Leaching of Heavy Metals from Farmland Soil in China: The Status and Ecological Risk Assessment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Leaching Models
2.2. Estimation of the Infiltration Water
2.3. Soil Heavy Metal Content and Other Parameters
2.4. Ecological Risks
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Average Annual Infiltration Water in China
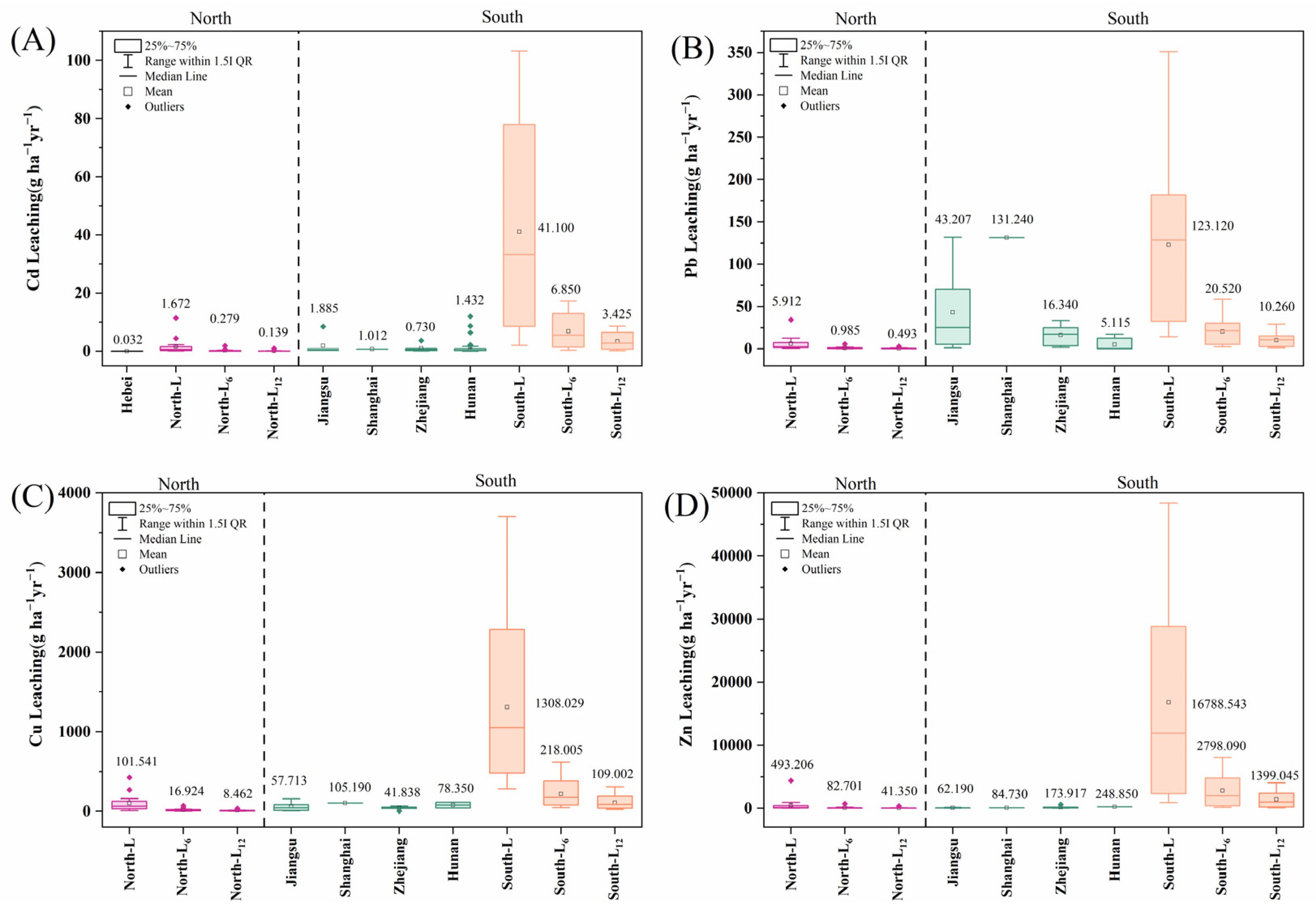
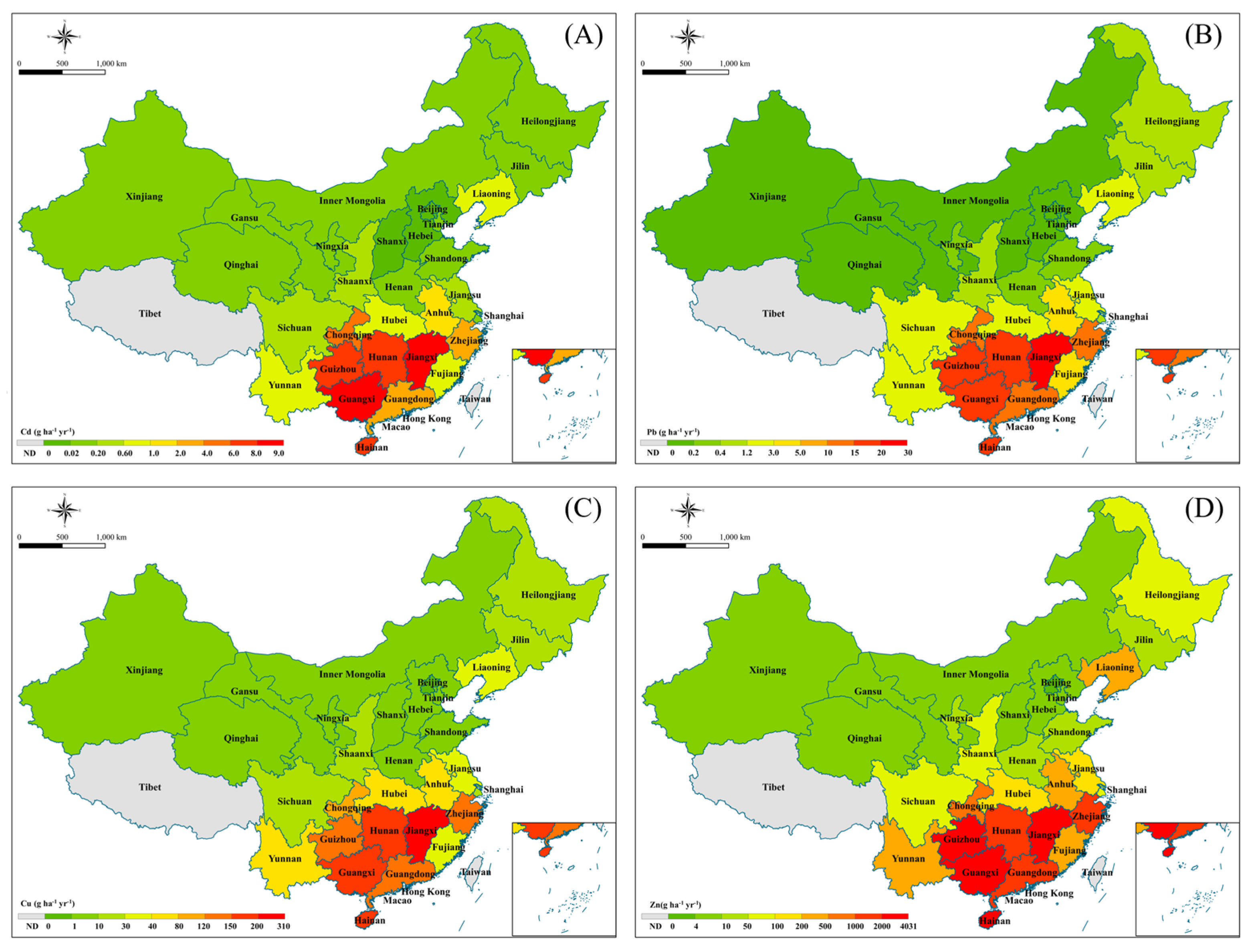
3.2. Average Annual Heavy Metal Leaching in China
3.2.1. Comparison of Model Prediction Results with Previous Literatures
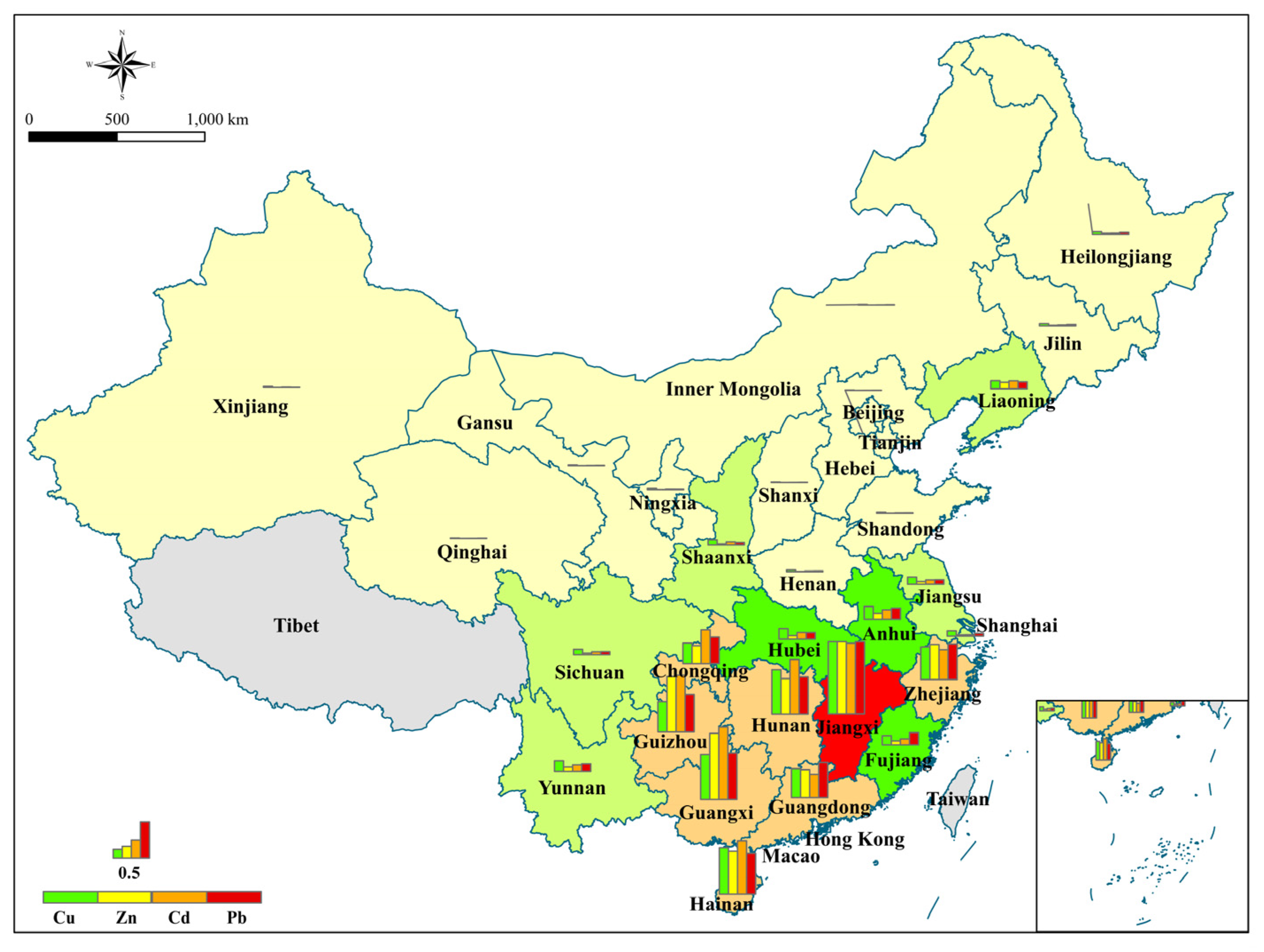
3.2.2. Average Annual Heavy Metal Leaching in Different Administrative Regions
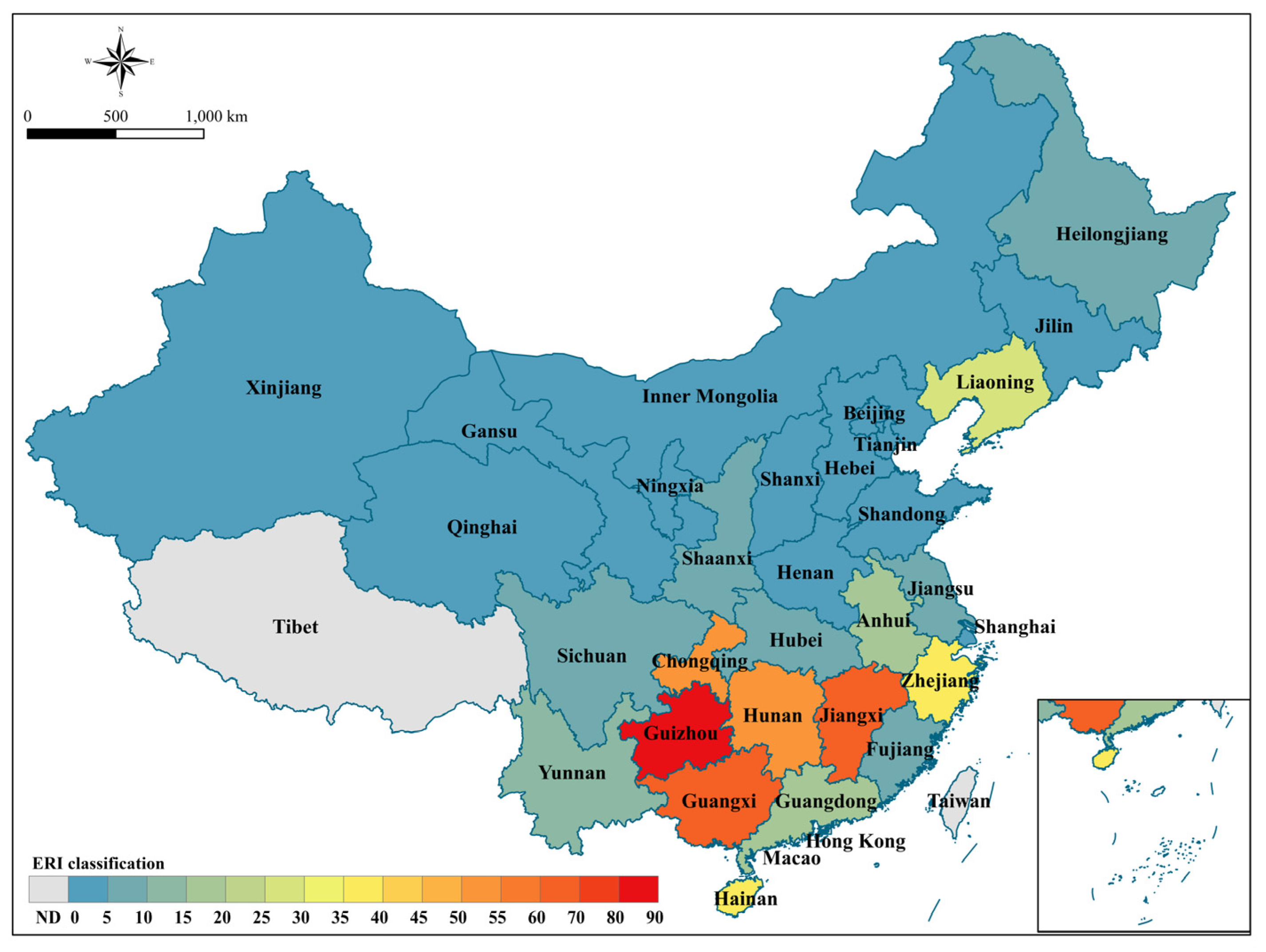
3.3. The Impact of Leaching on the Ecological Risk of Heavy Metals in Soil and Leachate
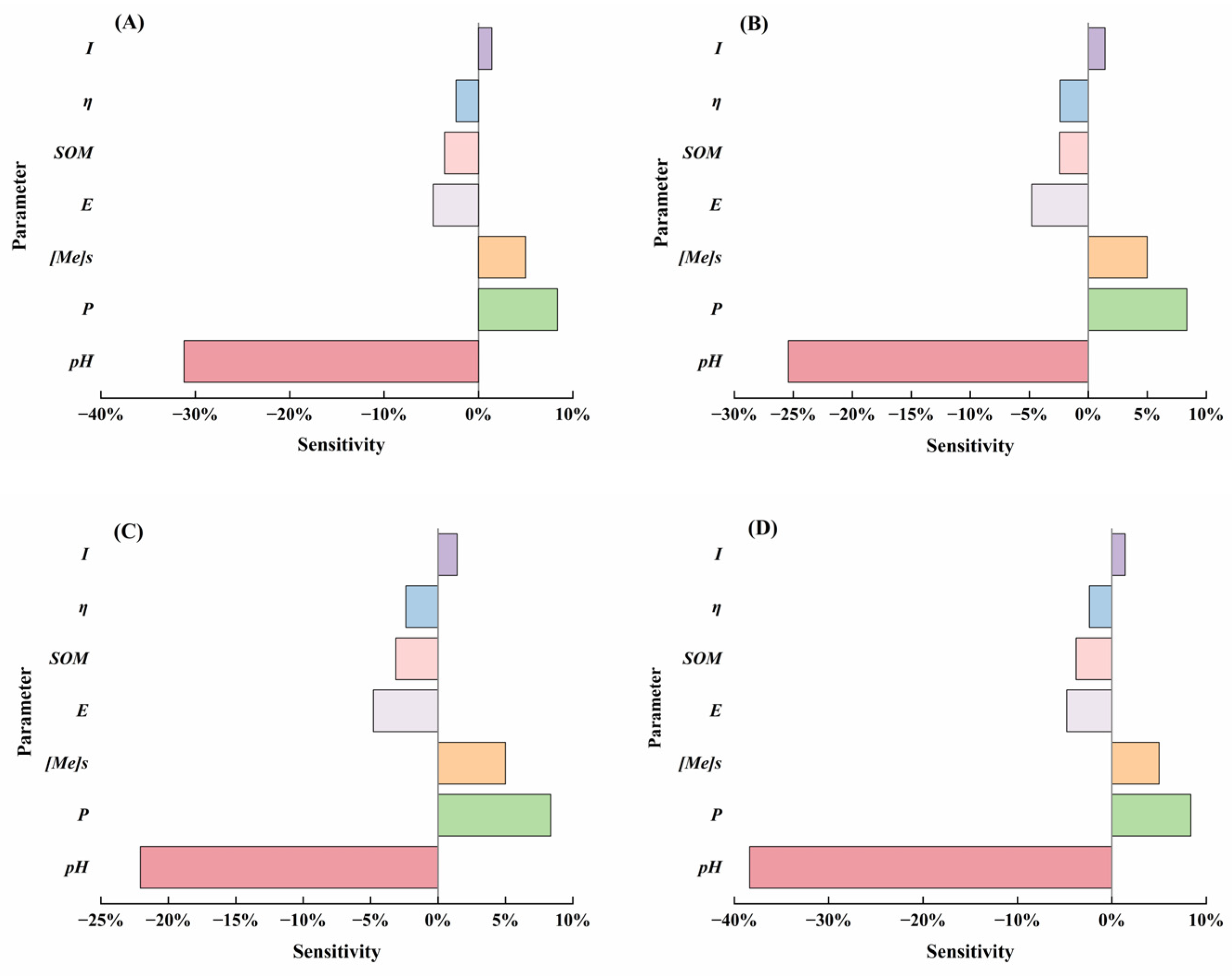
3.4. Factors Influencing Heavy Metals Leaching
3.5. Management Implications
4. Conclusions and Implication
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| OC | The soil organic carbon content |
| SOM | Soil organic matter |
| ERI | The ecological risk index |
References
- Cachada, A.; Rocha-Santos, T.; Duarte, A.C. Chapter 1—Soil and Pollution: An Introduction to the Main Issues. In Soil Pollution; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 1–28. ISBN 978-0-12-849873-6. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, B.; Shao, S.; Ni, H.; Fu, Z.; Hu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Min, X.; She, S.; Chen, S.; Huang, M.; et al. Current status, spatial features, health risks, and potential driving factors of soil heavy metal pollution in China at province level. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 114961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aralu, C.C.; Okoye, P.A.C.; Eze, V.C.; Abugu, H.O.; Abba, S.I.; Egbueri, J.C. Seasonality of Environmental Health Risks and Soil Pollution from an Unsanitary Landfill in Nigeria: Implications for Water Security, Agriculture, and Climate Adaptation. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2025, 17, 100597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.M.; Zheng, C.R.; Cong, T.; Zhu, Y.G. Heavy metal pollution in soils in China: Status and countermeasures. Ambio 1999, 28, 130–134. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, K.; Wu, Q.; Wei, H.; Yang, W.J.; Séré, G.; Wang, S.Z.; Echevarria, G.; Tang, Y.; Tao, J.; Morel, J.L.; et al. Ecosystem services provided by heavy metal-contaminated soils in China. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China (MEP). National Soil Pollution Investigation Bulletin; MEP: Beijing, China, 2014. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.; Zhang, S.; Han, Y.; Bate, B.; Ke, H.; Chen, Y. Soil Heavy Metal Pollution of Industrial Legacies in China and Health Risk Assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 816, 151632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ma, Z.; van der Kuijp, T.J.; Yuan, Z.; Huang, L. A Review of Soil Heavy Metal Pollution from Mines in China: Pollution and Health Risk Assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468–469, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Chen, Y.; Weng, L.; Ma, J.; Ma, Y.; Li, Y.; Islam, M.d.S. Comparisons of Heavy Metal Input Inventory in Agricultural Soils in North and South China: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 776–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Li, Z.; Lu, X.; Duan, Q.; Huang, L.; Bi, J. A Review of Soil Heavy Metal Pollution from Industrial and Agricultural Regions in China: Pollution and Risk Assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 