Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of Heat Shock Transcription Factor Family in Chenopodium quinoa Willd
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identification of Hsf Genes in the Quinoa Genome
2.2. Multiple Alignment, Phylogenetic, and Conserved Motif Analysis of CqHsfs
2.3. Interaction Network Analysis of CqHsfs
2.4. Expression Profiles Analysis of CqHsf Genes
2.5. Plant Growth, Heat Stress Treatment, and RT-PCR Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Genome-Wide Identification of Hsf Genes in Quinoa
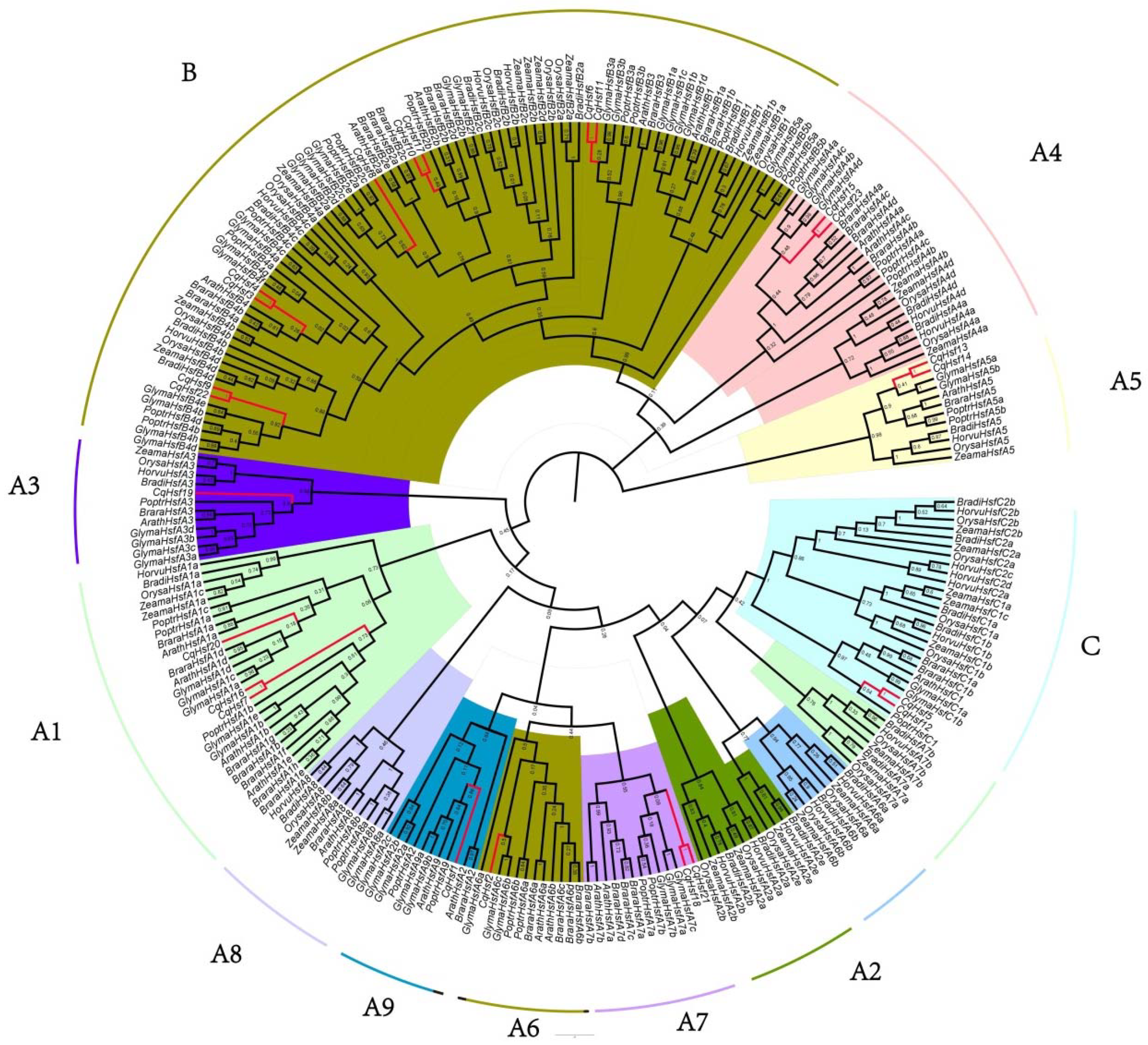
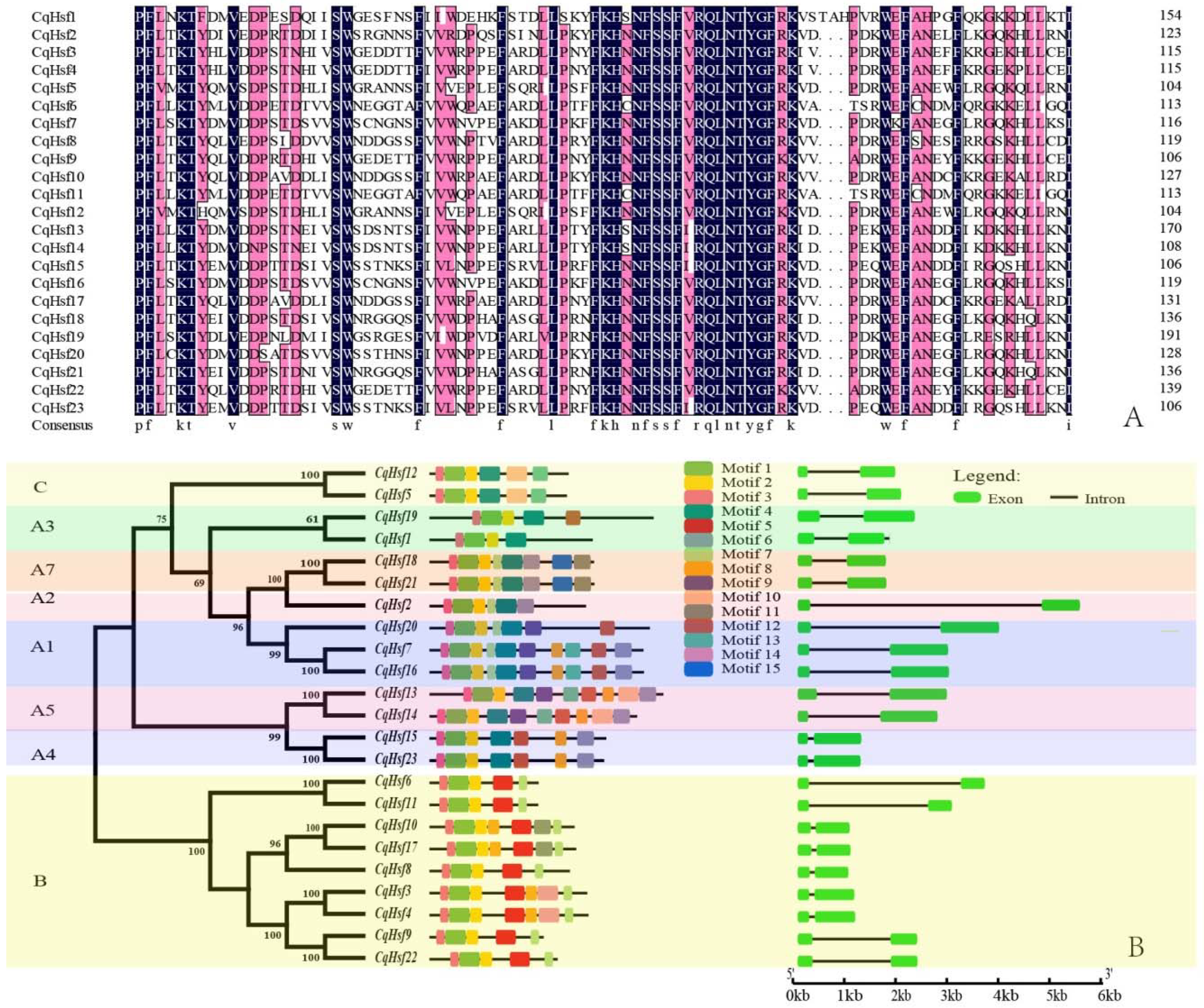
3.2. Multiple Alignment, Phylogenetic and Conserved Domains Analysis of CqHsfs
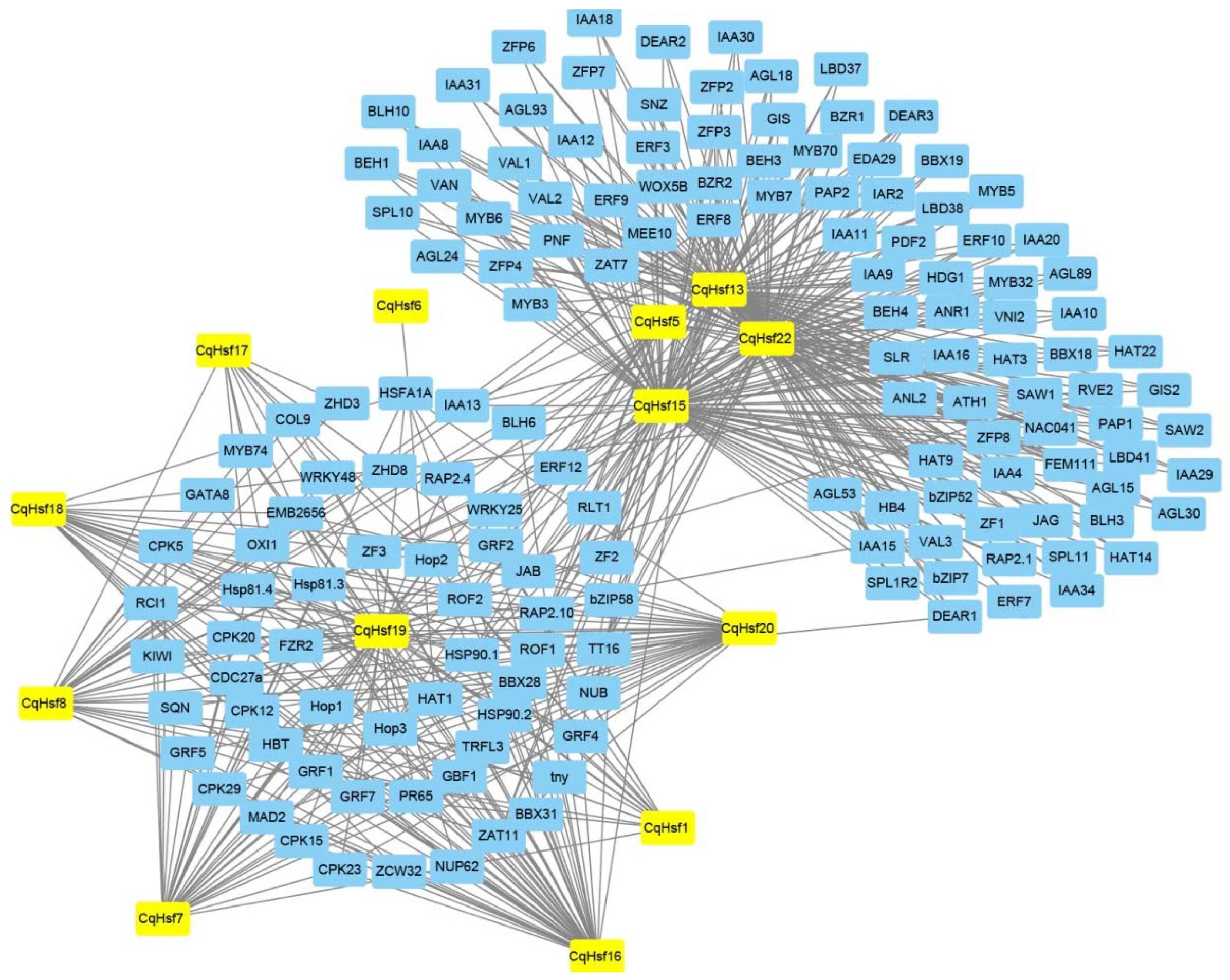
3.3. Interaction Network of CqHsfs
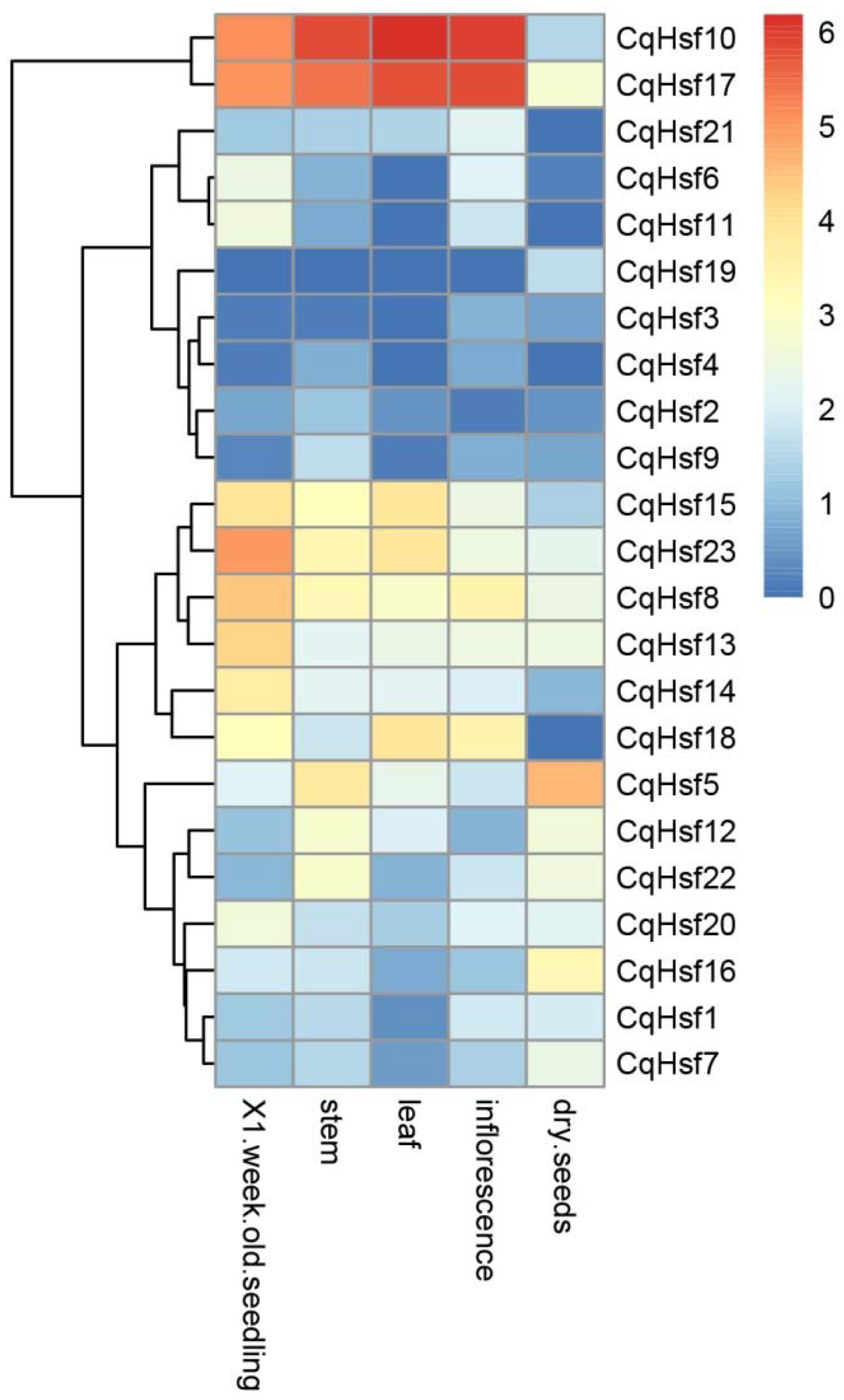
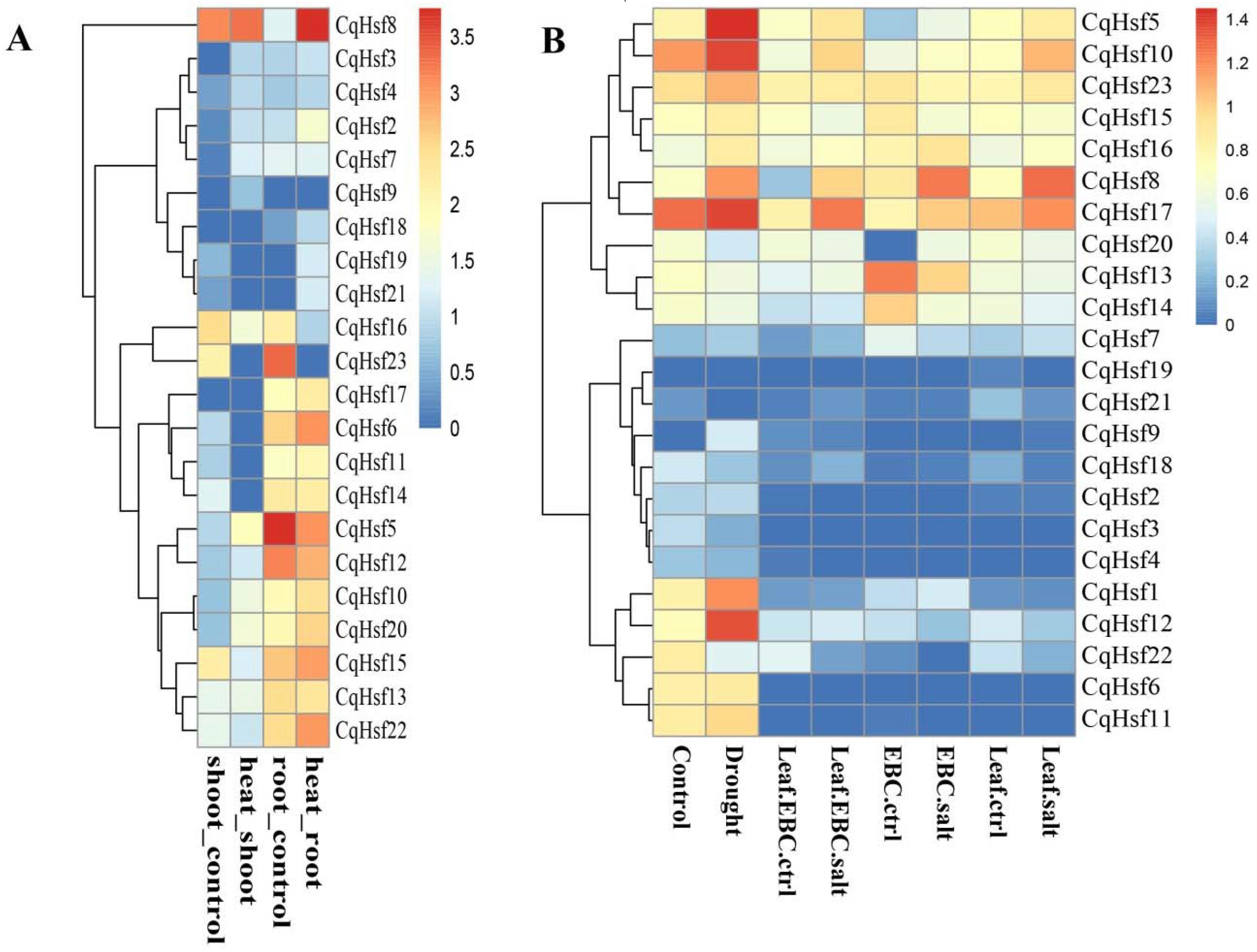
3.4. Expression Patterns of CqHsfs in Different Tissues or Organs
3.5. Expression Patterns of CqHsf Genes under Abiotic Stress Conditions
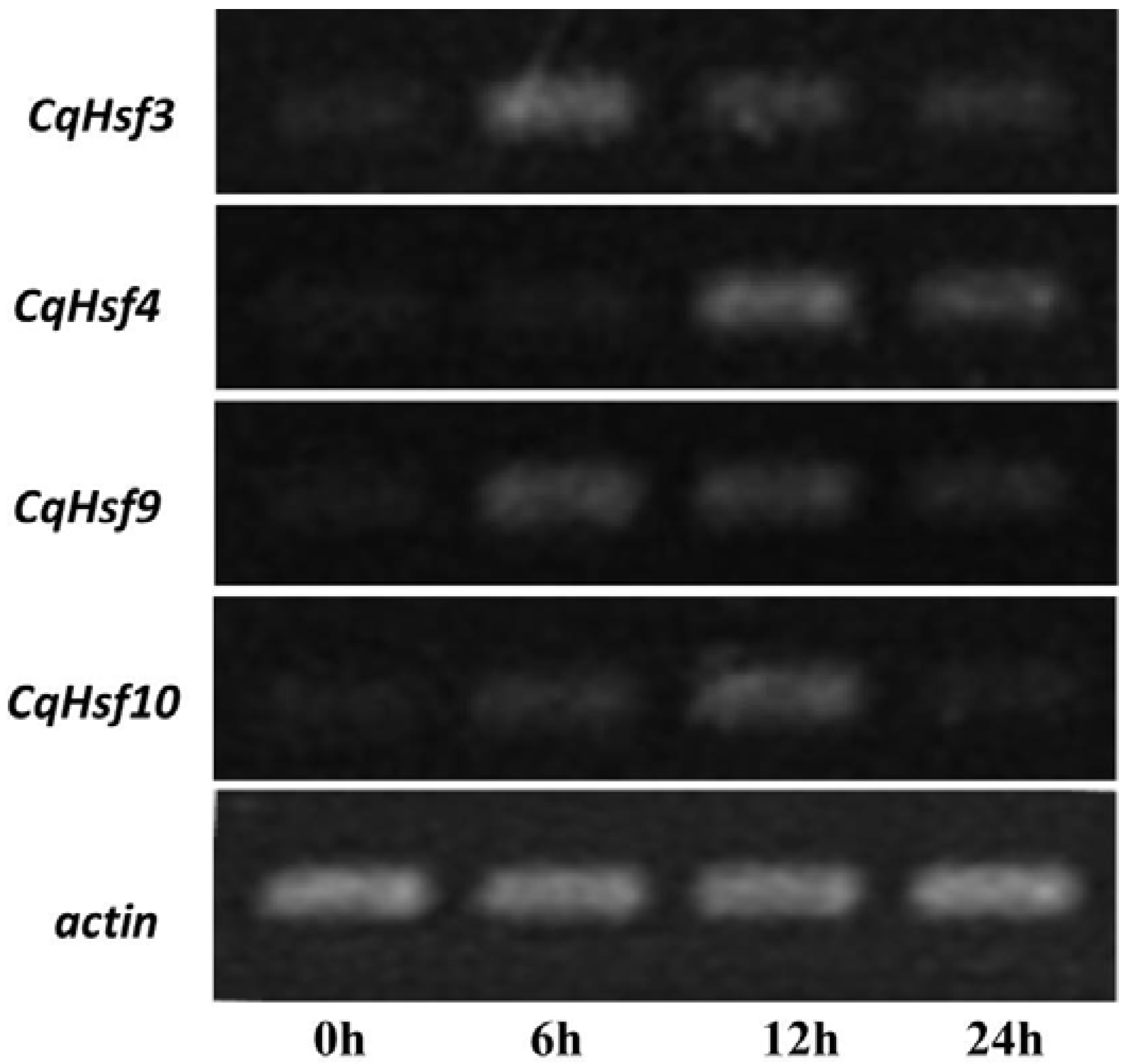
3.6. Validation of the Expression of CqHsfs by Semi-Quantitative RT-PCR Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, W.; Vinocur, B.; Altman, A. Plant responses to drought, salinity and extreme temperatures: Towards genetic engineering for stress tolerance. Planta 2013, 218, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahid, A.; Gelani, S.; Ashraf, M.; Foolad, M.R. Heat tolerance in plants: An overview. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2007, 61, 199–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.X.; Jiang, H.Y.; Chu, Z.X.; Tang, X.L.; Zhu, S.W.; Cheng, B.J. Genome-wide identification, classification and analysis of heat shock transcription factor family in maize. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nover, L.; Bharti, K.; Döring, P.; Mishra, S.K.; Ganguli, A.; Scharf, K.-D. Arabidopsis and the heat stress transcription factor world: How many heat stress transcription factors do we need? Cell Stress Chaperones 2011, 6, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damberger, F.F.; Pelton, J.G.; Harrison, C.J.; Nelson, H.C.M.; Wemmer, D.E. Solution structure of the DNA-binding domain of the heat shock transcription factor determined by multidimensional heteronuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Protein Sci. 1994, 3, 1806–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, C.J.; Bohm, A.A.; Nelson, H.C. Crystal structure of the DNA binding domain of the heat shock transcription factor. Science 1994, 263, 224–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuister, G.W.; Kim, S.-J.; Orosz, A.J.; Marquardt, J.; Wu, C.; Bax, A. Solution structure of the DNA-binding domain of Drosophila heat shock transcription factor. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1994, 1, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultheiss, J.; Kunert, O.; Gase, U.; Scharf, K.D.; Nover, L.; Rüterjans, H. Solution structure of the DNA-binding domain of the tomato heat-stress transcription factor HSF24. Eur. J. Biochem. 1996, 236, 911–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bienz, M.; Pelham, H.R.B. Mechanisms of heat-shock gene activation in higher eukaryotes. Adv. Genet. 