Improving Groundcover Establishment Through Seed Rate, Seed Ratio, and Hydrophilic Seed Coating
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
2.2. Field Plot Design
2.3. Seed Germination Testing
2.4. Field Plot Management
2.5. Soil pH Test
2.6. Data Collection
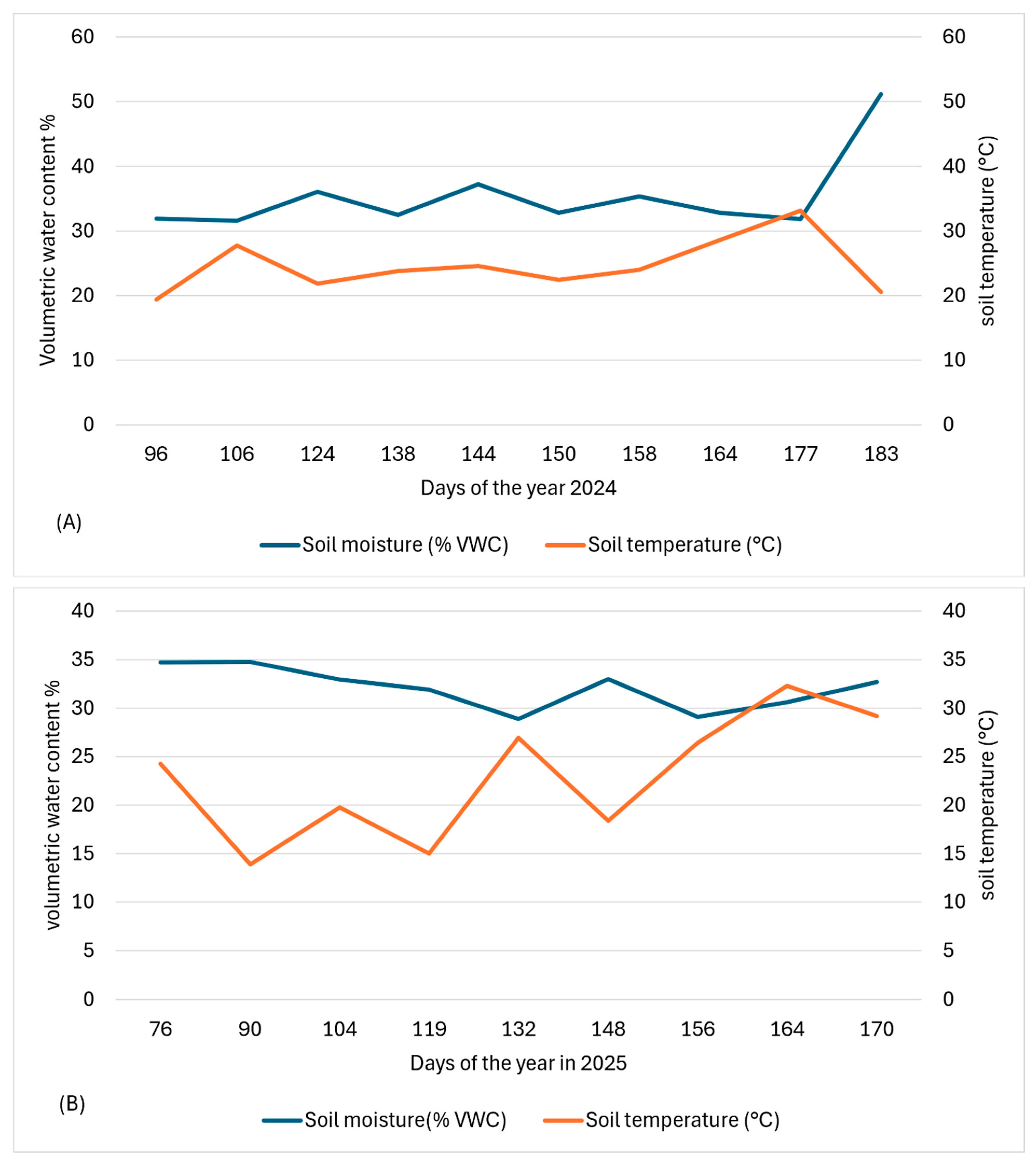
2.7. Weather Conditions
2.8. Species Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Environmental Conditions
3.2. Seed Germination Testing
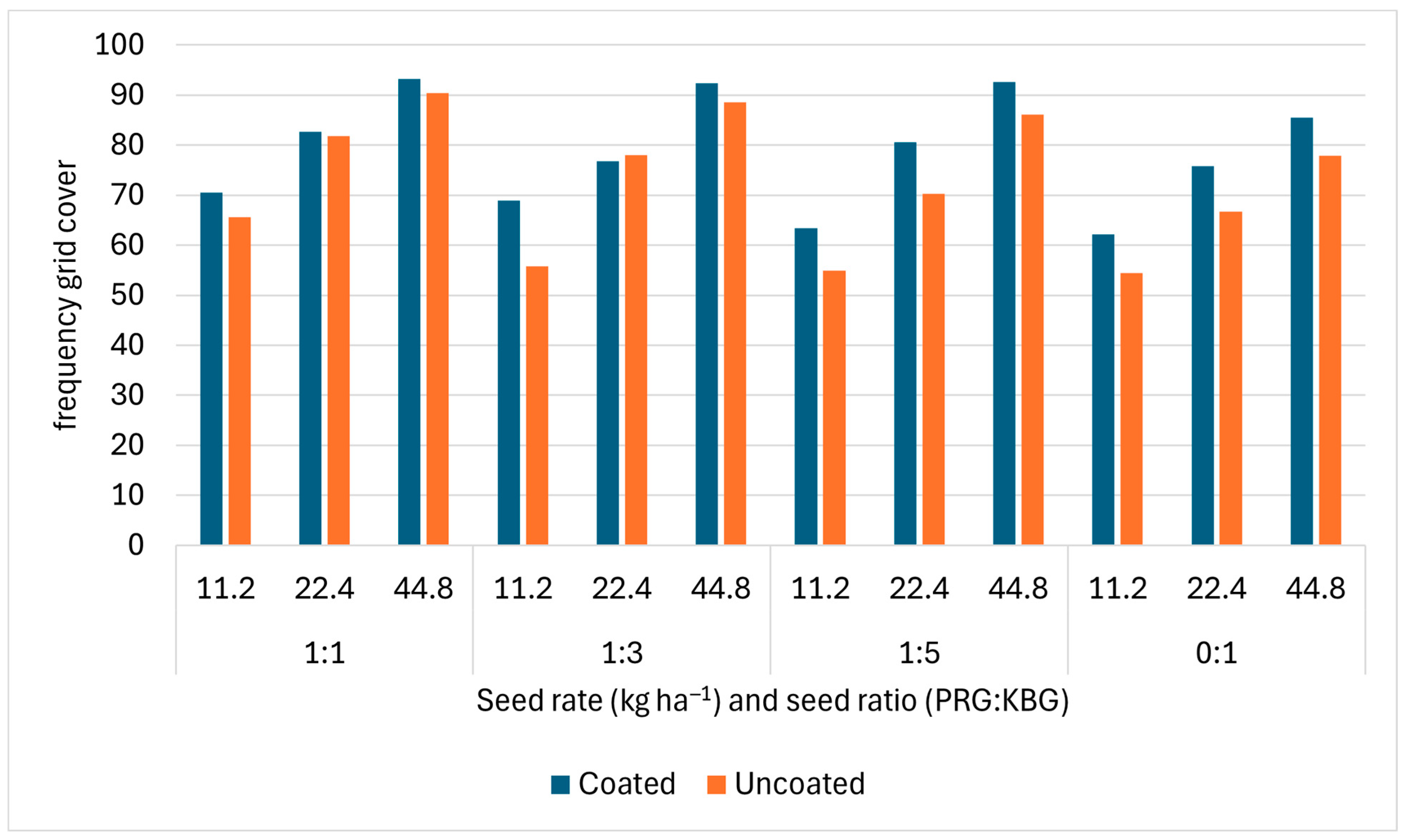
3.3. Fall Grid Cover Frequency
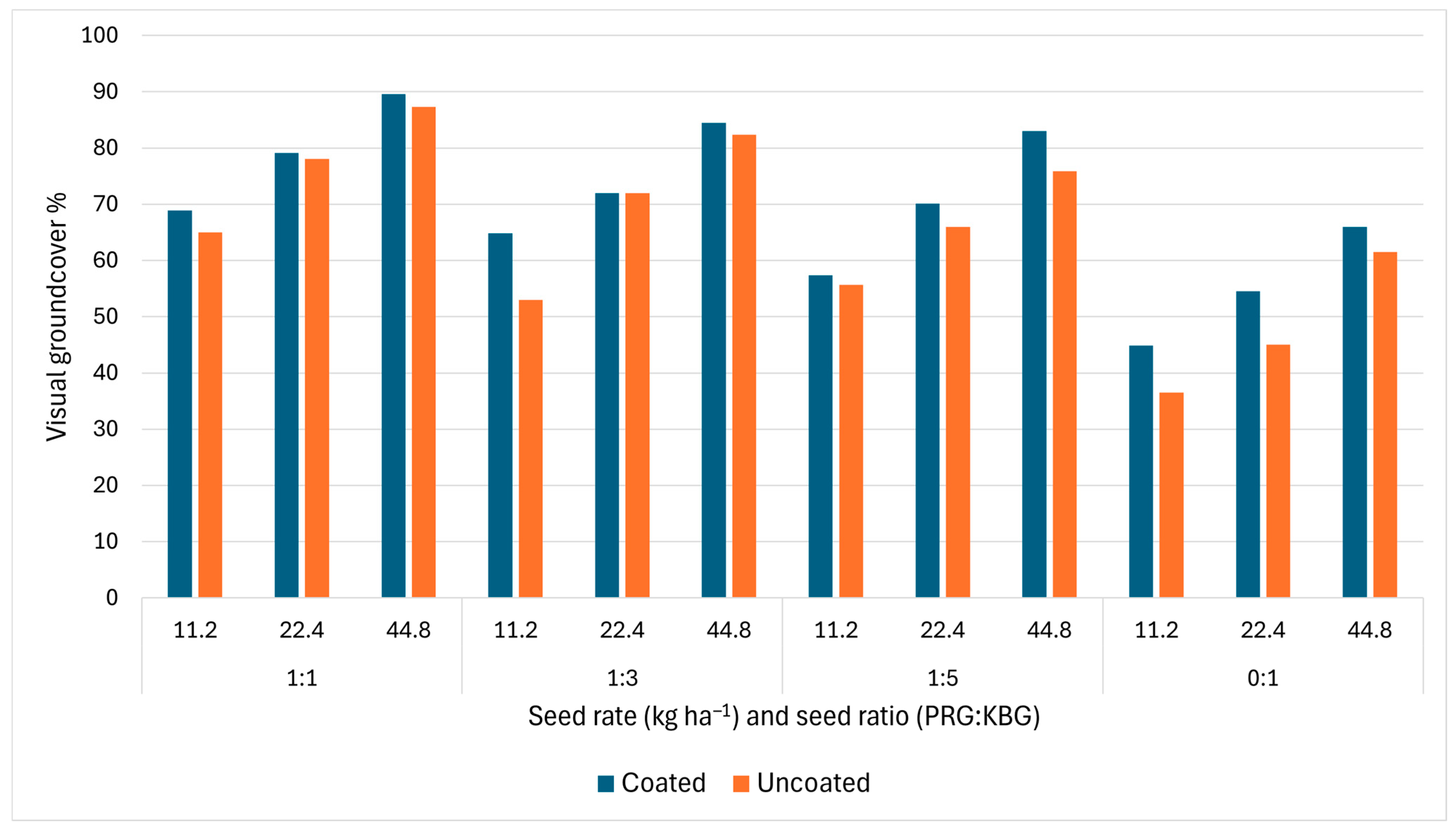
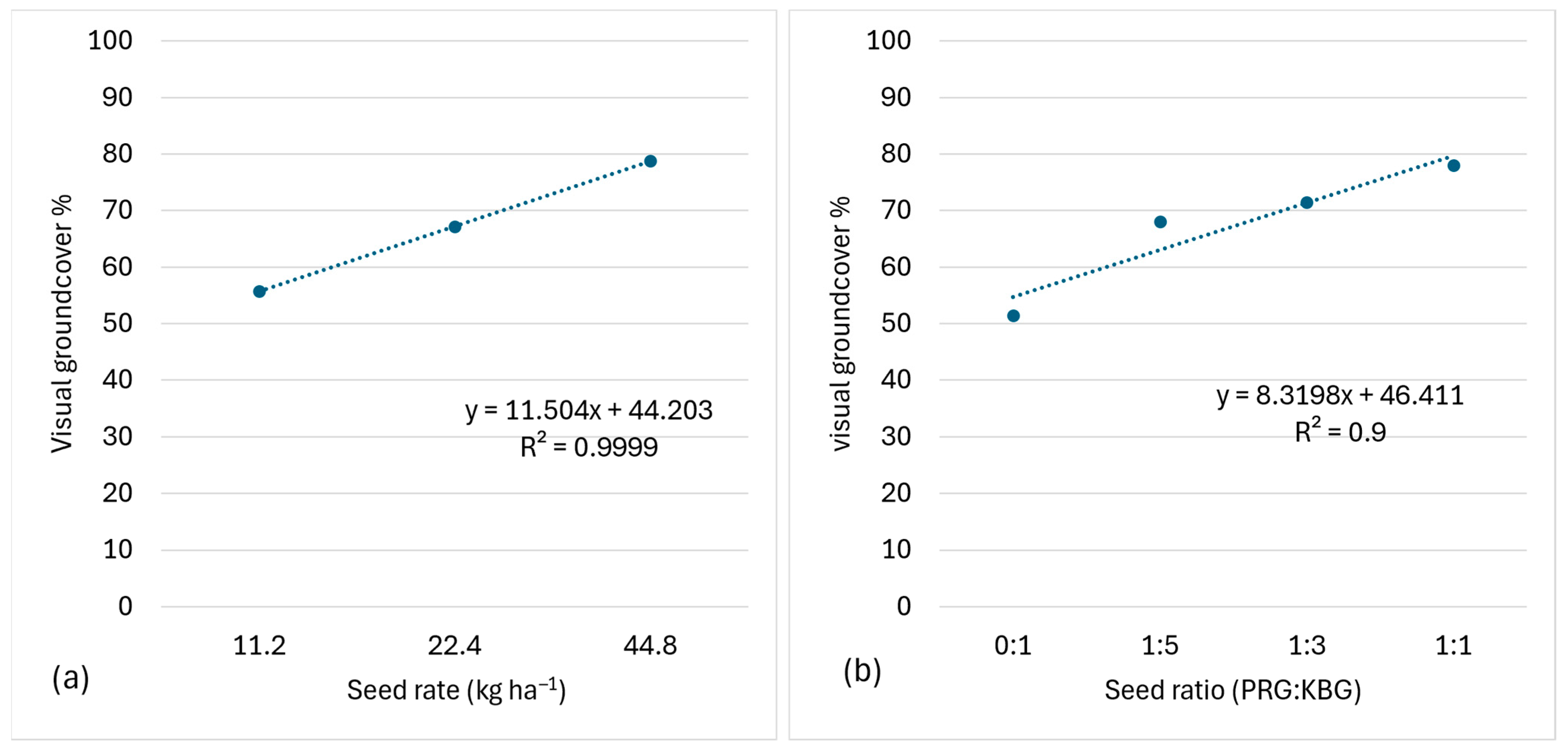
3.4. Spring/Summer Visual Ground Cover
3.5. Spring/Summer Greenness Rating
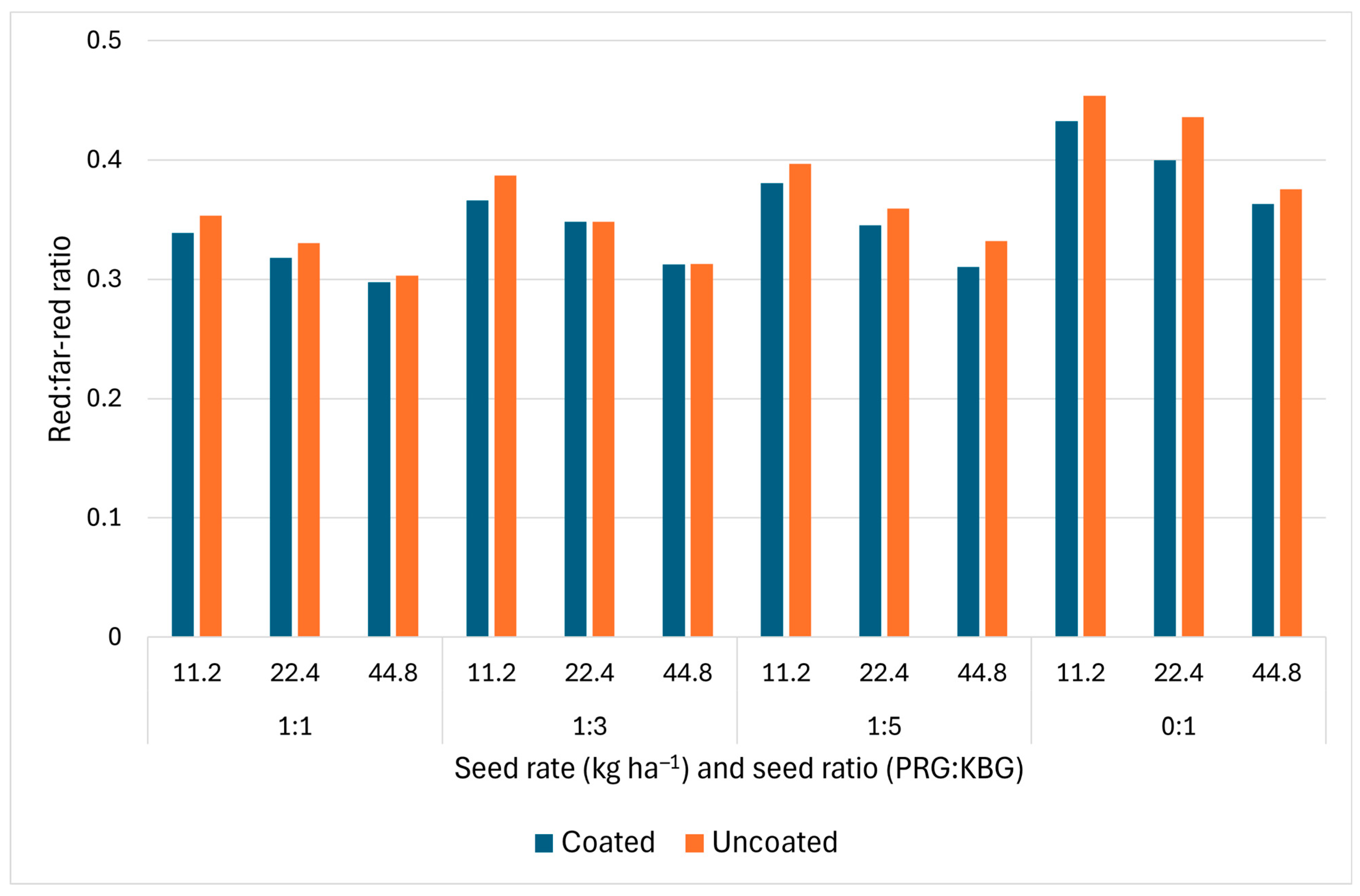
3.6. Spring/Summer Red:Far-Red Ratio
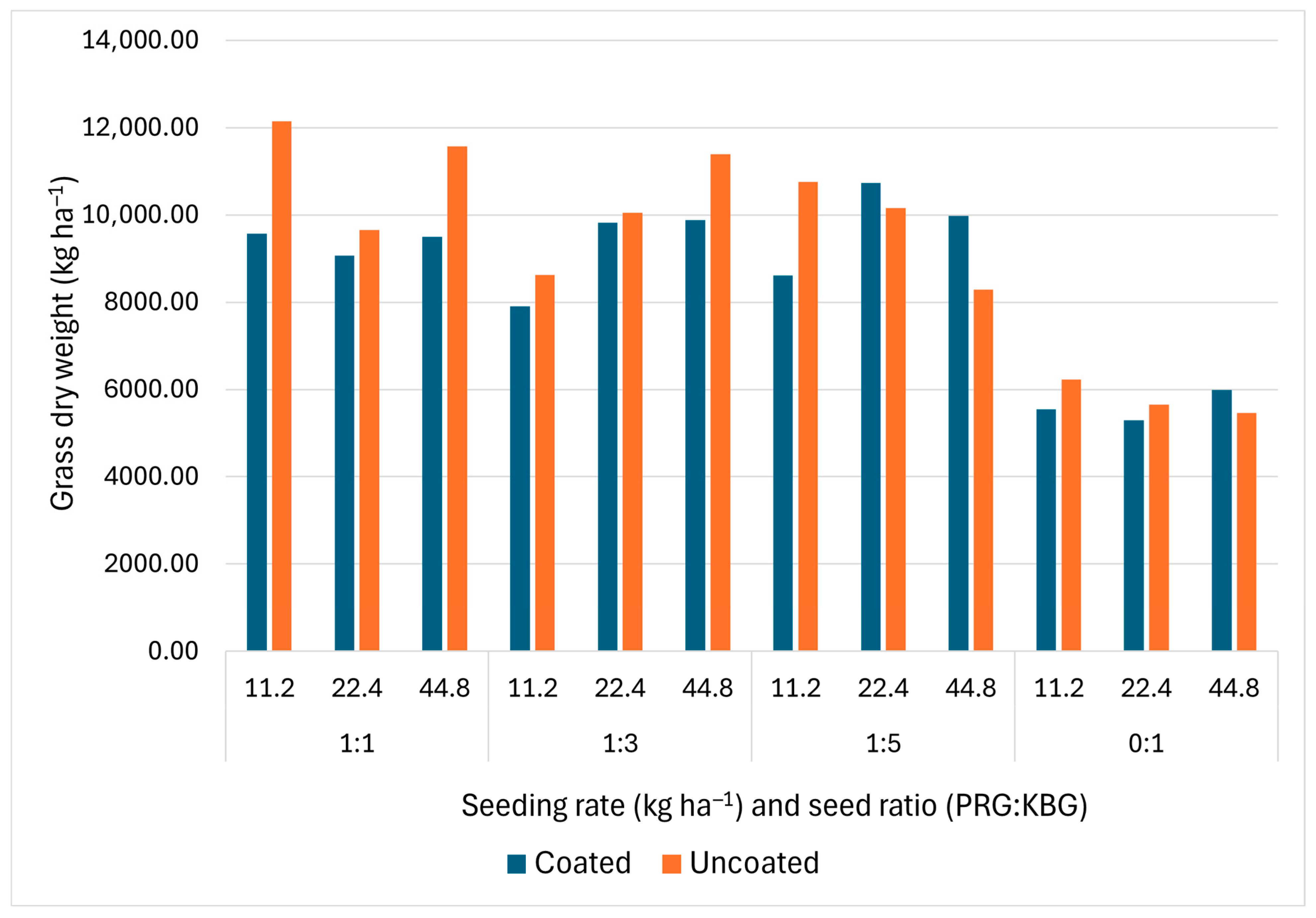
3.7. Summer Grass Dry Weight
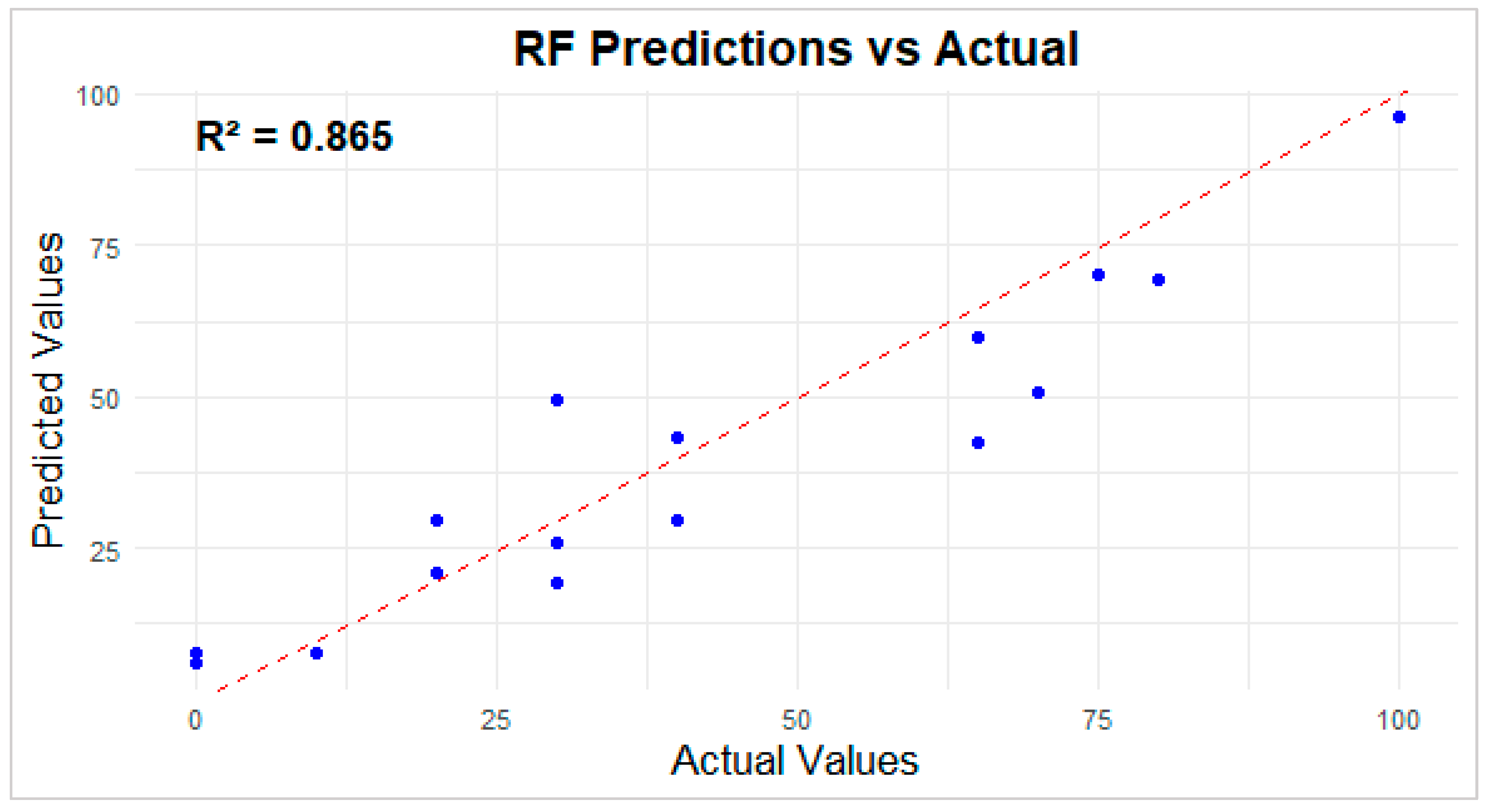
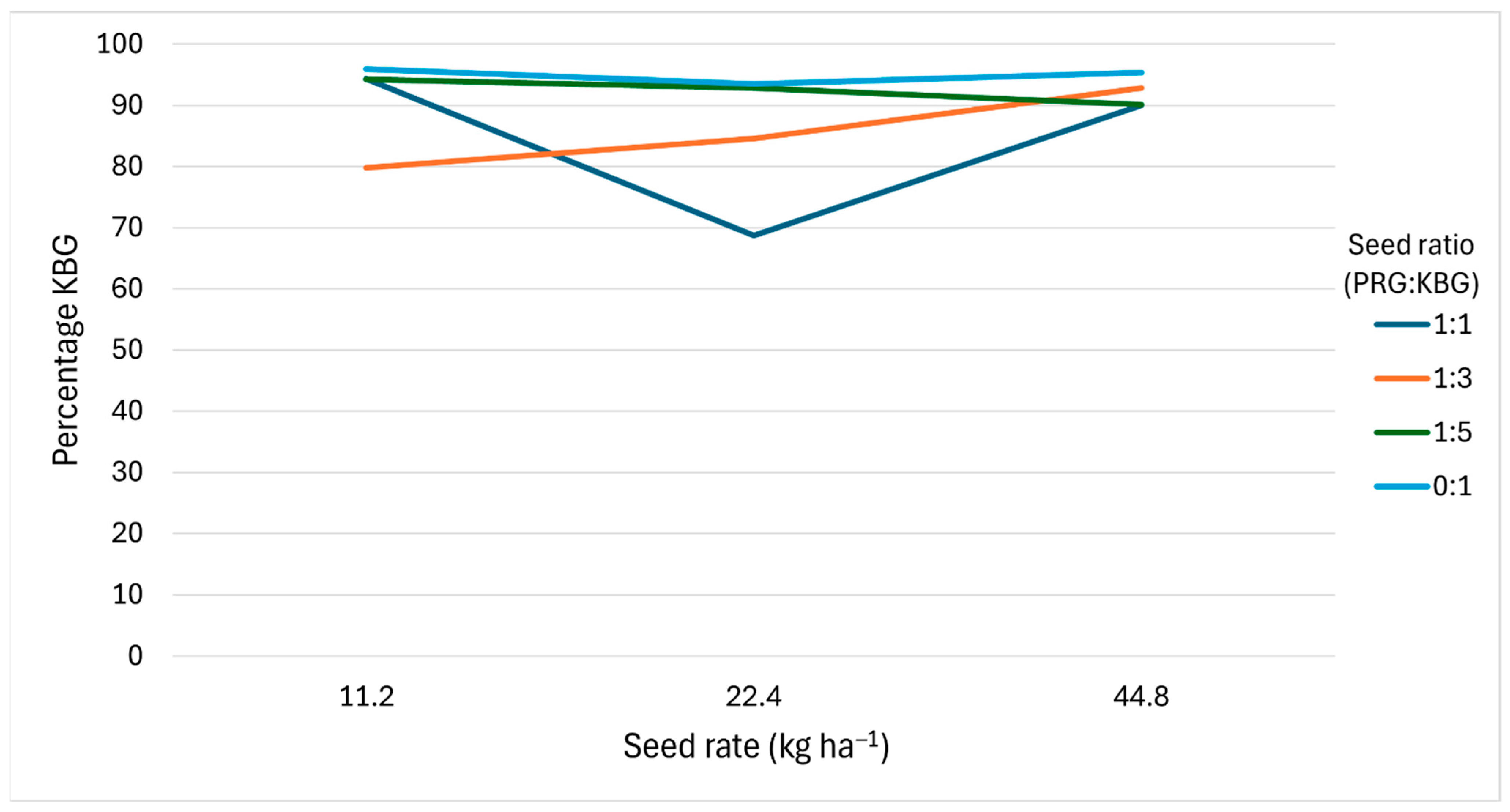
3.8. NIRS Grass Composition
4. Discussion
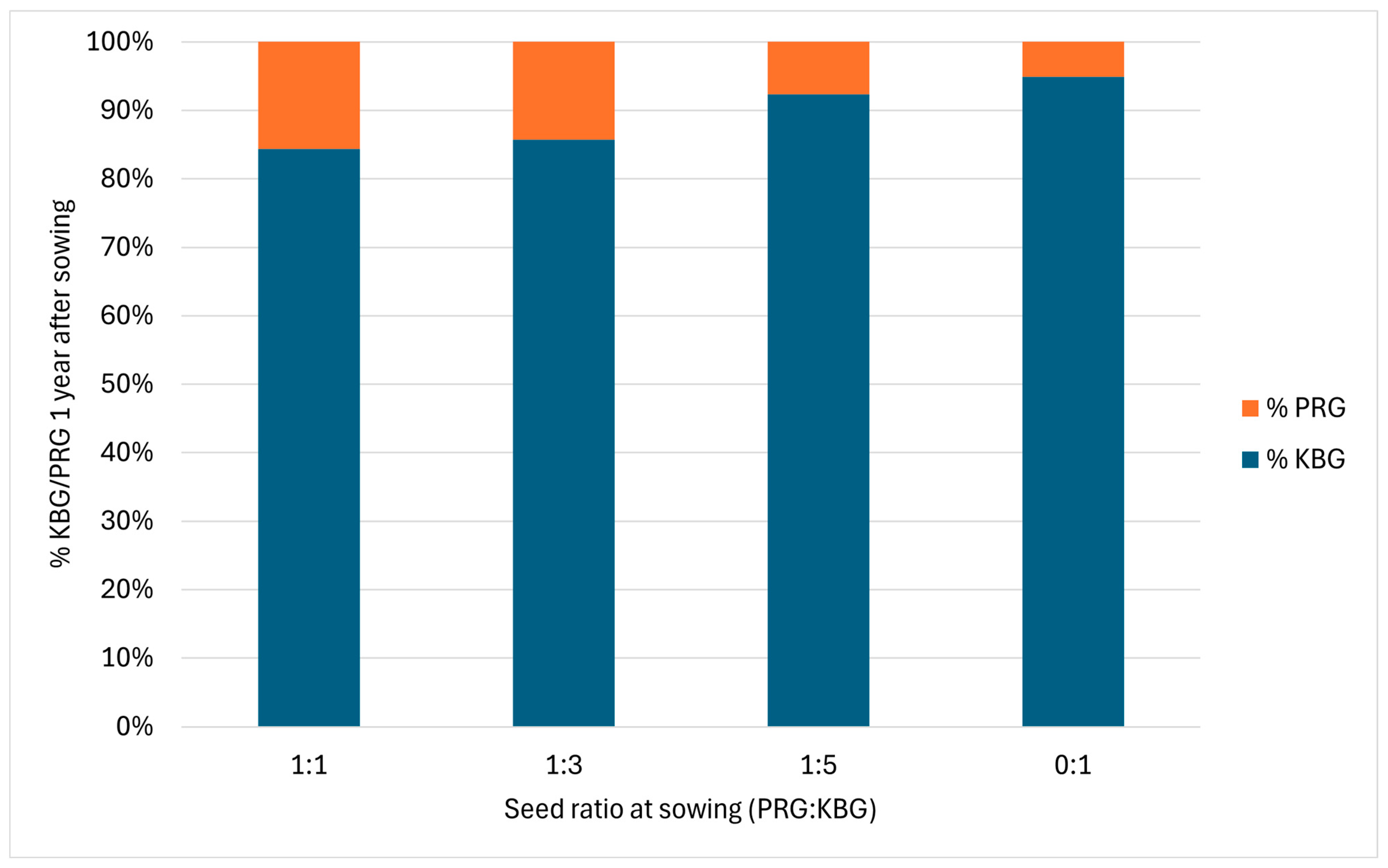
4.1. Seed Ratio
4.2. Seeding Rate
4.3. Hydrophilic Seed Coating
4.4. Species Composition
