Understanding Starch Structure: Recent Progress
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Starch Granule
2.1. Crystallinity
2.2. Lamellar Structure
2.3. Granular Rings
2.4. Blocklets
3. The Major Starch Components
3.1. Amylose
3.1.1. Molecular Structure
3.1.2. Amylose in the Granule
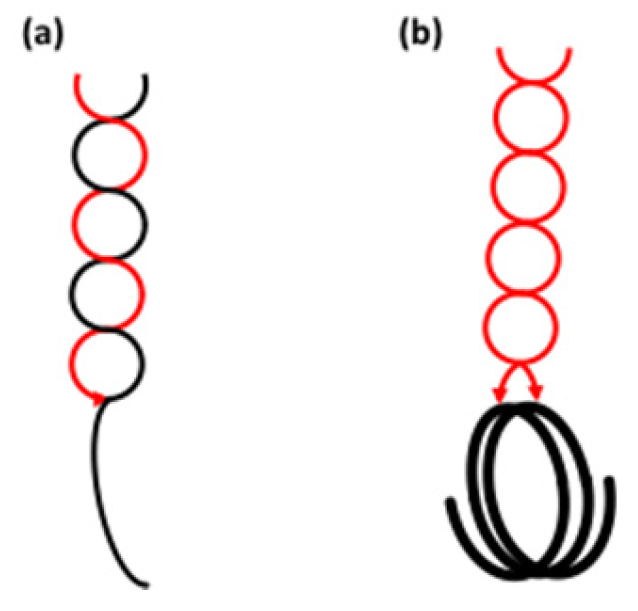
3.1.3. Helical Conformation
3.2. Amylopectin
3.2.1. Chain Categories
3.2.2. Structural Types
3.2.3. Branched Units
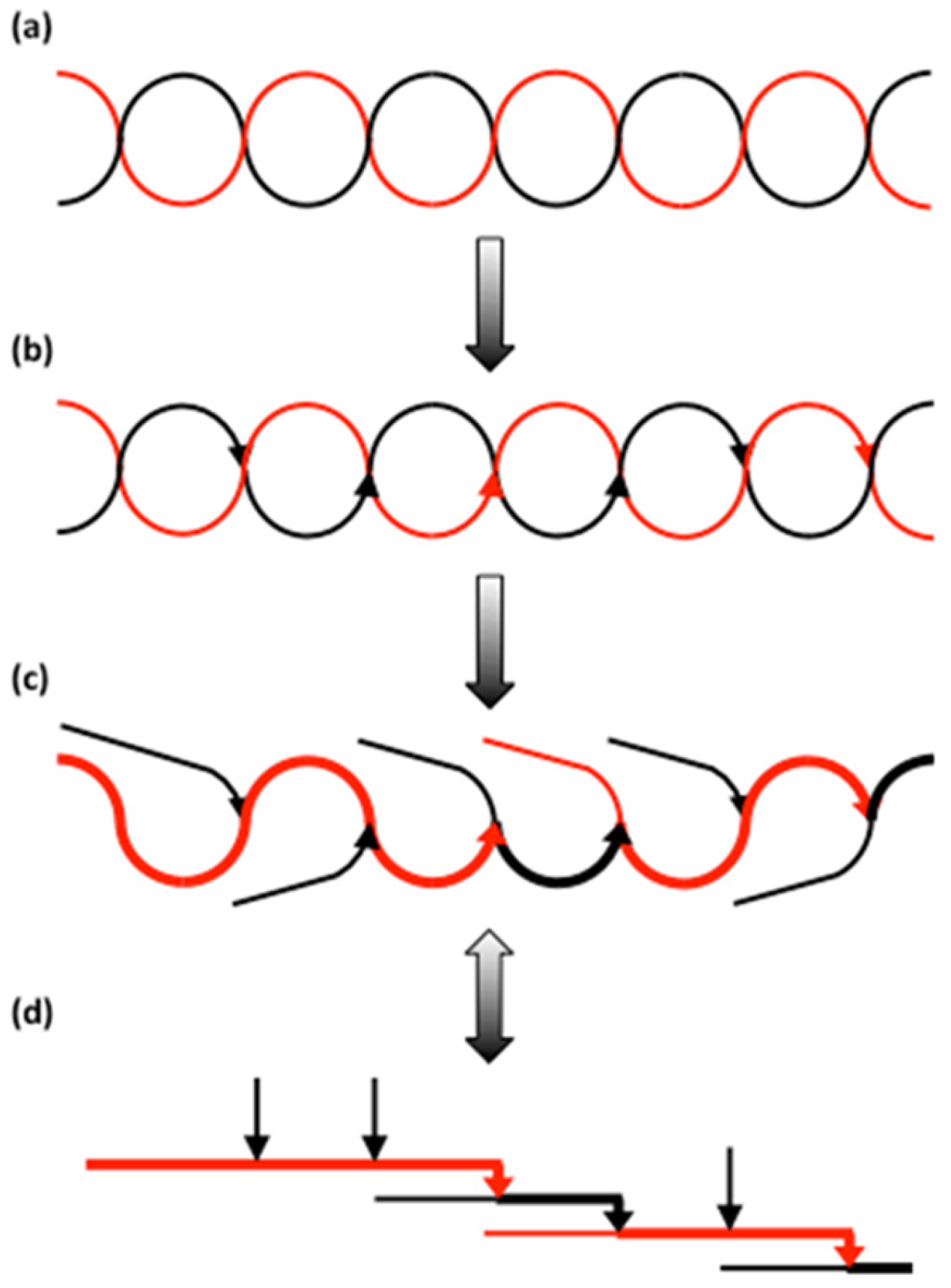
3.2.4. Organisation of Structural Units in Amylopectin
3.2.5. Possible Implications of the Backbone Structure on Starch Properties and Biosynthesis
4. Conclusions
References
- Jane, J.-L.; Kasemsuwan, T.; Leas, S.; Zobel, H.; Robyt, J.F. Anthology of starch granule morphology by scanning electron microscopy. Starch/Stärke 1994, 46, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geera, B.P.; Nelson, J.E.; Souza, E.; Huber, K.C. Composition and properties of A- and B-type starch granules pf wild-type, partial waxy, and waxy soft wheat. Cereal Chem. 2006, 83, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evers, A.D.; Greenwood, C.T.; Muir, D.D.; Venables, C. Studies on the biosynthesis of starch granules. Part 8. A comparison of the properties of the small and the large granules in mature cereal starches. Starch/Stärke 1974, 26, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, W.R.; Gadan, H. The amylose and lipid contents of starch granules in developing wheat endosperm. J. Cereal Sci. 1987, 5, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäkelä, M.J.; Korpela, T.; Laakso, S. Studies of starch size and distribution in 33 barley varieties with a celloscope. Starch/Stärke 1982, 34, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hizukuri, S.; Takeda, Y.; Yasuda, M.; Suzuki, A. Multi-branched nature of amylose and the action of de-branching enzymes. Carbohydr. Res. 1981, 94, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hizukuri, S.; Takeda, Y.; Maruta, N.; Juliano, B.O. Molecular structure of rice starch. Carbohydr. Res. 1989, 189, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, Y.; Hizukuri, S.; Takeda, C.; Suzuki, A. Structures of branched molecules of amyloses of various origins, and molecular fractions of branched and unbranched molecules. Carbohydr. Res. 1987, 165, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoft, E.; Piyachomkwan, K.; Chatakanonda, P.; Sriroth, K. Internal unit chain composition in amylopectins. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 74, 527–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanashiro, I.; Abe, J.-I.; Hizukuri, S. A periodic distribution of chain length of amylopectin as revealed by high-performance anion-exchange chromatography. Carbohydr. Res. 1996, 283, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imberty, A.; Buléon, A.; Tran, V.; Pérez, S. Recent advances in knowledge of starch structure. Starch/Stärke 1991, 43, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colonna, P.; Mercier, C. Gelatinization and melting of maize and pea starches with normal and high-amylose genotypes. Phytochemistry 1985, 24, 1667–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gérard, C.; Barron, C.; Colonna, P.; Planchot, V. Amylose determination in genetically modified starches. Carbohydr. Polym. 2001, 44, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.-C.; Capitani, T.; Trzasko, P.; Jeffcoat, R. Molecular structure of a low-amylopectin starch and other high-amylose maize starches. J. Cereal Sci. 1998, 27, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimoto, Y.; Tashiro, J.; Takenouchi, T.; Takeda, Y. Molecular structure and some physicochemical properties of high-amylose barley starches. Cereal Chem. 2000, 77, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carciofi, M.; Blennow, A.; Jensen, S.L.; Shaik, S.S.; Henriksen, A.; Buléon, A.; Holm, P.B.; Hebelstrup, K.H. Concerted suppression of all starch branching enzyme genes in barley produces amylose-only starch granules. BMC Plant Biol. 2012, 12, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gérard, C.; Colonna, P.; Buléon, A.; Planchot, V. Order in maize mutant starches revealed by mild acid hydolysis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2002, 48, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klucinec, J.D.; Thompson, D.B. Fractionation of high-amylose maize starches by differential alcohol precipitation and chromatography of the fractions. Cereal Chem. 1998, 75, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Jiang, H.; Campbell, M.; Blanco, M.; Jane, J.-L. Characterization of maize amylose-extender (ae) mutant starches. Part I: Relationship between resistant starch contents and molecular structures. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 74, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Jane, J. Characterization of barley starches of waxy, normal, and high amylose varieties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2000, 41, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colonna, P.; Mercier, C. Macromolecular structure of wrinkled- and smooth-pea starch components. Carbohydr. Res. 1984, 126, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-J.; White, P.; Pollak, L.; Jane, J. Amylopectin and intermediate materials in starches from mutant genotypes of the Oh43 inbred line. Cereal Chem. 1993, 70, 521–525. [Google Scholar]
- Han, W.; Zhang, B.; Li, J.; Zhao, S.; Niu, M.; Jia, C.; Xiong, S. Understanding the fine structure of intermediate materials of maize starches. Food Chem. 2017, 233, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waduge, R.N.; Kalinga, D.N.; Bertoft, E.; Seetharaman, K. Molecular structure and organization of starch granules from developing wheat endosperm. Cereal Chem. 2014, 91, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.-Z.; Benmoussa, M.; Gray, J.A.; BeMiller, J.N.; Hamaker, B.R. Detection of proteins in starch granule channels. Cereal Chem. 2005, 82, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.-Z.; Hamaker, B.R. Location of starch granule-associated proteins revealed by confocal laser scanning microscopy. J. Cereal Sci. 2002, 35, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borén, M.; Glaring, M.A.; Ghebremedhin, H.; Olsson, H.; Blennow, A.; Jansson, C. Molecular and physicochemical characterization of the high-amylose barley mutant Amo1. J. Cereal Sci. 2008, 47, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buléon, A.; Cotte, M.; Putaux, J.-L.; D’Hulst, C.; Susini, J. Tracking sulfur and phosphorus within single starch granules using synchrotron X-ray microfluorescence mapping. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1840, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.-S.; Huber, K.C. Channels within soft wheat starch A- and B-type granules. J. Cereal Sci. 2008, 48, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoover, R. Composition, molecular structure, and physicochemical properties of tuber and root starches: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2001, 45, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterschoot, J.; Gomand, S.V.; Fierens, E.; Delcour, J.A. Production, structure, physicochemical and functional properties of maize, cassava, wheat, potato and rice starches. Starch/Stärke 2015, 67, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, W.R. Starch lipids and how they relate to starch granule structure and functionality. Cereal Foods World 1995, 40, 437–446. [Google Scholar]
