IL-33 and Superantigenic Activation of Human Lung Mast Cells Induce the Release of Angiogenic and Lymphangiogenic Factors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Human Monoclonal IgM and IgE and Human Polyclonal IgG
2.3. Isolation of HLMCs
2.4. Histamine Release
2.5. VEGF-A and VEGF-C Release
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Human IgG Anti-IgE on the Release of Angiogenic and Lymphangiogenic Factors from HLMCs
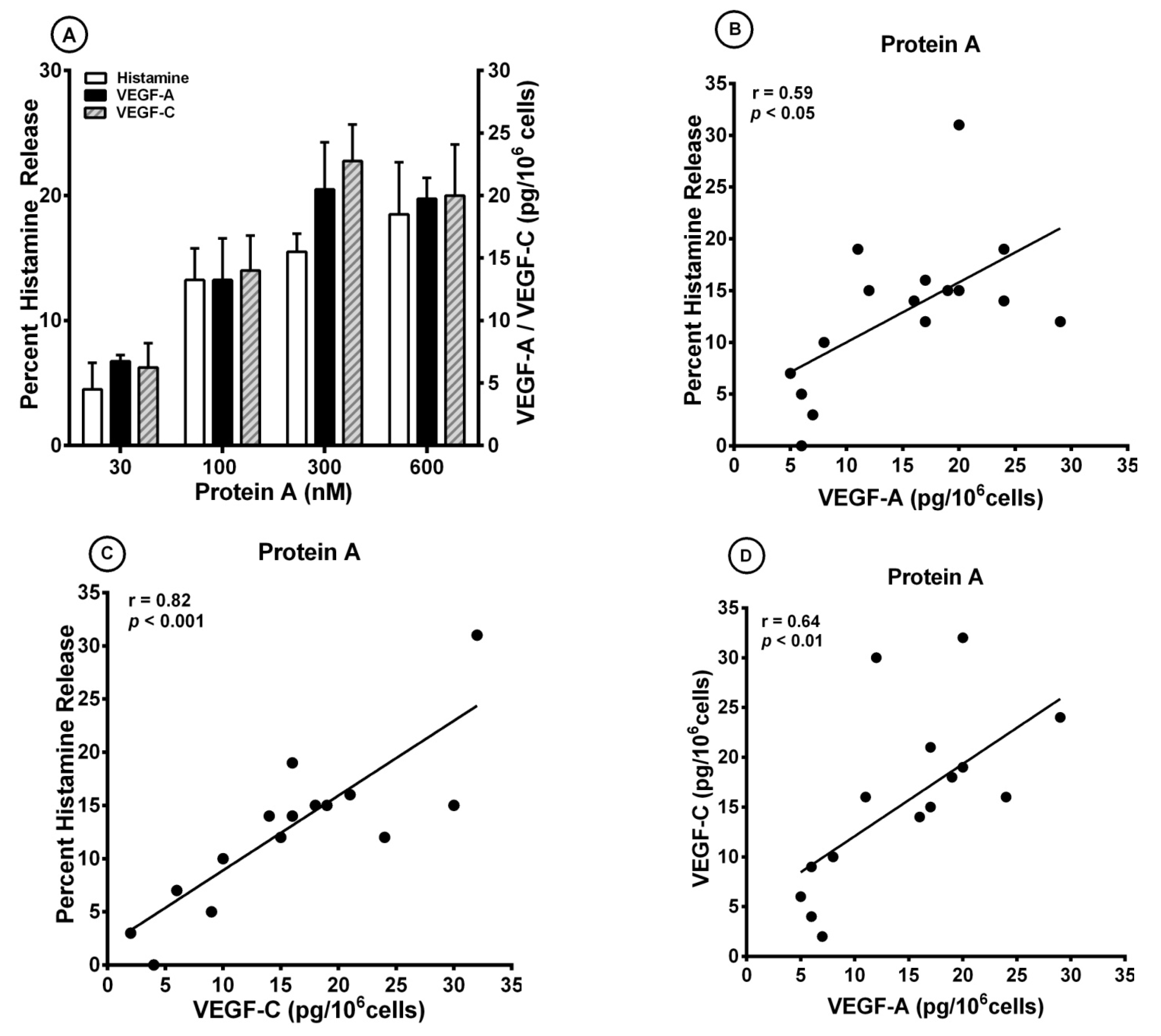
3.2. Effect of Superantigenic Protein A on the Release of Angiogenic and Lymphangiogenic Factors from HLMCs
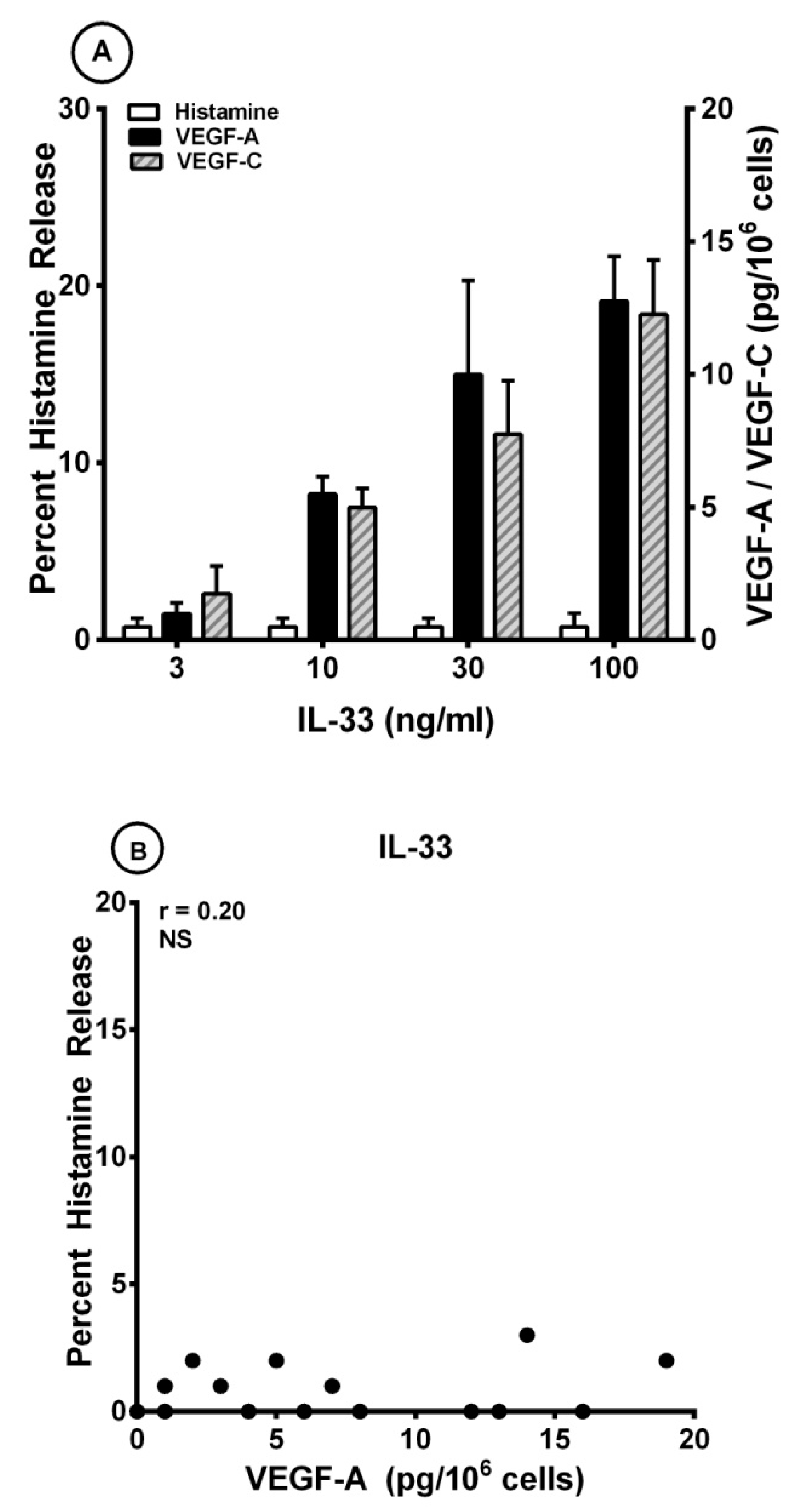
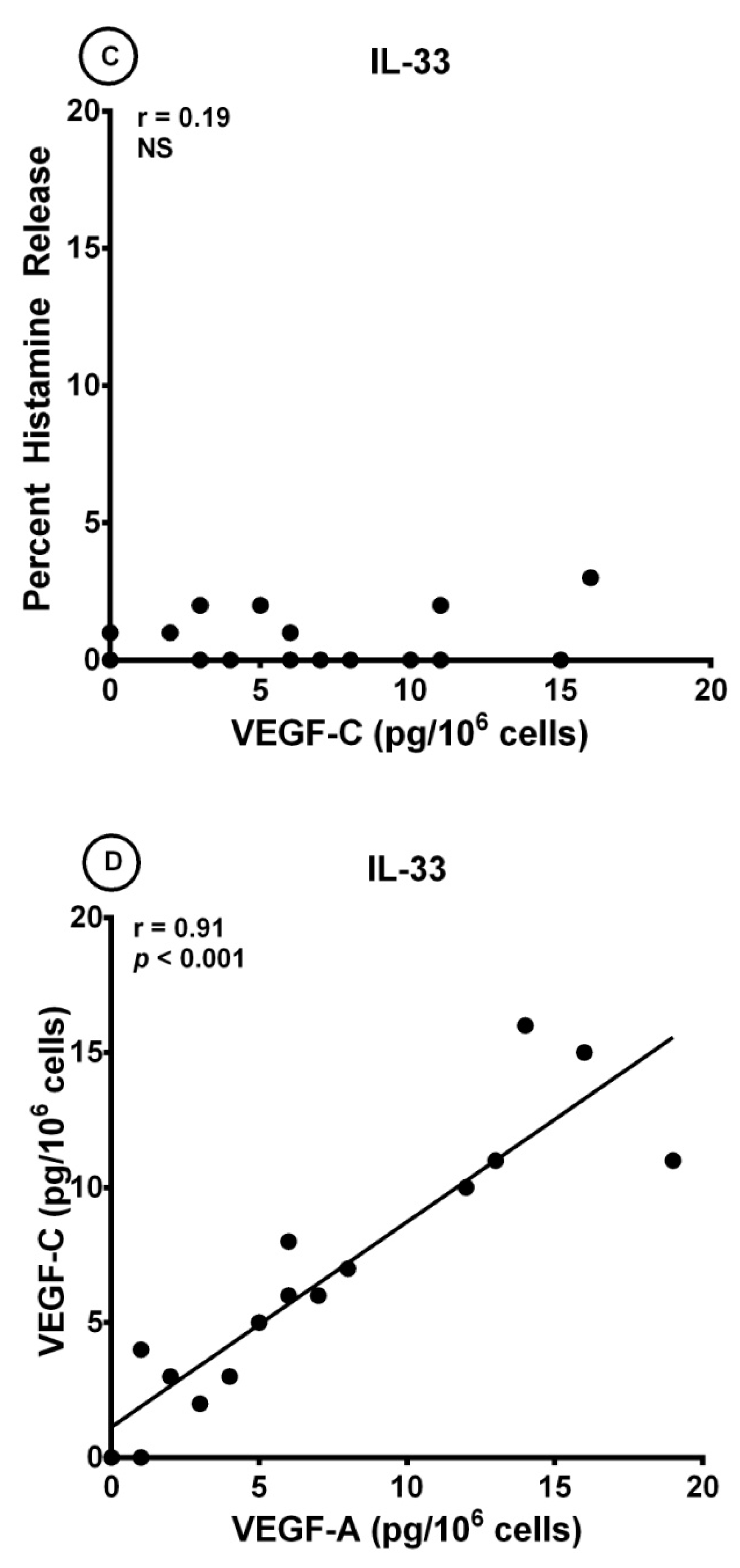
3.3. Effects of IL-33 on the Release of Angiogenic and Lymphangiogenic Factors from HLMCs
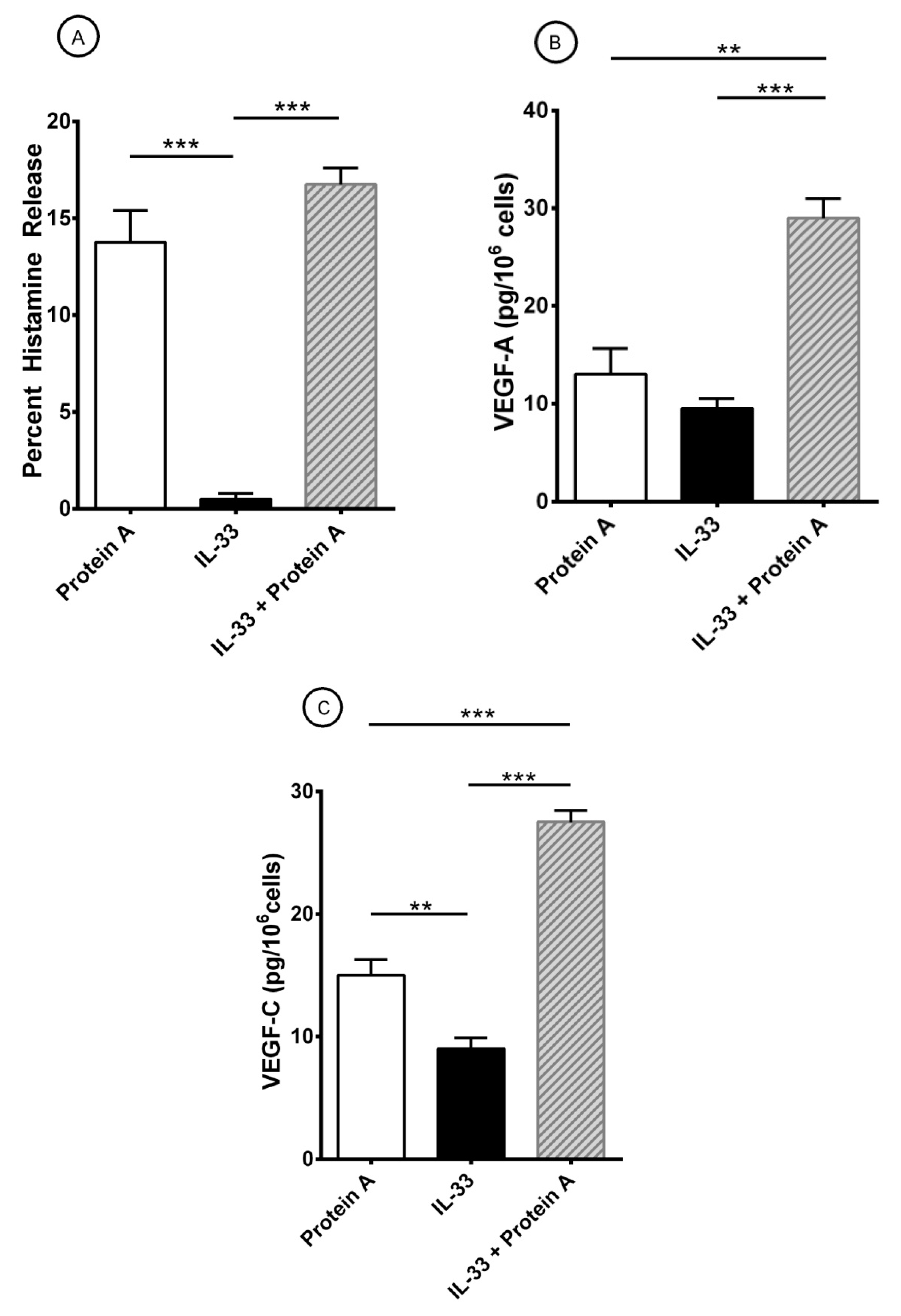
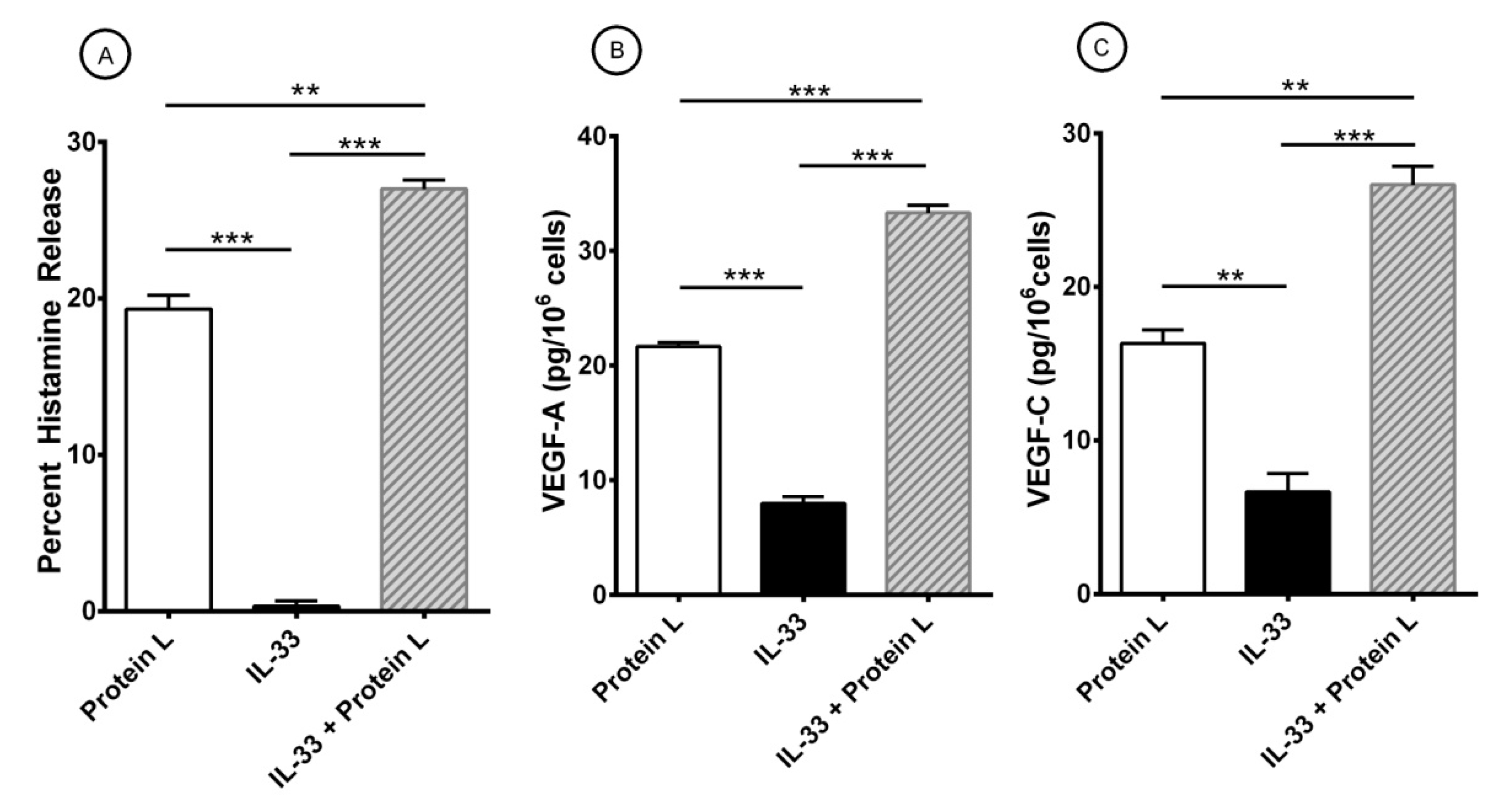
3.4. Effect of Short-Term Priming by IL-33 on Superantigenic Release of Mediators from HLMCs
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AHR | Airway hyperresponsiveness |
| ASM | Airway smooth muscle |
| BSA | Bovine serum albumin |
| COPD | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| CBMC | Cord blood-derived mast cell |
| FcεRI | High-affinity receptor for IgE |
| FCS | Fetal calf serum |
| H | Heavy |
| H-aIgE | Human IgG anti-IgE |
| HLMC | Human lung mast cell |
| Ig | Immunoglobulin |
| IL-33 | Interleukin-33 |
| IL | Interleukin |
| L | Light |
| LTC4 | Cysteinyl leukotriene C4 |
| mAb | Monoclonal antibody |
| P. magnus | Peptostreptococcus magnus |
| PBMC | Peripheral blood-derived mast cell |
| PGD2 | Prostaglandin D2 |
| S. aureus | Staphylococcus aureus |
| SAg | Superantigen |
| SE | Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins |
| SP | Substance P |
| TCR | T cell receptor |
| Treg | regulatory T cell |
| TSLP | Thymic stromal lymphopoietin |
| V | Variable |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
References
- Varricchi, G.; Rossi, F.W.; Galdiero, M.R.; Granata, F.; Criscuolo, G.; Spadaro, G.; de Paulis, A.; Marone, G. Physiological Roles of Mast Cells: Collegium Internationale Allergologicum Update 2019. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2019, 179, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borriello, F.; Granata, F.; Varricchi, G.; Genovese, A.; Triggiani, M.; Marone, G. Immunopharmacological Modulation of Mast Cells. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2014, 17, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casolaro, V.; Galeone, D.; Giacummo, A.; Sanduzzi, A.; Melillo, G.; Marone, G. Human Basophil/Mast Cell Releasability. V. Functional Comparisons of Cells Obtained from Peripheral Blood, Lung Parenchyma, and Bronchoalveolar Lavage in Asthmatics. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1989, 139, 1375–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zilionis, R.; Engblom, C.; Pfirschke, C.; Savova, V.; Zemmour, D.; Saatcioglu, H.D.; Krishnan, I.; Maroni, G.; Meyerovitz, C.V.; Kerwin, C.M.; et al. Single-Cell Transcriptomics of Human and Mouse Lung Cancers Reveals Conserved Myeloid Populations across Individuals and Species. Immunity 2019, 50, 1317–1334.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivera, A.; Beaven, M.A.; Metcalfe, D.D. Mast Cells Signal Their Importance in Health and Disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 142, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Piliponsky, A.M.; Romani, L. The Contribution of Mast Cells to Bacterial and Fungal Infection Immunity. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 282, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varricchi, G.; Raap, U.; Rivellese, F.; Marone, G.; Gibbs, B.F. Human Mast Cells and Basophils-How Are They Similar How Are They Different? Immunol. Rev. 2018, 282, 8–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukai, K.; Tsai, M.; Saito, H.; Galli, S.J. Mast Cells as Sources of Cytokines, Chemokines, and Growth Factors. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 282, 121–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradding, P.; Arthur, G. Mast Cells in Asthma--State of the Art. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2016, 46, 194–263. [Google Scholar]
- Marone, G.; Varricchi, G.; Loffredo, S.; Galdiero, M.R.; Rivellese, F.; de Paulis, A. Are Basophils and Mast Cells Masters in Hiv Infection? Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2016, 171, 158–165. [Google Scholar]
- Suurmond, J.; Rivellese, F.; Dorjee, A.L.; Bakker, A.M.; Rombouts, Y.J.; Rispens, T.; Wolbink, G.; Zaldumbide, A.; Hoeben, R.C.; Huizinga, T.W.; et al. Toll-Like Receptor Triggering Augments Activation of Human Mast Cells by Anti-Citrullinated Protein Antibodies. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 1915–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piliponsky, A.M.; Acharya, M.; Shubin, N.J. Mast Cells in Viral, Bacterial, and Fungal Infection Immunity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voehringer, D. Protective and Pathological Roles of Mast Cells and Basophils. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 362–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detoraki, A.; Staiano, R.I.; Granata, F.; Giannattasio, G.; Prevete, N.; de Paulis, A.; Ribatti, D.; Genovese, A.; Triggiani, M.; Marone, G. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factors Synthesized by Human Lung Mast Cells Exert Angiogenic Effects. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 123, 1142–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varricchi, G.; Loffredo, S.; Galdiero, M.R.; Marone, G.; Cristinziano, L.; Granata, F. Innate Effector Cells in Angiogenesis and Lymphangiogenesis. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2018, 53, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marone, G.; Varricchi, G.; Loffredo, S.; Granata, F. Mast Cells and Basophils in Inflammatory and Tumor Angiogenesis and Lymphangiogenesis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 778, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theoharides, T.C.; Zhang, B.; Kempuraj, D.; Tagen, M.; Vasiadi, M.; Angelidou, A.; Alysandratos, K.D.; Kalogeromitros, D.; Asadi, S.; Stavrianeas, N.; et al. Il-33 Augments Substance P-Induced Vegf Secretion from Human Mast Cells and Is Increased in Psoriatic Skin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 4448–4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detoraki, A.; Granata, F.; Staibano, S.; Rossi, F.W.; Marone, G.; Genovese, A. Angiogenesis and Lymphangiogenesis in Bronchial Asthma. Allergy 2010, 65, 946–958. [Google Scholar]
