Spatial and Temporal Trends of Irrigated Cotton Yield in the Southern High Plains
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
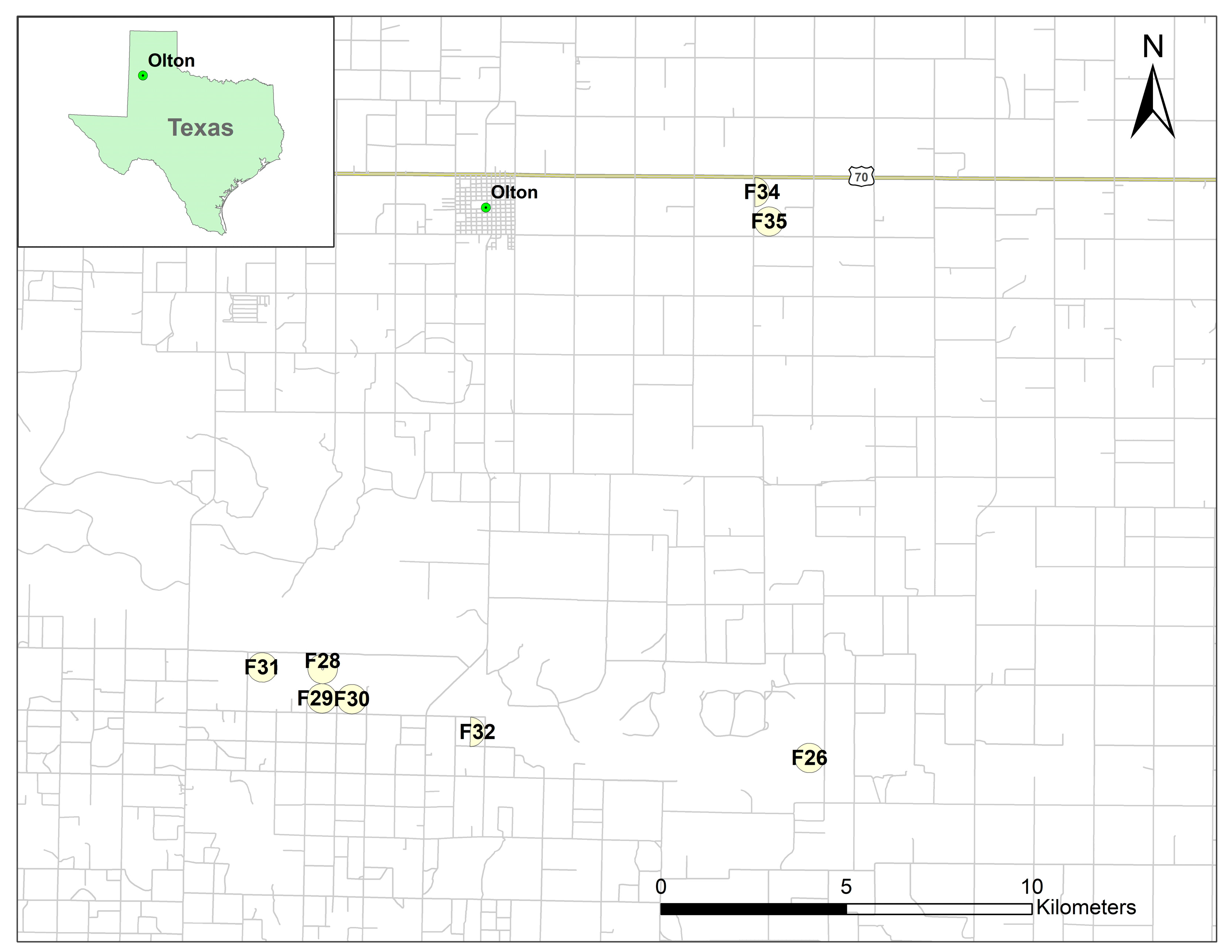
2.1. Study Sites
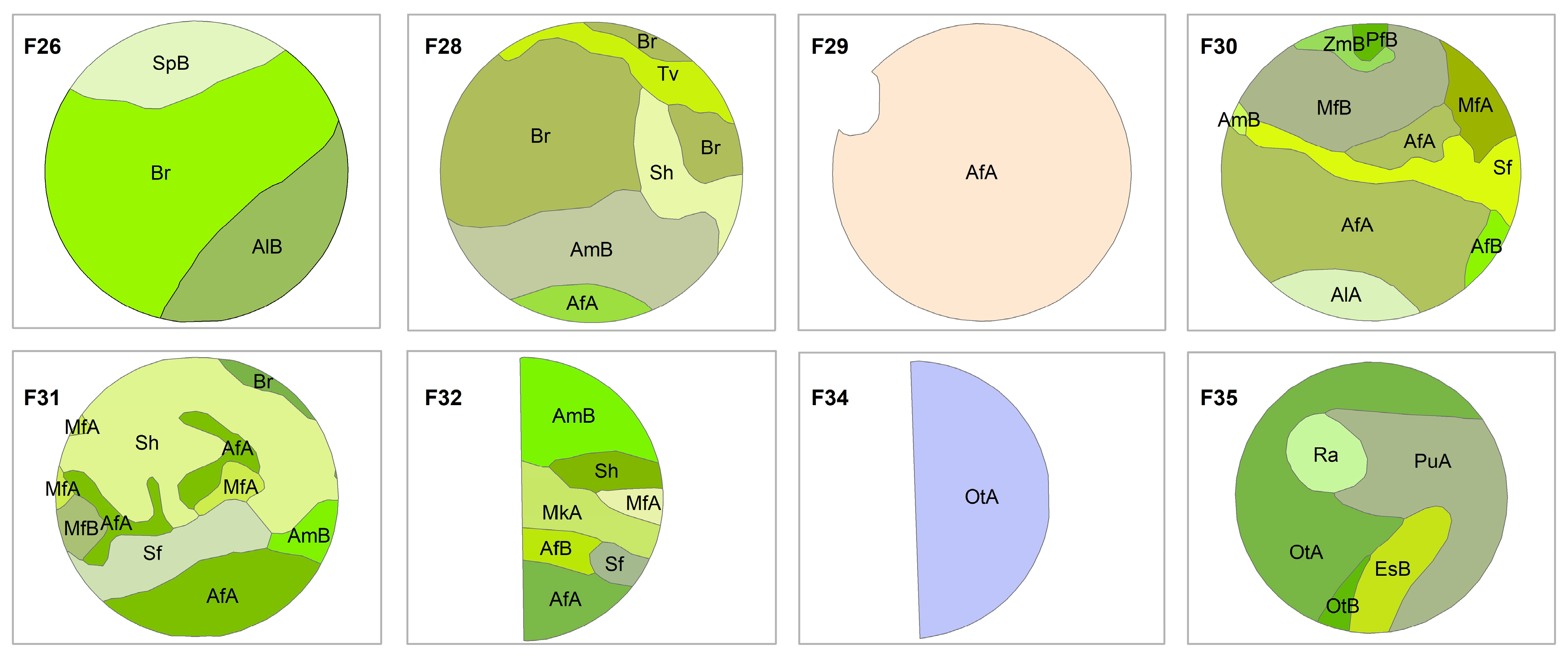
2.2. Soil Type
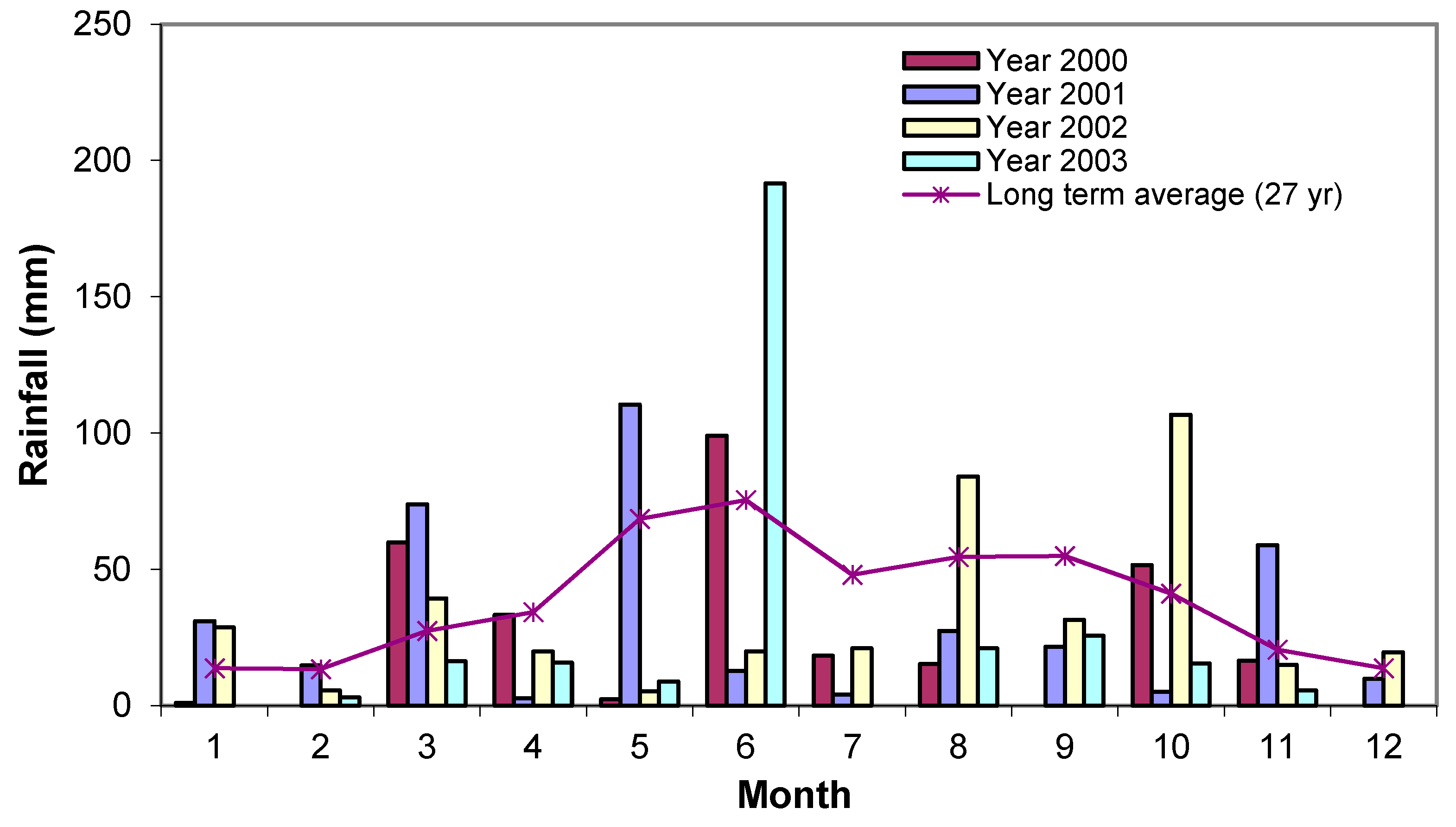
2.3. Data Collection and Preparation
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
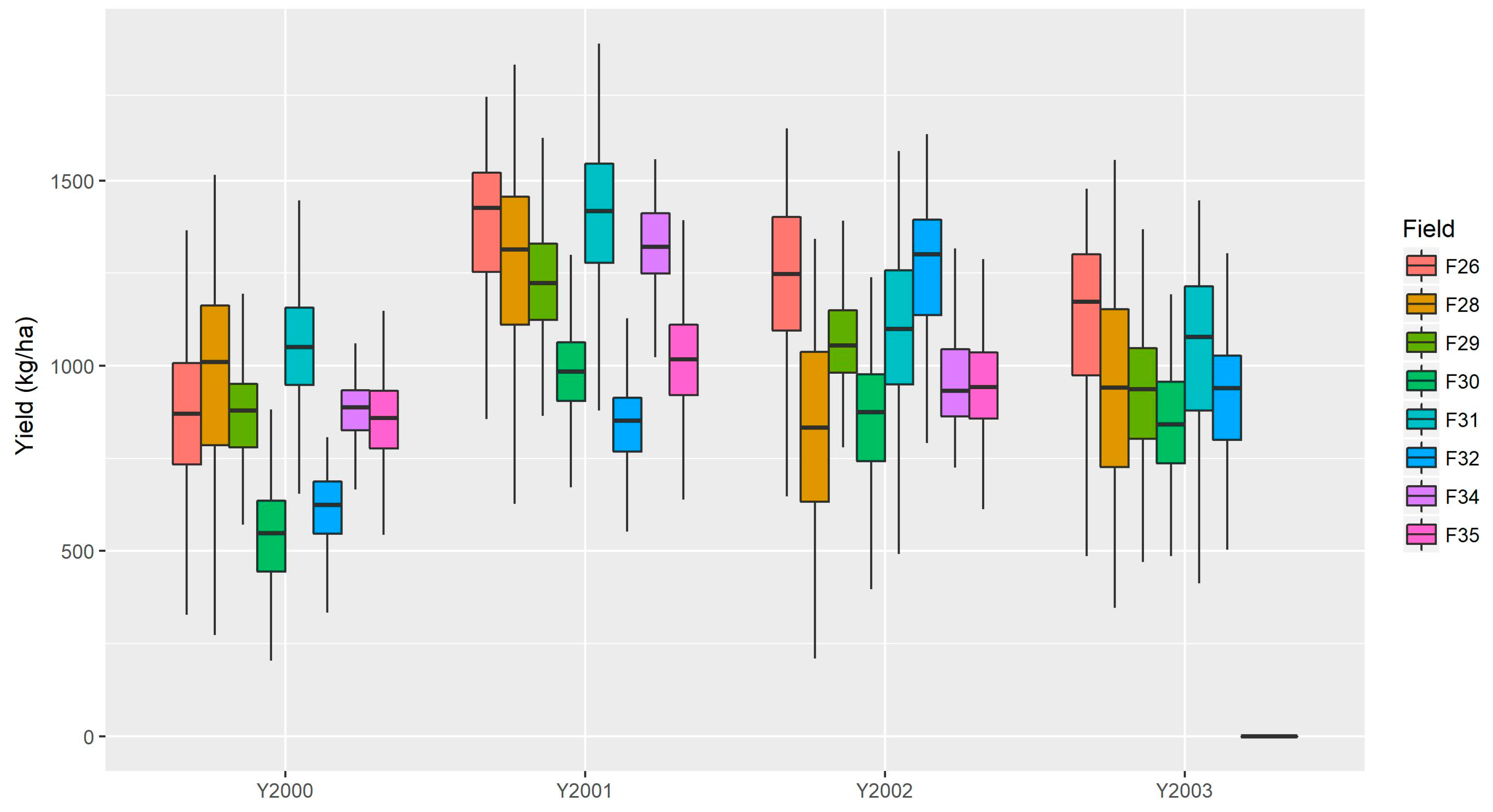
3.1. Yield Spatial Variability by Season
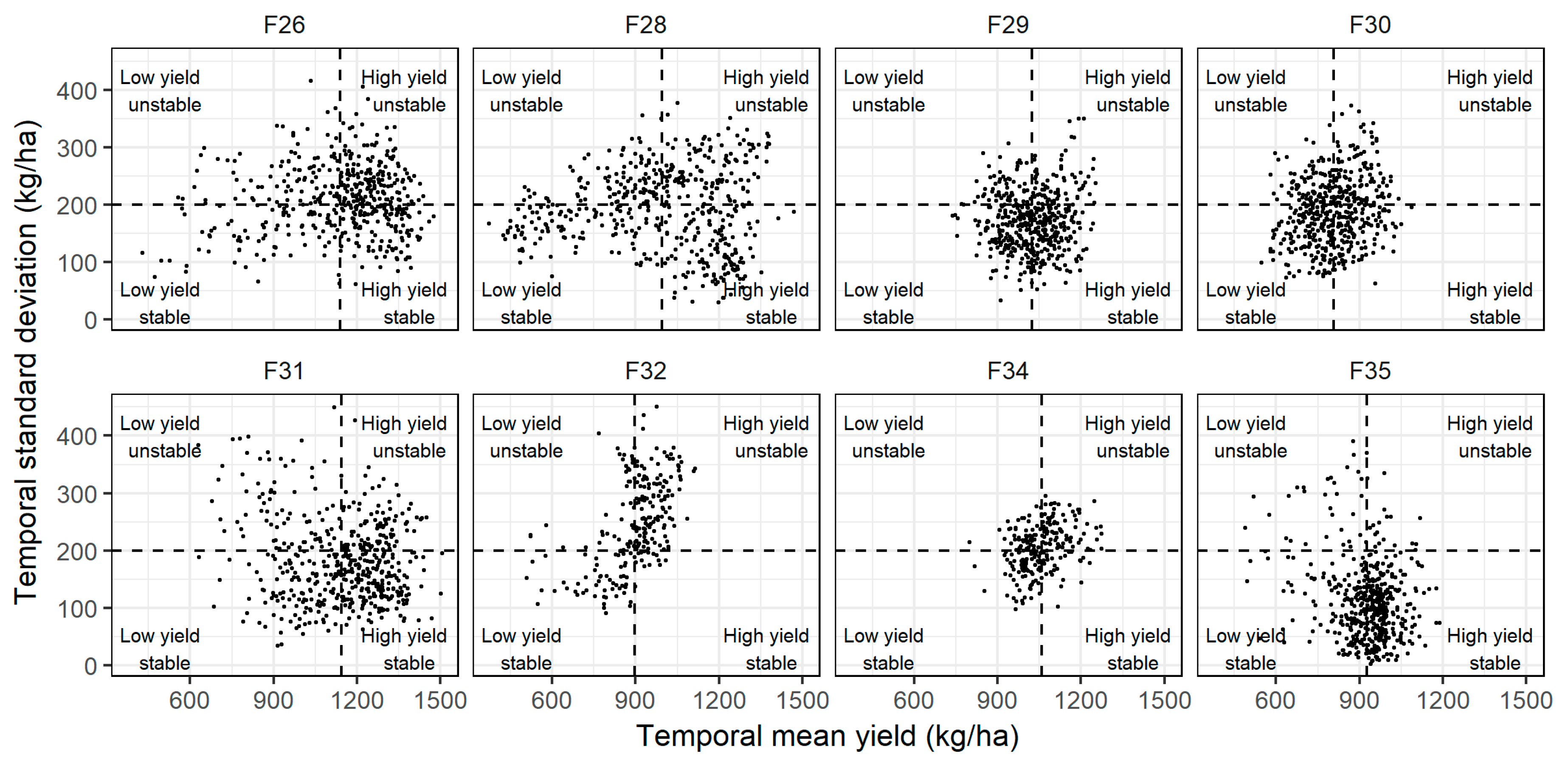
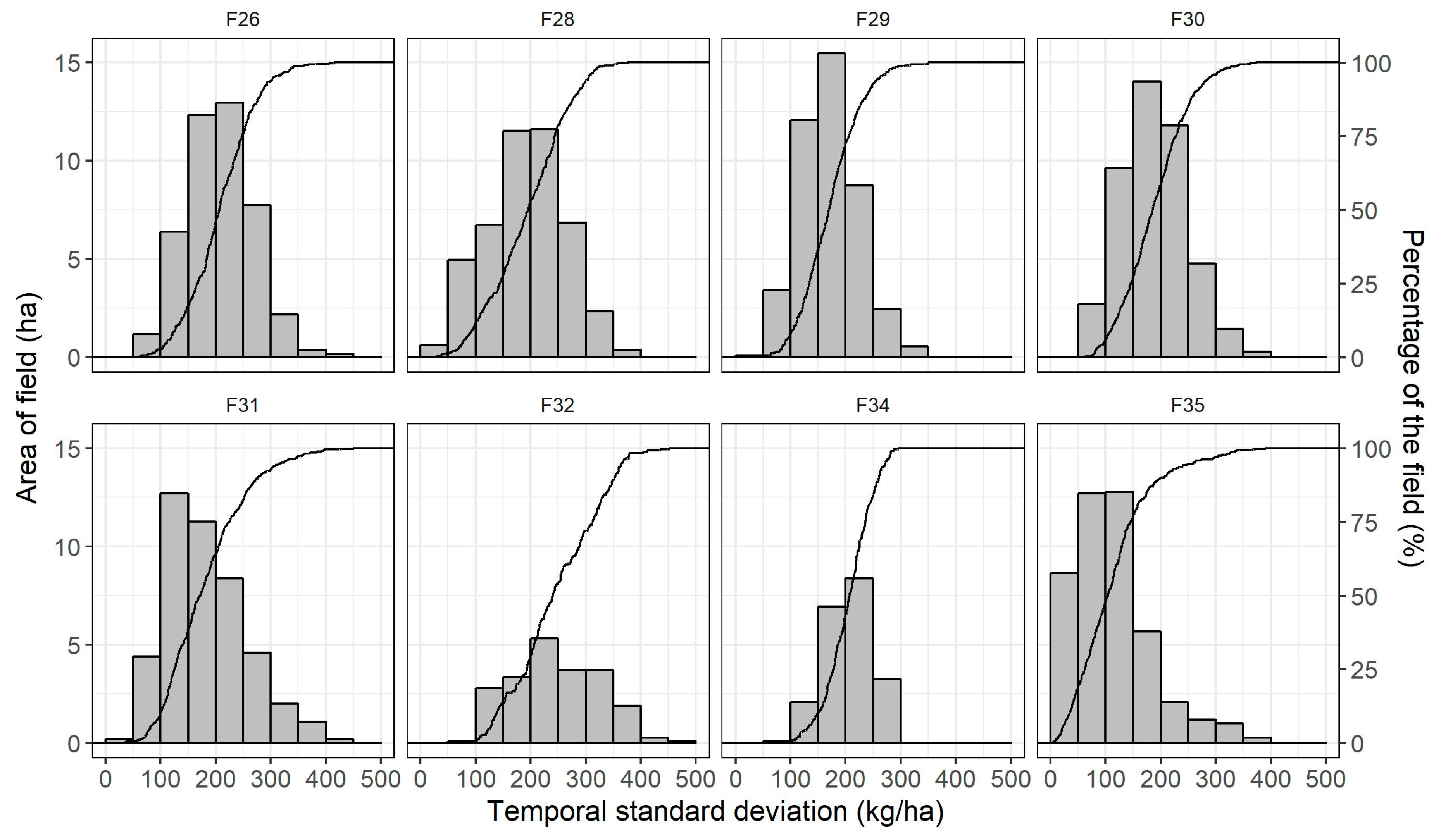
3.2. Spatial and Temporal Yield Variability
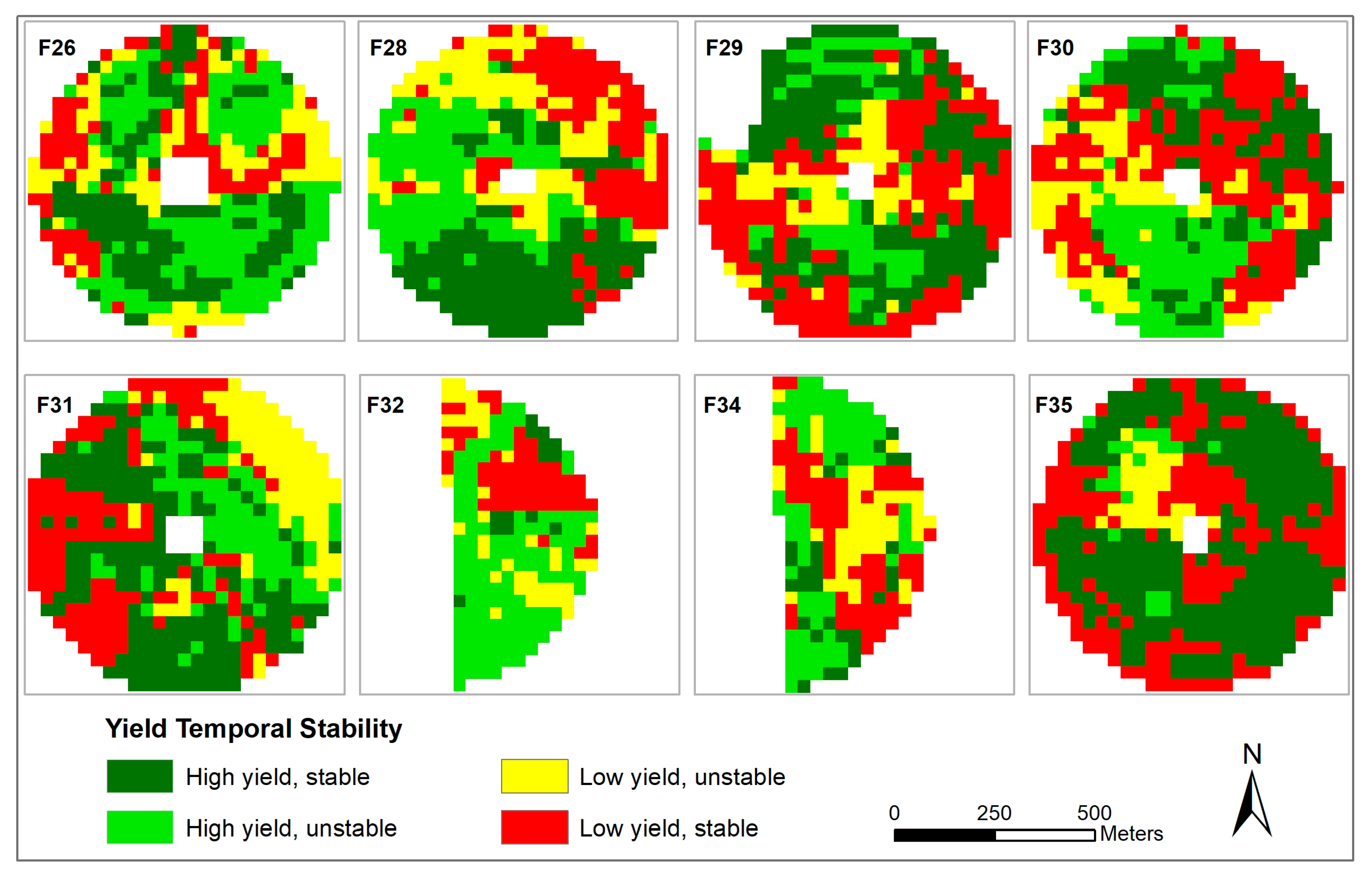
3.3. Temporal Stability
3.4. Spatial and Temporal Trend Maps
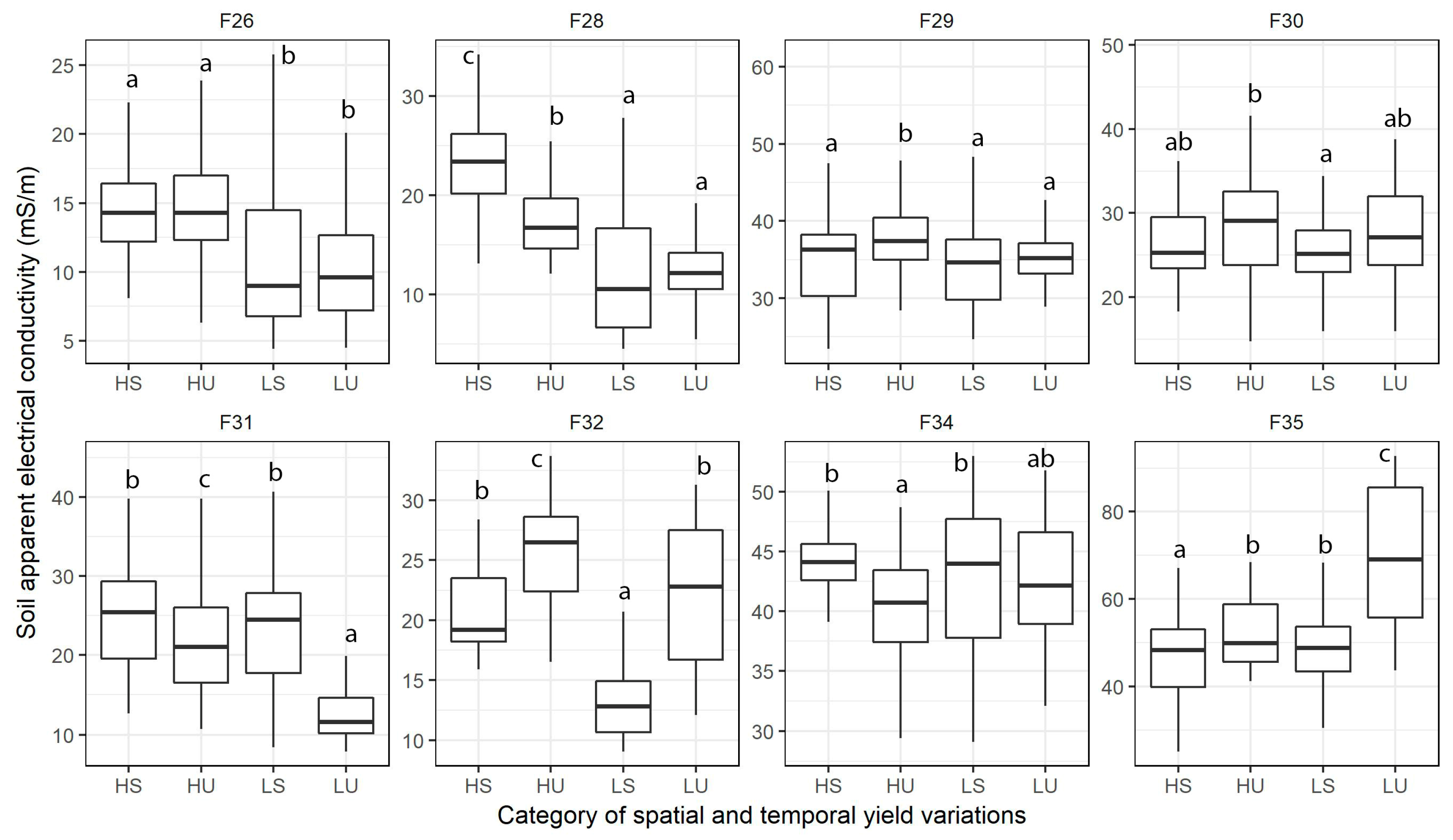
3.5. Relationship Between ECa and Spatial and Temporal Yield Variability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miller, M.P.; Singer, M.J.; Nielsen, D.R. Spatial variability of wheat yield and soil properties on complex hills. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1988, 52, 1133–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, F.J.; Nowak, P. Aspects of precision agriculture. Adv. Agron. 1999, 67, 1–85. [Google Scholar]
