Abstract
In order to identify saline–alkali-tolerant rapeseed varieties suitable for cultivation on moderately saline–alkali soils and to expand the use of such lands, six rapeseed varieties were selected as experimental materials. Field experiments were conducted to evaluate agronomic traits, photosynthesis, stress physiology, yield, and quality throughout the entire growth period. Statistical methods, including correlation analysis, principal component analysis, membership function analysis, and cluster analysis, were employed to evaluate and select saline–alkali-tolerant varieties. The results indicated that H62 and 20C14 yielded the highest seed production, reaching 2287.99 kg·hm−2 and 2277.15 kg·hm−2, respectively. During the mid-to-late growth stages, the majority of agronomic traits, photosynthetic parameters, and stress physiology indicators for 20C14 were significantly superior to those of the other varieties. The results of the principal component analysis showed that the total root length at maturity stage, root–shoot ratio at flowering stage, and proline content at maturity stage were the most important indicators for screening saline–alkali-tolerant rapeseed varieties. A comprehensive analysis of these indicators revealed the following descending order of saline–alkali tolerance among the varieties: 20C14 > 20C17 > 20C4 > H62 > H158 > 17C2. Cluster analysis was performed to classify the rapeseed into strong saline–alkali-tolerant type (20C14 and 20C17), moderate saline–alkali-tolerant type (20C4, H62, and H158), and weak saline–alkali-tolerant type (17C2). Consequently, 20C14 and 20C17 are recommended as suitable rapeseed varieties for cultivation on soda saline–alkali soils.
1. Introduction
Soil salinization has become one of the significant factors constraining agricultural development and the economic growth of farmers. In December 2024, the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) released its first Global Assessment of Salt-Affected Soils report in 50 years [1]. The report indicates that the world currently has 1.381 billion hectares of salt-affected land, accounting for approximately 10.7% of the global land area. China alone has about 36 million hectares of salt-affected land. In some countries, severe salinization has led to grain crop yield reductions of up to 70%, resulting in substantial losses. As a potential reserve resource for arable land, the rational development and utilization of saline–alkali land is crucial for the sustainable development of agriculture and the coordinated development of regional economies and societies. Current methods for improving saline–alkali land primarily include physical regulation, engineering measures, chemical amendment, and biological remediation [2,3]. Biological remediation, specifically through planting salt-tolerant plants, can improve saline–alkali land. This approach not only increases economic returns but can also enrich the soil microbial community structure, thereby enhancing soil quality. Crops currently used for ameliorating saline–alkali soils include rice (Oryza sativa L.), corn (Zea mays L.), cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.), and rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) [4].
As one of China’s four major oil crops, rapeseed has an annual planting area exceeding one hundred million mu, constituting 55% of the country’s total oil crop production, and plays a significant role in the nation’s edible oil supply [5]. Highly nutritious, rapeseed contains essential nutrients for the human body, including linoleic acid, fat-soluble vitamins, and polyphenols [6]. Beyond its edible value, rapeseed serves purposes in feed, fertilizer, and as an ornamental, and it notably enhances saline–alkali soils. Studies indicate that rapeseed has greater tolerance to saline–alkali conditions than major food crops such as wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and corn [7]. Under saline–alkali conditions, rapeseed employs various pathways and mechanisms to mitigate damage and adapt to the environment for normal growth: leaves regulate stomatal dynamics to reduce water transpiration and photosynthetic loss; cells maintain osmotic balance through osmotic regulatory substances like proline, soluble proteins, and betaine, and enhance antioxidant enzyme activity to scavenge reactive oxygen species, thereby reducing cell membrane damage [8,9]. Different varieties of rapeseed exhibit varying levels of saline–alkali tolerance. For instance, Li Jiming et al. [10] found that the relative seedling survival rates of saline–alkali resistant varieties such as Longyou 7 and Dongyou 8 were all above 0.8, whereas the survival rate of less tolerant varieties was only about 0.5. The activity levels of leaf protective enzyme systems, including superoxide dismutase (SOD), peroxidase (POD), catalase (CAT), and proline (Pro), are higher in saline–alkali-tolerant varieties than in sensitive ones, while the content of malondialdehyde (MDA) is lower in tolerant varieties [11]. It is noteworthy that many regions have initiated the promotion of saline–alkali-tolerant rapeseed varieties and have achieved significant results. For example, the Shaanxi Hybrid Rapeseed Research Center, in collaboration with the Weinan Agricultural Technology Promotion Center, demonstrated the cultivation of the rapeseed variety Qinyou 1618 in Changjia Village, Jingyao Town, Pucheng County, on low saline–alkali land. After three years of demonstration and promotion, the rapeseed planting area exceeded 1000 mu by 2021, with the highest yield per mu reaching 370 kg, and the average yield per mu reaching 260 kg in 2023 [12].
Saline–alkali tolerance is a complex trait that encompasses multiple indicators across various aspects of the crop. Scientifically and comprehensively evaluating the stress resistance of different varieties is crucial. Yuan Yuting et al. [13] used principal component and membership function analyses to comprehensively evaluate seven saline-tolerance-related indicators in 287 seedling-stage soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr) varieties. These studies demonstrate that using a single indicator to assess crop saline–alkali tolerance is insufficient and inaccurate; a comprehensive evaluation combining relevant indicators is necessary. Therefore, this study, through field trials, measured agronomic traits, photosynthesis, stress resistance physiology, and yield and quality-related indicators of six rapeseed varieties planted in moderately soda saline–alkali soil, employing correlation analysis, principal component analysis, membership function analysis, and cluster analysis, classified their salt–alkali tolerance, and screened out salt–alkali-tolerant rapeseed varieties, aiming to provide a theoretical foundation for variety (line) breeding.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
Rapeseed varieties: Huayouza 62 (H62), Huayouza 158 (H158), 20 Cai 4 (20C4), 20 Chong 14 (20C14), 20 Chong 17 (20C17), and 17 Cai 2 (17C2). All were provided by the National Rapeseed Engineering Technology Research Center of Huazhong Agricultural University.
2.2. Overview of the Test Site
This experiment was conducted in the test field of Renhui Planting Professional Cooperative, located in Yingxian County, Shuozhou City, Shanxi Province (112°58′~113°37′ E, 39°17′~39°45′ N). Yingxian County is situated in the northern part of Shanxi Province. The average monthly temperature during the test period was 20.7 °C, and the average monthly rainfall was 4.68 mm. The soil type is predominantly soda alkaline, characterized by a high concentration of sodium and bicarbonate ions. The average values of the basic physical and chemical properties of the soil before sowing are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Soil physical and chemical properties of 0-20cm soil layer in test field before sowing.
2.3. Experimental Design
The experiment utilized six rapeseed varieties as materials, arranged in a randomized block design with three replications, resulting in a total of 18 plots, each measuring 225 m2 (15 m × 15 m). A specialized fertilizer and seeding integrated machine for rapeseed was employed (Shandong, China), applying 600.0 kg·hm−2 of nitrogen–phosphorus–potassium compound fertilizer (N-P2O5-K2O = 15-15-15) and 3 kg·hm−2 of seeds, with a row spacing of 25 cm. After sowing, a closed-type herbicide was applied, and drip irrigation and weeding were uniformly managed. Samples were uniformly taken at the seedling stage (11 June 2023), flowering stage (9 July 2023), pod-setting stage (27 August 2023), and maturity stage (10 September 2023).
2.4. Measurement Indicators and Methods
2.4.1. Yield and Agronomic Traits
During each growth stage of rapeseed, five plants were randomly selected from each plot and taken back to the laboratory. The above-ground and underground parts of the plants were separated, and their fresh weights were measured using the weighing method. The plants were then blanched at 105 °C and dried to a constant weight at 75 °C to measure their dry weights. A root scanner (Model GT-X980, Epson, Nagano, Iapan) was used to determine the total root length (L) and root surface area (SA). The above-ground biomass (AGB), below-ground biomass (BGB), root-to-shoot ratio (RSR), specific root length (SRL), and specific root surface area (SSA) were calculated.
At the maturity stage, three representative 1 m2 rapeseed plant samples were taken from each plot, and the number of effective pods per plant (NES), number of seeds per pod (AN), and 1000-grain weight (1000−SW) were counted to calculate the theoretical yield (SY).
