Assessing the Regional Impacts of Climate Change on Grain Yield and Nitrogen Surplus in China (2000–2020)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Research Methods
2.3.1. Model Construction
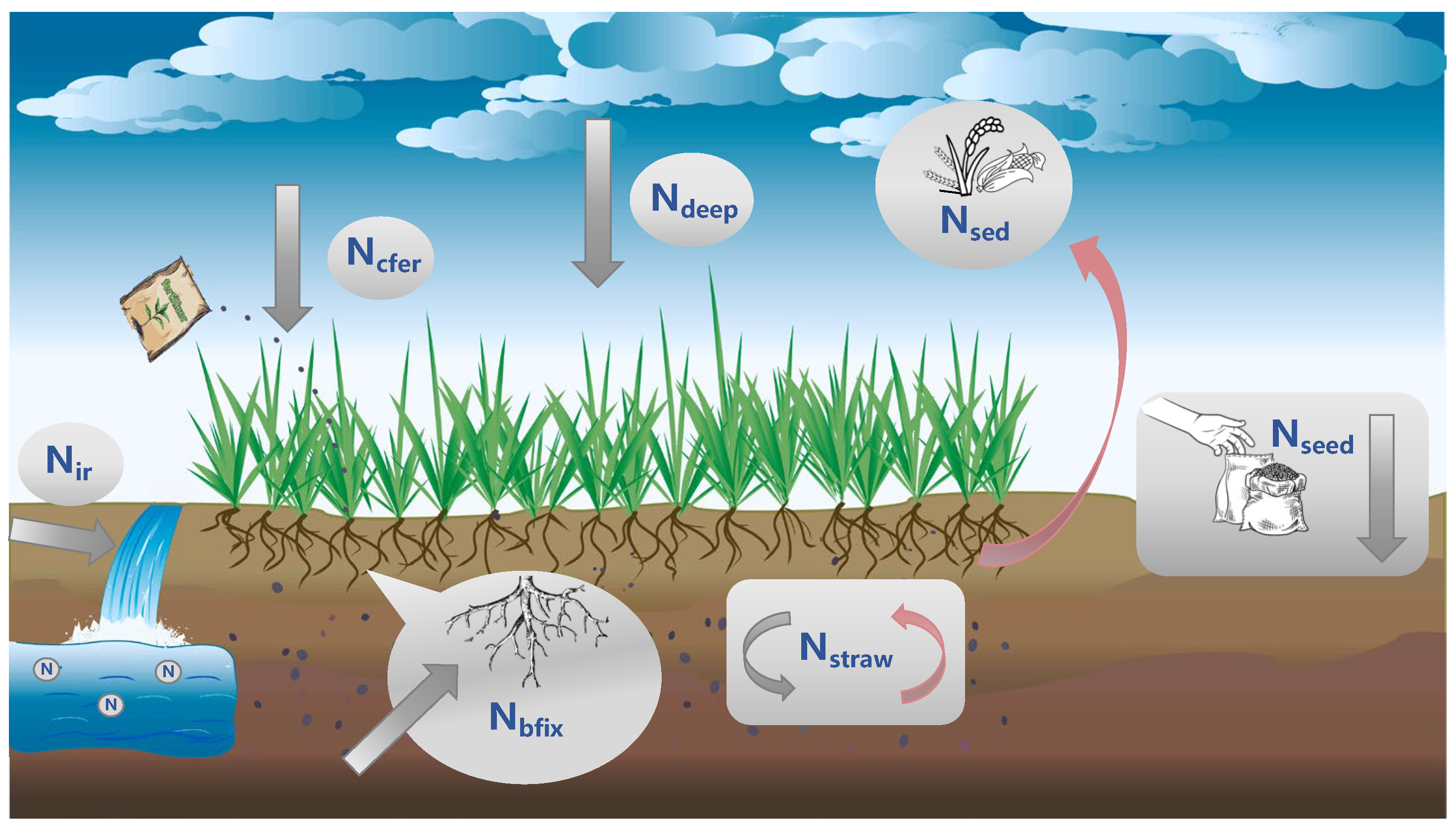
2.3.2. Nitrogen Surplus Calculation Method
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Characteristics of Climate Change in China
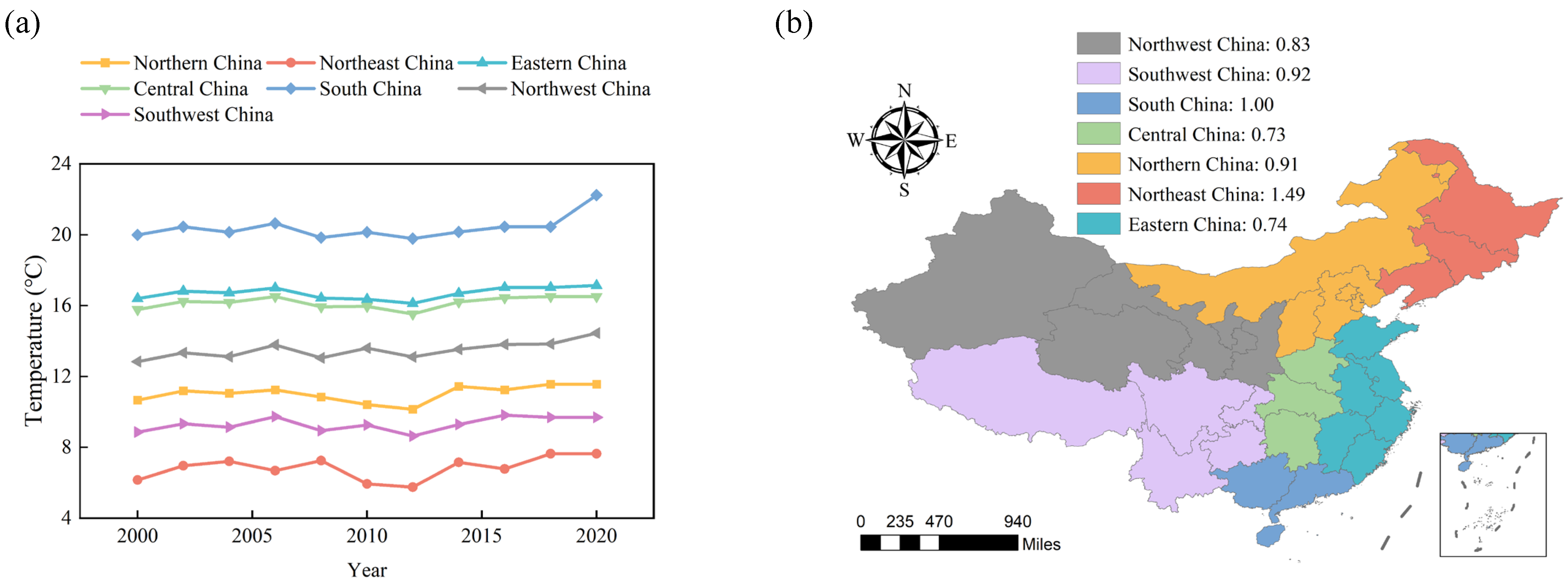
3.1.1. Temperature Variations
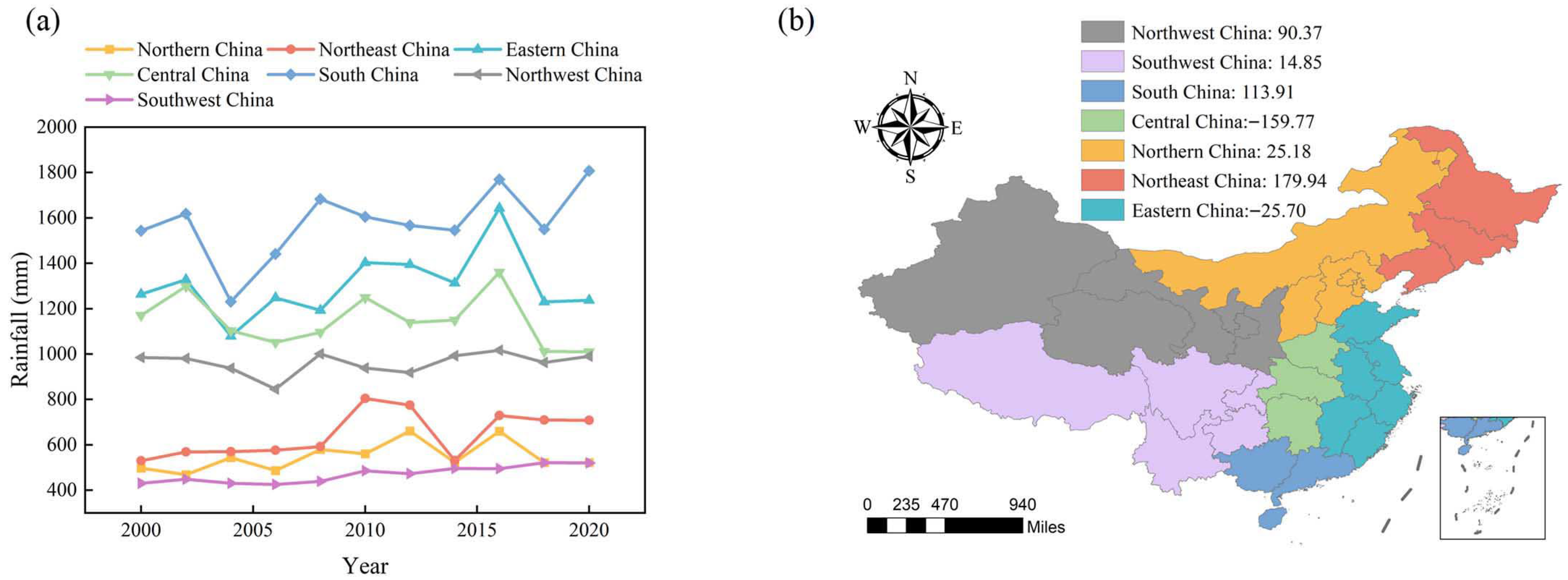
3.1.2. Rainfall Variations
3.2. Grain Yield and Nitrogen Surplus in China
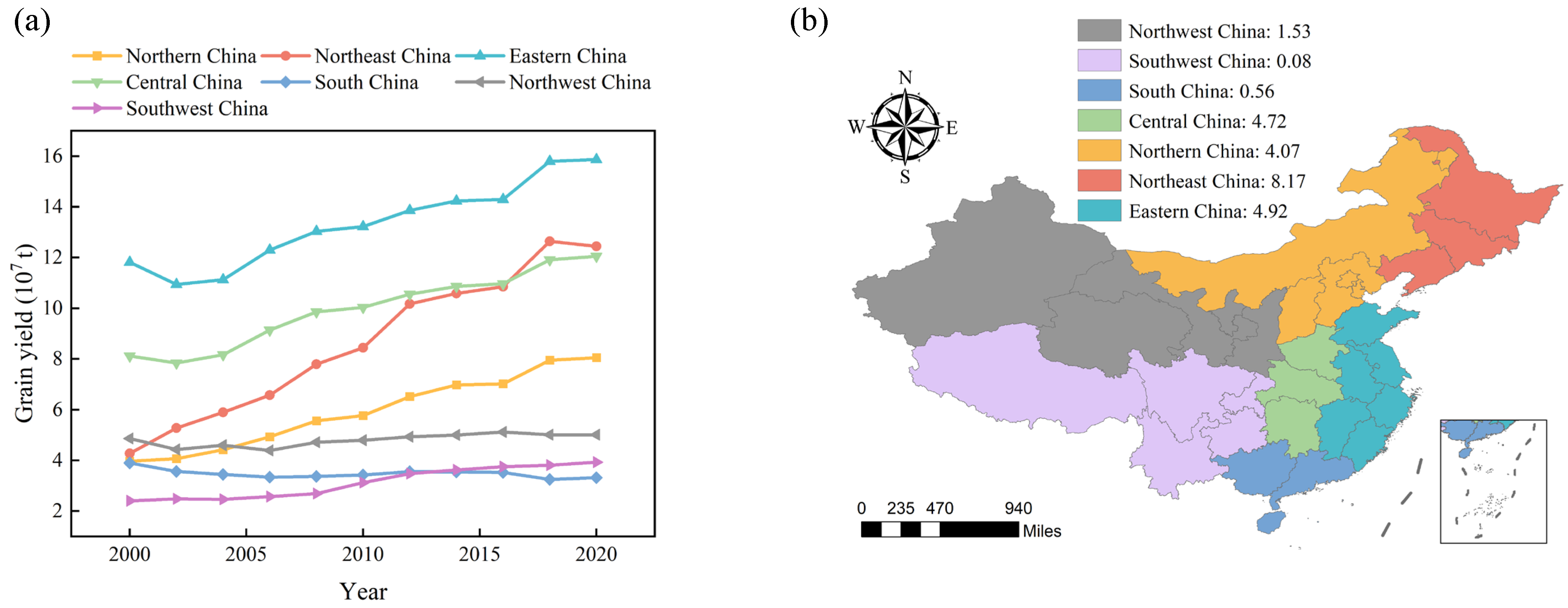
3.2.1. Changes in Grain Yield
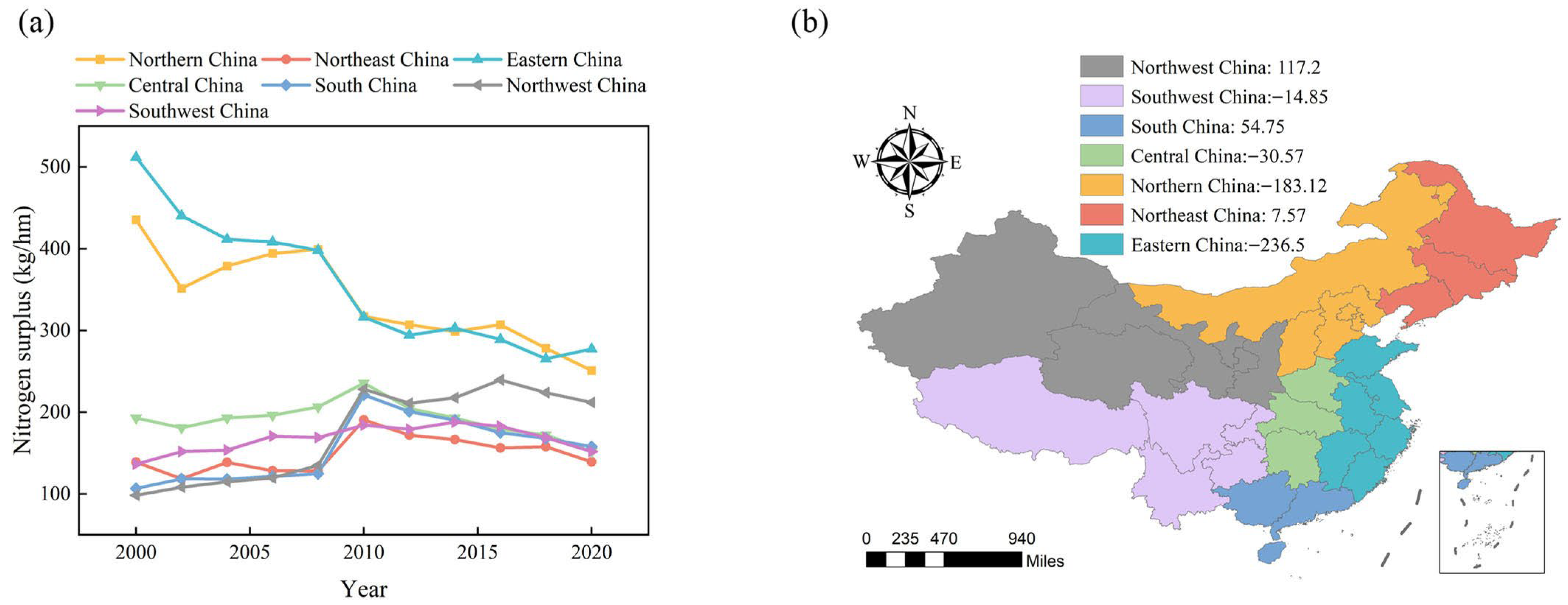
3.2.2. Changes in Nitrogen Surplus
3.3. Impact of Climate Change on Grain Yields
3.3.1. Impact of Temperature Changes on Grain Yields
3.3.2. Impact of Rainfall Changes on Grain Yields
3.4. Regional Analysis of Climate Change Impact on Nitrogen Surplus
3.4.1. Impact of Temperature Change on Nitrogen Surplus
3.4.2. Impact of Rainfall Changes on Nitrogen Surplus
4. Discussion
4.1. Characteristics of Climate Change
4.2. Impact of Climate Change on Grain Yield
4.3. Impact of Climate Change on Nitrogen Surplus
4.4. Implications and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, B. The Dominant Influencing Factors of Desertification Changes in the Source Region of Yellow River: Climate Change or Human Activity? Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 813, 152512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deming, D. Climatic Warming in North America: Analysis of Borehole Temperatures. Science 1995, 268, 1576–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X. Spatiotemporal Variations in Damages to Cropland from Agrometeorological Disasters in Mainland China during 1978–2018. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 785, 147247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimori, S.; Wu, W.; Doelman, J.; Frank, S.; Hristov, J.; Kyle, P.; Sands, R.; Van Zeist, W.