Neuron–Glia Interaction in the Developing and Adult Enteric Nervous System
Abstract
1. Introduction
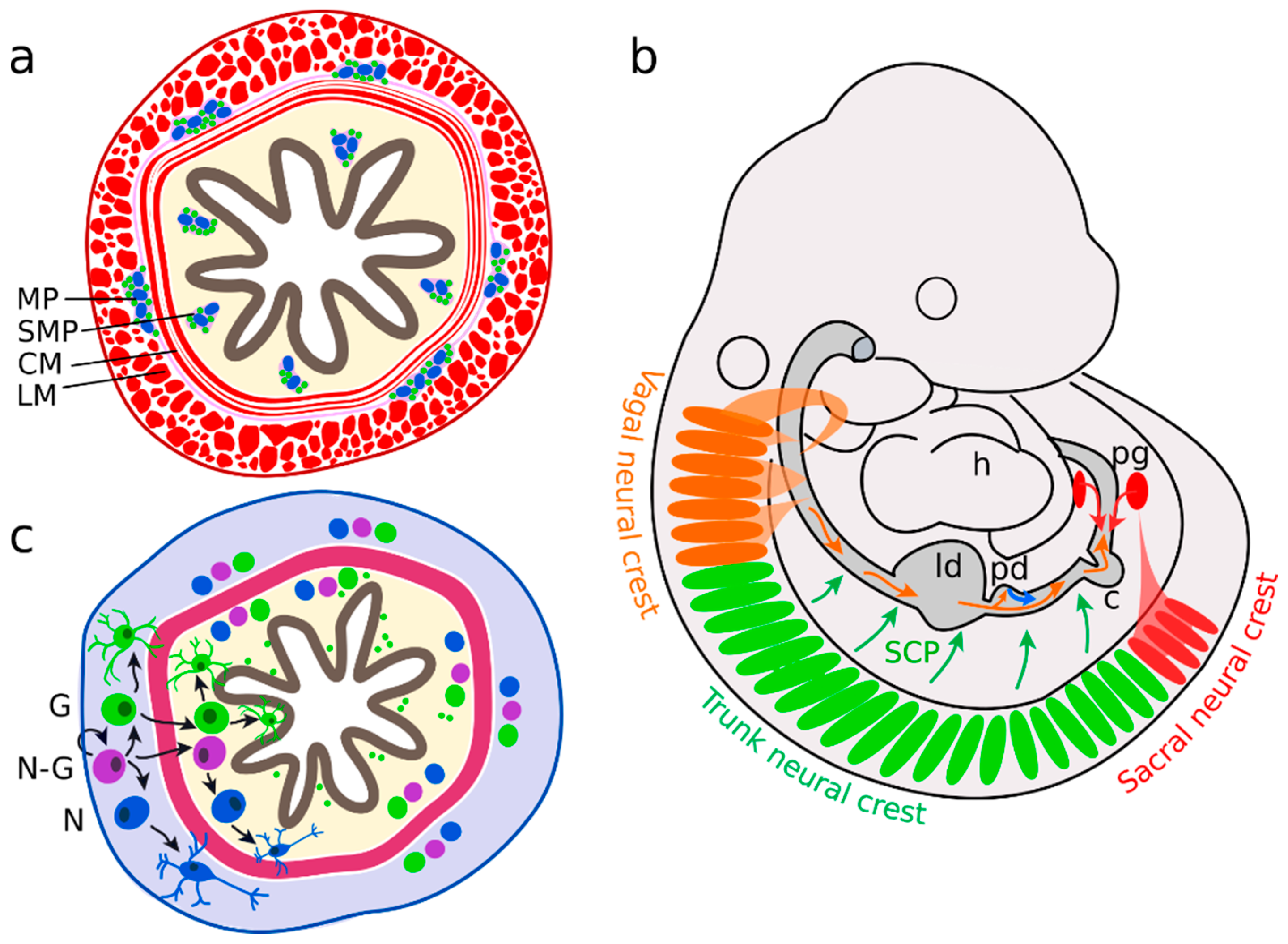
2. Neurons and Glia during Enteric Nervous System (ENS) Formation
2.1. Neural Precursors Arise from Multiple Sources
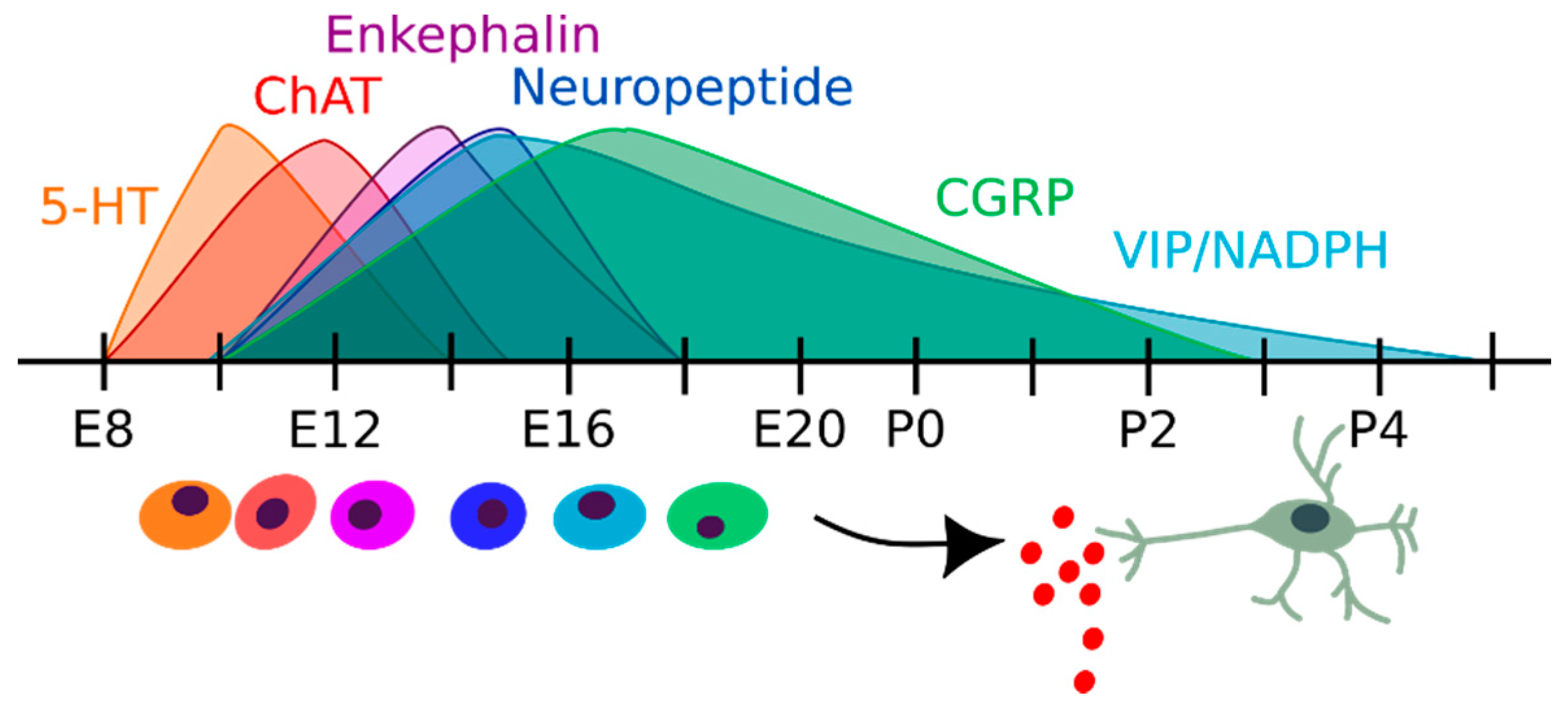
2.2. Enteric Neurons
2.3. Enteric Glial Cells
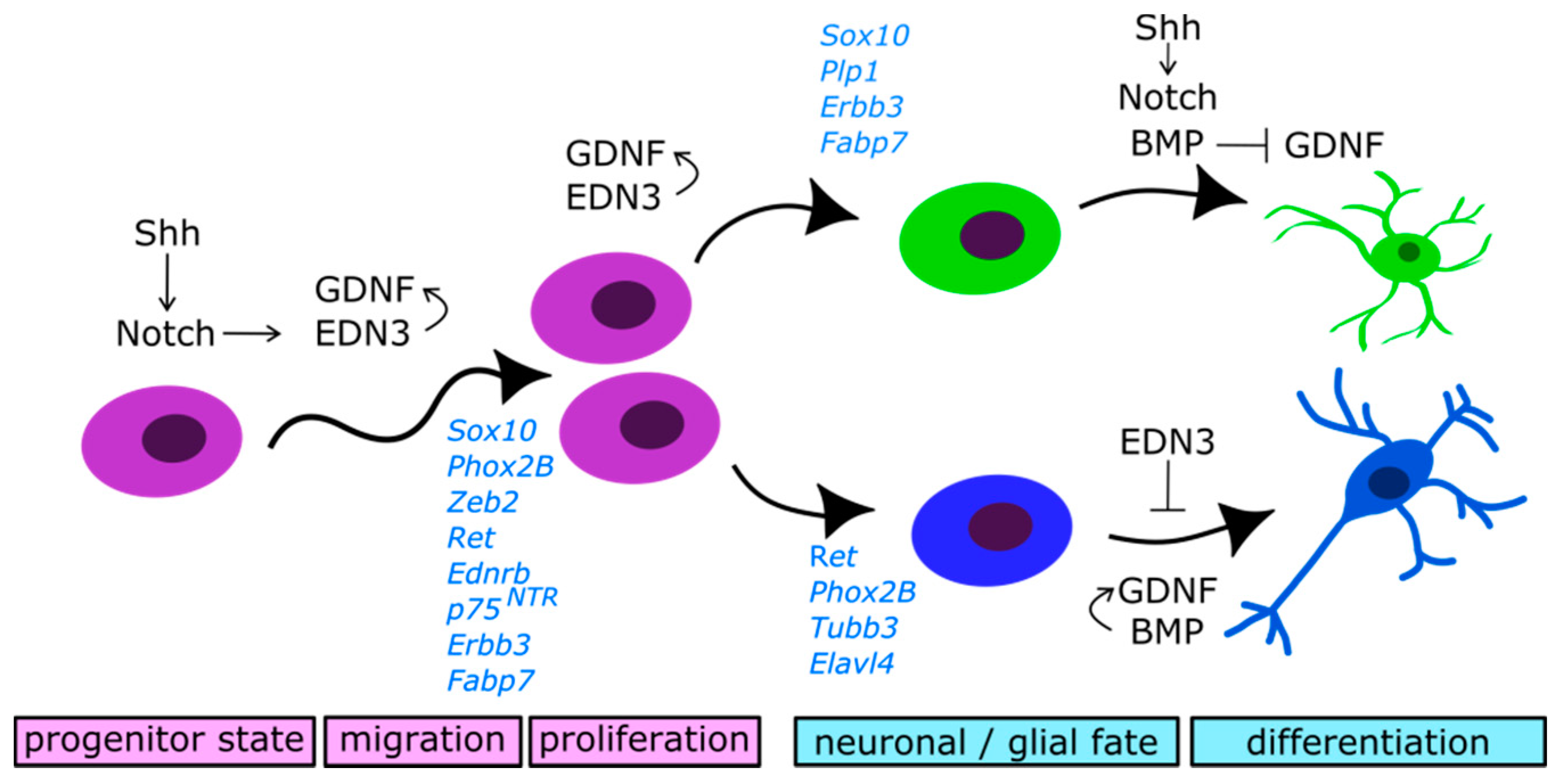
2.4. Molecular Control of Neural Precursors Migration and Differentiation
2.4.1. Glial Cell-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (GDNF)/RET Signalling
2.4.2. Endothelin 3/Endothelin Receptor Type B (EDN3/EDNRB) Signalling
2.4.3. Notch Signalling
2.4.4. Bone Morphogenetic Proteins (BMP) Signalling
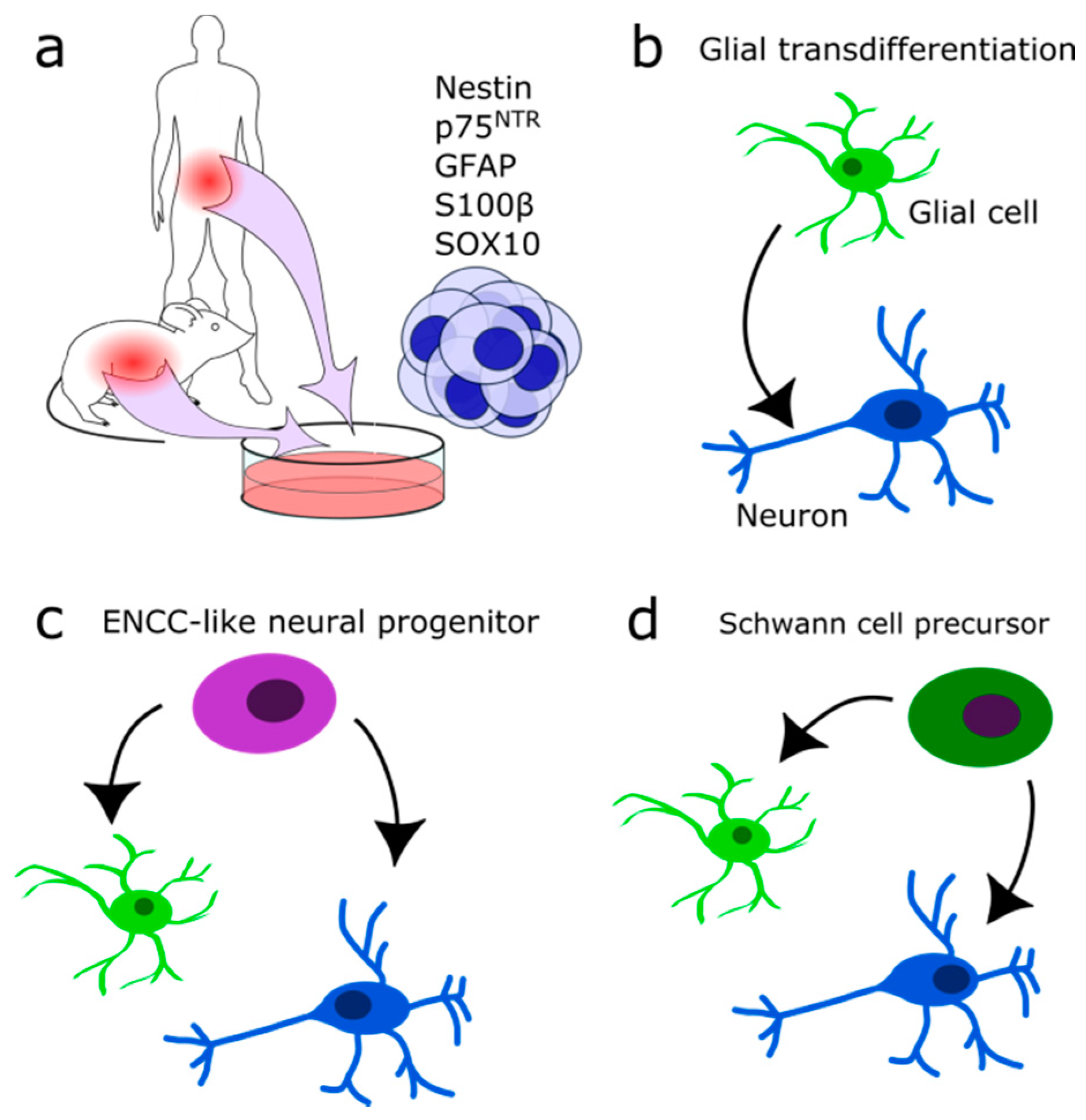
3. Neurons and Glial Cells in the Adult ENS
4. Diseases of the ENS and Therapeutic Approaches
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Furness, J.B.; Stebbing, M.J. The First Brain: Species Comparisons and Evolutionary Implications for the Enteric and Central Nervous Systems. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2018, 30, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furness, J.B. Enteric Nervous System. Scholarpedia 2007, 2, 4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, S.; Wright, C.M.; Heuckeroth, R.O. Unexpected Roles for the Second Brain: Enteric Nervous System as Master Regulator of Bowel Function. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2019, 81, 235–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beutler, L.R.; Chen, Y.; Ahn, J.S.; Lin, Y.C.; Essner, R.A.; Knight, Z.A. Dynamics of Gut-Brain Communication Underlying Hunger. Neuron 2017, 96, 461–475.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaelberer, M.M.; Buchanan, K.L.; Klein, M.E.; Barth, B.B.; Montoya, M.M.; Shen, X.; Bohórquez, D.V. A Gut-Brain Neural Circuit for Nutrient Sensory Transduction. Science 2018, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, W.; Tellez, L.A.; Perkins, M.H.; Perez, I.O.; Qu, T.; Ferreira, J.; Ferreira, T.L.; Quinn, D.; Liu, Z.W.; Gao, X.B.; et al. A Neural Circuit for Gut-Induced Reward. Cell 2018, 175, 665–678.e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suarez, A.N.; Hsu, T.M.; Liu, C.M.; Noble, E.E.; Cortella, A.M.; Nakamoto, E.M.; Hahn, J.D.; De Lartigue, G.; Kanoski, S.E. Gut Vagal Sensory Signaling Regulates Hippocampus Function through Multi-Order Pathways. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obata, Y.; Castaño, Á.; Boeing, S.; Bon-Frauches, A.C.; Fung, C.; Fallesen, T.; de Agüero, M.G.; Yilmaz, B.; Lopes, R.; Huseynova, A.; et al. Neuronal Programming by Microbiota Regulates Intestinal Physiology. Nature 2020, 578, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vadder, F.; Grasset, E.; Holm, L.M.; Karsenty, G.; Macpherson, A.J.; Olofsson, L.E.; Bäckhed, F. Gut Microbiota Regulates Maturation of the Adult Enteric Nervous System via Enteric Serotonin Networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 6458–6463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibiza, S.; García-Cassani, B.; Ribeiro, H.; Carvalho, T.; Almeida, L.; Marques, R.; Misic, A.M.; Bartow-Mckenney, C.; Larson, D.M.; Pavan, W.J.; et al. Glial-Cell-Derived Neuroregulators Control Type 3 Innate Lymphoid Cells and Gut Defence. Nature 2016, 535, 440–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalazonitis, A.; Rao, M. Enteric Nervous System Manifestations of Neurodegenerative Disease. Brain Res. 2018, 1693, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endres, K.; Schäfer, K.H. Influence of Commensal Microbiota on the Enteric Nervous System and Its Role in Neurodegenerative Diseases. J. Innate Immun. 2018, 10, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, S.; Ganz, J.; Bayrer, J.; Becker, L.; Bogunovic, M.; Rao, M. Advances in Enteric Neurobiology: The “Brain” in the Gut in Health and Disease. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 9346–9354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Soto, W.; Gulbransen, B.D. Enteric Glia: A New Player in Abdominal Pain. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 7, 433–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godlewski, J.; Kmiec, Z. Colorectal Cancer Invasion and Atrophy of the Enteric Nervous System: Potential Feedback and Impact on Cancer Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, P.A.; Schneeberger, M.; Matheis, F.; Wang, P.; Kerner, Z.; Ilanges, A.; Pellegrino, K.; Mármol, J.; Castro, T.B.R.; Furuichi, M.; et al. Microbiota Modulate Sympathetic Neurons via a Gut—Brain Circuit. Nature 2020, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furness, J.B. The Enteric Nervous System and Neurogastroenterology. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 9, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Berre-Scoul, C.; Chevalier, J.; Oleynikova, E.; Cossais, F.; Talon, S.; Neunlist, M.; Boudin, H. A Novel Enteric Neuron–Glia Coculture System Reveals the Role of Glia in Neuronal Development. J. Physiol. 2017, 595, 583–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, N.J.; Lyons, D.A. Glia as Architects of Central Nervous System Formation and Function. Science 2018, 185, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasel, P.; Dando, O.; Jiwaji, Z.; Baxter, P.; Todd, A.C.; Heron, S.; Márkus, N.M.; McQueen, J.; Hampton, D.W.; Torvell, M.; et al. Neurons and Neuronal Activity Control Gene Expression in Astrocytes to Regulate Their Development and Metabolism. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubé, A.C.; Cabarrocas, J.; Bauer, J.; Philippe, D.; Aubert, P.; Doulay, F.; Liblau, R.; Galmiche, J.P.; Neunlist, M. Changes in Enteric Neurone Phenotype and Intestinal Functions in a Transgenic Mouse Model of Enteric Glia Disruption. Gut 2006, 55, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdo, H.; Mahé, M.M.; Derkinderen, P.; Bach-Ngohou, K.; Neunlist, M.; Lardeux, B. The Omega-6 Fatty Acid Derivative 15-Deoxy-Δ12,14-Prostaglandin J2 Is Involved in Neuroprotection by Enteric Glial Cells against Oxidative Stress. J. Physiol. 2012, 590, 2739–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimou, L.; Götz, M. Glial Cells as Progenitors and Stem Cells: New Roles in the Healthy and Diseased Brain. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 709–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, M.; Gershon, M.D. Enteric Nervous System Development: What Could Possibly Go Wrong? Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2018, 19, 552–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obermayr, F.; Hotta, R.; Enomoto, H.; Young, H.M. Development and Developmental Disorders of the Enteric Nervous System. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heanue, T.A.; Pachnis, V. Enteric Nervous System Development and Hirschsprung’s Disease: Advances in Genetic and Stem Cell Studies. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 8, 466–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lake, J.I.; Heuckeroth, R.O. Enteric Nervous System Development: Migration, Differentiation, and Disease. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2013, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronner, M.E. Formation and Migration of Neural Crest Cells in the Vertebrate Embryo. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 138, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Douarin, N.M.; Kalcheim, C. The Neural Crest; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein, A.M.; Hofstra, R.M.W.; Burns, A.J. Building a Brain in the Gut: Development of the Enteric Nervous System. Clin. Genet. 2013, 83, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigetani, Y.; Aizawa, S.; Kuratani, S. Overlapping Origins of Pharyngeal Arch Crest Cells on the Postotic Hind-Brain. Dev. Growth Differ. 1995, 37, 733–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa-Medina, I.; Jevans, B.; Boismoreau, F.; Chettouh, Z.; Enomoto, H.; Müller, T.; Birchmeier, C.; Burns, A.J.; Brunet, J.F. Dual Origin of Enteric Neurons in Vagal Schwann Cell Precursors and the Sympathetic Neural Crest. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 11980–11985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simkin, J.E.; Zhang, D.; Stamp, L.A.; Newgreen, D.F. Fine Scale Differences within the Vagal Neural Crest for Enteric Nervous System Formation. Dev. Biol. 2019, 446, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durbec, P.L.; Larsson-Blomberg, L.B.; Schuchardt, A.; Costantini, F.; Pachnis, V. Common Origin and Developmental Dependence on C-Ret of Subsets of Enteric and Sympathetic Neuroblasts. Development 1996, 122, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Young, H.M.; Bergner, A.J.; Simpson, M.J.; McKeown, S.J.; Hao, M.M.; Anderson, C.R.; Enomoto, H. Colonizing While Migrating: How Do Individual Enteric Neural Crest Cells Behave? BMC Biol. 2014, 12, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, A.J.; Le Douarin, N.M. The Sacral Neural Crest Contributes Neurons and Glia to the Post-Umbilical Gut: Spatiotemporal Analysis of the Development of the Enteric Nervous System. Development 1998, 125, 4335–4347. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Chan, A.K.K.; Sham, M.H.; Burns, A.J.; Chan, W.Y. Analysis of the Sacral Neural Crest Cell Contribution to the Hindgut Enteric Nervous System in the Mouse Embryo. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 992–1002.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothman, T.P.; Gershon, M.D. Regionally Defective Colonization of the Terminal Bowel by the Precursors of Enteric Neurons in Lethal Spotted Mutant Mice. Neuroscience 1984, 12, 1293–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branchek, T.A.; Gershon, M.D. Time Course of Expression of Neuropeptide Y, Calcitonin Gene-related Peptide, and NADPH Diaphorase Activity in Neurons of the Developing Murine Bowel and the Appearance of 5-hydroxytryptamine in Mucosal Enterochromaffin Cells. J. Comp. Neurol. 1989, 285, 262–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, H.M.; Jones, B.R.; Mckeown, S.J. The Projections of Early Enteric Neurons Are Influenced by the Direction of Neural Crest Cell Migration. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 6005–6018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.D.; Gershon, M.D.; Rothman, T.P. Time of Origin of Neurons in the Murine Enteric Nervous System: Sequence in Relation to Phenotype. J. Comp. Neurol. 1991, 314, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hughes, I.; Planer, W.; Parsadanian, A.; Grider, J.R.; Vohra, B.P.S.; Keller-Peck, C.; Heuckeroth, R.O. The Timing and Location of Glial Cell Line-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Expression Determine Enteric Nervous System Structure and Function. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 1523–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, A.J.; Le Douarin, N.M. Enteric Nervous System Development: Analysis of the Selective Developmental Potentialities of Vagal and Sacral Neural Crest Cells Using Quail-Chick Chimeras. Anat. Rec. 2001, 262, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brokhman, I.; Xu, J.; Coles, B.L.K.; Razavi, R.; Engert, S.; Lickert, H.; Babona-Pilipos, R.; Morshead, C.M.; Sibley, E.; Chen, C.; et al. Dual Embryonic Origin of the Mammalian Enteric Nervous System. Dev. Biol. 2019, 445, 256–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchins, E.J.; Kunttas, E.; Piacentino, M.L.; Howard, A.G.A.; Bronner, M.E.; Uribe, R.A. Migration and Diversification of the Vagal Neural Crest. Dev. Biol. 2018, 444, S98–S109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, H.L.; Grapin-Botton, A. The Molecular and Morphogenetic Basis of Pancreas Organogenesis. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 66, 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uesaka, T.; Nagashimada, M.; Enomoto, H. Neuronal Differentiation in Schwann Cell Lineage Underlies Postnatal Neurogenesis in the Enteric Nervous System. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 9879–9888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, H.M.; Bergner, A.J.; Anderson, R.B.; Enomoto, H.; Milbrandt, J.; Newgreen, D.F.; Whitington, P.M. Dynamics of Neural Crest-Derived Cell Migration in the Embryonic Mouse Gut. Dev. Biol. 2004, 270, 455–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasrado, R.; Boesmans, W.; Kleinjung, J.; Pin, C.; Bell, D.; Bhaw, L.; McCallum, S.; Zong, H.; Luo, L.; Clevers, H.; et al. Neurodevelopment: Lineage-Dependent Spatial and Functional Organization of the Mammalian Enteric Nervous System. Science 2017, 356, 722–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lo, L.; Dormand, E.; Anderson, D.J. SOX10 Maintains Multipotency and Inhibits Neuronal Differentiation of Neural Crest Stem Cells. Neuron 2003, 38, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, B.B.; Mazmanian, S.K. The Enteric Network: Interactions between the Immune and Nervous Systems of the Gut. Immunity 2017, 46, 910–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, H.M.; Bergner, A.J.; Müller, T. Acquisition of Neuronal and Glial Markers by Neural Crest-Derived Cells in the Mouse Intestine. J. Comp. Neurol. 2003, 456, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeisel, A.; Hochgerner, H.; Lönnerberg, P.; Johnsson, A.; Memic, F.; van der Zwan, J.; Häring, M.; Braun, E.; Borm, L.E.; La Manno, G.; et al. Molecular Architecture of the Mouse Nervous System. Cell 2018, 174, 999–1014.e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drokhlyansky, E.; Smillie, C.; Van Wittenberghe, N.; Ericsson, M.; Griffin, G.K.; Eraslan, G.; Dionne, D.; Cuoco, M.; Goder-Reiser, M.; Sharova, T.; et al. The Human and Mouse Enteric Nervous System at Single-Cell Resolution. Cell 2020, 182, 1606–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fung, C.; Vanden Berghe, P. Functional Circuits and Signal Processing in the Enteric Nervous System. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, K.M.; Koh, S.D.; Ro, S.; Ward, S.M. Regulation of Gastrointestinal Motility-Insights from Smooth Muscle Biology. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 9, 633–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, K.M.; Kito, Y.; Hwang, S.J.; Ward, S.M. Regulation of Gastrointestinal Smooth Muscle Function by Interstitial Cells. Physiology 2016, 31, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vannucchi, M.G.; Traini, C. Interstitial Cells of Cajal and Telocytes in the Gut: Twins, Related or Simply Neighbor Cells? Biomol. Concepts 2016, 7, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, H.M.; Ciampoli, D.; Southwell, B.R.; Newgreen, D.F. Origin of Interstitial Cells of Cajal in the Mouse Intestine. Dev. Biol. 1996, 180, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klüppel, M.; Huizinga, J.D.; Malysz, J.; Bernstein, A. Developmental Origin and Kit-Dependent Development of the Interstitial Cells of Cajal in the Mammalian Small Intestine. Dev. Dyn. 1998, 211, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Traini, C.; Mischopoulou, M.; Gibbons, S.; Ligresti, G.; Faussone-Pellegrini, M.; Sha, L.; Farrugia, G.; Vannucchi, M.; Cipriani, G. Muscularis Macrophages Establish Cell-to-Cell Contacts with Telocytes/PDGFRα-Positive Cells and Smooth Muscle Cells in the Human and Mouse Gastrointestinal Tract. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2020, e13993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, K.M.; Ward, S.M.; Koh, S.D. Interstitial Cells: Regulators of Smooth Muscle Function. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 859–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoshkes-Carmel, M.; Wang, Y.J.; Wangensteen, K.J.; Tóth, B.; Kondo, A.; Massassa, E.E.; Itzkovitz, S.; Kaestner, K.H. Subepithelial Telocytes Are an Important Source of Wnts That Supports Intestinal Crypts. Nature 2018, 557, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaestner, K.H. The Intestinal Stem Cell Niche: A Central Role for Foxl1-Expressing Subepithelial Telocytes. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 8, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahar Halpern, K.; Massalha, H.; Zwick, R.K.; Moor, A.E.; Castillo-Azofeifa, D.; Rozenberg, M.; Farack, L.; Egozi, A.; Miller, D.R.; Averbukh, I.; et al. Lgr5+ Telocytes Are a Signaling Source at the Intestinal Villus Tip. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veress, B.; Ohlsson, B. Spatial Relationship between Telocytes, Interstitial Cells of Cajal and the Enteric Nervous System in the Human Ileum and Colon. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 3399–3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalazonitis, A.; D’Autréaux, F.; Pham, T.D.; Kessler, J.A.; Gershon, M.D. Bone Morphogenetic Proteins Regulate Enteric Gliogenesis by Modulating ErbB3 Signaling. Dev. Biol. 2011, 350, 64–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Boesmans, W.; Lasrado, R.; Vanden Berghe, P.; Pachnis, V. Heterogeneity and Phenotypic Plasticity of Glial Cells in the Mammalian Enteric Nervous System. Glia 2015, 63, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossais, F.; Durand, T.; Chevalier, J.; Boudaud, M.; Kermarrec, L.; Aubert, P.; Neveu, I.; Naveilhan, P.; Neunlist, M. Postnatal Development of the Myenteric Glial Network and Its Modulation by Butyrate. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2016, 310, G941–G951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.; Nelms, B.D.; Dong, L.; Salinas-Rios, V.; Rutlin, M.; Gershon, M.D.; Corfas, G. Enteric Glia Express Proteolipid Protein 1 and Are a Transcriptionally Unique Population of Glia in the Mammalian Nervous System. Glia 2015, 63, 2040–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanani, M.; Reichenbach, A. Morphology of Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP)-Injected Glial Cells in the Myenteric Plexus of the Guinea-Pig. Cell Tissue Res. 1994, 278, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charrier, B.; Pilon, N. Toward a Better Understanding of Enteric Gliogenesis. Neurogenesis 2017, 4, e1293958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savidge, T.C.; Newman, P.; Pothoulakis, C.; Ruhl, A.; Neunlist, M.; Bourreille, A.; Hurst, R.; Sofroniew, M.V. Enteric Glia Regulate Intestinal Barrier Function and Inflammation Via Release of S-Nitrosoglutathione. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 1344–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulbransen, B.D.; Sharkey, K.A. Novel Functional Roles for Enteric Glia in the Gastrointestinal Tract. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 9, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanderwinden, J.M.; Timmermans, J.P.; Schiffmann, S.N. Glial Cells, but Not Interstitial Cells, Express P2X7, an Ionotropic Purinergic Receptor, in Rat Gastrointestinal Musculature. Cell Tissue Res. 2003, 312, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkind-Gerson, J.; Graham, H.K.; Reynolds, J.; Hotta, R.; Nagy, N.; Cheng, L.; Kamionek, M.; Shi, H.N.; Aherne, C.M.; Goldstein, A.M. Colitis Promotes Neuronal Differentiation of Sox2+ and PLP1+ Enteric Cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, J.; Borojevic, R.; Verdu, E.F.; Huizinga, J.D.; Ratcliffe, E.M. Intestinal Microbiota Influence the Early Postnatal Development of the Enteric Nervous System. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2014, 26, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabouridis, P.S.; Lasrado, R.; McCallum, S.; Chng, S.H.; Snippert, H.J.; Clevers, H.; Pettersson, S.; Pachnis, V. Microbiota Controls the Homeostasis of Glial Cells in the Gut Lamina Propria. Neuron 2015, 85, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avetisyan, M.; Rood, J.E.; Lopez, S.H.; Sengupta, R.; Wright-Jin, E.; Dougherty, J.D.; Behrens, E.M.; Heuckeroth, R.O. Muscularis Macrophage Development in the Absence of an Enteric Nervous System. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 4696–4701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okabe, Y.; Medzhitov, R. Tissue-Specific Signals Control Reversible Program of Localization and Functional Polarization of Macrophages. Cell 2014, 157, 832–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, P.A.; Koscsó, B.; Rajani, G.M.; Stevanovic, K.; Berres, M.L.; Hashimoto, D.; Mortha, A.; Leboeuf, M.; Li, X.M.; Mucida, D.; et al. Crosstalk between Muscularis Macrophages and Enteric Neurons Regulates Gastrointestinal Motility. Cell 2014, 158, 300–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Schepper, S.; Verheijden, S.; Aguilera-Lizarraga, J.; Viola, M.F.; Boesmans, W.; Stakenborg, N.; Voytyuk, I.; Smidt, I.; Boeckx, B.; Dierckx de Casterlé, I.; et al. Self-Maintaining Gut Macrophages Are Essential for Intestinal Homeostasis. Cell 2018, 175, 400–415.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dora, D.; Arciero, E.; Hotta, R.; Barad, C.; Bhave, S.; Kovacs, T.; Balic, A.; Goldstein, A.M.; Nagy, N. Intraganglionic Macrophages: A New Population of Cells in the Enteric Ganglia. J. Anat. 2018, 233, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grubišić, V.; McClain, J.L.; Fried, D.E.; Grants, I.; Rajasekhar, P.; Csizmadia, E.; Ajijola, O.A.; Watson, R.E.; Poole, D.P.; Robson, S.C.; et al. Enteric Glia Modulate Macrophage Phenotype and Visceral Sensitivity Following Inflammation. Cell Rep. 2020, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, A.K.; Gulbransen, B.D. Potential Roles of Enteric Glia in Bridging Neuroimmune Communication in the Gut. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2017, 312, G145–G152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grubišić, V.; Gulbransen, B.D. Enteric Glia: The Most Alimentary of All Glia. J. Physiol. 2017, 595, 557–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veiga-Fernandes, H.; Pachnis, V. Neuroimmune Regulation during Intestinal Development and Homeostasis. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, N.; Goldstein, A.M. Enteric Nervous System Development: A Crest Cell’s Journey from Neural Tube to Colon. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 66, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasselli, V.; Pachnis, V.; Burns, A.J. The Enteric Nervous System. Dev. Biol. 2012, 366, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, H.M.; Newgreen, D.F.; Enomoto, H. Development of the Enteric Nervous System. Physiol. Gastrointest. Tract 2012, 1 (Suppl. IV), 475–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musser, M.A.; Michelle Southard-Smith, E. Balancing on the Crest—Evidence for Disruption of the Enteric Ganglia via Inappropriate Lineage Segregation and Consequences for Gastrointestinal Function. Dev. Biol. 2013, 382, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondurand, N.; Dufour, S.; Pingault, V. News from the Endothelin-3/EDNRB Signaling Pathway: Role during Enteric Nervous System Development and Involvement in Neural Crest-Associated Disorders. Dev. Biol. 2018, 444, S156–S169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heuckeroth, R. Hirschsprung Disease—Integrating Basic Science and Clinical Medicine to Improve Outcomes. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaroy, E.G.; Acosta-Jimenez, L.; Hotta, R.; Goldstein, A.M.; Emblem, R.; Klungland, A.; Ougland, R. “Too Much Guts and Not Enough Brains”: (Epi)Genetic Mechanisms and Future Therapies of Hirschsprung Disease—A Review. Clin. Epigenetics 2019, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, H.M.; Hearn, C.J.; Farlie, P.G.; Canty, A.J.; Thomas, P.Q.; Newgreen, D.F. GDNF Is a Chemoattractant for Enteric Neural Cells. Dev. Biol. 2001, 229, 503–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, D.M.; Li, A.Y.; Nair, D.G.; Blennerhassett, M.G. Glial Cell Line-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Is a Key Neurotrophin in the Postnatal Enteric Nervous System. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2011, 23, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Wang, W.; Chen, W.; Sun, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, C.; Yang, H. GDNF Is Involved in the Barrier-Inducing Effect of Enteric Glial Cells on Intestinal Epithelial Cells Under Acute Ischemia Reperfusion Stimulation. Mol. Neurobiol. 2014, 50, 274–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meir, M.; Flemming, S.; Burkard, N.; Bergauer, L.; Metzger, M.; Germer, C.T.; Schlegel, N. Glial Cell Line-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Promotes Barrier Maturation and Wound Healing in Intestinal Epithelial Cells in Vitro. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2015, 309, G613–G624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuchhardt, A.; D’Agati, V.; Larsson-Blomberg, L.; Costantini, F.; Pachnis, V. Defects in the Kidney and Enteric Nervous System of Mice Lacking the Tyrosine Kinase Receptor Ret. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 1994, 367, 380–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.W.; Kleint, R.D.; Fariiias, I.; Sauert, H.; Armaninit, M.; Phillipst, H.; Reichardt, L.F.; Ryan, A.M.; Carver-moore, K.; Rosenthalt, A. Renal and Neuronal Abnormalities in Mice Lacking GDNF. Nature 1996, 382, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichel, J.G.; Shen, L.; Sheng, H.Z.; Granholm, A.C.; Drago, J.; Grinberg, A.; Lee, E.J.; Huang, S.P.; Saarma, M.; Hoffer, B.J.; et al. Defects in Enteric Innervation and Kidney Development in Mice Lacking GDNF. Nature 1996, 382, 73–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, M.P.; Silos-Santiago, I.; Frisen, J.; He, B.; Lira, S.A.; Barbacid, M. Renal Agenesis and the Absence of Enteric Neurons in Mice Lacking GDNF. Nature 1996, 382, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacalano, G.; Fariñas, I.; Wang, L.C.; Hagler, K.; Forgie, A.; Moore, M.; Armanini, M.; Phillips, H.; Ryan, A.M.; Reichardt, L.F.; et al. GFRα1 Is an Essential Receptor Component for GDNF in the Developing Nervous System and Kidney. Neuron 1998, 21, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, D.; Marcos-gutierrez, C.; Pachnis, V.; De Graaff, E. Requirement of Signalling by Receptor Tyrosine Kinase RET for the Directed Migration of Enteric Nervous System Progenitor Cells during Mammalian Embryogenesis. Development 2002, 129, 5151–5160. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barlow, A.; De Graaff, E.; Pachnis, V. Enteric Nervous System Progenitors Are Coordinately Controlled by the G Protein-Coupled Receptor EDNRB and the Receptor Tyrosine Kinase RET. Neuron 2003, 40, 905–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondurand, N.; Natarajan, D.; Barlow, A.; Thapar, N.; Pachnis, V. Maintenance of Mammalian Enteric Nervous System Progenitors by SOX10 and Endothelin 3 Signalling. Development 2006, 133, 2075–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, Y.; Stanchina, L.; Lecerf, L.; Gacem, N.; Conidi, A.; Baral, V.; Pingault, V.; Huylebroeck, D.; Bondurand, N. Differentiation of Mouse Enteric Nervous System Progenitor Cells Is Controlled by Endothelin 3 and Requires Regulation of Ednrb by SOX10 and ZEB2. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 1139–1150.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazquez, E.; Watanabe, Y.; Broders-Bondon, F.; Paul-Gilloteaux, P.; Heysch, J.; Baral, V.; Bondurand, N.; Dufour, S. Endothelin-3 Stimulates Cell Adhesion and Cooperates with Β1-Integrins during Enteric Nervous System Ontogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breau, M.A.; Pietri, T.; Eder, O.; Blanche, M.; Brakebusch, C.; Fässler, R.; Thiery, J.P.; Dufour, S. Lack of Β1 Integrins in Enteric Neural Crest Cells Leads to a Hirschsprung-like Phenotype. Development 2006, 133, 1725–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, N.; Barad, C.; Hotta, R.; Bhave, S.; Arciero, E.; Dora, D.; Goldstein, A.M. Collagen 18 and Agrin Are Secreted by Neural Crest Cells to Remodel Their Microenvironment and Regulate Their Migration during Enteric Nervous System Development. Development 2018, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevalier, N.R.; Gazguez, E.; Bidault, L.; Guilbert, T.; Vias, C.; Vian, E.; Watanabe, Y.; Muller, L.; Germain, S.; Bondurand, N.; et al. How Tissue Mechanical Properties Affect Enteric Neural Crest Cell Migration. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druckenbrod, N.R.; Epstein, M.L. Age-Dependent Changes in the Gut Environment Restrict the Invasion of the Hindgut by Enteric Neural Progenitors. Development 2009, 136, 3195–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veríssimo, C.P.; da Carvalho, J.S.; da Silva, F.J.M.; Campanati, L.; Moura-Neto, V.; de Coelho-Aguiar, J.M. Laminin and Environmental Cues Act in the Inhibition of the Neuronal Differentiation of Enteric Glia in Vitro. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gershon, M.D. Developmental Determinants of the Independence and Complexity of the Enteric Nervous System. Trends Neurosci. 2010, 33, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamura, Y.; Saga, Y. Notch Signaling Is Required for the Maintenance of Enteric Neural Crest Progenitors. Development 2008, 135, 3555–3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Lee, H.; Jordan, C.S.; Cantrell, V.A.; Southard-smith, E.M.; Shin, M.K. Spatiotemporal Regulation of Endothelin Receptor-B by SOX10 in Neural Crest—Derived Enteric Neuron Precursors. Nat. Genet. 2004, 36, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngan, E.S.W.; Garcia-Barceló, M.M.; Yip, B.H.K.; Poon, H.C.; Lau, S.T.; Kwok, C.K.M.; Sat, E.; Sham, M.H.; Wong, K.K.Y.; Wainwright, B.J.; et al. Hedgehog/Notch-Induced Premature Gliogenesis Represents a New Disease Mechanism for Hirschsprung Disease in Mice and Humans. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 3467–3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicker, F.; Schmidt, M.H.H. EGFL7: A New Player in Homeostasis of the Nervous System. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 1263–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.H.H.; Bicker, F.; Nikolic, I.; Meister, J.; Babuke, T.; Picuric, S.; Müller-Esterl, W.; Plate, K.H.; Dikic, I. Epidermal Growth Factor-like Domain 7 (EGFL7) Modulates Notch Signalling and Affects Neural Stem Cell Renewal. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.K.; Yeager, K.; Morrison, S.J. Physiological Notch Signaling Promotes Gliogenesis in the Developing Peripheral and Central Nervous Systems. Development 2007, 134, 2435–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Kim, B.M.; Mao, J.; Rowan, S.; Shivdasani, R.A. Endodermal Hedgehog Signals Modulate Notch Pathway Activity in the Developing Digestive Tract Mesenchyme. Development 2011, 138, 3225–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, N.; Barad, C.; Graham, H.K.; Hotta, R.; Cheng, L.S.; Fejszak, N.; Goldstein, A.M. Sonic Hedgehog Controls Enteric Nervous System Development by Patterning the Extracellular Matrix. Development 2016, 143, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wouters, M.A.; Rigoutsos, I.; Chu, C.K.; Feng, L.L.; Sparrow, D.B.; Dunwoodie, S.L. Evolution of Distinct EGF Domains with Specific Functions. Protein Sci. 2005, 14, 1091–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalazonitis, A.; Pham, T.D.; Li, Z.; Roman, D.; Guha, U.; Gomes, W.; Kan, L.; Kessler, J.A.; Gershon, M.D. Bone Morphogenese Protein Regulation of Enteric Neuronal Phenotypic Diversity: Relationship to Timing of Cell Cycle Exit. J. Comp. Neurol. 2008, 509, 474–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, M.M.; Bornstein, J.C.; Vanden Berghe, P.; Lomax, A.E.; Young, H.M.; Foong, J.P.P. The Emergence of Neural Activity and Its Role in the Development of the Enteric Nervous System. Dev. Biol. 2013, 382, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, P.; Soret, R.; Suply, E.; Heloury, Y.; Neunlist, M. Postnatal Development of Myenteric Neurochemical Phenotype and Impact on Neuromuscular Transmission in the Rat Colon. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2010, 299, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, G.M.; Mosher, J.T.; Bixby, S.; Joseph, N.; Iwashita, T.; Morrison, S.J.; Arbor, A. Neural Crest Stem Cells Persist in the Adult Gut but Undergo Changes in Self-Renewal, Neuronal Subtype Potential, and Factor Responsiveness. Neuron 2002, 35, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez-Rodríguez, R.; Belkind-Gerson, J. Cultured Nestin-Positive Cells from Postnatal Mouse Small Bowel Differentiate Ex Vivo into Neurons, Glia, and Smooth Muscle. Stem Cells 2004, 22, 1373–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, M.; Caldwell, C.; Barlow, A.J.; Burns, A.J.; Thapar, N. Enteric Nervous System Stem Cells Derived From Human Gut Mucosa for the Treatment of Aganglionic Gut Disorders. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 2214–2225.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, N.M.; Núñez, G.; Morrison, S.J.; Joseph, N.M.; He, S.; Quintana, E.; Kim, Y.; Núñez, G.; Morrison, S.J. Enteric Glia Are Multipotent in Culture but Primarily Form Glia in the Adult Rodent Gut. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 3398–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, S.; Micci, M.A.; Leser, J.; Shin, C.; Tang, S.C.; Fu, Y.Y.; Liu, L.; Li, Q.; Saha, M.; Li, C.; et al. Adult Enteric Nervous System in Health Is Maintained by a Dynamic Balance between Neuronal Apoptosis and Neurogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E3709–E3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.T.; Kuan, Y.H.; Wang, J.; Hen, R.; Gershon, M.D. 5-HT4 Receptor-Mediated Neuroprotection and Neurogenesis in the Enteric Nervous System of Adult Mice. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 9683–9699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laranjeira, C.; Sandgren, K.; Kessaris, N.; Richardson, W.; Potocnik, A.; Vanden Berghe, P.; Pachnis, V. Glial Cells in the Mouse Enteric Nervous System Can Undergo Neurogenesis in Response to Injury. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 3412–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, K.; Kato, G.; Kawahara, I.; Luo, Y.; Obata, K.; Misawa, H.; Ishikawa, T.; Kuniyasu, H.; Nabekura, J.; Takaki, M. In Vivo Imaging of Enteric Neurogenesis in the Deep Tissue of Mouse Small Intestine. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belkind-Gerson, J.; Hotta, R.; Nagy, N.; Thomas, A.R.; Graham, H.; Cheng, L.; Solorzano, J.; Nguyen, D.; Kamionek, M.; Dietrich, J.; et al. Colitis Induces Enteric Neurogenesis through a 5-HT4-Dependent Mechanism. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 870–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Nachef, W.N.; Bronner, M.E. De Novo Enteric Neurogenesis in Post-Embryonic Zebrafish from Schwann Cell Precursors Rather than Resident Cell Types. Development 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa-Medina, I.; Outin, E.; Picard, C.A.; Chettouh, Z.; Dymecki, S.; Consalez, G.G.; Coppola, E.; Brunet, J.F. Parasympathetic Ganglia Derive from Schwann Cell Precursors. Science 2014, 345, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlan, A.; Adameyko, I. Schwann Cell Precursor: A Neural Crest Cell in Disguise? Dev. Biol. 2018, 444, S25–S35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, S.A.; Uy, B.R.; Bronner, M.E. Ancient Evolutionary Origin of Vertebrate Enteric Neurons from Trunk-Derived Neural Crest. Nature 2017, 544, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, T.G.; Savidge, T.C.; Freeman, T.C.; Cox, H.J.; Campbell, E.A.; Mucke, L.; Johnson, M.H.; Sofroniew, M.V. Fulminant Jejuno-Ileitis Following Ablation of Enteric Gila in Adult Transgenic Mice. Cell 1998, 93, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.; Rastelli, D.; Dong, L.; Chiu, S.; Setlik, W.; Gershon, M.D.; Corfas, G. Enteric Glia Regulate Gastrointestinal Motility but Are Not Required for Maintenance of the Epithelium in Mice. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 1068–1081.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Molina, J.A.; Molina, I. Chagas Disease. Lancet 2018, 391, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heanue, T.A.; Pachnis, V. Expression Profiling the Developing Mammalian Enteric Nervous System Identifies Marker and Candidate Hirschsprung Disease Genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 6919–6924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burzynski, G.M.; Nolte, I.M.; Bronda, A.; Bos, K.; Osinga, J.; Menacho, I.P.; Twigt, B.; Maas, S.; Brooks, A.S.; Verheij, J.B.G.M.; et al. Identifying Candidate Hirschsprung Disease-Associated RET Variants. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2005, 76, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emison, E.S.; McCallion, A.S.; Kashuk, C.S.; Bush, R.T.; Grice, E.; Lin, S.; Portnoy, M.E.; Culler, D.J.; Green, E.D.; Chakravarti, A. A Common Sex-Dependent Mutation in a RET Enhancer Underlies Hirschsprung Disease Risk. Nature 2005, 434, 857–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baynash, A.G.; Hosoda, K.; Giaid, A.; Richardson, J.A.; Emoto, N.; Hammer, R.E.; Yanagisawa, M. Interaction of Endothelin-3 with Endothelin-B Receptor Is Essential for Development of Epidermal Melanocytes and Enteric Neurons. Cell 1994, 79, 1277–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoda, K.; Hammer, R.E.; Richardson, J.A.; Baynash, A.G.; Cheung, J.C.; Giaid, A.; Yanagisawa, M. Targeted and Natural (Piebald-Lethal) Mutations of Endothelin-B Receptor Gene Produce Megacolon Associated with Spotted Coat Color in Mice. Cell 1994, 79, 1267–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puffenberger, E.G.; Hosoda, K.; Washington, S.S.; Nakao, K.; deWit, D.; Yanagisawa, M.; Chakravarti, A. A Missense Mutation of the Endothelin-B Receptor Gene in Multigenic Hirschsprung’s Disease. Cell 1994, 79, 1257–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gershon, M.D. Transplanting the Enteric Nervous System: A Step Closer to Treatment for Aganglionosis. Gut 2007, 56, 459–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamp, L.A.; Young, H.M. Recent Advances in Regenerative Medicine to Treat Enteric Neuropathies: Use of Human Cells. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2017, 29, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almond, S.; Lindley, R.M.; Kenny, S.E.; Connell, M.G.; Edgar, D.H. Characterisation and Transplantation of Enteric Nervous System Progenitor Cells. Gut 2007, 56, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattahi, F.; Steinbeck, J.A.; Kriks, S.; Tchieu, J.; Zimmer, B.; Kishinevsky, S.; Zeltner, N.; Mica, Y.; El-Nachef, W.; Zhao, H.; et al. Deriving Human ENS Lineages for Cell Therapy and Drug Discovery in Hirschsprung Disease. Nature 2016, 531, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, J.E.; Natarajan, D.; McCann, C.J.; Choudhury, S.; Godwin, H.; Burns, A.J.; Thapar, N. In Vivo Transplantation of Fetal Human Gut-Derived Enteric Neural Crest Cells. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2017, 29, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlieve, C.R.; Fowler, K.L.; Thornton, M.; Huang, S.; Hajjali, I.; Hou, X.; Grubbs, B.; Spence, J.R.; Grikscheit, T.C. Neural Crest Cell Implantation Restores Enteric Nervous System Function and Alters the Gastrointestinal Transcriptome in Human Tissue-Engineered Small Intestine. Stem Cell Rep. 2017, 9, 883–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondurand, N.; Natarajan, D.; Thapar, N.; Atkins, C.; Pachnis, V. Neuron and Glia Generating Progenitors of the Mammalian Enteric Nervous System Isolated from Foetal and Postnatal Gut Cultures. Development 2003, 130, 6387–6400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotta, R.; Stamp, L.A.; Foong, J.P.P.; McConnell, S.N.; Bergner, A.J.; Anderson, R.B.; Enomoto, H.; Newgreen, D.F.; Obermayr, F.; Furness, J.B.; et al. Transplanted Progenitors Generate Functional Enteric Neurons in the Postnatal Colon. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 1182–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Rollo, B.N.; Nagy, N.; Stamp, L.; Newgreen, D.F. The Enteric Neural Crest Progressively Loses Capacity to Form Enteric Nervous System. Dev. Biol. 2019, 446, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeown, S.J.; Mohsenipour, M.; Bergner, A.J.; Young, H.M.; Stamp, L.A. Exposure to GDNF Enhances the Ability of Enteric Neural Progenitors to Generate an Enteric Nervous System. Stem Cell Rep. 2017, 8, 476–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Seid, K.; Obermayr, F.; Just, L.; Neckel, P.H. Activation of Wnt Signaling Increases Numbers of Enteric Neurons Derived From Neonatal Mouse and Human Progenitor Cells. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 154–165.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, M.; Matano, M.; Toshimitsu, K.; Takano, A.; Mikami, Y.; Nishikori, S.; Sugimoto, S.; Sato, T. Human Intestinal Organoids Maintain Self-Renewal Capacity and Cellular Diversity in Niche-Inspired Culture Condition. Cell Stem Cell 2018, 23, 787–793.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeqdadi, M.; Mana, M.D.; Roper, J.; Yilmaz, Ö.H. Gut Organoids: Mini-Tissues in Culture to Study Intestinal Physiology and Disease. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2019, 317, C405–C419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachos, N.C.; Kovbasnjuk, O.; Foulke-Abel, J.; In, J.; Blutt, S.E.; De Jonge, H.R.; Estes, M.K.; Donowitz, M. Human Enteroids/Colonoids and Intestinal Organoids Functionally Recapitulate Normal Intestinal Physiology and Pathophysiology. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 3759–3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loffet, E.; Brossard, L.; Mahe, M.M. Pluripotent Stem Cell Derived Intestinal Organoids with an Enteric Nervous System, 1st ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Workman, M.J.; Mahe, M.M.; Trisno, S.; Poling, H.M.; Watson, C.L.; Sundaram, N.; Chang, C.F.; Schiesser, J.; Aubert, P.; Stanley, E.G.; et al. Engineered Human Pluripotent-Stem-Cell-Derived Intestinal Tissues with a Functional Enteric Nervous System. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soret, R.; Mennetrey, M.; Bergeron, K.F.; Dariel, A.; Neunlist, M.; Grunder, F.; Faure, C.; Silversides, D.W.; Pilon, N. A Collagen VI—Dependent Pathogenic Mechanism for Hirschsprung’s Disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 4483–4496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heuckeroth, R.O. Stem Cells Make the Bowel Nervous. Nature 2016, 531, 44–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soret, R.; Schneider, S.; Bernas, G.; Christophers, B.; Souchkova, O.; Charrier, B.; Righini-Grunder, F.; Aspirot, A.; Landry, M.; Kembel, S.W.; et al. Glial Cell-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Induces Enteric Neurogenesis and Improves Colon Structure and Function in Mouse Models of Hirschsprung Disease. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 1824–1838.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.K.; He, F.Q.; Li, T.K.; Pang, X.H.; Cui, D.; Xie, Q.; Huang, X.L.; Gan, H.T. Glial-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Regulates Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Function and Inflammation and Is Therapeutic for Murine Colitis. J. Pathol. 2010, 222, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meir, M.; Flemming, S.; Burkard, N.; Wagner, J.; Germer, C.T.; Schlegel, N. The Glial Cell-Line Derived Neurotrophic Factor: A Novel Regulator of Intestinal Barrier Function in Health and Disease. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2016, 310, G1118–G1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarandi, S.S.; Kulkarni, S.; Saha, M.; Sylvia, K.E.; Sears, C.L.; Pasricha, P.J. Intestinal Bacteria Maintain Adult Enteric Nervous System and Nitrergic Neurons via Toll-like Receptor 2-Induced Neurogenesis in Mice. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 200–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcvey Neufeld, K.A.; Perez-Burgos, A.; Mao, Y.K.; Bienenstock, J.; Kunze, W.A. The Gut Microbiome Restores Intrinsic and Extrinsic Nerve Function in Germ-Free Mice Accompanied by Changes in Calbindin. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2015, 27, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasset, E.; Puel, A.; Charpentier, J.; Collet, X.; Christensen, J.E.; Tercé, F.; Burcelin, R. A Specific Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis of Type 2 Diabetic Mice Induces GLP-1 Resistance through an Enteric NO-Dependent and Gut-Brain Axis Mechanism. Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 1075–1090.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundmann, D.; Loris, E.; Maas-Omlor, S.; Schäfer, K.H. Enteric Neurogenesis During Life Span Under Physiological and Pathophysiological Conditions. Anat. Rec. 2019, 302, 1345–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pawolski, V.; Schmidt, M.H.H. Neuron–Glia Interaction in the Developing and Adult Enteric Nervous System. Cells 2021, 10, 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10010047
Pawolski V, Schmidt MHH. Neuron–Glia Interaction in the Developing and Adult Enteric Nervous System. Cells. 2021; 10(1):47. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10010047
Chicago/Turabian StylePawolski, Verena, and Mirko H. H. Schmidt. 2021. "Neuron–Glia Interaction in the Developing and Adult Enteric Nervous System" Cells 10, no. 1: 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10010047
APA StylePawolski, V., & Schmidt, M. H. H. (2021). Neuron–Glia Interaction in the Developing and Adult Enteric Nervous System. Cells, 10(1), 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10010047