- Dobermann, A.; Ping, J.L.; Adamchuk, V.I.; Simbahan, G.C.; Ferguson, R.B. Classification of crop yield variability in irrigated production fields. Agron. J. 2003, 5, 1105–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibawa, W.D.; Dludlu, D.L.; Swenson, L.J.; Hopkins, D.G.; Dahnke, W.C. Variable fertilizer application based on yield goal, soil fertility, and soil map unit. JPA 1993, 6, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, S.; Bynum, E.D.; Archer, T.L.; Bordovsky, J.; Rosenow, D.T.; Peterson, C.; Bronson, K.; Nesmith, D.M.; Lascano, R.J.; Wilson, L.T.; et al. Spatial and temporal variability of sorghum grain yield: Influence of soil, water, pests, and diseases relationships. Precis. Agric. 2002, 3, 389–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackmore, S.; Godwin, R.J.; Fountas, S. The analysis of spatial and temporal trends in yield map data over six years. Biosyst. Eng. 2003, 84, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques da Silva, J.R. Analysis of the spatial and temporal variability of irrigated maize yield. Biosyst. Eng. 2006, 94, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.M.; Downer, R.G.; Bradow, J.M.; Bauer, P.J.; Sadler, E.J. Variability in cotton fiber yield, fiber quality, and soil properties in a Southeastern Coastal Plain. Agron. J. 2002, 94, 1305–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Everitt, J.H.; Bradford, J.M.; Murden, D. Airborne Hyperspectral imagery and yield monitor data for mapping cotton yield variability. Precis. Agric. 