-J.; Havlik, P.; Domínguez, I.P.; et al. Land-Based Climate Change Mitigation Measures Can Affect Agricultural Markets and Food Security. Nat. Food 2022, 3, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, L.; Shuang, M.; Xiaolin, L. Changing Multi-Scale Spatiotemporal Patterns in Food Security Risk in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 384, 135618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Sun, L.; Tian, Z.; Fischer, G.; Yan, H. Increase in Grain Production Potential of China under Climate Change. PNAS Nexus 2023, 2, pgad057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglesias, A.; Minguez, M.I. Modelling Crop-Climate Interactions in Spain: Vulnerability and Adaptation of Different Agricultural Systems to Climate Change. Mitig. Adapt. Strat. Glob. Change 1997, 1, 273–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Ren, X.; Shi, L.; He, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, Y. Vapor Pressure Deficit and Temperature Variability Drive Future Changes to Carbon Sink Stability in China’s Terrestrial Ecosystems. Front. For. Glob. Change 2024, 7, 1518578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Yang, S.; Qian, X.; Li, Z.; Fan, Y.; Manevski, K.; Chen, Y.; Gao, W. Bibliometric Network Analysis of Crop Yield Gap Research over the Past Three Decades. Agriculture 2023, 13, 2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Guo, M.; Li, J.; Wu, S.; Cheng, Y.; Shi, L.; Liu, S.; Ge, J.; Dong, Q.; Li, Y.; et al. Impact of Climate Change on the Winter Wheat Productivity Under Varying Climate Scenarios in the Loess Plateau: An APSIM Analysis (1961–2100). Agronomy 2024, 14, 2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, J.; Jin, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, W.; Li, Y.; Hao, Y. Impacts and Risk Assessments of Climate Change for the Yields of the Major Grain Crops in China, Japan, and Korea. Foods 2024, 13, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Yao, N.