Design and Optimization Experiment of a Cam-Swing Link Precision Metering Device for Peanut Based on Simulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
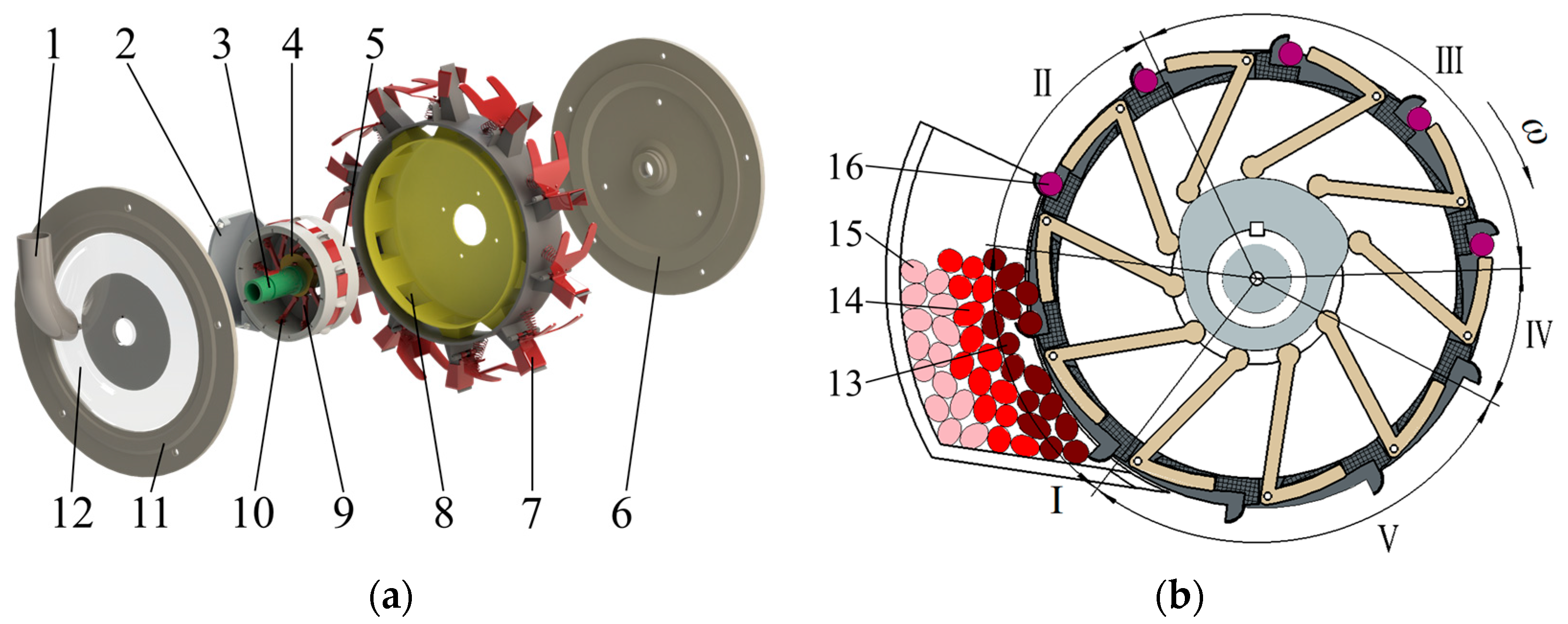
2.1. Overall Structure
2.2. Working Process
2.3. Key Component Design
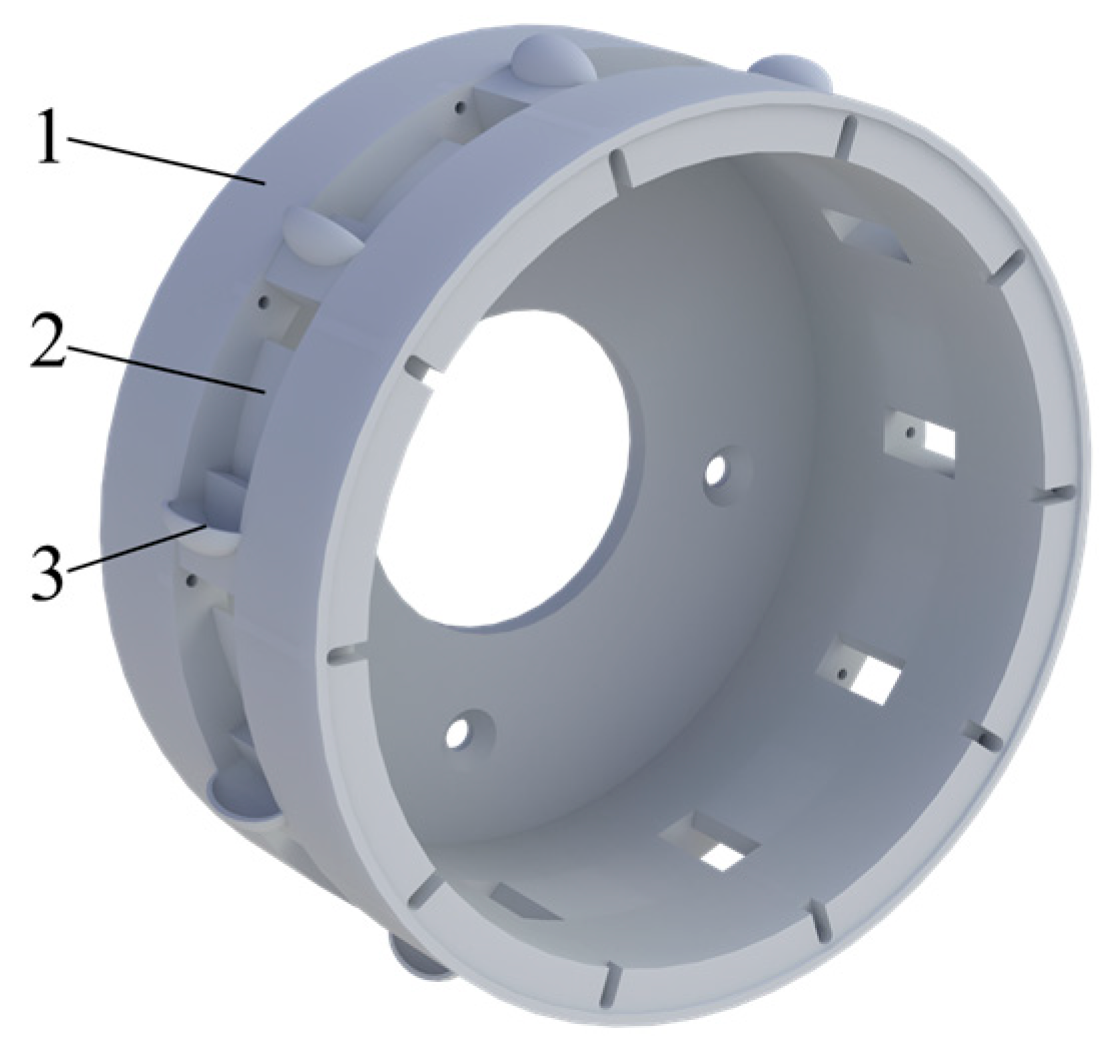
2.3.1. Seeding Disc Design
Type Hole Structure Design
Analysis of the Number of Type Holes
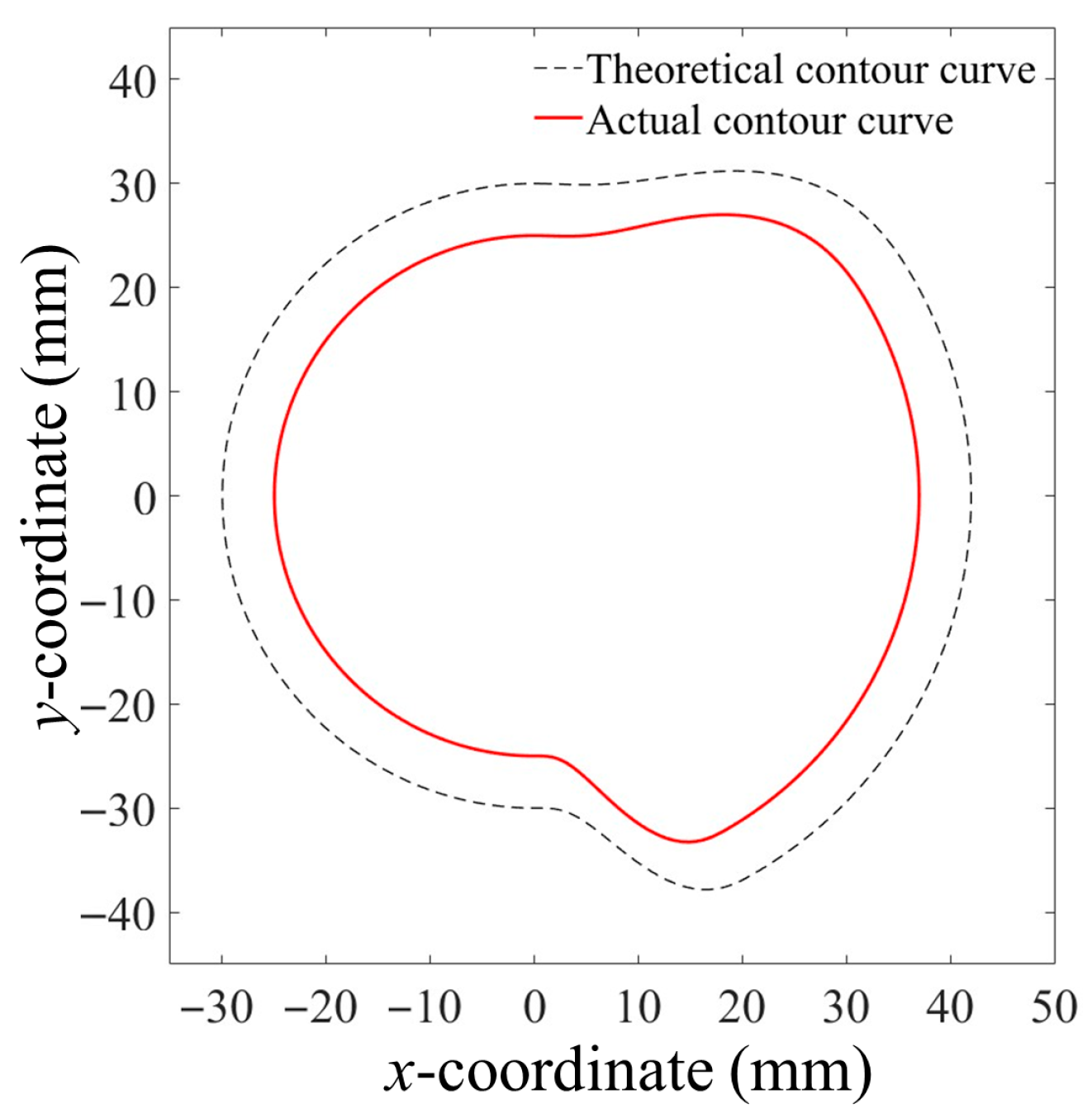
Curve Design of the Seed-Guiding Groove
2.3.2. Design of the Cam-Swing Link Mechanism
Analysis of Base Circle Diameter
Design of the Swing Link
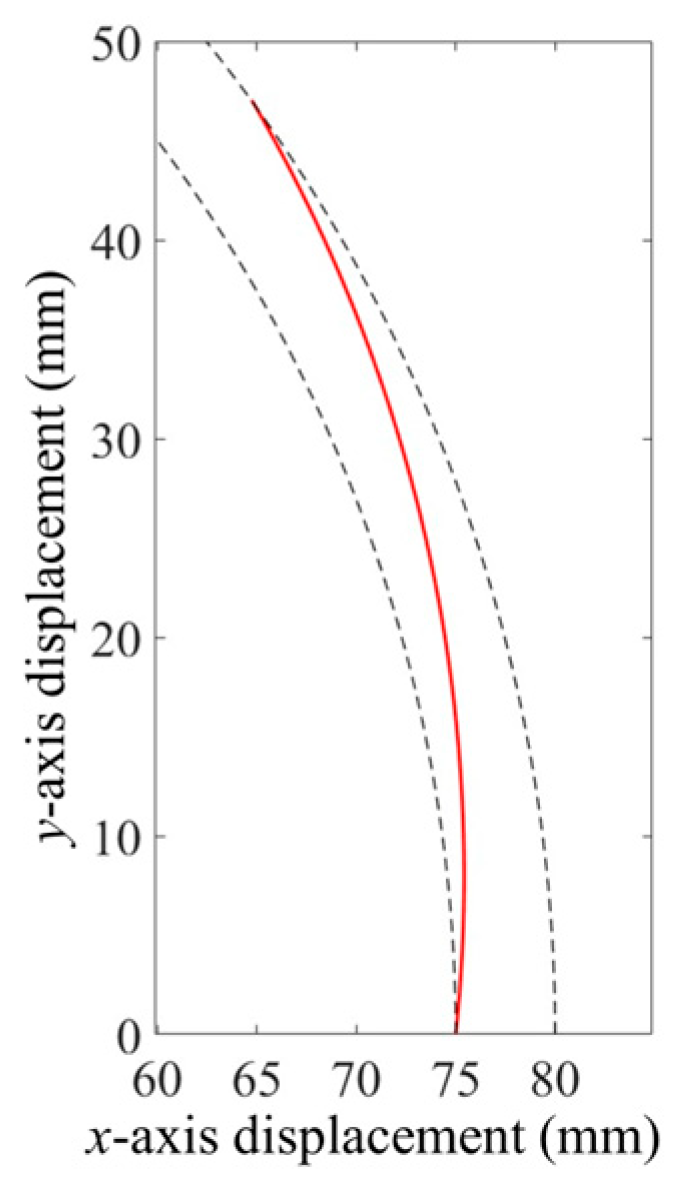
Motion Law of the Swing Link and Cam Profile Analysis
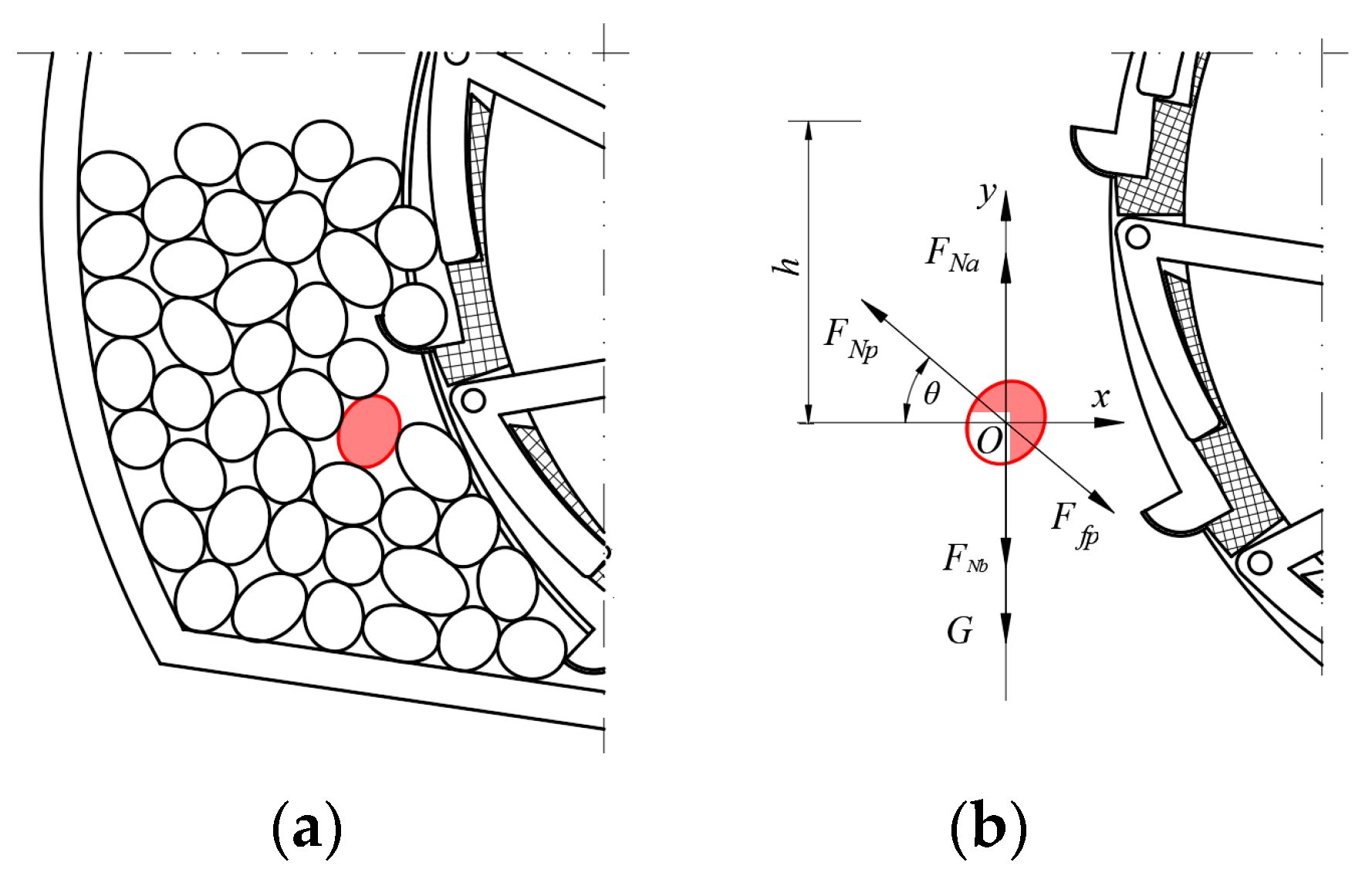
2.3.3. Analysis of Factors Influencing Seed-Filling Performance
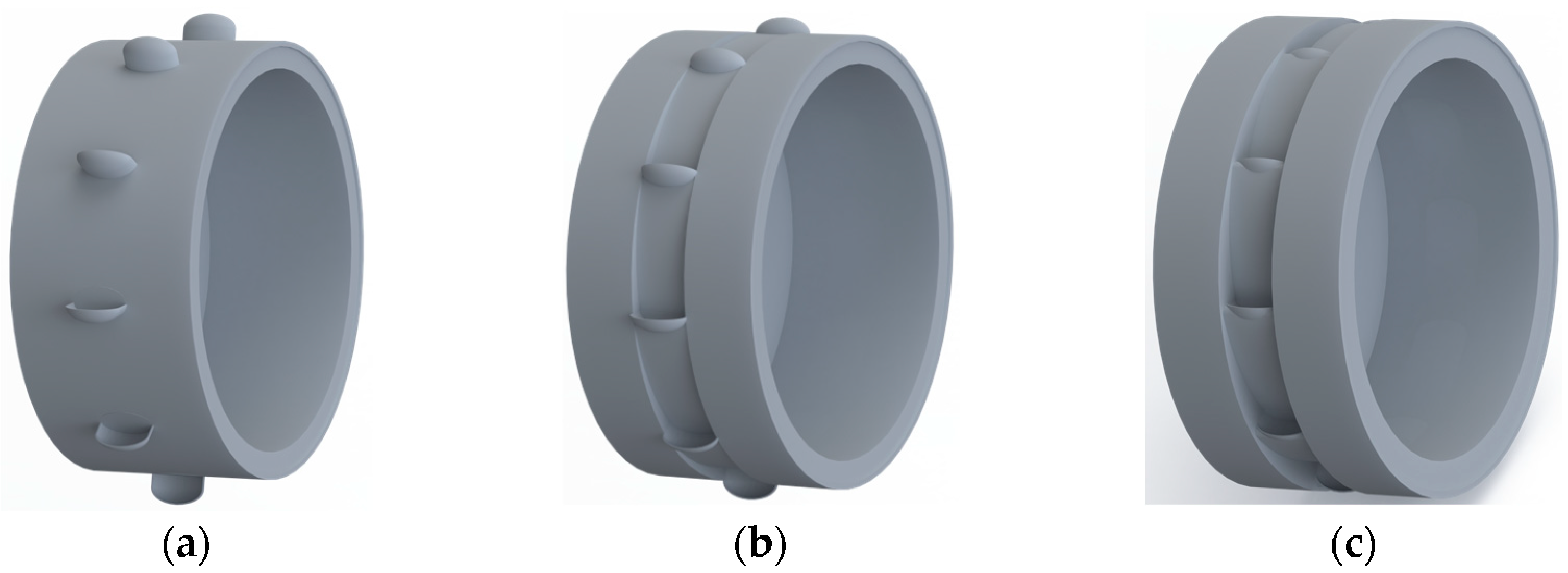
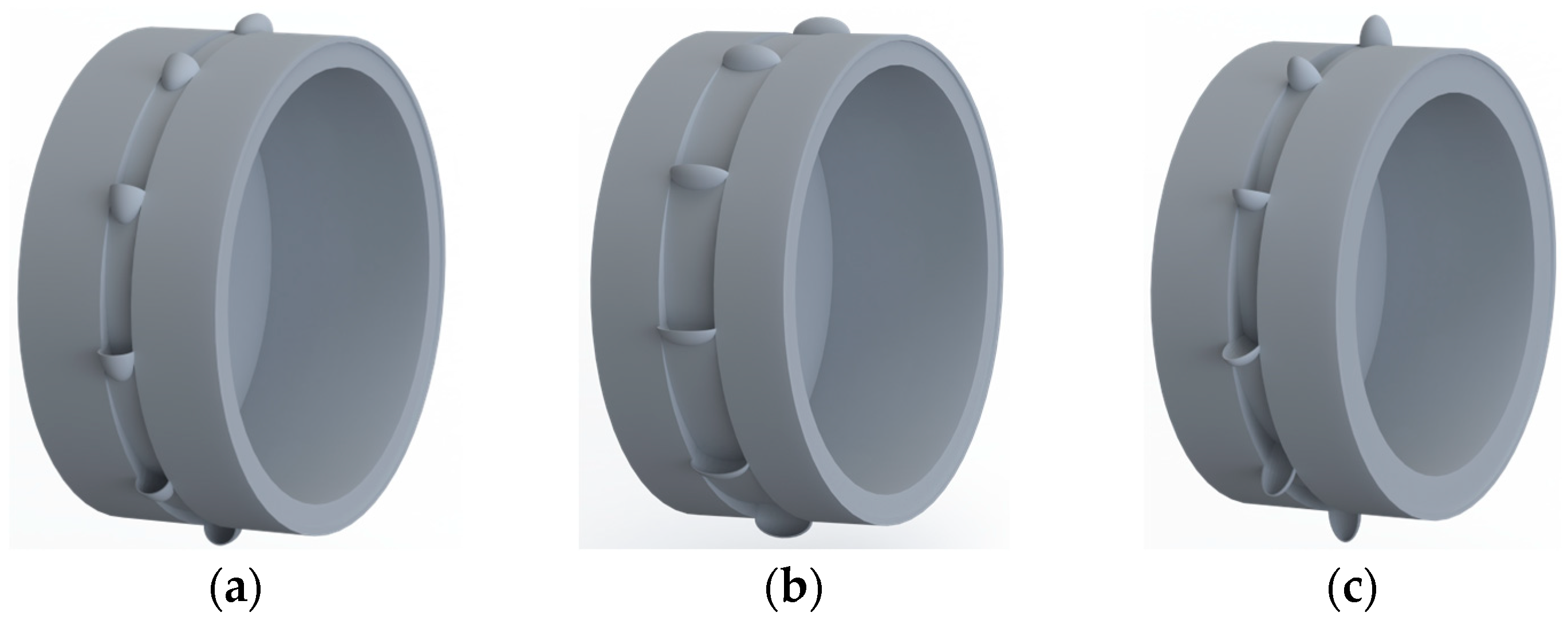
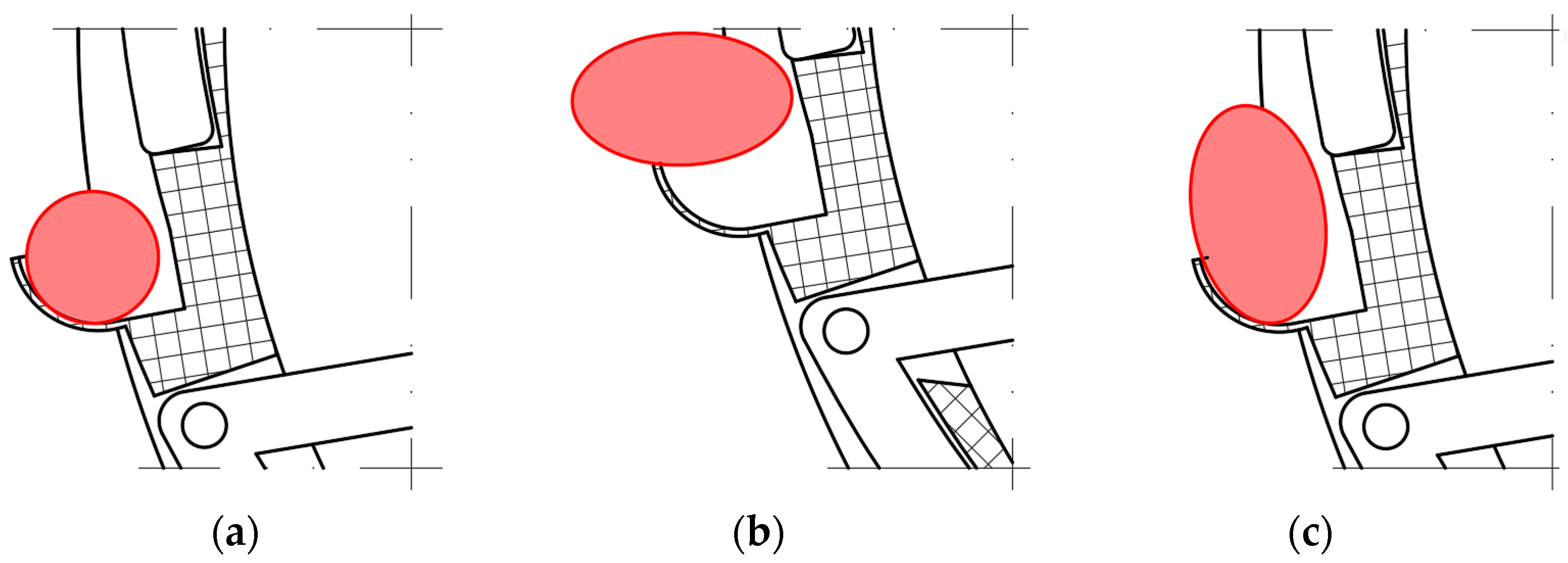
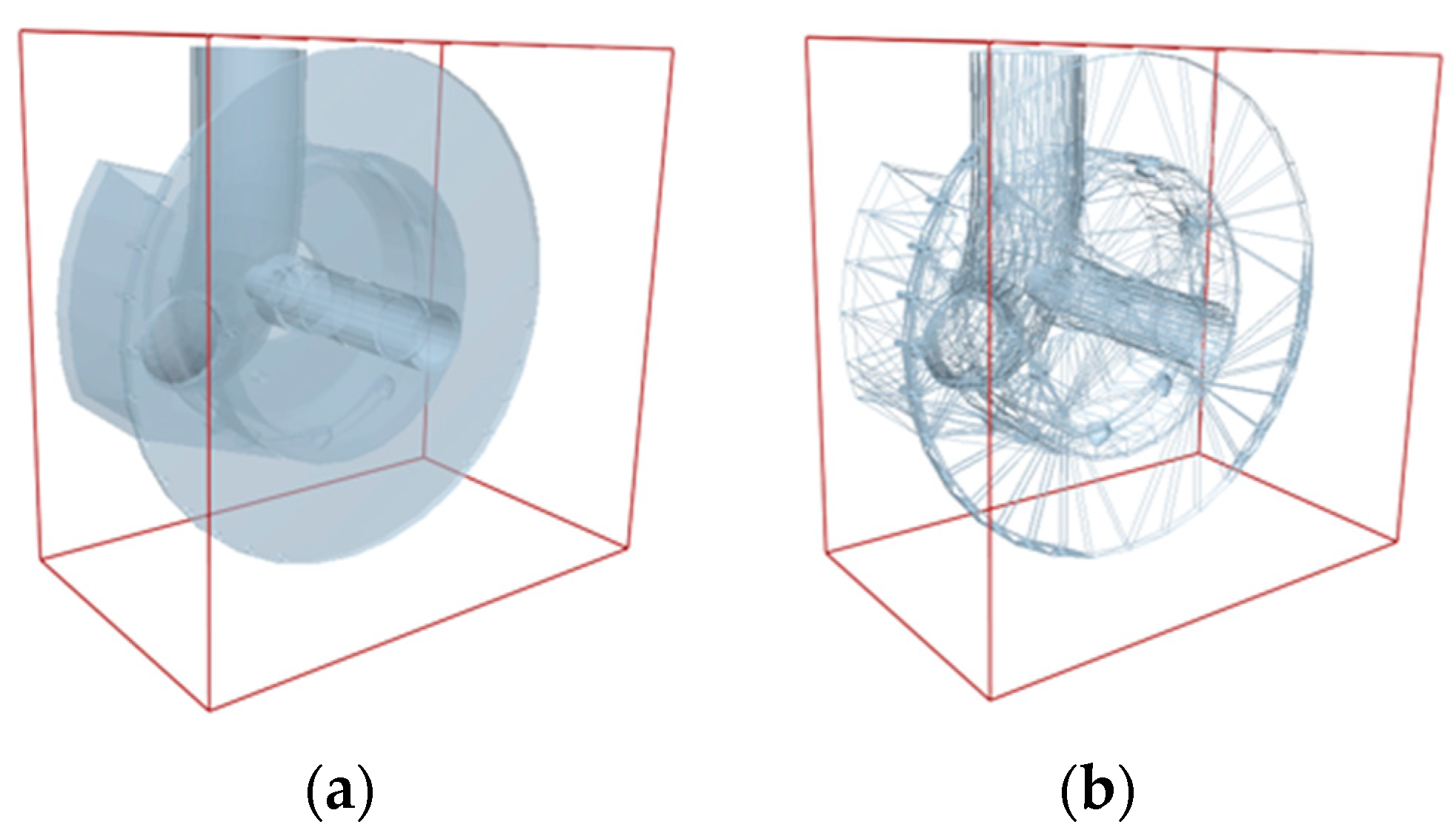
2.4. DEM Simulation of the Effect of Type Hole Installation Positions on Seed Cluster Disturbance
2.5. MBD–DEM Coupling Simulation of Seeding Performance
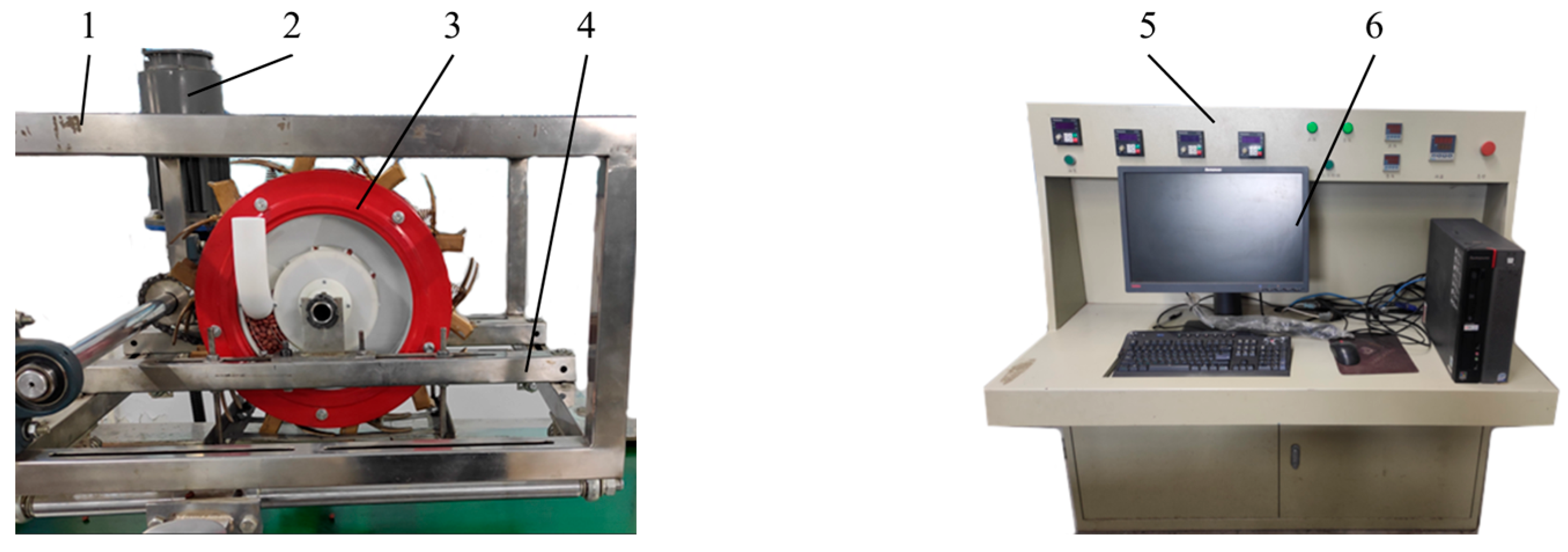
2.6. Bench Test for Optimization of Seeding Performance
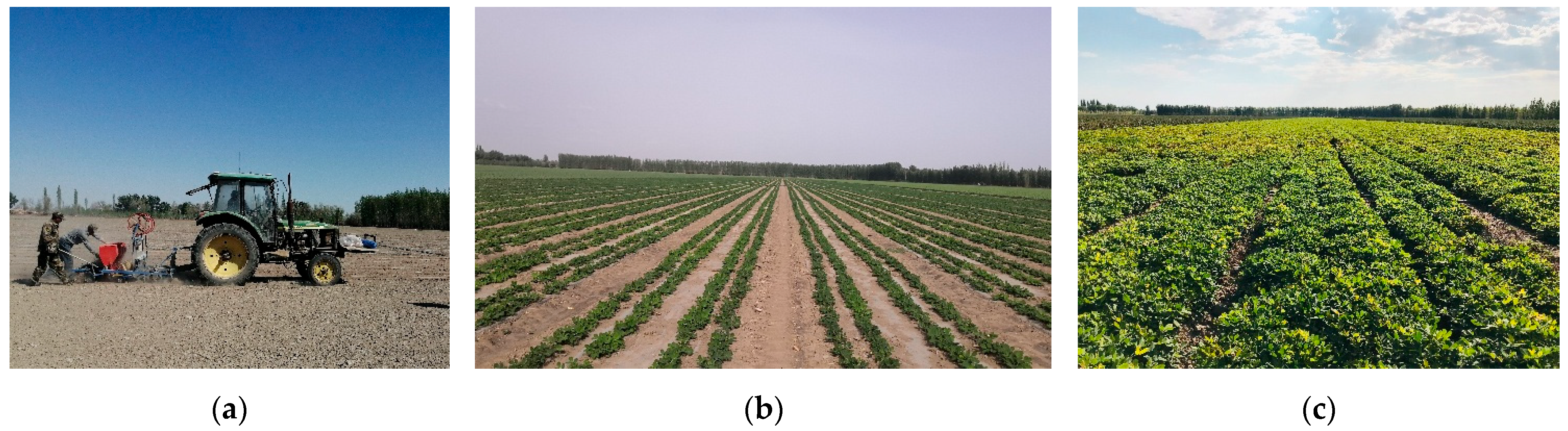
2.7. Field Validation Test of Optimized Operating Parameters for the Metering Device
3. Results
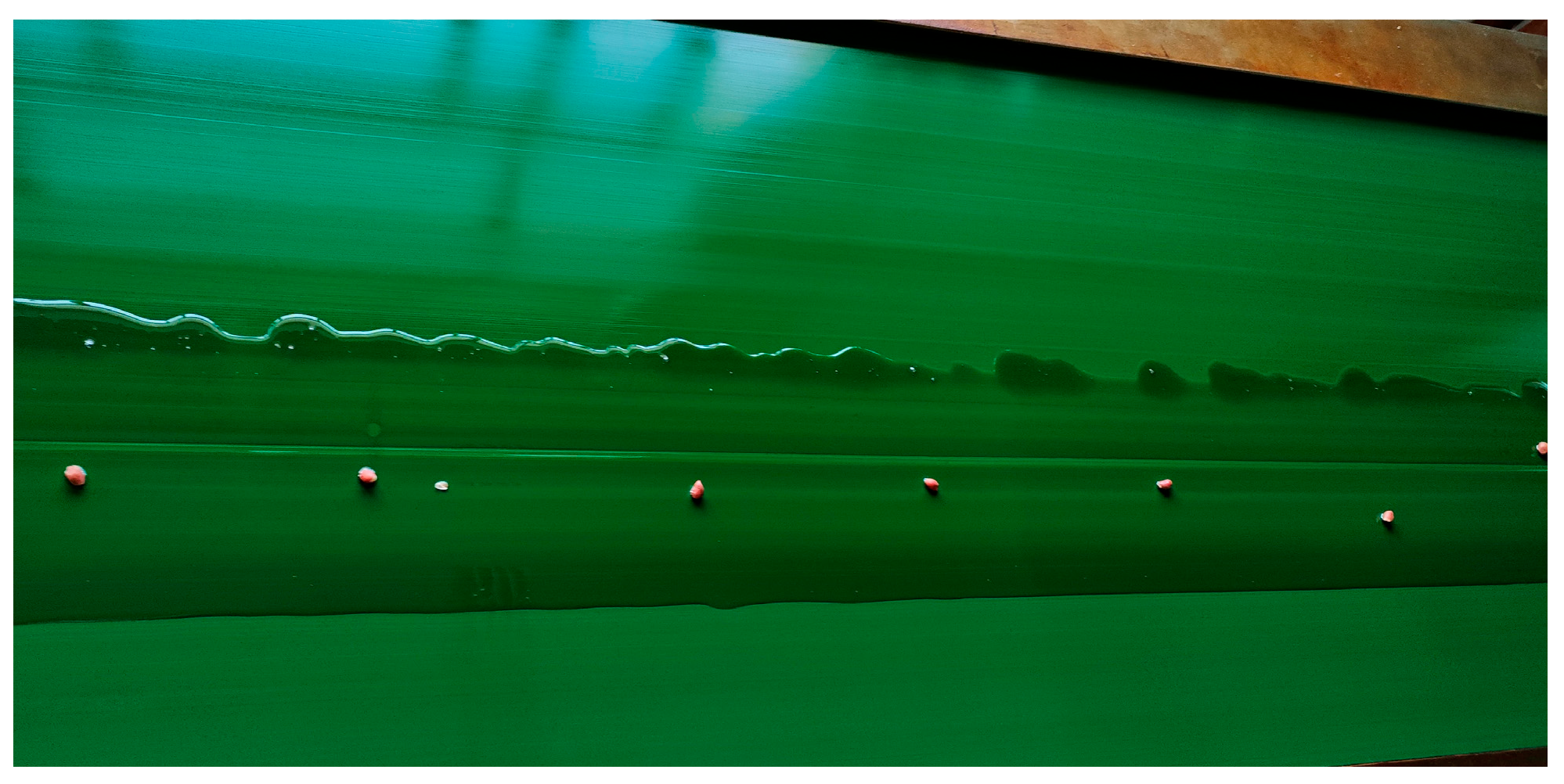
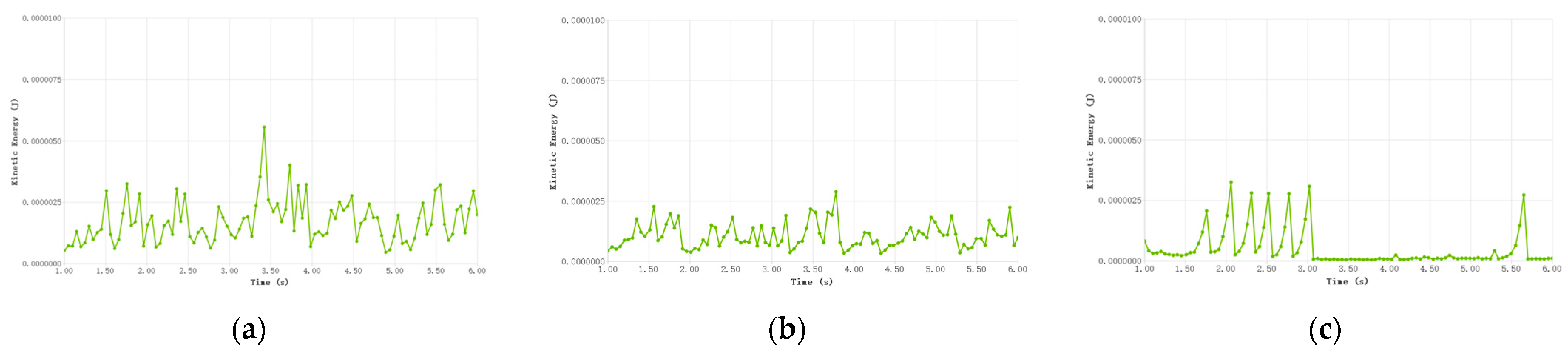
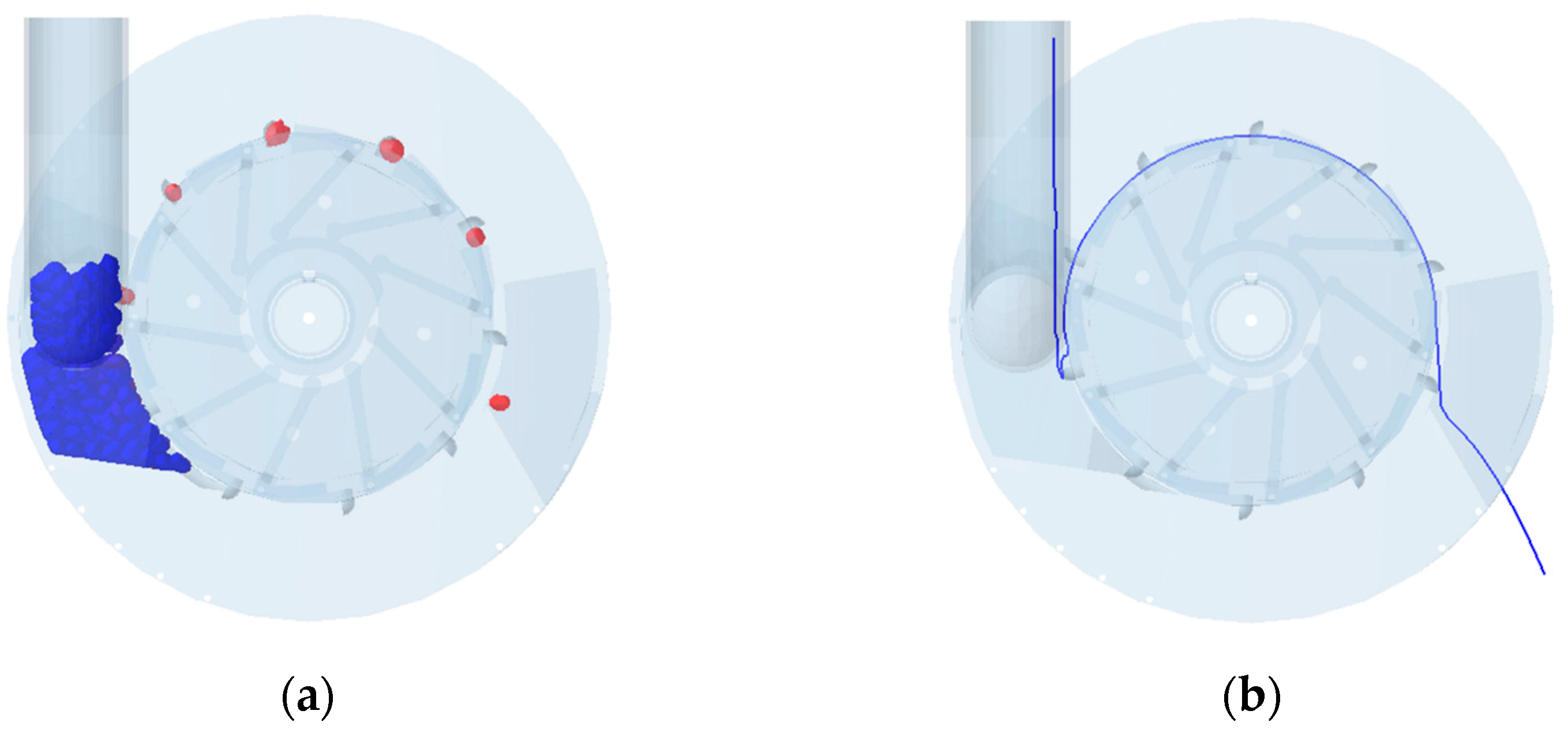
