DEM Parameter Calibration and Experimental Definition for White Tea Granular Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Materials
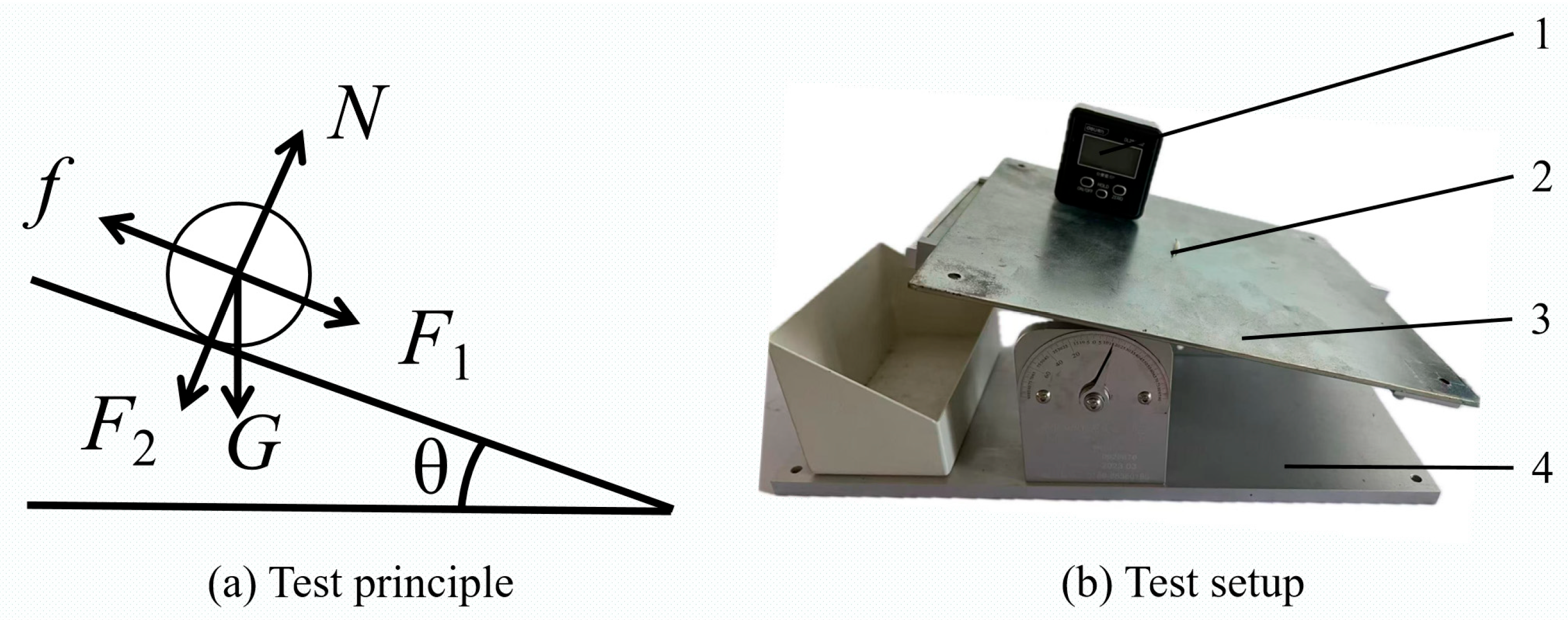
2.2. Static Friction Factor
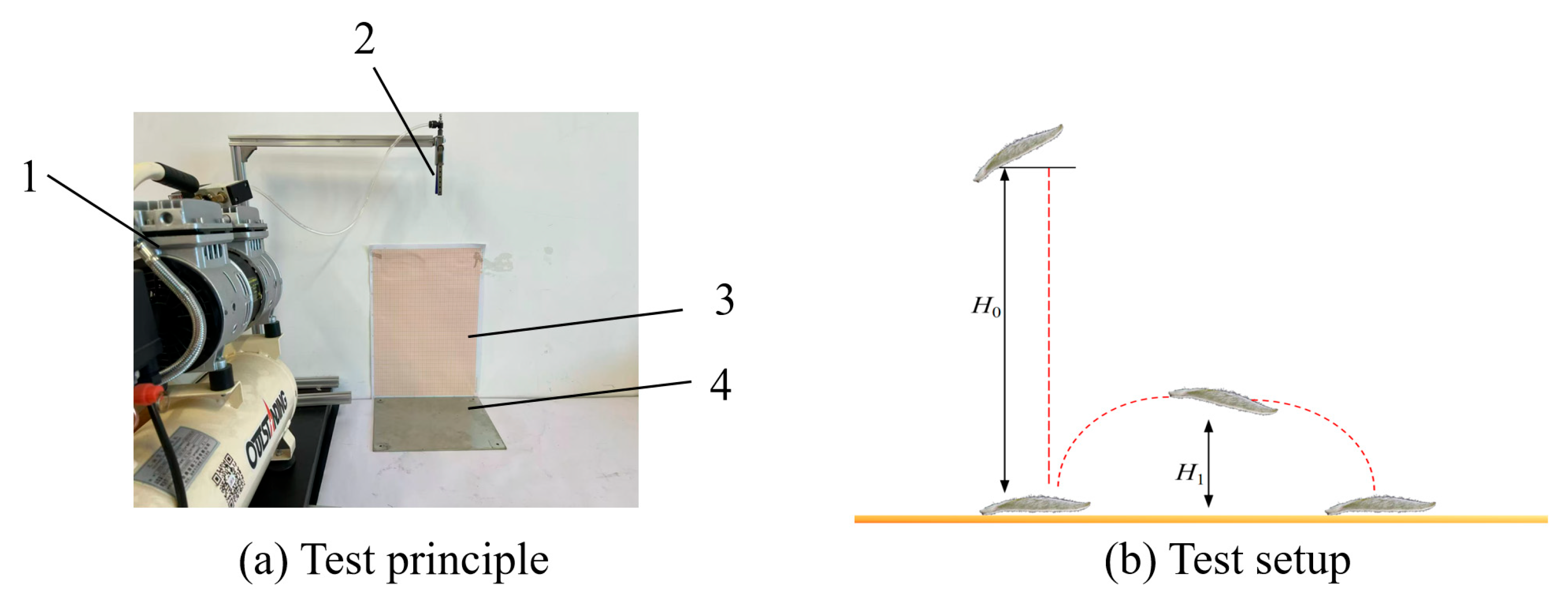
2.3. Collision Recovery Coefficient
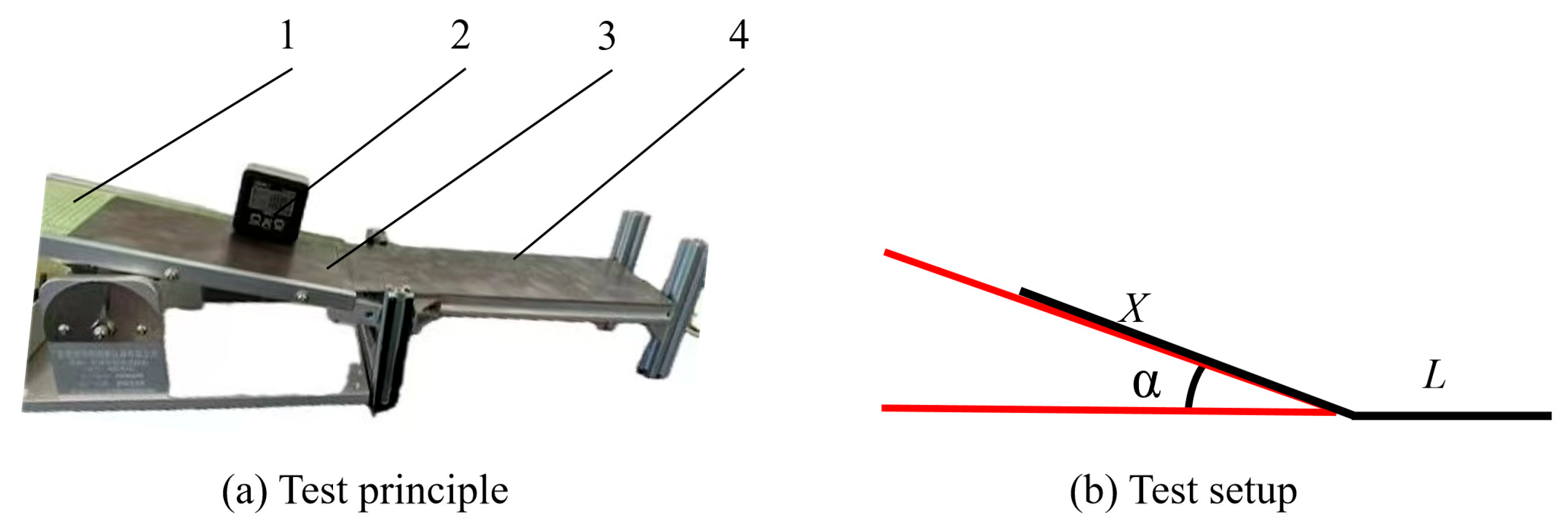
2.4. Rolling Friction Coefficient
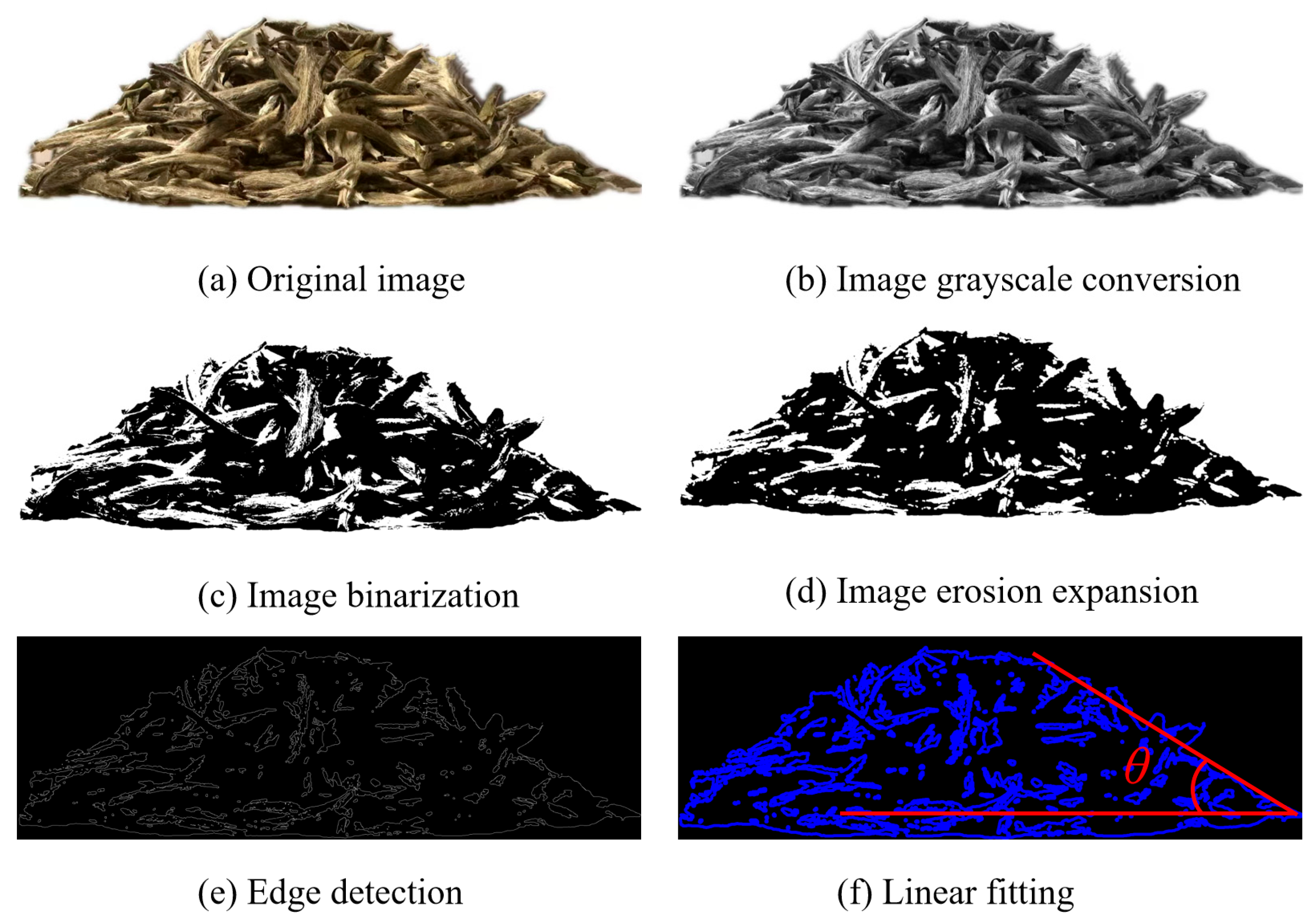
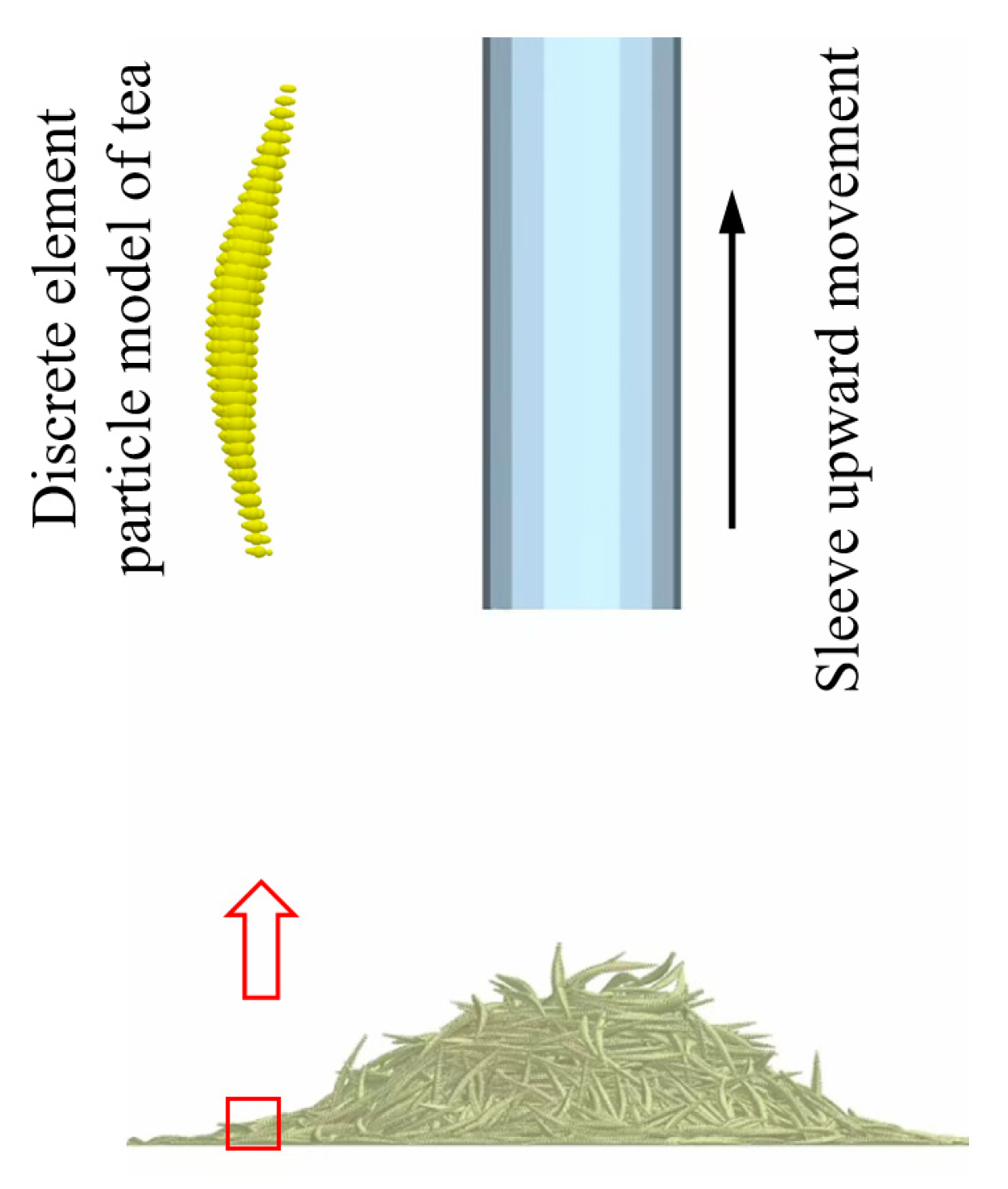
2.5. Physical Test of Repose Angle
2.6. Simulation Model
2.6.1. Establishment of the Tea Particle Model
2.6.2. Contact Model
2.6.3. Simulation Experiment of the Repose Angle of Tea Particles
3. Results
3.1. Determination Results of Relevant DEM Parameters for White Tea
3.2. The Steepest-Climb Test
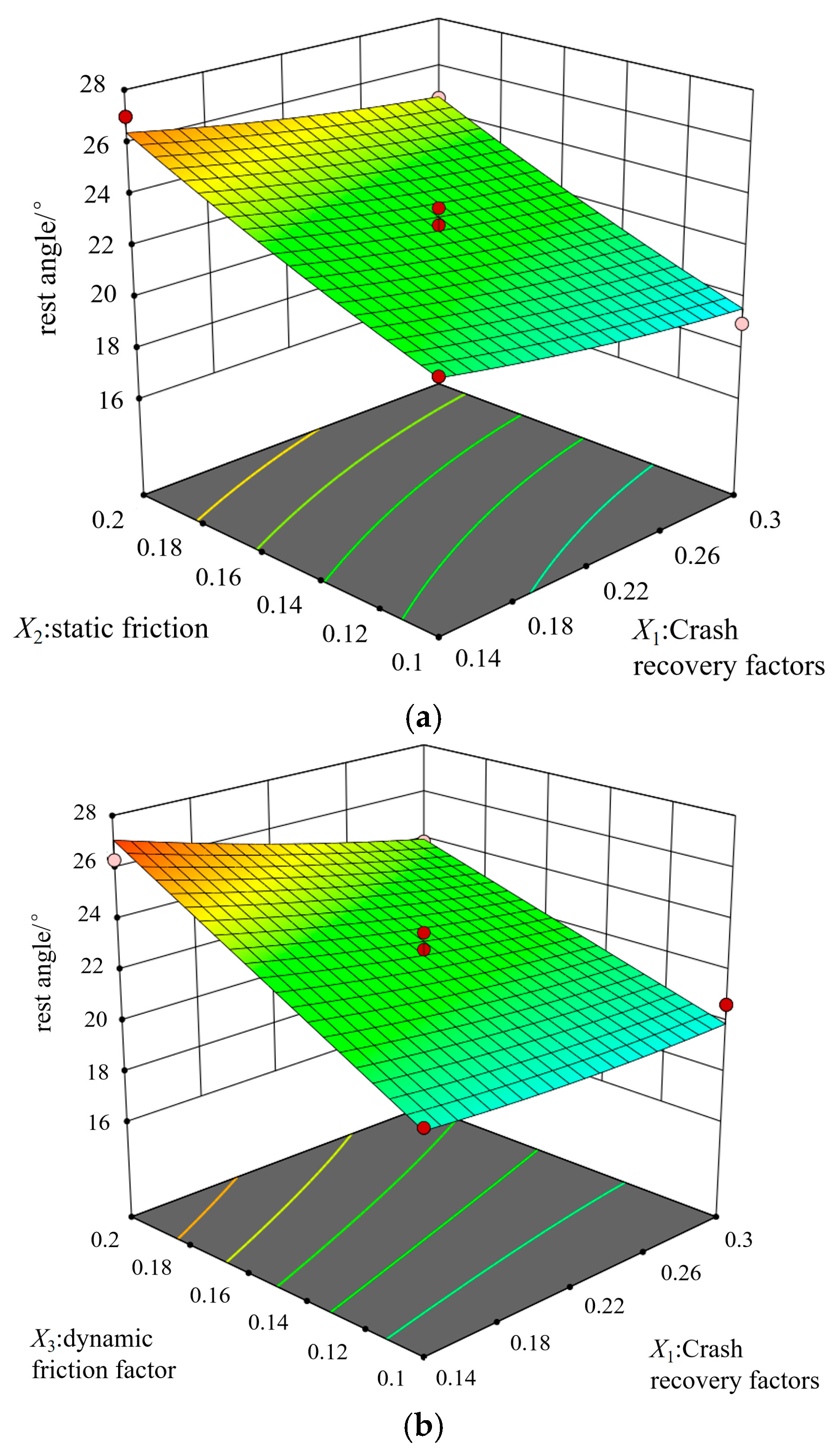
3.3. Box–Behnken Test
4. Discussion
4.1. Test Results and Analysis
4.2. Experimental Verification
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Q.C.; Shi, J.; Mu, B.; Chen, Z.; Dai, W.; Lin, Z. Metabolomics combined with proteomics provides a novel interpretation of the changes in nonvolatile compounds during white tea processing. Food Chem. 2020, 332, 127412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czernicka, M.; Zagula, G.; Bajcar, M.; Saletnik, B.; Puchalski, C. Study of nutritional value of dried tea leaves and infusions of black, green and white teas from Chinese plantations. Rocz. Państwowego Zakładu Hig. 2017, 68, 237–245. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, A.; Feng, H.; Jing, P.; Lan, Y.; Cao, X. White tea: A review on composition characteristics, extraction techniques, and application potentials. J. Tea Sci. Res. 2024, 14, 19–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.Z.; Zhu, C.; Li, X.; Chen, L.; Xie, S.-Y.; Chen, G.-W.; Zhang, H.; Lai, Z.-X.; Lin, Y.-L.; Guo, Y.-Q. Transcriptome and phytochemical analyses reveal the roles of characteristic metabolites in the taste formation of white tea during the withering process. J. Integr. Agric. 2022, 21, 862–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Wang, J.; Ye, M.; Wu, G. Development of a fully automatic tea bag packaging machine based on neural network algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2024 8th International Conference on Electrical, Mechanical and Computer Engineering (ICEMCE), Xi’an, China, 25–27 October 2024; pp. 1136–1140. [Google Scholar]
- Wanniarachchi, D.N.; Punchihewa, H.K.G.; Gunawardhana, S.D.; Ranaweera, R.K.P.S.; Gawarammana, M.B.M.L.B.; Mangala, K.H.J. Development of a Bulk Tea Packaging System. In Proceedings of the 2020 from Innovation to Impact (FITI), Colombo, Sri Lanka, 15 December 2020; Volume 1, pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, N.; Yu, G.; Zheng, H.; Chen, Z. Parameter calibration of tea garden soil based on discrete element method. Acta Agric. Zhejiangensis 2025, 37, 1353–1359. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Wang, P.; Wang, Y.; Ge, Y.F.; Tang, K.Y.; Li, D.Z. Calibration of Discrete Element Parameters of Corn Coated Seeds Based on Stacking Test. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2022, 24, 97–107, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wangm, J.; Yuan, J.; Yin, W.; Wang, Z.; Qian, Y. Analysis of threshed rice mixture separation through vibration screen using discrete element method. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2017, 10, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, D.; Lin, Z.; Qing, J.; Gao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Xie, L. Discrete element parameter calibration of soil-transplanting soil-touching parts of fungus under typical moisture content. J. Chin. Agric. Mech. 2025, 46, 279–286+294. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, W.; Ji, Y.; Qi, B.; Li, K. Parameter calibration of soil particles in annual rice wheat region based on diserete element method. J. Chin. Agric. Mech. 2020, 41, 153–159. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lai, Z.; Chen, Q.; Huang, L. Machine⁃learning⁃enabled discrete element method: Contact detection and resolution of irregular⁃shaped particles. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 2022, 46, 113–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W. Simulation Study of Sugarcane Havester Impurity Removal Based on CFD-DEM. Master’s Thesis, Guangxi University, Nanning, China, 2019. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X. Development of CFD-DEM-Based Wind Sorting Device for Wolfberry Picking Platform. Master’s Thesis, Ningxia University, Yinchuan, China, 2024. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zang, X.; Zhu, X. Simulation and experiment on the falling pattern of fresh tea leaves based on discrete elements. HortScience 2023, 58, 1057–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, G.; Qi, X.; Zhang, W.; Lv, Z.; Zhang, T.; Wang, S.; Wang, G. Parameter measurement andcalibration in discrete element simulation of broken sweet potato seedlings (Wang Gongpu translator). J. Chin. Agric. Mech. 2021, 42, 72–79. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qin, K.; Bu, K.; Shen, Z.; Cao, C.; Ge, J.; Fang, L. Tea Leaf Barber Optimization Design and Experiment of Continuous Compound. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2023, 54, 382–393. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jin, H.; Jiang, M.; Xu, C.; Shen, K.; Pan, F.D.; Fan, H.; Jiao, K.X. Modeling and Simulation Parameters Calibration of Flexible Tobacco Strips Based on Discrete Element. J. Shenyang Agric. Univ. 2023, 54, 563–571. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Wang, Z.; Zhai, G.; Tian, F.; Xing, K. Establishment and Parameter Calibration of Discrete Element Model of Alfalfa Plant. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2024, 55, 187–199. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Al-Hashemi, H.M.B.; Al-Amoudi, O.S.B. A review on the angle of repose of granular materials. Powder Technol. 2018, 330, 397–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Yan, J.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, X.; Niu, S.; Hu, Z. Simulation parameters calibration of needle-shaped tea based on pile-up test. J. Chin. Agric. Mech. 2024, 45, 66–73. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Song, J.; Li, Y.; Ma, T. Experiment and diserete element model of rice seed based on 3D laser scanning. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. (Trans. CSAE) 2016, 32, 294–300, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Gong, F.; Hu, M.; Bao, A.; Li, D.; Gao, T.; Wang, C. Parameter calibration and significance analysis of rice straw based on Hertz-Mindlin model. J. Southwest Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2022, 44, 186–196. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, H.; Xue, H.; Ni, C.; Wang, C. Calibration and Experiment of Discrete Element Parameters of Panax notoginseng Stem. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2023, 54, 61–70+91. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Gu, X.; Hu, J.; Zhou, Q. DEM simulation of small strain and large strain behaviors of granular soils with a coherent contact model. Granul. Matter 2022, 24, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dun, G.Q.; Gao, Z.Y.; Liu, Y.X.; Ji, W.; Mao, N.; Wu, X.; Liu, W. Optimization design of fertilizer apparatus owned arc gears based on discrete element method. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2021, 14, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, H.W.; Wu, C.Y.; Tu, Z.; Chen, J.N.; Jia, J.M.; Chen, Z.W.; Ye, Y. EDEM-based Optimization of Classification Parameters of Machine-picked Tea Fresh Leaf Vibratory Classifier. J. Tea Sci. 2022, 42, 120–130. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Li, W.; Bai, X.; Huang, J.H. Parameter Optimization and Experimental Study of Tea Twisting Machine Based on EDEM. J. Tea Sci. 2022, 42, 120–130. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, W.; Zhao, X.; Lyu, X. Design and Experiment of Drum-type Hot Air Re-dryer for Tea. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2020, 51, 377–386. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Bai, X.; Li, B. Optimization of structural parameters of drum type tea re-dryer. Acta Agric. Zhejiangensis 2020, 32, 348–358. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]

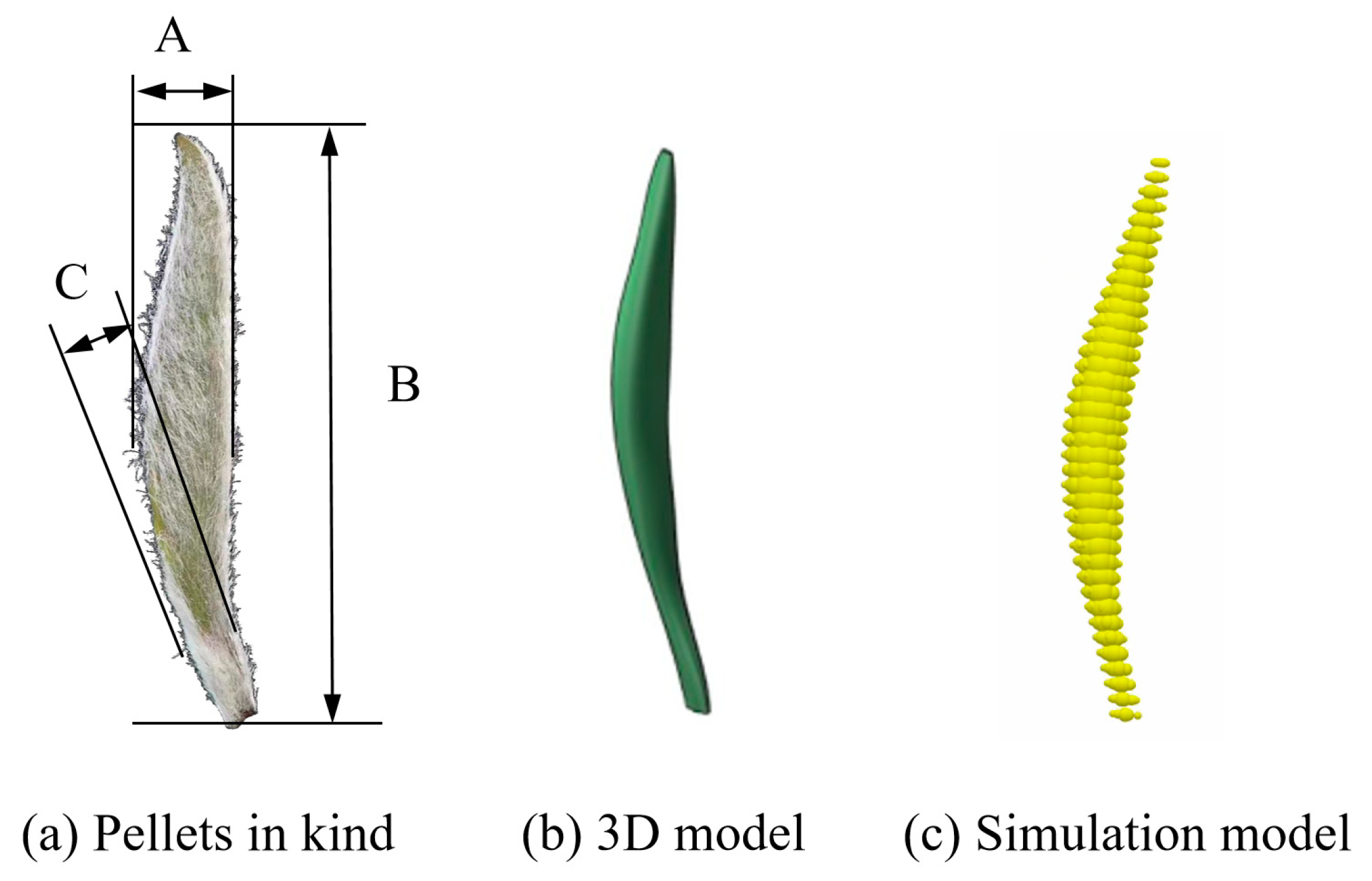


| Cross-Sectional Position | Average Width/mm | Average Thickness/mm |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.35 | 1.41 |
| 2 | 1.13 | 1.13 |
| 3 | 1.57 | 0.79 |
| 4 | 1.35 | 1.15 |
| 5 | 1.25 | 1.51 |
| 6 | 1.12 | 0.89 |
| 7 | 1.68 | 1.65 |
| 8 | 1.88 | 1.65 |
| 9 | 1.88 | 1.15 |
| 10 | 1.88 | 0.98 |
| 11 | 1.88 | 1.65 |
| 12 | 1.78 | 1.43 |
| 13 | 1.69 | 1.36 |
| 14 | 1.35 | 1.46 |
| 15 | 0.98 | 1.47 |
| Maximum Value | Minimum Value | Average Value | Standard Deviation | Coefficient of Variation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| e: the collision recovery coefficient e between the tea leaves and the steel plate | 0.450 | 0.226 | 0.326 | 0.04 | 0.09 |
| Tea leaves—static friction coefficient in contact with steel plate | 0.674 | 0.456 | 0.546 | 0.07 | 0.09 |
| Tea leaves—rolling friction coefficient of contact steel plates | 0.223 | 0.056 | 0.133 | 0.00014 | 0.076 |
| Serial Number | X1 | X2 | X3 | Angle of Repose/° | Relative Error/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 10.45 | 54.16 |