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, D.; Biswas, A.; Li, L.; Wang, T.; Chen, X. A Meta-Analysis of the Possible Impact of Climate Change on Global Cotton Yield Based on Crop Simulation Approaches. Agric. Syst. 2021, 193, 103221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Harrison, M.T.; Wang, X. Current State and Limiting Factors of Wheat Yield at the Farm Level in Hubei Province. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Ma, W.Q.; Velthof, G.L.; Wang, F.H.; Qin, W.; Zhang, F.S.; Oenema, O. Modeling Nutrient Flows in the Food Chain of China. J. Environ. Qual. 2010, 39, 1279–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H. Dry and Wet Atmospheric Deposition of Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Small Catchment Around Miyun Reservoir. Res. Environ. Sci. 2022, 35, 1419–1431, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D. Simulation of atmospheric nitrogen deposition in China in 2010. China Environ. Sci. 2014, 34, 1089–1097, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Duan, J.; Zhao, Z.; Ti, C.; Wang, G. A-High-Resolution Ammonia Emission Inventory for Cropland and Livestock Production in China. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2021, 29, 1973–1980, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Chou, J.; Xu, Y.; Dong, W.; Zhao, W.; Li, J.; Li, Y. An Economy-Climate Model for Quantitatively Projecting the Impact of Future Climate Change and Its Application. Front. Phys. 2021, 9, 723306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, B.; Fang, C.; Wang, C. Study on assessing total winter-wheat yield based on an economy-climate coupling model in Kunming city. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci. 2013, 26, 2241–2246, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Chou, J. New Ideas for Research on the Impact of Climate Change on China’s Food Security. Clim. Environ. Res. 2022, 27, 206–216, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, B. Impact