induces GHRH Neuronal Axon Elongation during Early Postnatal Life in Mice. Plos One 2017, 12, e0170083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Roith, D. Seminars in medicine of the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center. Insulin-like growth factors. New Engl. J. Med. 1997, 336, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delafontaine, P.; Song, Y.-H.; Li, Y. Expression, Regulation, and Function of IGF-1, IGF-1R, and IGF-1 Binding Proteins in Blood Vessels. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2004, 24, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewitt, M.S.; Boyd, G.W. The Role of Insulin-Like Growth Factors and Insulin-Like Growth Factor-Binding Proteins in the Nervous System. Biochem. Insights 2019, 12, 1178626419842176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kineman, R.D.; Rio-Moreno, M.d.; Sarmento-Cabral, A. 40 YEARS of IGF1: Understanding the tissue-specific roles of IGF1/IGF1R in regulating metabolism using the Cre/loxP system. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2018, 61, T187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, J.I.; Clemmons, D.R. Insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins: Biological actions. Endocr. Rev. 1995, 16, 3–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Wu, T. Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Proteins in Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamo, M.L.; Neuenschwander, S.; LeRoith, D.; Roberts, C.T., Jr. Structure, expression, and regulation of the IGF-I gene. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1993, 343, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Bikle, D.D.; Chang, W. Autocrine and Paracrine Actions of IGF-I Signaling in Skeletal Development. Bone Res. 2013, 1, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bondy, C.; Werner, H.; Roberts, C.T.; LeRoith, D. Cellular pattern of type-I insulin-like growth factor receptor gene expression during maturation of the rat brain: Comparison with insulin-like growth factors I and II. Neuroscience 1992, 46, 909–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eppler, E.; Jevdjovic, T.; Maake, C.; Reinecke, M. Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) and its receptor (IGF-1R) in the rat anterior pituitary. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2007, 25, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-H.; Park, M.-J. Effects of growth hormone on glucose metabolism and insulin resistance in human. Ann. Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 2017, 22, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, Z.; Huang, L.; Waters, M.J.; Chen, C. Insulin and Growth Hormone Balance: Implications for Obesity. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 31, 642–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y.; Murakami, Y.; Sohmiya, M.; Nishiki, M. Regulation of human growth hormone secretion and its disorders. Intern. Med. 2002, 41, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, M.; Flanagan, J.U.; Langley, R.J.; Hay, M.P.; Perry, J.K. Targeting growth hormone function: Strategies and therapeutic applications. Signal. Transduct Target. 2019, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poudel, S.B.; Dixit, M.; Neginskaya, M.; Nagaraj, K.; Pavlov, E.; Werner, H.; Yakar, S. Effects of GH/IGF on the Aging Mitochondria. Cells 2020, 9, 1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domené, H.M.; Hwa, V.; Jasper, H.G.; Rosenfeld, R.G. Acid-labile subunit (ALS) deficiency. Best Pr. Res. Clin. Endocrinol Metab 2011, 25, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haywood, N.J.; Slater, T.A.; Matthews, C.J.; Wheatcroft, S.B. The insulin like growth factor and binding protein family: Novel therapeutic targets in obesity & diabetes. Mol. Metab. 2019, 19, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, C.J.; Wolfe, A.; Law, Y.Y.; Costelloe, C.Z.; Miller, R.; Wondisford, F.; Radovick, S. Altered somatotroph feedback regulation improves metabolic efficiency and limits adipose deposition in male mice. Metabolism 2016, 65, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Samerria, S.; Aloqaily, B.; Negron, A.; Wondisford, F.E.; Radovick, S. Interrupted IGF-1 Feedback in GHRH Neurons and Somatotrophs Results in Impaired Weight Gain and Increased Energy Expenditure. J. Endocr. Soc. 2021, 5, A52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- List, E.O.; Berryman, D.E.; Buchman, M.; Jensen, E.A.; Funk, K.; Duran-Ortiz, S.; Qian, Y.; Young, J.A.; Slyby, J.; McKenna, S.; et al. GH Knockout Mice Have Increased Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue With Decreased Fibrosis and Enhanced Insulin Sensitivity. Endocrinology 2019, 160, 1743–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xu, B.C.; Maheshwari, H.G.; He, L.; Reed, M.; Lozykowski, M.; Okada, S.; Cataldo, L.; Coschigamo, K.; Wagner, T.E.; et al. A mammalian model for Laron syndrome produced by targeted disruption of the mouse growth hormone receptor/binding protein gene (the Laron mouse). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. United States Am. 1997, 94, 13215–13220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Slonim, A.E.; Bulone, L.; Damore, M.B.; Goldberg, T.; Wingertzahn, M.A.; McKinley, M.J. A preliminary study of growth hormone therapy for Crohn’s disease. New Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 1633–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- List, E.O.; Coschigano, K.T.; Kopchick, J.J. Growth hormone receptor/binding protein (GHR/BP) knockout mice: A 3-year update. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2001, 73, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- List, E.O.; Sackmann-Sala, L.; Berryman, D.E.; Funk, K.; Kelder, B.; Gosney, E.S.; Okada, S.; Ding, J.; Cruz-Topete, D.; Kopchick, J.J. Endocrine parameters and phenotypes of the growth hormone receptor gene disrupted (GHR-/-) mouse. Endocr. Rev. 2011, 32, 356–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.L.; Coschigano, K.T.; Robertson, K.; Lipsett, M.; Guo, Y.; Kopchick, J.J.; Kumar, U.; Liu, Y.L. Disruption of growth hormone receptor gene causes diminished pancreatic islet size and increased insulin sensitivity in mice. Am. J. Physiology. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 287, E405–E413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pilcher; Hreinsson, J.G. Money for old mice. Competition seeks world’s longest-lasting mouse. Nat. News 2003, 22, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday, W.H.; Hall, K.; Raben, M.S.; Salmon, W.D., Jr.; van den Brande, J.L.; van Wyk, J.J. Somatomedin: Proposed designation for sulphation factor. Nature 1972, 235, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakar, S.; Liu, J.L.; Stannard, B.; Butler, A.; Accili, D.; Sauer, B.; LeRoith, D. Normal growth and development in the absence of hepatic insulin-like growth factor I. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. United States Am. 1999, 96, 7324–7329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yakar, S.; Adamo, M.L. Insulin-like growth factor 1 physiology: Lessons from mouse models. Endocrinol Metab Clin. North. Am. 2012, 41, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yakar, S.; Liu, J.-L.; Fernandez, A.M.; Wu, Y.; Schally, A.V.; Frystyk, J.; Chernausek, S.D.; Mejia, W.; Le Roith, D. Liver-Specific igf-1 Gene Deletion Leads to Muscle Insulin Insensitivity. Diabetes 2001, 50, 1110–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Franceschi, C.; Valensin, S.; Bonafè, M.; Paolisso, G.; Yashin, A.I.; Monti, D.; De Benedictis, G. The network and the remodeling theories of aging: Historical background and new perspectives. Exp. Gerontol. 2000, 35, 879–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenyon, C.; Chang, J.; Gensch, E.; Rudner, A.; Tabtiang, R. A C. elegans mutant that lives twice as long as wild type. Nature 1993, 366, 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, K.D.; Tissenbaum, H.A.; Liu, Y.; Ruvkun, G. daf-2, an insulin receptor-like gene that regulates longevity and diapause in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science 1997, 277, 942–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappeler, L.; De Magalhaes Filho, C.; Dupont, J.; Leneuve, P.; Cervera, P.; Périn, L.; Loudes, C.; Blaise, A.; Klein, R.; Epelbaum, J.; et al. Brain IGF-1 receptors control mammalian growth and lifespan through a neuroendocrine mechanism. Plos Biol 2008, 6, e254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemmons, D.R. Metabolic actions of insulin-like growth factor-I in normal physiology and diabetes. Endocrinol Metab Clin. North. Am. 2012, 41, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clemmons, D.R. Role of insulin-like growth factor iin maintaining normal glucose homeostasis. Horm Res. 2004, 62 Suppl 1, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quipildor, G.F.; Mao, K.; Beltran, P.J.; Barzilai, N.; Huffman, D.M. Modulation of Glucose Production by Central Insulin Requires IGF-1 Receptors in AgRP Neurons. Diabetes 2021, 70, 2237–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seely, B.L.; Reichart, D.R.; Takata, Y.; Yip, C.; Olefsky, J.M. A functional assessment of insulin/insulin-like growth factor-I hybrid receptors. Endocrinology 1995, 136, 1635–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, K.; Lowman, H.B.; Clemmons, D.R. Increases in free, unbound insulin-like growth factor I enhance insulin responsiveness in human hepatoma G2 cells in culture. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 13620–13627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dimitriadis, G.; Parry-Billings, M.; Bevan, S.; Dunger, D.; Piva, T.; Krause, U.; Wegener, G.; Newsholme, E.A. Effects of insulin-like growth factor I on the rates of glucose transport and utilization in rat skeletal muscle in vitro. Biochem. J. 1992, 285 Pt 1, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernández, A.M.; Kim, J.K.; Yakar, S.; Dupont, J.; Hernandez-Sanchez, C.; Castle, A.L.; Filmore, J.; Shulman, G.I.; Le Roith, D. Functional inactivation of the IGF-I and insulin receptors in skeletal muscle causes type 2 diabetes. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 1926–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, H.; Cui, Z.