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Comer, P.J.; Hak, J.C.; Kindscher, K.; Muldavin, E.; Singhurst, J. Continent-Scale Landscape Conservation Design for Temperate Grasslands of the Great Plains and Chihuahuan Desert. Nat. Areas J. 2018, 38, 196–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nearing, M.A.; Xie, Y.; Liu, B.; Ye, Y. Natural and anthropogenic rates of soil erosion. Int. Soil. Water Conserv. Res. 2017, 5, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, C.A.; Jacobs, K.L.; Moore, K.J.; Raman, D.R. Anticipatory Technoeconomic Evaluation of Kentucky Bluegrass-Based Perennial Groundcover Implementations in Large-Scale Midwestern US Corn Production Systems. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, K.J.; Anex, R.P.; Elobeid, A.E.; Fei, S.; Flora, C.B.; Goggi, A.S.; Jacobs, K.L.; Jha, P.; Kaleita, A.L.; Karlen, D.L.; et al. Regenerating Agricultural Landscapes with Perennial Groundcover for Intensive Crop Production. Agronomy 2019, 9, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlautman, B.; Bartel, C.; Diaz-Garcia, L.; Fei, S.; Flynn, S.; Haramoto, E.; Moore, K.; Raman, D.R. Perennial groundcovers: An emerging technology for soil conservation and the sustainable intensification of agriculture. Emerg. Top. Life Sci. 2021, 5, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, C.A.; Archontoulis, S.V.; Lenssen, A.W.; Moore, K.J.; Huber, I.L.; Laird, D.A.; Dixon, P.M. Modeling perennial groundcover effects on annual maize grain crop growth with the Agricultural Production Systems sIMulator. Agron. J. 2020, 112, 1895–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.K.; Hartwig, N.L.; Hoffman, L.D. Cyanazine Losses in Runoff from No-Tillage Corn in “Living” and Dead Mulches vs. Unmulched, Conventional Tillage. J. Environ. Qual. 1984, 13, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olowoyeye, O.S.; Kaleita, A.L. Investigating Erosion under Perennial Ground Cover (PGC) Using a Rainfall Simulation Experiment. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2024, 40, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Fei, S.