of Climate Change on Rice Yield and Its Regional Heterogeneity in China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 1156, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Yan, L.; Zhang, W. Study on N Application and N Reduction Potential of Farmland in China. Env. Monit Assess 2023, 195, 1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Jiang, R.; He, P.; Yang, J.; Zhou, W.; Ma, J.; Liu, Y. Estimating Soil Nitrogen Balance at Regional Scale in China’s Croplands from 1984 to 2014. Agric. Syst. 2018, 167, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieling, K.; Kage, H.N. Balance as an Indicator of N Leaching in an Oilseed Rape—Winter Wheat—Winter Barley Rotation. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2006, 115, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Q.; Wang, F.; Luterbacher, J. Improved Estimation of Average Warming Trend of China from 1951–2010 Based on Satellite Observed Land-Use Data. Clim. Change 2013, 121, 365–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y. Study on the 60-Year’s Temperature Variation in China on Multiple Time Scales. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2010, 10, 2017–2022, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, W.; Xue, C.; Zhang, X. Characteristics of climate resources under global climate change in the North China Plain. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2010, 30, 3818–3827, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, S. Characteristics of drought events and their impacts on vegetation in Northern China from 1982 to 2019. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2023, 30, 251–259, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.; Xia, J.; Ren, H. The variations of rainfall belt and its impact in China. China Rural. Water Hydropower 2015, 5, 45–48, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- A, D.; Zhao, W.; Qu, X.; Jing, R.; Xiong, K. Spatio-Temporal Variation of Vegetation Coverage and Its Response to Climate Change in North China Plain in the Last 33 Years. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 53, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xiao, D.; Bai, K.; Tao, F. Research progress on the response and adaptation of crop phenology to climate change in China. Prog. Geogr. 2019, 38, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Lu, W.; Sun, X.; Yu, H. Regional Differences of Winter Wheat Phenophase and Grain Yields Response to Global Warming in the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain in China Since 1980s. Int. J. Plant Prod. 2018, 12, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlenker, W.; Roberts, M.J. Nonlinear Temperature Effects Indicate Severe Damages to U.S. Crop Yields under Climate Change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 15594–15598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; He, W.; He, L.; Yang, J.Y.; Qian, B.; Zhou, W.; He, P. Modelling Adaptation Strategies to Reduce Adverse Impacts of Climate Change on Maize Cropping System in Northeast China. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, H.; Lin, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H. Effect of irrigation on sugar content in flag leaf and grain, and yield of super-high-yield wheat at grain-filling stage. J. Triticeae Crops 2011, 31, 887–893, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Tian, H.; Yang, J.; Xu, R.; Lu, C.; Canadell, J.G.; Davidson, E.A.; Jackson, R.B.; Arneth, A.; Chang, J.; Ciais, P.; et al. Global Soil Nitrous Oxide Emissions since the Preindustrial Era Estimated by an Ensemble of Terrestrial Biosphere Models: Magnitude, Attribution, and Uncertainty. Glob. Change Biol. 2019, 25, 640–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Yin, S.; Liu, H. Analysis of agrometeorological disasters facing extreme climate events in Hebei, Shandong, and Henan provinces. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2023, 30, 327–337, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Z.; Leung, L.R.; Li, H.