-Z.; Zhu, L.; Fu, S.-P.; Rossi, M.; Cui, Y.-H.; Zhu, B.-M. Central IGF1 improves glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity in mice. Nutr. Diabetes 2017, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haththotuwa, R.N.; Wijeyaratne, C.N.; Senarath, U. Chapter 1—Worldwide epidemic of obesity. In Obesity and Obstetrics, 2nd ed.; Mahmood, T.A., Arulkumaran, S., Chervenak, F.A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2020; pp. 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, U.J.; Choi, M.S. Obesity and its metabolic complications: The role of adipokines and the relationship between obesity, inflammation, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 6184–6223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, P.; Spiegelman, B.M. Cell biology of fat storage. Mol. Biol. Cell 2016, 27, 2523–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, R.F.; Farmer, S.R. Insights into the transcriptional control of adipocyte differentiation. J. Cell. Biochem. 1999, 75 (Suppl. 32–33), 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scavo, L.M.; Karas, M.; Murray, M.; Leroith, D. Insulin-like growth factor-I stimulates both cell growth and lipogenesis during differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells into adipocytes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 3543–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiGirolamo, M.; Edén, S.; Enberg, G.; Isaksson, O.; Lönnroth, P.; Hall, K.; Smith, U. Specific binding of human growth hormone but not insulin-like growth factors by human adipocytes. Febs Lett. 1986, 205, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klöting, N.; Koch, L.; Wunderlich, T.; Kern, M.; Ruschke, K.; Krone, W.; Brüning, J.C.; Blüher, M. Autocrine IGF-1 action in adipocytes controls systemic IGF-1 concentrations and growth. Diabetes 2008, 57, 2074–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boucher, J.; Softic, S.; El Ouaamari, A.; Krumpoch, M.T.; Kleinridders, A.; Kulkarni, R.N.; O’Neill, B.T.; Kahn, C.R. Differential Roles of Insulin and IGF-1 Receptors in Adipose Tissue Development and Function. Diabetes 2016, 65, 2201–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davidovic, M.; Sevo, G.; Svorcan, P.; Milosevic, D.P.; Despotovic, N.; Erceg, P. Old age as a privilege of the “selfish ones”. Aging Dis. 2010, 1, 139–146. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, K. Modern Biological Theories of Aging. Aging Dis. 2010, 1, 72–74. [Google Scholar]
- Bartke, A.; Darcy, J. GH and ageing: Pitfalls and new insights. Best Pr. Res. Clin. Endocrinol Metab 2017, 31, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McCormack, S.; Yadav, S.; Shokal, U.; Kenney, E.; Cooper, D.; Eleftherianos, I. The insulin receptor substrate Chico regulates antibacterial immune function in Drosophila. Immun. Ageing 2016, 13, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Snell, G.D. DWARF, A NEW MENDELIAN RECESSIVE CHARACTER OF THE HOUSE MOUSE. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1929, 15, 733–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berryman, D.E.; Christiansen, J.S.; Johannsson, G.; Thorner, M.O.; Kopchick, J.J. Role of the GH/IGF-1 axis in lifespan and healthspan: Lessons from animal models. Growth Horm. Igf Res. 2008, 18, 455–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Heemst, D. Insulin, IGF-1 and longevity. Aging Dis. 2010, 1, 147–157. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, S.J.; Kahn, C.R. Endocrine regulation of ageing. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 2007, 8, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartke, A.; Wright, J.C.; Mattison, J.A.; Ingram, D.K.; Miller, R.A.; Roth, G.S. Extending the lifespan of long-lived mice. Nature 2001, 414, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, K.; Quipildor, G.F.; Tabrizian, T.; Novaj, A.; Guan, F.; Walters, R.O.; Delahaye, F.; Hubbard, G.B.; Ikeno, Y.; Ejima, K.; et al. Late-life targeting of the IGF-1 receptor improves healthspan and lifespan in female mice. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Samerria, S.; Radovick, S. The Role of Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 (IGF-1) in the Control of Neuroendocrine Regulation of Growth. Cells 2021, 10, 2664. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102664
Al-Samerria S, Radovick S. The Role of Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 (IGF-1) in the Control of Neuroendocrine Regulation of Growth. Cells. 2021; 10(10):2664. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102664
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Samerria, Sarmed, and Sally Radovick. 2021. "The Role of Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 (IGF-1) in the Control of Neuroendocrine Regulation of Growth" Cells 10, no. 10: 2664. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102664
APA StyleAl-Samerria, S., & Radovick, S. (2021). The Role of Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 (IGF-1) in the Control of Neuroendocrine Regulation of Growth. Cells, 10(10), 2664. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102664