Abstract
As an intensive eco-agricultural model, the rice–crayfish co-culture (RCC) system has been widely adopted in recent years due to its remarkable advantages in resource use, efficiency, and economic benefits. However, the long-term mechanisms by which this system affects the quantity and stability of soil aggregate, as well as the vertical distribution of soil organic carbon (SOC) within aggregate across soil profiles, remain unclear. This study investigated the effects of varying duration (4 and 8 years) of RCC in Qianjiang City, Hubei Province. Soil samples were collected from six depth layers (0–10 cm, 10–20 cm, 20–30 cm, 30–40 cm, 40–80 cm, and 80–120 cm) to analyze the distribution characteristics of soil aggregate and SOC. The results demonstrated that, compared to the field which used RCC for a duration of 4 years, the field which used RCC for a duration of 8 years significantly reduced bulk density (BD) by 16.3% in the 40–80 cm layer. However, prolonged flooding has led to a 9.6% increase in the BD of the plow pan layer (10–20 cm) due to hydrostatic pressure and mechanical disturbances. Furthermore, the use of RCC for a duration of 8 years significantly enhanced the mass fractions of water-stable aggregates > 2 mm in the 0–80 cm soil layer at 0–10 cm (25.9%), 10–20 cm (30.2%), 20–30 cm (141.8%), 30–40 cm (172.4%), and 40–80 cm (112.9%), and improved aggregate stability throughout the entire soil profile. In terms of SOC distribution, the SOC concentration increased significantly with prolonged RCC usage across all soil layers, particularly in the 0–20 cm layer. The SOC was primarily derived from >2 mm (Large aggregate). Notably, although < 0.053 mm (Silt and clay) constituted a small proportion of the 0–20 cm layer, their SOC concentration reached 15.3–20.55 g kg−1. Overall, extended RCC duration reduced BD in nearly all soil layers, promoted the formation of macro-aggregate, enhanced aggregate stability, and increased the SOC concentration within macro-aggregate, while strengthening the SOC stocks capacity of the 80–120 cm soil layer from 2.58 kg C m−2 to 4.35 kg C m−2, an increase of 68.6%.
1. Introduction
Persistent population expansion and intensifying extreme climate events generate compounding challenges, manifesting through food insecurity, diminishing soil and water resources for agricultural systems, and progressive land quality degradation [1,2]. Nowadays, the efficient utilization of limited water and soil resources has emerged as a pivotal strategy for agricultural sustainable development goals, effectively addressing dual pressures from food production demands and environmental conservation imperatives [3]. As a critical global staple crop, rice (Oryza sativa L.) occupies approximately 170 million hectares of cultivated land worldwide while providing the primary caloric source for nearly half of world’s population. Consequently, the intensification of rice production systems has become a focal point of global agricultural research and policy. The rice–crayfish co-culture (RCC) system not only innovatively integrates rice cultivation and crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) farming [4,5], but also takes into account both economic and social benefits [6,7]. From 0.56 million hectares in 2010 to 1.68 million hectares in 2023, the RCC system has accounted for a significant proportion of rice cultivation area in China [8], especially in the Jianghan Plain region of Hubei Province [9]. RCC adoption has increased exponentially in this region from initial pilot scales to dominant coverage across the region’s rice fields, and has developed into a distinctive local agricultural planting system [10].
Compared with traditional monoculture rice cultivation, the RCC system makes full use of the flooded environment and the winter leisure period [11], and constructs an annual planting system of “one season of rice, one season of crayfish.” This system establishes a mutually beneficial relationship between rice and crayfish. Specifically, crayfish utilize the rice stubble and pests in paddy fields as food sources, while their excrement and molted shells provide essential nutrients for rice growth, thereby creating an agricultural circular economy characterized by “crayfish nourishing rice and rice sustaining crayfish.” Furthermore, this integrated planting system demonstrates multiple advantages, including reduced fertilizer and pesticide application [12], effective pest suppression [13], improved soil fertility, and enhanced rice yield [14]. Although the benefits of the rice–crayfish co-culture (RCC) system in enhancing resource efficiency and agricultural profitability are well-documented, their long-term effects on critical soil ecological processes remain poorly understood.
Soil organic carbon (SOC) serves as a fundamental indicator of soil fertility [15] and plays a crucial role in sustaining crop growth through long-term SOC stocks [16]. The RCC system promotes efficient SOC accumulation through two primary mechanisms: (i) continuous high exogenous feed inputs coupled with biologically-mediated SOC incorporation processes [17]; and (ii) direct SOC input from rice fine roots (0–40 cm soil layer) via root exudation and plant residue decomposition [18]. Furthermore, the anaerobic flooded environments characteristic of RCC systems inhibits soil mineralization processes, thereby reducing microbial decomposition rates and SOC stability [19]. It has been shown that Bacillus sphaericus and soil organic carbon were significantly high in rice-fish co-federation in Thailand [20], a unique condition that greatly increased the concentration of SOC in topsoil [21,22]. Notably, the subsoil layers contain over two thirds of the total soil nutrient pool and demonstrate greater SOC stock potential compared to topsoil [23,24]. Moreover, the stable accumulation of SOC in subsoil layers contributes to improved soil structural stability, enhanced water-holding capacity, and regulated nutrient cycling—all critical factors for sustaining long-term agricultural productivity [25]. Nevertheless, current understanding of depth-dependent SOC stability patterns in long-term RCC systems remains limited, particularly regarding subsoil SOC accumulation mechanisms and their temporal dynamics. This knowledge gap warrants further investigation to fully comprehend the SOC stock potential of RCC systems across soil profiles. Soil aggregates, serving as crucial carriers of SOC, play a vital role in regulating SOC stabilization and stocks through integrated physical, chemical, and biological protection [26,27]. These aggregates are typically classified into four size fractions: (i) <0.053 mm (silt and clay); (ii) 0.053–0.25 mm (microaggregate); (iii) 0.25–2 mm (macroaggregate); and (iv) >2 mm (large aggregate). Generally, macroaggregate primarily protects humus carbon through physical encapsulation [28], while microaggregate enhances SOC stability via organo-mineral complexation [29]. Recent studies have increasingly focused on bioturbation effects in aggregate restructuring. For example, Zhang et al. [30] and Yu et al. [31] demonstrated that co-cultivation of rice with aquatic animals (crayfish, ducks, crabs, etc.) significantly increase soil macroporosity, though potentially at the expense of macroaggregate integrity. These pioneering studies established the fundamental understanding of topsoil (0–20 cm) pore structure and organic carbon dynamics under aquatic animal co-cultivation. Notably, SOC concentration and microporosity exhibit an inverse relationship with aggregate size, as smaller aggregates require less energy to maintain structural stability, thereby exhibiting greater resistance to degradation [32,33]. These findings highlight the need for systematic investigation of aggregate size, fraction distribution, and associated SOC concentration across soil profiles in long-term RCC systems. Such research would significantly advance understanding of SOC preservation mechanisms in these agroecosystems.