2.4.2. Osmotic Adjustment Substances
The samples were selected from the third leaf counted from the top of the plant. The proline (Pro) content was determined using the acidic ninhydrin method [14]: 0.2 g of the sample were weighed and placed into a mortar. Then, 10 mL of 80% ethanol was added, and the mixture was ground into a homogenate. The homogenate was extracted in the dark for 1 h. The supernatant was filtered, shaken for 15 min, and centrifuged at 3000 r/min for 5 min. Subsequently, 2 mL of the supernatant was taken, mixed with 2 mL of glacial acetic acid and 2 mL of ninhydrin solution. This mixture was heated in a boiling water bath for 20 min. After cooling, the optical density was measured at a wavelength of 515 nm. The proline content of the test sample was determined from the standard curve and substituted into the formula to calculate the proline content in the sample (All chemical reagents are from Tianjin, China).
C denotes the proline content of the test sample, as determined from the standard curve (μg); W represents the sample weight (g). The same applies below.
The soluble protein (SP) content was ascertained using the Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250 staining method [14]: 1.0 g of the sample was weighed into a mortar. Quartz sand and distilled water were added, and the mixture was ground into a homogenate. The homogenate was then transferred to a 100 mL volumetric flask and brought up to volume. The solution was shaken thoroughly, and 10 mL was taken out and centrifuged at 4000 r/min for 10 min. Subsequently, 3 mL of the supernatant was transferred to a test tube, mixed with 3 mL of Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250 staining solution, and shaken well. After 5 min, the absorbance was measured at a wavelength of 620 nm. The soluble protein concentration of the test sample was determined from the standard curve and substituted into the formula to calculate the soluble protein content in the sample.
n represents the dilution factor. The same is below.
2.4.3. Protective Enzyme System Activity
The samples were selected from the third leaf counted from the top of the plant. The malondialdehyde (MDA) content was determined using the thiobarbituric acid method [15]: 1.0 g of the sample was weighed and 5.0 mL of 10% trichloroacetic acid (TCA) was added. After grinding the sample into a homogenate, it was centrifuged at 4 °C and 10,000 r/min for 20 min. Then, 2.0 mL of the supernatant was taken (2.0 mL of 10% TCA solution was added to the control blank tube instead of the extract). Next, 2.0 mL of 0.67% TBA was added. After mixing, the mixture was boiled in a water bath for 20 min, cooled, and centrifuged again. The absorbance values of the supernatant were measured at wavelengths of 450 nm, 532 nm, and 600 nm, respectively.
Crude enzyme extract preparation: A 0.5 g fresh sample was combined with a small amount of calcium carbonate, quartz sand, and 5 mL of 50 mmol·L−1 phosphate buffer in a mortar and ground. Following centrifugation, the supernatant was collected and stored in a refrigerator (BCD-206STPP, Haier Smart Home Co., Ltd., Qingdao, China) at 4 °C for subsequent enzyme activity assays.
The catalase (CAT) activity was assessed using the potassium permanganate titration method [15]: 0.1 mL of 2% H2O2, 2 mL of phosphate buffer, and 0.1 mL of crude enzyme extract were mixed. The optical density was measured at 240 nm, with readings taken every minute for a total of five times. An absorbance decrease of 0.0436 per minute was defined as one unit of enzyme activity.
ΔE240 represents the average decrease in optical density per minute at a wavelength of 240 nm; V1 denotes the total sample volume; V2 denotes the measured sample volume.
The superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity was determined using the nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) photoreduction method [15]: Four test tubes were selected, and 3 mL of reaction solution was added to each. One tube received a buffer solution, one was kept in the dark, and the remaining two were exposed to 4000 Lux light conditions for 10 min, along with the enzyme solution (200 μL added). The absorbance was measured at a wavelength of 560 nm.
ACK represents the absorbance measured for the control; A represents the absorbance measured for the sample. The peroxidase (POD) activity was determined using the guaiacol method [15]: A reaction mixture was prepared by successively adding 50 mL of 100 mmol·L−1 phosphate buffer, 28 μL of guaiacol, and 19 μL of 30% hydrogen peroxide into a beaker. Then, 3 mL of the reaction mixture and 1 mL of enzyme solution were added (KH2PO4 was added to the control). The optical density was measured at 470 nm, recorded every 3 min, for a total of three times. A change of 0.01 in A470 per minute was defined as one peroxidase activity unit (U).
A2 − A1 represents the change in absorbance; t2 − t1 represents the change in time.
2.4.4. Photosynthetic Indices
A Plant photosynthesis analyzer (3051D, Zhejiang Top Yunnong Technology Co., Ltd., Hangzhou, China) was used to determine the photosynthetic parameters of the third leaf from the top of rapeseed plants, including net photosynthetic rate (Pn), stomatal conductance (Gs), intercellular CO2 concentration (Ci), and transpiration rate (Tr).
2.5. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
Microsoft Excel 2010 (Microsoft Co., Ltd., Redmond, WA, USA) was used for data processing, and IBM SPSS Statistics 26 program (IBM SPSS Statistics, IBM corp., Chicago, IL, USA) was used for one-way analysis of variance, correlation analysis, principal component analysis, membership function analysis, and cluster analysis; Origin 2025 (Origin Lab, Northampton, MA, USA) was used for plotting. The fuzzy membership function method was used to comprehensively evaluate the saline–alkali tolerance of rapeseed and calculate the membership function value:
μ(Xj) represents the membership function value of the j-th comprehensive index, Xj represents the j-th comprehensive index value, Xmax represents the maximum value of the j-th comprehensive index, Xmin represents the minimum value of the j-th comprehensive index; F(Xj) represents the score of each principal component, anj is the loading of each component, and Xnj is the standardized original data of each index; Wj represents the weight of the j-th comprehensive index among all comprehensive indexes, Pj is the contribution value of the j-th comprehensive index of the material, and is the cumulative contribution rate of the principal components of the material; and D represents the comprehensive evaluation value of the saline–alkali tolerance of each material [16].
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Saline–Alkali Stress on Rapeseed Yield and Its Components
As depicted in Figure 1A, H62 and 20C14 exhibited the highest yields, reaching 2287.99 kg·hm−2 and 2277.15 kg·hm−2, respectively. Conversely, 17C2 had the lowest yield at only 383.21 kg·hm−2. The number of effective pods per plant for H62 was significantly higher than that of the other five rapeseed varieties, with a count of 143.65, followed by 20C14 and 20C17. Notably, 17C2 also had the fewest number of effective pods, with a count of 66.58 (Figure 1B). Figure 1C,D illustrates that there were no significant differences in the number of seeds per pod and the 1000-grain weight among the six rapeseed varieties. In summary, the yield from highest to lowest was H62 ≈ 20C14 > 20C17 > 20C4 > H158 > 17C2.
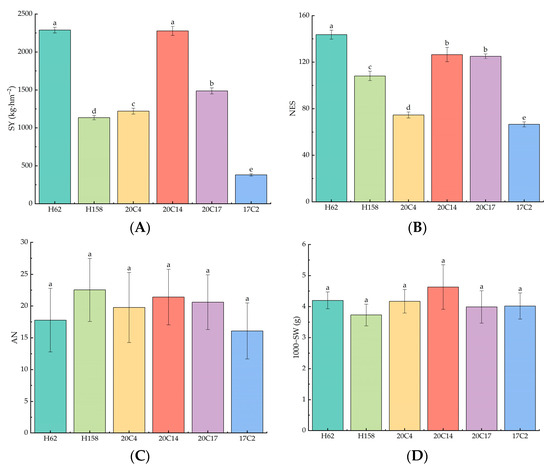
Figure 1.
Yield and yield components of six rapeseed varieties under saline–alkali stress. (A) Theoretical yield (SY); (B) number of effective pods per plant (NES); (C) number of seeds per pod (AN); (D) 1000-grain weight (1000-SW). One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used. Values are presented as mean ± standard error (n = 3). Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between treatments (p < 0.05).
