Combining Mineral Amendments Improves Wheat Yield and Soil Properties in a Coastal Saline Area
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
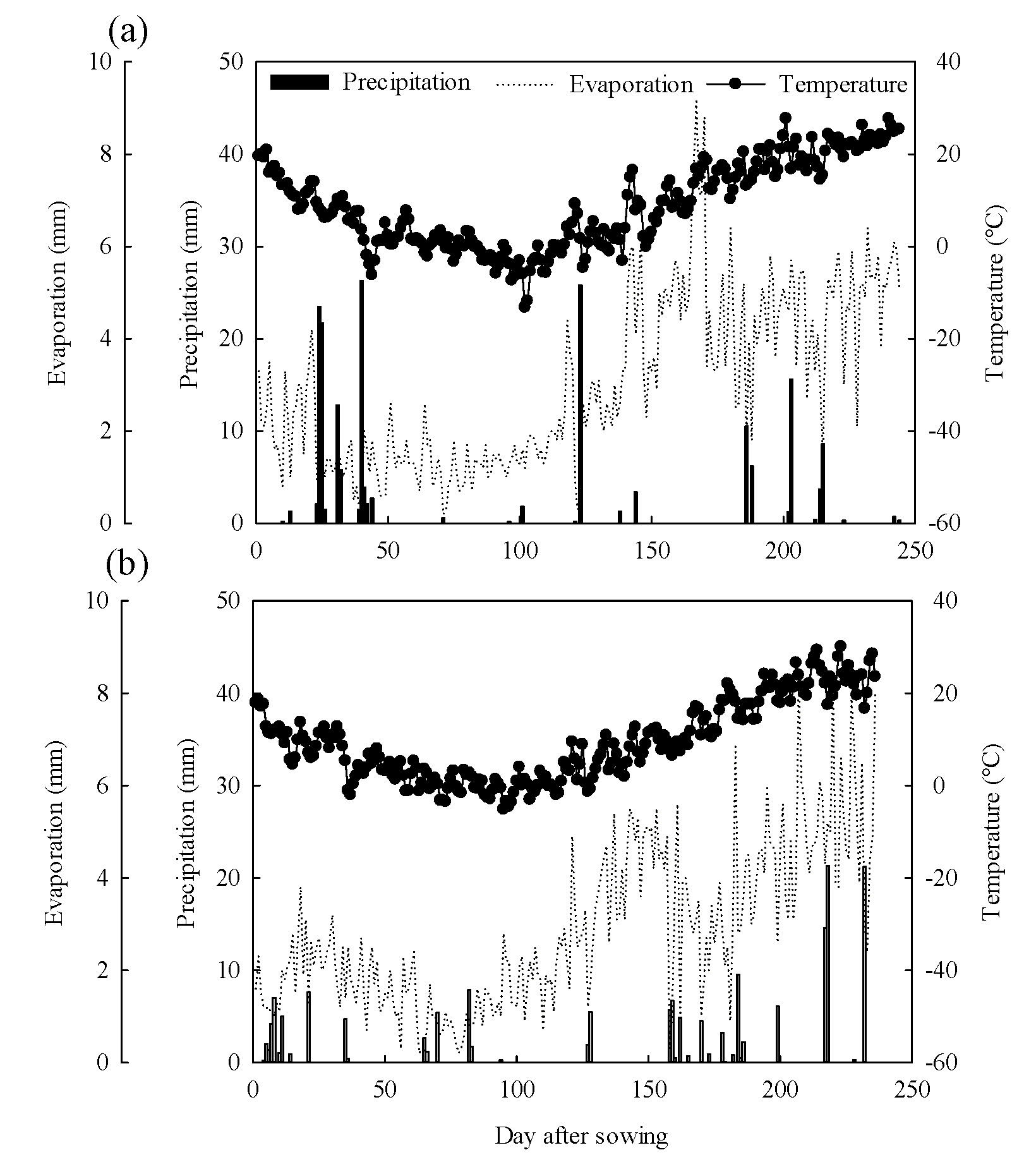
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Mineral Amendment Materials
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Sampling and Laboratory Procedures
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
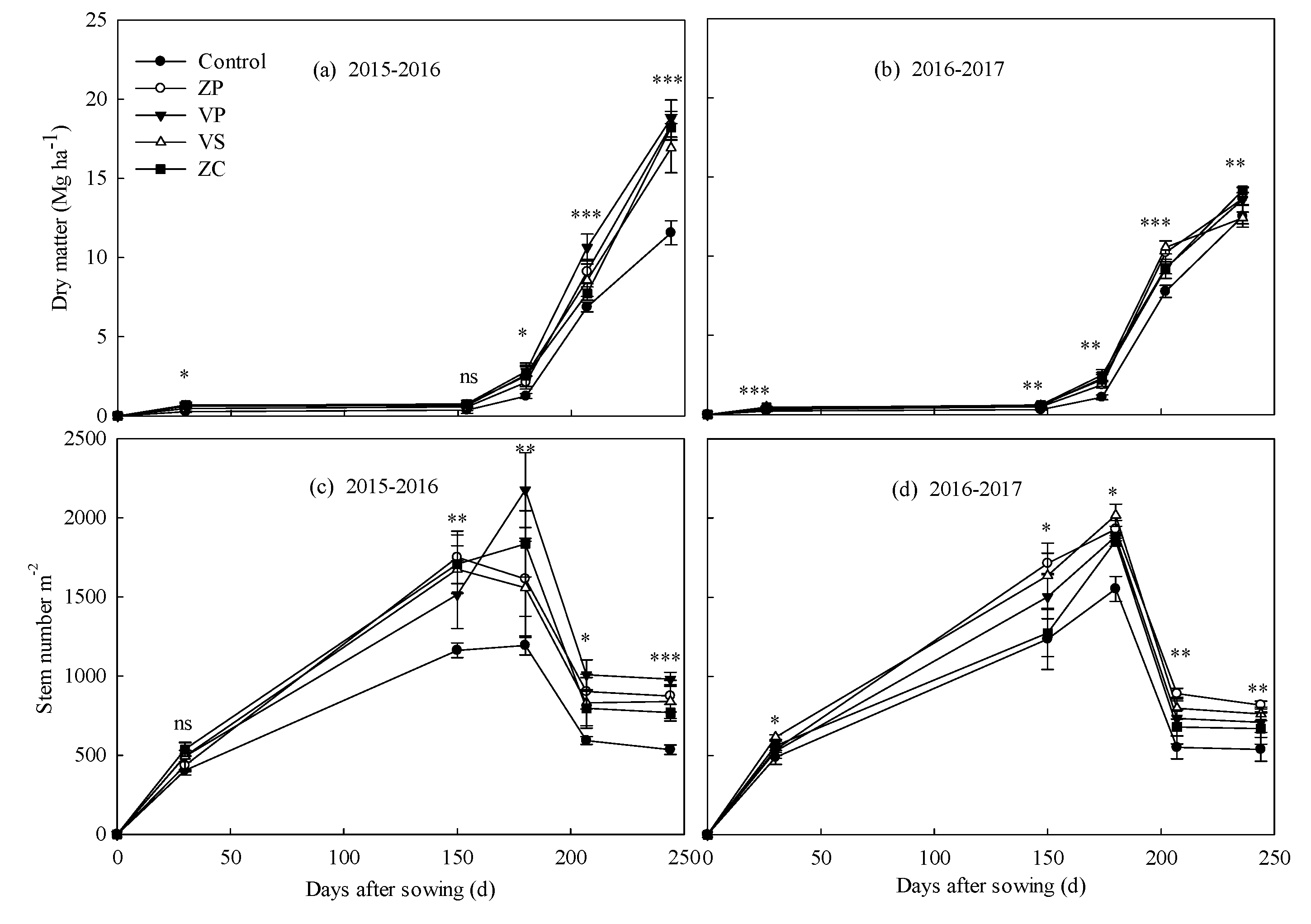
3.1. Wheat Grain Yield, Yield Components, and Dry Matter
3.2. Chemical Composition of Wheat Straw and Grain
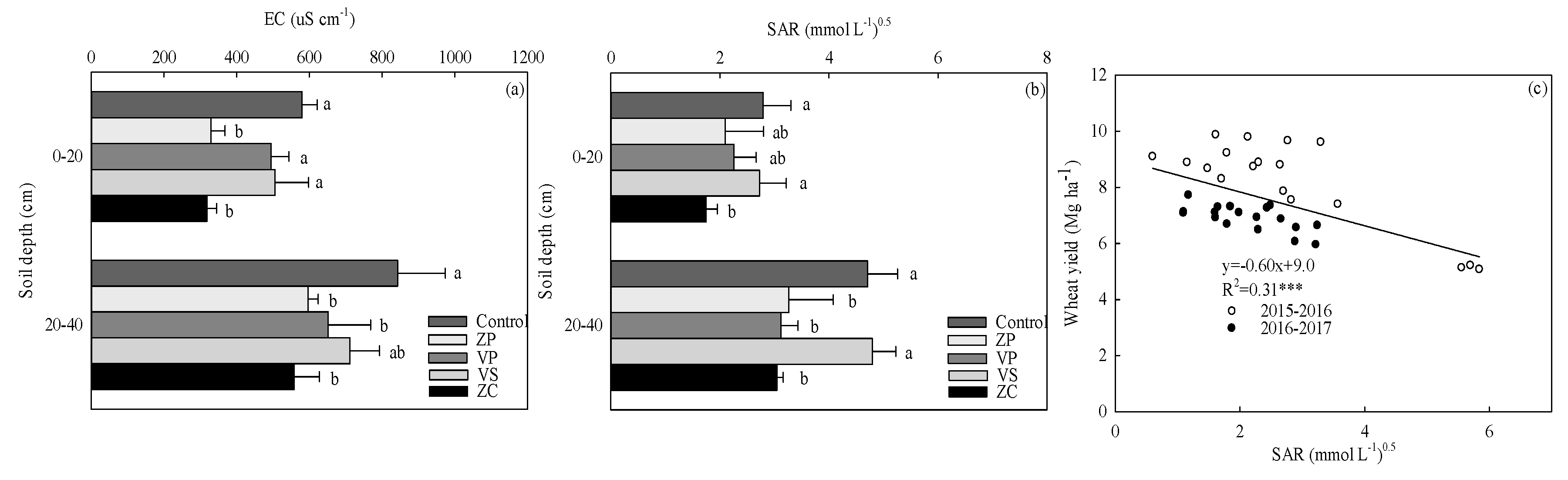
3.3. Soil Properties
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qadir, M.; Ghafoor, A.; Murtaza, G. Amelioration strategies for saline soils: A review. Land Degrad. Dev. 2001, 11, 501–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.; Hussain, M.; Wakeel, A.; Siddique, K.H. Salt stress in maize: Effects, resistance mechanisms, and management. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 35, 461–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, G.; Gao, M.; Chang, C. Spatial variability of soil salinity in coastal saline soil at different scales in the Yellow River Delta, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nan, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Lashari, M.S.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Du, Z. Effects of applying flue gas desulfurization gypsum and humic acid on soil physicochemical properties and rapeseed yield of a saline-sodic cropland in the eastern coastal area of China. J. Soil Sediments 2016, 16, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, A.; Muhammad, Z.; Ahmad, H. Plant growth promoting bacteria: Role in soil improvement, abiotic and biotic stress management of crops. Plant Cell Rep. 2018, 37, 1599–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jesus, J.M.; Danko, A.S.; Fiúza, A.; Borges, M.T. Phytoremediation of salt-affected soils: A review of processes, applicability, and the impact of climate change. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 6511–6525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nan, J.; Chen, X.; Chen, C.; Lashari, M.S.; Deng, J.; Du, Z. Impact of flue gas desulfurization gypsum and lignite humic acid application on soil organic matter and physical properties of a saline-sodic farmland soil in Eastern China. J. Soil Sediments 2016, 16, 2175–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasouli, F.; Pouya, A.K.; Karimian, N. Wheat yield and physico-chemical properties of a sodic soil from semi-arid area of Iran as affected by applied gypsum. Geoderma 2013, 193–194, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yan, Z.; Qin, J.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L. The potential of residues of furfural and biogas as calcareous soil amendments for corn seed production. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 6217–6226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.B.; Yang, J.S.; Yao, R.J.; Yu, S.P.; Li, F.R.; Hou, X.J. The effects of farmyard manure and mulch on soil physical properties in a reclaimed coastal tidal flat salt-affected soil. J. Integr. Agric. 2014, 13, 1782–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.J.; Jan, M.T.; Khan, A.U.; Arif, M.; Shafi, M. Management of saline sodic soils through cultural practices and gypsum. Pak. J. Bot. 2010, 42, 4143–4155. [Google Scholar]
- Oo, A.N.; Iwai, C.B.; Saenjan, P. Soil properties and maize growth in saline and nonsaline soils using cassava-industrial waste compost and vermicompost with or without earthworms. Land Degrad. Dev. 2015, 26, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejada, M.; Garcia, C.; Gonzalez, J.L.; Hernandez, M.T. Organic amendment based on fresh and composted beet vinasse. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2006, 70, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.P.; Long, X.H.; Shao, H.B.; Liu, Z.P.; Tao, Y.; Zhou, Q.S.; Zong, J.Q. Ameliorants improve saline–alkaline soils on a large scale in northern Jiangsu Province, China. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 81, 328–334. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, X.; Wang, B.; Zhang, J. Liquefaction of cotton seed in sub-critical water/ethanol with modified medical stone for bio-oil. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 197, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eroglu, N.; Emekci, M.; Athanassiou, C. Applications of natural zeolites on agriculture and food production. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 3487–3499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazrati, S.; Tahmasebi-Sarvestani, Z.; Mokhtassi-Bidgoli, A.; Modarres-Sanavy, S.A.M.; Mohammadi, H.; Nicola, S. Effects of zeolite and water stress on growth, yield and chemical compositions of Aloe vera L. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 181, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bybordi, A. Influence of zeolite, selenium and silicon upon some agronomic and physiologic characteristics of canola grown under salinity. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant. 2016, 47, 832–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malamis, S.; Katsou, E. A review on zinc and nickel adsorption on natural and modified zeolite, bentonite and vermiculite: Examination of process parameters, kinetics and isotherms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 252, 428–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaseen, M.; Malhi, S.S. Differential growth response of wheat genotypes to ammonium phosphate and rock phosphate phosphorus sources. J. Plant Nutr. 2009, 32, 410–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Awasthi, M.K.; Jiang, Y.; Li, R.; Ren, X.; Zhao, J.; Shen, F.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Z. Evaluation of medical stone amendment for the reduction of nitrogen loss and bioavailability of heavy metals during pig manure composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 220, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khodaei Joghan, A.; Ghalavand, A.; Aghaalikhani, M.; Gholamhoseini, M.; Dolatabadian, A. How organic and chemical nitrogen fertilizers, zeolite, and combinations influence wheat yield and grain mineral content. J. Crop Improv. 2012, 26, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polat, E.; Karaca, M.; Demir, H.; Onus, N.A. Use of natural zeolite (clinoptilolite) in agriculture. J. Fruit Ornam. Plant Res. 2004, 12, 183–189. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, N.; Ozawa, S.; Ochi, K.; Chikuma, T.; Watanabe, Y. Approaches for cesium uptake by vermiculite. J. Chem. Technol. Biot. 2013, 88, 1603–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, J.; Riley, J.P. A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal. Chom. Acta 1962, 27, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, L.A. Diagnosis and Improvement of Saline and Alkali Soils; USA Department of Agriculture Handbook 60; USDA Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1954.