This study was conducted in Qianjiang City, Hubei Province, the national flagship demonstration zone for RCC systems in China. Using a chronosequence approach, we systematically compared RCC systems with distinct cultivation duration (4 years vs. 8 years) to investigate: (i) the temporal effects of the RCC system on soil aggregate distribution and stability dynamics; (ii) the vertical stratification characteristics of SOC across 0–120 cm soil profiles; and (iii) the differential SOC stock capacities among various aggregate size fractions. The findings provide critical insights into pedogenic evolution and optimized SOC management in RCC systems.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Area
The sampling area (30°29′ N, 112°54′ E) was located in the Yunlianghu Management District of Qianjiang City (Figure 1a), Hubei Province, China, the global birthplace of the integrated RCC system [34]. Qianjiang City is situated in the central Jianghan Plain, with an average elevation of 26–30 m above sea level. The region has a subtropical monsoon climate characterized by distinct seasons, mild temperature, high humidity, synchronous rainfall and heat periods, and ample sunshine. The annual average precipitation is approximately 1100 mm. A well-developed water network comprising two lakes (Fanwan Lake and Jieliang Lake) and three rivers (Dongjing River, Tianguan River, and the Han River), provides abundant water resources that ensure agricultural practices. The dominant soil types in the area are Cambisol and Anthrosol [35], both of which have a clay loam texture (USDA texture classification), high SOC concentration, and strong water- and nutrient-retention capacities. These favorable natural conditions make the region particularly suitable for the implementation and expansion of RCC systems.
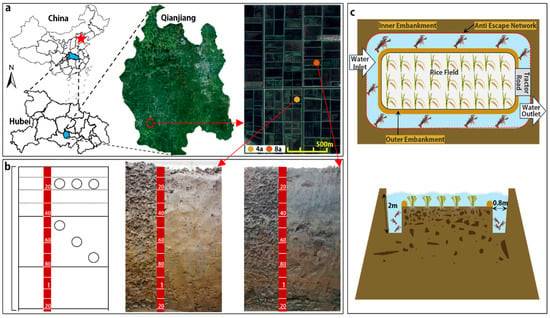
Figure 1.
The location of study sites (a), the sampling diagram and two soil profile photos (b), and the engineering schematic of a RCC system (c).
2.2. Sampling Design
Soil sampling was conducted in May 2024 before rice sowing in two RCC fields with similar soil properties but different farming duration: 4 years (4a) and 8 years (8a). In each field, a soil profile (2.5 m × 1.2 m × 1.2 m) was excavated at the center. After removing surface plant residues and gravels, soil samples were collected from six depth intervals: 0–10 cm, 10–20 cm, 20–30 cm, 30–40 cm, 40–80 cm, and 80–120 cm. Each of the samples were divided into two portions: one portion was carefully placed intact into rigid plastic boxes (21 cm × 15 cm × 8 cm) for soil aggregate structure and stability analysis; the other portion was stored in sealed bags for soil nutrient determination. Additionally, undisturbed soil core sampling (100 cm3, 5 cm diameter × 5 cm height) were collected to measure bulk density (BD). Sampling followed two approaches: (i) at 0–40 cm depth, samples were taken along a horizontal line; (ii) at depths of 40–80 cm and 80–120 cm, a diagonal sampling pattern was employed (Figure 1b). All subsamples in both soil pits (4a and 8a) were collected in triplicate to ensure representativeness.
2.3. Soil Physicochemical Properties
Soil texture was determined using the sieve pipette method (SPM). Soil pH and electrical conductivity (EC) were determined using the potentiometric method with Mettler Toledo (Greifensee, Switzerland) equipment in a 1:2.5 (weight/volume) soil-water suspension (Table 1). BD was determined in triplicate for each soil horizon using the core method with stainless steel cutting rings (100 cm3 internal volume). Samples were oven-dried at 105 °C for 48 h to constant mass. Total porosity was calculated from the measured BD values using the standard formula:
where particle density was taken as 2.65 g cm−3. Some basic physical and chemical properties of the soil are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Basic physical and chemical properties of soil different profiles.
2.4. Soil Aggregate Particle Size Distribution Determination and Calculate Stability Indices
The distribution and stability of soil aggregate were measured according to Kemper’s dry sieving method [36]. For the dry- and wet-sieving, 200 g of air-dried soil samples (<5 mm) were sieved by hand on a column of five sieves: 2, 1, 0.5, and 0.25 mm. The mass percentage of each size fraction was calculated.
Water-stable aggregate size distribution and stability were analyzed by wet-sieving (modified from Guo et al. [37]) employing sequentially stacked sieves (2.0, 1.0, 0.25, and 0.053 mm mesh sizes). Based on the mass percentage of dry-sieved aggregate at each level, 50 g of soil sample was prepared and placed on the top sieve (2 mm). The soil was evenly moistened using a mist sprayer until the surface was uniformly damp. The sieve nest was then immersed in deionized water for 5 min, followed by vertical oscillation using a soil aggregate analyzer (XY-100, Beijing Xiangyu Weiye Instrument Co., Beijing, China) for 10 min at 30 oscillations per minute with a 4 cm amplitude. Aggregate that retained on each sieve was backwashed into pre-weighed aluminum containers. All fractions were oven-dried at 60 °C for 48 h, and their dry weights were recorded.
The >0.25 mm of dry sieving residue (DR0.25) and water sieving residue (WR0.25), percentage aggregate destruction (PAD), geometric mean diameter (GMD), mean weight diameter (MWD) and fractal dimension (D) were calculated. The formulas for calculations are as below:
where, n is the number of particle size fractions. Specifically, i = 1, 2, 3 correspond to the particle size fractions > 2 mm, 1–2 mm, and 0.25–1 mm, respectively, and Wi is the proportion of the total sample mass occurring in the i size fraction.
where Xi is the mean diameter of the particle size fraction of the aggregate, Wi is the proportion of the particle size fraction of the aggregate, and n is the number of particle size fractions. Specifically, i = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 correspond to the particle size fractions > 2 mm, 1–2 mm, 0.25–1 mm, 0.053–0.25 mm, and <0.053 mm, respectively.
where DR>0.25 and WR>0.25 represent the mass percent of soil aggregate > 0.25 mm in mechanically-stabilized aggregate and water-stabilized aggregate, respectively (PAD>0.25).
