An Efficient and Green Ag/AgCl Nanoparticle Derived from Ginger Straw Waste Against Crop Soil-Borne Pathogens
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
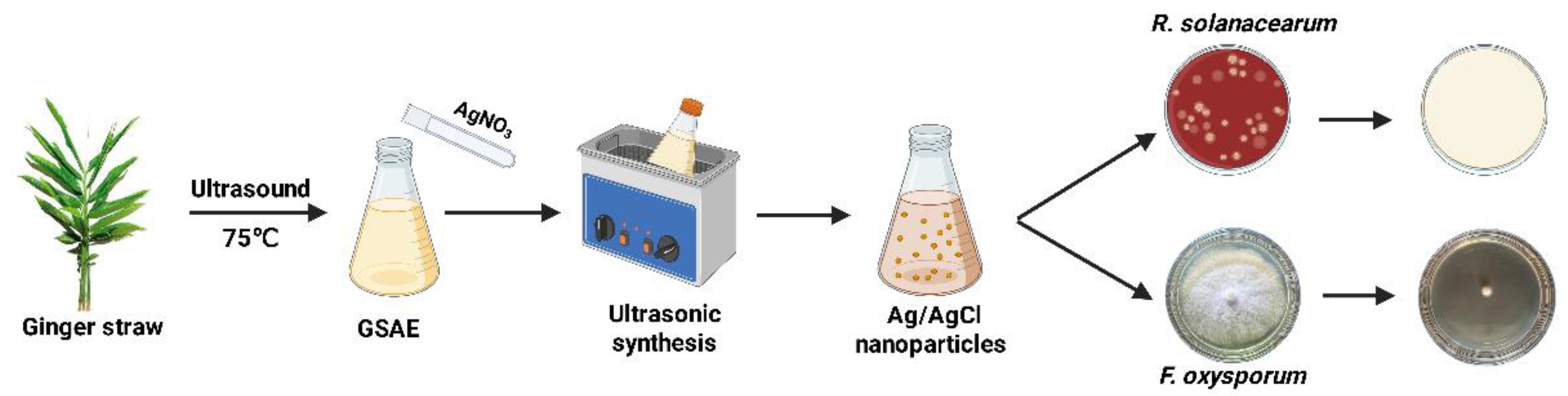
2.2. Preparation of Ag/AgCl-NPs
2.3. Characterization of Ag/AgCl-NPs
2.4. Antimicrobial-Activity Assay
2.5. Leakage of Cell Contents
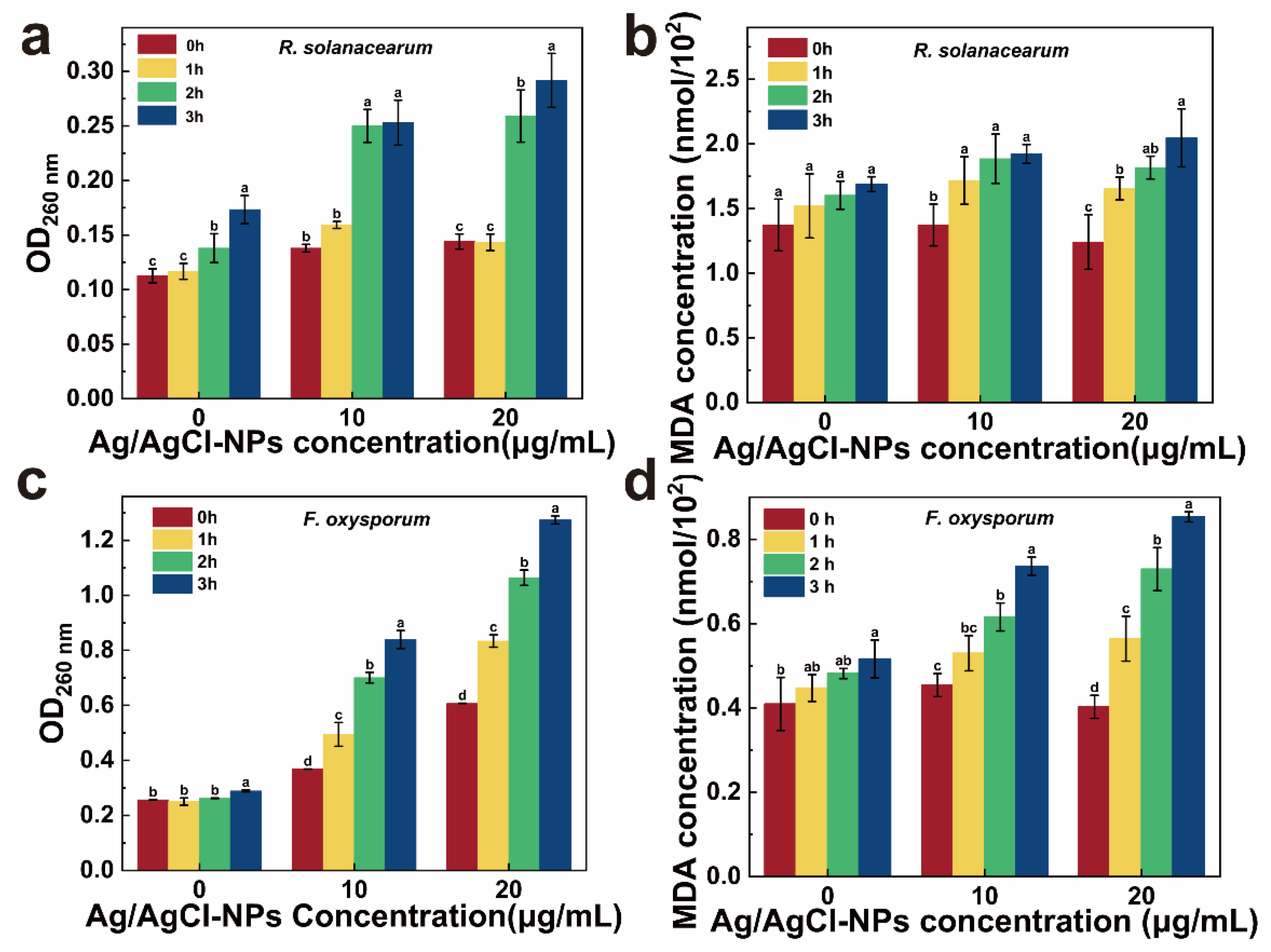
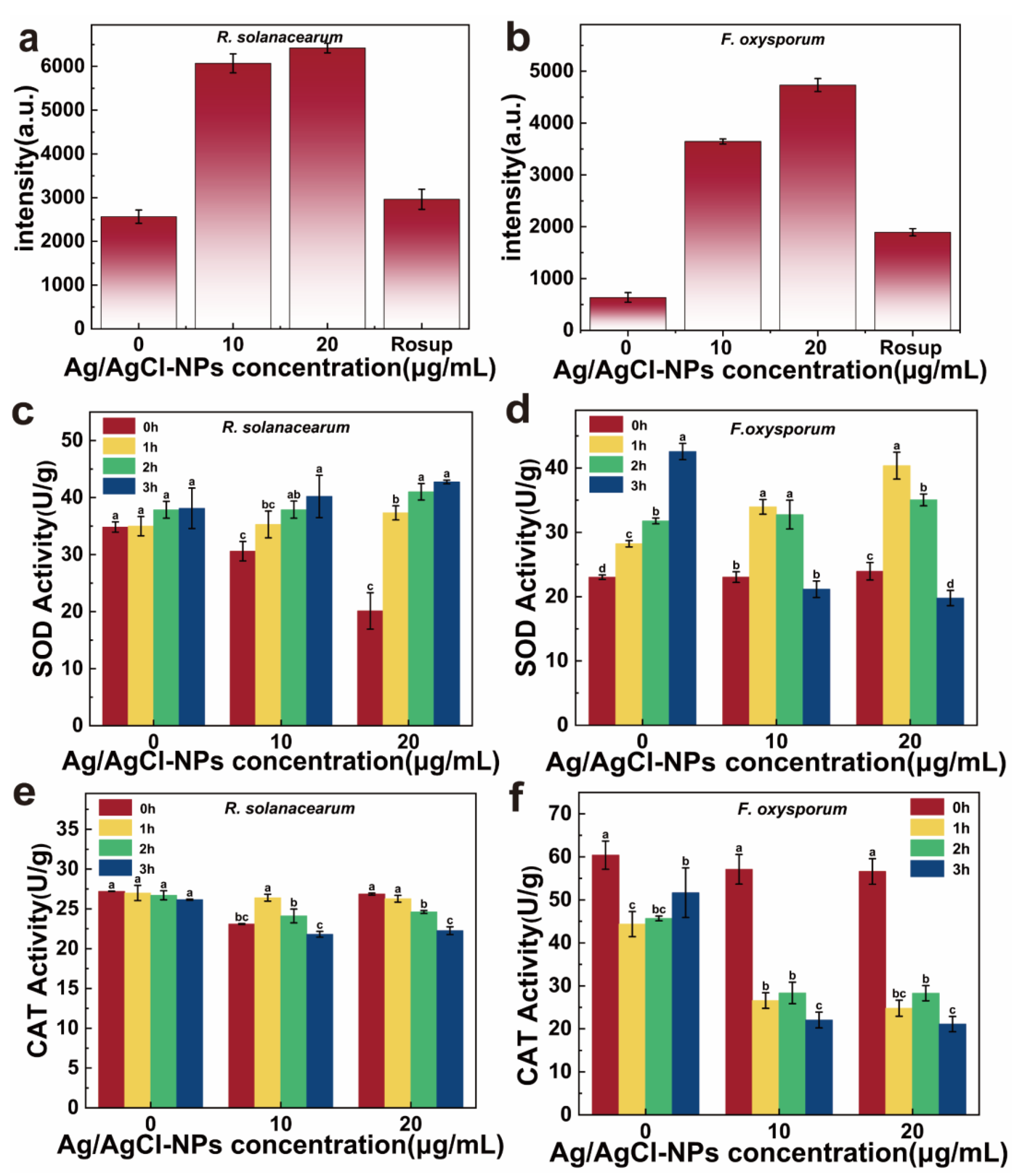
2.6. Determination of Intracellular ROS and Antioxidant Enzyme Activity
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
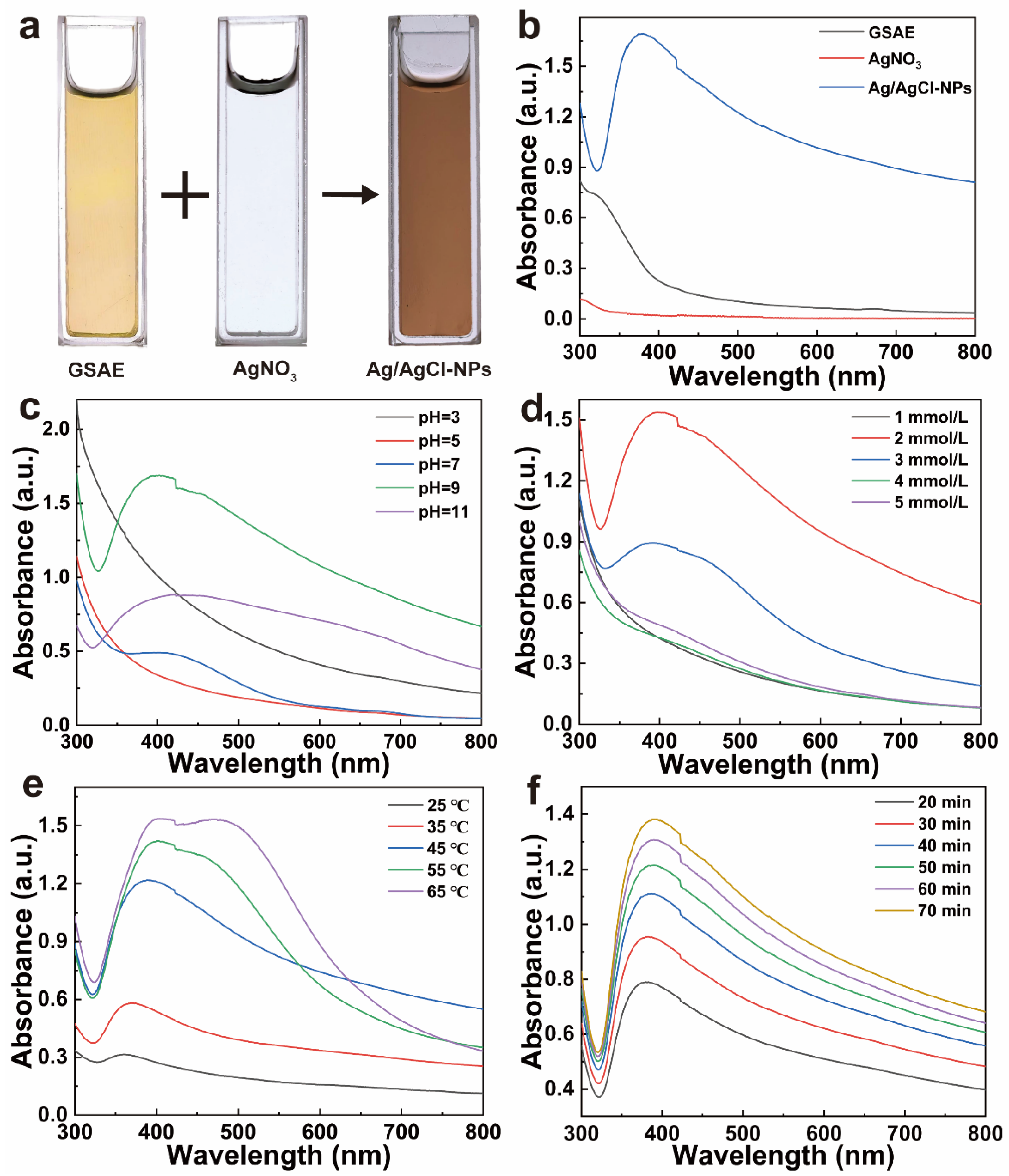
3.1. Preparation Parameters of Ag/AgCl-NPs
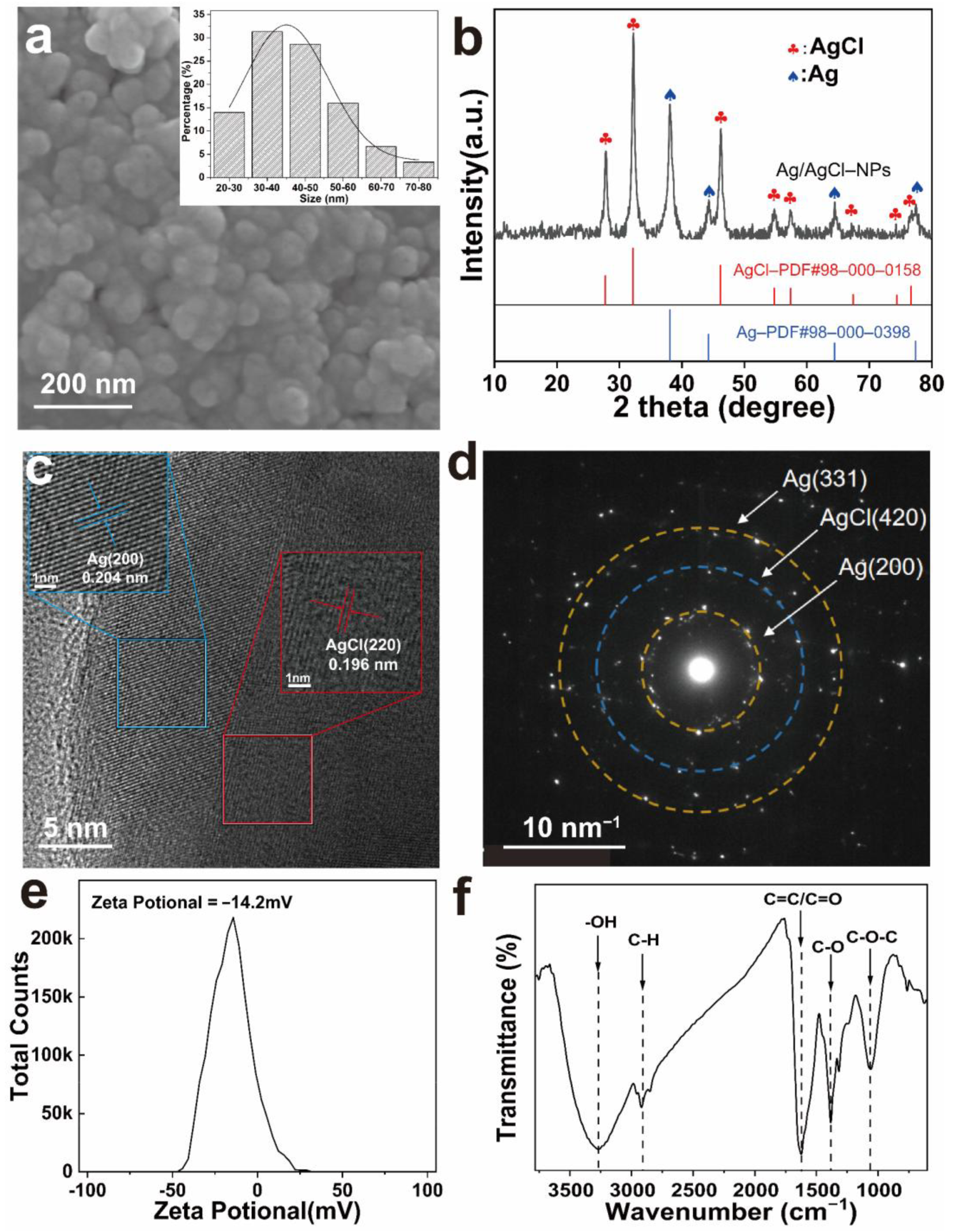
3.2. Physical and Chemical Characteristics of Ag/AgCl-NPs
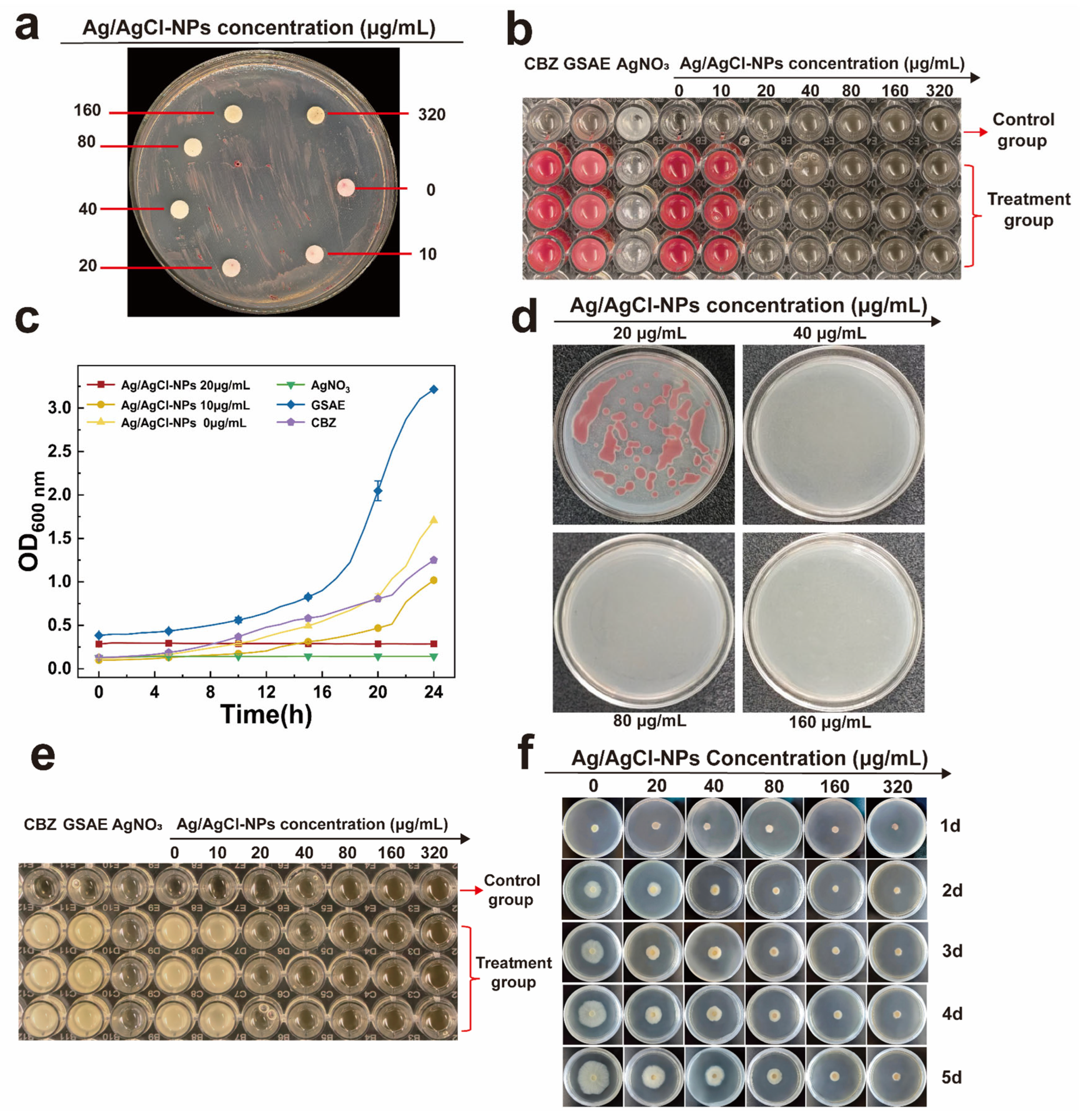
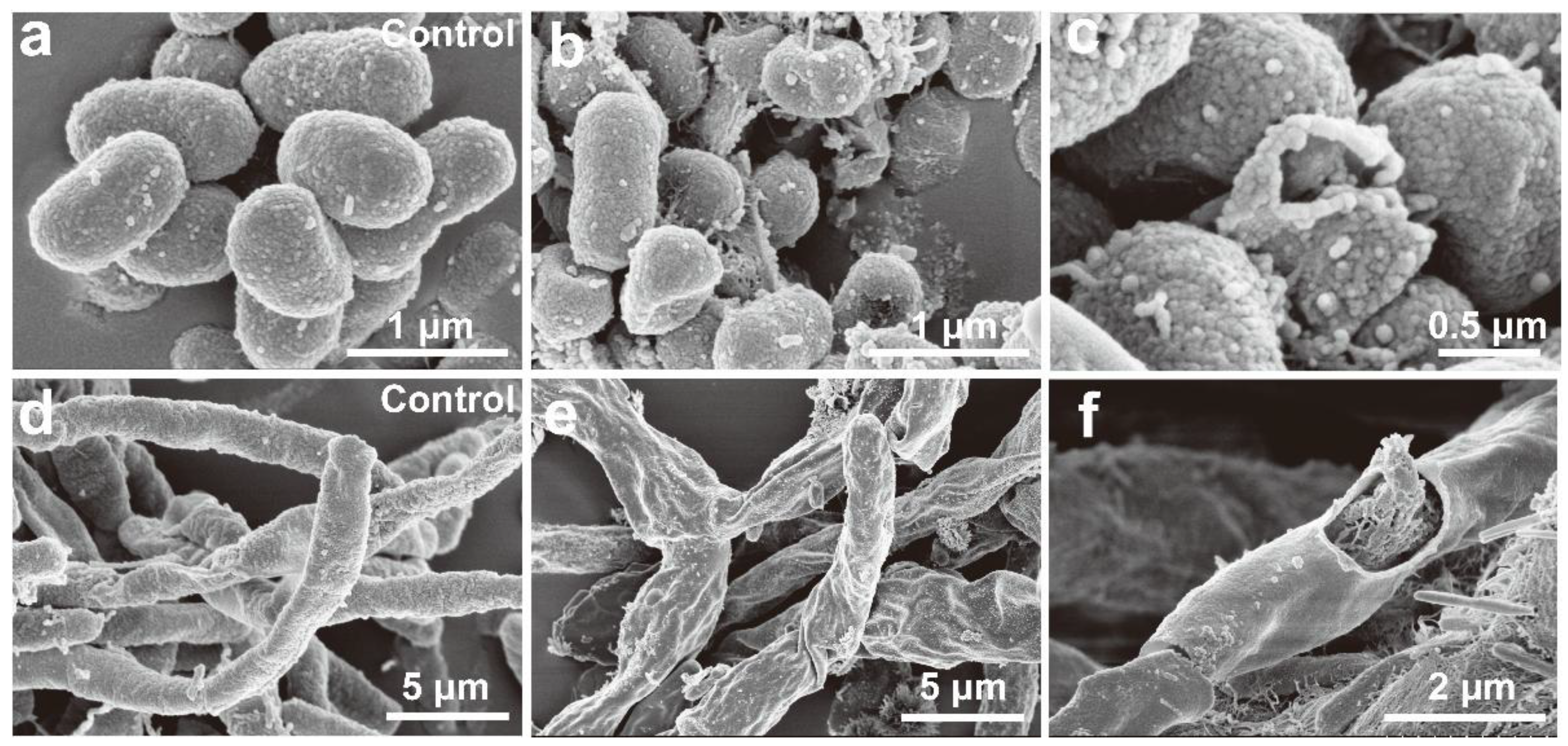
3.3. Antimicrobial Activity of Ag/AgCl-NPs
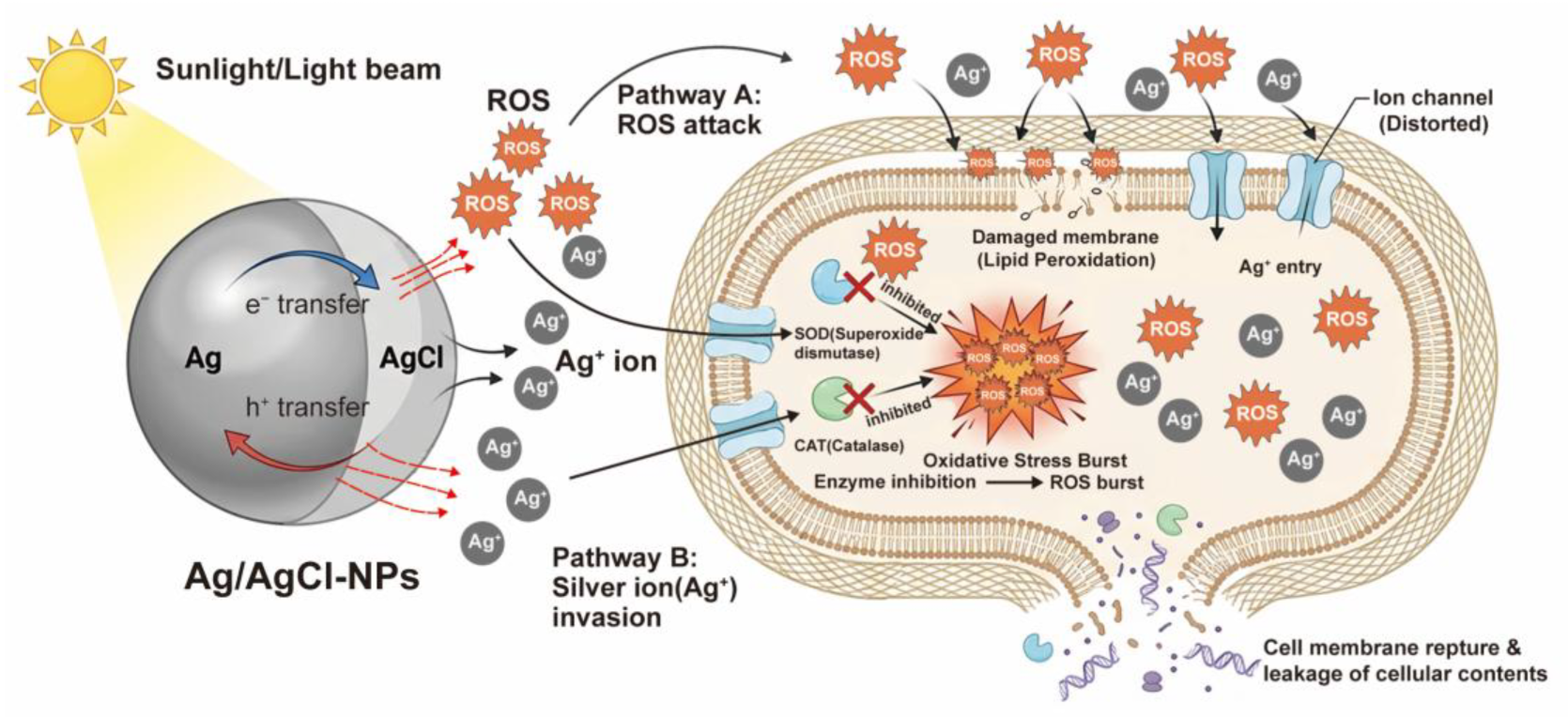
3.4. Antimicrobial Mechanism of Ag/AgCl-NPs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Strange, R.; Scott, P. Plant Disease: A Threat to Global Food Security. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2005, 43, 83–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Guerra, C.A.; Cano-Díaz, C.; Egidi, E.; Wang, J.-T.; Eisenhauer, N.; Singh, B.K.; Maestre, F.T. The proportion of soil-borne pathogens increases with warming at the global scale. Nat. Clim. Change 2020, 10, 550–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Thomashow, L.S.; Luo, Y.; Hu, H.; Deng, X.; Liu, H.; Shen, Z.; Li, R.; Shen, Q. Resistance to bacterial wilt caused by Ralstonia solanacearum depends on the nutrient condition in soil and applied fertilizers: A meta-analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 329, 107874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wei, Z.; Yang, K.; Wang, J.; Jousset, A.; Xu, Y.; Shen, Q.; Friman, V.-P. Phage combination therapies for bacterial wilt disease in tomato. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 1513–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; He, W.; Huang, M.; Feng, J.; Li, Y.; Yu, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, D.; Meng, C.; Cheng, D.; et al. Ralstonia solanacearum type III effector RipAS associates with potato type one protein phosphatase StTOPP6 to promote bacterial wilt. Hortic. Res. 2023, 10, uhad087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aysanew, E.; Alemayehu, D. Integrated management of ginger bacterial wilt (Ralstonia solanacearum) in Southwest Ethiopia. Cogent Food Agric. 