- Zhang, W.; Liu, D.; Liu, Y.; Cui, Z.; Chen, X.; Zou, C. Zinc uptake and accumulation in winter wheat relative to changes in root morphology and mycorrhizal colonization following varying phosphorus application on calcareous soil. Field Crop Res. 2016, 197, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAS System [Computer Program]; Version 6.12; SAS Institute Inc.: Cary, NC, USA, 1998.
- Lu, D.; Yue, S.; Lu, F.; Cui, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zou, C.; Chen, X. Integrated crop-N system management to establish high wheat yield population. Field Crop Res. 2016, 191, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Huang, W.; Zhang, C. Amelioration of salt stress on wheat plants growth in coastal saline soil by a phosphate solubilizing bacterium Enterobacteria sp. EnHy-401. Agric. Sci. Technol. Hunan 2010, 11, 141–146. [Google Scholar]
- Yazdanpanah, N.; Pazira, E.; Neshat, A.; Mahmoodabadi, M.; Sinobas, L.R. Reclamation of calcareous saline sodic soil with different amendments (II): Impact on nitrogen, phosphorous and potassium redistribution and on microbial respiration. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 120, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.M.; Wang, H.Y.; Liu, X.W.; Zhao, X.L.; Lu, D.J.; Zhou, J.M.; Li, C.Z. Changes in soil microbial community and organic carbon fractions under short-term straw return in a rice–wheat cropping system. Soil Till. Res. 2017, 165, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.L.; Penfold, C.; Marschner, P. Mobilisation of rock phosphate by surface application of compost. Biol. Fert. Soil. 2013, 49, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodabadi, M.; Yazdanpanah, N.; Sinobas, L.R.; Pazira, E.; Neshat, A. Reclamation of calcareous saline sodic soil with different amendments (I): Redistribution of soluble cations within the soil profile. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 120, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, R.; Dimitrios, P. Diffusion and cation exchange during the reclamation of saline-structured soils. Geoderma 2002, 107, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z. Optimization of the Nitrogen Fertilizer Management for a Winter Wheat-Summer Maize Rotation System in the North China Plain-from feld to region scale. Ph.D. Thesis, China Agricultural University, Beijing, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, D.; Lu, F.; Pan, J.; Cui, Z.; Zou, C.; Chen, X.; He, M.; Wang, Z. Manure limits wheat yield losses due to delayed seeding. Agron. J. 2015, 107, 2294–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mass, E.V.; Poss, J.A. Salt sensitivity of cowpea at various growth stages. Irrig. Sci. 1989, 10, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Soil Depth (cm) | Amendment Materials | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–20 | 20–40 | Zeolite | Vermiculite | Rock Phosphate | Medical Stone | Silica Calcium Soil Conditioner | |
| pH | 7.68 | 7.67 | 9.64 | 9.04 | 9.13 | 8.34 | 9.57 |
| EC (μS cm−1) | 917 | 692 | 146 | 531 | 3560 | 362 | 1991 |