3.2. Effects of Saline–Alkali Stress on Agronomic Traits, Stress Physiology, and Photosynthesis of Rapeseed
Figure 2A,B indicates that at the seedling stage, there was no significant difference in AGB and BGB among the six rapeseed varieties. However, in the middle and late growth stages, the biomass varied as follows: 20C14 > H62 > 20C4 > 20C17 > H158 > 17C2. Specifically, during the flowering stage, the AGB and BGB of 20C14 was 669.57% and 1106.53% higher, respectively, than that of 17C2. At the pod-setting stage, these values were 748.20% and 811.03% higher, and at the maturity stage, they were 196.19% and 810.95% higher. Figure 2C shows that at the flowering, pod-setting, and maturity stages, the total root length of 20C14 and 20C17 was significantly greater than that of the other four varieties. At the seedling and pod-setting stages, there was no significant difference in the root–shoot ratio among the six varieties (Figure 2D). At the flowering stage, the root–shoot ratios of 20C14 and 20C17 were significantly higher than those of the other varieties, with values of 0.20 and 0.23, respectively. In contrast, the root–shoot ratios of 20C4 and 17C2 were significantly lower, with values of 0.12 and 0.13, respectively. However, at the maturity stage, the root–shoot ratio of 20C14 was the smallest at 0.06, while that of 20C4 was the largest at 0.17. The specific root length and specific root surface area of the different rapeseed varieties exhibited a similar trend (Figure 2E,F), both generally decreasing with the growth period, except for 20C17. Notably, 20C4 had the smallest specific root length and specific root surface area, whereas 20C14 had a medium level in these parameters.
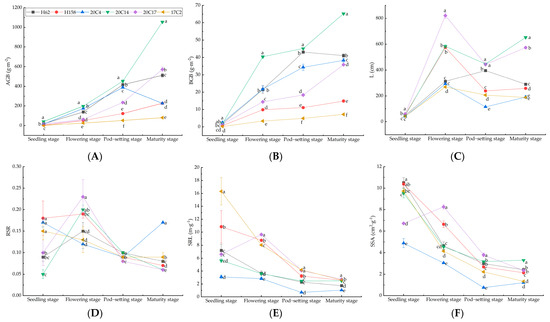
Figure 2.
Agronomic traits of different rapeseed varieties at different growth stages under salt–alkali stress. (A) Above-ground biomass (AGB); (B) below-ground biomass (BGB); (C) total root length (L); (D) root-to-shoot ratio (RSR); (E) specific root length (SRL); (F) specific root surface area (SSA). Values are presented as mean ± standard error (n = 3). Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between treatments (p < 0.05).
As depicted in Figure 3, under saline–alkali stress, the levels of SP, Pro, and CAT activity generally exhibited a downward trend as the growth period increased; conversely, POD activity displayed an upward trend. The expression levels of SOD and MDA typically followed a pattern of initial increase and subsequent decrease over the growth period. The highest soluble protein content was observed at the seedling stage (with the exception of H62), where varieties 20C14 and 20C17 had notably the highest levels at 26.77 mg·g−1 and 28.46 mg·g−1, respectively. By contrast, the mature stage exhibited the lowest soluble protein content, with variety 20C14 reaching the minimum at 2.86 mg·g−1 (Figure 3A). Figure 3B illustrates that the Pro content of 20C14 was significantly the highest at the seedling, flowering, and mature stages (242.10 μg·g−1, 245.87 μg·g−1, and 40.72 μg·g−1). At the seedling stage, 20C14 had the lowest CAT activity (20.31 U·g−1), but it surpassed other rapeseed varieties at the pod-setting and mature stages, with activities of 8.06 U·g−1 and 3.68 U·g−1 (Figure 3C). The MDA and POD activities of 20C14 demonstrated significant advantages during most periods (Figure 3D,E). The SOD activities of 20C4, H62, and 17C2 peaked at the seedling, flowering, and pod-setting stages, reaching 119.34 μg·g−1, 170.40 μg·g−1, and 282.75 μg·g−1 (Figure 3F), respectively, whereas the SOD activity of 20C14 was at a moderate level among the six rapeseed varieties.
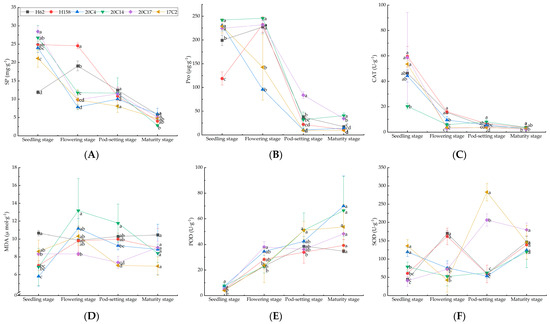
Figure 3.
Osmotic regulatory substances and protective enzyme system activities of different rapeseed varieties at different growth stages under salt–alkali stress. (A) Proline (SP); (B) soluble protein (Pro); (C) catalase (CAT); (D) malondialdehyde (MDA); (E) peroxidase (POD); (F) superoxide dismutase (SOD). Values are presented as mean ± standard error (n = 3). Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between treatments (p < 0.05).
Plants can modulate stomatal conductance and transpiration rate, influencing the dynamic variations in photosynthetic rate. As depicted in Figure 4, throughout the growth period, with the exception of rapeseed variety 17C2, the Pn, Tr, Ci, and Gs of other rapeseed varieties exhibited an upward trend to varying extents. During the seedling stage, rapeseed variety 17C2 displayed the highest Tr, Ci and Gs, followed by 20C14; variety 20C4 had the highest Pn, whereas 20C14 and H158 had the lowest Pn, at 5.89 μmol CO2·m−2·g−1 and 4.83 μmol CO2·m−2·g−1, respectively. At the seedling stage, H158 exhibited the lowest of the four photosynthetic indices. During the flowering stage, the Ci of H62 was notably higher than that of the other varieties, 122.72% above the variety with the lowest concentration. The Pn and Tr of 20C14 exceeded those of the other varieties, being 725.55% and 67.15% higher than the variety with the lowest rates, respectively. The photosynthetic indices of 17C2 were lower than those of the other varieties. Consequently, at the flowering stage, 20C14 and H62 exhibited the best photosynthetic capacity, while 17C2 had the poorest photosynthetic capacity.
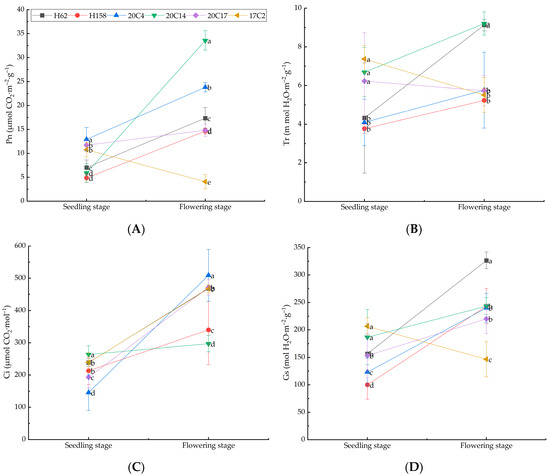
Figure 4.
Effects on photosynthetic parameters of rapeseed under salt–alkali stress. (A) Net photosynthetic rate (Pn); (B) transpiration rate (Tr); (C) intercellular CO2 concentration (Ci); (D) stomatal conductance (Gs). Values are presented as mean ± standard error (n = 3). Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between treatments (p < 0.05).
In conclusion, H62, 20C14, and 20C17 demonstrated relatively superior saline–alkaline tolerance. However, the ranking of rapeseed’s saline–alkali tolerance based on a single index is inconsistent, indicating that a single index cannot comprehensively and effectively evaluate rapeseed’s saline–alkali tolerance. Therefore, a comprehensive analysis of the aforementioned indices is necessary.
3.3. Variation Analysis of Each Index of Rapeseed
As indicated in Table 2, the variation coefficients for the 20 indices of the six rapeseed varieties ranged from 7.28% to 84.10%, indicating significant differences among the indices. During the seedling stage, the variation coefficient for AGB was the highest at 71.01%, followed by the RSR (57.76%) and underground biomass (55.32%), while the variation coefficient for L was the lowest at 14.46%. At the flowering stage, the variation coefficient for BGB was the greatest, followed by AGB and CAT, with values of 68.93%, 65.44%, and 65.20%, respectively. The smallest variation coefficient was observed for the MDA at 15.60%. Moving to the pod-setting stage, the top three indices with the highest variation coefficients were Pro at 84.10%, SOD at 81.67%, and BGB at 65.07%, whereas the index with the lowest variation coefficient was again the RSR at 11.11%. At the maturity stage, the variation coefficients for AGB (78.96%), Pro (61.34%), and BGB (61.13%) were the most pronounced, while the variation coefficient for the 1000-SW (7.28%) was the least. In all four growth stages, the variation coefficients of biomass are relatively large. These findings suggest that the tested materials are diverse, which facilitates comparison and selection.

Table 2.
Variation analysis of salt–alkali tolerance indicators in rapeseed.