| 2 | 0.14 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 18.56 | 18.59 |
| 3 | 0.22 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 23.35 | 2.41 |
| 4 | 0.30 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 29.51 | 29.42 |
| 5 | 0.38 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 33.14 | 45.35 |
| Serial Number | X1 | X2 | X3 | Angle of Repose/° |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.14 | 0.10 | 0.15 | 21.45 |
| 2 | 0.30 | 0.10 | 0.15 | 19.01 |
| 3 | 0.14 | 0.20 | 0.15 | 27.00 |
| 4 | 0.30 | 0.20 | 0.15 | 24.67 |
| 5 | 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.10 | 20.45 |
| 6 | 0.30 | 0.15 | 0.10 | 20.71 |
| 7 | 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.20 | 26.32 |
| 8 | 0.30 | 0.15 | 0.20 | 23.90 |
| 9 | 0.22 | 0.20 | 0.10 | 16.95 |
| 10 | 0.22 | 0.20 | 0.10 | 22.51 |
| 11 | 0.22 | 0.10 | 0.20 | 24.27 |
| 12 | 0.22 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 27.72 |
| 13 | 0.22 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 22.40 |
| 14 | 0.22 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 22.34 |
| 15 | 0.22 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 22.11 |
| 16 | 0.22 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 22.88 |
| 17 | 0.22 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 23.54 |
| Source of Variance | Sum of Squares | Degrees of Freedom | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| model | 118.61 | 9 | 13.18 | 21.67 | 0.0003 |
| X1 | 6.00 | 1 | 6.00 | 9.87 | 0.0163 * |