-Z.; Lenssen, A.W.; Moore, K.J. Evaluating cool-season grass species as potential perennial groundcover for maize production. Agron. J. 2022, 114, 2415–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beard, J.B. Turfgrass: Science and Culture; Pearson London: London, UK, 1972; ISBN 13-978-0139330025. [Google Scholar]
- Bartel, C.A.; Banik, C.; Lenssen, A.W.; Moore, K.J.; Laird, D.A.; Archontoulis, S.V.; Lamkey, K.R. Establishment of Perennial Groundcovers for Maize-Based Bioenergy Production Systems. Agron. J. 2017, 109, 822–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, E.S.; Moore, K.J.; Singer, J.W.; Lamkey, K.R. Evaluation of Grass and Legume Species as Perennial Ground Covers in Corn Production. Crop Sci. 2013, 53, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, J.E.; Sheley, R.L.; Hardegree, S.P.; Doescher, P.S.; James, J.J. Seed and seedling traits affecting critical life stage transitions and recruitment outcomes in dryland grasses. J. Appl. Ecol. 2015, 52, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, P.S.; Debaene-Gill, S.B.; Meyer, S.E. Regulation of germination timing in facultatively fall-emerging grasses. In Proceedings-Ecology and Management of Annual Rangelands; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 1994; Volume 213, pp. 215–219. [Google Scholar]