- Morrison, W.R.; Milligan, T.P.; Azudin, M.N. A relationship between the amylose and lipid contents of starches from diploid cereals. J. Cereal Sci. 1984, 2, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, W.R.; Scott, D.C.; Karkalas, J. Variation in the composition and physical properties of barley starches. Stärke 1986, 38, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamekh, S.; Forssell, P.; Poutanen, K. Solubility pattern and recrystallization behavior of oat starch. Starch/Stärke 1994, 46, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hizukuri, S.; Tabata, S.; Nikuni, Z. Studies on starch phosphate. Part 1. Estimation of glucose-6-phosphate residues in starch and the presence of other bound phosphate(s). Starch/Stärke 1970, 22, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blennow, A.; Bay-Smidt, A.M.; Olsen, C.E.; Møller, B.L. The distribution of covalently bound phosphate in the starch granule in relation to starch crystallinity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2000, 27, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blennow, A.; Bay-Smidt, A.M.; Wischmann, B.; Olsen, C.E.; Lindberg-Møller, B. The degree of starch phosphorylation is related to the chain length distribution of the neutral and the phosphorylated chains of amylopectin. Carbohydr. Res. 1998, 307, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blennow, A.; Engelsen, S.B.; Munck, L.; Møller, B.L. Starch molecular structure and phosphorylation investigated by a combined chromatographic and chemometric approach. Carbohydr. Polym. 2000, 41, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blennow, A.; Engelsen, S.B. Helix-breaking news: Fighting crystalline starch energy deposits in the cell. Trends Plant Sci. 2010, 15, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blennow, A.; Sjöland, A.K.; Andersson, R.; Kristiansson, P. The distribution of elements in the native starch granule as studied by particle-induced X-ray emission and complementary methods. Anal. Biochem. 2005, 347, 327–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambigaipalan, P.; Hoover, R.; Donner, E.; Liu, Q.; Jaiswal, S.; Chibbar, R.; Nantanga, K.K.M.; Seetharaman, K. Structure of faba bean, black bean and pinto bean starches at different levels of granule organization and their physicochemical properties. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 2962–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Yu, L.; Chen, L.; Li, X. Morphology and microstructure of maize starches with different amylose/amylopectin content. Starch/Stärke 2006, 58, 611–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varatharajan, V.; Hoover, R.; Li, J.; Vasanthan, T.; Nantanga, K.K.M.; Seetharaman, K.; Liu, Q.; Donner, E.; Jaiswal, S.; Chibbar, R.N. Impact of structural changes due to heat-moisture treatment at different temperatures on the susceptibility of normal and waxy potato starches towards hydrolysis by porcine pancreatic alpha amylase. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 2594–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, D. Fine structure of starch and its relationship to the organization of starch granules. J. Jpn. Soc. Starch Sci. 1972, 19, 8–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robin, J.P.; Mercier, C.; Charbonnière, R.; Guilbot, A. Lintnerized starches. Gel filtration and enzymatic studies of insoluble residues from prolonged acid treatment of potato starch. Cereal Chem. 1974, 51, 389–406. [Google Scholar]
- Biliaderis, C.G.; Grant, D.R.; Vose, J.R. Structural characterization of legume starches. II. Studies on acid-treated starches. Cereal Chem. 1981, 58, 502–507. [Google Scholar]
- Wikman, J.; Blennow, A.; Buléon, A.; Putaux, J.-L.; Pérez, S.; Seetharaman, K.; Bertoft, E. Influence of amylopectin structure and degree of phosphorylation on the molecular composition of potato starch lintners. Biopolymers 2014, 101, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srichuwong, S.; Isono, N.; Mishima, T.; Hisamatsu, M. Structure of linterized starch is related to X-ray diffraction pattern and susceptibility to acid and enzyme hydrolysis of starch granules. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2005, 37, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Copeland, L. Effect of acid hydrolysis on starch structure and functionality: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 55, 1081–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoft, E. Lintnerisation of two amylose-free starches of A- and B-crystalline types, respectively. Starch/Stärke 2004, 56, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikman, J.; Blennow, A.; Bertoft, E. Effect of amylose deposition on potato tuber starch granule architecture and dynamics as studied by lintnerization. Biopolymers 2013, 99, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imberty, A.; Pérez, S. Conformational analysis and molecular modelling of the branching point of amylopectin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1989, 11, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, J.S.; Daniels, R.D.; Donald, A.M.; Blennow, A.; Engelsen, S.B. Exploratory SAXS and HPAEC-PAD studies of starches from diverse plant genotypes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2006, 64, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogracheva, T.Y.; Morris, V.J.; Ring, S.G.; Hedley, C.L. The granular structure of C-type pea starch and its role in gelatinization. Biopolymers 1998, 45, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buléon, A.; Gérard, C.; Riekel, C.; Vuong, R.; Chanzy, H. Details of the crystalline ultrastructure of C-starch granules revealed by synchrotron microfocus mapping. Macromolecules 1998, 31, 6605–6610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, D.; Buléon, A.; Burghammer, M.; Chanzy, H.; Montesanti, N.; Putaux, J.-L.; Potocki-Véronèse, G.; Riekel, C. Crystal structure of A-amylose: A revisit from synchrotron microdiffraction analysis of single crystals. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imberty, A.; Pérez, S. A revisit to the three-dimensional structure of B-type starch. Biopolymers 1988, 27, 1205–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buléon, A.; Colonna, P.; Planchot, V.; Ball, S. Starch granules: Structure and biosynthesis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1998, 23, 85–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomand, S.V.; Lamberts, L.; Derde, L.J.; Goesaert, H.; Vandeputte, G.E.; Goderis, B.; Visser, R.G.F.; Delcour, J.A. Structural properties and gelatinisation characteristics of potato and cassava starches and mutants thereof. Food Hydrocoll. 2010, 24, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matalanis, A.M.; Campanella, O.H.; Hamaker, B.R. Storage retrogradation behavior of sorghum, maize and rice starch pastes related to amylopectin fine structure. J. Cereal Sci. 2009, 50, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S. Comparative analysis of some physicochemical properties of 19 kinds of native starches. Starch/Stärke 2017, 68, 1600367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srichuwong, S.; Sunarti, T.C.; Mishima, T.; Isono, N.; Hisamatsu, M. Starches from different botanical sources I: Contribution of amylopectin fine structure to thermal properties and enzyme digestibility. Carbohydr. Polym. 2005, 60, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterling, C. A low angle spacing in starch. J. Polym. Sci. 1962, 56, S10–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazek, J.; Salman, H.; Rubio, A.L.; Gilbert, E.; Hanley, T.; Copeland, L. Structural characterization of wheat starch granules differing in amylose content and functional characteristics. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 75, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, P.J.; Cameron, R.E.; Donald, A.M. A universal feature in the structure of starch granules from different botanical sources. Starch/Stärke 1993, 45, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putaux, J.