The above equation can be simplified to:
where Xi Represents the mean diameter of mechanically-stabilized aggregate or water-stabilized aggregate for each particle size fraction (mm), Wi represents the proportion of the corresponding aggregate fraction weight to the total sample weight (%), Xi-j represents the cumulative mass of mechanically-stabilized aggregate or water-stabilized aggregate (mm), MT represents the total mass of mechanically-stabilized aggregate or water-stabilized aggregate (g), and Xmax represents the mean diameter of the aggregate with the maximum particle size (mm).
2.5. Determination of the SOC Concentration and Carbon Stock Related Calculations
The SOC concentration was determined by H2SO4-K2Cr2O7 oxidation followed by titration with FeSO4; iPOC concentration was measured in the same manner [38]. The specific method is as follows: dry soil samples (2 mm sieved and particle size less than 150 microns) are digested with potassium dichromate and concentrated sulfuric acid at 170–180 °C for 5 min. Then, the unreacted potassium dichromate is titrated with a standardized ammonium ferrous sulfate solution (using phthalamide as an indicator). The SOC content is calculated based on the titration difference and corrected using a recovery coefficient of 1.32 to account for approximately 76% oxidation efficiency.
where SOCs are soil organic carbon stocks (CS) (g C m−2), H represents soil depth (cm), BD represents soil bulk density (g cm−3), and SOC represents soil organic carbon concentration (g kg−1).
where Wi denotes the mass fraction of organic carbon storage within the corresponding aggregate size fraction (%), SOMi represents the organic matter content of the corresponding aggregate (g kg−1), and Mi indicates the mass fraction of the corresponding aggregate (%).
2.6. Methods of Statistical Analysis
The data were analyzed using SPSS 27.0 software’s functions of significance analysis (LSD method, p < 0.05), descriptive statistical analysis, and plotting using Origin 2024 to visualize the data.
3. Results
3.1. Soil Profiles Physical Properties
3.1.1. Soil Mechanical Composition in Different RCC Duration Profiles
Soil profile analysis revealed that as the duration of rice–crayfish farming increased (Figure 2), the soil particle composition exhibited distinct vertical differentiation: in 4a, the sand content in the 40–80 cm soil layer reached a maximum of 22%, significantly higher than in other soil layers (p < 0.05); whereas in 8a, the sand content peaked at 23.4% in the 80–120 cm soil layer. In the surface soil layer (0–10 cm), as the duration of rice–crayfish farming increased, the clay content decreased significantly (p < 0.05), while the silt content increased significantly by 37.7% (p < 0.05). In contrast, the 10–20 cm and 20–30 cm soil layers exhibited the opposite trend, with clay content increasing and silt content decreasing.
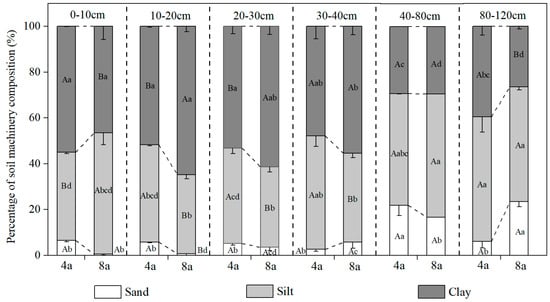
Figure 2.
Soil machinery composition of different soil layers (0–120 cm). Note: 4a, rice–crayfish co-culture for 4 years; 8a, rice–crayfish co-culture for 8 years. Clay represents the <0.002 mm size class; silt represents the 0.002–0.02 mm size class; and sand represents 0.02–2 mm size class. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences in the same grain size between different soil layers in the same rice–crayfish co-cultivation year (p < 0.05). Different capital letters indicate significant differences in the same grain size between different rice–crayfish co-cultivation years in the same soil layer (p < 0.05).
3.1.2. Soil BD and Porosity in Different RCC Duration Profiles
The statistical results showed that with the increase of soil depth, both soil BD and porosity showed a nonlinear trend of increasing and then decreasing under the two RCC durations (4a and 8a; Figure 3). At the 40–80 cm depth, the BD of 8a was significantly (p < 0.05) lower than that of 4a by 16.3%, whereas the porosity of the corresponding soil layer increased significantly (p < 0.05) from 49.1% to 57.4%. It is noteworthy that the longer RCC duration increased the soil BD from 1.25 g cm−3 to 1.37 g cm−3 in the 10–20 cm surface layer.
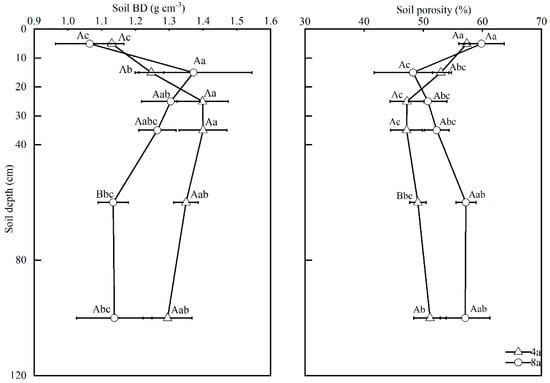
Figure 3.
Soil BD and soil porosity of different soil layers (0–120 cm). Note: 4a, rice–crayfish co-culture for 4 years; 8a, rice–crayfish co-culture for 8 years. Different capital letters represent significant differences between different rice-crayfish co-culture years at the same soil profile depth (p < 0.05). Different lowercase letters represent significant differences between different soil profile depths in the same rice–crayfish co-culture year (p < 0.05).
3.1.3. Soil Aggregate Size Distribution in Different RCC Duration Profiles
Different RCC durations significantly changed the particle size distribution of soil mechanically-stabilized aggregate (Figure 4). Overall, the proportion of 4a and 8a > 2 mm aggregate decreased with deeper soil layers. In 4a, the proportion of <0.053 mm aggregate in the 40–80 cm soil layer amounted to 8.4%, which was significantly higher than that in the adjacent soil layer (p < 0.05). In 8a, 0.053–0.25 mm aggregate in the 80–120 cm soil layer was significantly higher than that of the other soil layers (p < 0.05). However, >2 mm aggregate continued to account for the highest percentage of aggregate in all soil layers, which was significantly higher than the other grain sizes (p < 0.05). Compared with 4a, 8a significantly increased the proportion of <0.053 mm (0–10 cm), 0.053–0.25 mm (30–40 cm), and <0.053 mm (80–120 cm) aggregate.