2022, 8, 2125033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edel-Hermann, V.; Lecomte, C. Current status of Fusarium oxysporum formae speciales and races. Phytopathology 2019, 109, 512–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mbasa, W.V.; Nene, W.A.; Kapinga, F.A.; Lilai, S.A.; Tibuhwa, D.D. Characterization and chemical management of Cashew Fusarium Wilt Disease caused by Fusarium oxysporum in Tanzania. Crop Prot. 2021, 139, 105379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everts, K.L.; Egel, D.S.; Langston, D.; Zhou, X.-G. Chemical management of Fusarium wilt of watermelon. Crop Prot. 2014, 66, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Zhou, L.; Yang, C.; Cao, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X. Tomato Fusarium wilt and its chemical control strategies in a hydroponic system. Crop Prot. 2004, 23, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prameela, T.P.; Suseela Bhai, R. Bacterial wilt of ginger (Zingiber officinale Rosc.) incited by Ralstonia pseudosolanacearum—A review based on pathogen diversity, diagnostics and management. J. Plant Pathol. 2020, 102, 709–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; He, D.; Wang, L. Advances in Fusarium drug resistance research. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2021, 24, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, P.I.; Manjula, M.; Bhavani, R.V. Agrochemicals, Environment, and Human Health. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2022, 47, 399–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasmi, F.; Hamitouche, H.; Laribi-Habchi, H.; Benguerba, Y.; Chafai, N. Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs), Methods of Synthesis, Characterization, and Their Application: A Review. Plasmonics 2025, 20, 9455–9488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Jadhav, N.D.; Lonikar, V.V.; Kulkarni, A.N.; Zhang, H.; Sankapal, B.R.; Ren, J.; Xu, B.B.; Pathan, H.M.; Ma, Y.; et al. An overview of green synthesized silver nanoparticles towards bioactive antibacterial, antimicrobial and antifungal applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 323, 103053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, C.G.A.; Kumar, V.G.; Dhas, T.S.; Karthick, V.; Govindaraju, K.; Joselin, J.M.; Baalamurugan, J. Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles (biosynthesis): A short review on recent advances. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 27, 101593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatun, N.; Ruhul-Amin, M.; Parvin, S.; Siddika, A.; Hasan, I.; Kabir, S.R.; Asaduzzaman, A.K.M. Green synthesis of silver/silver chloride nanoparticles derived from Elaeocarpus floribundus leaf extract and study of its anticancer potential against EAC and MCF-7 cells with antioxidant and antibacterial properties. Results Chem. 2024, 7, 101287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabassum, R.Z.; Mehmood, A.; Khalid, A.u.R.; Ahmad, K.S.; Rauf Khan, M.A.; Amjad, M.S.; Raffi, M.; Khan, G.-e.-l.; Mustafa, A. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles for antifungal activity against tomato fusarium wilt caused by Fusarium oxysporum. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2024, 61, 103376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanti, G.L.; Kurjogi, M.; Basavesha, K.N.; Teradal, N.L.; Masaphy, S.; Nargund, V.B. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of solanum torvum mediated silver nanoparticle against Xxanthomonas axonopodis pv.punicae and Ralstonia solanacearum. J. Biotechnol. 2020, 309, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izak-Nau, E.; Huk, A.; Reidy, B.; Uggerud, H.; Vadset, M.; Eiden, S.; Voetz, M.; Himly, M.; Duschl, A.; Dusinska, M.; et al. Impact of storage conditions and storage time on silver nanoparticles’ physicochemical properties and implications for their biological effects. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 84172–84185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maji, S.K.; Kim, D.H. AgInS2-Coated Upconversion Nanoparticle as a Photocatalyst for Near-Infrared Light-Activated Photodynamic Therapy of Cancer Cells. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2018, 1, 1628–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchal, P.; Paul, D.R.; Sharma, A.; Choudhary, P.; Meena, P.; Nehra, S.P. Biogenic mediated Ag/ZnO nanocomposites for photocatalytic and antibacterial activities towards disinfection of water. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 563, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-López, J.L.; Lázaro-Mass, S.; De la Rosa-García, S.; Alvarez-Lemus, M.A.; Gómez-Rivera, A.; López-González, R.; Lobato-García, C.E.; Morales-Mendoza, G.; Gómez-Cornelio, S. Medicinal Plants Extract for the Bio-Assisted Synthesis of Ag/AgCl Nanoparticles with Antibacterial Activity. J. Clust. Sci. 2024, 36, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Xiang, Y.; Liu, X.; Cui, Z.; Yang, X.; Yeung, K.W.K.; Pan, H.; Wang, X.; Chu, P.K.; Wu, S. Photo-Inspired Antibacterial Activity and Wound Healing Acceleration by Hydrogel Embedded with Ag/Ag@AgCl/ZnO Nanostructures. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 9010–9021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, P.; Meng, W.; Cui, E.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, H.; Dai, Y.; et al. Photococatalytic anticancer performance of naked Ag/AgCl nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 131265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, K.T.; Ibraheem, I.J.; Hassan, O.M.; Obaid, A.S.; Ali, H.H.; Salih, T.A.; Kadhim, M.S. Facile green synthesis of Ag/AgCl nanoparticles derived from Chara algae extract and evaluating their antibacterial activity and synergistic effect with antibiotics. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirubuvanesvari-Duraivelu, P.; Abd Gani, S.S.; Hassan, M.; Halmi, M.I.E.; Abutayeh, R.F.; Al-Najjar, M.A.A.; Abu-Odeh, A. Phytofabrication of Ag/AgCl silver nanoparticles from the extract of Phoenix dactylifera L. Medjool date seeds: Synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial properties. RSC Adv. 2025, 15, 27723–27737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulzar, R.; Afzaal, M.; Saeed, F.; Samar, N.; Shahbaz, A.; Ateeq, H.; Farooq, M.U.; Akram, N.; Asghar, A.; Rasheed, A.; et al. Bio valorization and industrial applications of ginger waste: A review. Int. J. Food Prop. 2023, 26, 2772–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadi, M.; Azizi, M.; Dianat-Moghadam, H.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Abyadeh, M.; Milani, M. Antibacterial activity of green gold and silver nanoparticles using ginger root extract. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2022, 45, 1905–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivarajan, Y.; Ishak, K.A.; Yaacob, J.S. Green Synthesis of Tin Oxide (SnO2) Nanoparticles Using Ginger Extracts for Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Dyes in Wastewater. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2025, 197, 5668–5693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliannezhadi, M.; Mirsanaee, S.Z.; Jamali, M.; Shariatmadar Tehrani, F. The physical properties and photocatalytic activities of green synthesized ZnO nanostructures using different ginger extract concentrations. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Cao, Y.; Li, H.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, S.; Wei, W. An efficient heterogeneous acid catalyst derived from waste ginger straw for biodiesel production. Renew. Energy 2021, 176, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inthalaeng, N.; Gao, Y.; Remón, J.; Dugmore, T.I.J.; Ozel, M.Z.; Sulaeman, A.; Matharu, A.S. Ginger waste as a potential feedstock for a zero-waste ginger biorefinery: A review. RSC Sustain. 2023, 1, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Hu, K.; Ou, M.; Li, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhan, X.; Liao, X.; Li, M.; Li, R. Synergistic antifungal activity and mechanism of carvacrol/citral combination against Fusarium oxysporum in Dendrobium officinale. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2025, 215, 106671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Sheng, L.; Yang, X.; Sun, J.; Ye, Y.; Geng, S.; Ning, D.; Zheng, J.; Fan, M.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Natural biomass-derived carbon dots as potent antimicrobial agents against multidrug-resistant bacteria and their biofilms. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2023, 36, e00584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pariona, N.; Mtz-Enriquez, A.I.; Sánchez-Rangel, D.; Carrión, G.; Paraguay-Delgado, F.; Rosas-Saito, G. Green-synthesized copper nanoparticles as a potential antifungal against plant pathogens. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 18835–18843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Liu, Q.; Jing, M.; Wan, J.; Huo, C.; Zong, W.; Tang, J.; Liu, R. Toxic mechanism on phenanthrene-induced cytotoxicity, oxidative stress and activity changes of superoxide dismutase and catalase in earthworm (Eisenia foetida): A combined molecular and cellular study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 418, 126302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchal, P.; Meena, P.; Nehra, S.P. A rapid green synthesis of Ag/AgCl-NC photocatalyst for environmental applications. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 3972–3982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Qi, Z.; Shan, S.; Lu, K.; Zhou, J.; Yang, L.; Tan, X. Aqueous assembly of AgNPs with camellia seed cake polyphenols and its application as a postharvest anti-Penicillium digitatum agent via increasing reactive oxygen species generation. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2023, 206, 112516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohrabnezhad, S.; Rassa, M.; Seifi, A. Green synthesis of Ag nanoparticles in montmorillonite. Mater. Lett. 2016, 168, 28–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Yao, Y.; Lian, Y.; Chen, Y.; Shah, R.; Zhao, X.; Chen, M.; Peng, Y.; Deng, Z. A Double-Buffering Strategy to Boost the Lithium Storage of Botryoid MnO(x)/C Anodes. Small 2019, 15, 1900015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Xie, P.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, H.; Tao, R.; Popov, S.A.; Yang, G.; Shults, E.E.; Wang, C. Synthesis of novel ursolic acid-gallate hybrids via 1,2,3-triazole linkage and its anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory activity study. Arab. J. Chem. 2024, 17, 105762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadakkan, K.; Rumjit, N.P.; Ngangbam, A.K.; Vijayanand, S.; Nedumpillil, N.K. Novel advancements in the sustainable green synthesis approach of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) for antibacterial therapeutic applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2024, 499, 215528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachem, Z.; Kashmar, R.; Abdallah, A.M.; Awad, R.; Khalil, M.I. Characterization, antioxidant, antibacterial, and antibiofilm properties of biosynthesized Ag/AgCl nanoparticles using Origanum ehrenbergii Boiss. Results Mater. 2024, 21, 100550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, S.; Kato, R.; Balamurugan, M.; Kaushik, S.; Soga, T. Efficiency improvement in dye sensitized solar cells by the plasmonic effect of green synthesized silver nanoparticles. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2017, 2, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nortjie, E.; Basitere, M.; Moyo, D.; Nyamukamba, P. Assessing the Efficiency of Antimicrobial Plant Extracts from Artemisia afra and Eucalyptus globulus as Coatings for Textiles. Plants 2024, 13, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boonupara, T.; Kajitvichyanukul, P. Facile synthesis of plasmonic Ag/AgCl nanoparticles with aqueous garlic extract (Allium Sativum L.) for visible-light triggered antibacterial activity. Mater. Lett. 2020, 277, 128362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazman, Ö.; Khamidov, G.; Yilmaz, M.A.; Bozkurt, M.F.; Kargioğlu, M.; Tukhtaev, D.; Erol, I. Environmentally friendly silver nanoparticles synthesized from Verbascum nudatum var. extract and evaluation of its versatile biological properties and dye degradation activity. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 33482–33494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Li, M.; Li, P.; Yang, L.; Wu, L.; Gao, F.; Qi, X.; Zhang, Z. Hydrothermal synthesis of magnetic sludge biochar for tetracycline and ciprofloxacin adsorptive removal. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 319, 124199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Ye, X.; Chen, D.; Xiao, W.; Zhao, S.; Li, J.; Li, H. Chromium(VI) removal from synthetic solution using novel zero-valent iron biochar composites derived from iron-rich sludge via one-pot synthesis. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 47, 102720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, D.B.; Mungmai, L.; Vimolmangkang, S.; Uputinan, S.; Panprommin, D.; Pathom-aree, W.; Auputinan, P. TLC-bioautography-guided valorization of vetiver (Chrysopogon spp.) leaf extracts into an anti-acne gel. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2025, 12, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, K.; Jia, X.; Fu, C.; Yu, H.; Wang, Y. Antioxidant peptides, the guardian of life from oxidative stress. Med. Res. Rev. 2024, 44, 275–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.-y.; Li, P.-j.; Xie, R.-s.; Cao, X.-y.; Su, D.-l.; Shan, Y. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticle composites based on hesperidin and pectin and their synergistic antibacterial mechanism. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 214, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Xiang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Yeung, K.W.K.; Cui, Z.; Yang, X.; Li, Z.; Liang, Y.; Zhu, S.; et al. Local Photothermal/Photodynamic Synergistic Therapy by Disrupting Bacterial Membrane To Accelerate Reactive Oxygen Species Permeation and Protein Leakage. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 17902–17914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Xu, Y.; Liang, H.; Yuan, G.; Wu, X.; Zheng, D. Genome-Wide Identification of Ralstonia solanacearum Genes Required for Survival in Tomato Plants. mSystems 2021, 6, e00838-00821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rtimi, S.