Acquired Glucocorticoid Resistance Due to Homologous Glucocorticoid Receptor Downregulation: A Modern Look at an Age-Old Problem
Abstract
:1. Introduction
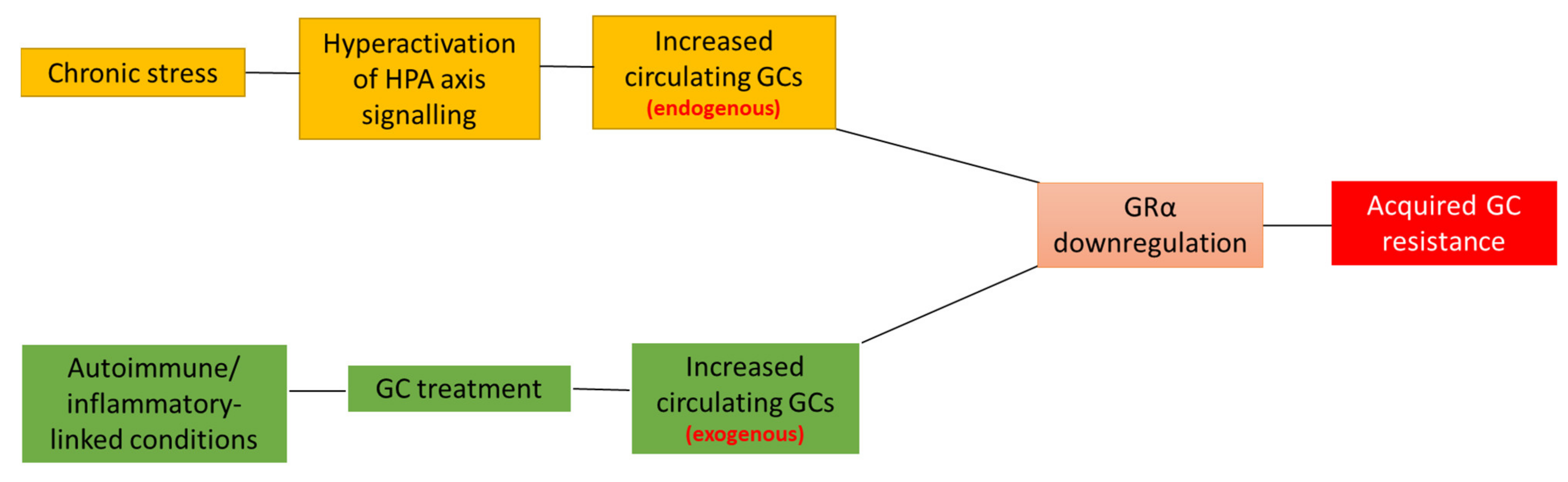
2. Acquired GC Resistance
3. Molecular Mechanisms Involved in the Homologous Downregulation of GRα
3.1. GRα mRNA Regulation
3.1.1. Epigenetic Regulation
3.1.2. Transcriptional Regulation
3.1.3. Post-Transcriptional Regulation
3.2. GRα Protein Regulation
3.2.1. Post-Translational Regulation
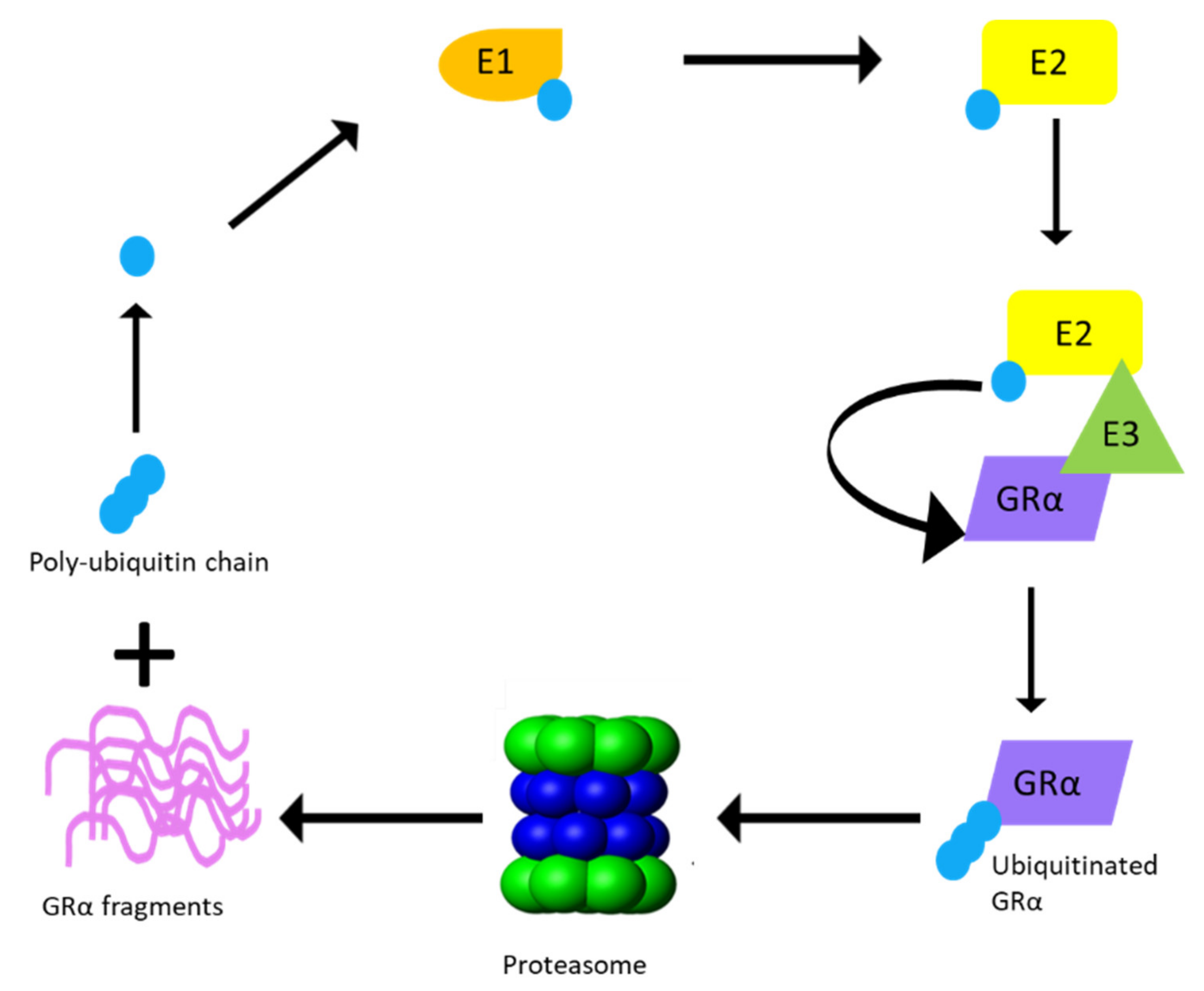
3.2.2. UPS Enzymes That Modulate GRα Protein Levels
3.2.3. Hsp90 as a Modulator of GRα Stability
4. GRα Downregulation and Receptor Conformation
4.1. Proposed Model for GC-Mediated GRα Regulation
4.1.1. Promotion of GRα Dimerization
4.1.2. Restriction of GRα Dimerization
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Solis-Cohen, S. The use of adrenal substances in the treatment of Asthma. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1900, 34, 1164–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, P.J. Glucocorticoids Chem. Immunol. Allergy 2014, 100, 311–316. [Google Scholar]
- Brewis, R.A.L. (Ed.) Classical Papers in Asthma; Science Press: London, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Ten, S.; New, M.; Maclaren, N. Addison ’s Disease 2001. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 2909–2922. [Google Scholar]
- Timmermans, S.; Souffriau, J.; Libert, C. A general introduction to glucocorticoid biology. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Simoni, R.D.; Hill, R.L.; Vaughan, M. The isolation of thyroxine and cortisone: The work of Edward C. Kendall. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 21–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarett, L.H. Partial synthesis of pregnene-4-triol-17β, 20β, 21-dione-3,11 and pregnene-4-diol-17β, 21-trione-3,11,20 monoacetate. J. Biol. Chem. 1946, 162, 601–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandewalle, J.; Luypaert, A.; De Bosscher, K.; Libert, C. Therapeutic Mechanisms of Glucocorticoids. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 29, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, J.B.; White, A.G.; Scarpati, L.M.; Wan, G.; Nelson, W.W. Long-term Systemic Corticosteroid Exposure: A Systematic Literature Review. Clin. Ther. 2017, 39, 2216–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bollet, A.J.; Black, R.; Bunim, J.J. Major undesirable side effects side-effects from Prednisolone and Prednisone. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1955, 158, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, D.A. 6-Methyl prednisolone in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Ulster Med. J. 1958, 27, 130–136. [Google Scholar]
- Berliner, D.L. Studies of the Mechanisms by Which Cells Become Resistant to Corticosteroids. Cancer Res. 1965, 25, 1085–1095. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, H.J.; Lowell, F.C.; James, C.M. Steroid Resistance in Bronchial Asthma. Ann. Intern. Med. 1968, 69, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadmiel, M.; Cidlowski, J.A. Glucocorticoid receptor signaling in health and disease. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 34, 518–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Bosscher, K.; Beck, I.M.; Ratman, D.; Berghe, W.V.; Libert, C. Activation of the Glucocorticoid Receptor in Acute Inflammation: The, SEDIGRAM Concept. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 37, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakley, R.; Cidlowski, J. The Biology of the Glucocorticoid Receptor: New Signaling Mechanisms in Health and Disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 1033–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gjerstad, J.K.; Lightman, S.L.; Spiga, F. Role of glucocorticoid negative feedback in the regulation of HPA axis pulsatility. Stress 2018, 21, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Desmet, S.J.; De Bosscher, K. Glucocorticoid receptors: Finding the middle ground. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 1136–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grad, I.; Picard, D. The glucocorticoid responses are shaped by molecular chaperones. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2007, 275, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weikum, E.R.; De Vera, I.M.S.; Nwachukwu, J.C.; Hudson, W.H.; Nettles, K.W.; Kojetin, D.J.; Ortlund, E.A. Tethering not required: The glucocorticoid receptor binds directly to activator protein-1 recognition motifs to repress inflammatory genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 8596–8608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louw, A. GR Dimerization and the Impact of GR Dimerization on GR Protein Stability and Half-Life. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cain, D.W.; Cidlowski, J.A. Immune regulation by glucocorticoids. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundahl, N.; Bridelance, J.; Libert, C.; De Bosscher, K.; Beck, I.M. Selective glucocorticoid receptor modulation: New directions with non-steroidal scaffolds. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 152, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Bosscher, K.; Beck, I.M.; Haegeman, G. Classic glucocorticoids versus non-steroidal glucocorticoid receptor modulators: Survival of the fittest regulator of the immune system? Brain. Behav. Immun. 2010, 24, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewint, P.; Gossye, V.; De Bosscher, K.; Vanden Berghe, W.; Van Beneden, K.; Deforce, D.; Van Calenbergh, S.; Müller-Ladner, U.; Vander Cruyssen, B.; Verbruggen, G.; et al. A plant-derived ligand favoring monomeric glucocorticoid receptor conformation with impaired transactivation potential attenuates collagen-induced arthritis. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 2608–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Bosscher, K.; Vanden, B.W.; Beck, I.M.E.; Van Molle, W.; Hennuyer, N.; Hapgood, J.; Libert, C.; Staels, B.; Louw, A.; Haegeman, G. A fully dissociated compound of plant origin for inflammatory gene repression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15827–15832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Schluesener, H.J. Compound A, a Plant Origin Ligand of Glucocorticoid Receptors, Increases Regulatory, T.Cells and M2 Macrophages to Attenuate Experimental Autoimmune Neuritis with Reduced Side Effects. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 3081–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, P.J.; Adcock, I.M. Glucocorticoid resistance in inflammatory diseases. Lancet 2009, 373, 1905–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fardet, L.; Petersen, I.; Nazareth, I. Monitoring of patients on long-term glucocorticoid therapy. Medicine 2009, 94, e647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, L.; Verhoog, N.J.D.; Louw, A. Disease-and treatment-associated acquired glucocorticoid resistance. Endocr. Connect. 