3.4. Correlation Analysis of Each Index
Upon examining the correlation coefficients of each index in Figure 5, it is evident that AGB exhibits an extremely significant positive correlation with BGB, SRL is extremely significantly positively correlated with SSA, and L is extremely significantly positively correlated with Pro, with respective correlation coefficients of 0.97, 0.99, and 0.92 (Appendix A (Table A1)). Additionally, five indexes are significantly positively correlated with SY: AGB (0.90), BGB (0.88), MDA (0.87), NES (0.87), and Gs (0.86) (Table A1), indicating that these indicators may have a synergistic effect in the growth of rapeseed and the physiological process of coping with salt–alkali stress, and are correlated and interact with each other. There are three indicators that are significantly or extremely significantly positively correlated with above-ground biomass, indicating that above-ground fresh weight and yield can be used as auxiliary indicators to measure the salt–alkali tolerance of rapeseed, which provides a basis for indirectly evaluating the salt–alkali tolerance of rapeseed through some easy-to-observe or easy-to-determine indicators. However, because there are also correlations of varying degrees between other indicators, and the role of each indicator in the salt–alkali stress of rapeseed is also different, further comprehensive analysis is needed to evaluate the salt–alkali tolerance of rapeseed. However, due to the different degrees of correlation between various indicators in the figure, each indicator plays a different role in the salt–alkali stress of rapeseed. If only a single indicator is used to evaluate the salt–alkali tolerance of rapeseed, the evaluation results may be biased due to the interrelationship between indicators and the diversity of roles, and the true salt–alkali tolerance of rapeseed cannot be fully and accurately reflected. Therefore, it is necessary to carry out the correction analysis of index traits. By comprehensively considering multiple indicators and their interrelationships, the weights and influences of various indicators are reasonably corrected and integrated, so as to evaluate the salt–alkali tolerance of rapeseed more scientifically and comprehensively.
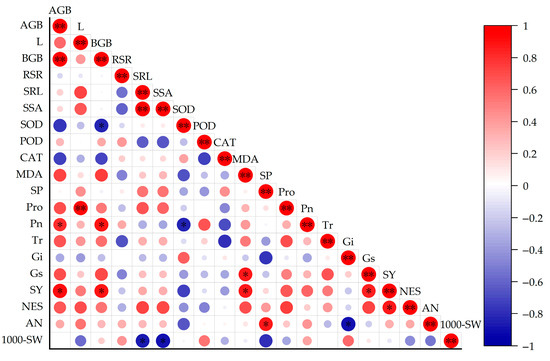
Figure 5.
Correlation analysis of index traits of rapeseed varieties.* p ≤ 0.05,** p ≤ 0.01.
3.5. Principal Component Analysis of Each Index
Principal component analysis was conducted on the indices of six rapeseed varieties across four periods, with the results presented in Table A2. The contribution rates of the first four principal components were 34.009%, 25.228%, 16.694%, and 14.371%, respectively, yielding a cumulative contribution rate of 90.303%, which exceeds 85%. This suggests that these four principal component indices can represent most of the information of the original indices. The first and second principal components are presented in the form of a PCS plot (Figure 6). Most indicators fall within the 95% confidence interval, indicating statistical significance. In the established comprehensive indices, the eigenvalues in the first principal component were higher for SY (0.947), seedling stage AGB (0.933), flowering stage BGB (0.918), maturity stage AGB (0.910), and maturity stage BGB (0.909), all exceeding 0.9. In the second principal component, the flowering stage SSA (0.902), pod-setting stage SSA (0.857), seedling stage L (0.855), maturity stage SSA (0.824), and pod-setting SRL (0.819) were greater than other indices. The third principal component had higher positive loadings for seedling stage Tr (0.884) and Pro (0.722). The fourth principal component had the largest loading value for flowering stage POD (0.934), indicating that the fourth principal component was primarily composed of flowering stage POD (Table A2). As can be seen from Figure 6, 20C14 is close to indicators such as SY, H_Tr, and H_Gs, which suggests that it performs well in these indicators, while 17C2 and 20C4 are located in the third quadrant of the plot, far from the arrows of most indicators positively correlated with salt–alkali tolerance, which may imply that they perform poorly in these salt–alkali tolerance-related indicators. H158, 20C17, and H62 are relatively close to each other, indicating that the comprehensive indicator characteristics of these three rapeseed varieties are more similar.
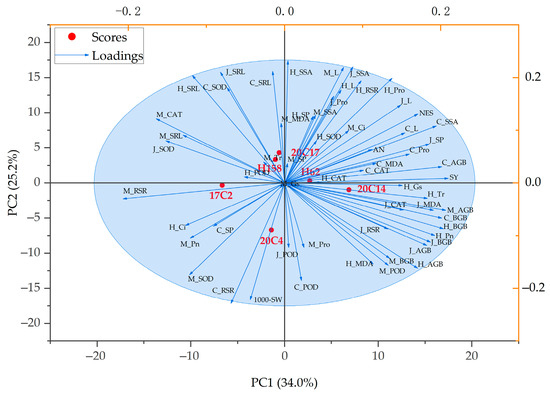
Figure 6.
Principal component analysis of rapeseed under salt–alkali stress during the whole growth period. PC1 stands for the first principal component, and PC2 stands for the second principal component. Red dots represent different rapeseed varieties; blue arrows represent indicators related to salt–alkali tolerance; blue circles indicate the 95% confidence interval.
Multiply the load value corresponding to the index by its corresponding contribution rate in the four principal components, and then sum them up. The larger the total load value, the stronger the positive impact of the index on the saline–alkali tolerance of rapeseed, indicating that the saline–alkali tolerance index of rapeseed is more significant. Through calculation, the top five indices for evaluating the saline–alkali tolerance of rapeseed were maturity stage L (45.273), flowering stage RSR (43.507), maturity stage Pro (43.476), pod-setting stage L (42.746), and maturity stage SSA (41.163) (Table A2).
3.6. Comprehensive Evaluation
The membership function method was utilized to perform a comprehensive evaluation of six rapeseed varieties, with the results displayed in Table 3. The comprehensive evaluation values (D) for the six rapeseed varieties ranged from 0.498 to 7.381. Upon sorting, the varieties with D values from highest to lowest were 20C14, 20C17, 20C4, H62, H158, and 17C2. Cluster analysis was conducted on the six rapeseed varieties. It can be observed from Figure 7 that the six rapeseed varieties are divided into three branches of different colors. The shorter the branch, the closer the distance between the two varieties and the higher the feature similarity. The branches of 20C14 and 20C17 are shorter, indicating that their salt–alkali tolerance features are more similar; the branches of H158 and 20C4 are also short, and their salt–alkali tolerance features are also more similar, while the branch of 17C2 is long compared with other varieties, indicating that its salt–alkali tolerance features are quite different from those of other varieties. Therefore, the salt–alkali tolerance of rapeseed is divided into three categories: the first category with the strongest salt–alkali tolerance includes varieties 20C14 and 20C17, the second category with general salt–alkali tolerance includes varieties H62, 20C4, and H158, and the third category with the weakest salt–alkali tolerance is 17C2. By conducting cluster analysis on the six rapeseed varieties, varieties with similar salt–alkali tolerance features can be grouped into one category according to the differences in their performance in indicators related to salt–alkali tolerance. Thus, the strength levels of salt–alkali tolerance of different rapeseed varieties can be clearly and intuitively divided, which is convenient for quickly identifying excellent varieties with strong salt–alkali tolerance. It provides a more targeted basis for the screening, breeding, and research on the salt–alkali tolerance mechanism of salt–alkali-tolerant rapeseed varieties, and also helps to carry out more in-depth relevant experiments and application explorations according to different salt–alkali tolerance categories in the future.

Table 3.
Comprehensive evaluation of salinity tolerance index of six rapeseed species.
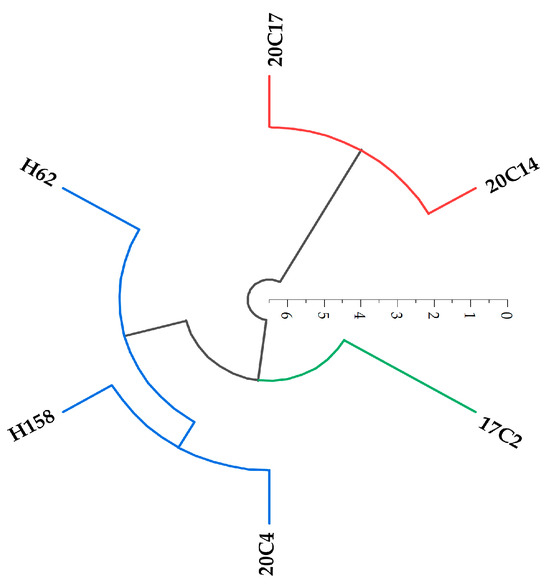
Figure 7.
