Interannual Variability in Precipitation Modulates Grazing-Induced Vertical Translocation of Soil Organic Carbon in a Semi-Arid Steppe
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
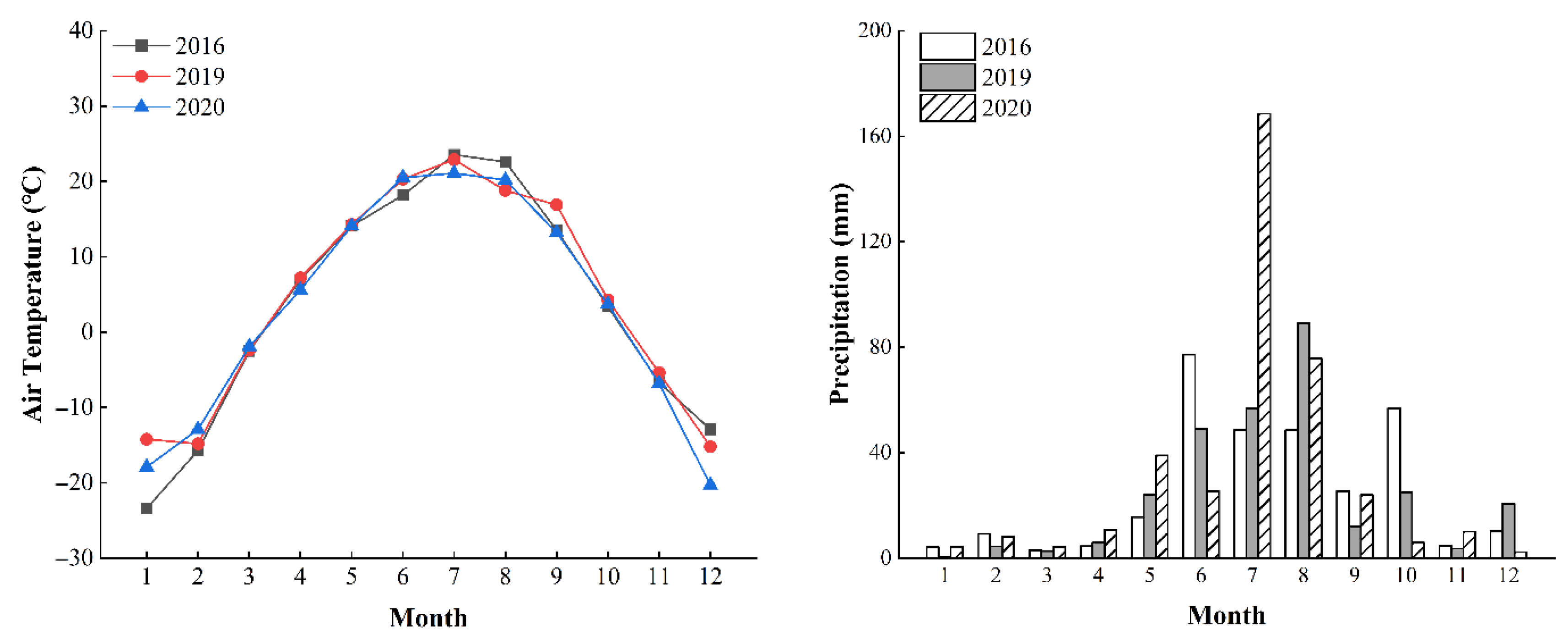
2.1. Study Site Description