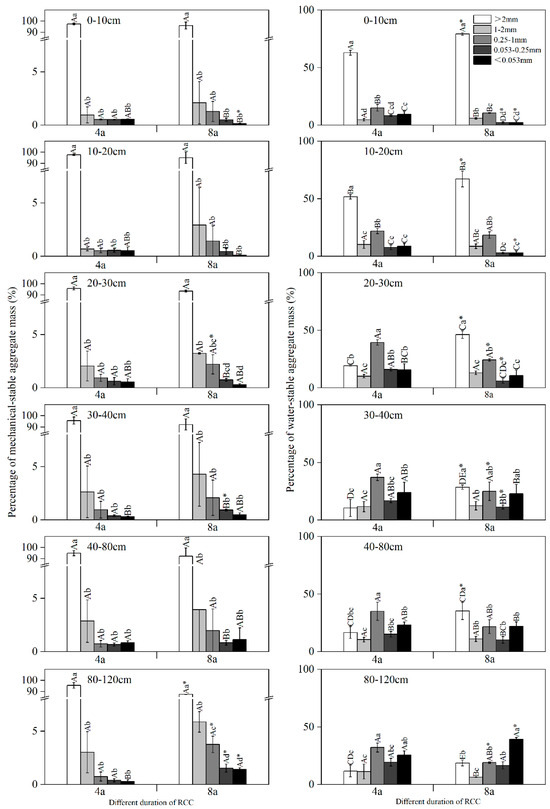
Figure 4.
The mass distribution of different aggregate size percentage at 0–120 cm in the 4a and 8a soil profiles. Note: 4a, rice–crayfish co-culture for 4 years; 8a, rice–crayfish co-culture for 8 years. Different capital letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) in different soil layers of the same size aggregate in the same rice–crayfish co-culture year. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) for different sizes of aggregate in the same soil layer for the same rice–crayfish co-culture year. Asterisks (*) indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) in the same size aggregate in the same soil layer for different rice–crayfish co-culture years.
Different durations of RCC also significantly affected the particle size distribution of soil water-stabilized aggregate (Figure 4). The proportion of >2 mm aggregate in 4a and 8a showed a decreasing, then increasing, then decreasing trend with soil deepening, ranging from 10.5%–62.9% and 18.7%–79.2%, respectively. The proportion of >2 mm aggregate in the 0–20 cm soil layer of both 4a and 8a exceeded 50%, which was significantly higher than that of other grain sizes (p < 0.05); in the soil layer below 20 cm, 4a had the highest proportion of 0.25–1 mm aggregate, while 8a was dominated by <0.053 mm aggregate. Increased RCC duration significantly increased the proportion of >2 mm (0–10 cm, 40–80 cm) and <0.053 mm (80–120 cm) aggregate, while significantly decreasing the proportion of 0.25–1 mm (20–30 cm), 0.053–0.25 mm (20–40 cm) and <0.053 mm (80–120 cm) aggregate (p < 0.05).
3.1.4. Soil Aggregate Stability in Different RCC Duration Profiles
Continuous RCC of different durations affected the stability of soil mechanically-stabilized aggregate and water-stabilized aggregate in the 0–120 cm soil layer (Table 2). The stability of mechanically- and water-stabilized aggregate was inversely proportional to soil depth for both 4a and 8a, except for 80–120 cm. At 0–10 cm and 40–80 cm, soil–water stability aggregate stability was significantly increased (p < 0.05) under 8a compared to 4a, with MWDW increased by 24.3% and 73.6%, and GMDW increased by 100% and 69.2%, respectively (p < 0.05). At the same time, there was also a significant decrease of 48.4%–76.5% in PAD>0.25 from 0–30 cm (p < 0.05), and the prolongation of RCC duration caused GMDD and DD at 80–120 cm to show the opposite change from 0–80 cm (p < 0.05).

Table 2.
Effects of different RCC duration on MWD, GMD, PAD, and D in the 0–120 cm soil layer.
3.2. Soil Profile Chemical Properties
3.2.1. The Concentration of SOC and SOC Stocks in Different RCC Duration Soil Profiles
Long-term RCC farming significantly increased SOC concentration throughout the entire soil profile (p < 0.05; Figure 5). The SOC concentration in the 0–30 cm soil layer of 8a reached more than 95.0% of that of 4a (p < 0.05). Moreover, the SOC concentration exhibited a significant decreasing trend with soil depth in both systems (p < 0.05). In 4a, SOC declined from 12.28 to 4.97 g kg−1 across the profile. For 8a, the SOC concentration in successive soil layers (10–20, 20–30, 30–40, 40–80, and 80–120 cm) showed progressive reductions of 25.5%, 46.1%, 57.1%, 62.1%, and 61.0%, respectively, relative to the 0–10 cm surface layer. Meanwhile, long-term RCC farming significantly increased SOC stocks (0–120 cm).
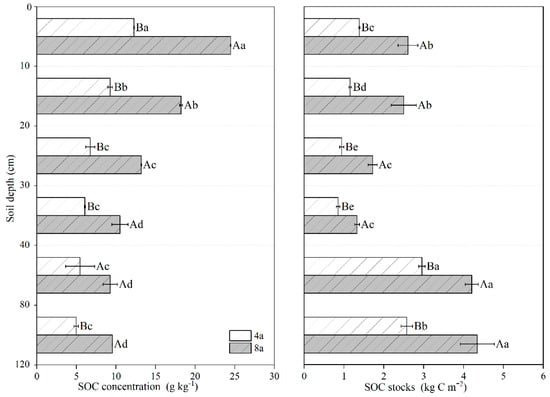
Figure 5.
Effects of different RCC durations on the SOC concentration and SOC stocks in the 0–120 cm soil layers. Note: 4a, rice–crayfish co-culture for 4 years; 8a, rice–crayfish co-culture for 8 years. Different capital letters represent significant differences between different rice-crayfish co-culture years at the same soil profile depth (p < 0.05). Different lowercase letters represent significant differences between different soil profile depths in the same rice–crayfish co-culture year. (p < 0.05).
3.2.2. The Concentration of SOC in Different RCC Duration Profiles
Longer-term RCC resulted in increased SOC concentration within all water-stabilized aggregate size classes at various soil depths (Figure 6). This was concentrated in the 0–30 cm, where all clusters in this depth interval showed a significant increase in SOC concentration within the change. In 4a, the SOC concentration within different aggregate sizes decreased from 0–20 cm to 20–120 cm, though the trend was inconsistent. In contrast, 8a exhibited significant SOC accumulation in the 0–20 cm, with concentration markedly higher (p < 0.05) than in the four underlying soil layers. Notably, in 8a, the deeper soils show higher SOC concentration associated with larger aggregate sizes, a phenomenon that is markedly different from the changes observed in 4a.