3.1. Effect of Type Hole Installation Position on Seed Cluster Disturbance
3.2. Seeding Performance Based on MBD–DEM Coupling Simulation
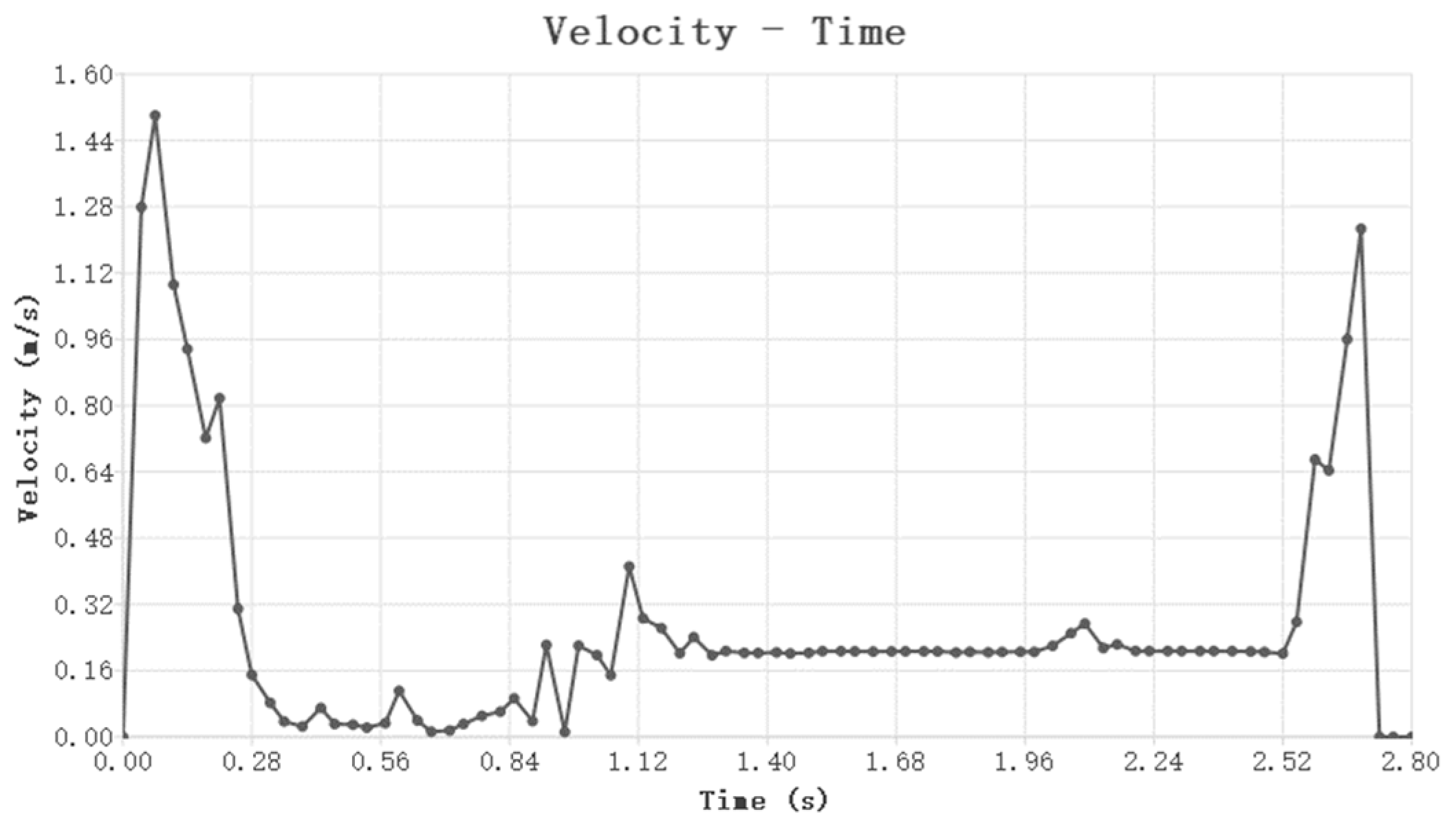
3.2.1. Seed Trajectory During the Seeding Process
3.2.2. Effects of Seeding Disc Rotational Speed and Seed Cluster Wrap Angle on Seeding Performance
3.3. Bench Testing for Optimization of Seeding Performance
3.4. Field Validation Test of the Metering Device
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Fan, Y.; Qiu, D.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Gong, F.; Yin, D. Comprehensive analysis of high-oil peanut cultivars in China: Agronomic performance, disease resistance, and breeding insights. Reprod. Breed. 2025, 5, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Li, S.; Yang, J.; Zhao, X.; Du, L.; He, K.; Liu, J. Diversified crop rotation: Synergistically enhancing peanut yield and soil organic carbon stability. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2025, 382, 109497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wu, H.; Jin, T.; Liu, H.; Men, J.; Cai, G.; Cernava, T.; Duan, G.; Jin, D. Biodegradable mulch films significantly affected rhizosphere microbial communities and increased peanut yield. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 871, 162034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, Z.; Lai, H.; Zhao, M.; Zhu, Q.; Zhao, C.; Yang, D.; Li, X. The impacts of soil tillage combined with plastic film management practices on soil quality, carbon footprint, and peanut yield. Eur. J. Agron. 