- Varricchi, G.; Granata, F.; Loffredo, S.; Genovese, A.; Marone, G. Angiogenesis and Lymphangiogenesis in Inflammatory Skin Disorders. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2015, 73, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivellese, F.; Suurmond, J.; Habets, K.; Dorjee, A.L.; Ramamoorthi, N.; Townsend, M.J.; de Paulis, A.; Marone, G.; Huizinga, T.W.; Pitzalis, C.; et al. Ability of Interleukin-33- and Immune Complex-Triggered Activation of Human Mast Cells to Down-Regulate Monocyte-Mediated Immune Responses. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 2343–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivellese, F.; Nerviani, A.; Rossi, F.W.; Marone, G.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; de Paulis, A.; Pitzalis, C. Mast Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Friends or Foes? Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivellese, F.; Mauro, D.; Nerviani, A.; Pagani, S.; Fossati-Jimack, L.; Messemaker, T.; Kurreeman, F.A.S.; Toes, R.E.M.; Ramming, A.; Rauber, S.; et al. Mast Cells in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Associate with Disease Severity and Support B Cell Autoantibody Production. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 1773–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visciano, C.; Liotti, F.; Prevete, N.; Cali, G.; Franco, R.; Collina, F.; de Paulis, A.; Marone, G.; Santoro, M.; Melillo, R.M. Mast Cells Induce Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and Stem Cell Features in Human Thyroid Cancer Cells through an Il-8-Akt-Slug Pathway. Oncogene 2015, 34, 5175–5186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galdiero, M.R.; Varricchi, G.; Marone, G. The Immune Network in Thyroid Cancer. Oncoimmunology 2016, 5, e1168556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varricchi, G.; Galdiero, M.R.; Loffredo, S.; Marone, G.; Iannone, R.; Granata, F. Are Mast Cells Masters in Cancer? Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varricchi, G.; Galdiero, M.R.; Marone, G.; Granata, F.; Borriello, F. Controversial Role of Mast Cells in Skin Cancers. Exp. Dermatol. 2017, 26, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, J.W.; Godfrey, R.C. The Number and Affinity of Ige Receptors on Dispersed Human Lung Mast Cells. Immunology 1981, 44, 859–863. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.B.; Kagey-Sobotka, A.; Lichtenstein, L.M.; Bochner, B.S. Immunophenotyping and Functional Analysis of Purified Human Uterine Mast Cells. Blood 1992, 79, 708–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravetch, J.V.; Kinet, J.P. Fc Receptors. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1991, 9, 457–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blank, U.; Ra, C.S.; Kinet, J.P. Characterization of Truncated Alpha Chain Products from Human, Rat, and Mouse High Affinity Receptor for Immunoglobulin E. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 2639–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinet, J.P. The High-Affinity Ige Receptor (Fc Epsilon Ri): From Physiology to Pathology. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1999, 17, 931–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorak, A.M.; Schulman, E.S.; Peters, S.P.; MacGlashan, D.W.; Newball, H.H., Jr.; Schleimer, R.P.; Lichtenstein, L.M. Immunoglobulin E-Mediated Degranulation of Isolated Human Lung Mast Cells. Lab Investig. 1985, 53, 45–56. [Google Scholar]
- MacGlashan, D., Jr.; Lichtenstein, L.M. Basic Characteristics of Human Lung Mast Cell Desensitization. J. Immunol. 1987, 139, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burke, S.M.; Issekutz, T.B.; Mohan, K.; Lee, P.W.; Shmulevitz, M.; Marshall, J.S. Human Mast Cell Activation with Virus-Associated Stimuli Leads to the Selective Chemotaxis of Natural Killer Cells by a Cxcl8-Dependent Mechanism. Blood 2008, 111, 5467–5476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allakhverdi, Z.; Smith, D.E.; Comeau, M.R.; Delespesse, G. Cutting Edge: The St2 Ligand Il-33 Potently Activates and Drives Maturation of Human Mast Cells. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 2051–2054. [Google Scholar]
- Staiano, R.I.; Loffredo, S.; Borriello, F.; Iannotti, F.A.; Piscitelli, F.; Orlando, P.; Secondo, A.; Granata, F.; Lepore, M.T.; Fiorelli, A.; et al. Human Lung-Resident Macrophages Express Cb1 and Cb2 Receptors Whose Activation Inhibits the Release of Angiogenic and Lymphangiogenic Factors. J. Leukoc Biol. 2016, 99, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paulis, A.; Prevete, N.; Fiorentino, I.; Rossi, F.W.; Staibano, S.; Montuori, N.; Ragno, P.; Longobardi, A.; Liccardo, B.; Genovese, A.; et al. Expression and Functions of the Vascular Endothelial Growth Factors and Their Receptors in Human Basophils. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 7322–7331. [Google Scholar]