- Brede, A.D.; Duich, J.M. Establishment Characteristics of Kentucky Bluegrass-Perennial Ryegrass Turf Mixtures as Affected by Seeding Rate and Ratio1. Agron. J. 1984, 76, 875–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- England, F. Competition in mixtures of herbage grasses. J. Appl. Ecol. 1968, 5, 227–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, J.H.; Ervin, E.H.; Fresenburg, B.S. Turf performance of mixtures and blends of tall fescue, Kentucky bluegrass, and perennial ryegrass. HortScience 2002, 37, 214–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proctor, C.A.; Weisenberger, D.V.; Reicher, Z.J. Kentucky Bluegrass and Perennial Ryegrass Mixtures for Establishing Midwest Lawns. HortScience 2015, 50, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madison, J.H. Optimum Rates of Seeding Turfgrasses. Agron. J. 1966, 58, 441–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leinauer, B.; Serena, M.; Singh, D. Seed Coating and Seeding Rate Effects on Turfgrass Germination and Establishment. HortTechnol. Hortte 2010, 20, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, M.D.; Hignight, K.W. Seedling Emergence of Tall Fescue and Kentucky Bluegrass, as Affected by Two Seed Coating Techniques. HortTechnol. Hortte 2010, 20, 415–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, J.; Goggi, A.S.; Moore, K.J.; Fei, S. Investigating Seed Treatments and Soil Amendments to Improve the Establishment of Kentucky Bluegrass as a Perennial Groundcover. Seeds 2025, 4, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Follett, R.F.; Kimble, J.M. Soil Organic Carbon Input from Urban Turfgrasses. Soil. Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2010, 74, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natural Resource Conservation Service (NRCS). Web Soil Survey; NRCS: Washington, DC, USA, 2024.
- AOSA (Association of Official Seed Analysts). 2024 Rules for Testing Seeds: Principles and Procedures; AOSA: Wichita, KS, USA, 2024; Volume 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, G.W. Soil pH and Soil Acidity. In Methods of Soil Analysis; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1996; pp. 475–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, K.P.; Masters, R.A. Frequency Grid—A Simple Tool for Measuring Grassland Establishment. J. Range Manag. 2001, 54, 653–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, K.J.; Roberts, C.A.; Fritz, J.O. Indirect Estimation of Botanical Composition of Alfalfa-Smooth Bromegrass Mixtures. Agron. J. 1990, 82, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing Computer Software, version 4.4.0; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2025.
- Kursa, M.B.; Rudnicki, W.R. Feature Selection with the Boruta Package. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 36, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, J.; Zhang, C.; Xu, B.; Xue, Y.; Ren, Y. The predictive performances of random forest models with limited sample size and different species traits. Fish. Res. 2020, 227, 105534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAS Institute Inc. SAS Computer Software, version 9.4; SAS Institute Inc.: Cary, NC, USA, 2013.