Figure 6.
The mass distribution of different aggregate SOC concentration at 0–120 cm under 4a and 8a. Note: 4a, rice–crayfish co-culture for 4 years; 8a, rice–crayfish co-culture for 8 years. Different capital letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) in different soil layers of the same size aggregate in the same rice–crayfish co-culture year. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) for different sizes of aggregate in the same soil layer for the same rice–crayfish co-culture year. Asterisks (*) indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) in the same size aggregate in the same soil layer for different rice–crayfish co-culture years.
3.2.3. The Stocks of SOC in Soil Aggregate in Different RCC of Different Duration
Significant differences in SOC accumulation patterns were observed across aggregate size fractions (p < 0.05), with variation dependent on both RCC duration and vertical soil profile position (Figure 7). In the 0–20 cm surface soil layer, >2 mm aggregate contributed the most to SOC stocks in both 4a and 8a, accounting for 63.6%–76.4% and 69.8%–81.2%, respectively (p < 0.05). As the soil depth increased, 0.25–1 mm aggregates became the dominant contributor to SOC stocks in 4a, whereas >2 mm aggregates in 8a still maintained a high contribution. Notably, in the 80–120 cm soil layer at 8a, the <0.053 mm aggregate contributed significantly more to SOC stocks, accounting for 29.8% (p < 0.05).
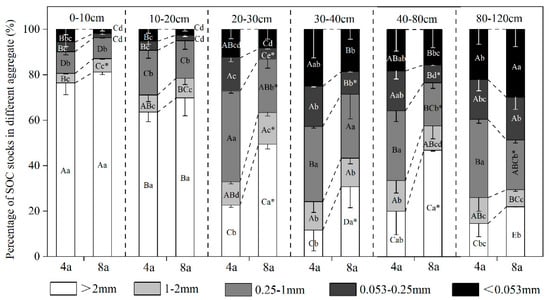
Figure 7.
SOC stocks in different particle size aggregate within the 0–120 cm soil layer. Note: 4a, rice–crayfish co-culture for 4 years; 8a, rice–crayfish co-culture for 8 years. Different capital letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) in different soil layers of the same size aggregate in the same rice–crayfish co-culture year. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) for different sizes of aggregate in the same soil layer for the same rice–crayfish co-culture year. Asterisks (*) indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) in the same size aggregate in the same soil layer for different rice–crayfish co-culture years.
3.2.4. The Concentration of iPOC in Different Aggregate
Compared to 4a, there was a significantly higher concentration of iPOC within soil aggregate across all size fractions throughout the soil profile of 8a (Figure 8). In the topsoil layer (0–20 cm) of the 4a field, iPOC concentration were significantly higher (p < 0.05) in >2 mm aggregate (4.28–5.28 g kg−1) compared to smaller aggregate fractions. Although a similar trend was observed in the 8a field, the iPOC concentration in the topsoil (0–20 cm) did not differ significantly between <0.053 mm and >2 mm aggregate, ranging from 6.49 to 9.99 g kg−1. As soil depth increased, the aggregate fraction with the highest iPOC concentration shifted in both systems: in 4a, 1–2 mm aggregate became dominant, while in 8a, the peak iPOC concentration transitioned from 0.25–1 mm to 0.053–0.25 mm aggregate.
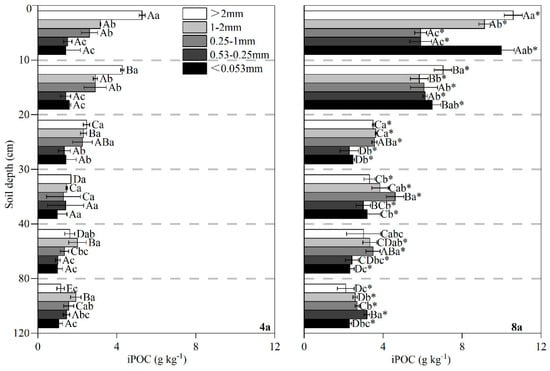
Figure 8.
The concentration of iPOC in different aggregate of 0–120 cm soil layer under different duration of RCC. Note: 4a, rice–crayfish co-culture for 4 years; 8a, rice–crayfish co-culture for 8 years. Different capital letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) in different soil layers of the same size aggregate in the same rice–crayfish co-culture year. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) for different sizes of aggregate in the same soil layer for the same rice–crayfish co-culture year. Asterisks (*) indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) in the same size aggregate in the same soil layer for different rice–crayfish co-culture years.
4. Discussion
4.1. RCC Affects Soil BD
Generally, soil BD exhibits a decreasing trend with the progression of RCC age [39]. In this study, the prolongation of the RCC duration significantly reduced the BD of the 40–80 cm soil layer, but did not reduce the BD of the entire soil profile, and the BD of the 10–20 cm layer showed an increase rather than a decrease. The significant decrease in soil BD in the 40–80 cm soil layer may be due to the influence of crayfish burrowing activities, and their burrow depths are closely related to the water table, which is usually concentrated in the range of 50–80 cm. Consequently, crayfish exhibit greater activity within this depth interval, resulting in more intensive soil disturbance [40]. Moreover, the frequent dry-wet alternation process can significantly affect the soil structure, which in turn has an important impact on the values of weight capacity [41]. In the rice–crayfish co-culture system, although the management practice of maintaining a shallow water layer for a long period of time reduces the occurrence of extreme wet-dry alternations, the soil still experiences different degrees of moisture changes during the seasonal drainage of the sun-dried field [42]. The observed increase in BD within the 10–20 cm layer may result from progressive compaction of the plow pan under sustained hydrostatic pressure. In the 8-year-old RCC system, prolonged inundation likely caused surface layer consolidation, reducing porosity and increasing soil BD in this subsurface horizon. Secondly, the sampling period coincided with the construction phase of shrimp trench digging, and the disturbance and compaction of the soil by the mechanical operation may be another important reason for the elevation of the BD of the 10–20 cm soil layer. The combination of these two factors makes this soil layer exhibit a different trend in BD than other soil layers.