- Loffredo, S.; Borriello, F.; Iannone, R.; Ferrara, A.L.; Galdiero, M.R.; Gigantino, V.; Esposito, P.; Varricchi, G.; Lambeau, G.; Cassatella, M.A.; et al. Group V Secreted Phospholipase A2 Induces the Release of Proangiogenic and Antiangiogenic Factors by Human Neutrophils. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.; Chou, S.; Dauwalder, O.; Lina, G. Diversity in Staphylococcus Aureus Enterotoxins. Chem. Immunol. Allergy 2007, 93, 24–41. [Google Scholar]
- Abdurrahman, G.; Schmiedeke, F.; Bachert, C.; Broker, B.M.; Holtfreter, S. Allergy-a New Role for T Cell Superantigens of Staphylococcus Aureus? Toxins (Basel) 2020, 12, 176. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, S.; Frankel, M.B.; Schneewind, O.; Missiakas, D. Release of Protein a from the Cell Wall of Staphylococcus Aureus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 1574–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forsgren, A.; Sjoquist, J. Protein a from S. Aureus. I. Pseudo-Immune Reaction with Human Gamma-Globulin. J. Immunol. 1966, 97, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Inganas, M. Comparison of Mechanisms of Interaction between Protein a from Staphylococcus Aureus and Human Monoclonal Igg, Iga and Igm in Relation to the Classical Fc Gamma and the Alternative F(Ab’)2 Epsilon Protein a Interactions. Scand. J. Immunol. 1981, 13, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodyear, C.S.; Silverman, G.J. B Cell Superantigens: A Microbe’s Answer to Innate-Like B Cells and Natural Antibodies. Springer Semin. Immunopathol. 2005, 26, 463–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjorck, L.; Protein, L. A Novel Bacterial Cell Wall Protein with Affinity for Ig L Chains. J. Immunol. 1988, 140, 1194–1197. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Patella, V.; Casolaro, V.; Bjorck, L.; Marone, G.; Protein, L. A Bacterial Ig-Binding Protein That Activates Human Basophils and Mast Cells. J. Immunol. 1990, 145, 3054–3061. [Google Scholar]
- Genovese, A.; Bouvet, J.P.; Florio, G.; Lamparter-Schummert, B.; Bjorck, L.; Marone, G. Bacterial Immunoglobulin Superantigen Proteins a and L Activate Human Heart Mast Cells by Interacting with Immunoglobulin E. Infect Immun. 2000, 68, 5517–5524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovese, A.; Borgia, G.; Bjorck, L.; Petraroli, A.; de Paulis, A.; Piazza, M.; Marone, G. Immunoglobulin Superantigen Protein L Induces Il-4 and Il-13 Secretion from Human Fc Epsilon Ri+ Cells through Interaction with the Kappa Light Chains of Ige. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 1854–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilson, B.H.; Solomon, A.; Bjorck, L.; Akerstrom, B. Protein L from Peptostreptococcus Magnus Binds to the Kappa Light Chain Variable Domain. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 2234–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marone, G.; Rossi, F.W.; Detoraki, A.; Granata, F.; Genovese, A.; Spadaro, G. Role of Superallergens in Allergic Disorders. Chem. Immunol. Allergy 2007, 93, 195–213. [Google Scholar]
- Rha, M.S.; Kim, S.W.; Chang, D.Y.; Lee, J.K.; Kim, J.; Park, S.H.; Khalmuratova, R.; Lim, H.S.; Eun, K.M.; Hong, S.N.; et al. Superantigen-Related Th2 Cd4(+) T Cells in Nonasthmatic Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 145, 1378–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teufelberger, A.R.; Broker, B.M.; Krysko, D.V.; Bachert, C.; Krysko, O. Staphylococcus Aureus Orchestrates Type 2 Airway Diseases. Trends Mol. Med. 2019, 25, 696–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsilochristou, O.; Toit, G.d.; Sayre, P.H.; Roberts, G.; Lawson, K.; Sever, M.L.; Bahnson, H.T.; Radulovic, S.; Basting, M.; Plaut, M.; et al. Association of Staphylococcus Aureus Colonization with Food Allergy Occurs Independently of Eczema Severity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 144, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachert, C.; Gevaert, P.; Zhang, N.; van Zele, T.; Perez-Novo, C. Role of Staphylococcal Superantigens in Airway Disease. Chem. Immunol. Allergy 2007, 93, 214–236. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.C.; Won, H.K.; Lee, J.W.; Sohn, K.H.; Kim, M.H.; Kim, T.B.; Chang, Y.S.; Lee, B.J.; Cho, S.H.; Bachert, C.; et al. Staphylococcus Aureus Nasal Colonization and Asthma in Adults: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2019, 7, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yang, J.; Lu, Y.W.; Wu, S.; Wang, M.R.; Zhu, J.M. Possible Role of Staphylococcal Enterotoxin B in the Pathogenesis of Autoimmune Diseases. Viral Immunol. 2015, 28, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viau, M.; Zouali, M. B-Lymphocytes, Innate Immunity, and Autoimmunity. Clin. Immunol. 2005, 114, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Sun, Y.; Ren, Y.; Qiao, L.; Guo, R.; Du, J.; Zhu, X.; Liu, Y.; Lin, J. The T Cell Activating Properties and Antitumour Activity of Staphylococcal Enterotoxin-Like Q. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2019, 208, 781–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golob-Urbanc, A.; Rajcevic, U.; Strmsek, Z.; Jerala, R. Design of Split Superantigen Fusion Proteins for Cancer Immunotherapy. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 6294–6305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agheli, R.; Emkanian, B.; Halabian, R.; Mehrabadi, J.F.; Fooladi, A.A.I. Recombinant Staphylococcal Enterotoxin Type a Stimulate Antitumoral Cytokines. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat 2017, 16, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, J.; Owyang, A.; Oldham, E.; Song, Y.; Murphy, E.; McClanahan, T.K.; Zurawski, G.; Moshrefi, M.; Qin, J.; Li, X.; et al. Il-33, an Interleukin-1-Like Cytokine That Signals Via the Il-1 Receptor-Related Protein St2 and Induces T Helper Type 2-Associated Cytokines. Immunity 2005, 23, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cayrol, C.; Girard, J.P. Interleukin-33 (Il-33): A Nuclear Cytokine from the Il-1 Family. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 281, 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boraschi, D.; Italiani, P.; Weil, S.; Martin, M.U. The Family of the Interleukin-1 Receptors. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 281, 197–232. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Martin, N.T.; Martin, M.U. Interleukin 33 Is a Guardian of Barriers and a Local Alarmin. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moussion, C.; Ortega, N.; Girard, J.P. The Il-1-Like Cytokine Il-33 Is Constitutively Expressed in the Nucleus of Endothelial Cells and Epithelial Cells in Vivo: A Novel ‘Alarmin’? PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afferni, C.; Buccione, C.; Andreone, S.; Galdiero, M.R.; Varricchi, G.; Marone, G.; Mattei, F.; Schiavoni, G. The Pleiotropic Immunomodulatory Functions of Il-33 and Its Implications in Tumor Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, L.Y.; Kita, H. Il-33: Biological Properties, Functions, and Roles in Airway Disease. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 278, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babina, M.; Wang, Z.; Franke, K.; Guhl, S.; Artuc, M.; Zuberbier, T. Yin-Yang of Il-33 in Human Skin Mast Cells: Reduced Degranulation, but Augmented Histamine Synthesis through P38 Activation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 139, 1516–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joulia, R.; L’Faqihi, F.E.; Valitutti, S.; Espinosa, E. Il-33 Fine Tunes Mast Cell Degranulation and Chemokine Production at the Single-Cell Level. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, H.; Arae, K.; Unno, H.; Miyauchi, K.; Toyama, S.; Nambu, A.; Oboki, K.; Ohno, T.; Motomura, K.; Matsuda, A.; et al. An Interleukin-33-Mast Cell-Interleukin-2 Axis Suppresses Papain-Induced Allergic Inflammation by Promoting Regulatory T Cell Numbers. Immunity 2015, 43, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taracanova, A.; Alevizos, M.; Karagkouni, A.; Weng, Z.; Norwitz, E.; Conti, P.; Leeman, S.E.; Theoharides, T.C. Sp and Il-33 Together Markedly Enhance Tnf Synthesis and Secretion from Human Mast Cells Mediated by the Interaction of Their Receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E4002–E4009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandara, G.; Beaven, M.A.; Olivera, A.; Gilfillan, A.M.; Metcalfe, D.D. Activated Mast Cells Synthesize and Release Soluble St2-a Decoy Receptor for Il-33. Eur. J. Immunol. 2015, 45, 3034–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salamon, P.; Shefler, I.; Moshkovits, I.; Munitz, A.; Klotzman, D.H.; Mekori, Y.A.; Hershko, A.Y. Il-33 and Ige Stimulate Mast Cell Production of Il-2 and Regulatory T Cell Expansion in Allergic Dermatitis. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2017, 47, 1409–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Guhl, S.; Franke, K.; Artuc, M.; Zuberbier, T.; Babina, M. Il-33 and Mrgprx2-Triggered Activation of Human Skin Mast Cells-Elimination of Receptor Expression on Chronic Exposure, but Reinforced Degranulation on Acute Priming. Cells 2019, 8, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjota, M.Y.; Williams, J.W.; Lu, T.; Clay, B.S.; Byrd, T.; Hrusch, C.L.; Decker, D.C.; de Araujo, C.A.; Bryce, P.J.; Sperling, A.I. Il-33-Dependent Induction of Allergic Lung Inflammation by Fcgammariii Signaling. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 2287–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loxham, M.; Davies, D.E. Phenotypic and Genetic Aspects of Epithelial Barrier Function in Asthmatic Patients. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, 1736–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayrol, C.; Duval, A.; Schmitt, P.; Roga, S.; Camus, M.; Stella, A.; Burlet-Schiltz, O.; Gonzalez-de-Peredo, A.; Girard, J.P. Environmental Allergens Induce Allergic Inflammation through Proteolytic Maturation of Il-33. Nat. Immunol. 2018, 19, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, M.C.; Lai, Y.; Nolin, J.D.; Long, S.; Chen, C.C.; Piliponsky, A.M.; Altemeier, W.A.; Larmore, M.; Frevert, C.W.; Mulligan, M.S.; et al. Airway Epithelium-Shifted Mast Cell Infiltration Regulates Asthmatic Inflammation Via Il-33 Signaling. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 4979–4991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werder, R.B.; Zhang, V.; Lynch, J.P.; Snape, N.; Upham, J.W.; Spann, K.; Phipps, S. Chronic Il-33 Expression Predisposes to Virus-Induced Asthma Exacerbations by Increasing Type 2 Inflammation and Dampening Antiviral Immunity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1607–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves-Filho, J.C.; Sonego, F.; Souto, F.O.; Freitas, A.; Verri, W.A.; Auxiliadora-Martins, M., Jr.; Basile-Filho, A.; McKenzie, A.N.; Xu, D.; Cunha, F.Q.; et al. Interleukin-33 Attenuates Sepsis by Enhancing Neutrophil Influx to the Site of Infection. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 708–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearley, J.; Silver, J.S.; Sanden, C.; Liu, Z.; Berlin, A.A.; White, N.; Mori, M.; Pham, T.H.; Ward, C.K.; Criner, G.J.; et al. Cigarette Smoke Silences Innate Lymphoid Cell Function and Facilitates an Exacerbated Type I Interleukin-33-Dependent Response to Infection. Immunity 2015, 42, 566–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zizzo, G.; Cohen, P.L. Imperfect Storm: Is Interleukin-33 the Achilles Heel of Covid-19? Lancet Rheumatol. 