Dendrogram of cluster analysis of salt–alkali tolerance in six rapeseed varieties. Hierarchical cluster analysis was performed using D value and Origin; Branches of different colors represent different cluster groups, where red stands for the strong salt–alkali tolerance type, blue for the moderate salt–alkali tolerance type, and green for the weak salt–alkali tolerance type; the coordinate axis represents Euclidean distance, and those with similar squared Euclidean distances were divided into one cluster.
4. Discussion
4.1. Relationship Between Rapeseed Phenotype, Physiological Characteristics, Photosynthetic Indexes, Yield, and Saline–Alkali Tolerance
Saline–alkali stress impedes the growth and development of crops, decelerating their growth rate or even halting it altogether. Factors influencing crop growth rate in saline–alkali soils encompass crop species, the concentration of saline–alkali, the developmental stage of the crop, and the amount of fertilizer applied [17]. Crop characteristics are markedly influenced by saline–alkali stress, with these effects typically manifesting at molecular, cellular, metabolic, physiological, and phenotypic levels [18]. Consequently, when assessing the saline–alkali tolerance of crops, it often relies on crop phenotypes, physiological indicators, photosynthetic indicators, and yields. The influence of saline–alkali stress on the phenotypic traits of rapeseed throughout its growth period is evident, and numerous morphological traits, such as seed germination rate, root length, and plant biomass, are deemed suitable evaluation indicators for identifying salt-tolerant crops [19]. Studies have indicated that during the germination and seedling stages of rapeseed, at a certain concentration, the root length and stem length of rapeseed are most affected by saline–alkali, followed by fresh weight [20]. Hence, the greater the saline–alkali tolerance, the lesser the impact on rapeseed phenotypes. Wang Yifan et al. [21] conducted a comprehensive analysis of the phenotypes of rice varieties and discovered that all indicators of rice varieties with strong tolerance to soda saline–alkali were higher than those of saline–alkali-intolerant rice varieties, and the decline range was lower than that of saline–alkali-intolerant rice varieties, aligning with the outcomes of this experiment. In the present experiment, the above-ground biomass and underground biomass of the rapeseed variety 20C14, which exhibits the strongest saline–alkali tolerance, were higher than those of other rapeseed varieties across all growth periods, whereas the above-ground and underground biomass of the rapeseed variety 17C2, which has the weakest saline–alkali tolerance, were lower than those of other rapeseed varieties throughout all growth periods. The total root length of 20C14 and 20C17 was also significantly greater than that of other rapeseed varieties.
An increase in Na+ and Cl− affects lipid peroxidation of cell membranes, leading to a decrease in osmotic potential and an increase in water potential, thereby influencing seed germination [22]. Meanwhile, excessive Na+ can replace Ca2+ to bind with cell wall polysaccharides, thereby damaging the elasticity and stability of the cell wall, while Cl− can decompose cell wall components, resulting in impaired cell integrity [23]. Saline–alkali stress may also cause disorders in cellular metabolism, affecting DNA replication and transcription, reducing the activity of RNA polymerase in the nucleus, inhibiting protein synthesis, and decreasing the activity of amylase, thus impacting physiological and biochemical processes such as cell division, differentiation, glycogen hydrolysis, and cellular respiration [24,25]. Saline–alkali-tolerant varieties can effectively inhibit or sequester Na+ and Cl−, thereby reducing intracellular salt concentration levels, while enhancing the absorption and accumulation of K+ to maintain ion balance inside and outside the cells. In contrast, saline–alkali-sensitive varieties have poor ability or no ability to balance ion levels inside and outside the cells [26]. When crops are subjected to saline–alkali stress, ionic toxicity and changes in cellular metabolism occur, producing reactive oxygen species (ROS) that damage cell membrane structures. MDA, a product of lipid peroxidation, is a representative substance indicating cell membrane damage when plants are exposed to adverse conditions [27]. Saline–alkali-tolerant varieties increase the synthesis and accumulation of osmotic regulators in their cells, such as proline and soluble sugars, to improve osmotic balance inside and outside the cells, thereby alleviating the impact of salt stress on cells and resisting damage to rapeseed [28]. In addition, higher ROS-scavenging antioxidant enzyme activities are associated with salt tolerance, and saline–alkali-tolerant plants protect themselves from oxidative stress by activating antioxidant systems [29]. Aycan M et al. [30] found that the activities of SP, CAT, SOD, and GR in salt-tolerant varieties were higher than those in other varieties. The conclusions of this study are consistent with these findings; the results show that the SP, Pro, CAT, and POD of the strongly saline–alkali-tolerant lines 20C14 and 20C17 were higher than those of other rapeseed varieties during most growth periods of rapeseed.
One of the factors contributing to the slow growth and reduced biomass of plants is the damage caused by saline–alkali stress to the photosynthesis of plant cells. The impact of saline–alkali stress on photosynthesis may primarily lie in restricting the opening and closing of stomata and inhibiting the synthesis of photosynthetic pigments. Excessive Na+ in plant leaf tissues can hinder the synthesis of chlorophyll, causing the leaves to turn yellow and ultimately reducing photosynthesis [31]. Deng P et al. [32] found that when the salt concentration of rapeseed was 150 mM, Pn, Gs, Ci, and Tr decreased significantly. However, this study indicates that the Ci of 20C14 was significantly the lowest during the flowering period, while other photosynthetic indicators were significantly the highest during the seedling and flowering periods, suggesting that stomata are not the main factor affecting the photosynthesis of 20C14. The photosynthetic indicators of 17C2 during the seedling stage were higher than those during the flowering stage, whereas for other rapeseed varieties, the photosynthetic indicators during the flowering stage were higher than those during the seedling stage. This is because the leaf area of rapeseed plants reaches its maximum during the flowering stage, providing a broader surface for photosynthesis. Moreover, the photosynthetic structures of rapeseed during the flowering stage are more mature and complete than those during the seedling stage, allowing for more efficient photosynthesis. In addition, the growth of rapeseed during the seedling stage primarily focuses on the development of roots and leaves, with photosynthetic products mainly used for vegetative growth. However, during the flowering stage, reproductive growth of rapeseed becomes dominant, and photosynthetic products need to provide energy and material for the growth of branches, inflorescences, and seed setting, in addition to supporting the growth and development of the plant itself. This promotes the enhancement of photosynthesis to meet the needs of reproductive growth [33]. This is consistent with the above-ground biomass in this experiment: the above-ground biomass of 17C2 showed little difference across the four periods, while the above-ground biomass of other varieties of rapeseed increased significantly with the growth period.
The aim of cultivating high-quality varieties is to develop strains that offer high yields and rich nutritional value, satisfying human needs while enhancing economic benefits. Consequently, yield and its components are crucial criteria for selecting salt–alkali-tolerant varieties. These factors are not only linked to the genetic traits of the rapeseed varieties themselves but may also be influenced by ion toxicity, osmotic stress, and imbalanced nutrient uptake resulting from soil salinization. Moreover, saline–alkali soils often lack phosphorus and potassium, which can impede the growth and development of both crop roots and above-ground parts. This leads to a notable decrease in traits such as emergence rate, biomass, and 1000-grain weight, ultimately affecting crop yield negatively [10]. Salt–alkali-tolerant varieties can mitigate the damage from salt–alkali stress by regulating osmotic balance, ensuring a smaller yield reduction compared to salt–alkali-sensitive varieties. In this study, the yield and the number of effective pods per plant for the salt–alkali-tolerant rapeseed varieties H62 and 20C14 were significantly higher than those of other rapeseed varieties. Different halophytes adopt various strategies to cope with soil salinity and alkalinity, which can be categorized into salt exclusion, salt secretion, and salt dilution [34,35]. Salt-excluding plants primarily prevent external salts from entering the plant or store the absorbed salts in the roots, only transporting a portion to the above-ground parts; whereas salt-diluting and salt-secreting plants maintain osmotic balance by accumulating inorganic ions [36]. The six rapeseed varieties in this experiment displayed significant variations in salt–alkali tolerance, with some varieties exhibiting high yields despite not having strong comprehensive salt–alkali tolerance. This discrepancy may stem from the different salt–alkali tolerance mechanisms employed by various rapeseed varieties. Further experimental investigation is required to determine the specific type of salt–alkali tolerance mechanism that each rapeseed variety possesses.