690–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, K.X.; Fan, W.; Chen, J.Y.; Jiang, S.H.; Huang, S.J.; Peng, L.; Zeng, Q.; Luo, S. Annual input and output fluxes of heavy metals to paddy fields in four types of contaminated areas in Hunan Province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aralu, C.C.; Okoye, P.A.C.; Abugu, H.O.; Egbueri, J.C.; Eze, V.C. Impacts of Unregulated Dumpsites: A Study on Toxic Soil Contamination, Associated Risks, and Call for Sustainable Environmental Protection in Nnewi, Nigeria. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2024, 15, 100442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, L.; Yang, F.; Xu, C.; Yang, H.; Liu, W. Status of Metal Accumulation in Farmland Soils across China: From Distribution to Risk Assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 176, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.T.; Long, T.; Lu, Y.; Yang, L.; Mi, N.; Xia, F.Y.; Wang, X.; Deng, S.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, F. Meta-analysis of Cd input-output fluxes in agricultural soil. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 134974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.Q.; Yang, Z.F.; Cui, Y.J.; Li, Y.S.; Hou, Q.Y.; Yu, T. Soil heavy metal concentrations and their typical input and output fluxes on the southern Song-nen Plain, Heilongjiang Province, China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 139, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.Y.; Yang, Z.F.; Ji, J.F.; Yu, T.; Chen, G.G.; Li, J.; Xia, X.; Zhang, M.; Yuan, X. Annual net input fluxes of heavy metals of the agro-ecosystem in the Yangtze River delta, China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 139, 