1987, 24, 31–72. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pelham, H.R.B. A regulatory upstream promoter element in the Drosophila Hsp70 heat-shock gene. Cell 1982, 30, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peteranderl, R.; Rabenstein, M.; Shin, Y.-K.; Liu, C.W.; Wemmer, D.E.; King, D.S.; Nelson, H.C.M. Biochemical and biophysical characterization of the trimerization domain from the heat shock transcription factor. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 3559–3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyck, R.; Harmening, U.; Höhfeld, I.; Treuter, E.; Scharf, K.-D.; Nover, L. Intracellular distribution and identification of the nuclear localization signals of two plant heat-stress transcription factors. Planta 1997, 202, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Heerklotz, D.; Döring, P.; Bonzelius, F.; Winkelhaus, S.; Nover, L. The Balance of nuclear import and export determines the intracellular distribution and function of tomato heat stress transcription factor HsfA2. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 1759–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotak, S.; Port, M.; Ganguli, A.; Bicker, F.; Von Koskull-Döring, P. Characterization of C-terminal domains of Arabidopsis heat stress transcription factors (Hsfs) and identification of a new signature combination of plant class A Hsfs with AHA and NES motifs essential for activator function and intracellular localization. Plant J. 2004, 39, 98–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Döring, P.; Treuter, E.; Kistner, C.; Lyck, R.; Chen, A.; Nover, L. The role of AHA motifs in the activator function of tomato heat stress transcription factors HsfA1 and HsfA2. Plant J. 2000, 12, 265–279. [Google Scholar]