4.2. Identification, Evaluation, and Germplasm Screening of Rapeseed Saline–Alkali Tolerance
The salt–alkali tolerance of crops is a complex trait, influenced by multiple genes and environmental factors [37,38]. Evaluating this tolerance is a complex endeavor, as there are numerous indicators for assessing the salt–alkali tolerance of rapeseed, and these indicators exhibit certain correlations with one another. Thus, relying on a single indicator to evaluate the salt–alkali tolerance of rapeseed is often inaccurate. Various statistical methods can be employed to comprehensively evaluate the indicators of salt–alkali tolerance [39]. Currently, statistical methods such as principal component analysis, cluster analysis, and comprehensive analysis have been effectively utilized to screen for salt–alkali-tolerant varieties among crops like corn, oats (Avena sativa L.), rice, wheat, and sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench). Kaur M et al. [40] utilized cluster analysis to group sorghum genotypes with correlated germination and growth parameters into clusters, ultimately identifying four genotypes (SSG59-3, HC308, 2077A, and PSC1) with the highest salinity tolerance. Aycan M et al. [30] employed PCA analysis to effectively classify wheat varieties into salt-tolerant, moderately salt-tolerant, and salt-sensitive categories based on their responses to salt stress, with Cv 4 and Cv 6 identified as salt-tolerant, Cv 10 and Cv 15 as salt-sensitive, and the remaining varieties as moderately salt-tolerant. In this study, statistical methods such as correlation analysis, principal component analysis, membership function analysis, and comprehensive evaluation value (D value) were used to comprehensively evaluate the measured indicators. The results indicated that 20C14 exhibited the strongest salt–alkali tolerance, while 17C2 had the weakest. Additionally, cluster analysis was used to categorize the six rapeseed varieties into strong, moderate, and weak salt–alkali-tolerant types. Among them, although H62 did not possess the strongest comprehensive salt–alkali tolerance, it had the highest yield, possibly due to its strategy of salt exclusion, preventing salts from entering the plant, resulting in lower salt–alkali tolerance indicators but minimal impact on yield. Consequently, H62 offers high economic benefits and is suitable for grain harvesting; 20C14, with both high comprehensive salt–alkali tolerance and high yield, is suitable for use as green manure or for grain harvesting, yielding the highest economic benefits. 20C17 also possesses strong comprehensive salt–alkali tolerance, but its yield is not the highest. Therefore, rapeseed varieties can be selected based on their specific uses.
In the subsequent phase, the phenotypes of the screened varieties exhibiting robust salt–alkali tolerance can be integrated with genomic tools like quantitative trait loci (QTL) and genome-wide association study (GWAS) [41]. Utilizing molecular biology techniques, the pivotal genes conferring salt–alkali tolerance can be identified and used to breed varieties that are both highly tolerant to salt–alkali conditions and yield-rich. Furthermore, the selected superior varieties can serve as parental lines, with salt–alkali tolerance genes being introduced into high-yielding, good quality varieties that lack strong stress tolerance through hybridization [42], backcrossing, and other methodologies. This approach aims to develop innovative varieties that are not only salt–alkali tolerant but also yield-rich and of good quality. The cultivation of salt–alkali-tolerant varieties in saline–alkali soils eliminates the need for supplementary inputs such as soil conditioners, thereby reducing costs. Simultaneously, the use of high-yielding varieties can enhance farmers’ economic benefits and provide resources for the exploitation and enhancement of saline–alkali soils [43].
5. Conclusions
This study evaluated the salt–alkali tolerance of different rapeseed varieties throughout their entire growth period and screened out varieties suitable for cultivation in saline–alkali soils. By determining indicators such as agronomic traits, physiological and biochemical properties, photosynthetic parameters, and yield components of six rapeseed varieties in soda saline–alkali soil during the whole growth period, and conducting a comprehensive analysis and evaluation of their salt tolerance, the order of salt–alkali tolerance from strongest to weakest was determined as follows: 20C14 > 20C17 > 20C4 > H62 > H158 > 17C2. Through cluster analysis based on the comprehensive salt tolerance index, two salt–alkali-tolerant rapeseed varieties were screened out, namely 20C14 and 20C17. These two varieties have great potential and can be popularized and cultivated in soda saline–alkali soils. This study provides germplasm resources for the breeding of high-yield salt–alkali-tolerant rapeseed and lays the foundation for further research on the improvement effect and mechanism of salt–alkali-tolerant rapeseed on saline–alkali soils.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.J., H.A., W.Y., X.Z. and Z.Y.; Data curation, H.J. and H.A.; Formal analysis, H.J. and Y.H.; Investigation, H.A. and J.C.; Methodology, H.A.; Project administration, Z.Y.; Resources, W.Y. and X.Z.; Software, H.J.; Supervision, B.W., G.Z. and Z.Y.; Validation, B.W., G.Z. and T.F.; Writing—original draft, H.J., J.C. and Y.H.; Writing—review and editing, W.Y., X.Z., B.W., G.Z., T.F. and Z.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Central Guiding Local Science and Technology Development Fund Project (YDZJSX2021A032), the earmarked fund for Modern Agro-industry Technology Research System of Shanxi Province (2025CYJSTX18), the Shanxi Agricultural University “Industry-Academia-Research Integration Promotion Project” (2024CXYRH-047), and the Subject of Co-innovation Center for High Quality and Efficient Production of Characteristic Crops in Loess Plateau jointly built by Provincial and Ministerial Authorities (SBGJXTZX-21).
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
I sincerely appreciate all individuals and institutions that have provided support and assistance during the implementation of this project. I would like to express my gratitude for the funding support from various projects and research topics, as well as the advanced equipment and experimental environment provided by Shanxi Agricultural University and the Shanxi Key Laboratory of Crop Ecology and Water Use Efficiency. These have laid a solid foundation for our research work. I am grateful to the teachers for their guidance throughout the process, from experimental design, conducting experiments to the final writing of the paper, which enabled us to successfully complete the experiments and the paper. Thanks are extended to the Yingxian Service Center and cooperatives for providing the field experiment sites. At the same time, I highly appreciate the valuable feedback and professional suggestions from the reviewers and editors, which have played a crucial role in improving the quality of the paper. They have allowed me to articulate the research viewpoints more accurately and present the experimental data more rigorously. Your hard work and selfless dedication have collectively promoted the progress and development of academic research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AGB | Above-ground biomass |
| BGB | Below-ground biomass |
| RSR | root-to-shoot ratio |
| SRL | specific root length |
| SSA | specific root surface area |
| L | total root length |
| NES | number of effective pods per plant |
| AN | number of seeds per pod |
| 1000-SW | 1000-grain weight |
| SY | theoretical yield |
| SP | soluble protein |
| Pro | proline |
| MDA | malondialdehyde |
| CAT | catalase |
| SOD | superoxide dismutase |
| POD | peroxidase |
| Pn | net photosynthetic rate |
| Gs | stomatal conductance |
| Ci | intercellular CO2 concentration |
| Tr | transpiration rate |
Appendix A

Table A1.
Correlation analysis.
Table A1.
Correlation analysis.
| Index | AGB | L | BGB | SRL | MDA | SP | Gs | SY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BGB | 0.97 ** | |||||||
| SSA | 0.99 ** | |||||||
| Pro | 0.92 * | |||||||
| Pn | 0.82 * | 0.88 * | ||||||
| Gs | 0.88 * | |||||||
| SY | 0.90 * | 0.88 * | 0.87 * | 0.86 * | ||||
| NES | 0.87 * | |||||||
| AN | 0.87 * |
Note: Correlation analysis of indexes of six rapeseed varieties using the Pearson correlation coefficient method; only the significant parameter differences are retained. ** indicates a significant correlation at the level of 0.01; * indicates a significant correlation at the level of 0.05.

Table A2.
Contribution rate of principal components to rapeseed salinity–alkalinity tolerance.
Table A2.