2023, 148, 126881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wei, H.; Yan, J.; Bao, G.; Du, Y.; Xie, H. Parameter calibration of peanut pods discrete element simulation. J. Chin. Agric. Mech. 2022, 43, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, B.; Moses, S.C.; D’Souza, P.M.; Alam, R.N. Study of physical properties of groundnut seeds relevant to design of planter. J. Exp. Agric. Int. 2025, 47, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Zheng, X.; Wang, D.; Hou, J.; Zhao, Z. Design and experiment of precision seed metering device with pneumatic assisted seed-filling for peanut. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2024, 55, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Kang, J.; Zhang, N.; Peng, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X. Design and experiment of seed separation tray of air-suction roller dibbler for peanut. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2023, 54, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Xiang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Peng, Q.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, N.; Wang, X.; Tang, C. Analysis and experiments of the seed feeding performance of air-suction roller dibbler for peanuts. Trans. CSAE 2022, 38, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Qin, J.; Yang, S.; Ai, Q.; Ma, Z. Design and experiments of a precision sowing unit with the spoon clip for single peanut seed planting in plot. Trans. CSAE 2023, 39, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.; Chang, X.; Liu, B.; Yang, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, D.; Gao, Z. Study on the design and performance of a seed discharger for peanut plot breeding based on the CFD-DEM method. Agriculture 2025, 15, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Kang, J.; Peng, Q.; Zhang, N.; Wang, X. Analysis and optimization test of the peanut seeding process with an air-suction roller dibbler. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Costa, E.; Yazgi, A. Mathematical modelling and optimization of seed metering unit performance in precision peanut seeding. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Cong, J.; Yan, Q.; Zhu, T.; Peng, X.; Wang, Y. Calibration and experiments for discrete element simulation parameters of peanut seed particles. Trans. CSAE 2020, 36, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, C.; Song, J.; Du, X.; Zhang, F. Design and seed-filling test of cell-type precision seed-metering device with vibration technology. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2018, 49, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, S.; Chang, X.; Zhang, N.; He, X.; Li, M.; Wang, D. Design and verification of material-laying seed meter test bench. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2025, 56, 186–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wei, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, D.; Cui, T.; Zhang, K. Design and experiment of mung bean precision seed-metering device with disturbance for promoting seed filling. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2020, 51, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Ji, R.; He, X.; Guo, P.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, C. Drive-guided combination slot-assisted seed-attached air-absorbing peanut high-speed precision seed meter. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2023, 54, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, W.; Fan, S.; Fan, S. Analysis of structural design defects in parallel overloading mechanisms with cam transmission mechanism. Appl. Math. Model. 2022, 107, 717–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liao, Q.; Xi, R.; Li, X.; Liao, Y. Influence of an equal width polygon groove-tooth wheel on feeding performance of the seed feeding device for wheat. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 217, 108565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Li, H.; He, J.; Lu, C.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Tong, Z.; Gao, Z. Research on vibration characteristics of no-tillage seeding unit based on the MBD-DEM coupling. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2025, 230, 109877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Category | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Peanut seed | Poisson’s ratio | 0.30 |
| Shear modulus (Pa) | 5.72 × 107 | |
| Density (kg·m−3) | 1030 | |
| Acrylic | Poisson’s ratio | 0.50 |
| Shear modulus (Pa) | 1.37 × 108 | |
| Density (kg·m−3) | 1197 | |
| Photosensitive resin | Poisson’s ratio | 0.35 |
| Shear modulus (Pa) | 1.2 × 108 | |
| Density (kg·m−3) | 1455 | |
| Seed–seed | Restitution coefficient | 0.36 |
| Static friction coefficient | 0.42 | |
| Dynamic friction coefficient | 0.06 | |
| Seed–acrylic | Restitution coefficient | 0.68 |
| Static friction coefficient | 0.36 | |
| Dynamic friction coefficient | 0.03 | |
| Seed–resin | Restitution coefficient | 0.6 |
| Static friction coefficient | 0.34 | |
| Dynamic friction coefficient | 0.04 |
| Code Value | Rotational Speed (X1) (rpm) | Wrap Angle (X2) (°) |
|---|---|---|
| −1.414 | 15 | 20 |
| −1 | 18.66 | 27.32 |
| 0 | 27.5 | 45 |
| 1 | 36.34 | 62.68 |
| 1.414 | 40 | 70 |
| Rotational Speed (rpm) | Qualified Index (%) | Multiples Index (%) | Missed Index (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 65.2 | 5.6 | 29.2 |
| 15 | 82.3 | 9.5 | 8.2 |
| 20 | 84.6 | 8.2 | 7.2 |
| 25 | 87.1 | 6.3 | 6.6 |
| 30 | 82.7 | 5.9 | 11.4 |
| 35 | 80.3 | 5.1 | 14.6 |
| 40 | 76.7 | 4.7 | 18.6 |
| Wrap Angle (°) | Qualified Index (%) | Multiples Index (%) | Missed Index (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 75.6 | 4.7 | 19.7 |
| 32.5 | 80.7 | 6.4 | 12.9 |
| 45 | 88.5 | 6.7 | 4.8 |
| 57.5 | 85.3 | 11.3 | 3.4 |
| 70 | 82.1 | 14.7 | 3.2 |