2004, 5, 445–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corwin, D.L.; Lesch, S.M.; Shouse, P.J.; Soppe, R.; Ayars, J.E. Identifying soil properties that influence cotton yield using soil sampling directed by apparent soil electrical conductivity. Agron. J. 2003, 95, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, J.L.; Green, C.J.; Bronson, K.F.; Zartman, R.E.; Dobermann, A. Identification of relationships between cotton yield, quality, and soil properties. Agron. J. 2004, 96, 1588–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronson, K.F.; Wayne Keeling, J.; Booker, J.D.; Chua, T.T.; Wheeler, T.A.; Boman, R.K.; Lascano, R.J. Influence of landscape position, soil series, and phosphorus fertilizer on cotton lint yield. Agron. J. 2003, 95, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elms, M.K.; Green, C.J.; Johnson, P.N. Variability of cotton yield and quality. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2001, 32, 351–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Maas, S.J.; Bronson, K.F. Relationship between cotton yield and soil electrical conductivity, topography, and Landsat imagery. Precis. Agric. 2012, 13, 678–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swinton, S.M.; Lowenberg-DeBoer, J. Evaluating the profitability of site-specific farming. JPA 1998, 11, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravchenko, A.N.; Bullock, D.G. Correlation of corn and soybean grain yield with topography and soil properties. Agron. J. 2000, 92, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corwin, D.L.; Lesch, S.M. Application of soil electrical conductivity to precision agriculture. Agron. J. 2003, 95, 455–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corwin, D.L.; Lesch, S.M. Apparent soil electrical conductivity measurements in agriculture. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2005, 46, 11–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravchenko, A.N.; Thelen, K.D.; Bullock, D.G.; Miller, N.R. Relationship among crop grain yield, topography, and soil electrical conductivity studied with cross-correlograms. Agron. J. 2003, 95, 1132–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronson, K.F.; Onken, A.B.; Booker, J.D.; Lascano, R.J.; Provin, T.L.; Torbert, H.A. Irrigated cotton lint yields as affected by phosphorus fertilizer and landscape position. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2001, 32, 1959–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, E.D.; Christy, C.D.; Drummond, P.E. Using yield and soil electrical conductivity (EC) maps to derive crop production performance information. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Precision Agriculture, Bloomington, MN, USA, 16–19 July 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Clay, D.E.; Chang, J.; Malo, D.D.; Carlson, C.G.; Reese, C.; Clay, S.A.; Ellsbury, M.; Berg, B. Factors influencing spatial variability of soil apparent electrical conductivity. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2001, 32, 2993–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, W.N.; de Queiroz, D.M.; Valente, D.S.; de Carvalho Pinto, F.D.; Melo, C.A. The temporal stability of the variability in apparent soil electrical conductivity. Biosci. J. 2016, 32, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, G.; Williard, K.; Schoonover, J. Spatial relation of apparent soil electrical conductivity with crop yields and soil properties at different topographic positions in a small Agricultural Watershed. Agronomy 2016, 6, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchen, N.R.; Drummond, S.T.; Lund, E.D.; Sudduth, K.A.; Buchleiter, G.W. Soil electrical conductivity and topography related to yield for three contrasting soil-crop systems. Agron. J. 2003, 95, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, M.T.; Raun, W.R.; Martin, K.L.; Freeman, K.W.; Johnson, G.V.; Stone, M.L. Indirect estimates of soil electrical conductivity for improved prediction of wheat grain yield. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2005, 35, 2639–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadler, A.; Rudolph, S.; Kupisch, M.; Langensiepen, M.; van der Kruk, J.; Ewert, F. Quantifying the effects of soil variability on crop growth using apparent soil electrical conductivity measurements. Eur. J. Agron. 2015, 64, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholizadeh, A.; Amin Mohd Soom, M.; Anuar, A.R.; Aimrun, W. Relationship between apparent electrical conductivity and soil physical properties in a Malaysian paddy field. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2012, 58, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezrin, M.H.; Amin, M.S.M.; Anuar, A.R.; Aimrun, W. Relationship between rice yield and apparent electrical conductivity of paddy soils. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2010, 7, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.S.; Amin, M.S.; Lee, T.S.; Mohammud, C.H. Apparent soil electrical conductivity as an indicator of paddy soil productivity. J. Trop. Agric. Food Sci. 2008, 36, 145–153. [Google Scholar]