- Scharf, K.D.; Berberich, T.; Ebersberger, I.; Nover, L. The plant heat stress transcription factor (Hsf) family: Structure, function and evolution. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1819, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Liu, J.H.; Ma, X.; Luo, D.X.; Gong, Z.H.; Lu, M.H. The Plant Heat Stress Transcription Factors (HSFs): Structure, Regulation, and Function in Response to Abiotic Stresses. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Liu, G.; Duan, W.; Liu, T.; Huang, Z.; Ren, J.; Li, Y.; Hou, X. Genome-wide identification, classification and expression analysis of the heat shock transcription factor family in Chinese cabbage. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2014, 289, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.S.; Yu, T.F.; He, G.H.; Chen, M.; Zhou, Y.B.; Chai, S.C.; Xu, Z.S.; Ma, Y.Z. Genome-wide analysis of the Hsf family in soybean and functional identification of GmHsf-34 involvement in drought and heat stresses. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Wu, J.; Ji, Q.; Wang, C.; Luo, L.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J. Genome-wide analysis of heat shock transcription factor families in rice and Arabidopsis. J. Genet. Genom. 2008, 35, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, G.P.; Sadat, S.; Drenth, J.; McIntyre, C.L. The heat shock factor family from Triticum aestivum in response to heat and other major abiotic stresses and their role in regulation of heat shock protein genes. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 539–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delatorre-Herrera, J. Current use of Quinoa in Chile. Food Rev. Int. 2003, 19, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, A.; Shukla, S.; Ohri, D. Chenopodium quinoa—An Indian perspective. Ind. Crops Prod. 2006, 23, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.X.; Wang, R.M.; Liu, W.J.; Zhang, H.L.; Guo, Y.D.; Wen, R.Y. Genome-Wide Characterization of Heat-Shock Protein 70s from Chenopodium quinoa and Expression Analyses of Cqhsp70s in Response to Drought Stress. Genes 2018, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Yue, H.; Feng, K.; Deng, P.; Song, W.; Nie, X. Genome-wide identification, phylogeny and expressional profiles of mitogen activated protein kinase kinase kinase (MAPKKK) gene family in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kersey, P.J.; Allen, J.E.; Armean, I.; Boddu, S.; Bolt, B.J.; Carvalho-Silva, D.; Christensen, M.; Davis, P.; Falin, L.J.; Grabmueller, C.; et al. Ensembl Genomes 2016: More genomes, more complexity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 44, D574–D580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finn, R.D.; Mistry, J.; Schuster-Böckler, B.; Griffiths-Jones, S.; Hollich, V.; Lassmann, T.; Moxon, S.; Marshall, M.; Khanna, A.; Durbin, R.; et al. PFAM: Clans, web tools and services. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, D247–D251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, T.J.; Eddy, S.R. NHMMER: DNA homology search with profile HMMs. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 2487–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larkin, M.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol. Boil. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, T.L.; Boden, M.; Buske, F.A.; Frith, M.; Grant, C.E.; Clementi, L.; Ren, J.; Li, W.W.; Noble, W.S. MEME SUITE: Tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W202–W208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Jin, J.; Guo, A.Y.; Zhang, H.; Luo, J.; Gao, Ge. GSDS 2.0: An upgraded gene feature visualization server. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1296–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pertea, M.; Kim, D.; Pertea, G.M.; Leek, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. Transcript-level expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with HISAT, StringTie and Ballgown. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 1650–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Hu, W.; Tan, S.; Wang, M.; Ma, Z.; Zhou, S.; Deng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, C.; Yang, G.; et al. Genome-wide identification and analysis of MAPK and MAPKK gene families in Brachypodium distachyon. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higashi, Y.; Ohama, N.; Ishikawa, T.; Katori, T.; Shimura, A.; Kusakabe, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K.; Ishida, J.; Tanaka, M.; Seki, M.; et al. HsfA1d, a protein identified via FOX hunting using Thellungiella salsuginea cDNAs improves heat tolerance by regulating heat-stress-responsive gene expression. Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busch, W.; Wunderlich, M.; Schöffl, F. Identification of novel heat shock factor-dependent genes and biochemical pathways in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2005, 41, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giorno, F.; Guerriero, G.; Baric, S.; Mariani, C. Heat shock transcriptional factors in Malus domestica: Identification, classification and expression analysis. BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murshid, A.; Prince, T.L.; Lang, B.; Calderwood, S.K. Role of Heat Shock Factors in Stress-Induced Transcription. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1709, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| Gene | Gene ID | Amino Acid Length (aa) | PI | Mw (Kda) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CqHsf1 | LOC110683052 | 380 | 5.49 | 43.14 |
| CqHsf2 | LOC110685407 | 364 | 5.08 | 41.86 |
| CqHsf3 | LOC110686357 | 367 | 8.15 | 41.00 |
| CqHsf4 | LOC110688732 | 370 | 8.43 | 41.32 |
| CqHsf5 | LOC110691034 | 319 | 5.90 | 36.75 |
| CqHsf6 | LOC110691517 | 252 | 8.70 | 29.08 |
| CqHsf7 | LOC110693028 | 500 | 5.14 | 55.45 |
| CqHsf8 | LOC110697083 | 326 | 5.54 | 36.46 |
| CqHsf9 | LOC110700989 | 264 | 7.22 | 30.59 |
| CqHsf10 | LOC110702486 | 337 | 5.00 | 35.97 |
| CqHsf11 | LOC110707299 | 251 | 8.49 | 28.95 |
| CqHsf12 | LOC110707798 | 323 | 6.36 | 37.18 |
| CqHsf13 | LOC110711608 | 547 | 6.30 | 60.68 |
| CqHsf14 | LOC110714795 | 485 | 5.81 | 53.67 |
| CqHsf15 | LOC110716129 | 412 | 5.26 | 47.49 |