Contribution rate of principal components to rapeseed salinity–alkalinity tolerance.
| Index | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | The Total Number of Loads | Ranking of the Best Indicators |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M_AGB | 0.933 * | −0.202 | 0.293 | 0.022 | 31.842 | 15 |
| M_BGB | 0.608 | −0.555 | −0.039 | 0.561 | 14.087 | 31 |
| M_L | 0.342 | 0.855 * | 0.007 | 0.378 | 38.750 | 9 |
| M_RSR | −0.934 | −0.116 | −0.205 | −0.129 | −39.967 | 60 |
| M_SRL | −0.587 | 0.355 | 0.126 | −0.717 | −19.208 | 54 |
| M_SSA | 0.166 | 0.494 | −0.287 | −0.796 | 1.878 | 42 |
| M_SOD | −0.549 | −0.679 | 0.303 | −0.356 | −35.859 | 59 |
| M_POD | 0.600 | −0.607 | 0.299 | 0.244 | 13.590 | 33 |
| M_CAT | −0.743 | 0.474 | −0.346 | 0.323 | −14.445 | 53 |
| M_MDA | −0.019 | 0.441 | −0.261 | −0.193 | 3.349 | 40 |
| M_SP | 0.016 | 0.145 | 0.632 | 0.328 | 19.467 | 23 |
| M_Pro | 0.113 | −0.476 | 0.722 * | 0.100 | 5.325 | 39 |
| M_Pn | −0.545 | −0.407 | 0.378 | 0.569 | −14.315 | 52 |
| M_Tr | −0.121 | 0.155 | 0.884 * | −0.338 | 9.695 | 36 |
| M_Gi | 0.371 | 0.387 | 0.177 | −0.788 | 14.011 | 32 |
| M_Gs | −0.025 | −0.035 | 0.667 | −0.508 | 2.101 | 41 |
| H_AGB | 0.770 * | −0.630 | 0.011 | 0.096 | 11.857 | 34 |
| H_BGB | 0.918 * | −0.337 | 0.209 | 0.000 | 26.207 | 19 |
| H_L | 0.328 | 0.688 | 0.364 | 0.439 | 40.897 | 6 |
| H_RSR | 0.444 | 0.756 * | 0.319 | 0.279 | 43.507 | 2 |
| H_SRL | −0.534 | 0.795 * | 0.180 | 0.091 | 6.208 | 38 |
| H_SSA | 0.020 | 0.902 * | 0.091 | 0.400 | 30.703 | 17 |
| H_SOD | 0.186 | 0.311 | −0.931 | 0.026 | −0.997 | 46 |
| H_POD | −0.232 | 0.045 | 0.146 | 0.934 * | 9.105 | 37 |
| H_CAT | 0.213 | 0.004 | −0.962 | −0.104 | −10.209 | 51 |
| H_MDA | 0.513 | −0.597 | 0.265 | −0.494 | −0.290 | 44 |
| H_SP | 0.179 | 0.500 | −0.761 | −0.289 | 1.844 | 43 |
| H_Pro | 0.622 | 0.774 * | −0.032 | −0.115 | 38.493 | 11 |
| H_Pn | 0.869 * | −0.387 | 0.136 | 0.123 | 23.829 | 20 |
| H_Tr | 0.827 * | −0.112 | −0.032 | −0.306 | 20.368 | 22 |
| H_Gi | −0.572 | −0.313 | −0.104 | 0.496 | −21.958 | 56 |
| H_Gs | 0.681 | −0.018 | −0.657 | 0.201 | 14.627 | 30 |
| J_AGB | 0.823 * | −0.462 | −0.053 | 0.223 | 18.654 | 24 |
| J_BGB | 0.845 * | −0.437 | −0.099 | 0.088 | 17.325 | 25 |
| J_L | 0.673 | 0.577 | 0.284 | 0.039 | 42.746 | 4 |
| J_RSR | 0.597 | −0.339 | −0.285 | −0.637 | −2.161 | 47 |
| J_SRL | −0.371 | 0.819 * | 0.364 | −0.220 | 10.959 | 35 |
| J_SSA | 0.396 | 0.857 * | 0.232 | −0.018 | 38.702 | 10 |
| J_SOD | −0.686 | 0.312 | 0.569 | −0.104 | −7.455 | 49 |
| J_POD | 0.025 | −0.475 | 0.628 | −0.598 | −9.243 | 50 |
| J_CAT | 0.687 | −0.201 | −0.017 | −0.232 | 14.675 | 29 |
| J_MDA | 0.861 * | −0.202 | −0.290 | −0.276 | 15.378 | 27 |
| J_SP | 0.837 * | 0.286 | −0.303 | 0.307 | 35.034 | 13 |
| J_Pro | 0.286 | 0.642 | 0.274 | 0.596 | 39.062 | 8 |
| C_AGB | 0.910 * | 0.121 | 0.389 | −0.010 | 40.351 | 7 |
| C_BGB | 0.909 * | −0.259 | 0.251 | 0.174 | 31.071 | 16 |
| C_L | 0.696 | 0.370 | 0.592 | 0.166 | 45.273 | 1 |
| C_RSR | −0.310 | −0.889 | −0.141 | 0.307 | −30.912 | 58 |
| C_SRL | −0.070 | 0.824 * | 0.433 | −0.326 | 20.951 | 21 |
| C_SSA | 0.877 | 0.420 | 0.177 | −0.154 | 41.163 | 5 |
| C_SOD | −0.332 | 0.704 | 0.120 | 0.476 | 15.313 | 28 |
| C_POD | 0.097 | −0.721 | 0.615 | 0.082 | −3.445 | 48 |
| C_CAT | 0.456 | 0.094 | −0.504 | −0.697 | −0.551 | 45 |
| C_MDA | 0.530 | 0.147 | −0.667 | 0.425 | 16.706 | 26 |
| C_SP | −0.412 | −0.318 | −0.428 | 0.530 | −21.563 | 55 |
| C_Pro | 0.722 * | 0.213 | 0.617 | 0.226 | 43.476 | 3 |
| SY | 0.947 * | 0.033 | −0.138 | 0.099 | 32.158 | 14 |
| NES | 0.771 | 0.509 | −0.206 | 0.128 | 37.463 | 12 |
| AN | 0.506 | 0.249 | −0.054 | 0.318 | 27.159 | 18 |
| 1000-SW | −0.198 | −0.861 | 0.047 | 0.259 | −23.948 | 57 |
| Eigenvalue | 20.406 | 15.137 | 10.017 | 8.623 | ||
| Contribution rate (%) | 34.009 | 25.228 | 16.694 | 14.371 | ||
| Cumulative contribution rate (%) | 34.009 | 59.238 | 75.932 | 90.303 |
*: Factor loadings > 0.700.
