1,8-Cineole Affects Agonists-Induced Platelet Activation, Thrombus Formation and Haemostasis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
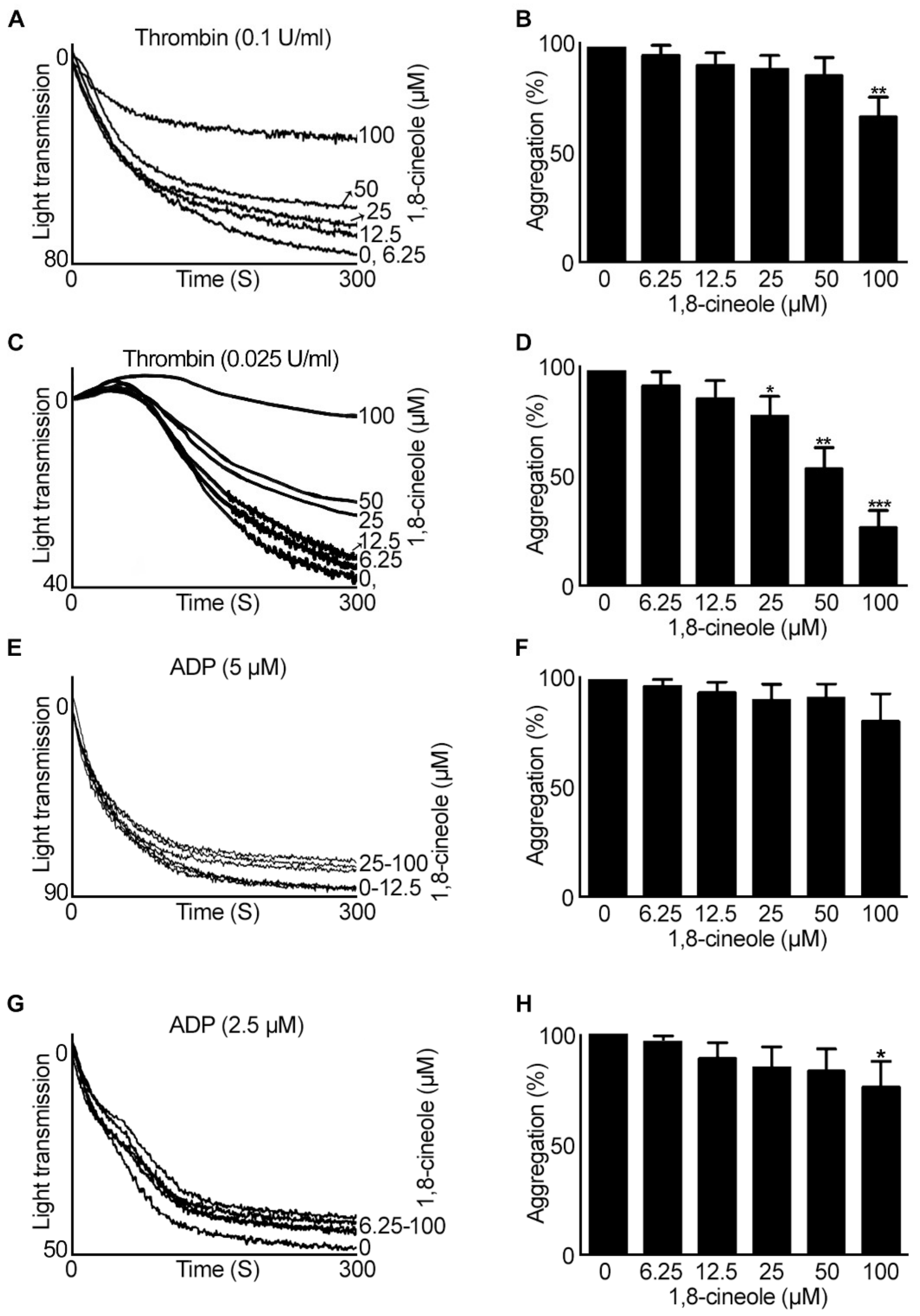
2.1. 1,8-. Cineole Largely Inhibits Platelet Aggregation Induced by GPVI Agonists
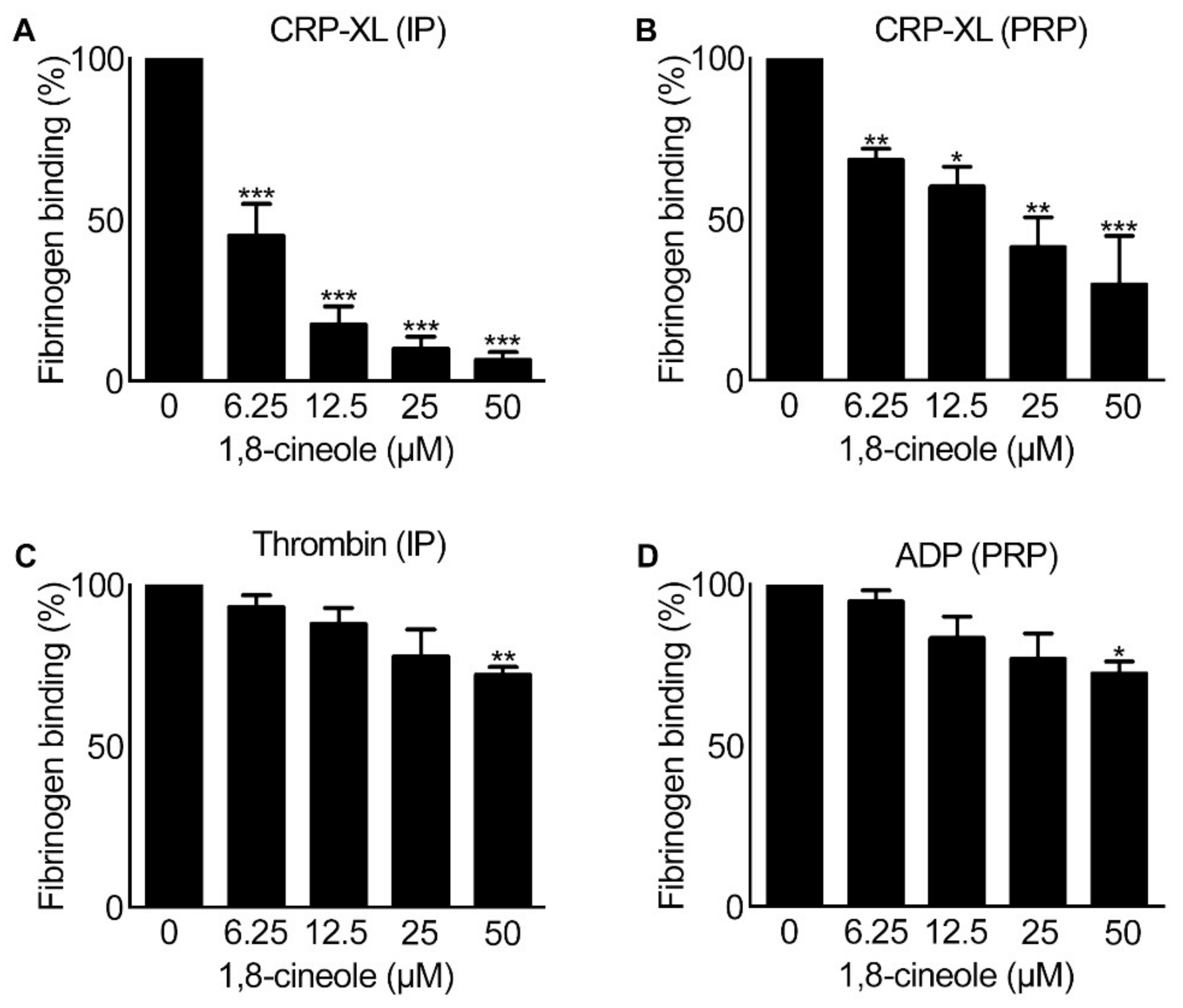
2.2. Inside-out Signalling to Integrin αIIbβ3 Is Affected by 1,8-Cineole
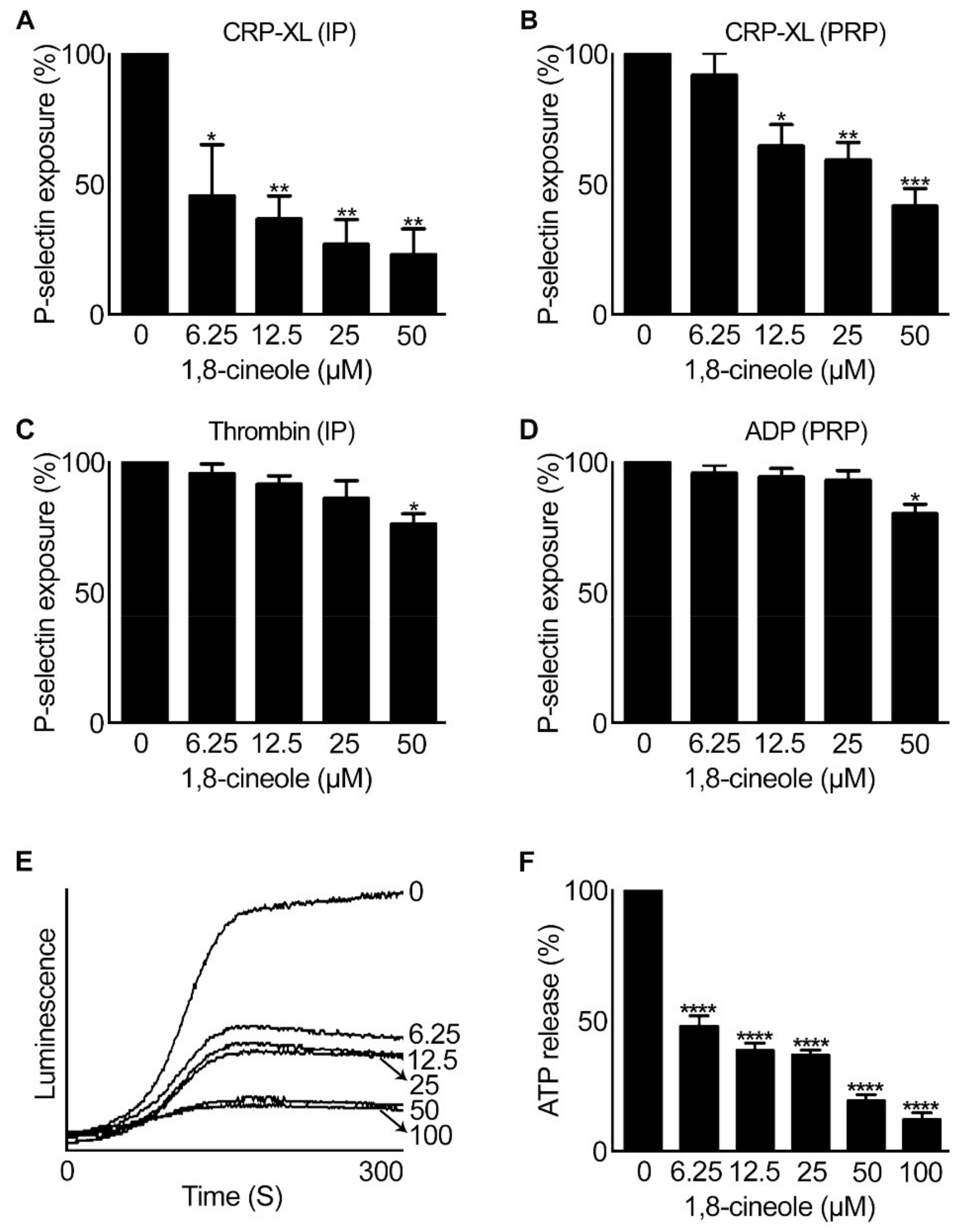
2.3. 1,8-. Cineole Affects Granule Secretion in Platelets
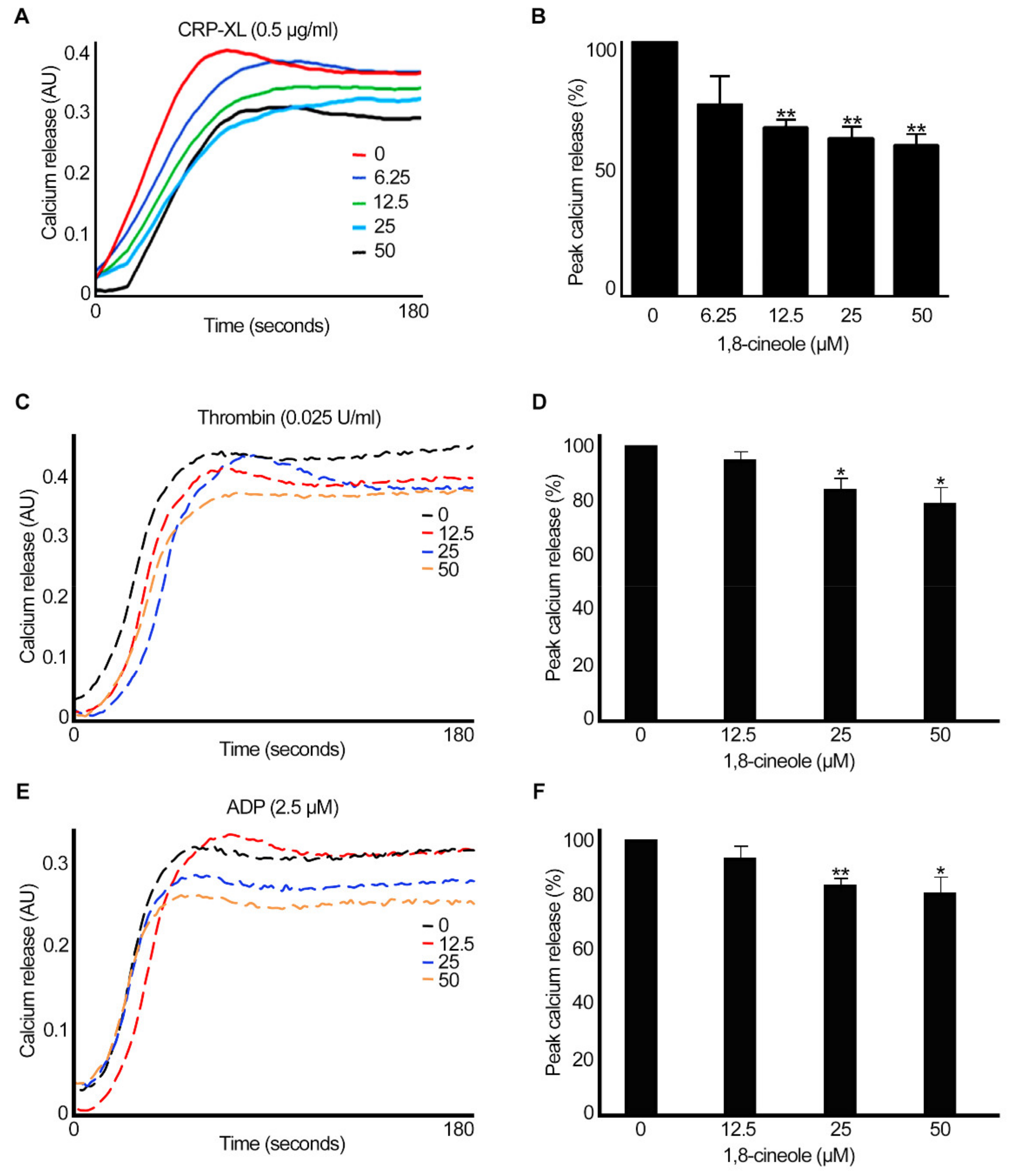
2.4. 1,8-. Cineole Inhibits Intracellular Calcium Mobilisation in Platelets
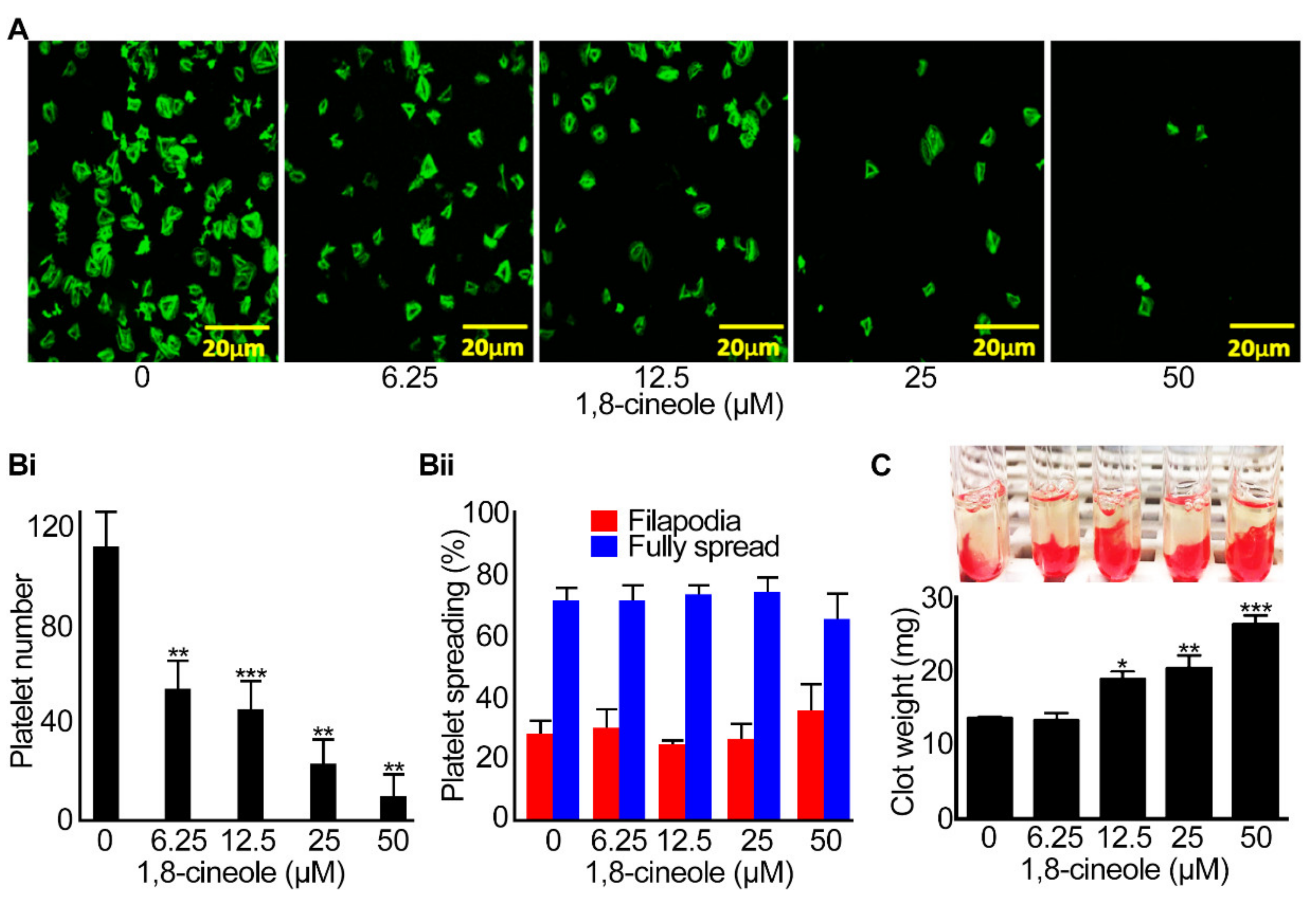
2.5. Integrin αIIbβ3-Mediated Outside-in Signalling Is Affected by 1,8-cineole
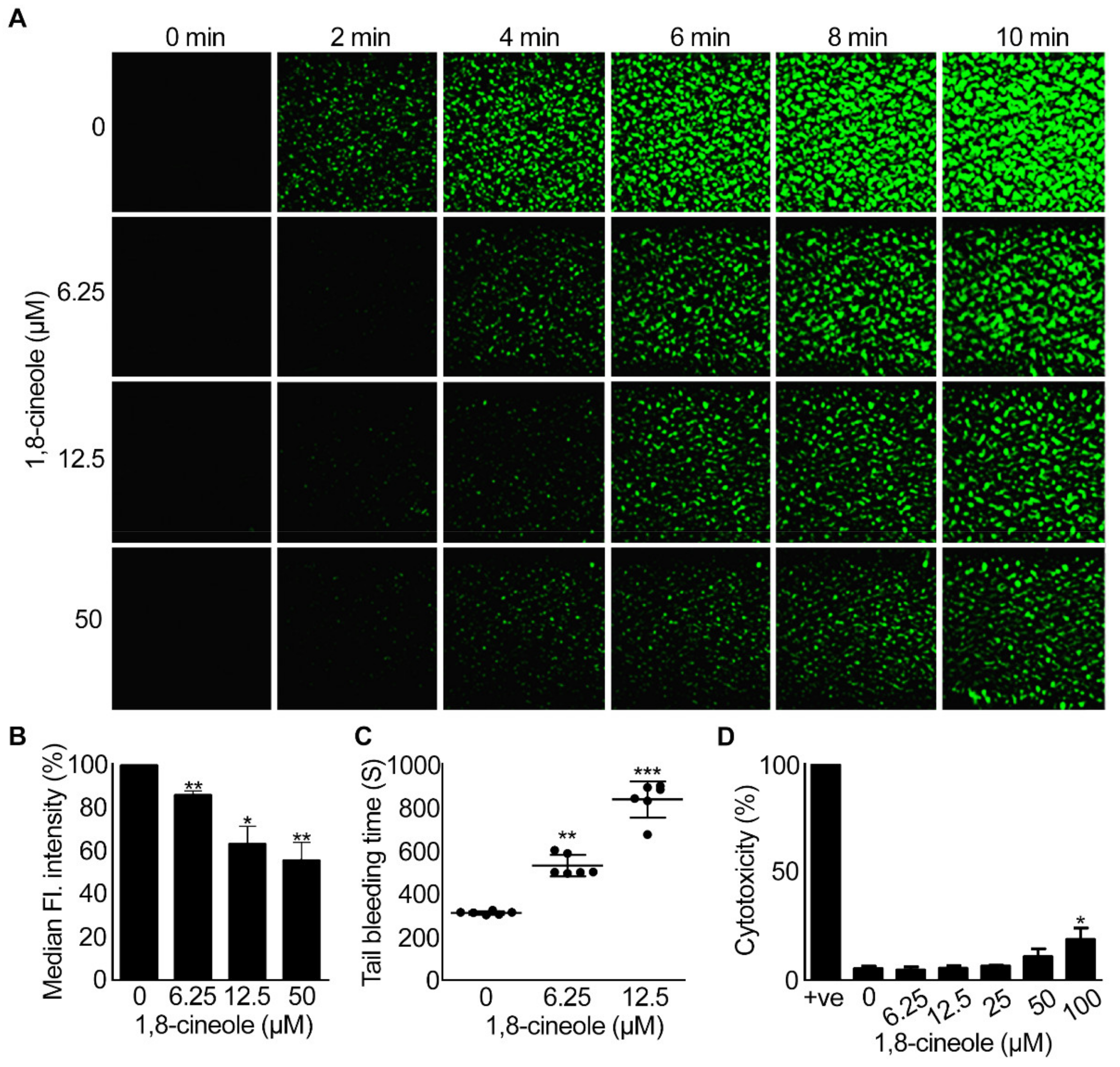
2.6. 1,8-Cineole Reduces Thrombus Formation under Arterial Flow Conditions
2.7. 1,8-. Cineole Affects Haemostasis in Mice
2.8. 1,8-. Cineole Is Not Cytotoxic to Platelets at Lower Concentrations
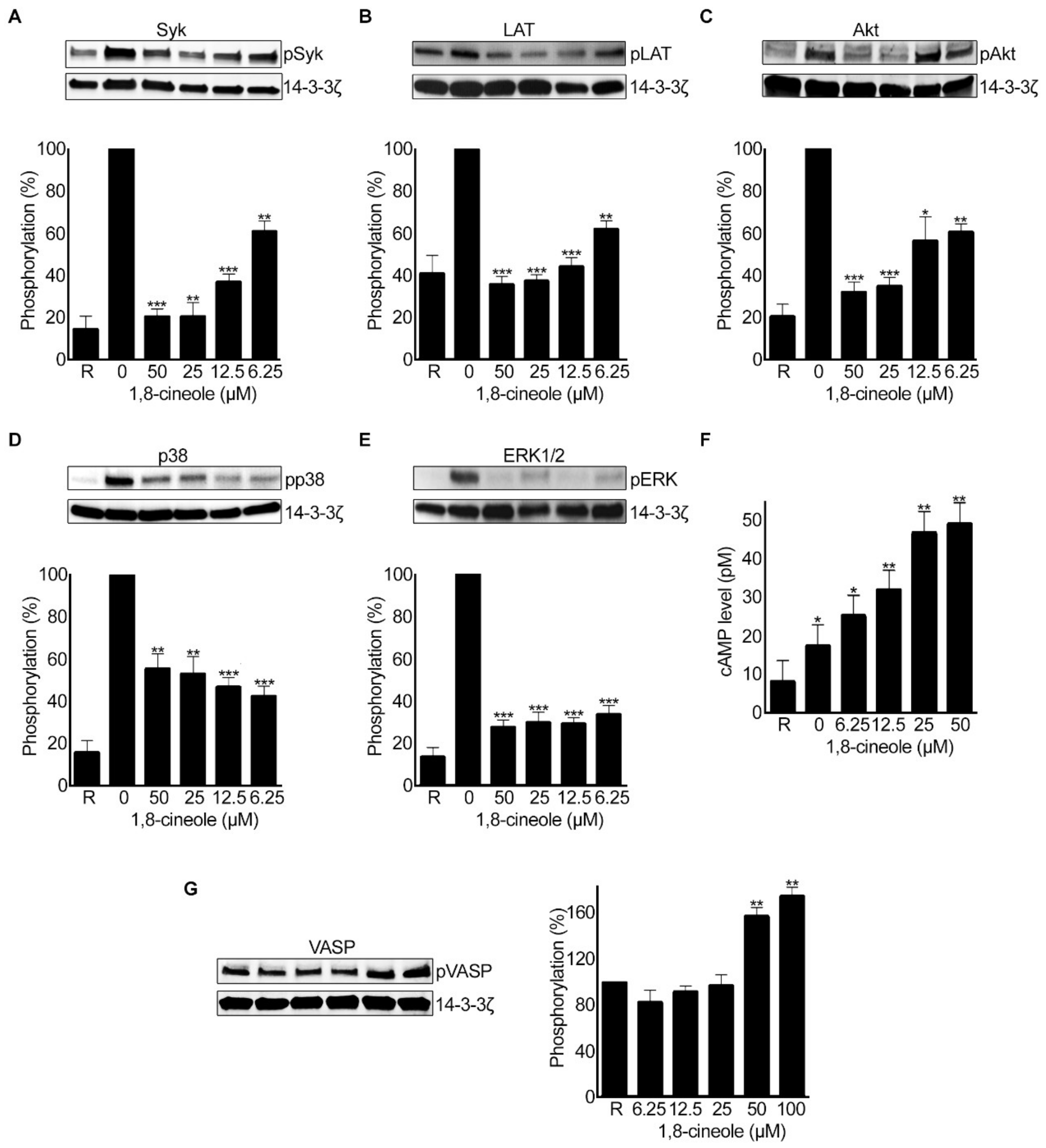
2.9. 1,8-. Cineole Affects Various Signalling Pathways in Platelets
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials Used
4.2. Platelet Preparation
4.3. Preparation of 1,8-Cineole
4.4. Aggregation and ATP Release Assays
4.5. Flow Cytometry-Based Assays
4.6. Calcium Mobilisation
4.7. Clot Retraction Assay
4.8. In Vitro Thrombus Formation
4.9. Tail Bleeding Assay
4.10. LDH Cytotoxicity Assay
4.11. Immunoblotting Analysis
4.12. Quantification of cAMP Levels in Platelets
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gibbins, J.M. Platelet adhesion signalling and the regulation of thrombus formation. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 3415–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barrett, N.E.; Holbrook, L.; Jones, S.; Kaiser, W.J.; Moraes, L.A.; Rana, R.; Sage, T.; Stanley, R.G.; Tucker, K.L.; Wright, B.; et al. Future innovations in anti-platelet therapies. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 154, 918–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cragg, G.M.; Newman, D.J. Natural products: A continuing source of novel drug leads. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2013, 1830, 3670–3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dhifi, W.; Bellili, S.; Jazi, S.; Bahloul, N.; Mnif, W. Essential Oils’ Chemical Characterization and Investigation of Some Biological Activities: A Critical Review. Medicines 2016, 3, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dagli, N.; Dagli, R.J.; Mahmoud, R.S.; Baroudi, K. Essential oils, their therapeutic properties, and implication in dentistry: A review. J. Int. Soc. Prev. Community Dent. 2015, 5, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burt, S. Essential oils: Their antibacterial properties and potential applications in foods—A review. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 94, 223–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, D.; Jones, T. Aromatherapy: Using Essential Oils as a Supportive Therapy. Clin. J. Oncol. Nurs. 2017, 21, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edris, A.E. Pharmaceutical and therapeutic Potentials of essential oils and their individual volatile constituents: A review. Phytotherapy Res. 2007, 21, 308–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakad, A.K.; Pandey, V.V.; Beg, S.; Rawat, J.M.; Singh, A. Biological, medicinal and toxicological significance ofEucalyptusleaf essential oil: A review. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 833–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadlon, A.E.; Lamson, D.W. Immune-modifying and antimicrobial effects of Eucalyptus oil and simple inhalation devices. Altern. Med. Rev. A J. Clin. Ther. 2010, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, S.K.; Garver, W.S.; Orlando, R.A. 1,8-cineole: An Underappreciated Anti-inflammatory Therapeutic. J. Biomol. Res. Ther. 2017, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seol, G.H.; Kim, K.Y. Eucalyptol and its role in chronic diseases. In Drug Discovery from Mother Nature; Gupta, S.C., Prasad, S., Aggarwal, B.B., Eds.; Springer: Houston, TX, USA, 2016; pp. 389–398. [Google Scholar]