| Organic carbon (g kg−1) | 6.34 | 3.72 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Total N content (g kg−1) | 0.81 | 0.58 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Available P (mg kg−1) | 7.38 | 6.07 | 247 | 197 | 2169 | 279 | 354 |
| Soluble Ca2+ (mg kg−1) | 275 | 150 | 19.1 | 74.1 | 3931 | 191 | 3336 |
| Soluble K+ (mg kg−1) | 24.4 | 14.9 | 6.83 | 28.8 | 353 | 887 | 26.3 |
| Soluble Mg2+ (mg kg−1) | 96 | 47.2 | 51 | 14.8 | 353 | 66 | 175 |
| Soluble Na+ (mg kg−1) | 444 | 254 | 36.6 | 383 | 671 | 810 | 101 |
| Year | Control | ZP | VP | VS | ZC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yield (Mg ha−1) | |||||
| 2015–2016 | 5.15c | 9.45a | 9.17a | 7.61b | 9.15a |
| 2016–2017 | 6.17c | 6.79b | 7.32a | 6.82b | 7.11ab |
| Spike number (104 ha−1) | |||||
| 2015–2016 | 535c | 873ab | 979a | 839b | 769b |
| 2016–2017 | 539c | 818a | 711ab | 762ab | 671b |
| Grain number per spike | |||||
| 2015–2016 | 23.9d | 30.2b | 28.9c | 29.7bc | 34.1a |
| 2016–2017 | 29.8ab | 30.9ab | 31.9a | 29.1b | 30ab |
| Grain weight (g 1000−1) | |||||
| 2015–2016 | 38.9b | 41.8a | 42.0a | 37.9b | 42.2a |
| 2016–2017 | 37.4ab | 36.5bc | 38.8a | 34.7c | 35.2c |
| Harvest index | |||||
| 2015–2016 | 0.39b | 0.45a | 0.43ab | 0.40b | 0.44ab |
| 2016–2017 | 0.43b | 0.44b | 0.47a | 0.48a | 0.44b |
| ANOVA | Sum of Squares | Degrees of Freedom | Mean of the Squares | F Value | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yield (Mg ha−1) | |||||
| Year | 11.946 | 1.000 | 11.946 | 104.200 | <0.001 |
| Treatment | 28.785 | 4.000 | 7.196 | 62.773 | <0.001 |
| Year × Treatment | 12.544 | 4.000 | 3.136 | 27.355 | <0.001 |
| Spike number (104 ha−1) | |||||
| Year | 11.946 | 1.000 | 11.946 | 104.200 | <0.001 |
| Treatment | 28.785 | 4.000 | 7.196 | 62.773 | <0.001 |
| Year × Treatment | 12.544 | 4.000 | 3.136 | 27.355 | <0.001 |
| Grain number per spike | |||||
| Year | 7.618 | 1.000 | 7.618 | 8.706 | 0.008 |
| Treatment | 87.307 | 4.000 | 21.827 | 24.946 | <0.001 |
| Year × Treatment | 85.401 | 4.000 | 21.350 | 24.401 | <0.001 |
| Grain weight (g 1000−1) | |||||
| Year | 122.143 | 1.000 | 122.143 | 133.789 | <0.001 |
| Treatment | 53.742 | 4.000 | 13.435 | 14.717 | <0.001 |
| Year × Treatment | 27.753 | 4.000 | 6.938 | 7.600 | 0.001 |
| Harvest index | |||||
| Year | 0.007 | 1.000 | 0.007 | 13.485 | 0.002 |
| Treatment | 0.005 | 4.000 | 0.001 | 2.469 | 0.078 |
| Year × Treatment | 0.010 | 4.000 | 0.002 | 4.491 | 0.009 |
| Cropping Years | Treatment | Wheat Straw | Wheat Grain | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | Ca | Mg | K | Na | P | Ca | Mg | K | Na | ||
| g kg−1 | g kg−1 | g kg−1 | g kg−1 | mg kg−1 | g kg−1 | g kg−1 | g kg−1 | g kg−1 | mg kg−1 | ||
| 2015–2016 | Control | 0.40a | 3.61ab | 1.72a | 20.0b | 1852a | 3.07b | 0.48a | 1.60a | 4.37b | 87.7a |
| ZP | 0.45a | 2.95c | 1.34c | 24.3a | 623c | 3.25a | 0.48a | 1.55ab | 4.46b | 28.9b | |
| VP | 0.44a | 3.41b | 1.53b | 26.4a | 1010b | 3.10b | 0.48a | 1.52b | 4.75a | 36.6b | |
| VS | 0.36a | 3.81a | 1.57ab | 26.1a | 1024b | 2.73c | 0.48a | 1.52b | 4.53b | 32.0b | |
| ZC | 0.38a | 3.07c | 1.36c | 24.7a | 827bc | 3.09b | 0.46a | 1.52b | 4.75a | 26.5b | |