| CqHsf16 | LOC110717375 | 501 | 5.02 | 55.58 |
| CqHsf17 | LOC110719484 | 341 | 4.93 | 36.06 |
| CqHsf18 | LOC110728975 | 383 | 5.75 | 43.47 |
| CqHsf19 | LOC110729384 | 524 | 4.88 | 57.97 |
| CqHsf20 | LOC110730144 | 515 | 4.74 | 57.13 |
| CqHsf21 | LOC110734445 | 384 | 5.66 | 43.57 |
| CqHsf22 | LOC110736313 | 297 | 7.12 | 34.70 |
| CqHsf23 | LOC110736449 | 407 | 5.30 | 46.84 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tashi, G.; Zhan, H.; Xing, G.; Chang, X.; Zhang, H.; Nie, X.; Ji, W. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of Heat Shock Transcription Factor Family in Chenopodium quinoa Willd. Agronomy 2018, 8, 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy8070103
Tashi G, Zhan H, Xing G, Chang X, Zhang H, Nie X, Ji W. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of Heat Shock Transcription Factor Family in Chenopodium quinoa Willd. Agronomy. 2018; 8(7):103. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy8070103
Chicago/Turabian StyleTashi, Gongbo, Haoshuang Zhan, Guangwei Xing, Xi Chang, Hong Zhang, Xioajun Nie, and Wanquan Ji. 2018. "Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of Heat Shock Transcription Factor Family in Chenopodium quinoa Willd" Agronomy 8, no. 7: 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy8070103
APA StyleTashi, G., Zhan, H., Xing, G., Chang, X., Zhang, H., Nie, X., & Ji, W. (2018). Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of Heat Shock Transcription Factor Family in Chenopodium quinoa Willd. Agronomy, 8(7), 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy8070103