- Juska, F.V.; Hanson, A.A. Effects of Interval and Height of Mowing on Growth of Merion and Common Kentucky Bluegrass (Poa pratensis L.). Agron. J. 1961, 53, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lickfeldt, D.W.; Voigt, T.B.; Hamblin, A.M. Composition and characteristics of blended Kentucky bluegrass stands. HortScience 2002, 37, 1124–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, K.; Gunn, E. Characterization of Kentucky Bluegrass Cultivars. Res. Rep. 2004, 18, 6–23. [Google Scholar]
- Samudio, S.H.; Brede, A.D. Registration of ‘Top Gun’ Perennial Ryegrass. Crop Sci. 2000, 40, 853. [Google Scholar]
- Serena, M.; Leinauer, B.; Sallenave, R.; Schiavon, M.; Maier, B. Turfgrass Establishment from Polymer-coated Seed Under Saline Irrigation. HortScience Horts 2012, 47, 1789–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loschinkohl, C.; Boehm, M.J. Composted biosolids incorporation improves turfgrass establishment on disturbed urban soil and reduces leaf rust severity. HortScience 2001, 36, 790–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, R.C.; Watkins, E.; Hollman, A.B.; Mihelich, N.T.; Patton, A.J. Investigation of cool-season species, seeding rate, and nitrogen fertilization in sod production: I. Establishment and sod tensile strength. Agron. J. 2021, 113, 4176–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, A.J. Effects of different seed treatments and coatings on the germination and establishment of four grass species. J. Turfgrass Sci. 1997, 73, 67–72. [Google Scholar]
- Blaser, E.A. Seedling competition in establishing forage plants. Agron. J. 1956, 48, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wu, X.; Li, X.; Hu, J.; Shi, H.; Guo, F.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, X. Pathways of Leymus chinensis individual aboveground biomass decline in natural semiarid grassland induced by overgrazing: A study at the plant functional trait scale. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Fei, S.-Z.; Arora, R.; Brummer, E.C.; Barker, R.E.; Jung, G.; Warnke, S.E. Identification of quantitative trait loci controlling winter hardiness in an annual × perennial ryegrass interspecific hybrid population. Mol. Breed. 2007, 19, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebman, M.; Dyck, E. Crop Rotation and Intercropping Strategies for Weed Management. Ecol. Appl. 1993, 3, 92–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohler, C.L.; Liebman, M. Weed productivity and composition in sole crops and intercrops of barley and field pea. J. Appl. Ecol. 1987, 24, 685–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haramoto, E.R. Species, Seeding Rate, and Planting Method Influence Cover Crop Services Prior To Soybean. Agron. J. 2019, 111, 1068–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehler-Cole, K.; Elmore, R.W. Seeding Rates and Productivity of Broadcast Interseeded Cover Crops. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greipsson, S. Seed coating improves establishment of surface seeded Poa pratensis used in revegetation. Seed Sci. Technol. 1999, 27, 1029–1032. [Google Scholar]
- Berdahl, J.D.; Barker, R.E. Germination and Emergence of Russian Wildrye Seeds Coated with Hydrophilic Materials1. Agron. J. 1980, 72, 1006–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruneau, A.H.; Peacock, C.H.; DiPaola, J.M. Cool season turfgrass establishment with fertilizer coated seed. Intl. Turfgrass Soc. Res. J. 1989, 6, 263–265. [Google Scholar]
- Hummel, N.W. Coated seed. In Turfgrass Handbook; Academic Press (Elsevier): Cambridge, MA, USA, 1991; pp. 56–60. [Google Scholar]
- Munshaw, G.C.; Layton, J.M.; Stewart, B.R.; Philley, H.W.; Beasley, J.S.; Lemus, R.W. The germination responses of five bermudagrass cultivars to seedcoating and temperature. HortScience 2014, 49, 1225–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D. Effects of seed coating on establishment. N. Z. J. Ag. Res. 1975, 18, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorim, L.; Asch, F. Seed coating reduces respiration losses and affects sugar metabolism during germination and early seedling growth in cereals. Funct. Plant Biol. 2014, 42, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorim, L.; Asch, F. Seed coating with hydro-absorbers as potential mitigation of early season drought in Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L. Moench). Biology 2017, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hathcock, A.L.; Dernoeden, P.H.; Turner, T.R.; McIntosh, M.S. Tall Fescue and Kentucky Bluegrass Response to Fertilizer and Lime Seed Coatings. Agron. J. 1984, 76, 879–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vartha, E.W.; Clifford, P.T.P. Effects of seed coating on establishment and survival of grasses, surface-sown on tussock grasslands. N. Z. J. Exp. Agric. 1973, 1, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.R., III. Effect of Cultural Factors on Tall Fescue-Kentucky Bluegrass Sod Quality and Botanical Composition. In Proceedings of the Third International Turfgrass Research Conference; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1980; pp. 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiang, T.; Carey, K.; He, B.; Eggens, J.L. Composition of mixtures of four turfgrass species four years after seeding under non-wear conditions. Int. Turfgrass Soc. Res. J. 1997, 8, 671–679. [Google Scholar]


| Trt # | Seeding Rate (kg/ha) | PRG:KBG Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 11:2 | 0:1 |
| 2 | 11:2 | 1:1 |
| 3 | 11:2 | 1:3 |
| 4 | 11:2 | 1:5 |
| 5 | 22:4 | 0:1 |
| 6 | 22:4 | 1:1 |
| 7 | 22:4 | 1:3 |
| 8 | 22:4 | 1:5 |
| 9 | 44:8 | 0:1 |
| 10 | 44:8 | 1:1 |
| 11 | 44:8 | 1:3 |
| 12 | 44:8 | 1:5 |
| Mean Temperature (°C) | Total Rainfall (mm) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | 2023 | 2024 | 30-yr. avg. | 2023 | 2024 | 30-yr. avg. |
| August | 21.5 | 21.2 | 21.6 | 38.3 | 43.7 | 95.3 |
| September | 19 | 18.5 | 17.7 | 36.6 | 6.9 | 84.2 |
| October | 11.6 | 13.2 | 10.5 | 71.9 | 48.8 | 72.2 |
| November | 3.6 | 4.6 | 2.9 | 6.6 | 74.2 | 44.8 |
| December | 1.4 | −2.3 | −3.8 | 29 | 35.6 | 35.8 |
| Mean Temperature (°C) | Total Rainfall (mm) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | 2024 | 2025 | 30-yr. avg. | 2024 | 2025 | 30-yr. avg. |
| January | −6.8 | −8.1 | −7.1 | 54.6 | 6.6 | 25.7 |
| February | 2.1 | −6.9 | −5.1 | 4.3 | 6.7 | 27.4 |
| March | 4.1 | 5.0 | 2 | 47.2 | 72.4 | 49 |
| April | 9.9 | 8.5 | 8.9 | 89 | 99.8 | 95.1 |
| May | 15.8 | 14.7 | 15.4 | 245.4 | 76.2 | 133.4 |
| June | 22 | 21.2 | 121.1 | 142.4 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moran, J.; Goggi, A.S.; Moore, K.J.; Fei, S.-z.; Gruss, S. Improving Groundcover Establishment Through Seed Rate, Seed Ratio, and Hydrophilic Seed Coating. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1927. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081927
Moran J, Goggi AS, Moore KJ, Fei S-z, Gruss S. Improving Groundcover Establishment Through Seed Rate, Seed Ratio, and Hydrophilic Seed Coating. Agronomy. 2025; 15(8):1927. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081927
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoran, Jack, A. Susana Goggi, Ken J. Moore, Shui-zhang Fei, and Shelby Gruss. 2025. "Improving Groundcover Establishment Through Seed Rate, Seed Ratio, and Hydrophilic Seed Coating" Agronomy 15, no. 8: 1927. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081927
APA StyleMoran, J., Goggi, A. S., Moore, K. J., Fei, S.-z., & Gruss, S. (2025). Improving Groundcover Establishment Through Seed Rate, Seed Ratio, and Hydrophilic Seed Coating. Agronomy, 15(8), 1927. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081927