| 2016–2017 | Control | 0.38b | 2.86a | 1.26a | 19.3b | 1721a | 3.47b | 0.41a | 1.65a | 4.77b | 77.2a |
| ZP | 0.49a | 2.39cd | 1.01bc | 22.4a | 632d | 3.09c | 0.36a | 1.50b | 4.65b | 33.3c | |
| VP | 0.52a | 2.73ab | 1.06b | 23.2a | 1032c | 3.79a | 0.39a | 1.63a | 5.06a | 44.1c | |
| VS | 0.36bc | 2.53bc | 1.04b | 18.8b | 1283b | 3.84a | 0.40a | 1.68a | 5.00a | 58.1b | |
| ZC | 0.27c | 2.24d | 0.94c | 21.7a | 554d | 3.61b | 0.38a | 1.61a | 5.14a | 32.4c | |
| Source of variation (p value) | |||||||||||
| Year (Y) | 0.8959 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.6273 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0014 | <0.0001 | 0.0561 | |
| Treatment (T) | 0.0003 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0010 | <0.0001 | 0.0004 | 0.6074 | 0.0249 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |
| Y × T | 0.0818 | 0.0060 | 0.1577 | 0.0356 | 0.0230 | <0.0001 | 0.6495 | 0.0140 | 0.0785 | 0.0388 | |
| Soil Depth | Treatment | pH | Soil Organic Carbon (g kg−1) | Total N (g kg−1) | Available P (mg kg−1) | Soluble Ions (mg kg−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ca2+ | K+ | Mg2+ | Na+ | ||||||
| 0–20 cm | Control | 7.57a | 6.99b | 0.83c | 12.1b | 179a | 18.9c | 58.8a | 268a |
| ZP | 7.58a | 8.70a | 0.99ab | 16.8a | 122b | 29.4ab | 28.9b | 159bc | |
| VP | 7.59a | 7.58b | 0.98ab | 16.3a | 188a | 32.0a | 51.5a | 216abc | |
| VS | 7.60a | 7.85ab | 0.87bc | 14.9a | 171a | 19.9c | 50.6a | 251ab | |
| ZC | 7.59a | 8.71a | 1.04a | 14.6ab | 142ab | 24.3bc | 34.1b | 142c | |
| p value | 0.7264 | 0.0173 | 0.0273 | 0.0223 | 0.0537 | 0.0084 | 0.0008 | 0.0569 | |
| 20–40 cm | Control | 7.55c | 4.43b | 0.61b | 5.9c | 182a | 6.84b | 75.0a | 492a |
| ZP | 7.58bc | 5.72a | 0.77a | 7.66bc | 208a | 7.74b | 53.7a | 312b | |
| VP | 7.54c | 5.45ab | 0.67b | 10.5a | 162a | 15.1a | 66.4a | 319b | |
| VS | 7.64b | 4.78ab | 0.64b | 8.79ab | 209a | 7.41b | 57.4a | 442a | |
| ZC | 7.72a | 5.59a | 0.69ab | 8.07abc | 164a | 7.89b | 60.5a | 284b | |
| p value | 0.0017 | 0.1060 | 0.0256 | 0.0246 | 0.5343 | 0.0017 | 0.3389 | 0.0133 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Jiang, X.; Miao, Q.; Yu, B.; Xu, L.; Cui, Z. Combining Mineral Amendments Improves Wheat Yield and Soil Properties in a Coastal Saline Area. Agronomy 2019, 9, 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9020048
Zhang J, Jiang X, Miao Q, Yu B, Xu L, Cui Z. Combining Mineral Amendments Improves Wheat Yield and Soil Properties in a Coastal Saline Area. Agronomy. 2019; 9(2):48. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9020048
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jishi, Xilong Jiang, Qi Miao, Botao Yu, Liming Xu, and Zhenling Cui. 2019. "Combining Mineral Amendments Improves Wheat Yield and Soil Properties in a Coastal Saline Area" Agronomy 9, no. 2: 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9020048
APA StyleZhang, J., Jiang, X., Miao, Q., Yu, B., Xu, L., & Cui, Z. (2019). Combining Mineral Amendments Improves Wheat Yield and Soil Properties in a Coastal Saline Area. Agronomy, 9(2), 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9020048