- McBratney, A.; Whelan, B.; Ancev, T.; Bouma, J. Future directions of precision agriculture. Precis. Agric. 2005, 6, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauget, S.A.; Adhikari, P.; Leiker, G.; Baumhardt, R.L.; Thorp, K.R.; Ale, S. Modeling the effects of management and elevation on West Texas dryland cotton production. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 247, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA Soil Conservation Service. Soil Survey of Lamb County, Texas; Newman, A.L., Ed.; United States Department of Agriculture, Soil Conservation Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1962.
- USDA Soil Conservation Service. Soil Survey of Hale County, Texas; Blakely, E.R., Koos, W.M., Eds.; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 1974.
- Kleinjan, J.; Chang, J.; Wilson, J.; Humburg, D.; Carlson, G.; Clay, D.; Long, D. Cleaning Yield Data; SDSU Publication: San Diego, CA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Simbahan, G.C.; Dobermann, A.; Ping, J.L. Site specific management: Screening yield monitor data improves grain yield maps. Agron. J. 2004, 96, 1091–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; The R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jaynes, D.B.; Colvin, T.S.; Ambuel, J. Yield mapping by electromagnetic induction. In Proceedings of the Site Specific Management for Agricultural Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 27–30 March 1994; pp. 383–393. [Google Scholar]