68–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Ma, J.; Wu, X.; Ju, T.; Lin, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Gong, Y.; Hou, H.; Zhao, L.; et al. Inventories of Heavy Metal Inputs and Outputs to and from Agricultural Soils: A Review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 164, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, W.L.; Guo, Z.H.; Xiao, X.Y.; Peng, C.; Shi, L.; Ran, H.Z.; Xu, W. A dynamic model to evaluate the critical loads of heavy metals in agricultural soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 197, 110607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.L.; Zhao, W.C.; Yang, X.; Liu, C.C.; Zhou, Y.Y. Input–output balance of cadmium in typical agriculture soils with historical sewage irrigation in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 276, 111298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, D.W.; Zhan, Y.; Zhou, W.J.; Zhu, L.Z. Current status and temporal trend of heavy metals in farmland soil of the Yangtze River Delta Region: Field survey and meta-analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Li, Y.; Cao, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhao, Y. Experimental and Numerical Study on Cu and Cd Migration in Different Functional-Area Soils under Simulated Rainfall Conditions. Environ. Res. 2022, 208, 112239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolders, E.; Six, L. Revisiting and Updating the Effect of Phosphate Fertilizers to Cadmium Accumulation in European Agricultural Soils; Division of Soil and Water Management: Heverlee, Belgium, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Baes, C.F.; Sharp, R.D. A Proposal for Estimation of Soil Leaching and Leaching Constants for Use in Assessment Models. J. Environ. Qual. 1983, 12, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schipper, P.N.M.; Bonten, L.T.C.; Plette, A.C.C.; Moolenaar, S.W. Measures