-L.; Molina-Boisseau, S.; Momaur, T.; Dufresne, A. Platelet nanocrystals resulting from the disruption of waxy maize starch granules by acid hydrolysis. Biomacromolecules 2003, 4, 1198–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, S.; Bertoft, E. The molecular structures of starch components and their contribution to the architecture of starch granules: A comprehensive review. Starch/Stärke 2010, 62, 389–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koroteeva, D.A.; Kiseleva, V.I.; Krivandin, A.V.; Shatalova, O.V.; Blaszczak, W.; Bertoft, E.; Piyachomkwan, K.; Yuryev, V.P. Structural and thermodynamic properties of rice starches with different genetic background. Part 2. Defectiveness of different supramolecular structures in starch granules. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2007, 41, 534–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozlov, S.S.; Blennow, A.; Krivandin, A.V.; Yuryev, V.P. Structural and thermodynamic properties of starches extracted from GBSS and GWD suppressed potato lines. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2007, 40, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozlov, S.S.; Krivandin, A.V.; Shatalova, O.V.; Noda, T.; Bertoft, E.; Fornal, J.; Yuryev, V.P. Structure of starches extracted from near-isogenic wheat lines. Part II. Molecular organization of amylopectin clusters. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2007, 87, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, P.J.; Donald, A.M. The influence of amylose on starch granule structure. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1995, 17, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donald, A.M.; Kato, K.L.; Perry, P.A.; Waigh, T.A. Scattering studies of the internal structure of starch granules. Starch/Stärke 2001, 53, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallant, D.J.; Bouchet, B.; Baldwin, P.M. Microscopy of starch: Evidence of a new level of granule organization. Carbohydr. Polym. 1997, 32, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Mitsunaga, T.; Kawamura, Y. Molecular arrangement in blocklets and starch granules architecture. Carbohydr. Polym. 2006, 63, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttrose, M.S. The influence of environment on the shell structure of starch granules. J. Cell Biol. 1962, 14, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilling, E.; Smith, A.M. Growth ring formation in the starch granules of potato tubers. Plant Physiol. 2003, 132, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sande-Bakhuizen, H.L.V.D. The structure of starch grains from wheat grown under constant conditions. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1926, 24, 302–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, A.; Annor, G.; Vamadevan, V.; Tetlow, I.; Kirkensgaard, J.J.K.; Mortensen, K.; Blennow, A.; Hebelstrup, K.H.; Bertoft, E. Influence of diurnal photosynthetic activity on the morphology, structure, and thermal properties of normal and waxy barley starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 98, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, K.C.; BeMiller, J.N. Visualization of channels and cavities of corn and sorghum starch granules. Cereal Chem. 1997, 74, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fannon, J.E.; Hauber, R.J.; BeMiller, J.N. Surface pores of starch granules. Cereal Chem. 1992, 69, 284–288. [Google Scholar]
- Glaring, M.A.; Koch, C.B.; Blennow, A. Genotype-specific spatial distribution of starch molecules in the starch granule: A combined CLSM and SEM approach. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 2310–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naguleswaran, S.; Li, J.; Vasanthan, T.; Bressler, D. Distribution of granule channels, protein, and phospholipid in triticale and corn starches as revealed by confocal laser scanning microscopy. Cereal Chem. 2011, 88, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fannon, J.E.; Shull, J.M.; BeMiller, J.N. Interior channels of starch granules. Cereal Chem. 1993, 70, 611–613. [Google Scholar]
- Huber, K.C.; BeMiller, J.N. Location of sites of reaction within starch granules. Cereal Chem. 2001, 78, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, J.A.; BeMiller, J.N. Accessibility of starch granules to fatty acyl amides. Cereal Chem. 2001, 78, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtani, T.; Yoshino, T.; Hagiwara, S.; Maekawa, T. High-resolution imaging of starch granule structure using atomic force microscopy. Starch/Stärke 2000, 52, 150–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, P.M.; Adler, J.; Davies, M.C.; Melia, C.D. High resolution imaging of starch granule surfaces by atomic force microscopy. J. Cereal Sci. 1998, 27, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waduge, R.N.; Xu, S.; Bertoft, E.; Seetharaman, K. Exploring the surface morphology of developing wheat starch granules by using atomic force microscopy. Starch/Stärke 2013, 65, 398–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkin, N.J.; Abeysekera, R.M.; Cheng, S.L.; Robards, A.W. An experimentally-based predictive model for the separation of amylopectin subunits during starch gelatinization. Carbohydr. Polym. 1998, 36, 173–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, A.A.; Miles, M.J.; Helbert, W. Internal structure of the starch granule revealed by AFM. Carbohydr. Res. 2001, 330, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, E.A.; Katz, J.R. Abhandlungen zur physikalischen Chemie der Stärke und der Brotbereitung. XVIII. Weitere Versuche die gewachsene Struktur des Stärkekorns mikroskopisch sichtbar zu machen. Z. Physikal. Ch. (A) 1934, 169, 135–142. [Google Scholar]
- Hanson, E.A.; Katz, J.R. Abhandlungen zur physikalischen Chemie der Stärke und der Brotbereitung. XVII. Über Versuche die gewachsene Struktur des Stärkekorns mikroskopisch sichtbar zu machen besonders an lintnerisierter Stärke. Z. Physikal. Ch. (A) 1934, 168, 339–352. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, J.M.C.; Copeland, L. Imaging rice grains using atomic force microscopy. J. Cereal Sci. 2003, 37, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wei, N.; Li, H.; Liu, S.; Yang, D. Outer shell, inner blocklets, and granule architecture of potato starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 103, 355–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, F.; Seetharaman, K. On the organization of chains in amylopectin. Starch/Stärke 2013, 65, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buléon, A.; Bizot, H.; Delage, M.M.; Multon, J.L. Evolution of crystallinity and specific gravity of potato starch versus water ad- and desorption. Starch/Stärke 1982, 34, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waigh, T.A.; Kato, K.L.; Donald, A.M.; Gidley, M.J.; Clarke, C.J.; Riekel, C. Side-chain liquid-crystalline model for starch. Starch/Stärke 2000, 52, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Herrera, M.; Vasanthan, T.; Hoover, R. Characterization of maize starch nanoparticles prepared by acid hydrolysis. Cereal Chem. 2017, 93, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Xu, S.; Seetharaman, K. A novel in situ atomic force microscopy imaging technique to probe surface morphological features of starch granules. Carbohydr. Res. 2011, 346, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lineback, D.R. Current concepts of starch structure and its impact on properties. J. Jpn. Soc. Starch Sci. 1986, 33, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zobel, H.F. Molecules to granules: A comprehensive starch review. Starch/Stärke 1988, 40, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saibene, D.; Seetharaman, K. Amylose involvement in the amylopectin clusters from potato starch granules. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 82, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoch, T.J. Fractionation of starch by selective precipitation with butanol. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1942, 64, 2957–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, Y.; Maruta, N.; Hizukuri, S. Structures of amylose subfractions with different molecular sizes. Carbohydr. Res. 1992, 226, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, Y.; Maruta, N.; Hizukuri, S. Examination of the structure of amylose by tritium labelling of the reducing terminal. Carbohydr. Res. 1992, 227, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, Y.; Shitaozono, T.; Hizukuri, S. Structures of sub-fractions of corn amylose. Carbohydr. Res. 1990, 199, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, Y.; Tomooka, S.; Hizukuri, S. Structures of branched and linear molecules of rice amylose. Carbohydr. Res. 1993, 246, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, Y.; Takeda, C.; Mizukami, H.; Hanashiro, I. Structures of large, medium and small starch granules of barley grain. Carbohydr. Polym. 1999, 38, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, Y.; Shitaozono, T.; Hizukuri, S. Molecular structure of corn starch. Starch/Stärke 1988, 40, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibanuma, K.; Takeda, Y.; Hizukuri, S.; Shibata, S. Molecular structures of some wheat starches. Carbohydr. Polym. 1994, 25, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanashiro, I.; Takeda, Y. Examination of number-average degree of polymerization and molar-based distribution of amylose by fluorescent labeling with 2-aminopyridine. Carbohydr. Res. 1998, 306, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, Y.; Hizukuri, S.; Juliano, B.O. Structures and amounts of branched molecules in rice amyloses. Carbohydr. Res. 1989, 186, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, W.R.; Laignelet, B. An improved colorimetric procedure for determining apparent and total amylose in cereal and other starches. J. Cereal Sci. 1983, 1, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredriksson, H.; Silverio, J.; Andersson, R.; Eliasson, A.-C.; Åman, P. The influence of amylose and amylopectin characteristics on gelatinization and retrogradation properties of different starches. Carbohydr. Polym. 1998, 35, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Z.; White, P.J. Structure and physicochemical properties of starches from oats with different lipid contents. Cereal Chem. 1994, 71, 443–450. [Google Scholar]
- Manelius, R.; Bertoft, E. The effect of Ca2+-ions on the α-amylolysis of granular starches from oats and waxy-maize. J. Cereal Sci. 1996, 24, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, Z.; Jane, J.-L. Characterization and modeling of the A- and B-granule starches of wheat, triticale, and barley. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 67, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blennow, A.; Bay-Smidt, A.M.; Bauer, R. Amylopectin aggregation as a function of starch phosphate content studied by size exclusion chromatography and on-line refractive index and light scattering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2001, 28, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, C.M.L.; Wong, K.-S.; Yoo, S.-H.; Jane, J.-L. Structural and functional characteristics of selected soft wheat starches. Cereal Chem. 2002, 79, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidley, M.J.; Cooke, D.; Darke, A.H.; Hoffmann, R.A.; Russell, A.L.; Greenwell, P. Molecular order and structure in enzyme-resistant retrograded starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 1995, 28, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, L.A.; Ostenson, A.M.; Rayas-Duarte, P. Determination of amylose and amylopectin of wheat starch using high performance size-exclusion chromatography (HPSEC). Cereal Chem. 2002, 79, 771–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jane, J.; Chen, Y.Y.; Lee, L.F.; McPherson, A.E.; Wong, K.S.; Radosavljevic, M.; Kasemsuwan, T. Effects of amylopectin branch chain length and amylose content on gelatinization and pasting properties of starch. Cereal Chem. 1999, 76, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollings, J. Enzymatic depolymerization of polysaccharides. Carbohydr. Polym. 1985, 5, 37–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, T.; Matsuki, J. Effect of wheat starch structure on swelling power. Cereal Chem. 1998, 75, 525–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, Y.; Hizukuri, S.; Juliano, B.O. Purification and structure of amylose from rice starch. Carbohydr. Res. 1986, 148, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, Y.; Preiss, J. Structures of B90 (sugary) and W64A (normal) maize starches. Carbohydr. Res. 1993, 240, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verwimp, T.; Vandeputte, G.E.; Marrant, K.; Delcour, J.A. Isolation and characterisation of rye starch. J. Cereal Sci. 2004, 39, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimoto, Y.; Takenoushi, T.; Takeda, Y. Molecular structure and some physicochemical properties of waxy and low-amylose barley starches. Carbohydr. Polym. 2002, 47, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, Y.; Shirasaka, K.; Hizukuri, S. Examination of the purity and structure of amylose by gel-permeation chromatography. Carbohydr. Res. 1984, 132, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuph, M.; Tester, R.F.; Ansell, R.; Snape, C.E. Composition and properties of starches extracted from tubers of different potato varieties grown under the same environmental conditions. Food Chem. 2003, 82, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanashiro, I.; Sakaguchi, I.; Yamashita, H. Branched structures of rice amylose examined by differential fluorescence detection of side-chain distribution. J. Appl. Glycosci. 2013, 60, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jane, J.-L. Mechanism of starch gelatinization in neutral salt solutions. Starch/Stärke 1993, 45, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, K.; Jane, J.-L. Morphological changes of granules of different starches by surface gelatinization with calcium chloride. Cereal Chem. 2000, 77, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuakpetoon, D.; Wang, Y.-J. Internal structure and physicochemical properties of corn starches as revealed by chemical surface gelatinization. Carbohydr. Res. 2007, 342, 2253–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jane, J.-L.; Shen, J.J. Internal structure of the potato starch granule revealed by chemical gelatinization. Carbohydr. Res. 1993, 247, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.D.; Jane, J.-L. Internal structure of normal maize starch granules revealed by chemical surface gelatinization. Biomacromolecules 2000, 1, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blennow, A.; Hansen, M.; Schulz, A.; Jørgensen, K.; Donald, A.M.; Sanderson, J. The molecular deposition of transgenically modified starch in the starch granule as imaged by functional microscopy. J. Struct. Biol. 2003, 143, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myllärinen, P.; Autio, K.; Schulman, A.H.; Poutanen, K. Heat-induced changes of small and large barley starch granules. J. Inst. Brew. 1998, 104, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, B.K.; Saibene, D.; Seetharaman, K. Restriction of starch granule swelling by iodine during heating. Cereal Chem. 2006, 83, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jane, J.-L.; Xu, A.; Radosavljevic, M.; Seib, P.A. Location of amylose in normal starch granules. I. Susceptibility of amylose and amylopectin to cross-linking reagents. Cereal Chem. 1992, 69, 405–409. [Google Scholar]