- Juergens, U.; Dethlefsen, U.; Steinkamp, G.; Gillissen, A.; Repges, R.; Vetter, H. Anti-inflammatory activity of 1.8-cineol (eucalyptol) in bronchial asthma: A double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Respir. Med. 2003, 97, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Juergens, U.R.; Engelen, T.; Racké, K.; Stöber, M.; Gillissen, A.; Vetter, H. Inhibitory activity of 1,8-cineol (eucalyptol) on cytokine production in cultured human lymphocytes and monocytes. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 17, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, J.F.-W.; Müller, J.; Zeuner, M.-T.; Hauser, S.; Seidel, T.; Klenke, C.; Grunwald, L.-M.; Schomann, T.; Widera, D.; Sudhoff, H.; et al. 1,8-Cineol inhibits nuclear translocation of NF-κB p65 and NF-κB-dependent transcriptional activity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenerg. 2013, 1833, 2866–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shattil, S.J.; Kashiwagi, H.; Pampori, N. Integrin signaling: The platelet paradigm. Blood 1998, 91, 2645–2657, Epub 1998/05/16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nieswandt, B.; Varga-Szabo, D.; Elvers, M. Integrins in platelet activation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 7, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, J.G.; Estensen, R.D. Degranulation of Discoid Platelets. Am. J. Pathol. 1972, 68, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blair, P.; Flaumenhaft, R. Platelet α-granules: Basic biology and clinical correlates. Blood Rev. 2009, 23, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Whiteheart, S. Platelet granules: Surprise packages. Blood 2011, 118, 1190–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga-Szabo, D.; Braun, A.; Nieswandt, B. Calcium signaling in platelets. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 7, 1057–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrant, T.N.; van den Bosch, M.T.; Hers, I. Integrin αIIbβ3 outside-in signaling. Blood 2017, 130, 1607–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, B.; Delaney, M.K.; Du, X. Inside-out, outside-in, and inside–outside-in: G protein signaling in integrin-mediated cell adhesion, spreading, and retraction. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2012, 24, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Broos, K.; Feys, H.; De Meyer, S.; Vanhoorelbeke, K.; Deckmyn, H. Platelets at work in primary hemostasis. Blood Rev. 2011, 25, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.V.; Mistry, B.M.; Shinde, S.K.; Syed, R.; Singh, V.; Shin, H.-S. Therapeutic potential of quercetin as a cardiovascular agent. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 155, 889–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yao, J.; Han, C.; Yang, J.; Chaudhry, M.T.; Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Yin, Y. Quercetin, Inflammation and Immunity. Nutrients 2016, 8, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerimi, A.; Williamson, G. The cardiovascular benefits of dark chocolate. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2015, 71, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carnevale, R.; Loffredo, L.; Nocella, C.; Bartimoccia, S.; Bucci, T.; De Falco, E.; Peruzzi, M.; Chimenti, I.; Biondi-Zoccai, G.; Pignatelli, P.; et al. Epicatechin and Catechin Modulate Endothelial Activation Induced by Platelets of Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2014, 2014, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaiyapuri, S.; Ali, M.S.; Moraes, L.A.; Sage, T.; Lewis, K.R.; Jones, C.I.; Gibbins, J.M. Tangeretin Regulates Platelet Function Through Inhibition of Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase and Cyclic Nucleotide Signaling. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2013, 33, 2740–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaiyapuri, S.; Roweth, H.; Ali, M.S.; Unsworth, A.; Stainer, A.; Flora, G.; Crescente, M.; Jones, C.; Moraes, L.A.; Gibbins, J.M. Pharmacological actions of nobiletin in the modulation of platelet function. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 4133–4145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jayakumar, T.; Lin, K.-C.; Lu, W.-J.; Lin, C.-Y.; Pitchairaj, G.; Li, J.-Y.; Sheu, J.-R. Nobiletin, a citrus flavonoid, activates vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein in human platelets through non-cyclic nucleotide-related mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 39, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harb, A.A.; Bustanji, Y.K.; Almasri, I.M.; Abdalla, S.S. Eugenol Reduces LDL Cholesterol and Hepatic Steatosis in Hypercholesterolemic Rats by Modulating TRPV1 Receptor. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasni, S.; Imaizumi, K.; Sin, K.; Sugano, M.; Nonaka, G. Sidik Identification of an active principle in essential oils and hexane-soluble fractions of Curcuma xanthorrhiza Roxb. Showing triglyceride-lowering action in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1994, 32, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballabeni, V.; Tognolini, M.; Chiavarini, M.; Impicciatore, M.; Bruni, R.; Bianchi, A.; Barocelli, E. Novel antiplatelet and antithrombotic activities of essential oil from Lavandula hybrida Reverchon “grosso”. Phytomedicine 2004, 11, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.-J.; Wang, M.-H.; Chen, I.-J. Antiplatelet and calcium inhibitory properties of eugenol and sodium eugenol acetate. Gen. Pharmacol. Vasc. Syst. 1996, 27, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, M.; Hill, J.; Galluppi, G.; McLean, M. Plasma Protein Binding in Drug Discovery and Development. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2010, 13, 170–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, B.; Gibson, T.; Spencer, J.; Lovegrove, J.A.; Gibbins, J. Platelet-Mediated Metabolism of the Common Dietary Flavonoid, Quercetin. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janssens, J.; Laekeman, G.M.; Pieters, L.A.; Totte, J.; Herman, A.G.; Vlietinck, A.J. Nutmeg oil: Identification and quantitation of its most active constituents as inhibitors of platelet aggregation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1990, 29, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, K.; Justesen, U. Inhibition of platelet aggregation and reduced formation of thromboxane and lipoxygenase products in platelets by oil of cloves. Prostaglandins Leukot. Med. 1987, 29, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grice, I.D.; Rogers, K.L.; Griffiths, L. Isolation of Bioactive Compounds That Relate to the Anti-Platelet Activity ofCymbopogon ambiguus. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2011, 2011, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raghavendra, R.; Naidu, K.A. Spice active principles as the inhibitors of human platelet aggregation and thromboxane biosynthesis. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2009, 81, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslan, J.E.; Itakura, A.; Gertz, J.M.; Mccarty, O.J.T. Platelet Shape Change and Spreading. Adv. Struct. Saf. Stud. 2011, 788, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravishankar, D.; Salamah, M.; Attina, A.; Pothi, R.; Vallance, T.; Javed, M.; Williams, H.F.; Alzahrani, E.M.S.; Kabova, E.; Vaiyapuri, R.; et al. Ruthenium-conjugated chrysin analogues modulate platelet activity, thrombus formation and haemostasis with enhanced efficacy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tucker, K.L.; Sage, T.; Gibbins, J.M. Clot retraction. In Platelets and Megakaryocytes; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 101–107. [Google Scholar]
- Ballabeni, V.; Tognolini, M.; Bertoni, S.; Bruni, R.; Guerrini, A.; Rueda, G.M.; Barocelli, E. Antiplatelet and antithrombotic activities of essential oil from wild Ocotea quixos (Lam.) Kosterm. (Lauraceae) calices from Amazonian Ecuador. Pharmacol. Res. 2007, 55, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tognolini, M.; Ballabeni, V.; Bertoni, S.; Bruni, R.; Impicciatore, M.; Barocelli, E. Protective effect of Foeniculum vulgare essential oil and anethole in an experimental model of thrombosis. Pharmacol. Res. 2007, 56, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, N.V.; Assreuy, A.M.S.; Coelho-De-Souza, A.N.; Ceccatto, V.M.; Magalhães, P.J.C.; Lahlou, S.; Leal-Cardoso, J.H. Endothelium-dependent vasorelaxant effects of the essential oil from aerial parts of Alpinia zerumbet and its main constituent 1,8-cineole in rats. Phytomedicine 2009, 16, 1151–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayes, J.; Watson, S.P.; Nieswandt, B. Functional significance of the platelet immune receptors GPVI and CLEC-2. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suzuki-Inoue, K.; Hughes, C.; Inoue, O.; Kaneko, M.; Cuyun-Lira, O.; Takafuta, T.; Watson, S.; Ozaki, Y. Involvement of Src kinases and PLCγ2 in clot retraction. Thromb. Res. 2007, 120, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.; Jin, J.; Kunapuli, S.P. Akt Activation in Platelets Depends on Gi Signaling Pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 4186–4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murata, S.; Ogawa, K.; Matsuzaka, T.; Chiba, M.; Nakayama, K.; Iwasaki, K.; Kurokawa, T.; Sano, N.; Tanoi, T.; Ohkohchi, N. 1,8-Cineole Ameliorates Steatosis of Pten Liver Specific KO Mice via Akt Inactivation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 12051–12063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murata, S.; Shiragami, R.; Kosugi, C.; Tezuka, T.; Yamazaki, M.; Hirano, A.; Yoshimura, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Shuto, K.; Ohkohchi, N.; et al. Antitumor effect of 1, 8-cineole against colon cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 30, 2647–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bruchhage, K.-L.; Koennecke, M.; Drenckhan, M.; Plötze-Martin, K.; Pries, R.; Wollenberg, B. 1,8-cineol inhibits the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway through GSK-3 dephosphorylation in nasal polyps of chronic rhinosinusitis patients. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 835, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.Y.; Lee, H.S.; Seol, G.H. Eucalyptol suppresses matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression through an extracellular signal-regulated kinase-dependent nuclear factor-kappa B pathway to exert anti-inflammatory effects in an acute lung inflammation model. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2015, 67, 1066–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamah, M.F.; Ravishankar, D.; Kodji, X.; Moraes, L.A.; Williams, H.F.; Vallance, T.; Albadawi, D.A.; Vaiyapuri, R.; Watson, K.; Gibbins, J.; et al. The endogenous antimicrobial cathelicidin LL37 induces platelet activation and augments thrombus formation. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 2973–2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.I.; Sage, T.; Moraes, L.A.; Vaiyapuri, S.; Hussain, U.; Tucker, K.L.; Barrett, N.E.; Gibbins, J.M. Platelet Endothelial Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 Inhibits Platelet Response to Thrombin and von Willebrand Factor by Regulating the Internalization of Glycoprotein Ib via AKT/Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3/Dynamin and Integrin αIIbβ3. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 1968–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elashry, M.; Collins-Hooper, H.; Vaiyapuri, S.; Patel, K. Characterisation of connective tissue from the hypertrophic skeletal muscle of myostatin null mice. J. Anat. 2012, 220, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaiyapuri, S.; Sage, T.; Rana, R.H.; Schenk, M.P.; Ali, M.S.; Unsworth, A.; Jones, C.; Stainer, A.; Kriek, N.; Moraes, L.A.; et al. EphB2 regulates contact-dependent and contact-independent signaling to control platelet function. Blood 2015, 125, 720–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alatawi, K.A.; Ravishankar, D.; Patra, P.H.; Bye, A.P.; Stainer, A.R.; Patel, K.; Widera, D.; Vaiyapuri, S. 1,8-Cineole Affects Agonists-Induced Platelet Activation, Thrombus Formation and Haemostasis. Cells 2021, 10, 2616. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102616
Alatawi KA, Ravishankar D, Patra PH, Bye AP, Stainer AR, Patel K, Widera D, Vaiyapuri S. 1,8-Cineole Affects Agonists-Induced Platelet Activation, Thrombus Formation and Haemostasis. Cells. 2021; 10(10):2616. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102616
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlatawi, Kahdr A., Divyashree Ravishankar, Pabitra H. Patra, Alexander P. Bye, Alexander R. Stainer, Ketan Patel, Darius Widera, and Sakthivel Vaiyapuri. 2021. "1,8-Cineole Affects Agonists-Induced Platelet Activation, Thrombus Formation and Haemostasis" Cells 10, no. 10: 2616. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102616
APA StyleAlatawi, K. A., Ravishankar, D., Patra, P. H., Bye, A. P., Stainer, A. R., Patel, K., Widera, D., & Vaiyapuri, S. (2021). 1,8-Cineole Affects Agonists-Induced Platelet Activation, Thrombus Formation and Haemostasis. Cells, 10(10), 2616. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102616