to diminish leaching of heavy metals to surface waters from agricultural soils. Desalination 2008, 226, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egbueri, J.C.; Ukah, B.U.; Ubido, O.E.; Unigwe, C.O. A chemometric approach to source apportionment, ecological and health risk assessment of heavy metal. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 102, 3399–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, I.; Singh, U.K.; Singh, R.P.; Anshumali Kumari, D.; Jha, P.K.; Mehta, P. Characterization of heavy metal pollution in an anthropogenically and geologically influenced semi-arid region of east India and assessment of ecological and human health risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 135801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, Z.; Hossaini, S.M.T.; Renella, G. Risk assessment for sediment and stream water polluted by heavy metals released by a municipal solid waste composting plant. J. Geochem. Explor. 2016, 169, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, M.; Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Lei, K.; Li, Y.; Li, F.; Zheng, D.; Fang, X.; Cao, Y. Heavy Metal Contamination Risk Assessment and Correlation Analysis of Heavy Metal Contents in Soil and Crops. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 278, 116911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China National Environmental Monitoring Center (CNEMC). National Soil Environment Monitoring Network. Available online: https://www.cnemc.cn/zzjj/jcwl/trhjjcwl/202412/t20241219_1098896.shtml (accessed on 4 August 2025).
- China National Environmental Monitoring Center (CNEMC). National Groundwater Environmental Monitoring Network. Available online: https://www.cnemc.cn/zzjj/jcwl/trhjjcwl/202412/t20241219_1098897.shtml (accessed on 4 August 2025).