- Kozlov, S.S.; Noda, T.; Bertoft, E.; Yuryev, V.P. Structure of starches extracted from near isogenic wheat lines. Part I. Effect of different GBSS I combinations. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2006, 86, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiseleva, V.I.; Krivandin, A.V.; Fornal, J.; Blaszczak, W.; Jelinski, T.; Yuryev, V.P. Annealing of normal and mutant wheat starches. LM, SEM, DSC, and SAXS studies. Carbohydr. Res. 2005, 340, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koroteeva, D.A.; Kiseleva, V.I.; Sriroth, K.; Piyachomkwan, K.; Bertoft, E.; Yuryev, P.V.; Yuryev, V.P. Structural and thermodynamic properties of rice starches with different genetic background. Part 1. Differentiation of amylopectin and amylose defects. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2007, 41, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banks, W.; Greenwood, C.T. Starch and Its Components; Edinburgh University Press: Edinburgh, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Banks, W.; Greenwood, C.T. The conformation of amylose in dilute solution. Starch/Stärke 1971, 23, 300–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheetham, N.W.H.; Tao, L. Amylose conformational transitions in binary DMSO/water mixtures. Starch/Stärke 1997, 49, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamori, E.; Senior, M.B. Kinetic and hydrodynamic studies relating to the structure of the amylose macromolecule in aqueous solution. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1973, 210, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmgren, H. Helical conformation of amylose in aqueous solution. I. Viscosity measurements. Biopolymers 1984, 23, 2525–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, M.; Noda, H.; Katama, T. Conformation of amylose in water. I. Light-scattering and sedimentation-equilibrium measurements. Biopolymers 1978, 17, 985–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senior, M.B.; Hamori, E. Investigation of the effect of amylose/iodine complexation on the conformation of amylose in aqueous solution. Biopolymers 1973, 12, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, A.; Kinoshita, K.; Miyake, Y. The conformation of amylose in solution. I. Polymer J. 1981, 13, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfannemüller, B.; Mayerhöfer, H.; Schulz, R.C. Conformation of amylose in aqueous solution: Optical rotatory dispersion and circular dichroism of amylose-iodine complexes and dependence on chain lenght of retrogradation of amylose. Biopolymers 1971, 10, 243–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidley, M.J. Molecular mechanisms underlying amylose aggregation and gelation. Macromolecules 1989, 22, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, A.D. Allowed and preferred shapes of amylose. Bakers Digest 1979, 53, 39–54. [Google Scholar]
- French, A.D.; Murphy, V.G. Computer modeling in the study of starch. Cereal Foods World 1977, 22, 61–70. [Google Scholar]
- Katz, J.R.; Itallie, T.B.V. Abhandlungen zur physikalischen Chemie der Stärke und der Brotbereitung. V. Alle Stärkearten haben das gleiche Retrogradtionsspektrum. Z. Physikal. Ch. (A) 1930, 150, 90–99. [Google Scholar]
- Gernat, C.; Radosta, S.; Anger, H.; Damaschun, G. Crystalline parts of three different conformations detected in native and enzymatically degraded starches. Starch/Stärke 1993, 45, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waduge, R.N.; Xu, S.; Seetharaman, K. Iodine absorption properties and its effect on the crystallinity of developing wheat starch granules. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 82, 786–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vamadevan, V.; Hoover, R.; Bertoft, E.; Seetharaman, K. Hydrothermal treatment and iodine binding provide insights into the organization of glucan chains within the semi-crystalline lamellae of corn starch granules. Biopolymers 2014, 101, 871–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varatharajan, V.; Hoover, R.; Liu, Q.; Seetharaman, K. The impact of heat-moisture treatment on the molecular structure and physicochemical properties of normal and waxy potato starches. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 81, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, W.R.; Law, R.V.; Snape, C.E. Evidence for inclusion complexes of lipids with V-amylose in maize, rice and oat starches. J. Cereal Sci. 1993, 18, 107–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aberle, T.; Burchard, W.; Vorwerg, W.; Radosta, S. Conformational contributions of amylose and amylopectin to the structural properties of starches from various sources. Starch/Stärke 1994, 46, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, W.; Greenwood, C.T.; Walker, J.T. Studies on the starches of barley genotypes: The waxy starch. Starch/Stärke 1970, 22, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelievre, J.; Lewis, J.A.; Marsden, K. The size and shape of amylopectin: A study using analytical ultracentrifugation. Carbohydr. Res. 1986, 153, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Rea, D.; Bergenståhl, B.; Nilsson, L. Development and evaluation of methods for starch dissolution using asymmetrical flow field-flow fractionation. Part I: Dissolution of amylopectin. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 4315–4326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoyama, W.; Renner-Nantz, J.J.; Shoemaker, C.F. Starch molecular mass and size by size-exclusion chromatography in DMSO-LiBr coupled with multiple angle laser light scattering. Cereal Chem. 1998, 75, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, A.P.; Mukerjea, R.; Robyt, J.F. Reducing values: Dinitrosalicylate gives over-oxidation and invalid results whereas copper bicinchoninate gives no over-oxidation and valid results. Carbohydr. Res. 2013, 380, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charoenkul, N.; Uttapap, D.; Pathipanawat, W.; Takeda, Y. Molecular structure of starches from cassava varieties having different cooked root textures. Starch/Stärke 2006, 58, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacy, C.J.; Foster, J.F. Molecular weight heterogeneity in starch amylopectins. J. Polym. Sci. Part A 1957, 25, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, Y.; Shibahara, S.; Hanashiro, I. Examination of the structure of amylopectin molecules by fluorescent labeling. Carbohydr. Res. 2003, 338, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hizukuri, S. Relationship between the distribution of the chain length of amylopectin and the crystalline structure of starch granules. Carbohydr. Res. 1985, 141, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalichevsky, M.T.; Orford, P.D.; Ring, S.G. The retrogradation and gelation of amylopectins from various botanical sources. Carbohydr. Res. 1990, 198, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, C.D.; Liu, K.-C. The interaction of endosperm genotype and genetic background. Part I. Differences in chromatographic profiles of starches from nonmutant and mutant endosperms. Starch/Stärke 1985, 37, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koizumi, K.; Fukuda, M.; Hizukuri, S. Estimation of the distributions of chain length of amylopectins by high-performance liquid chromatography with pulsed amperometric detection. J. Chromatogr. 1991, 585, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morell, M.K.; Samuel, M.S.; O’Shea, M.G. Analysis of starch structure using fluorophore-assisted carbohydrate electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 1998, 19, 2603–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Shea, M.G.; Morell, M.K. High resolution slab gel electrophoresis of 8-amino-1,3,6-pyrenetrisulfonic acid (APTS) tagged oligosaccharides using a DNA sequencer. Electrophoresis 1996, 17, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Shea, M.G.; Samuel, M.S.; Konik, C.M.; Morell, M.K. Fluorophore-assisted carbohydrate electrophoresis (FACE) of oligosaccharides: Efficiency of labelling and high-resolution separation. Carbohydr. Res. 1998, 307, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peat, S.; Whelan, W.J.; Thomas, G.J. Evidence of multiple branching in waxy maize starch. J. Chem. Soc. 1952, 4546–4548. [Google Scholar]