4.2. Influence of RCC System on Soil Aggregate
In this study, the RCC system seeded for 8 years of enhanced agglomerate stability within 80 cm depth was compared to the RCC system seeded for 4 years. This is consistent with the findings of Guo et al. [43]. The enhanced soil stability likely stems from crayfish-mediated straw decomposition dynamics. Through their feeding activities on rice residues, crayfish accelerate straw fragmentation, thereby promoting the generation of organic binding agents [44]. This biochemical process significantly enhances aggregate water stability [45], ultimately yielding a soil system with superior water retention and structural integrity during rice cultivation periods. Crayfish metabolic byproducts (exuviae and excreta) contribute significantly to soil organic matter accumulation in RCC systems. During decomposition, these materials are transformed by soil microbes into protein-polysaccharide complexes that serve as effective binding agents [8]. These biogenic adhesives enhance soil aggregation through two complementary mechanisms: microaggregate cohesion via surface interactions and macroaggregate stabilization through polymeric network formation. The continuous input of these crayfish-derived organic compounds may establish creates a positive feedback loop that could potentially sustain aggregate formation and enhance soil structural stability soil structure stability. In our study, the observed increase in nutrient availability appeared to stimulate rice root proliferation, as evidenced by the development of an extensive root network [46]. Our findings suggest that this enhanced root system may contribute to soil structure stabilization through three putative mechanisms: (1) physical entanglement of soil particles by root hairs, (2) exudation of binding compounds such as mucilage and polysaccharides from root tips, and (3) formation of biopores that may facilitate soil aeration. These hypothesized biophysical interactions appear to work synergistically with organic cementation processes, potentially leading to more stable soil aggregates that demonstrate increased resistance to hydraulic and mechanical stresses in our measurements. In addition, the synergistic effect of straw decomposition products and crayfish metabolites further strengthened the dominant position of fungi, which secreted organic cementing materials and combined fine soil particles through their physical entanglement, significantly contributing to the formation and stabilization of soil aggregate [47]. However, continued prolongation of rice–shrimp farming can lead to a decrease in the proportion of soil macroaggregate and increase the risk of increasing the percentage of sediment and clay fractions [30].
4.3. Depth Partitioning of SOC and the Protective Effect of Agglomerates in a RCC System
Different from previous studies, this study found that long-term RCC not only significantly enhanced the SOC concentration of 0–40 cm surface soil, but also effectively promoted the accumulation of SOC in deep soil (>40 cm). The mechanism likely involves crayfish gnawing-induced straw fragmentation, substantially increasing straw’s specific surface area [17]. This physical modification enhances microbial colonization and growth, thereby stimulating extracellular enzyme production that accelerates straw decomposition and significantly boosts organic matter generation. In addition, long-term enrichment of organic matter such as soil surface feed residues and crayfish excreta allows these exogenous organic inputs to be rapidly converted to organic cementitious materials under flooded conditions [48]. The deep soil SOC enrichment primarily results from: (1) rice root-derived carbon inputs through exudates and residues, (2) continuous water flooding transporting dissolved nutrients and SOC into deeper soil layers [49], and, crucially, (3) crayfish burrow-induced “biopores” [50], which may serve as pathways promoting the transport of organic matter between the surface and deeper layers. This vertical carbon coupling mechanism confers superior SOC stock potential to RCC systems compared to conventional rice monoculture.
In the RCC system with a planting duration of 4 years (4a), we found that the SOC and iPOC in the 0–20 cm soil layer were mainly assigned to >2 mm aggregate. After the planting period reached 8 years (8a), the SOC and iPOC concentrations in aggregate of different grain sizes in each soil layer were also significantly elevated due to the increase in SOC concentration throughout the soil profile. It is worth noting that even though the mass share of >2 mm aggregate was significantly higher than that of <0.053 mm aggregate in the 0–20 cm soil layer, both contributed equally to the SOC pool [51]. This phenomenon stems from complementary protective mechanisms: while macroaggregates dominate SOC storage through physical mass, microaggregates provide superior stabilization via physicochemical protection [52]. The dense architecture of microaggregates restricts microbial access, with organo-mineral complexes and anoxic microenvironments further inhibiting decomposition [53]. These synergistic mechanisms prolong SOC turnover, granting microaggregates distinctive preservation advantages. Notably, their high specific surface area and abundant organic-mineral interfaces significantly enhance SOC adsorption and immobilization capacity [54]. Collectively, these characteristics endow microaggregates with more durable SOC preservation potential and greater sequestration efficiency compared to macroaggregates.
5. Conclusions
By comparing the effects of different durations of RCC farming (4a, rice–crayfish co-culture for 4 years; 8a, rice–crayfish co-culture for 8 years) on the physical and chemical properties of paddy soils, it was found that crayfish activities play an vital role in improving soil structure, enhancing the potential of soil organic carbon (SOC) stocks, and boosting the concentration of SOC within the aggregate. Overall, extended RCC duration resulted in a notable reduction in bulk density (BD) throughout the majority of the soil profile, with a particularly significant decrease of 17.0% observed at the 40–80 cm depth interval. Meanwhile, an increase in the proportion of water-stabilized aggregate (>2 mm) significantly improved the erosion resistance of the soil, indicating an increase in soil structural stability. 8a resulted in a significant increase in SOC concentration across the soil profile compared to 4a. While >2 mm aggregate remains the primary hosting vehicle for SOC, <0.053 mm aggregate represents a secondary reservoir of sequestered and mineralized carbon through physical protection and chemical binding mechanisms. In addition, compaction of the plow subsoil (10.1% increase in 10–20 cm) and disturbance by mechanical operations due to prolonged flooding suggest the need to optimize field management to balance ecological benefits. Further quantification of the contribution of crayfish activities to vertical SOC transport is needed in the future.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.Z., T.Y. and W.F.; Data curation, C.Z., J.W., Y.T., J.B., D.G. and W.F.; Formal analysis, C.Z., T.Y., J.W., Y.T., J.B., D.G. and W.F.; Funding acquisition, T.Y., and W.F.; Investigation, C.Z., J.W. and W.F.; Methodology, T.Y. and W.F.; Project administration, C.Z., T.Y. and W.F.; Resources, T.Y. and W.F.; Software, C.Z., T.Y., Y.T., J.B., D.G. and W.F.; Supervision, T.Y. and W.F.; Validation, C.Z., T.Y., J.W., Y.T., J.B., D.G. and W.F.; Visualization, C.Z., T.Y., J.W., Y.T., J.B., D.G. and W.F.; Writing—original draft, C.Z.; Writing—review & editing, T.Y. and W.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the Open Fund of the Engineering Research Center of Ecology and Agricultural Use of Wetland Ministry of Education (KFG202402, KFG202415).
