Controlled-Release Nitrogen Fertilizer Enhances Saline–Alkali Soil Organic Carbon by Activating Straw Decomposition Agents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Sampling in Field Experiment
2.2. Soil Incubation Experiment
2.3. Soil Properties Analysis
2.4. High-Throughput Sequencing
2.5. Bioinformatic Analyses of Sequencing Data
2.6. Calculations
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
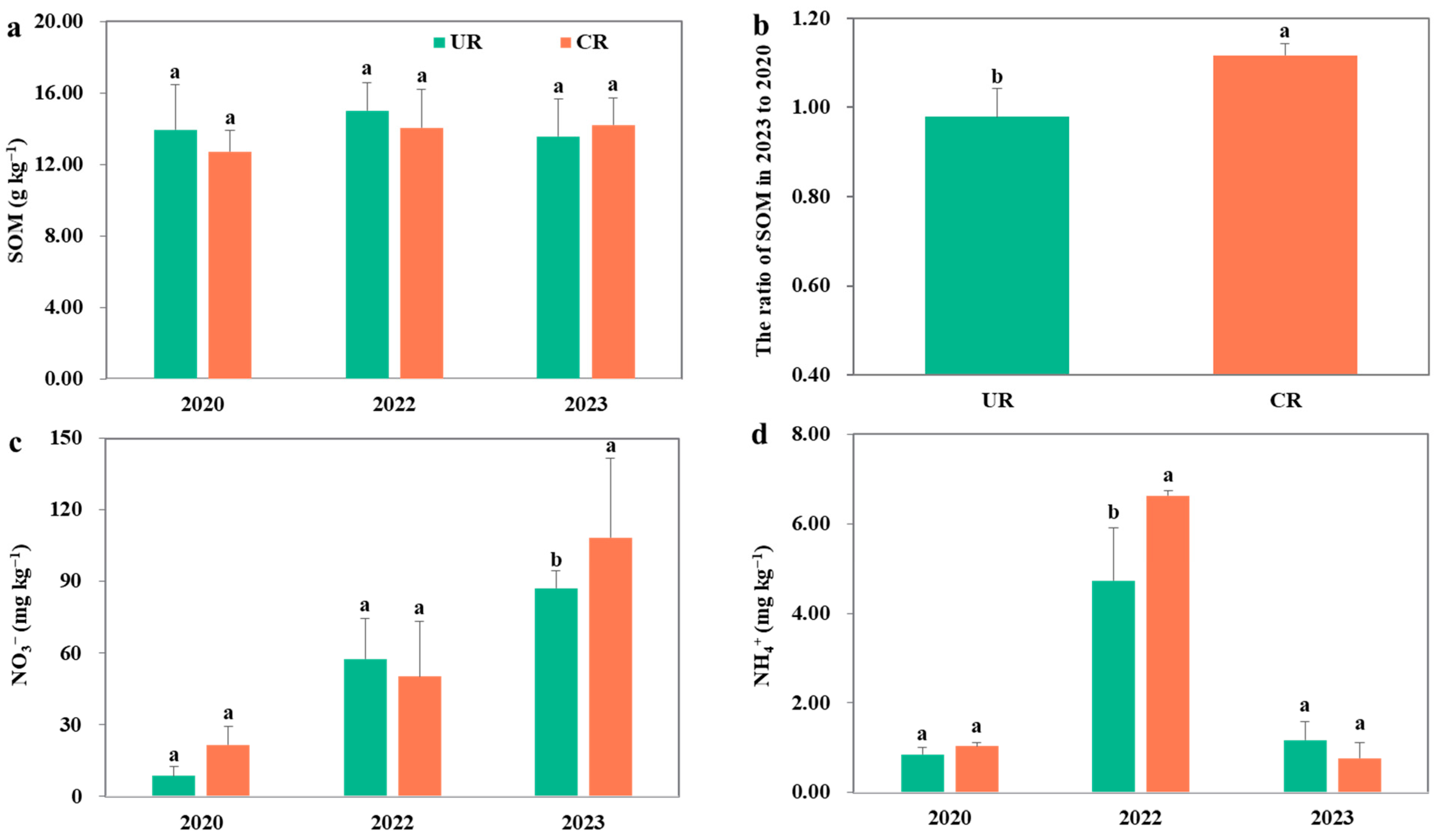
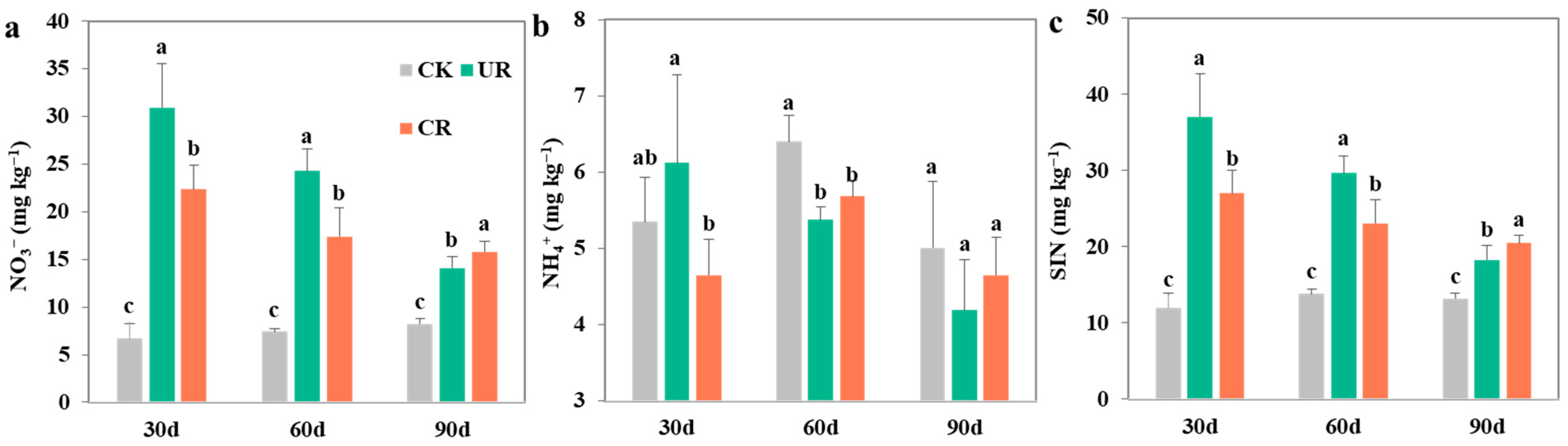
3.1. Soil Organic Matter and Nitrogen
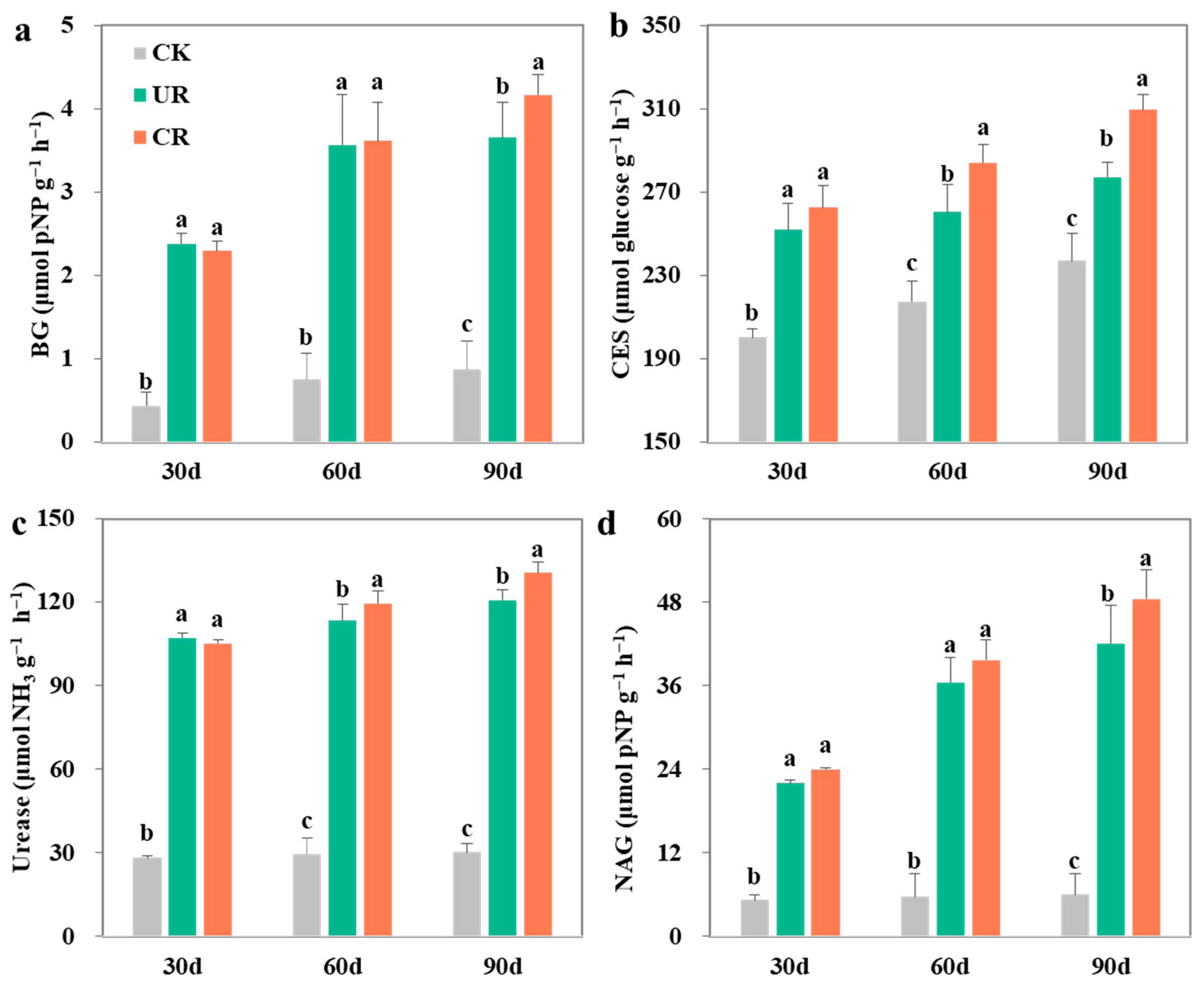
3.2. Extracellular Enzyme Activity Targeting Soil Carbon and Nitrogen
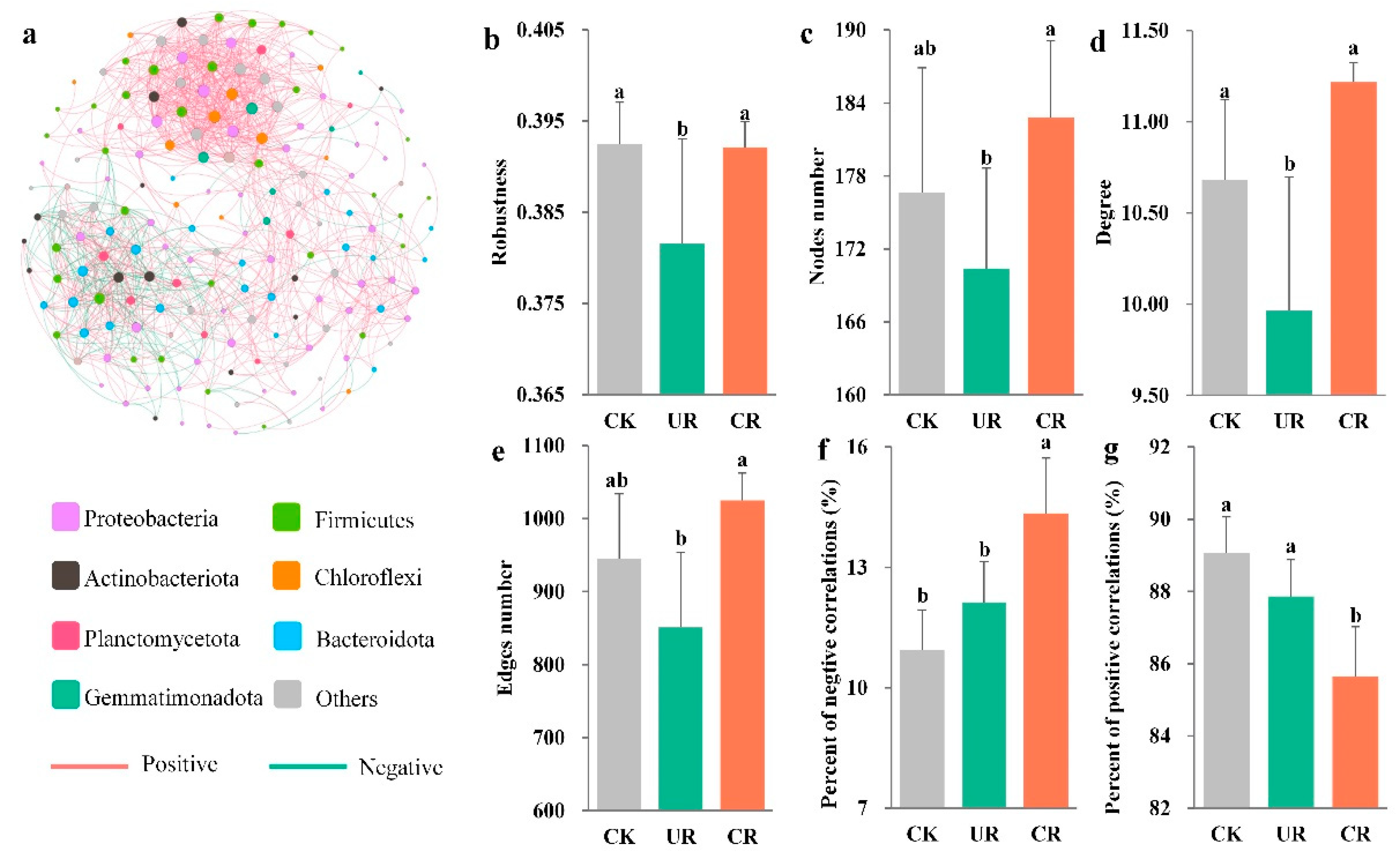
3.3. Soil Bacterial Community Composition and Interactions
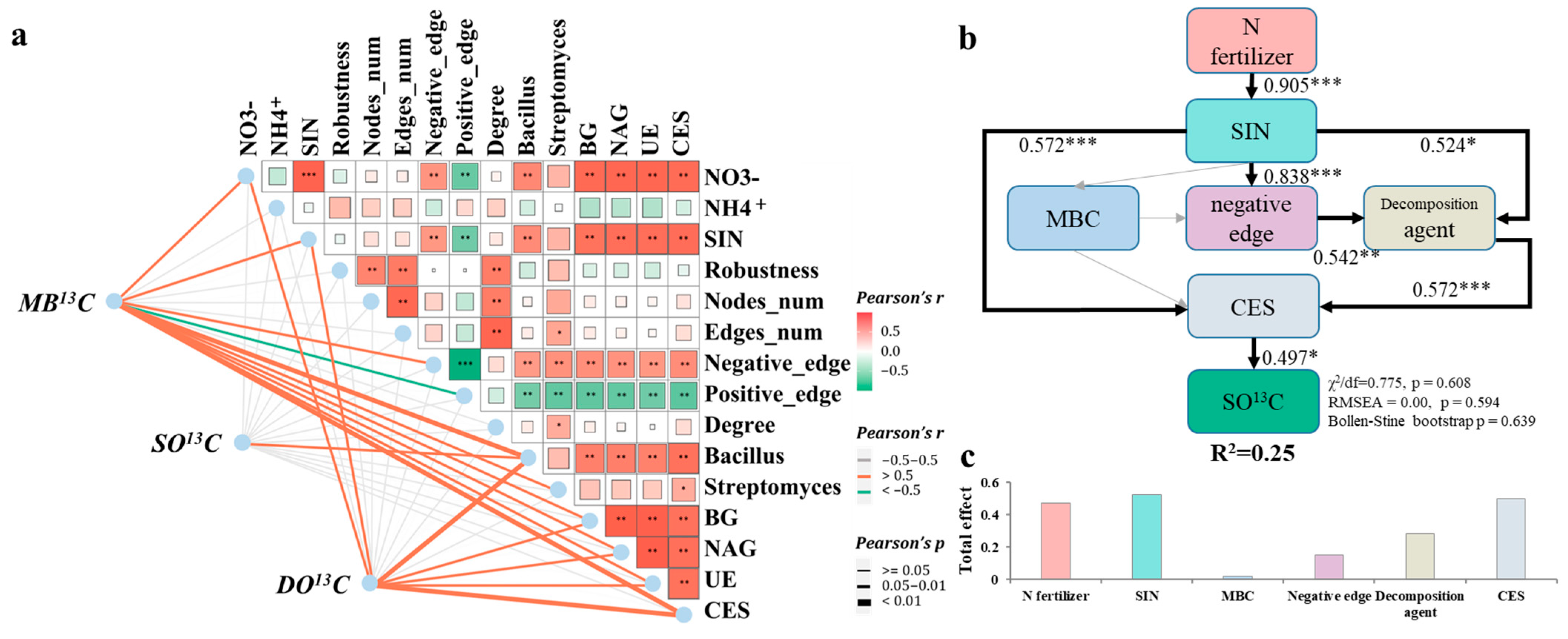
3.4. The Impacts of Bacterial Community on Soil Organic Carbon
4. Discussion
4.1. Response of SOC Stocks to N Fertilization
4.2. Controlled-Release Fertilizer Strengthens the Stability and Interaction of Soil Bacterial Community
4.3. Controlled-Release Fertilizer Increases SOC by Strengthening the Functions of Straw Decomposition Agent
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chabbi, A.; Lehmann, J.; Ciais, P.; Loescher, H.W.; Cotrufo, M.F.; Don, A.; SanClements, M.; Schipper, L.; Six, J.; Smith, P.; et al. Aligning agriculture and climate policy. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2017, 7, 307–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Crop residues as soil amendments and feedstock for bioethanol production. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, X.; Morrien, E.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lu, C.; Xie, H.; Liang, W.; Li, Q.; Liang, C. Exogenous carbon turnover within the soil food web strengthens soil carbon sequestration through microbial necromass accumulation. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2003, 29, 4069–4080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, G.; Shu, H.; Hu, W.; Han, H.; Liu, R.; Guo, Z. Straw return increases crop production by improving soil organic carbon sequestration and soil aggregation in a long-term wheat- cotton cropping system. J. Integr. Agric. 2024, 23, 669–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.L.; Wang, X.X.; Carrion, V.J.; Yin, S.; Yue, Z.F.; Liao, Y.W.K.; Dong, Y.H.; Li, X.G. Acidic amelioration of soil amendments improves soil health by impacting rhizosphere microbial assemblies. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 167, 108599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Yu, D.L.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Moorhead, D.L.; Andersen, M.N.; Smith, P.; Song, Y.T.; Li, X.Q.; Huang, Q.Y.; Liu, Y.R.; et al. Trade-offs in carbon-degrading enzyme activities limit long-term soil carbon sequestration with biochar addition. Biol. Rev. 2023, 98, 1184–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, M.; Ananth, C.; Ayyandurai, M.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Alshehri, M.A.; Ma, Y. Sustainable strategies for enhancing soil carbon sequestration and their beneficial impacts on soil fertility: A comprehensive review. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 204, 105752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.J.; Whalen, J.K.; Wu, J.T.; Yang, J.N.; Mao, X.R.; Wan, B.B.; Tian, S.Y.; Hu, F.; Chen, X.Y.; Liu, M.Q. Soil food web structure coordinated by soil omnivores sustains soil multifunctionality in moderate vermicompost amended fields. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 192, 109391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.K.; Fang, Y.Y.; Zhang, B.G.; Luo, Y.; Yi, X.Y.; Wu, J.S.; Chen, Y.C.; Sarker, T.C.; Cai, Y.J.; Chang, S.X. Land-use-driven change in soil labile carbon affects microbial community composition and function. Geoderma 2022, 426, 116056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.T.; Zhang, X.C.; Li, Y.N.; Jiao, Y.P.; Fan, L.C.; Jiang, Y.J.; Qu, C.Y.; Filimonenko, E.; Jiang, Y.H.; Tian, X.H.; et al. Nitrogen fertilizer builds soil organic carbon under straw return mainly via microbial necromass formation. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 188, 109223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandick, A.K.; Dick, R.P. Field management effects on soil enzyme activities. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1991, 31, 1471–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderstraeten, J.; Lamote, B.; da Fonseca, M.J.M.; De Groote, P.; Briers, Y. Conversion of the free Cellvibrio japonicus xyloglucan degradation system to the cellulosomal mode. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 5495–5509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.Z.; Wang, J.; Guo, H.N.; Cao, Y.H. The enzymatic characters of heterologous expressed novel β-1, 4-glucosidase originated from Aspergillus fresenii. 