- Hizukuri, S. Polymodal distribution of the chain lengths of amylopectins, and its significance. Carbohydr. Res. 1986, 147, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanashiro, I.; Itoh, K.; Kuratomi, Y.; Yamazaki, M.; Igarashi, T.; Matsugasako, J.-I.; Takeda, Y. Granule-bound starch synthase I is responsible for biosynthesis of extra-long unit chains of amylopectin in rice. Plant Cell Physiol. 2008, 49, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, Y.; Hizukuri, S.; Juliano, B.O. Structures of rice amylopectins with low and high affinities for iodine. Carbohydr. Res. 1987, 168, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoenkul, N.; Uttapap, D.; Pathipanawat, W.; Takeda, Y. Simultaneous determination of amylose content & unit chain distribution of amylopectins of cassava starches by fluorescent labeling/HPSEC. Carbohydr. Polym. 2006, 65, 102–108. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, S.-H.; Jane, J.-L. Structural and physical characteristics of waxy and other wheat starches. Carbohydr. Polym. 2002, 49, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, T.; Takigawa, S.; Matsuura-Endo, C.; Kim, S.-J.; Hashimoto, N.; Yamauchi, H.; Hanashiro, I.; Takeda, Y. Physicochemical properties and amylopectin structures of large, small, and extremely small potato starch granules. Carbohydr. Polym. 2005, 60, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanashiro, I.; Matsugasako, J.-I.; Egashira, T.; Takeda, Y. Structural characterization of long unit-chains of amylopectin. J. Appl. Glycosci. 2005, 52, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laohaphatanaleart, K.; Piyachomkwan, K.; Sriroth, K.; Santisopasri, V.; Bertoft, E. A study of the internal structure in cassava and rice amylopectin. Starch/Stärke 2009, 61, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanashiro, I.; Tagawa, M.; Shibahara, S.; Iwata, K.; Takeda, Y. Examination of molar-based distribution of A, B and C chains of amylopectin by fluorescent labeling with 2-aminopyridine. Carbohydr. Res. 2002, 337, 1211–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annor, G.A.; Marcone, M.; Bertoft, E.; Seetharaman, K. Unit and internal chain profile of millet amylopectin. Cereal Chem. 2014, 91, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayin, J.; Abdel-Aal, E.-S.M.; Manful, J.; Bertoft, E. Unit and internal chain profile of African rice (Oryza glaberrima) amylopectin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 137, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, A.; Annor, G.; Blennow, A.; Bertoft, E. Effect of diurnal photosynthetic activity on the fine structure of amylopectin from normal and waxy barley starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 102, 924–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalinga, D.N.; Waduge, R.; Liu, Q.; Yada, R.Y.; Bertoft, E.; Seetharaman, K. On the differences in granular architechture and starch structure between pericarp and endosperm wheat starches. Starch/Stärke 2013, 65, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Bertoft, E.; Bao, J.; Corke, H. Molecular structure of amylopectin from amaranth starch and its effect on physicochemical properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2008, 43, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.; Bertoft, E.; Källman, A.; Myers, A.M.; Seetharaman, K. Molecular structure of starches from maize mutants deficient in starch synthase III. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 9899–9907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manners, D.J. Recent developments in our understanding of amylopectin structure. Carbohydr. Polym. 1989, 11, 87–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoft, E. Investigation of the fine structure of alpha-dextrins derived from amylopectin and their relation to the structure of waxy-maize starch. Carbohydr. Res. 1991, 212, 229–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matheson, N.K. The chemical structure of amylose and amylopectin fractions of starch from tobacco leaves during development and diurnally-nocturnally. Carbohydr. Res. 1996, 282, 247–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanes, C.S. The reversible formation of starch from glucose-1-phosphate catalysed by potato phosphorylase. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 1940, 129, 174–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hestrin, S. Action pattern of crystalline muscle phosphorylase. J. Biol. Chem. 1949, 179, 943–955. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meyer, K.H. The past and present of starch chemistry. Experientia 1952, 8, 405–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, G.J.; Whelan, W.J. The mechanism of carbohydrase action. 8. Structures of the muscle-phosphorylase limit dextrins of glycogen and amylopectin. Biochem. J. 1960, 76, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoft, E. Partial characterisation of amylopectin alpha-dextrins. Carbohydr. Res. 1989, 189, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoft, E. On the nature of categories of chains in amylopectin and their connection to the super helix model. Carbohydr. Polym. 2004, 57, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summer, R.; French, D. Action of β-amylase on branched oligosaccharides. J. Biol. Chem. 1956, 222, 469–477. [Google Scholar]
- Akai, H.; Yokobayashi, K.; Misaki, A.; Harada, T. Complete hydrolysis of branching linkages in glycogen by Pseudomonas isoamylase: Distribution of linear chains. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1971, 237, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, T.; Misaki, A.; Akai, H.; Yokobayashi, K.; Sugimoto, K. Characterization of Pseudomonas isoamylase by its actions on amylopectin and glycogen: Comparison with Aerobacter pullulanase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1972, 268, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokobayashi, K.; Akai, H.; Sugimoto, T.; Hirao, M.; Sugimoto, K.; Harada, T. Comparison of the kinetic parameters of Pseudomonas isoamylase and Aerobacter pullulanase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1973, 293, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokobayashi, K.; Misaki, A.; Harada, T. Purification and properties of Pseudomonas isoamylase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1970, 212, 458–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kainuma, K.; Kobayashi, S.; Harada, T. Action of Pseudomonas isoamylase on various branched oligo- and polysaccharides. Carbohydr. Res. 1978, 61, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidley, M.J.; Bulpin, P.V. Crystallisation of malto-oligosaccharides as models of the crystalline forms of starch: Minimum chain-length requirement for the formation of double helices. Carbohydr. Res. 1987, 161, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Corke, H.; Bertoft, E. Fine structure characterization of amylopectins from grain amaranth starch. Carbohydr. Res. 2009, 344, 1701–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalinga, D.N.; Bertoft, E.; Tetlow, I.; Liu, Q.; Yada, R.Y.; Seetharaman, K. Evolution of amylopectin structure in developing wheat endosperm. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 112, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bijttebier, A.; Goesaert, H.; Delcour, J.A. Hydrolysis of amylopectin by amylolytic enzymes: Structural analysis of the residual amylopectin population. Carbohydr. Res. 2010, 345, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robyt, J.; French, D. Action pattern and specificity of an amylase from Bacillus subtilis. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1963, 100, 451–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoma, J.A.; Brothers, C.; Spradlin, J. Subsite mapping of enzymes. Studies on Bacillus subtilis amylase. Biochemistry 1970, 9, 1768–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoft, E. Hydrolysis of amylopectin by the alpha-amylase of B. subtilis. Carbohydr. Res. 1986, 149, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoft, E. The Use of Alpha-Amylase in Structural Studies of Amylopectin. Ph.D. Thesis, Åbo Akademi University, Turku, Finland, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Bertoft, E.; Koch, K. Composition of chains in waxy-rice starch and its structural units. Carbohydr. Polym. 2000, 41, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoft, E.; Qin, Z.; Manelius, R. Studies on the structure of pea starches. Part 3: Amylopectin of smooth pea starch. Starch/Stärke 1993, 45, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoft, E.; Åvall, A.-K. Structural analysis on the amylopectin of waxy-barley large starch granules. J. Inst. Brew. 1992, 98, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gérard, C.; Planchot, V.; Colonna, P.; Bertoft, E. Relationship between branching density and crystalline structure of A- and B-type maize mutant starches. Carbohydr. Res. 2000, 326, 130–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Bertoft, E. Composition and structural analysis of alpha-dextrins from potato amylopectin. Carbohydr. Res. 1996, 288, 155–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoft, E. Composition of building blocks in clusters from potato amylopectin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 70, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoft, E.; Zhu, Q.; Andtfolk, H.; Jungner, M. Structural heterogeneity in waxy-rice starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 1999, 38, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laohaphatanaleart, K.; Piyachomkwan, K.; Sriroth, K.; Bertoft, E. The fine structure of cassava amylopectin. Part 1. Organization of clusters. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2010, 47, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.; Corke, H.; Åman, P.; Bertoft, E. Structures of clusters in sweetpotato amylopectin. Carbohydr. Res. 2011, 346, 1112–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoft, E. Composition of clusters and their arrangement in potato amylopectin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 68, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoft, E.; Källman, A.; Koch, K.; Andersson, R.; Åman, P. The cluster structure of barley amylopectins of different genetic backgrounds. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011, 49, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoft, E.; Koch, K.; Åman, P. Building block organisation of clusters in amylopectin of different structural types. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2012, 50, 1212–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.; Corke, H.; Åman, P.; Bertoft, E. Structures of building blocks in clusters of sweetpotato amylopectin. Carbohydr. Res. 2011, 346, 2913–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoft, E.; Källman, A.; Koch, K.; Andersson, R.; Åman, P. The building block structure of barley amylopectin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011, 49, 900–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoft, E.; Laohaphatanaleart, K.; Piyachomkwan, K.; Sriroth, K. The fine structure of cassava amylopectin. Part 2. Building block structure of clusters. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2010, 47, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoft, E.; Koch, K.; Åman, P. Structure of building blocks in amylopectins. Carbohydr. Res. 2012, 361, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gayin, J.; Abdel-Aal, E.-S.M.; Marcone, M.; Manful, J.; Bertoft, E. Structure of clusters and building blocks in amylopectin from African rice accessions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 148, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalinga, D.N.; Bertoft, E.; Tetlow, I.; Seetharaman, K. Structure of clusters and building blocks in amylopectin from developing wheat endosperm. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 112, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.; Bertoft, E.; Seetharaman, K. Composition of clusters and building blocks in amylopectins of starch mutants deficient in starch synthase III. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 12345–12355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.; Bertoft, E.; Szydlowski, N.; D’Hulst, C.; Seetharaman, K. Branching patterns in leaf starches from Arabidopsis mutants deficient in diverse starch synthases. Carbohydr. Res. 2015, 401, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalinga, D.N.; Bertoft, E. Internal structure of amylopectin from the pericarp tissue of developing wheat kernels. Starch/Stärke 2015, 67, 1070–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peymanpour, G.; Marcone, M.; Ragaee, S.; Tetlow, I.; Lane, C.C.; Seetharaman, K.; Bertoft, E. On the molecular structure of the amylopectin fraction isolated from “high-amylose” ae maize starches. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 91, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vamadevan, V.; Bertoft, E.; Seetharaman, K. On the importance of organization of glucan chains on thermal properties of starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 1653–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seetharaman, K.; Bertoft, E. Perspectives on the history of research on starch. Part V: On the conceptualization of amylopectin structure. Starch/Stärke 2013, 65, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikuni, Z. Starch and cooking. Sci. Cook. 1969, 2, 6–14. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs, H.; Eerlingen, R.C.; Rouseu, N.; Colonna, P.; Delcour, J.A. Acid hydrolysis of native and annealed wheat, potato and pea starches—DSC melting features and chain length distributions of lintnerised starches. Carbohydr. Res. 1998, 308, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akai, H.; Yokobayashi, K.; Misaki, A.; Harada, T. Structural analysis of amylopectin using Pseudomonas isoamylase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1971, 252, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manners, D.J.; Matheson, N.K. The fine structure of amylopectin. Carbohydr. Res. 1981, 90, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, H.; Siebert, R.; Stadler-Szöke, A. Can cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase be useful for the investigation of the fine structure of amylopectins? Characterisation of highly branched clusters isolated from digests with potato and maize starches. Carbohydr. Res. 1982, 110, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finch, P.; Sebesta, D.W. The amylase of Pseudomonas stutzeri as a probe of the structure of amylopectin. Carbohydr. Res. 1992, 227, c1–c4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoft, E.; Henriksnäs, H. Initial stages in α-amylolysis of barley starch. J. Inst. Brew. 1982, 88, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, A.C.; Pérez, S. The relationship between internal chain length of amylopectin and crystallinity in starch. Biopolymers 1999, 50, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoft, E. On the building block and backbone concepts of amylopectin structure. Cereal Chem. 2013, 90, 294–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Källman, A.; Bertoft, E.; Koch, K.; Åman, P.; Andersson, R. On the interconnection of clusters and building blocks in barley amylopectin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 55, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoft, E.; Nilsson, L. Starch. Analytical and structural aspects. In Carbohydrates in Food; Eliasson, A.-C., Ed.; CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 377–478. [Google Scholar]