2018, 7, R328–R349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quax, R.A.; Manenschijn, L.; Koper, J.W.; Hazes, J.M.; Lamberts, S.W.J.; Van Rossum, E.F.C.; Feelders, R.A. Glucocorticoid sensitivity in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2013, 9, 670–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaides, N.C.; Lamprokostopoulou, A.; Sertedaki, A.; Charmandari, E. Recent advances in the molecular mechanisms causing primary generalized glucocorticoid resistance. Hormones 2016, 15, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petta, I.; Dejager, L.; Ballegeer, M.; Lievens, S.; Tavernier, J.; De Bosscher, K.; Libert, C. The Interactome of the Glucocorticoid Receptor and Its Influence on the Actions of Glucocorticoids in Combatting Inflammatory and Infectious Diseases. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 495–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramamoorthy, S.; Cidlowski, J.A. Corticosteroids. Mechanisms of Action in Health and Disease Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 42, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nicolaides, N.C.; Charmandari, E. Chrousos syndrome: From molecular pathogenesis to therapeutic management. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 45, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charmandari, E. Primary generalized glucocorticoid resistance and hypersensitivity. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2011, 76, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaaf, M.J.M.; Cidlowski, J.A. Molecular mechanisms of glucocorticoid action and resistance. J. Steriod Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2003, 83, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheridan, J.F.; Powell, N.; Reader, B.; Tarr, A.; Kim, T.; Wang, Y.; Jung, S.H. Molecular Mechanisms of Repeated Social Defeat-Induced Glucocorticoid Resistance: Role of microRNA. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 44, 195–206. [Google Scholar]
- Niknazar, S.; Nahavandi, A.; Peyvandi, A.A.; Peyvandi, H.; Roozbahany, N.A.; Abbaszadeh, H.A. Hippocampal NR3C1 DNA methylation can mediate part of preconception paternal stress effects in rat offspring. Behav. Brain Res. 2017, 324, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, M.J.; Knable, M.B.; O’Grady, J.; Orthmann, J.; Weickert, C.S. Regional specificity of brain glucocorticoid receptor mRNA alterations in subjects with schizophrenia and mood disorders. Mol. Psychiatry 2002, 7, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inui, S.; Sumikawa, Y.; Asada, H.; Itami, S. Glucocorticoid resistance in atopic dermatitis associated with decreased expression of glucocorticoid receptor-α in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J. Dermatol. 2010, 37, 496–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Fang, M.; Liang, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Jia, Z.; Sun, X.; Wang, Y.; Qin, J. Low expression of glucocorticoid receptor alpha isoform in adult immune thrombocytopenia correlates with glucocorticoid resistance. Ann. Hematol. 2013, 92, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enki, D.G.; Sinha, A.; Stimpson, M.L.; Collins, P.L.; Williams, E.L.; Dhanda, A.D.; Lee, R.W. Development and validation of a novel bioassay to determine glucocorticoid sensitivity. Biomark. Res. 2016, 4, 26. [Google Scholar]
- Labonte, B.; Yerko, V.; Gross, J.; Mechawar, N.; Meaney, M.J.; Szyf, M.; Turecki, G. Differential glucocorticoid receptor exon 1B, 1C, and 1H expression and methylation in suicide completers with a history of childhood abuse. Biol. Psychiatry 2012, 72, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGowan, P.; Sasaki, A.; D’Alessio, A.; Dymov, S.; Labonté, B.; Szyf, M.; Turecki, G.; Meaney, M. Epigenetic regulation of the glucocorticoid receptor in human brain associates with childhood abuse. Nat. Neurosci. 2010, 12, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yao, R.; Hao, T.; Cao, J.; Huang, H.; Wang, L.; Wu, Y. Enhanced neuroinflammation mediated by DNA methylation of the glucocorticoid receptor triggers cognitive dysfunction after sevoflurane anesthesia in adult rats subjected to maternal separation during the neonatal period. J. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 14, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Feng, J.; Ji, C.; Mu, X.; Ma, Q.; Fan, Y.; Chen, C.; Gao, C.; Ma, X.C.; Zhu, F. Increased methylation of glucocorticoid receptor gene promoter 1F in peripheral blood of patients with generalized anxiety disorder. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2017, 91, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, B.R.; Bale, T.L. Sex-specific programming of offspring emotionality after stress early in pregnancy. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 9055–9065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arborelius, L.; Owens, M.J.; Plotsky, P.M.; Nemeroff, C.B. The role of corticotropin-releasing factor in depression and anxiety disorders. J. Endocrinol. 1999, 160, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- López, J.F.; Chalmers, D.T.; Little, K.Y.; Watson, S.J. Regulation of serotonin1A, glucocorticoid, and mineralocorticoid receptor in rat and human hippocampus: Implications for the neurobiology of depression. Biol. Psychiatry 1998, 43, 547–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pariante, C.M. Why are depressed patients inflamed? A reflection on 20 years of research on depression, glucocorticoid resistance and inflammation. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017, 27, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Fan, J.; Shou, Q.; Zhang, L.; Ma, H.; Fan, Y. Hypermethylation of glucocorticoid receptor gene promoter results in glucocorticoid receptor gene low expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatol. Int. 2015, 35, 1335–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sher, E.R.; Leung, D.Y.M.; Surs, W.; Kam, J.C.; Zieg, G.; Kamada, A.K.; Szefler, S.J. Steroid-resistant asthma. Cellular mechanisms contributing to inadequate response to glucocorticoid therapy. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 93, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sousa, A.R.; Lane, S.J.; Cidlowski, J.A.; Staynov, D.Z.; Lee, T.H. Glucocorticoid resistance in asthma is associated with elevated in vivo expression of the glucocorticoid receptor β-isoform. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2000, 105, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pujols, L.; Xaubet, A.; Ramírez, J.; Mullol, J.; Roca-Ferrer, J.; Torrego, A.; Cidlowski, J.A.; Picado, C. Expression of glucocorticoid receptors α and β in steroid sensitive and steroid insensitive interstitial lung diseases. Thorax 2004, 59, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marwick, J.A.; Caramori, G.; Stevenson, C.S.; Casolari, P.; Jazrawi, E.; Barnes, P.J.; Ito, K.; Adcock, I.M.; Kirkham, P.A.; Papi, A. Inhibition of PI3Kδ restores glucocorticoid function in smoking-induced airway inflammation in mice. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 179, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patki, M.; Gadgeel, S.; Huang, Y.; McFall, T.; Shields, A.F.; Matherly, L.H.; Bepler, G.; Ratnam, M. Glucocorticoid receptor status is a principal determinant of variability in the sensitivity of non-small-cell lung cancer cells to pemetrexed. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kay, P.; Schlossmacher, G.; Matthews, L.; Sommer, P.; Singh, D.; White, A.; Ray, D. Loss of glucocorticoid receptor expression by DNA methylation prevents glucocorticoid induced apoptosis in human small cell lung cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2001, 6, e24839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, S.; Irving, J.A.E.; Minto, L.; Matheson, E.; Nicholson, L.; Ploner, A.; Parson, W.; Kofler, A.; Amort, M.; Erdel, M.; et al. Glucocorticoid resistance in two key models of acute lymphoblastic leukemia occurs at the level of the glucocorticoid receptor. FASEB J. 2006, 20, 2600–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griese, M. Glucocorticoid receptors in mononuclear blood cells and their correlation to endogenous and exogenous corticoids in healthy and asthmatic children. Eur. J. Pediatr. 1988, 147, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, A.D.; Cidlowski, J.A. Proteasome-mediated Glucocorticoid Receptor Degradation Restricts Transcriptional Signaling by Glucocorticoids. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 42714–42721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kleinschnitz, C.; Blecharz, K.; Kahles, T.; Schwarz, T.; Kraft, P.; Göbel, K.; Meuth, S.G.; Burek, M.; Thum, T.; Stoll, G.; et al. Glucocorticoid insensitivity at the hypoxic blood-brain barrier can be reversed by inhibition of the proteasome. Stroke 2001, 42, 1081–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ling, C.; Li, Y.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, M. Ginsenosides may reverse the dexamethasone-induced down-regulation of glucocorticoid receptor. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2005, 140, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, C.M.; Powell-Oliver, F.E.; Jewell, C.M.; Sar, M.; Allgood, V.E.; Cidlowski, J.A. Regulation of the human glucocorticoid receptor by long-term and chronic treatment with glucocorticoid. Steroids 1994, 59, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujols, L.; Mullol, J.; Pérez, M.; Roca-Ferrer, J.; Juan, M.; Xaubet, A.; Cidlowski, J.A.; Picado, C. Expression of the human glucocorticoid receptor α and β isoforms in human respiratory epithelial cells and their regulation by dexamethasone. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2001, 24, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wallace, A.D.; Cao, Y.; Chandramouleeswaran, S.; Cidlowski, J.A. Lysine 419 targets human glucocorticoid receptor for proteasomal degradation. Steroids 2010, 75, 1016–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Visser, K.; Smith, C.; Louw, A. Interplay of the Inflammatory and Stress Systems in a Hepatic Cell Line: Interactions between Glucocorticoid receptor Agonists and Interleukin-6. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 5279–5293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramamoorthy, S.; Cidlowski, J.A. Ligand-Induced Repression of the Glucocorticoid Receptor Gene Is Mediated by an NCoR1 Repression Complex Formed by Long-Range Chromatin Interactions with Intragenic Glucocorticoid Response Elements. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2013, 33, 1711–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilkinson, L.; Verhoog, N.; Louw, A. Novel role for receptor dimerization in post-translational processing and turnover of the GRα. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, T.; Yin, Y.; Huang, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, D.; Li, W. Chronic dexamethasone treatment results in hippocampal neurons injury due to activate NLRP1 inflammasome in vitro. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 49, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guess, A.; Agrawal, S.; Wei, C.C.; Ransom, R.F.; Benndorf, R.; Smoyer, W.E. Dose-and time-dependent glucocorticoid receptor signaling in podocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2010, 299, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, W.; Yin, Y.; Huang, D.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Li, W. Chronic glucocorticoids exposure enhances neurodegeneration in the frontal cortex and hippocampus via NLRP-1 inflammasome activation in male mice. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2016, 52, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djordjevic-Markovic, R.; Radic, O.; Jelic, V.; Radojcic, M.; Rapic-Otrin, V.; Ruzdijic, S.; Krstic-Demonacos, M.; Kanazir, S.; Kanazir, D. Glucocorticoid receptors in ageing rats. Exp. Gerontol. 1999, 34, 971–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, T.J.; Vig, E.; Vedeckis, W.V. Coordinate Regulation of Glucocorticoid Receptor and c-jun Gene Expression Is Cell Type-Specific and Exhibits Differential Hormonal Sensitivity for Down- and Up-Regulation. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 9746–9753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimojo, M. Differences in down-regulation of glucocorticoid receptor mRNA by cortisol, prednisolone and dexamethasone in HeLa cells. J. Med. Soc. Toho Univ. 1995, 42, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andreae, J.; Tripmacher, R.; Weltrich, R.; Rohde, W.; Keitzer, R.; Wahn, U.; Paul, K.; Buttgereit, F. Effect of glucocorticoid therapy on glucocorticoid receptors in children with autoimmune diseases. Pediatr. Res. 2001, 49, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peeters, R.P.; Hagendorf, A.; Vanhorebeek, I.; Visser, T.J.; Klootwijk, W.; Mesotten, D.; Wouters, P.J.; Koper, J.W.; De Jong, F.H.; Feelders, R.A.; et al. Tissue mRNA expression of the glucocorticoid receptor and its splice variants in fatal critical illness. Clin. Endocrinol. 2009, 71, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berki, T.; Tavakoli, A.; Nagy, K.K.; Nagy, G.; Németh, P. Alterations of glucocorticoid receptor expression during glucocorticoid hormone therapy in renal transplant patients. Transpl. Int. 2002, 15, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urzua, C.A.; Guerrero, J.; Gatica, H.; Velasquez, V.; Goecke, A. Evaluation of the glucocorticoid receptor as a biomarker of treatment response in Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada disease. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2017, 58, 974–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vandevyver, S.; Dejager, L.; Libert, C. Comprehensive overview of the structure and regulation of the glucocorticoid receptor. Endocr. Rev. 2014, 35, 671–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turner, J.D.; Alt, S.R.; Cao, L.; Vernocchi, S.; Trifonova, S.; Battello, N.; Muller, C.P. Transcriptional control of the glucocorticoid receptor: CpG islands, epigenetics and more. Biochem Pharmacol 2010, 80, 1860–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gatta, E.; Saudagar, V.; Auta, J.; Grayson, D.R.; Guidotti, A. Epigenetic landscape of stress surfeit disorders: Key role for DNA methylation dynamics. Int. Rev. Neurobiol 2021, 156, 127. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Turecki, G.; Meaney, M.J. Effects of the social environment and stress on glucocorticoid receptor gene methylation: A systematic review. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 79, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mifsud, K.R.; Saunderson, E.A.; Spiers, H.; Carter, S.D.; Trollope, A.F.; Mill, J.; Reul, J.M.H.M. Rapid downregulation of glucocorticoid receptor gene expression in the dentate gyrus after acute stress in vivo: Role of DNA Methylation and microRNA Activity. Neuroendocrinology 2017, 104, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, J.A.; Lyons, V.; Jacobson, M.D.; Noble, J.; Diorio, J.; Nyirenda, M.; Weaver, S.; Ester, W.; Yau, J.L.W.; Meaney, M.J.; et al. 5′-heterogeneity of glucocorticoid receptor messenger RNA is tissue specific: Differential regulation of variant transcripts by early-life events. Mol. Endocrinol. 2000, 14, 506–517. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Witzmann, S.R.; Turner, J.D.; Mériaux, S.B.; Meijer, O.C.; Muller, C.P. Epigenetic regulation of the glucocorticoid receptor promoter 1(7) in adult rats. Epigenetics 2012, 7, 1290–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nesset, K.A.; Perri, A.M.; Mueller, C.R. Frequent promoter hypermethylation and expression reduction of the glucocorticoid receptor gene in breast tumors. Epigenetics 2014, 9, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alt, S.R.; Turner, J.D.; Klok, M.D.; Meijer, O.C.; Lakke, E.A.; DeRijk, R.H.; Muller, C.P. Differential expression of glucocorticoid receptor transcripts in major depressive disorder is not epigenetically programmed. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2010, 35, 544–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.D.; Muller, C.P. Structure of the glucocorticoid receptor (NR3C1) gene 5′ untranslated region: Identification, and tissue distribution of multiple new human exon 1. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2005, 35, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burnstein, K.L.; Cidlowski, J.A. At the cutting edge: The down side of glucocorticoid receptor regulation. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1992, 83, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnstein, K.L.; Jewell, C.M.; Sar, M.; Cidlowski, J.A. Intragenic sequences of the human glucocorticoid receptor complementary DNA mediate hormone-inducible receptor messenger RNA down-regulation through multiple mechanisms. Mol. Endocrinol. 1994, 8, 1764–1773. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burnstein, K.L.; Bellingham, D.L.; Jewell, C.M.; Powell-Oliver, F.E.; Cidlowski, J.A. Autoregulation of glucocorticoid receptor gene expression. Steroids 1991, 56, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, G.; Paulen, L.; Chambon, P. GR SUMOylation and formation of a SUMO-SMRT/NCoR1-HDAC3 repressing complex is mandatory for GC-induced IR nGRE-mediated transrepression. Pharmacology 2015, 10, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hua, G.; Ganti, K.; Chambon, P. Glucocorticoid-induced tethered transrepression requires SUMOylation of GR and formation of a SUMO-SMRT / NCoR1-HDAC3 repressing complex. Pharmacology 2015, 10, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lim, L.P.; Lau, N.C.; Weinstein, E.G.; Abdelhakim, A.; Yekta, S.; Rhoades, M.W.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. The microRNAs of Caenorhabditis elgans. Genes Dev. 2003, 17, 991–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNA Target Recognition and Regulatory Functions. Trop. Grasslands 2010, 44, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bagga, S.; Bracht, J.; Hunter, S.; Massirer, K.; Holtz, J.; Eachus, R.; Pasquinelli, A.E. Regulation by let-7 and lin-4 miRNAs results in target mRNA degradation. Cell 2005, 122, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lam, J.K.W.; Chow, M.Y.T.; Zhang, Y.; Leung, S.W.S. siRNA versus miRNA as therapeutics for gene silencing. Mol. Ther. -Nucleic Acids 2015, 4, e252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riester, A.; Issler, O.; Spyroglou, A.; Rodrig, S.H.; Chen, A.; Beuschlein, F. ACTH-dependent regulation of MicroRNA as endogenous modulators of glucocorticoid receptor expression in the adrenal gland. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vreugdenhil, E.; Verissimo, C.S.L.; Mariman, R.; Kamphorst, J.T.; Barbosa, J.S.; Zweers, T.; Champagne, D.L.; Schouten, T.; Meijer, O.C.; De Ron Kloet, E.; et al. MicroRNA 18 and 124a down-regulate the glucocorticoid receptor: Implications for glucocorticoid responsiveness in the brain. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 2220–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liang, Y.N.; Tang, Y.L.; Ke, Z.Y.; Chen, Y.Q.; Luo, X.Q.; Zhang, H.; Huang, L.B. MiR-124 contributes to glucocorticoid resistance in acute lymphoblastic leukemia by promoting proliferation, inhibiting apoptosis and targeting the glucocorticoid receptor. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 172, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Gou, X.; Jiang, T.; Ouyang, J. The effects of microRNAs on glucocorticoid responsiveness. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 143, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, M.; Zhang, X.; Jia, H.; Li, D.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, H.; Hong, M.; Jiang, T.; Jiang, Q.; Lu, J.; et al. An oncogenic role of miR-142-3p in human T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) by targeting glucocorticoid receptor-α and cAMP/PKA pathways. Leukemia 2012, 26, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shimizu, S.; Tanaka, T.; Tohyama, M.; Miyata, S. Yokukansan normalizes glucocorticoid receptor protein expression in oligodendrocytes of the corpus callosum by regulating microRNA-124a expression after stress exposure. Brain Res. Bull. 2015, 114, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Gao, X.; Dykema, K.J.; Martin, K.R.; Ke, J.; Hudson, E.A.; Khoo, S.K.; Resau, J.H.; et al. Identification of a Lysosomal Pathway That Modulates Glucocorticoid Signaling and the Inflammatory Response. Sci. Signal. 