| Field | HS, % | LS, % | Sum S, % | HU, % | LU, % | Sum U, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F26 | 27.7 | 18.3 | 46.0 | 34.2 | 19.8 | 54.0 |
| F28 | 30.2 | 22.8 | 53.0 | 25.8 | 21.2 | 47.0 |
| F29 | 36.4 | 36.3 | 72.7 | 14.5 | 12.8 | 27.3 |
| F30 | 25.0 | 34.1 | 59.1 | 23.8 | 17.1 | 40.9 |
| F31 | 37.6 | 26.2 | 63.8 | 19.5 | 16.7 | 36.2 |
| F32 | 6.0 | 23.4 | 29.4 | 53.2 | 17.4 | 70.6 |
| F34 | 12.7 | 31.3 | 44.0 | 34.3 | 21.7 | 56.0 |
| F35 | 56.1 | 33.7 | 89.8 | 3.9 | 6.3 | 10.2 |
© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, W. Spatial and Temporal Trends of Irrigated Cotton Yield in the Southern High Plains. Agronomy 2018, 8, 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy8120298
Guo W. Spatial and Temporal Trends of Irrigated Cotton Yield in the Southern High Plains. Agronomy. 2018; 8(12):298. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy8120298
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Wenxuan. 2018. "Spatial and Temporal Trends of Irrigated Cotton Yield in the Southern High Plains" Agronomy 8, no. 12: 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy8120298
APA StyleGuo, W. (2018). Spatial and Temporal Trends of Irrigated Cotton Yield in the Southern High Plains. Agronomy, 8(12), 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy8120298