- Feng, W.L.; Guo, Z.H.; Peng, C.; Xiao, X.Y.; Shi, L.; Han, X.Q.; Ran, H. Modelling mass balance of cadmium in paddy soils under long term control scenarios. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2018, 20, 1158–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterckeman, T.; Gossiaux, L.; Guimont, S.; Sirguey, C.; Lin, Z. Cadmium mass balance in French soils under annual crops: Scenarios for the next century. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 1440–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.D.; Jiang, K.C. Dataset of Frequency Distribution Parameters of Annual Land Precipitation in China. Resource and Environmental Science Data Registration and Publishing System. 2022. Available online: https://www.resdc.cn/DOI/DOI.aspx?DOIID=103 (accessed on 3 March 2024).
- Ministry of Water Resources of the People’s Republic of China (MWR). China Water Resources Bulletin 2019. Available online: http://www.mwr.gov.cn/sj/tjgb/szygb/202008/t20200803_1430726.html (accessed on 3 March 2024).
- Ministry of Water Resources of the People’s Republic of China (MWR). China Water Resources Bulletin 2020. Available online: http://www.mwr.gov.cn/sj/tjgb/szygb/202107/t20210709_1528208.html (accessed on 3 March 2024).
- Ministry of Water Resources of the People’s Republic of China (MWR). China Water Resources Bulletin 2021. Available online: http://www.mwr.gov.cn/sj/tjgb/szygb/202206/t20220615_1579315.html (accessed on 3 March 2024).
- Ma, N.; Jozsef, S.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, W. Terrestrial Evapotranspiration Dataset Across China (1982–2017); National Tibetan Plateau/Third Pole Environment Data Center: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauvé, S.; Hendershot, W.; Allen, H.E. Solid-solution partitioning of metals in contaminated soils: Dependence on pH, total metal burden, and organic matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degryse, F.; Smolders, E.; Parker, D.R. Partitioning of metals (Cd, Co, Cu, Ni, Pb, Zn) in soils: Concepts, methodologies, prediction and applications—A review. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2009, 60, 590–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.X.; Li, Q.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Z.J. Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Pollution Evaluation of Heavy Metals in Arable Land Soil of China. Environ. Sci. 2020, 41, 2823–2833. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Rühlmann, J.; Krschens, M.; Graefe, J. A new approach to calculate the particle density of soils considering properties of the soil organic matter and the mineral matrix. Geoderma 2006, 130, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 14848-2017; Standard for Groundwater Quality. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Sun, D.; Yang, H.; Guan, D.; Yang, M.; Wu, J.B.; Yuan, F.H.; Jin, C.; Wang, A.; Zhang, Y. The effects of land use change on soil infiltration capacity in China: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 626, 1394–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.R. Prediction and Early-Warning Forecast on Heavy Metals and Their Pollution Status in Agricultural Soils in Zhejiang Province, China Based on Input-Output Inventory. Ph.D. Dissertation, Northwest A&F University, Xianyang, China, 2019. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Liang, Z.; Webster, R.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, Y.; Teng, H.; Hu, B.; Arrouays, D.; Shi, Z. A High-Resolution Map of Soil pH in China Made by Hybrid Modelling of Sparse Soil Data and Environmental Covariates and Its Implications for Pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhong, Q.; Chen, Q.; Liu, A.; Yang, J.; Pang, J. Spatiotemporal Variations of Precipitation Concentration Influenced by Large-Scale Climatic Factors and Potential Links to Flood-Drought Events across China 1958–2019. Atmos. Res. 2023, 282, 106507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, T.; Okazaki, M.; Toyota, K.; Motobayashi, T.; Kato, M. The input-output balance of cadmium in a paddy field of Tokyo. Chemosphere 2007, 67, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Six, L.; Smolders, E. Future trends in soil cadmium concentration under current cadmium fluxes to European agricultural soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 485–486, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Feng, W.; Wang, S.; Chen, L.; Zheng, X.; Li, X.; Zhou, D. Farmland Heavy Metals Can Migrate to Deep Soil at a Regional Scale: A Case Study on a Wastewater-Irrigated Area in China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 281, 116977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 5749-2022; Standards for Drinking Water Quality. State Administration for Market Regulation of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2022.