- Ball, S.; Guan, H.-P.; James, M.; Myers, A.; Keeling, P.; Mouille, G.; Buléon, A.; Colonna, P.; Preiss, J. From glycogen to amylopectin: A model for the biogenesis of the plant starch granule. Cell 1996, 86, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debet, M.R.; Gidley, M.J. Three classes of starch granule swelling: Influence of surface proteins and lipids. Carbohydr. Polym. 2006, 64, 452–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Tester, R.F.; Snape, C.E.; Ansell, R. Molecular basis of the gelatinisation and swelling characteristics of waxy rice starches grown in the same location during the same season. J. Cereal Sci. 2003, 37, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tester, R.F.; Morrison, W.R. Swelling and gelatinization of cereal starches. I. Effects of amylopectin, amylose, and lipids. Cereal Chem. 1990, 67, 551–557. [Google Scholar]
- Dhillon, S.; Abdel-Aal, E.-S.M.; Seetharaman, K. Effect of iodine on polymer leaching and granule swelling of starches from different sources. J. Cereal Sci. 2011, 54, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, P.J.; Donald, A.M. Gelatinisation of starch: A combined SAXS/WAXS/DSC and SANS study. Carbohydr. Res. 1998, 308, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Singh, J.; Kaur, L.; Sodhi, N.S.; Gill, B.S. Morphological, thermal and rheological properties of starches from different botanical sources. Food Chem. 2003, 81, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandeputte, G.E.; Vermeylen, R.; Geeroms, J.; Delcour, J.A. Rice starches. II. Structural aspects provide insight into swelling and pasting properties. J. Cereal Sci. 2003, 38, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donald, A.M. Plasticization and self assembly in the starch granule. Cereal Chem. 2001, 78, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, P.A.; Donald, A.M. The role of plasticization in starch granules assembly. Biomacromolecules 2000, 1, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waigh, T.A.; Gidley, M.J.; Komanshek, B.U.; Donald, A.M. The phase transformations in starch during gelatinisation: A liquid crystalline approach. Carbohydr. Res. 2000, 328, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vamadevan, V.; Bertoft, E.; Soldatov, D.V.; Seetharaman, K. Impact on molecular organization of amylopectin in starch granules upon annealing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 98, 1045–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoft, E.; Annor, G.A.; Shen, X.; Rumpagaporn, P.; Seetharaman, K.; Hamaker, B.R. Small differences in amylopectin fine structure may explain large functional differences of starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 140, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.; Bertoft, E.; Zhang, G.; Hamaker, B.R. Iodine binding to explore the conformational state of internal chains of amylopectin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 98, 778–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manion, B.; Ye, M.; Holbein, B.E.; Seetharaman, K. Quantification of total iodine in intact granular starches of different botanical origin exposed to iodine vapor at various water activities. Carbohydr. Res. 2011, 346, 2482–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saibene, D.; Seetharaman, K. Use of iodine as a tool to understand wheat starch pasting properties. Starch/Stärke 2008, 60, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saibene, D.; Seetharaman, K. Segmental mobility of polymers in starch granules at low moisture contents. Carbohydr. Polym. 2006, 64, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetlow, I.J. Starch biosynthesis in developing seeds. Seed Sci. Res. 2011, 21, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borovsky, D.; Smith, E.E.; Whelan, W.J.; French, D.; Kikumoto, S. The mechanism of Q-enzyme action and its influence on the structure of amylopectin. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1979, 198, 627–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haworth, W.N.; Hirst, E.L.; Isherwood, F.A. Polysaccharides. Part XXIII. Determination of the chain length of glycogen. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1937, 577–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
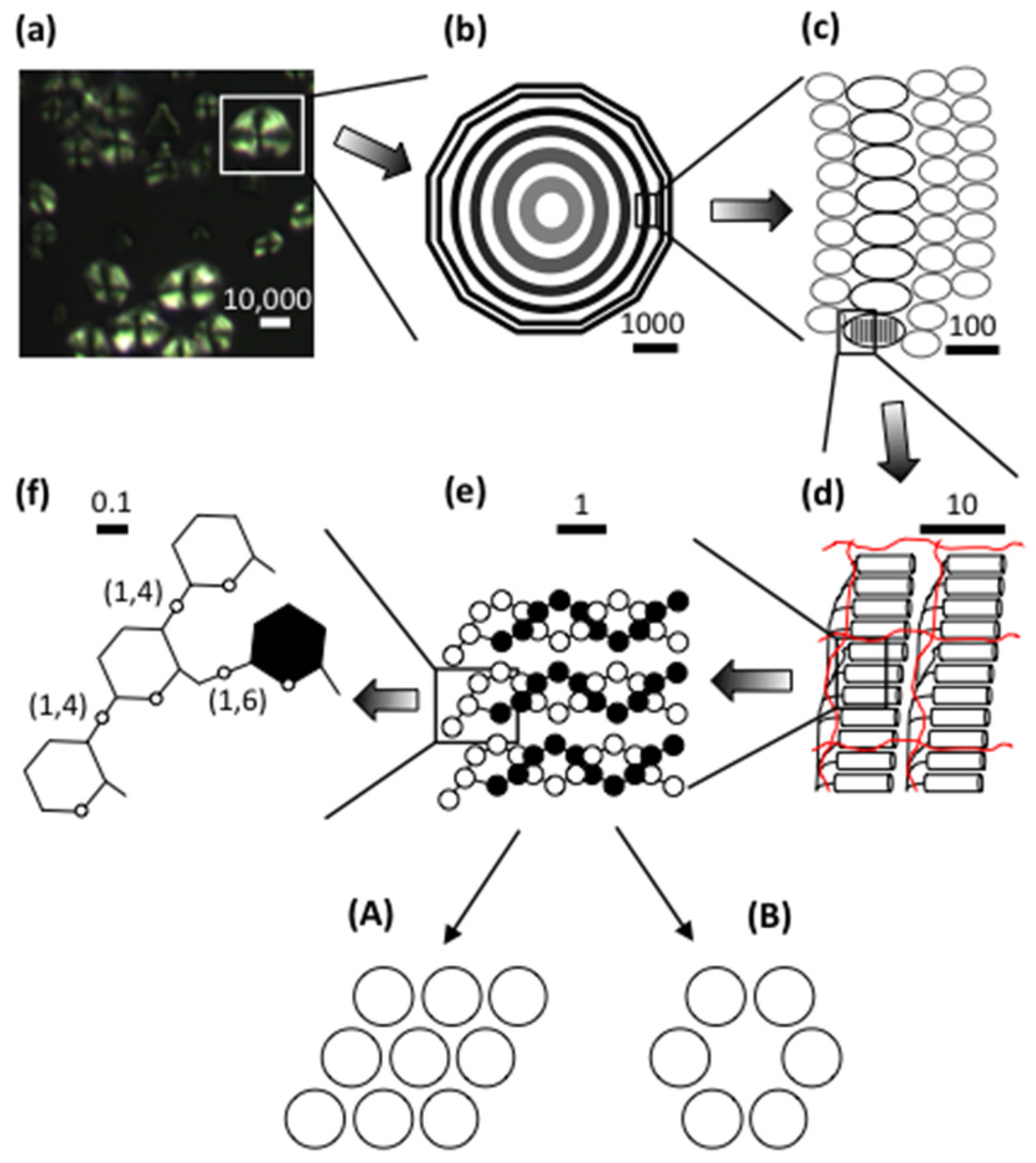
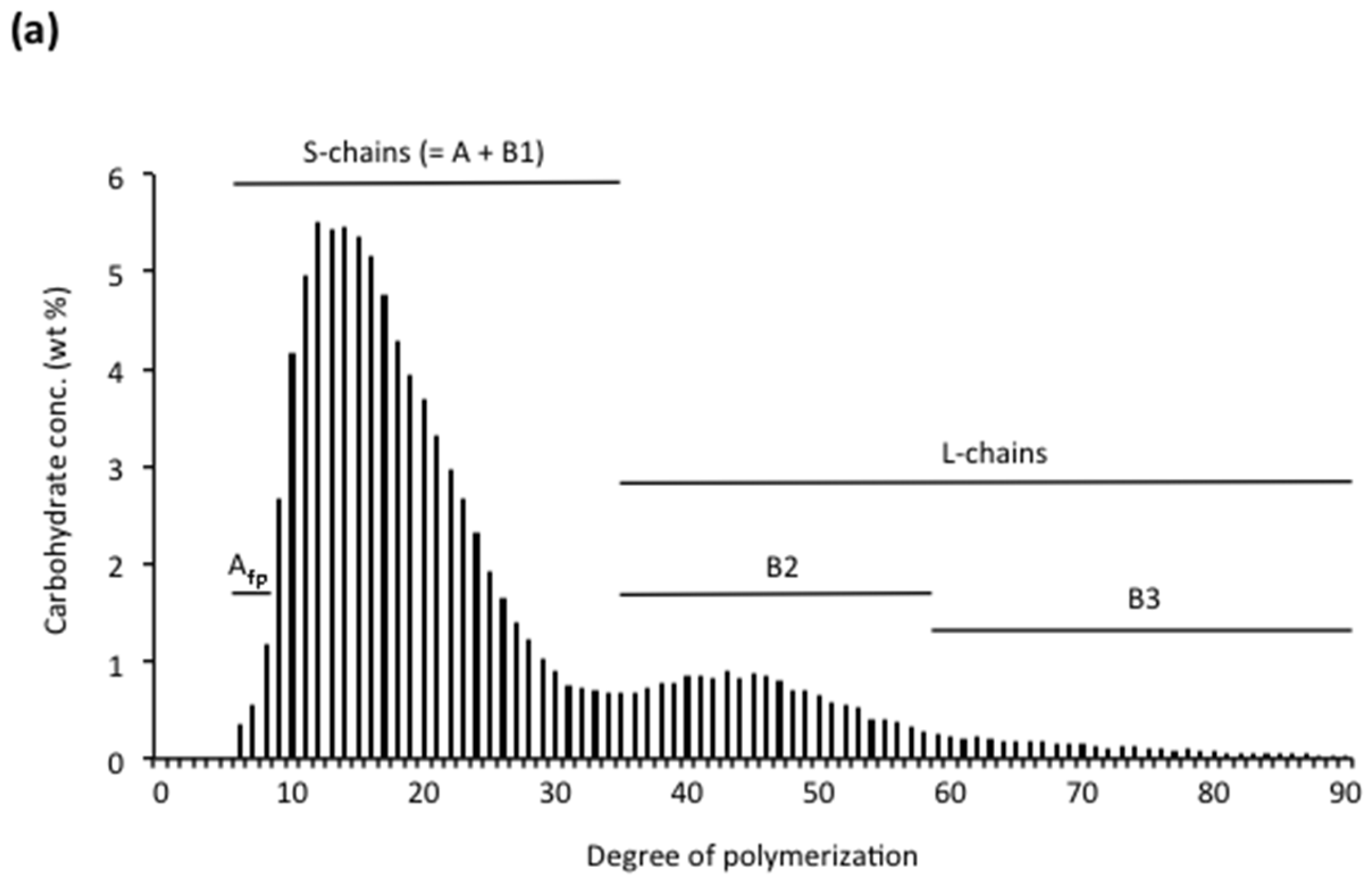
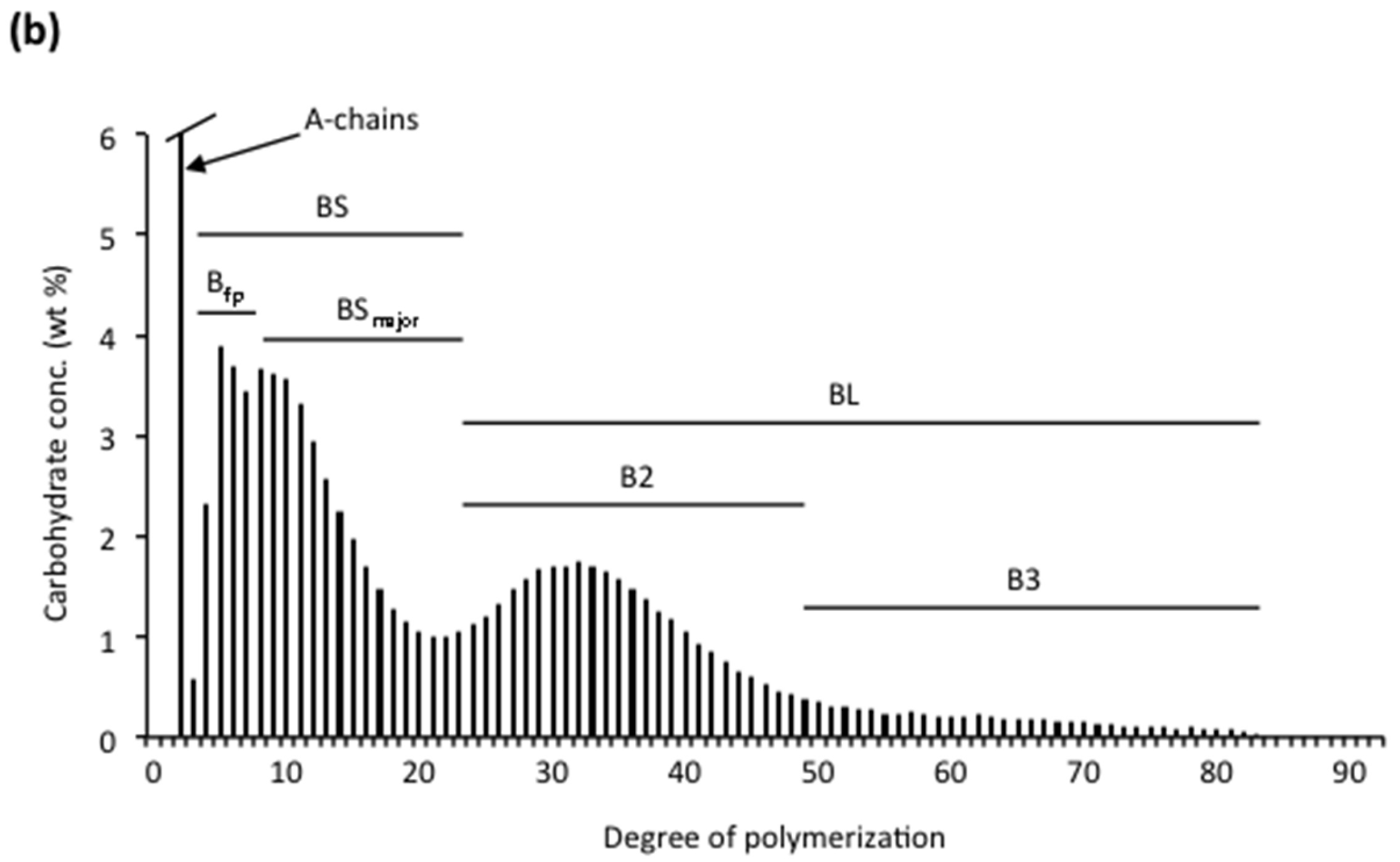
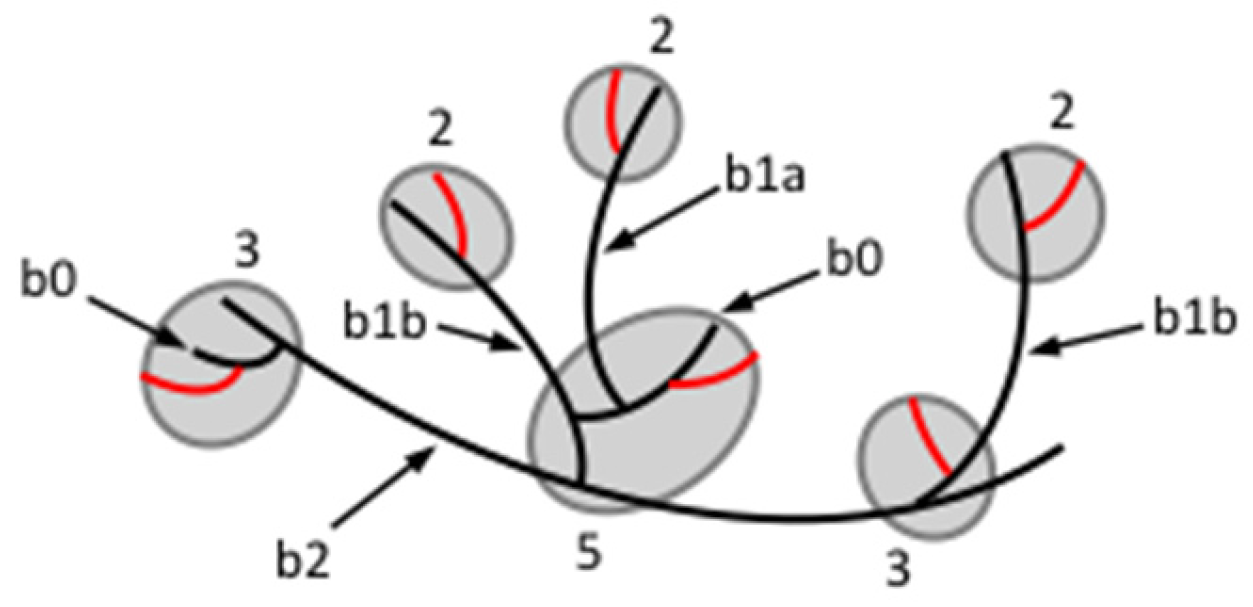

| Source | Amylose (%) | DPn a | CLn b | β-LV (%) c | Nbranched (%) d | NCbranched e |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wheat | 17–34 | 980–1570 | 135–270 | 79–85 | 26–44 | 12.9–20.7 |
| Rye | 26–30 | n.a. f | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. |
| Triticale | 23–27 | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. |
| Barley | 22–27 | 1220–1680 | 315–510 | 76–82 | 21–45 | 6.1–13.8 |
| Oat | 18–29 | n.a. | 592–907 g | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. |
| Rice | 17–29 | 920–1110 | 230–370 | 73–87 | 31–69 | 5.7–9.7 |
| Maize | 20–28 | 960–830 | 305–340 | 81–84 | 44–48 | 5.3–5.4 |
| Sorghum | 22–30 | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. |
| Sweet potato | 19–20 | 3280 | 335 | 76 | 70 | 13.6 |
| Potato | 25–31 | 4920–6340 | 520–670 | 68–80 | n.a. | n.a. |
| Source | Structure b | CL | ECL | TICL | ICL | S:L | BS:BL | A:B |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wheat | A:1–2 | 17.7 | 12.3 | 12.7 | 4.4 | 16.2 | 6.8 | 1.4 |
| Rye | A:1 | 17.4 | 10.7 | 12.6 | 5.3 | 16.2 | 7.3 | 1.1 |
| Barley | A:1 | 17.6 | 11.5 | 12.3 | 5.1 | 17.9 | 8.6 | 1.0 |
| Oat | A:1 | 17.0 | 10.7 | 12.6 | 5.3 | 18.2 | 8.6 | 1.0 |
| Asian rice c | A:2 | 16.9 | 10.7 | 12.4 | 5.2 | 14.2 | 5.4 | 1.0 |
| African rice d | A:2 | 18.1 | 12.1 | 11.9 | 5.0 | 11.7 | 5.0 | 1.0 |
| Maize | A:2 | 19.7 | 13.1 | 12.6 | 5.6 | 9.9 | 6.3 | 1.1 |
| Pearl Millet | A:2 | 18.0 | 12.0 | 11.9 | 5.0 | 15.9 | 7.4 | 1.0 |
| Amaranth | A:2–3 | 17.7 | 11.4 | 13.4 | 5.3 | 10.0 | 4.2 | 1.1 |
| Cassava | A:3 | 18.8 | 12.4 | 14.6 | 5.3 | 11.0 | 4.6 | 1.3 |
| Potato | B:4 | 23.1 | 14.1 | 19.9 | 8.0 | 6.3 | 2.3 | 1.2 |
| Source | Structure b | NC | CL | TICL | ICL | IB-CL | NBbl | Molar Distribution of Building Blocks (%) c | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | ||||||||
| Wheat | A:1–2 | 14.2 | 5.8 | 11.9 | 3.6 | 6.4 | 6.3 | 57 | 24 | 10 | 8 | 1 |
| Rye | A:1 | 11.5 | 6.1 | 10.5 | 4.0 | 5.9 | 5.5 | 55 | 28 | 9 | 7 | 1 |
| Barley | A:1 | 19.5 | 6.3 | 10.0 | 4.0 | 6.0 | 10.4 | 65 | 25 | 5 | 4 | 1 |
| Oat | A:1 | 11.8 | 6.1 | 10.4 | 4.1 | 5.7 | 5.7 | 55 | 27 | 9 | 7 | 2 |
| Asian rice d | A:2 | 12.0 | 6.8 | 7.9 | 4.7 | 6.9 | 5.7 | 50 | 29 | 11 | 9 | 1 |
| African rice e | A:2 | 14.1 | 5.9 | 7.9 | 3.8 | 6.5 | 5.1 | 40 | 29 | 13 | 14 | 4 |
| Maize | A:2 | 12.5 | 5.4 | 10.5 | 3.3 | 6.2 | 4.2 | 51 | 27 | 10 | 12 f | |
| Amaranth | A:2–3 | 8.8 | 6.4 | 10.3 | 4.5 | 6.8 | 4.2 | 55 | 29 | 8 | 8 f | |
| Cassava | A:3 | 10.0 | 7.0 | 12.0 | 4.6 | 7.1 | 5.1 | 59 | 30 | 5 | 6 f | |
| Waxy potato | B:4 | 6.2 | 7.9 | 12.4 | 5.4 | 8.0 | 3.1 | 48 | 31 | 13 | 8 f | |
© 2017 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bertoft, E. Understanding Starch Structure: Recent Progress. Agronomy 2017, 7, 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy7030056
Bertoft E. Understanding Starch Structure: Recent Progress. Agronomy. 2017; 7(3):56. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy7030056
Chicago/Turabian StyleBertoft, Eric. 2017. "Understanding Starch Structure: Recent Progress" Agronomy 7, no. 3: 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy7030056
APA StyleBertoft, E. (2017). Understanding Starch Structure: Recent Progress. Agronomy, 7(3), 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy7030056