References
- FAO. Global Status of Salt-Affected Soils—Main Report; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhao, H.L.; Chen, X.B. Research Status and Prospects of Saline-alkali Land Amelioration in the Coastal Region of China. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2022, 38, 67–74. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, J.; Li, X.Y.; Li, Z.Q.; Wang, X.T.; Hou, N.; Li, D.P. Remediation of soda-saline-alkali soil through soil amendments: Microbially mediated carbon and nitrogen cycles and remediation mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 924, 171641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C. Genetic mechanisms of salt stress responses in halophytes. Plant Signal. Behav. 2020, 15, 1704528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.S.; Lian, X.J.; Wang, W.; Zhao, T.K.; Li, H.J. Research progress of green manure in China. Pratacult. Sci. 2013, 30, 1135–1140. [Google Scholar]
- Zhen, J.D. Effects of Soil Salt Content on Photosynthesis, Biomass Accumulation and Carbon and Nitrogen Physiology of Rapeseed. Master’s Thesis, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.M.; Li, Y.Y.; Huang, Y.H.; Wang, Y.; Qu, W.T.; Lin, Y.W.; Wang, L.; Lin, G.B.; Zuo, Q.S. Response of rapeseed growth to soil salinity content and its improvement effect on coastal saline soil. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 16, 1601627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Guo, L.; Wang, S.B.; Wang, X.Y.; Ren, M.; Zhao, P.J.; Huang, Z.Y.; Jia, H.J.; Wang, J.H.; Lin, A.J. Effective strategies for reclamation of saline-alkali soil and response mechanisms of the soil-plant system. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Y.; Peng, T.; Xue, S.W. Mechanisms of plant saline-alkaline tolerance. J. Plant Physiol. 2023, 281, 153916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.M.; Li, A.G.; Li, H.P.; Guan, M.W.; Wu, J.Y.; Shun, W.C.; Zhai, L.J.; Ma, L.; Guo, A.Q. Identification and screening of saline-alkali tolerant winter rapeseed varieties in the Bohai Rim region. Chin. J. Oil Crop Sci. 2025, 47, 402–412. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Lian, Y.T.; Li, S.Y.; Fahim, A.M.; Hou, X.F.; Liu, L.J.; Pu, Y.Y.; Yang, G.; Wang, W.T.; Wu, J.Y.; et al. Integrated transcriptome and metabolome analysis revealed molecular regulatory mechanism of saline-alkali stress tolerance and identified bHLH142 in winter rapeseed (Brassica rapa). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 295, 139542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Z.B.; Dong, Y.H.; Li, G.T.; Zhong, Z.X. Cultivation Technology of Rapeseed in Salt-Alkali Land in Weibei Area of Shaanxi. China Seed Ind. 2024, 5, 173–175. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.T.; Zhang, X.Y.; Wu, G.F.; Huang, L.; Yuan, X.X.; Chen, X.; Liu, X.Y.; Xue, C.C. Comprehensive Evaluation of Salt Tolerance of Soybean Germplasm Resources Based on Principal Component and Membership Function Analysis. Soybean Sci. 2025, 44, 22–32. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.S. Plant Physiology Experiment Guidance, 5th ed.; Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.K. Principles and Techniques of Plant Physiology and Biochemical Experiments, 2nd ed.; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Yin, Z.Q.; Wu, B.C.; Xu, M.L.; Liu, C.; Shi, H.S.; Pang, B.; Miao, X.F. Effects of Compound Saline-Alkali Stress on Germination Period of Different Foxtail Millet Varieties and Screening of Saline-Alkali Tolerance Varieties. Crops 2024, 3, 207–215. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, N.J.; Yu, M.L.; Li, Y.; Jin, D.; Zhang, D.F. Prohexadione-calcium alleviates saline-alkali stress in soybean seedlings by improving the photosynthesis and up-regulating antioxidant defense. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 220, 112369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Ye, M.Y.; Wu, T.T.; Ma, H. Evaluation and Heritability Analysis of the Seed Vigor of Soybean Strains Tested in the Huanghuaihai Regional Test of China. Plants 2023, 12, 1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.Y.; Tian, Y.M.; Qu, Z.P.; Wang, J.X.; Han, D.Z.; Dong, S.K. Comparing the Salt Tolerance of Different Spring Soybean Varieties at the Germination Stage. Plants 2023, 12, 2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, W.H.; Pu, H.M.; Zhang, J.F.; Qi, C.K.; Zhang, X.K. Screening of Brassica napus for salinity tolerance at germination stage. Chin. J. Oil Crop Sci. 2013, 35, 271–275. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.F.; Mou, J.M.; Dang, K.; Shao, X.W.; Geng, Y.Q.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, L.T.; Guo, L.Y. Insights into physiological, biochemical and molecular responses in wheat under salt stress. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2024, 52, 112–122. [Google Scholar]
- Kesh, H.; Devi, S.; Kumar, N.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, A.; Dhansu, P.; Sheoran, P.; Mann, A. Insights into Physiological, Biochemical and Molecular Responses in Wheat under Salt Stress. In Wheat-Recent Advances, 10th ed.; Ansari, M.-u.-R., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shao, Y.; Feng, X.H.; Otie, V.; Matsuura, A.; Irshad, M.; Zheng, Y.R.; An, P. Cell Wall Components and Extensibility Regulate Root Growth in Suaeda salsa and Spinacia oleracea under Salinity. Plants 2022, 11, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehzadi, S.; Faiza, G.G.Y. Effect of Salt Stress on the Germination and Early Seedling Growth in Okra (Abelmoschus esculentus). Sarhad J. Agric. 2022, 38, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montez, M.; Majchrowska, M.; Krzyszton, M.; Bokota, G.; Sacharowski, S.; Wrona, M.; Yatusevich, R.; Massana, F.; Plewczynski, D.; Swiezewski, S. Promoter-pervasive transcription causes RNA polymerase II pausing to boost DOG1 expression in response to salt. EMBO J. 2023, 42, e112443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.J.; Weng, X.L.; Jiang, L.Q.; Huang, Y.; Wu, H.; Wang, K.J.; Li, K.; Guo, X.Q.; Zhu, G.L.; Zhou, G.S. Screening and Evaluation of Salt-Tolerant Wheat Germplasm Based on the Main Morphological Indices at the Germination and Seedling Stages. Plants 2024, 13, 3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeeshan, M.; Lu, M.; Sehar, S.; Holford, P.; Wu, F. Comparison of Biochemical, Anatomical, Morphological, and Physiological Responses to Salinity Stress in Wheat and Barley Genotypes Deferring in Salinity Tolerance. Agronomy 2020, 10, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, R.; Zhan, N.; Geng, R.D.; Xu, K.; Zhou, X.C.; Li, L.X.; Yan, G.X.; Zhou, F.L.; Cai, G.Q. Progress on Salt Tolerance in Brassica napus. Plants 2024, 13, 1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, B.; Huang, B. Mechanism of salinity tolerance in plants: Physiological, biochemical, and molecular characterization. Int. J. Genom. 2014, 2014, 701596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aycan, M.; Baslam, M.; Mitsui, T.; Yildiz, M. Assessing Contrasting Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Cultivars Responsiveness to Salinity at the Seedling Stage and Screening of Tolerance Marker Traits. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2024, 43, 2646–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najar, R.; Aydi, S.; Sassi-Aydi, S.; Zarai, A.; Abdelly, C. Effect of salt stress on photosynthesis and chlorophyll fluorescence in Medicago truncatula. Plant Biosyst. 2019, 153, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, P.; Feng, N.; Zheng, D. Regulation of Photosynthetic Capacity and Ion Metabolism of Oilseed Rape Under Salt Stress by Prohexadione-Calcium Priming. 2024. Available online: https://www.preprints.org/manuscript/202403.1080/v1 (accessed on 11 July 2025).
- Wang, C.L.; Hai, J.B.; Yang, J.L.; Tian, J.H.; Chen, W.J.; Chen, T.; Luo, H.B.; Wang, H. Influence of leaf and silique photosynthesis on seeds yield and seeds oil quality of oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Eur. J. Agron. 2016, 74, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.Q. Study on the Mechanism of Salt Exclusion in the Roots of Suaeda salsa in Different Habitats. Master’s Thesis, Shandong Normal University, Jinan, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Liu, C.X.; Xu, B.; Dong, R.S.; Huan, H.F.; Huang, C.Q.; Yan, L.Q.; Wang, W.Q.; Yang, H.B.; Yu, D.G.; et al. Plant Salt-exclusion Mechanism: A Review. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2023, 39, 86–94. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.X.; Zhang, J.L.; Lu, N.; Wang, S.M. The characteristics of free proline distribution in various types of salt-resistant plants. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 2006, 1, 36–41. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.C.; Xia, Z.L.; Zhou, C.J.; Wang, G.; Meng, X.; Yin, P.C. Insights into Salinity Tolerance in Wheat. Genes 2024, 15, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Latef, A.A.H.; Abu Alhmad, M.F.; Kordrostami, M.; Abo Baker, A.A.; Zakir, A. Inoculation with Azospirillum lipoferum or Azotobacter chroococcum Reinforces Maize Growth by Improving Physiological Activities Under Saline Conditions. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2020, 39, 1293–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.Q.; Xie, N.; Cui, S.Q.; Shun, G.T.; Pan, X.; Zhang, L.F.; Liu, Z.K.; Liu, Z.Y.; Zhang, H.F.; Li, Y.N.; et al. Evaluation of Salt Tolerance of 16 Alfalfa Varieties under Different Salt Concentration Stress at Germination Stage. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 2025, 33, 472–480. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, M.; Gupta, N.; Kaur, N.; Sohu, R.S.; Mahal, A.K.; Choudhary, A. Preliminary screening of sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L.) germplasm for salinity stress tolerance at the early seedling stage. Cereal Res. Commun. 2023, 51, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.B.; Song, H.F.; Zhang, L.Y. New Insight into Plant Saline-Alkali Tolerance Mechanisms and Application to Breeding. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Song, J.W.; Fan, W.; He, Z.L.; Zhang, X.Y. Evaluation of comprehensive alkali resistance in tomato germplasm seedlings. Euphytica 2025, 221, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Takano, T.; Liu, S.K. Screening and Evaluation of Saline—Alkaline Tolerant Germplasm of Rice (Oryza sativa L.) in Soda Saline—Alkali Soil. Agronomy 2018, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).