-Y.; Tesfa, T.; Zhu, Q.; Yang, X.; Liu, Y.; Huang, M. Increased Extreme Rains Intensify Erosional Nitrogen and Phosphorus Fluxes to the Northern Gulf of Mexico in Recent Decades. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 054080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, T.; Yin, Y.; Ying, H.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, F. Targeting Hotspots to Achieve Sustainable Nitrogen Management in China’s Smallholder-Dominated Cereal Production. Agronomy 2021, 11, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Xu, H.; Huang, K.; Wang, J.; Zhao, H.; Qian, X.; Wang, J. Concurrent Response of Greenhouse Soil NO3− Concentration and N2O Emissions to Nitrogen and Irrigation Management in China: A Meta-Analysis. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Nie, T.; Lu, D.; Zhang, P.; Li, J.; Li, F.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, P.; Jiang, L.; Dai, C.; et al. Effects of Different Irrigation Management and Nitrogen Rate on Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L.) Growth, Yield and Soil Nitrogen Accumulation with Drip Irrigation. Agronomy 2024, 14, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, A.; Singh, K.B.; Gupta, R.K.; Alataway, A.; Dewidar, A.Z.; Mattar, M.A. Interactive Effects of Nitrogen Application and Irrigation on Water Use, Growth and Tuber Yield of Potato under Subsurface Drip Irrigation. Agronomy 2022, 13, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Hu, T.; Li, Y.; Cui, X.; Cheng, M.; Yan, S.; Xiang, Y.; Fan, J.; Zhang, F.; Xiong, Y. Effects of Different Water Management Strategies on Critical Nitrogen Concentration Dilution Curves, Nitrogen Accumulation, and Grain Yield in Winter Wheat. Agric. Commun. 