| Test No. | Factors | Performance Indicators | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 (rpm) | X2 (°) | Qualified Index A (%) | Multiples Index D (%) | Missed Index M (%) | |
| 1 | 0 | 1.414 | 86.7 | 9.7 | 3.6 |
| 2 | 0 | −1.414 | 83.2 | 5.7 | 11.1 |
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 88.6 | 6.2 | 5.2 |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 87.9 | 7.3 | 4.8 |
| 5 | −1.414 | 0 | 86.1 | 10.5 | 3.4 |
| 6 | 1 | 1 | 84.6 | 7.8 | 7.6 |
| 7 | 0 | 0 | 87.5 | 7.1 | 5.4 |
| 8 | 1.414 | 0 | 81.0 | 6.6 | 12.4 |
| 9 | −1 | 1 | 85.3 | 11.8 | 2.9 |
| 10 | 0 | 0 | 88.3 | 6.6 | 5.1 |
| 11 | 1 | −1 | 78.4 | 6.9 | 14.7 |
| 12 | 0 | 0 | 88.1 | 6.3 | 5.6 |
| 13 | −1 | −1 | 85.2 | 7.9 | 6.9 |
| Source | Qualified Index A | Multiples Index D | Missed Index M | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sum of Squares | Degree of Freedom | F Value | p Value | Sum of Squares | Degree of Freedom | F Value | p Value | Sum of Squares | Degree of Freedom | F Value | p Value | |
| Model | 110.17 | 5 | 62.77 | <0.0001 | 38.97 | 5 | 35.98 | <0.0001 | 162.04 | 5 | 312.93 | <0.0001 |
| X1 | 27.06 | 1 | 77.07 | <0.0001 | 13.82 | 1 | 63.81 | <0.0001 | 79.56 | 1 | 768.21 | <0.0001 |
| X2 | 15.82 | 1 | 45.06 | 0.0003 | 13.67 | 1 | 63.10 | <0.0001 | 58.90 | 1 | 568.72 | <0.0001 |
| X1X2 | 9.30 | 1 | 26.50 | 0.0013 | 2.25 | 1 | 10.39 | 0.0146 | 2.40 | 1 | 23.20 | 0.0019 |
| X12 | 42.91 | 1 | 122.24 | <0.0001 | 7.58 | 1 | 34.99 | 0.0006 | 14.43 | 1 | 139.29 | <0.0001 |
| X22 | 22.13 | 1 | 63.05 | <0.0001 | 2.66 | 1 | 12.30 | 0.0099 | 9.44 | 1 | 91.17 | <0.0001 |