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interest or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- FAO; IFAD; UNICEF; WFP; WHO. The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World 2024–Financing to End Hunger, Food Insecurity and Malnutrition in All Its Forms; FAO; IFAD; UNICEF; WFP; WHO: Rome, Italy, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouteska, A.; Sharif, T.; Bhuiyan, F.; Abedin, M.Z. Impacts of the changing climate on agricultural productivity and food security: Evidence from Ethiopia. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 449, 141793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.W.; Yang, F.; Zhang, J.Y.; Tang, Y.L. An integrated model chain for diagnosing and predicting conflicts between production-living-ecological space in lake network regions: A case of the Dongting Lake region, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Wang, X.L.; Xu, Q.; Cao, Y.Y.; Zhang, D.Y.; Zhu, J.Q. Rice-crayfish systems are not a panacea for sustaining cleaner food production. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 22913–22926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Feng, L.; Xu, Q.; Jiang, L.; Liu, Y.Z.; Xia, L.L.; Zhu, Y.G.; Liu, B.B.; Zhuang, M.H.; Yang, Y. Sustainable blue foods from rice–animal coculture systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 5310–5324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Peng, X.; Guo, H.L.; Che, Y.; Dou, Z.; Xing, Z.P.; Hou, J.; Styles, D.; Gao, H.; Zhang, H.C. Rice-crayfish coculture delivers more nutrition at a lower environmental cost. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2022, 29, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.X.; Li, W.B.; Ding, K.X.; Shi, X.Y.; Kalkhajeh, Y.K.; Wei, Z.Y.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, C. Co-culture of rice and aquatic animals enhances soil organic carbon: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 955, 176819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.E.; Wei, S.B.; Liu, X.; Sun, D.X.; Shi, Y.J. Progress and prospects of integrated rice and fishery breeding research. J. South China Agric. Univ. 2024, 45, 812–824+808, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.T.; Wang, X.C.; Yan, L.; Yi, J.; Xia, T.; Zeng, Z.; Yu, G.L.; Chai, M.; Velpuri, N.M.; Thaneerat, A. Mapping rice-crayfish co-culture (RCC) fields with Sentinel-1 and-2 time series in China’s primary crayfish production region Jianghan Plain. Sci. Remote Sens. 2024, 10, 100151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Styles, D.; Cao, Y.X.; Ye, X.X. The sustainability of rice-crayfish coculture systems: A mini review of evidence from Jianghan plain in China. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 3843–3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, P.L.; Li, X.H.; Ni, M.L.; Cao, C.G.; Jiang, L.G.; Iqbal, A.; Wang, J.P. Effects of straw return and feed addition on the environment and nitrogen use efficiency under different nitrogen application rates in the rice–crayfish system. Plant Soil 2022, 475, 411–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Wang, X.L.; Xiao, B.; Hu, K.L. Rice-crab coculture to sustain cleaner food production in Liaohe River Basin, China: An economic and environmental assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 208, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, P.L.; Wang, J.P.; Chen, S.W.; Guo, Y.; Cao, C.G. Certified rice–crayfish as an alternative farming modality in waterlogged land in the Jianghan Plain region of China. Agron. J. 2021, 113, 4568–4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Zhang, T.Y.; Wang, G.L.; Ju, J.; Mao, W.; Zhao, H.T. Response of rice grain yield and soil fertility to fertilization management under three rice-based cropping systems in reclaimed soil. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockmann, U.; Padarian, J.; McBratney, A.; Minasny, B.; de Brogniez, D.; Montanarella, L.; Hong, S.Y.; Rawlins, B.G.; Field, D.J. Global Soil Organic Carbon Assessment. Glob. Food Secur. 2015, 6, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesmeier, M.; Urbanski, L.; Hobley, E.; Lang, B.; von Lützow, M.; Marin-Spiotta, E.; van Wesemael, B.; Rabot, E.; Ließ, M.; Garcia-Franco, N.; et al. Soil organic carbon storage as a key function of soils—A review of drivers and indicators at various scales. Geoderma 2019, 333, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.J.; Ren, M.L.; Ye, J.L.; Zhao, L.F.; Dai, R.X.; Zhang, T.J.; Luo, Q.Y.; Tang, J.J.; Hu, L.L.; Chen, X. The role of partner species in the crop cocultures: A meta-analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 367, 108992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzyakov, Y.; Blagodatskaya, E. Microbial hotspots and hot moments in soil: Concept & review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 83, 184–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, G.H.; Zhu, X.X.; Peng, C.L.; Yuan, J.F.; Zhao, S.J.; Xu, D.B.; Xie, Y.Y.; Zhou, J.X.; Yang, X.H. Effects of crayfish on aggregate characteristics and organic carbon distribution of paddy soil under integrated rice-crayfish system. J. Agric.-Environ. Sci. 2024, 43, 590–596, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunrat, N.; Sansupa, C.; Kongsurakan, P.; Sereenonchai, S.; Hatano, R. Soil microbial diversity and community composition in rice–fish co-culture and rice monoculture farming system. Biology 2022, 11, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Xiao, Z.Y.; Shaaban, M.; Núñez-Delgado, A.; Sun, G.; Yu, Y.L.; Xiao, Z.H.; et al. Effects of long-term rice-crayfish farming on soil CNP storage and stoichiometry. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 235, 105882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Li, G.; Zhu, J.Q.; Peng, L.; Li, J.F.; Wu, Q.X. Effects of Rice-crawfish rotation on soil physicochemical properties in Jianghan plain. J. Soil Sci. 2019, 56, 217–226, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.M.; Teng, Y.; Ren, W.J.; Li, Y.T.; Yang, T.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.M.; Kuramae, E.E. Variations of bacterial and Diazotrophic community assemblies throughout the soil profile in distinct Paddy soil types and their contributions to soil functionality. Msystems 2022, 7, e01047-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, M.W.I.; Torn, M.S.; Abiven, S.; Dittmar, T.; Guggenberger, G.; Janssens, I.A.; Kleber, M.; Kögel-Knabner, I.; Lehmann, J.; Manning, D.A.C.; et al. Persistence of soil organic matter as an ecosystem property. Nature 2011, 478, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumpel, C.; Kögel-Knabner, I. Deep soil organic matter—A key but poorly understood component of terrestrial C cycle. Plant Soil 2011, 338, 143–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.N.; Yao, Y.Z.; Han, B.B.; Willcock, S.; Storkey, J.; Dong, X.Z.; Zhong, Y.Y.; Wang, X.Z.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, W.; et al. Nature–based nutrient management through returning agricultural organic waste enhances soil aggregate organic carbon stability. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2025, 381, 109467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaplot, V.; Cooper, M. Soil aggregate stability to predict organic carbon outputs from soils. Geoderma 2015, 243, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndzelu, B.S.; Dou, S.; Zhang, X.W.; Zhang, Y.F.; Ma, R.; Liu, X. Tillage effects on humus composition and humic acid structural characteristics in soil aggregate-size fractions. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 213, 105090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.C.; Zhang, M.; Han, X.Z.; Lu, X.C.; Chen, X.; Feng, H.L.; Wu, Z.M.; Liu, C.Z.; Yan, J.; Zou, W.X. Evaluation of the soil aggregate stability under long term manure and chemical fertilizer applications: Insights from organic carbon and humic acid structure in aggregates. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 376, 109217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.Y.; Wu, J.Q.; Xu, M.S.; Ma, T.Q.; Lu, J.W.; Zhu, J.; Ren, T.; Cong, R.H.; Lu, Z.F.; Zhang, Y.Y.; et al. Rice-crayfish farming increases soil organic carbon stocks by promoting aggregate protection and microbial necromass accumulation. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2025, 383, 109519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.Y.; Zhang, X.C.; Shen, W.Y.; Yao, H.Y.; Meng, X.T.; Zeng, J.Y.; Zhang, G.B.; Zamanien, K. A meta-analysis of ecological functions and economic benefits of co-culture models in paddy fields. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 341, 108195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbi, S.M.F.; Wilson, B.R.; Lockwood, P.V.; Daniel, H.; Young, I.M. Soil organic carbon mineralization rates in aggregate under contrasting land uses. Geoderma 2014, 216, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, M.H.; Ai, X.Y.; Huang, B.C.; Zhu, M.K.; Liu, Z.Y.; Ai, Y.W. Effects of biochar additions on the mechanical stability of soil aggregates and their role in the dynamic renewal of aggregates in slope ecological restoration. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 898, 165478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Cao, C.G. Crayfish–rice integrated system of production: An agriculture success story in China. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 41, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantel, S.; Dondeyne, S.; Deckers, S. World reference base for soil resources (WRB). Encycl. Soils Environ. 2023, 4, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemper, W.D.; Rosenau, R.C. Aggregate stability and size distribution. Methods Soil Anal. Part 1 Phys. Miner. Methods 1986, 5, 425–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Hu, Q.Y.; Liu, T.Q.; Du, Y.F.; Li, C.F.; Zhang, X.L.; Liu, J.; Cao, C.G. Long-term rice–crayfish coculture increases plant lignin but not microbial necromass contribution to soil organic carbon. Soil Tillage Res. 2025, 248, 106424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.W.; Sommers, L.E. Total carbon, organic carbon, and organic matter. Methods Soil Anal. Part 2 Chem. Microbiol. Prop. 1982, 9, 539–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, P.l.; Wang, J.P.; Li, C.F.; Cao, C.G. Long-term rice–crayfish farming aggravates soil gleying and induced changes of soil iron morphology. Soil Use Manag. 2022, 38, 757–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, G.H.; Peng, C.L.; Yuan, J.F.; Xu, X.Y.; Zhao, S.J.; Xu, D.B.; Wu, J.S. Changes in soil microbial community composition and organic carbon fractions in an integrated rice–crayfish farming system in subtropical China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, A.N.A.; Uddin, M.K.; Sulaiman, M.F.; Amin, A.M.; Hossain, M.; Aziz, A.A.; Mosharrof, M. Impact of organic amendment with alternate wetting and drying irrigation on rice yield, water use efficiency and physicochemical properties of soil. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arce, J.A.; Diéguez-Uribeondo, J. Structural damage caused by the invasive crayfish Procambarus clarkii (Girard, 1852) in rice fields of the Iberian Peninsula: A study case. Fundam. Appl. Limnol. 2015, 186, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Quan, W.B.; Yuan, P.L.; Liu, T.Q.; Wang, J.P.; Cao, C.G. Variations in the profile distribution of soil aggregate and organic carbon under rice-crayfish coculture system in Jianghan Plain, China. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 243, 106175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, Z.R.; Ma, S.T.; Liu, Q.Y.; Liu, B.Y.; Virk, A.L.; Qi, J.Y.; Zhao, X.; Lal, R.; Zhang, H.Z. Carbon stocks and mineralization in soil aggregate under long-term conservation tillage in the North China Plain. Catena 2020, 188, 104428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, T.Q.; Wang, C.Y.; Xu, Y.L.; Zhou, X.Y.; Huang, F.; Yu, L. Impact of Integrated rice-crayfish farming on soil aggregate and organic matter distribution. Agronomy 2023, 14, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichmann, M.; Blanc, L.; Lampurlanés, J.; Simon-Miquel, G.; Plaza-Bonilla, D. Does Intercropping improve soil aggregation and organic carbon protection? A case—study in the Semi—Arid Mediterranean. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2025, 385, 109563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wu, G.G.; Li, Y.J.; Hu, C.; Ge, L.; Zheng, X.Q.; Zhang, J.Q.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.L.; Bai, N.L.; et al. Long-term rice-crayfish-turtle co-culture maintains high crop yields by improving soil health and increasing soil microbial community stability. Geoderma 2022, 413, 115745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Du, L.S.; Xiao, Z.Y.; Li, C.W.; Wang, Z.C.; Zhou, P.Y.; Sun, G.; Ye, Y.Y.; Hu, T.; Wang, H. Rice-crayfish farming increases soil organic carbon. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 329, 107857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunrat, N.; Sereenonchai, S.; Kongsurakan, P.; Hatano, R. Assessing soil organic carbon, soil nutrients and soil erodibility under terraced paddy fields and upland rice in Northern Thailand. Agronomy 2022, 12, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, G.H.; Yuan, J.F.; Xu, X.Y.; Zhao, S.J.; Peng, C.L.; Wu, J.S.; Zhou, Z.Q. Effects of an integrated rice-crayfish farming system on soil organic carbon, enzyme activity, and microbial diversity in waterlogged paddy soil. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweizer, S.A.; Bucka, F.B.; Graf-Rosenfellner, M.; Kögel-Knabner, I. Soil microaggregate size composition and organic matter distribution as affected by clay content. Geoderma 2019, 355, 113901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehndorff, E.; Rodionov, A.; Plümer, L.; Rottmann, P.; Spiering, B.; Dultz, S.; Amelung, W. Spatial organization of soil microaggregate. Geoderma 2021, 386, 114915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Bossuyt, H.; Degryze, S.; Denef, K. A history of research on the link between (micro) aggregate, soil biota, and soil organic matter dynamics. Soil Tillage Res. 2004, 79, 7–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Kinyangi, J.; Solomon, D. Organic matter stabilization in soil microaggregate: Implications from spatial heterogeneity of organic carbon contents and carbon forms. Biogeochemistry 2007, 85, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).