| X2 | 51.11 | 1 | 51.11 | 84.04 | <0.01 ** |
| X3 | 58.27 | 1 | 58.27 | 95.82 | <0.01 ** |
| X1X2 | 0.0030 | 1 | 0.0030 | 0.0050 | 0.9457 |
| X1X3 | 1.80 | 1 | 1.80 | 2.95 | 0.1294 |
| X2X3 | 1.11 | 1 | 1.11 | 1.83 | 0.2182 |
| X12 | 0.1372 | 1 | 0.1372 | 0.2256 | 0.6493 |
| X22 | 0.1651 | 1 | 0.1651 | 0.2714 | 0.6184 |
| X32 | 0.0005 | 1 | 0.0005 | 0.0008 | 0.9787 |
| residual | 4.26 | 7 | 0.6081 | ||
| missing item | 2.96 | 3 | 0.9872 | 3.05 | 0.1548 |
| error | 1.30 | 4 | 0.3238 | ||
| total | 122.87 | 16 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, D.; Gao, Y.; Qi, Y.; Wang, H.; Wu, R.; Weng, H. DEM Parameter Calibration and Experimental Definition for White Tea Granular Systems. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1909. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081909
Ye D, Gao Y, Qi Y, Wang H, Wu R, Weng H. DEM Parameter Calibration and Experimental Definition for White Tea Granular Systems. Agronomy. 2025; 15(8):1909. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081909
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Dapeng, Yuxuan Gao, Yanlin Qi, Hao Wang, Renye Wu, and Haiyong Weng. 2025. "DEM Parameter Calibration and Experimental Definition for White Tea Granular Systems" Agronomy 15, no. 8: 1909. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081909
APA StyleYe, D., Gao, Y., Qi, Y., Wang, H., Wu, R., & Weng, H. (2025). DEM Parameter Calibration and Experimental Definition for White Tea Granular Systems. Agronomy, 15(8), 1909. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081909