- Fernández-Luqueño, F.; López-Valdez, F.; Gamero-Melo, P.; Luna-Suárez, S.; Aguilera-González, E.N.; Martínez, A.I.; García-Guillermo, M.D.S.; Hernández-Martínez, G.; Herrera-Mendoza, R.; Álvarez-Garza, M.A.; et al. Heavy Metal Pollution in Drinking Water—A Global Risk for Human Health: A Review. Afr. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 7, 567–584. [Google Scholar]
- Egbueri, J.C. Heavy Metals Pollution Source Identification and Probabilistic Health Risk Assessment of Shallow Groundwater in Onitsha, Nigeria. Anal. Lett. 2020, 53, 1620–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Zou, Q.; Chen, Z.L.; Cao, Y.J.; Wang, S.; Zhu, F.; Liu, X.L. Analysis of Hydrochemical Characteristics and Causes of Drinking Water Sources in South China: A Case Study in Zhanjiang City. Processes 2023, 11, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kicińska, A.; Pomykała, R.; Izquierdo-Diaz, M. Changes in soil pH and mobility of heavy metals in contaminated soils. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2022, 73, 13203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scokart, P.O.; Meeus-Verdinne, K.; De Borger, R. Mobility of Heavy Metals in Polluted Soils near Zinc Smelters. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1983, 20, 451–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidu, R.; Bolan, N.S.; Kookana, R.S.; Tiller, K.G. Ionic-strength and pH effects on the sorption of cadmium and the surface charge of soils. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1994, 45, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.D.; Xu, X.J.; Ning, Y.W.; Zhang, H.; Ma, H.B.; Zhang, Y.C. Progresses in Agricultural Driving Factors on Accelerated Acidification of Soils. Soils 2015, 47, 627–633. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Han, T.F.; Liu, K.L.; Huang, J.; Ma, C.B.; Zheng, L.; Wang, H.Y.; Qu, X.-L.; Ren, Y.; Yu, Z.-K.; Zhang, H.-M. Spatio-temporal evolution of soil pH and its driving factors in the main Chinese farmland during past 30 years. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2020, 26, 2137–2149. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Luo, L.; Ma, Y.B.; Zhang, S.Z.; Wei, D.P.; Zhu, Y.G. An inventory of trace element inputs to agricultural soils in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2524–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.Y.; Wu, Y.J.; Wen, J.H. Future changes in precipitation characteristics in China. Int. J. Climatol. 2019, 39, 3558–3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, R.; Chen, Z.; Cai, C.; Tie, B.; Liu, X.; Reid, B.J.; Huang, Q.; Lei, M.; Sun, G.; Baltrėnaitė, E. Mitigating Heavy Metal Accumulation into Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Using Biochar Amendment—A Field Experiment in Hunan, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 11097–11108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Huang, Z.; Li, X.; Chen, W.; Deng, Y.; Han, C. Lime and Phosphate Amendment Can Significantly Reduce Uptake of Cd and Pb by Field-Grown Rice. Sustainability 2017, 9, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambier, P.; Pot, V.; Mercier, V.; Michaud, A.; Benoit, P.; Revallier, A. Impact of long-term organic residue recycling in agriculture on soil solution composition and trace metal leaching in soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 499, 560–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipović, V.; Cambier, P.; Filipović, L.; Coquet, Y.; Pot, V.; Bodineau, G. Modeling Copper and Cadmium Mobility in an Albeluvisol Amended with Urban Waste Composts. Vadose Zone J. 2016, 15, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson, H.; Alvenäs, G.; Nilsson, S.I.; Hultman, B.; Öborn, I. Cadmium, copper and zinc leaching and surface run-off losses at the Öjebyn farm in Northern Sweden-Temporal and spatial variation. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2006, 113, 120–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.G.; Wu, M.; Wu, H.W.; Zhang, W.J. External Lead Stabilization Characteristics in Soils and Responses to Soil Properties. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2021, 31, 1702–1709. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Y.X. Study on Effect of Soil Properties on Phosphorus Fertilizer Availability and Phosphate Adsorption-Desorption. Master’s Dissertation, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing, China, 2011. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, S.A.; Zheng, X.Q.; Li, X.C.; Liu, S.T.; Yao, X.R. Aging Process of Cr(III) in 22 Typical Soils of China and Influence Factors Analysis. Environ. Sci. 2013, 34, 698–704. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Feng, P.Y.; Li, Z.; Zhe, Y.Y.; Huang, J.; Liang, D.L. Selenate Adsorption and Desorption in 18 Kinds of Chinese Soil with Their Physicochemical Properties. Environ. Sci. 2016, 37, 3160–3168. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.Y.; Lv, J.L.; Dai, Y.C.; Zhang, R.L. Differences in exogenous As(V) adsorption and the relationship with soil physicochemical properties in major farmland types in China. J. Northwest A F Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2014, 42, 144–148. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, F.; Liu, Z.Z.; Wang, R.H.; Huang, Y.F.; Li, Q. Effects of Soil Physicochemical Properties on the Adsorption-Desorption of Bensulfuron-Methyl. Res. Environ. Sci. 2015, 28, 1107–1113. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.H.; Liang, D.L.; Wei, W.; Wang, D. Relationship between soil physico-chemical properties and selenium species based on path analysis. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2011, 48, 823–830. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bao, J.D.; Shi, M.; Zhang, M.T.; Liang, D.L.; Wu, X.P. Nitrification of Main Soils in China and Its Relationship with Soil Properties. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2011, 44, 1390–1398. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Y.F.; He, M.; Li, J.L.; Kim, C.S.; Yuuyin, Y.; Iwasaki, K.; Han, W. Correlation between Contents of Heavy Metals and Physical-Chemical Properties of Agricultural Soils in Fengxian, Shanghai. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. Agric. Sci. 2009, 28, 601–605. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.H.; Hu, P.; Shao, Y.P.; Xu, S.; He, M. Physico-chemical properties of the main agro-soils in Jiading District, Shanghai. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. Agric. Sci. 2003, 21, 313–319. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dao, E.L. Study on Influence Factors and Spatial Variability of Soil Physical and Chemical Properties in Upper Reaches of Heihe River Basin on Southern Slope of Qilian Mountains. Master’s Dissertation, Qinghai Normal University, Xining, China, 2019. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Wen, X.; Lu, J.; Wu, J.; Lin, Y.; Luo, Y. Influence of coastal groundwater salinization on the distribution and risks of heavy metals. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soil Environmental Background Values in China; State Bureau of Environmental Conservation, China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 1990. (In Chinese)
- Xu, S.Q.; Wang, H.M.; Fu, S.J. Distribution characteristics and source analysis of heavy metals in agricultural soil on Hainan Island based on receptor model and geostatistics. Environ. Pollut. Control. 2021, 43, 1164–1169. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bao, L.R.; Deng, H.; Jia, Z.M.; Li, Y.; Dong, J.X.; Yan, M.S.; Zhang, F.L. Ecological and health risk assessment of heavy metals in farmland soil of northwest Xiushan, Chongqing. Geol. China 2020, 47, 1625–1636. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]

| Province | ERI of Heavy Metals in Soil | Variation, % | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | 10 years | 20 years | 100 years | 10 years | 20 years | 100 years | |
| Beijing | 72.55 | 72.54 | 72.53 | 72.44 | −0.01 | −0.03 | −0.15 |
| Tianjin | 129.92 | 129.87 | 129.82 | 129.41 | −0.04 | −0.08 | −0.39 |
| Hebei | 71.00 | 70.97 | 70.94 | 70.68 | −0.04 | −0.08 | −0.45 |
| Shanxi | 57.69 | 57.67 | 57.65 | 57.48 | −0.03 | −0.07 | −0.36 |
| Inner Mongolia | 96.67 | 96.61 | 96.54 | 96.01 | −0.06 | −0.13 | −0.68 |
| Liaoning | 74.76 | 73.55 | 72.35 | 63.60 | −1.62 | −3.22 | −14.93 |
| Jilin | 70.72 | 70.55 | 70.36 | 68.93 | −0.24 | −0.51 | −2.53 |
| Heilongjiang | 59.69 | 59.39 | 59.10 | 56.80 | −0.50 | −0.99 | −4.84 |
| Shanghai | 41.85 | 41.66 | 41.47 | 40.04 | −0.45 | −0.91 | −4.32 |
| Jiangsu | 71.77 | 71.19 | 70.61 | 66.19 | −0.81 | −1.62 | −7.77 |
| Zhejiang | 105.04 | 98.34 | 92.14 | 56.08 | −6.38 | −12.28 | −46.61 |
| Anhui | 90.32 | 88.71 | 87.15 | 75.65 | −1.78 | −3.51 | −16.24 |
| Fujian | 110.27 | 108.95 | 107.68 | 97.93 | −1.20 | −2.35 | −11.19 |
| Jiangxi | 76.51 | 66.48 | 57.98 | 22.85 | −13.11 | −24.22 | −70.13 |
| Shandong | 81.91 | 81.82 | 81.72 | 80.94 | −0.11 | −0.23 | −1.18 |
| Henan | 119.58 | 119.42 | 119.25 | 117.93 | −0.13 | −0.28 | −1.38 |
| Hubei | 56.93 | 56.29 | 55.66 | 50.89 | −1.12 | −2.23 | −10.61 |
| Hunan | 105.51 | 98.77 | 92.49 | 55.82 | −6.39 | −12.34 | −47.10 |
| Guangdong | 119.40 | 112.82 | 106.64 | 68.65 | −5.51 | −10.69 | −42.50 |
| Guangxi | 48.87 | 44.51 | 40.63 | 21.55 | −8.92 | −16.86 | −55.90 |
| Hainan | 73.51 | 67.56 | 62.15 | 33.06 | −8.09 | −15.45 | −55.03 |
| Chongqing | 58.33 | 56.37 | 54.47 | 41.94 | −3.36 | −6.62 | −28.10 |
| Sichuan | 113.20 | 112.60 | 111.99 | 107.33 | −0.53 | −1.07 | −5.19 |
| Guizhou | 27.72 | 26.21 | 24.81 | 16.85 | −5.45 | −10.50 | −39.21 |
| Yunnan | 43.23 | 42.73 | 42.26 | 38.64 | −1.16 | −2.24 | −10.62 |
| Tibet | / | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| Shaanxi | 116.94 | 116.4 | 115.87 | 111.68 | −0.46 | −0.91 | −4.5 |
| Gansu | 69.24 | 69.18 | 69.14 | 68.77 | −0.09 | −0.14 | −0.68 |
| Qinghai | 50.35 | 50.32 | 50.3 | 50.11 | −0.06 | −0.1 | −0.48 |
| Ningxia | 68.45 | 68.34 | 68.23 | 67.36 | −0.16 | −0.32 | −1.59 |
| Xinjiang | 80.47 | 80.4 | 80.33 | 79.8 | −0.09 | −0.17 | −0.83 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mi, N.; Lu, Y.; Song, Z.; Sheng, F.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Z.; He, J.; Fan, T. Leaching of Heavy Metals from Farmland Soil in China: The Status and Ecological Risk Assessment. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2126. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092126
Mi N, Lu Y, Song Z, Sheng F, Chen Y, Chen Z, He J, Fan T. Leaching of Heavy Metals from Farmland Soil in China: The Status and Ecological Risk Assessment. Agronomy. 2025; 15(9):2126. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092126
Chicago/Turabian StyleMi, Na, Yuanyuan Lu, Zhen Song, Feng Sheng, Yun Chen, Zhanghao Chen, Jianzhou He, and Tingting Fan. 2025. "Leaching of Heavy Metals from Farmland Soil in China: The Status and Ecological Risk Assessment" Agronomy 15, no. 9: 2126. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092126
APA StyleMi, N., Lu, Y., Song, Z., Sheng, F., Chen, Y., Chen, Z., He, J., & Fan, T. (2025). Leaching of Heavy Metals from Farmland Soil in China: The Status and Ecological Risk Assessment. Agronomy, 15(9), 2126. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092126