2024, 2, 100052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, V.R.; Ghimire, R.; Marsalis, M.A. Cover Crops for Resilience of a Limited-Irrigation Winter Wheat–Sorghum–Fallow Rotation: Soil Carbon, Nitrogen, and Sorghum Yield Responses. Agronomy 2021, 11, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Heng, T.; He, X. Optimizing Cotton Irrigation Strategies in Arid Regions Under Water–Salt–Nitrogen Interactions and Projected Climate Impacts. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Independent Variable | Northern China | Northeast China | Eastern China | Central China | Southern China | Southwest China | Northwest China |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient | Coefficient | Coefficient | Coefficient | Coefficient | Coefficient | Coefficient | |
| ln(A) | 7,327,655 ** | 5,681,065 * | 5,161,118 | 1,144,625 | −1,027,137 ** | 343,466 | −2,753,201 |
| ln(B) | 5218.252 * | 2673.781 | −506.584 | −854.947 | 354.975 ** | 6912.806 | 1137.686 |
| ln(C) | 0.094 | 0.200 | 0.137 *** | 0.073 | 0.236 *** | 0.152 ** | 0.135 ** |
| ln(D) | 12.236 | 4.284 | 8.028 | 8.349 *** | 6.659 | 0.882 | 3.557 |
| ln(E) | −0.012 * | 0.006 | −0.002 | −0.001 | −0.007 ** | 0.002 | −0.006 |
| R2 | 0.996 | 0.995 | 0.993 | 0.995 | 0.969 | 0.981 | 0.884 |
| AdjR2 | 0.993 | 0.991 | 0.987 | 0.990 | 0.938 | 0.963 | 0.769 |
| Northern China | Northeast China | Eastern China | Central China | Southern China | Southwest China | Northwest China | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The temperature rises by 1 °C | 3.05% | 2.44% | 2.99% | 0.93% | −1.22% | 0.42% | −15.70% |
| Rainfall increased by 100 mm | 0.21% | 0.11% | −0.02% | −0.06% | 0.04% | 0.86% | 0.64% |
| Independent Variable | Northern China | Northeast China | Eastern China | Central China | Southern China | Southwest China | Northwest China |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient | Coefficient | Coefficient | Coefficient | Coefficient | Coefficient | Coefficient | |
| ln(A) | −556,573,960 ** | −38,589,402 * | −519,937,268 * | −90,985,481 | −4,386,974 ** | 31,888,514 * | 26,928,862 |
| ln(B) | −376,799 ** | −20,843 | 1770 | −13,633 | 1681 *** | −5617 | −139,624 ** |