2020, 2, e779–e790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, F.Y.; Girard, J.P.; Turnquist, H.R. Interleukin-33 in Health and Disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 676–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollande, C.; Boussier, J.; Ziai, J.; Nozawa, T.; Bondet, V.; Phung, W.; Lu, B.; Duffy, D.; Paradis, V.; Mallet, V.; et al. Inhibition of the Dipeptidyl Peptidase Dpp4 (Cd26) Reveals Il-33-Dependent Eosinophil-Mediated Control of Tumor Growth. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marone, G.; Casolaro, V.; Paganelli, R.; Quinti, I. Igg Anti-Ige from Atopic Dermatitis Induces Mediator Release from Basophils and Mast Cells. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1989, 93, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marone, G.; Spadaro, G.; Palumbo, C.; Condorelli, G. The Anti-Ige/Anti-Fcepsilonrialpha Autoantibody Network in Allergic and Autoimmune Diseases. Clin. Exp. Allergy 1999, 29, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patella, V.; Marino, I.; Arbustini, E.; Lamparter-Schummert, B.; Verga, L.; Adt, M.; Marone, G. Stem Cell Factor in Mast Cells and Increased Mast Cell Density in Idiopathic and Ischemic Cardiomyopathy. Circulation 1998, 97, 971–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patella, V.; Giuliano, A.; Bouvet, J.P.; Marone, G. Endogenous Superallergen Protein Fv Induces Il-4 Secretion from Human Fc Epsilon Ri+ Cells through Interaction with the Vh3 Region of Ige. J. Immunol. 1998, 161, 5647–5655. [Google Scholar]
- Marone, G.; Tamburini, M.; Giudizi, M.G.; Biagiotti, R.; Almerigogna, F.; Romagnani, S. Mechanism of Activation of Human Basophils by Staphylococcus Aureus Cowan 1. Infect Immun. 1987, 55, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, P.; Tonutti, E.; Ruscio, M.; Colle, R.; Antonutto, G.; Falconieri, G. Ige Myeloma. Report of a New Case and Review of the Literature. Haematologica 1981, 66, 787–795. [Google Scholar]
- Patella, V.; de Crescenzo, G.; Marino, I.; Genovese, A.; Adt, M.; Gleich, G.J.; Marone, G. Eosinophil Granule Proteins Activate Human Heart Mast Cells. J. Immunol. 1996, 157, 1219–1225. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Siraganian, R.P. An Automated Continuous-Flow System for the Extraction and Fluorometric Analysis of Histamine. Anal. Biochem. 1974, 57, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loffredo, S.; Ferrara, A.L.; Bova, M.; Borriello, F.; Suffritti, C.; Veszeli, N.; Petraroli, A.; Galdiero, M.R.; Varricchi, G.; Granata, F.; et al. Secreted Phospholipases A2 in Hereditary Angioedema with C1-Inhibitor Deficiency. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marone, G.; Rossi, F.W.; Pecoraro, A.; Pucino, V.; Criscuolo, G.; Paulis, A.; Spadaro, G.; Varricchi, G. Hiv Gp120 Induces the Release of Proinflammatory, Angiogenic, and Lymphangiogenic Factors from Human Lung Mast Cells. Vaccines (Basel) 2020, 8, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stentzel, S.; Teufelberger, A.; Nordengrun, M.; Kolata, J.; Schmidt, F.; van Crombruggen, K.; Michalik, S.; Kumpfmuller, J.; Tischer, S.; Schweder, T.; et al. Staphylococcal Serine Protease-Like Proteins Are Pacemakers of Allergic Airway Reactions to Staphylococcus Aureus. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huvenne, W.; Callebaut, I.; Plantinga, M.; Vanoirbeek, J.A.; Krysko, O.; Bullens, D.M.; Gevaert, P.; van Cauwenberge, P.; Lambrecht, B.N.; Ceuppens, J.L.; et al. Staphylococcus Aureus Enterotoxin B Facilitates Allergic Sensitization in Experimental Asthma. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2010, 40, 1079–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha-de-Souza, C.M.; Berent-Maoz, B.; Mankuta, D.; Moses, A.E.; Levi-Schaffer, F. Human Mast Cell Activation by Staphylococcus Aureus: Interleukin-8 and Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Release and the Role of Toll-Like Receptor 2 and Cd48 Molecules. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 4489–4497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varricchi, G.; Loffredo, S.; Borriello, F.; Pecoraro, A.; Rivellese, F.; Genovese, A.; Spadaro, G.; Marone, G. Superantigenic Activation of Human Cardiac Mast Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, D.; Gomez, E.; Doe, C.; Berair, R.; Woodman, L.; Saunders, R.; Hollins, F.; Rose, F.R.; Amrani, Y.; May, R.; et al. Il-33 Drives Airway Hyper-Responsiveness through Il-13-Mediated Mast Cell: Airway Smooth Muscle Crosstalk. Allergy 2015, 70, 556–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, L.H.; Ohno, T.; Oboki, K.; Kajiwara, N.; Suto, H.; Iikura, M.; Okayama, Y.; Akira, S.; Saito, H.; Galli, S.J.; et al. Il-33 Induces Il-13 Production by Mouse Mast Cells Independently of Ige-Fcepsilonri Signals. J. Leukoc Biol. 2007, 82, 1481–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiwakura, J.; Yanagisawa, M.; Lee, H.; Okamura, Y.; Sasaki-Sakamoto, T.; Saito, S.; Tokuhashi, Y.; Ra, C.; Okayama, Y. Interleukin-33 Synergistically Enhances Immune Complex-Induced Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha and Interleukin-8 Production in Cultured Human Synovium-Derived Mast Cells. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2013, 161 (Suppl. 2), 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myhre, E.B.; Erntell, M. A Non-Immune Interaction between the Light Chain of Human Immunoglobulin and a Surface Component of a Peptococcus Magnus Strain. Mol. Immunol. 