3 Biotech 2020, 10, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.; Aoyagi, R.; Kitayama, K.; Mo, J.M. Does the ratio of β-1,4-glucosidase to β-1,4-N-acetylglucosaminidase indicate the relative resource allocation of soil microbes to C and N acquisition? Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 160, 108363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Chen, L.; Huang, H.Y.; Qu, P.; Wei, Z.G. Impacts of crop residues on soil health: A review. Environ. Pollut. Bioavailab. 2021, 33, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.X.; Song, X.Y.; Fu, H.Y.; Liu, C.G.; Yang, F.S. Effects of the decomposition agent application on the physicochemical properties and microbial community structure of wheat straw-returning soil. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2024, 35, 103668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.J.; Zou, H.T.; Qian, C.R.; Yu, Y.; Hao, Y.B.; Li, L.; Wang, Q.J.; Jiang, Y.B.; Ma, J.T. Construction of in situ degradation bacteria of corn straw and analysis of its degradation efficiency. Ann. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, F.; Yang, D.; Wang, X.; Crowther, T.W.; Vinay, N.; Luo, Z.; Yu, K.; Sun, S.; Zhang, F.; Xiong, Y.; et al. Nutrient limitation of soil organic carbon stocks under straw return. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 192, 109360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, M.; Homyak, P.M.M.; Xie, J.; Penuelas, J.; Ryan, M.G.G.; Xiong, X.; Sardans, J.; Lin, W.; Wang, M.; Chen, G.; et al. Litter quality controls tradeoffs in soil carbon decomposition and replenishment in a subtropical forest. J. Ecol. 2023, 111, 2181–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbaz, M.; Kumar, A.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Börjesson, G.; Blagodatskaya, E. Priming effects induced by glucose and decaying plant residues on SOM decomposition: A three-source 13C/14C partitioning study. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 121, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Dungait, J.A.J.; Xu, X.; Bol, R.; Zhang, X.; Wu, W. Coupled incorporation of maize (Zea mays L.) straw with nitrogen fertilizer increased soil organic carbon in Fluvic Cambisol. Geoderma 2017, 304, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.Q.; Zhou, L.Y.; Dai, J.P.; Chen, J.; Yang, X.P.; Wang, X.W.; Wang, Z.F.; Feng, L. Effects of the C/N ratio on the microbial community and lignocellulose degradation, during branch waste composting. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2022, 45, 1163–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.K.; Zhou, J.; Shahbaz, M.; Tang, H.M.; Liu, S.L.; Zhang, W.J.; Yuan, H.Z.; Zhou, P.; Alharbi, H.; Wu, J.S.; et al. Microorganisms maintain C:N stoichiometric balance by regulating the priming effect in long-term fertilized soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 167, 104033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.X.; Feng, H.J.; Zhang, M.; Shao, Y.Q.; Wang, J.Q.; Liu, Y.L.; Li, C.L. Straw returning combined with controlled-release nitrogen fertilizer affected organic carbon storage and crop yield by changing humic acid composition and aggregate distribution. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 415, 105045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, T.; Schaeffer, S.; Li, S.; Fu, S.; Pei, J.; Li, H.; Zhuang, J.; Radosevich, M.; Wang, J. Carbon fluxes from plants to soil and dynamics of microbial immobilization under plastic film mulching and fertilizer application using 13C pulse-labeling. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 80, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, E.D.; Brookes, P.C.; Jenkinson, D.S. An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1987, 19, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sui, Y.; Yu, Z.; Shi, Y.; Chu, H.; Jin, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, G. High throughput sequencing analysis of biogeographical distribution of bacterial communities in the black soils of northeast China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 70, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, S.T.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Caporaso, J.G.; Walters, W.A.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. Examining the global distribution of dominant archaeal populations in soil. ISME J. 2011, 5, 908–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donohue, I.; Petchey, O.L.; Montoya, J.M.; Jackson, A.L.; McNally, L.; Viana, M.; Healy, K.; Lurgi, M.; O’Connor, N.E.; Emmerson, M.C. On the dimensionality of ecological stability. Ecol. Lett. 2013, 16, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.M.; Guo, X.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, N.; Ning, D.; Shi, Z.; Zhou, X.S.; Wu, L.Y.; Yang, Y.F.; et al. Climate warming enhances microbial network complexity and stability. Nat. Clim. Change 2021, 1, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poll, C.; Marhan, S.; Ingwersen, J.; Kandeler, E. Dynamics of litter carbon turnover and microbial abundance in a rye detritusphere. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2008, 40, 1306–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, B.; Schnecker, J.; Alves, R.J.E.; Barsukov, P.; Bárta, J.; Čapek, P.; Gentsch, N.; Gittel, A.; Guggenberger, G.; Lashchinskiy, N.; et al. Input of easily available organic C and N stimulates microbial decomposition of soil organic matter in arctic permafrost soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 75, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaud, A.; Lerch, T.Z.; Chevallier, T.; Nunan, N.; Chenu, C.; Brauman, A. Dynamics of bacterial communities in relation to soil aggregate formation during the decomposition of 13C-labelled rice straw. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2012, 53, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Qiu, S.; Chen, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhao, X.; Christie, P.; Xu, M. Allocation of photosynthestically-fixed carbon in plant and soil during growth of reed (Phragmites australis) in two saline soils. Plant Soil. 2016, 404, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Qiu, L.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Wu, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, J.; Li, W.; et al. Long-term application of controlled-release potassium chloride increases maize yield by affecting soil bacterial ecology, enzymatic activity and nutrient supply. Field Crops Res. 2023, 297, 108946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.J.A.; Finley, B.K.; Mau, R.L.; Schwartz, E.; Dijkstra, P.; Bowker, M.A.; Hungate, B.A. The soil priming effect: Consistent across ecosystems, elusive mechanisms. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 140, 107617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.B.; Yin, L.M.; Dijkstra, F.A.; Wang, P.; Cheng, W.X. Priming effect on soil carbon decomposition by root exudate surrogates: A meta-analysis. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2023, 178, 108955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, K.M.; Murphy, D.N.; Rousk, J. The microbial community size, structure, and process rates along natural gradients of soil salinity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 138, 107607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.W.; Wang, C.; Liu, M.L.; Yu, Y.C. Integrated reclamation of saline soil nitrogen transformation in the hyphosphere by earthworms and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 135, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Xi, J.Z.; Pang, R.; Gunina, A.; Zhou, S.R. Competition for nitrogen between plants and microorganisms in grasslands: Effect of nitrogen application rate and plant acquisition strategy. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2024, 60, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkby, C.A.; Richardson, A.E.; Wade, L.J.; Passioura, J.B.; Batten, G.D.; Blanchard, C.; Kirkegaard, J.A. Nutrient availability limits carbon sequestration in arable soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 68, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Zhang, L.; Lin, Y.; Wen, D.; Hou, E. Nitrogen availability mediates soil organic carbon cycling in response to phosphorus supply: A global meta-analysis. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2023, 185, 109158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barberán, A.; Bates, S.T.; Casamayor, E.O.; Fierer, N. Using network analysis to explore co-occurrence patterns in soil microbial communities. ISME J. 2012, 6, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, T.T.; Shi, J.J.; Zhang, X.Q.; Zhao, X.Q.; Zhang, D.J.; Chen, L.Y.; Lu, Z.Y.; Cheng, Y.C.; Hao, Y.H.; Zhao, X.Y.; et al. Slow-release nitrogen fertilizer application regulated rhizosphere microbial diversity to increase maize yield. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1481465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyte, K.Z.; Schluter, J.; Foster, K.R. The ecology of the microbiome: Networks, competition, and stability. Science 2015, 350, 663–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Xu, L.; Montoya, L.; Madera, M.; Hollingsworth, J.; Chen, L.; Purdom, E.; Singan, V.; Vogel, J.; Hutmacher, R.B.; et al. Co-occurrence networks reveal more complexity than community composition in resistance and resilience of microbial communities. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, T.; Shi, J.; Zhang, X.; Ge, G.; Cheng, Y.; Rong, M.; Chen, L.; Zhao, X.; Wang, X.; Lu, Z. Slow-Release Nitrogen Fertilizer Promotes the Bacterial Diversity to Drive Soil Multifunctionality. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, P.T.; Du, X.; Zhou, J.C.; Peng, Y.J.; Li, X.L.; Tao, P.J.; Zhang, Y.C. Network Analysis Reveals the Combination of Controlled-Release and Regular Urea Enhances Microbial Interactions and Improves Maize Yields. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 825787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Ren, C.; Wu, L.; Zhang, X.; Mao, X.; Fan, Z.; Cui, W.; Zhang, W.; Wei, G.; Shu, D. Fertilizing-induced alterations of microbial functional profiles in soil nitrogen cycling closely associate with crop yield. Environ. Res. 2023, 231, 116194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konopka, A.; Lindemann, S.; Fredrickson, J. Dynamics in microbial communities: Unraveling mechanisms to identify principles. ISME J. 2015, 9, 1488–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Gao, J.; Tang, M.; Zhou, T.; Zhu, D.; Yang, X.; Chen, B. Urbanization reduces the stability of soil microbial community by reshaping the diversity and network complexity. Chemosphere 2024, 364, 143177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Li, P.; Wang, X.; Che, Y.; Long, H.; Zhang, X.; Cai, X.; Huang, A.; Zeng, Y.; Xie, Z. Cross-habitat distribution pattern of Bacillus communities and their capacities of producing industrial hydrolytic enzymes in Paracel Islands: Habitat-dependent differential contributions of the environment. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 323, 116252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siu-Rodas, Y.; de los Angeles Calixto-Romo, M.; Guillen-Navarro, K.; Sanchez, J.E.; Alejandro Zamora-Briseno, J.; Amaya-Delgado, L. Bacillus subtilis with endocellulase and exocellulase activities isolated in the thermophilic phase from composting with coffee residues. Rev. Argent. Microbiol. 2018, 50, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, X.; Yu, X.; Fu, L.; Liu, Y.; Ma, L.; Zhai, C. High-Level Expression of Endo-β-N-Acetylglucosaminidase H from Streptomyces plicatus in Pichia pastoris and Its Application for the Deglycosylation of Glycoproteins. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120458. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, C.; Wang, S.; Xie, H.; Jiang, N.; Chen, Z.; Wei, K.; Bao, X.; Song, X.; Bai, Z. Stover and biochar can improve soil microbial necromass carbon, and enzymatic transformation at the genetic level. Glob. Change Biol. Bioenergy 2022, 14, 1082–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Yuan, X.; Chen, K.; Luo, Y.; He, Z.; Huang, X.; Deng, P.; et al. Enhancing rice ecological production: Synergistic effects of wheat-straw decomposition and microbial agents on soil health and yield. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1368184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Guan, D.W.; Zhou, B.K.; Zhao, B.S.; Ma, M.C.; Qin, J.; Jiang, X.; Chen, S.F.; Cao, F.M.; Shen, D.L.; et al. Influence of 34-years of fertilization on bacterial communities in an intensively cultivated black soil in northeast China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 90, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, F.T.; Griffiths, R.I.; Bailey, M.; Craig, H.; Girlanda, M.; Gweon, H.S.; Hallin, S.; Kaisermann, A.; Keith, A.M.; Kretzschmar, M.; et al. Soil bacterial networks are less stable under drought than fungal networks. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borham, A.; Bkhit, M.; Wang, J.; Qian, X. Immobilization of fungal laccase onto red seaweed biomass as a novel support for efficient dye decolorization. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2025, 38, 104143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Zheng, H.J.; Xu, H.X.; Cheng, S.Q.; Yu, C.H.; Wu, J.J.; Meng, K.; Xie, G.F. Response of soil fungi to textile dye contamination. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 359, 124577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xue, R.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Song, K.; Yuan, S.; Wang, M.; Shen, Y.; Ji, G.; Lin, H. Controlled-Release Nitrogen Fertilizer Enhances Saline–Alkali Soil Organic Carbon by Activating Straw Decomposition Agents. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2053. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092053
Xue R, Wang Z, Liu Q, Song K, Yuan S, Wang M, Shen Y, Ji G, Lin H. Controlled-Release Nitrogen Fertilizer Enhances Saline–Alkali Soil Organic Carbon by Activating Straw Decomposition Agents. Agronomy. 2025; 15(9):2053. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092053
Chicago/Turabian StyleXue, Rui, Zhengrui Wang, Qing Liu, Kun Song, Shanda Yuan, Mei Wang, Yuwen Shen, Guangqing Ji, and Haitao Lin. 2025. "Controlled-Release Nitrogen Fertilizer Enhances Saline–Alkali Soil Organic Carbon by Activating Straw Decomposition Agents" Agronomy 15, no. 9: 2053. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092053
APA StyleXue, R., Wang, Z., Liu, Q., Song, K., Yuan, S., Wang, M., Shen, Y., Ji, G., & Lin, H. (2025). Controlled-Release Nitrogen Fertilizer Enhances Saline–Alkali Soil Organic Carbon by Activating Straw Decomposition Agents. Agronomy, 15(9), 2053. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092053