| ln(Y) | −10.383 ** | −0.2227 | −12.530 | −13.603 ** | −0.0224 | −3.236 | −5.893 |
| ln(D) | −253.457 ** | 20.035 | 176.75 ** | 202.995 ** | 31.072 | 59.221 ** | 81.627 ** |
| ln(E) | 0.995 ** | −0.059 | 0.9931 ** | 0.616 ** | −0.053 ** | 0.312 | 0.404 |
| R2 | 0.845 | 0.699 | 0.956 | 0.889 | 0.996 | 0.993 | 0.995 |
| AdjR2 | 0.690 | 0.399 | 0.913 | 0.779 | 0.993 | 0.987 | 0.990 |
| Northern China | Northeast China | Eastern China | Central China | Southern China | Southwest China | Northwest China | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The temperature rises by 1 °C | 3.05% | 2.44% | 2.99% | 0.93% | −1.22% | 0.42% | −15.70% |
| Rainfall increased by 100 mm | 0.39% | 0.38% | 0% | −0.07% | 0.10% | −0.03% | −1.13% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Yang, Z.; Chen, H.; Yang, J.; Wei, Y.; Wang, Z.; Jiao, H.; Yin, G.; Li, W.; Wen, H. Assessing the Regional Impacts of Climate Change on Grain Yield and Nitrogen Surplus in China (2000–2020). Agronomy 2025, 15, 1908. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081908
Wang H, Yang Z, Chen H, Yang J, Wei Y, Wang Z, Jiao H, Yin G, Li W, Wen H. Assessing the Regional Impacts of Climate Change on Grain Yield and Nitrogen Surplus in China (2000–2020). Agronomy. 2025; 15(8):1908. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081908
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Hao, Ziwei Yang, Hanting Chen, Jianjin Yang, Yueying Wei, Ziqun Wang, Huiqing Jiao, Gaofei Yin, Wenchao Li, and Hongda Wen. 2025. "Assessing the Regional Impacts of Climate Change on Grain Yield and Nitrogen Surplus in China (2000–2020)" Agronomy 15, no. 8: 1908. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081908
APA StyleWang, H., Yang, Z., Chen, H., Yang, J., Wei, Y., Wang, Z., Jiao, H., Yin, G., Li, W., & Wen, H. (2025). Assessing the Regional Impacts of Climate Change on Grain Yield and Nitrogen Surplus in China (2000–2020). Agronomy, 15(8), 1908. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081908