1985, 22, 879–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambrecht, B.N.; Hammad, H.; Fahy, J.V. The Cytokines of Asthma. Immunity 2019, 50, 975–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, M.C.; Wenzel, S.E. Intersection of Biology and Therapeutics: Type 2 Targeted Therapeutics for Adult Asthma. Lancet 2020, 395, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maun, H.R.; Jackman, J.K.; Choy, D.F.; Loyet, K.M.; Staton, T.L.; Jia, G.; Dressen, A.; Hackney, J.A.; Bremer, M.; Walters, B.T.; et al. An Allosteric Anti-Tryptase Antibody for the Treatment of Mast Cell-Mediated Severe Asthma. Cell 2019, 179, 417–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigna, J.J.; Kenne, A.M.; Asangbeh, S.L.; Sibetcheu, A.T. Prevalence of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease in the Global Population with Hiv: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2018, 6, e193–e202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elieh Ali Komi, D.; Bjermer, L. Mast Cell-Mediated Orchestration of the Immune Responses in Human Allergic Asthma: Current Insights. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2019, 56, 234–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamon, P.; Mekori, Y.A.; Shefler, I. Lung Cancer-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: A Possible Mediator of Mast Cell Activation in the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2020, 69, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDowell, P.J.; Heaney, L.G. Different Endotypes and Phenotypes Drive the Heterogeneity in Severe Asthma. Allergy 2020, 75, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sze, E.; Bhalla, A.; Nair, P. Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies for Non-T2 Asthma. Allergy 2020, 75, 311–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samitas, K.; Zervas, E.; Gaga, M. T2-Low Asthma: Current Approach to Diagnosis and Therapy. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2017, 23, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.F.; Peng, R.D.; McCormack, M.C.; Matsui, E.C. Staphylococcus Aureus Colonization Is Associated with Wheeze and Asthma among Us Children and Young Adults. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 135, 811–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachert, C.; van Steen, K.; Zhang, N.; Holtappels, G.; Cattaert, T.; Maus, B.; Buhl, R.; Taube, C.; Korn, S.; Kowalski, M.; et al. Specific Ige against Staphylococcus Aureus Enterotoxins: An Independent Risk Factor for Asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 130, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alitalo, K. The Lymphatic Vasculature in Disease. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1371–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brakenhielm, E.; Alitalo, K. Cardiac Lymphatics in Health and Disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2019, 16, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachert, C.; Zhang, N.; Holtappels, G.; de Lobel, L.; van Cauwenberge, P.; Liu, S.; Lin, P.; Bousquet, J.; van Steen, K. Presence of Il-5 Protein and Ige Antibodies to Staphylococcal Enterotoxins in Nasal Polyps Is Associated with Comorbid Asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 126, 962–968.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aman, M.J. Superantigens of a Superbug: Major Culprits of Staphylococcus Aureus Disease? Virulence 2017, 8, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Teufelberger, A.R.; Nordengrun, M.; Braun, H.; Maes, T.; de Grove, K.; Holtappels, G.; O’Brien, C.; Provoost, S.; Hammad, H.; Goncalves, A.; et al. The Il-33/St2 Axis Is Crucial in Type 2 Airway Responses Induced by Staphylococcus Aureus-Derived Serine Protease-Like Protein D. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachert, C.; Claeys, S.E.; Tomassen, P.; van Zele, T.; Zhang, N. Rhinosinusitis and Asthma: A Link for Asthma Severity. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2010, 10, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomassen, P.; Vandeplas, G.; van Zele, T.; Cardell, L.O.; Arebro, J.; Olze, H.; Forster-Ruhrmann, U.; Kowalski, M.L.; Olszewska-Ziaber, A.; Holtappels, G.; et al. Inflammatory Endotypes of Chronic Rhinosinusitis Based on Cluster Analysis of Biomarkers. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 1449–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigorito, C.; Giordano, A.; Cirillo, R.; Genovese, A.; Rengo, F.; Marone, G. Metabolic and Hemodynamic Effects of Peptide Leukotriene C4 and D4 in Man. Int. J. Clin. Lab. Res. 1997, 27, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varricchi, G.; Galdiero, M.R.; Tocchetti, C.G. Cardiac Toxicity of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: Cardio-Oncology Meets Immunology. Circulation 2017, 136, 1989–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varricchi, G.; Marone, G.; Kovanen, P.T. Cardiac Mast Cells: Underappreciated Immune Cells in Cardiovascular Homeostasis and Disease. Trends Immunol. 2020, 41, 734–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, J.F.; Thompson, L.J.; Ziegler, S.F. Tslp Drives Acute Th2-Cell Differentiation in Lungs. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 146, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marone, G.; Spadaro, G.; Braile, M.; Poto, R.; Criscuolo, G.; Pahima, H.; Loffredo, S.; Levi-Schaffer, F.; Varricchi, G. Tezepelumab: A Novel Biological Therapy for the Treatment of Severe Uncontrolled Asthma. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2019, 28, 931–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varricchi, G.; Pecoraro, A.; Marone, G.; Criscuolo, G.; Spadaro, G.; Genovese, A. Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin Isoforms, Inflammatory Disorders, and Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, D.K.; Llop-Guevara, A.; Walker, T.D.; Flader, K.; Goncharova, S.; Boudreau, J.E.; Moore, C.L.; In, T.S.; Waserman, S.; Coyle, A.J.; et al. Il-33, but Not Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin or Il-25, Is Central to Mite and Peanut Allergic Sensitization. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 131, 187–200.e1-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Hara, K.; Kephart, G.M.; Ziegler, S.F.; McKenzie, A.N.; Kita, H. Il-33 and Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin Mediate Immune Pathology in Response to Chronic Airborne Allergen Exposure. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 1549–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prefontaine, D.; Nadigel, J.; Chouiali, F.; Audusseau, S.; Semlali, A.; Chakir, J.; Martin, J.G.; Hamid, Q. Increased Il-33 Expression by Epithelial Cells in Bronchial Asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, 752–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beale, J.; Jayaraman, A.; Jackson, D.J.; Macintyre, J.D.R.; Edwards, M.R.; Walton, R.P.; Zhu, J.; Ching, Y.M.; Shamji, B.; Edwards, M.; et al. Rhinovirus-Induced Il-25 in Asthma Exacerbation Drives Type 2 Immunity and Allergic Pulmonary Inflammation. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 256ra134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambrecht, B.N.; Hammad, H. The Immunology of Asthma. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, S.; O’Connor, B.; Ratoff, J.; Meng, Q.; Mallett, K.; Cousins, D.; Robinson, D.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, J.; Lee, T.H.; et al. Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin Expression Is Increased in Asthmatic Airways and Correlates with Expression of Th2-Attracting Chemokines and Disease Severity. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 8183–8190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enoksson, M.; Lyberg, K.; Moller-Westerberg, C.; Fallon, P.G.; Nilsson, G.; Lunderius-Andersson, C. Mast Cells as Sensors of Cell Injury through Il-33 Recognition. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 2523–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatari, N.; Movassagh, H.; Shan, L.; Koussih, L.; Gounni, A.S. Semaphorin 3e Inhibits House Dust Mite-Induced Angiogenesis in a Mouse Model of Allergic Asthma. Am. J. Pathol. 2019, 189, 762–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Heukamp, L.C.; Siobal, M.; Schottle, J.; Wieczorek, C.; Peifer, M.; Frasca, D.; Koker, M.; Konig, K.; Meder, L.; et al. Tumor Vegf:Vegfr2 Autocrine Feed-Forward Loop Triggers Angiogenesis in Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 1732–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosisio, D.; Ronca, R.; Salvi, V.; Presta, M.; Sozzani, S. Dendritic Cells in Inflammatory Angiogenesis and Lymphangiogenesis. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2018, 53, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.M.; Shao, Z.; Grenier, V.; Mawambo, G.; Daudelin, J.F.; Dejda, A.; Pilon, F.; Popovic, N.; Boulet, S.; Parinot, C.; et al. Neuropilin-1 Expression in Adipose Tissue Macrophages Protects against Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome. Sci. Immunol. 2018, 3, eaan4626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stump, B.; Cui, Y.; Kidambi, P.; Lamattina, A.M.; El-Chemaly, S. Lymphatic Changes in Respiratory Diseases: More Than Just Remodeling of the Lung? Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2017, 57, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.C.; Baluk, P.; Feng, J.; McDonald, D.M. Steroid-Resistant Lymphatic Remodeling in Chronically Inflamed Mouse Airways. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 176, 1525–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardavella, G.; Tzortzaki, E.G.; Siozopoulou, V.; Galanis, P.; Vlachaki, E.; Avgousti, M.; Stefanou, D.; Siafakas, N.M. Lymphangiogenesis in Copd: Another Link in the Pathogenesis of the Disease. Respir. Med. 2012, 106, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, M.; Andersson, C.K.; Graham, G.J.; Lofdahl, C.G.; Erjefalt, J.S. Increased Number and Altered Phenotype of Lymphatic Vessels in Peripheral Lung Compartments of Patients with Copd. Respir. Res. 2013, 14, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspelund, A.; Robciuc, M.R.; Karaman, S.; Makinen, T.; Alitalo, K. Lymphatic System in Cardiovascular Medicine. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 515–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varricchi, G.; de Paulis, A.; Marone, G.; Galli, S.J. Future Needs in Mast Cell Biology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.; Aspelund, A.; Alitalo, K. Lymphangiogenic Factors, Mechanisms, and Applications. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 878–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Kataru, R.P.; Koh, G.Y. Inflammation-Associated Lymphangiogenesis: A Double-Edged Sword? J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 936–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, S.; Nath, S.; Meininger, C.J.; Gashev, A.A. Emerging Roles of Mast Cells in the Regulation of Lymphatic Immuno-Physiology. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammarco, G.; Varricchi, G.; Ferraro, V.; Ammendola, M.; de Fazio, M.; Altomare, D.F.; Luposella, M.; Maltese, L.; Curro, G.; Marone, G.; et al. Mast Cells, Angiogenesis and Lymphangiogenesis in Human Gastric Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fankhauser, M.; Broggi, M.A.S.; Potin, L.; Bordry, N.; Jeanbart, L.; Lund, A.W.; da Costa, E.; Hauert, S.; Rincon-Restrepo, M.; Tremblay, C.; et al. Tumor Lymphangiogenesis Promotes T Cell Infiltration and Potentiates Immunotherapy in Melanoma. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaal4712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henri, O.; Pouehe, C.; Houssari, M.; Galas, L.; Nicol, L.; Edwards-Levy, F.; Henry, J.P.; Dumesnil, A.; Boukhalfa, I.; Banquet, S.; et al. Selective Stimulation of Cardiac Lymphangiogenesis Reduces Myocardial Edema and Fibrosis Leading to Improved Cardiac Function Following Myocardial Infarction. Circulation 2016, 133, 1484–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klotz, L.; Norman, S.; Vieira, J.M.; Masters, M.; Rohling, M.; Dube, K.N.; Bollini, S.; Matsuzaki, F.; Carr, C.A.; Riley, P.R. Cardiac Lymphatics Are Heterogeneous in Origin and Respond to Injury. Nature 2015, 522, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.H.; Lavine, K.J.; Randolph, G.J. Cardiac Lymphatic Vessels, Transport, and Healing of the Infarcted Heart. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2017, 2, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, J.M.; Norman, S.; del Campo, C.V.; Cahill, T.J.; Barnette, D.N.; Gunadasa-Rohling, M.; Johnson, L.A.; Greaves, D.R.; Carr, C.A.; Jackson, D.G.; et al. The Cardiac Lymphatic System Stimulates Resolution of Inflammation Following Myocardial Infarction. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 3402–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallstrand, T.S.; Hackett, T.L.; Altemeier, W.A.; Matute-Bello, G.; Hansbro, P.M.; Knight, D.A. Airway Epithelial Regulation of Pulmonary Immune Homeostasis and Inflammation. Clin. Immunol. 2014, 151, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchuk, O.; Tuccitto, A.; Citterio, D.; Huber, V.; Camisaschi, C.; Milione, M.; Vergani, B.; Villa, A.; Alison, M.R.; Carradori, S.; et al. Ph Regulators to Target the Tumor Immune Microenvironment in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1445452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulliksson, M.; Carvalho, R.F.; Ulleras, E.; Nilsson, G. Mast Cell Survival and Mediator Secretion in Response to Hypoxia. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez-Moreno, I.G.; Ibarra-Sanchez, A.; Castillo-Arellano, J.I.; Blank, U.; Gonzalez-Espinosa, C. Mast Cells Localize in Hypoxic Zones of Tumors and Secrete Ccl-2 under Hypoxia through Activation of L-Type Calcium Channels. J. Immunol. 2020, 204, 1056–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abebayehu, D.; Spence, A.J.; Qayum, A.A.; Taruselli, M.T.; McLeod, J.J.; Caslin, H.L.; Chumanevich, A.P.; Kolawole, E.M.; Paranjape, A.; Baker, B.; et al. Lactic Acid Suppresses Il-33-Mediated Mast Cell Inflammatory Responses Via Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1alpha-Dependent Mir-155 Suppression. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 2909–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorzalczany, Y.; Akiva, E.; Klein, O.; Merimsky, O.; Sagi-Eisenberg, R. Mast Cells Are Directly Activated by Contact with Cancer Cells by a Mechanism Involving Autocrine Formation of Adenosine and Autocrine/Paracrine Signaling of the Adenosine A3 Receptor. Cancer Lett. 2017, 397, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cekic, C.; Linden, J. Purinergic Regulation of the Immune System. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Monoclonal Antibody (mAb) Anti-FcεRI (μg/mL) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10−1 | 1 | 3 | ||
| Percent Histamine Release | 14.0 ± 3.21 | 23.33 ± 4.80 | 24.66 ± 3.84 | |
| VEGF-A (pg/106 cells) | 16.33 ± 3.28 | 28.66 ± 1.45 | 51.33 ± 3.84 | |
| VEGF-C (pg/106 cells) | 16.33 ± 4.91 | 29.33 ± 6.43 | 45.0 ± 8.14 | |
| Human Polyclonal IgG (μg/mL) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10−2 | 10−1 | 1 | 3 | |
| Percent Histamine Release | 1.66 ± 1.20 | 1.66 ± 0.88 | 1.33 ± 0.88 | 1.83 ± 1.01 |
| VEGF-A (pg/106 cells) | 0.33 ± 0.33 | 2.30 ± 0.33 | 1.66 ± 1.20 | 0.66 ± 0.66 |
| VEGF-C (pg/106 cells) | 1.16 ± 0.60 | 0.50 ± 0.50 | 1.4 ± 0.94 | 0.83 ± 0.44 |
| Stimulus | Percent Histamine Release |
|---|---|
| Protein A | 18.3 ± 0.9 |
| IgM VH3+ | 0.3 ± 0.3 |
| IgM VH3+ + Protein A | 3.0 ± 0.6 *** |
| IgM VH6+ | 0.7 ± 0.6 |
| IgM VH6+ + Protein A | 18.7 ± 0.3 |
| Stimulus | Percent Histamine Release |
|---|---|
| Protein L (100 nM) | 19.0 ± 1.5 |
| IgE λ (0.3 μg/mL) + Protein L | 18.7 ± 1.8 |
| IgE λ (1 μg/mL) + Protein L | 18.3 ± 2.0 |
| IgE κ (0.3 μg/mL) + Protein L | 13.7 ± 0.7 * |
| IgE κ (1 μg/mL) + Protein L | 3.7 ± 1.2 ** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cristinziano, L.; Poto, R.; Criscuolo, G.; Ferrara, A.L.; Galdiero, M.R.; Modestino, L.; Loffredo, S.; de Paulis, A.; Marone, G.; Spadaro, G.; et al. IL-33 and Superantigenic Activation of Human Lung Mast Cells Induce the Release of Angiogenic and Lymphangiogenic Factors. Cells 2021, 10, 145. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10010145
Cristinziano L, Poto R, Criscuolo G, Ferrara AL, Galdiero MR, Modestino L, Loffredo S, de Paulis A, Marone G, Spadaro G, et al. IL-33 and Superantigenic Activation of Human Lung Mast Cells Induce the Release of Angiogenic and Lymphangiogenic Factors. Cells. 2021; 10(1):145. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10010145
Chicago/Turabian StyleCristinziano, Leonardo, Remo Poto, Gjada Criscuolo, Anne Lise Ferrara, Maria Rosaria Galdiero, Luca Modestino, Stefania Loffredo, Amato de Paulis, Gianni Marone, Giuseppe Spadaro, and et al. 2021. "IL-33 and Superantigenic Activation of Human Lung Mast Cells Induce the Release of Angiogenic and Lymphangiogenic Factors" Cells 10, no. 1: 145. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10010145
APA StyleCristinziano, L., Poto, R., Criscuolo, G., Ferrara, A. L., Galdiero, M. R., Modestino, L., Loffredo, S., de Paulis, A., Marone, G., Spadaro, G., & Varricchi, G. (2021). IL-33 and Superantigenic Activation of Human Lung Mast Cells Induce the Release of Angiogenic and Lymphangiogenic Factors. Cells, 10(1), 145. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10010145