| Residual | 2.46 | 7 | 1.52 | 7 | 0.72 | 7 | ||||||
| Lack of fit | 1.77 | 3 | 3.43 | 0.1324 | 0.58 | 3 | 0.82 | 0.5478 | 0.36 | 3 | 1.29 | 0.3914 |
| Pure error | 0.69 | 4 | 0.94 | 4 | 0.37 | 4 | ||||||
| Total | 112.63 | 12 | 40.48 | 12 | 162.76 | 12 | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cong, J.; Wang, J.; Xie, Y.; Ouyang, K.; Wu, S.; Cao, K.; Wang, L. Design and Optimization Experiment of a Cam-Swing Link Precision Metering Device for Peanut Based on Simulation. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1917. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081917
Cong J, Wang J, Xie Y, Ouyang K, Wu S, Cao K, Wang L. Design and Optimization Experiment of a Cam-Swing Link Precision Metering Device for Peanut Based on Simulation. Agronomy. 2025; 15(8):1917. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081917
Chicago/Turabian StyleCong, Jinling, Jiaming Wang, Yunlong Xie, Kaiqi Ouyang, Shisen Wu, Kun Cao, and Lei Wang. 2025. "Design and Optimization Experiment of a Cam-Swing Link Precision Metering Device for Peanut Based on Simulation" Agronomy 15, no. 8: 1917. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081917
APA StyleCong, J., Wang, J., Xie, Y., Ouyang, K., Wu, S., Cao, K., & Wang, L. (2025). Design and Optimization Experiment of a Cam-Swing Link Precision Metering Device for Peanut Based on Simulation. Agronomy, 15(8), 1917. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081917