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Pillai, S.C.; Kiwi, J. Advances in catalytic/photocatalytic bacterial inactivation by nano Ag and Cu coated surfaces and medical devices. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 240, 291–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, R.; He, T.; Xu, K.; Du, D.; Zhao, N.; Cheng, X.; Yang, J.; Shi, H.; Lin, Y. Biomedical Potential of Ultrafine Ag/AgCl Nanoparticles Coated on Graphene with Special Reference to Antimicrobial Performances and Burn Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 15067–15075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| c0 (μg/mL) | Colony Diameter/mm | Inhibition Rate/% | Virulence Regression Model | EC50/(μg/mL) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 56.37 ± 2.54 a | 0 ± 0 e | |||
| 20 | 40.26 ± 0.45 b | 28.56 ± 0.79 d | |||
| 40 | 35.07 ± 1.67 c | 37.78 ± 2.95 c | y = 1.117x − 2.021 | 64.596 | 0.956 |
| 80 | 24.31 ± 1.94 d | 56.87 ± 3.45 b | |||
| 160 | 16.50 ± 1.00 e | 70.74 ± 1.77 a | |||
| 320 | 14.09 ± 0.40 e | 75.00 ± 0.70 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Gong, Z.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, Y.; Liao, Q.; Jiang, L.; Li, H.; Li, Z.; Huang, K.; Zhang, W.; et al. An Efficient and Green Ag/AgCl Nanoparticle Derived from Ginger Straw Waste Against Crop Soil-Borne Pathogens. Agronomy 2026, 16, 254. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy16020254
Gong Z, Liu M, Zhang Q, Yu Y, Liao Q, Jiang L, Li H, Li Z, Huang K, Zhang W, et al. An Efficient and Green Ag/AgCl Nanoparticle Derived from Ginger Straw Waste Against Crop Soil-Borne Pathogens. Agronomy. 2026; 16(2):254. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy16020254
Chicago/Turabian StyleGong, Zhuhua, Mingwan Liu, Qi Zhang, Yu Yu, Qinhong Liao, Lihui Jiang, Honglei Li, Zhexin Li, Ke Huang, Wenlin Zhang, and et al. 2026. "An Efficient and Green Ag/AgCl Nanoparticle Derived from Ginger Straw Waste Against Crop Soil-Borne Pathogens" Agronomy 16, no. 2: 254. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy16020254
APA StyleGong, Z., Liu, M., Zhang, Q., Yu, Y., Liao, Q., Jiang, L., Li, H., Li, Z., Huang, K., Zhang, W., & Liu, Y. (2026). An Efficient and Green Ag/AgCl Nanoparticle Derived from Ginger Straw Waste Against Crop Soil-Borne Pathogens. Agronomy, 16(2), 254. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy16020254