2011, 4, ra44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kalimi, M. Role of lysosomotrophic reagents in glucocorticoid hormone action. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gen. Subj. 1986, 883, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbalagan, M.; Huderson, B.; Murphy, L.; Rowan, B.G. Post-Translational Modifications of Nuclear Receptors and Human Disease. Nucl. Recept. Signal. 2014, 10, nrs.10001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duma, D.; Jewell, C.M.; Cidlowski, J.A. Multiple glucocorticoid receptor isoforms and mechanisms of post-translational modification. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2006, 102, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Drean, Y.; Mincheneau, N.; Le Goff, P.; Michel, D. Potentiation of glucocorticoid receptor transcriptional activity by sumoylation. Endocrinology 2002, 143, 3482–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galliher-Beckley, A.J.; Williams, J.G.; Collins, J.B.; Cidlowski, J.A. Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3β-Mediated Serine Phosphorylation of the Human Glucocorticoid Receptor Redirects Gene Expression Profiles. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 7309–7322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ismaili, N.; Blind, R.; Garabedian, M.J. Stabilization of the unliganded glucocorticoid receptor by TSG101. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 11120–11126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; DeFranco, D.B. Alternative effects of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway on glucocorticoid receptor down-regulation and transactivation are mediated by CHIP, an E3 ligase. Mol. Endocrinol. 2005, 19, 1474–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paakinaho, V.; Kaikkonen, S.; Makkonen, H.; Benes, V.; Palvimo, J.J. SUMOylation regulates the chromatin occupancy and anti-proliferative gene programs of glucocorticoid receptor. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 1575–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Müller, S.; Hoege, C.; Pyrowolakis, G.; Jentsch, S. SUMO, ubiquitin’s mysterious cousin. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 2, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Druker, J.; Liberman, A.C.; Gerez, J.; Paez-pereda, M.; Rein, T.; Holsboer, F.; Arzt, E. RSUME Enhances Glucocorticoid Receptor SUMOylation and Transcriptional Activity. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2013, 33, 2116–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sha, T.; Hetti, P.; Palvimo, J.J.; Janne, O.A. Small ubiquitin-related modifier-1 (SUMO-1) modification of the glucocorticoid receptor. Biochem. J. 2002, 367, 907–911. [Google Scholar]
- Ramamoorthy, S.; Nawaz, Z. E6-associated protein (E6-AP) is a dual function coactivator of steroid hormone receptors. Nucl. Recept. Signal. 2008, 6, nrs-06006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.L.; DeVera, D.G.; Lamb, D.J.; Nawaz, Z.; Jiang, Y.-H.; Beaudet, A.L.; O’Malley, B.W. Genetic ablation of the steroid receptor coactivator-ubiquitin ligase, E6-AP, results in tissue-selective steroid hormone resistance and defects in reproduction. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 22, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garside, H.; Waters, C.; Berry, A.; Rice, L.; Ardley, H.C.; White, A.; Robinson, P.A.; Ray, D.W. UbcH7 interacts with the glucocorticoid receptor and mediates receptor autoregulation. J. Endocrinol. 2006, 190, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hittelman, A.B.; Burakov, D.; Iñiguez-Lluhí, J.A.; Freedman, L.P.; Garabedian, M.J. Differential regulation of glucocorticoid receptor transcriptional activation via AF-1-associated proteins. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 5380–5388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilkinson, L. Homologous Down-Regulation of the Glucocorticoid Receptor is Influenced by the Dimerization State of the Receptor. Ph.D. Thesis, Stellenbosch University, Stellenbosch, South Africa, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Metzger, M.B.; Hristova, V.A.; Weissman, A.M. HECT and RING finger families of E3 ubiquitin ligases at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joazeiro, C.A.P.; Weissman, A.M. RING finger proteins: Mediators of ubiquitin ligase activity. Cell 2000, 102, 549–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Helzer, K.T.; Hooper, C.; Miyamoto, S.; Alarid, E.T. Ubiquitylation of nuclear receptors: New linkages and therapeutic implications. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2015, 54, R151–R167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malyukova, A.; Brown, S.; Papa, R.; O’Brien, R.; Giles, J.; Trahair, T.N.; Dalla Pozza, L.; Sutton, R.; Liu, T.; Haber, M.; et al. FBXW7 regulates glucocorticoid response in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia by targeting the glucocorticoid receptor for degradation. Leukemia 2012, 27, 1053–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koepp, D.M.; Schaefer, L.K.; Ye, X.; Elledge, S.J. Phosphorylation-dependent ubiquitination of cyclin E by the SCFFbw7 ubiquitin ligase. Science 2001, 294, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballinger, C.A.; Connell, P.; Wu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Thompson, L.J.; Yin, L.Y.; Patterson, C. Identification of CHIP, a novel tetratricopeptide repeat-containing protein that interacts with heat shock proteins and negatively regulates chaperone functions. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 4535–4545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morishima, Y.; Wang, A.M.; Yu, Z.; Pratt, W.B.; Osawa, Y.; Lieberman, A.P. CHIP deletion reveals functional redundancy of E3 ligases in promoting degradation of both signaling proteins and expanded glutamine proteins. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2008, 17, 3942–3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, Z.; Li, G.; Shao, Q.; Yang, G.; Zheng, L. CHIP: A new modulator of human malignant disorders. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 29864–29874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paul, I.; Ghosh, M.K. The E3 Ligase CHIP: Insights into Its Structure and Regulation. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 918183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Connell, P.; Ballinger, C.A.; Jiang, J.; Wu, Y.; Thompson, L.J.; Höhfeld, J.; Patterson, C. The co-chaperone CHIP regulates protein triage decisions mediated by heat-shock proteins. Nat. Cell Biol. 2001, 3, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, S.; Wasylyk, B. Ligand-dependent interaction of the glucocorticoid receptor with p53 enhances their degradation by Hdm2. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 2367–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sengupta, S. Negative cross-talk between p53 and the glucocorticoid receptor and its role in neuroblastoma cells. EMBO J. 2002, 19, 6051–6064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davies, L.; Paraskevopoulou, E.; Sadeq, M.; Symeou, C.; Pantelidou, C.; Demonacos, C.; Krstic-Demonacos, M. Regulation of glucocorticoid receptor activity by a stress responsive transcriptional cofactor. Mol. Endocrinol. 2011, 25, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patt, M.; Gysi, J.; Faresse, N.; Cidlowski, J.A.; Odermatt, A. Protein phosphatase 1 alpha enhances glucocorticoid receptor activity by a mechanism involving phosphorylation of serine-211. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2020, 518, 110873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinyamu, H.K.; Archer, T.K. Estrogen Receptor-Dependent Proteasomal Degradation of the Glucocorticoid Receptor Is Coupled to an Increase in Mdm2 Protein Expression. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 5867–5881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petrillo, M.G.; Oakley, R.H.; Cidlowski, J.A. β-Arrestin-1 inhibits glucocorticoid receptor turnover and alters glucocorticoid signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 11225–11239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, R.; Theodoraki, M.A.; Caplan, A.J. Specificity in the actions of the UBR1 ubiquitin ligase in the degradation of nuclear receptors. FEBS Open Bio 2013, 3, 394–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vu, T.T.M.; Mitchell, D.C.; Gygi, S.P.; Varshavsky, A. The Arg/N-degron pathway targets transcription factors and regulates specific genes. Biochemistry 2020, 117, 31094–31104. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.; Xu, X.; Mao, C.Y.; Han, K.K.; Xu, Y.J.; Cao, B.Y.; Zhang, Z.B.; Sethi, G.; Tang, X.W.; Mao, X.L. RNF6 promotes myeloma cell proliferation and survival by inducing glucocorticoid receptor polyubiquitination. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2020, 41, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, S.J.; Taylor, J.L.; Batdorf, H.M.; Noland, R.C.; Burk, D.H.; Yu, Y.; Elizabeth Floyd, Z.; Jason Collier, J. The ubiquitin ligase siah2 negatively regulates glucocorticoid receptor activity and abundance. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avenant, C.; Ronacher, K.; Stubsrud, E.; Louw, A.; Hapgood, J.P. Role of ligand-dependent GR phosphorylation and half-life in determination of ligand-specific transcriptional activity. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2010, 327, 72–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strohmaier, H.; Spruck, C.H.; Kaiser, P.; Won, K.A.; Sangfelt, O.; Reed, S.I. Human F-box protein hCdc4 targets cyclin E for proteolysis and is mutated in a breast cancer cell line. Nature 2001, 413, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.F.; Toft, D.O. Steroid receptors and their associated proteins. Mol. Endocrinol. 1993, 7, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pratt, W.B.; Morishima, Y.; Osawa, Y. The Hsp90 Chaperone Machinery Regulates Signaling by Modulating Ligand Binding Clefts. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 22885–22889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morishima, Y.; Mehta, R.K.; Yoshimura, M.; Lau, M.; Southworth, D.R.; Lawrence, T.S.; Pratt, W.B.; Nyati, M.K.; Osawa, Y. Chaperone Activity and Dimerization Properties of Hsp90 a and Hsp90 b in Glucocorticoid Receptor Activation by the Multiprotein Hsp90 / Hsp70-Dependent Chaperone Machinery. Mol. Pharmacol. 2018, 90, 984–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tateishi, Y.; Kawabe, Y.I.; Chiba, T.; Murata, S.; Ichikawa, K.; Murayama, A.; Tanaka, K.; Baba, T.; Kato, S.; Yanagisawa, J. Ligand-dependent switching of ubiquitin-proteasome pathways for estrogen receptor. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 4813–4823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.; Jin, W.; Shao-Cong, S. Peli1 facilitates TRIF-dependent Toll-like receptor signaling and proinflammatory cytokine production. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 1089–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, M.; Jin, W.; Chang, J.-H.; Xiao, Y.; Brittain, G.; Yu, J.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Y.-H.; Cheng, X.; Li, P.; et al. Peli1 negatively regulates T-cell activation and prevents autoimmunity. Nat. Immunol. 2012, 12, 1002–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, D.; Tavana, O.; Sun, S.-C.; Gu, W. Peli1 modulates the subcellular localization and activity of Mdmx. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 2897–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, C.W.; Ryu, K.Y. Cellular ubiquitin pool dynamics and homeostasis. BMB Rep. 2014, 47, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Theodoraki, M.A.; Caplan, A.J. Quality control and fate determination of Hsp90 client proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2012, 1823, 683–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sultana, R.; Theodoraki, M.A.; Caplan, A.J. UBR1 promotes protein kinase quality control and sensitizes cells to Hsp90 inhibition. Exp. Cell Res. 2012, 318, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lambert, S.A.; Jolma, A.; Campitelli, L.F.; Das, P.K.; Yin, Y.; Albu, M.; Chen, X.; Taipale, J.; Hughes, T.R.; Weirauch, M.T. The Human Transcription Factors. Cell 2018, 172, 650–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, K.; Shimelis, H.; Linn, D.E.; Jiang, R.; Yang, X.; Sun, F.; Guo, Z.; Chen, H.; Li, W.; Chen, H.; et al. Regulation of androgen receptor transcriptional activity and specificity by RNF6-induced ubiquitination. Cancer Cell 2010, 15, 270–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, Q.; Ma, D.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Z.; Sun, T.T.; Shen, C.; Yan, T.; Tian, X.; Yu, T.C.; Guo, F.; et al. RING-finger protein 6 amplification activates JAK/STAT3 pathway by modifying SHP-1 ubiquitylation and associates with poor outcome in colorectal cancer Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 1473–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Han, K.; Tang, X.; Zeng, Y.; Lin, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, B.; Wu, D.; Mao, X. The ring finger protein RNF6 induces leukemia cell proliferation as a direct target of pre-b-cell leukemia homeobox 1. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 9617–9628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kilroy, G.; Carter, L.E.; Newman, S.; Burk, D.H.; Manuel, J.; Möller, A.; Bowtell, D.D.; Mynatt, R.L.; Ghosh, S.; Floyd, Z.E. The ubiquitin ligase Siah2 regulates obesity-induced adipose tissue inflammation. Obesity 2015, 23, 2223–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kilroy, G.; Burk, D.H.; Floyd, Z.E. Siah2 protein mediates early events in commitment to an adipogenic pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 27289–27297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schulz, M.; Eggert, M.; Baniahmad, A.; Dostert, A.; Heinzel, T.; Renkawitz, R. RU486-induced glucocorticoid receptor agonism is controlled by the receptor N terminus and by corepressor binding. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 26238–26243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galigniana, M.D.; Echeverría, P.C.; Erlejman, A.G.; Piwien-Pilipuk, G. Role of molecular chaperones and TPR-domain proteins in the cytoplasmic transport of steroid receptors and their passage through the nuclear pore. Nucleus 2010, 1, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fang, L.; Ricketson, D.; Getubig, L.; Darimont, B. Unliganded and hormone-bound glucocorticoid receptors interact with distinct hydrophobic sites in the Hsp90 C-terminal domain. Biochemistry 2006, 103, 18487–18492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kirschke, E.; Goswami, D.; Southworth, D.; Griffin, P.R.; Agard, D.A. Glucocorticoid Receptor Function Regulated by Coordinated Action of the Hsp90 and Hsp70 Chaperone Cycles. Cell 2015, 157, 1685–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaziales, A.; Barkovits, K.; Marcus, K.; Richter, K. Glucocorticoid receptor complexes form cooperatively with the Hsp90 cochaperones Pp5 and FKBPs. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickner, S.; Maurizi, M.R.; Gottesman, S. Posttranslational quality control: Folding, refolding, and degrading proteins. Science 1999, 286, 1888–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichardt, S.D.; Föller, M.; Rexhepaj, R.; Pathare, G.; Minnich, K.; Tuckermann, J.P.; Lang, F.; Reichardt, H.M. Glucocorticoids enhance intestinal glucose uptake via the dimerized glucocorticoid receptor in enterocytes. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 1783–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wüst, S.; Tischner, D.; John, M.; Tuckermann, J.P.; Menzfeld, C.; Hanisch, U.K.; van den Brandt, J.; Lühder, F.; Reichardt, H.M. Therapeutic and adverse effects of a non-steroidal glucocorticoid receptor ligand in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e8202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heck, S.; Kullmann, M.; Gast, A.; Ponta, H.; Rahmsdorf, H.J.; Herrlich, P.; Cato, A.C. A distinct modulating domain in glucocorticoid receptor monomers in the repression of activity of the transcription factor AP-1. EMBO J. 1994, 13, 4087–4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louw, A.; Swart, P. Salsola tuberculatiformis Botschantzev and an Aziridine Precursor Analog Mediate the in Vivo Increase in Free Corticosterone and Decrease in Corticosteroid-Binding Globulin in Female Wistar Rats. Endocrinology 1999, 140, 2044–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louw, A.; Swart, P.; Allie, F. Influence of an aziridine precursor on the in vitro binding parameters of rat and ovine corticosteroid-binding globulin (CBG). Biochem. Pharmacol. 2000, 59, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, K.C.; Grunwitz, C.R.; Kaminski, B.M.; Steinhilber, D.; Radeke, H.; Stein, J. Selective Glucocorticoid Receptor Agonists for the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Studies in Mice with Acute Trinitrobenzene Sulfonic Acid Colitis. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2012, 341, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Presman, D.M.; Ogara, M.F.; Stortz, M.; Alvarez, L.D.; Pooley, J.R.; Schiltz, R.L.; Grøntved, L.; Johnson, T.A.; Mittelstadt, P.R.; Ashwell, J.D.; et al. Live Cell Imaging Unveils Multiple Domain Requirements for In Vivo Dimerization of the Glucocorticoid Receptor. PLoS Biol. 2014, 12, e1001813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robertson, S.; Rohwer, J.M.; Hapgood, J.P.; Louw, A. Impact of Glucocorticoid Receptor Density on Ligand-Independent Dimerization, Cooperative Ligand-Binding and Basal Priming of Transactivation: A Cell Culture Model. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Robertson, S.; Allie-Reid, F.; Berghe, W.V.; Visser, K.; Binder, A.; Africander, D.; Vismer, M.; De Bosscher, K.; Hapgood, J.; Haegeman, G.; et al. Abrogation of Glucocorticoid Receptor Dimerization Correlates with Dissociated Glucocorticoid Behavior of Compound A. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 8061–8075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gossye, V.; Elewaut, D.; Van Beneden, K.; Dewint, P.; Haegeman, G.; De Bosscher, K. A plant-derived glucocorticoid receptor modulator attenuates inflammation without provoking ligand-induced resistance. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 69, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Glantschnig, C.; Koenen, M.; Gil-Lozano, M.; Karbiener, M.; Pickrahn, I.; Williams-Dautovich, J.; Patel, R.; Cummins, C.L.; Giroud, M.; Hartleben, G.; et al. A miR-29a-driven negative feedback loop regulates peripheral glucocorticoid receptor signaling. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 5924–5941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichardt, H.M.; Kaestner, K.H.; Tuckermann, J.; Kretz, O.; Wessely, O.; Bock, R.; Gass, P.; Schmid, W.; Herrlich, P.; Angel, P.; et al. DNA binding of the glucocorticoid receptor is not essential for survival. Cell 1998, 93, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tiwari, M.; Oasa, S.; Yamamoto, J.; Mikuni, S.; Kinjo, M. A Quantitative Study of Internal and External Interactions of Homodimeric Glucocorticoid Receptor Using Fluorescence Cross-Correlation Spectroscopy in a Live Cell. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oasa, S.; Sasaki, A.; Yamamoto, J.; Mikuni, S.; Kinjo, M. Homodimerization of glucocorticoid receptor from single cells investigated using fluorescence correlation spectroscopy and microwells. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 2171–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frijters, R.; Fleuren, W.; Toonen, E.J.M.; Tuckermann, J.P.; Reichardt, H.M.; van der Maaden, H.; van Elsas, A.; van Lierop, M.J.; Dokter, W.; de Vlieg, J.; et al. Prednisolone-induced differential gene expression in mouse liver carrying wild type or a dimerization-defective glucocorticoid receptor. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalvisa, A.; Siersbæk, M.S.; Præstholm, S.M.; Christensen, L.J.L.; Nielsen, R.; Stohr, O.; Vettorazzi, S.; Tuckermann, J.; White, M.; Mandrup, S.; et al. Insulin signaling and reduced glucocorticoid receptor activity attenuate postprandial gene expression in liver. PLoS Biol. 2018, 16, e2006249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoeck, W.; Rusconi, S.; Groner, B. Down-regulation and phosphorylation of glucocorticoid receptors in cultured cells. Investigations with a monospecific antiserum against a bacterially expressed fragment. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 14396–14402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presman, D.M.; Alvarez, L.D.; Levi, V.; Eduardo, S.; Digman, M.A.; Martí, M.A.; Veleiro, A.S.; Burton, G.; Pecci, A. Insights on glucocorticoid receptor activity modulation through the binding of rigid steroids. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parsonnet, N.V.; Lammer, N.C.; Holmes, Z.E.; Batey, R.T.; Wuttke, D.S. The glucocorticoid receptor DNA-binding domain recognizes RNA hairpin structures with high affinity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 8180–8192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kino, M.; Hur, D.E.; Ichijo, T.; Nader, N.; Chrousos, G.P. Noncoding, RNA.gas5 is a growth arrest- and starvation-associated repressor of the glucocorticoid receptor. Sci. Signal. 2010, 3, ra8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hudson, W.H.; Pickard, M.R.; de Vera, I.M.S.; Kuiper, E.G.; Mourtada-Maarabouni, M.; Conn, G.L.; Kojetin, D.J.; Williams, G.T.; Ortlund, E.A. Conserved sequence-specific lincRNA-steroid receptor interactions drive transcriptional repression and direct cell fate. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spies, L.-M.L. The Effect of Glucocorticoid Receptor Alpha Dimerization State on Receptor Turnover. Master’s Thesis, Stellenbosch University, Stellenbosch, South Africa, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Clayton, S.A.; Jones, S.W.; Kurowska-Stolarska, M.; Clark, A.R. The role of microRNAs in glucocorticoid action. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 1865–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.J.; Shizu, R.; Negishi, M. Glucocorticoid receptor dimerization in the cytoplasm might be essential for nuclear localization. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 553, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Jin, J.; Schlisio, S.; Harper, J.W.; Kaelin, W.G.J. The v-Jun point mutation allows c-Jun to escape GSK3-dependent recognition and destruction by the Fbw7 ubiquitin ligase. Cancer Cell 2005, 8, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, Y.; Sangfelt, O.; Spruck, C. The Fbxw7/hCdc4 tumor suppressor in human cancer. Cancer Lett. 2008, 271, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäcke, H.; Döcke, W.-D.; Asadullah, K. Mechanisms involved in the side effects of glucocorticoids. Pharmacol. Ther. 2002, 96, 23–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Ramírez, P.; Tliba, O. Glucocorticoid Receptor β (GRβ): Beyond Its Dominant-Negative Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tago, K.; Tsukahara, F.; Naruse, M.; Yoshioka, T.; Takano, K. Regulation of nuclear retention of glucocorticoid receptor by nuclear Hsp90. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2004, 213, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reits, E.A.J.; Benham, A.M.; Plougastel, B.; Neefjes, J.; Trowsdale, J. Dynamics of proteasome distribution in living cells. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 6087–6094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ádori, C.; Lőw, P.; Moszkovkin, G.; Bagdy, G.; László, L.; Kovács, G.G. Subcellular Distribution of Components of the Ubiquitin-Proteasome System in Non-diseased Human and Rat Brain. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2006, 54, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Savulescu, A.; Shorer, H.; Kleifeld, O.; Cohen, I.; Gruber, R.; Glickman, M.H.; Harel, A. Nuclear import of an intact preassembled proteasome particle. Mol. Biol. Cell 2011, 22, 880–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, I.M.E.; Vanden Berghe, W.; Vermeulen, L.; Yamamoto, K.R.; Haegeman, G.; De Bosscher, K. Crosstalk in inflammation: The interplay of glucocorticoid receptor-based mechanisms and kinases and phosphatases. Endocr. Rev. 2009, 30, 830–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bosscher, K.; Haegeman, G.; Elewaut, D. Targeting inflammation using selective glucocorticoid receptor modulators. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2010, 10, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somvanshi, P.; Mellon, S.; Yehuda, R.; Flory, J.D.; Makotkine, I.; Bierer, L.; Marmar, C.; Jett, M.; Doyle, F.J. Role of enhanced glucocorticoid receptor sensitivity in inflammation in PTSD: Insights from computational model for circadian-neuendocrine-immune interactions. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 319, 48–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Name | Type of UPS Enzyme | GRα Ligand-Binding Status | GRα Phosphorylation Status | Effect on GRα Protein Level | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UbcH7 | E2 conjugating enzyme | Liganded | Hyperphosphorylated | Reduce | [119] |
| TSG101 | Inactive E2 conjugating enzyme | Unliganded | Hypophosphorylated | Stabilize | [111,120,121] |
| FBXW7α | E3 ligase (RING finger family) [122,123,124] | Liganded | Hyperphosphorylated | Reduce | [69,121,124,125,126] |
| CHIP | Ligand-independent | Phosphorylation-independent | Reduce | [112,124,127,128,129,130,131] | |
| Mdm2/Hdm2 | Ligand-independent but requires p53 | Phosphorylation-independent | Reduce | [124,132,133,134,135,136] | |
| Pellino-1 | Liganded | Hyperphosphorylated | Reduce | [137] | |
| UBR1 | Unliganded | Hypophosphorylated | Reduce | [124,138,139] | |
| RNF6 | Ligand-independent | Phosphorylation-independent | Stabilize | [140] | |
| Siah2 | Ligand-independent | Hyperphosphorylated | Reduce | [141] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Spies, L.-M.L.; Verhoog, N.J.D.; Louw, A. Acquired Glucocorticoid Resistance Due to Homologous Glucocorticoid Receptor Downregulation: A Modern Look at an Age-Old Problem. Cells 2021, 10, 2529. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102529
Spies L-ML, Verhoog NJD, Louw A. Acquired Glucocorticoid Resistance Due to Homologous Glucocorticoid Receptor Downregulation: A Modern Look at an Age-Old Problem. Cells. 2021; 10(10):2529. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102529
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpies, Lee-Maine L., Nicolette J. D. Verhoog, and Ann Louw. 2021. "Acquired Glucocorticoid Resistance Due to Homologous Glucocorticoid Receptor Downregulation: A Modern Look at an Age-Old Problem" Cells 10, no. 10: 2529. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102529
APA StyleSpies, L.-M. L., Verhoog, N. J. D., & Louw, A. (2021). Acquired Glucocorticoid Resistance Due to Homologous Glucocorticoid Receptor Downregulation: A Modern Look at an Age-Old Problem. Cells, 10(10), 2529. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102529