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Plant Sampling and Analysis
2.4. Soil Sampling and Analysis
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
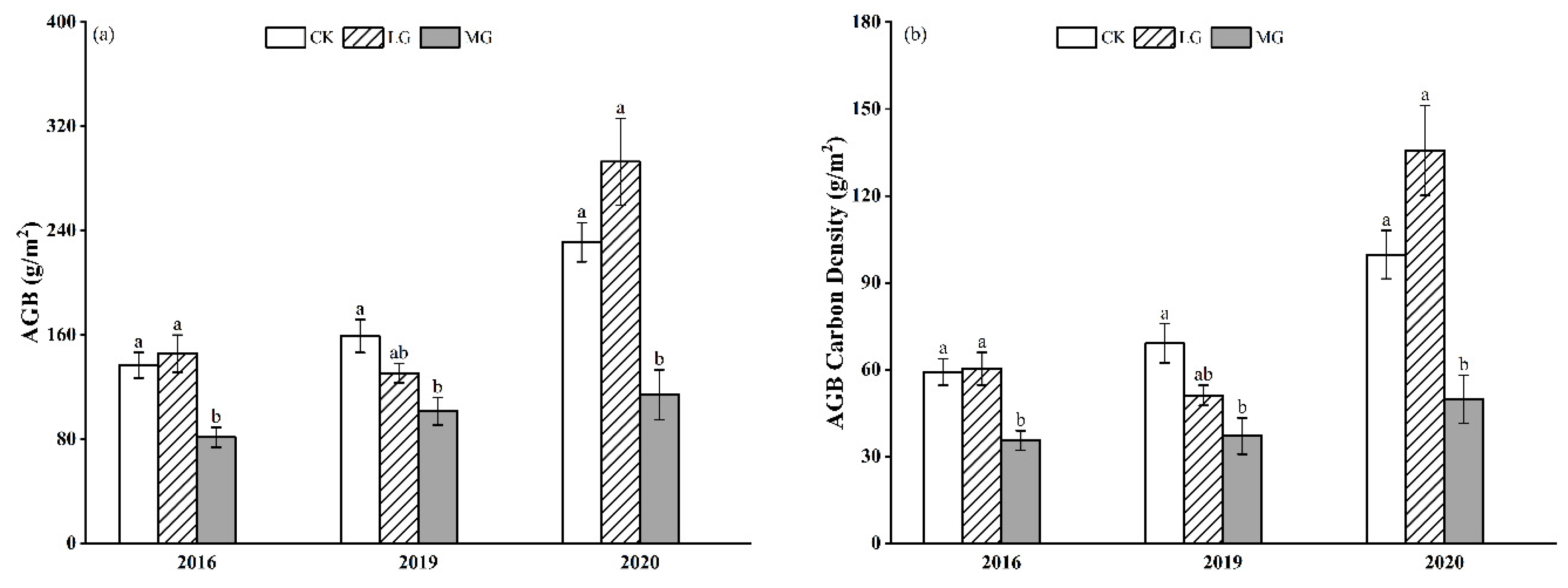
3.1. Aboveground Biomass (AGB) and AGB Carbon Density
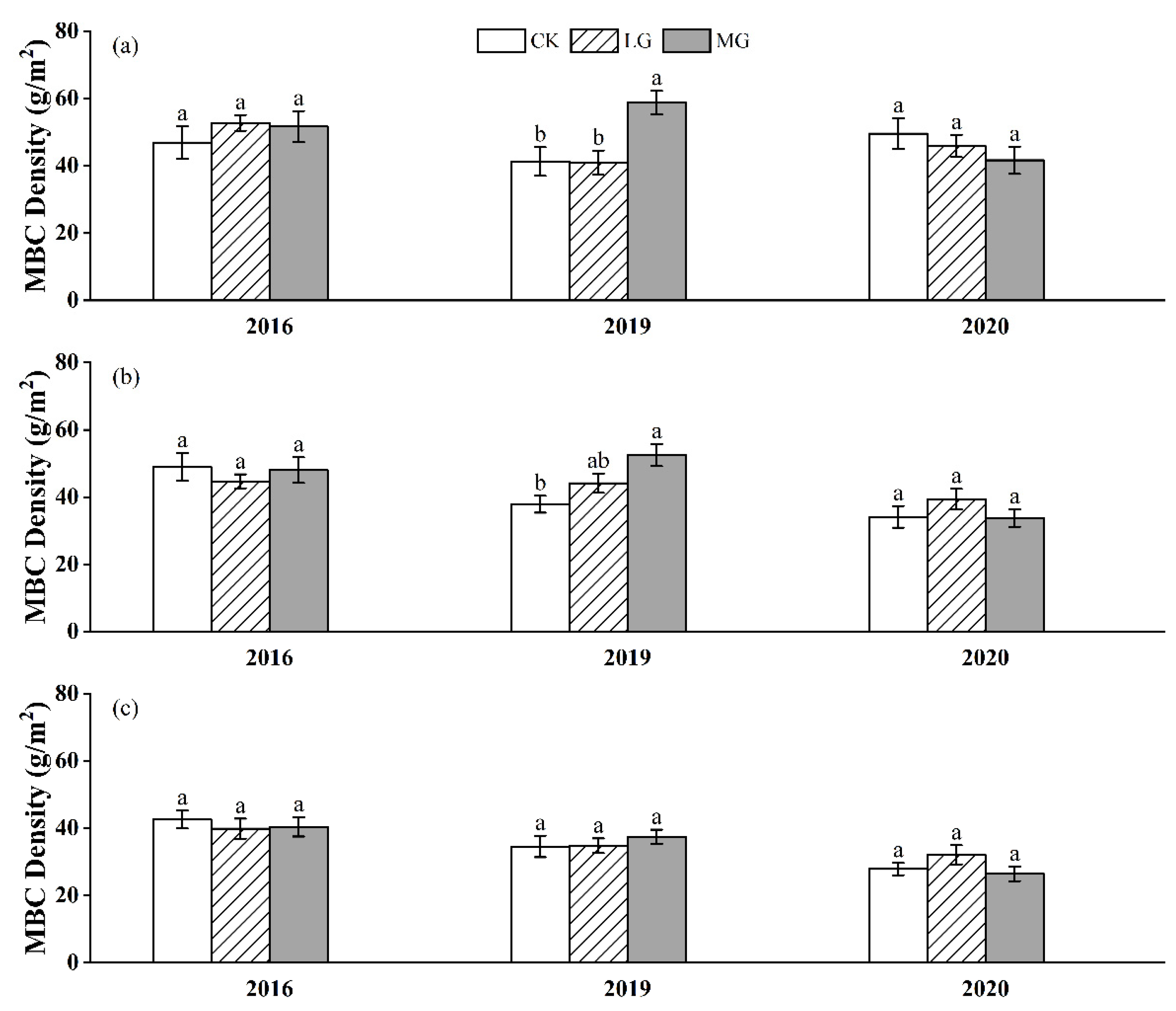
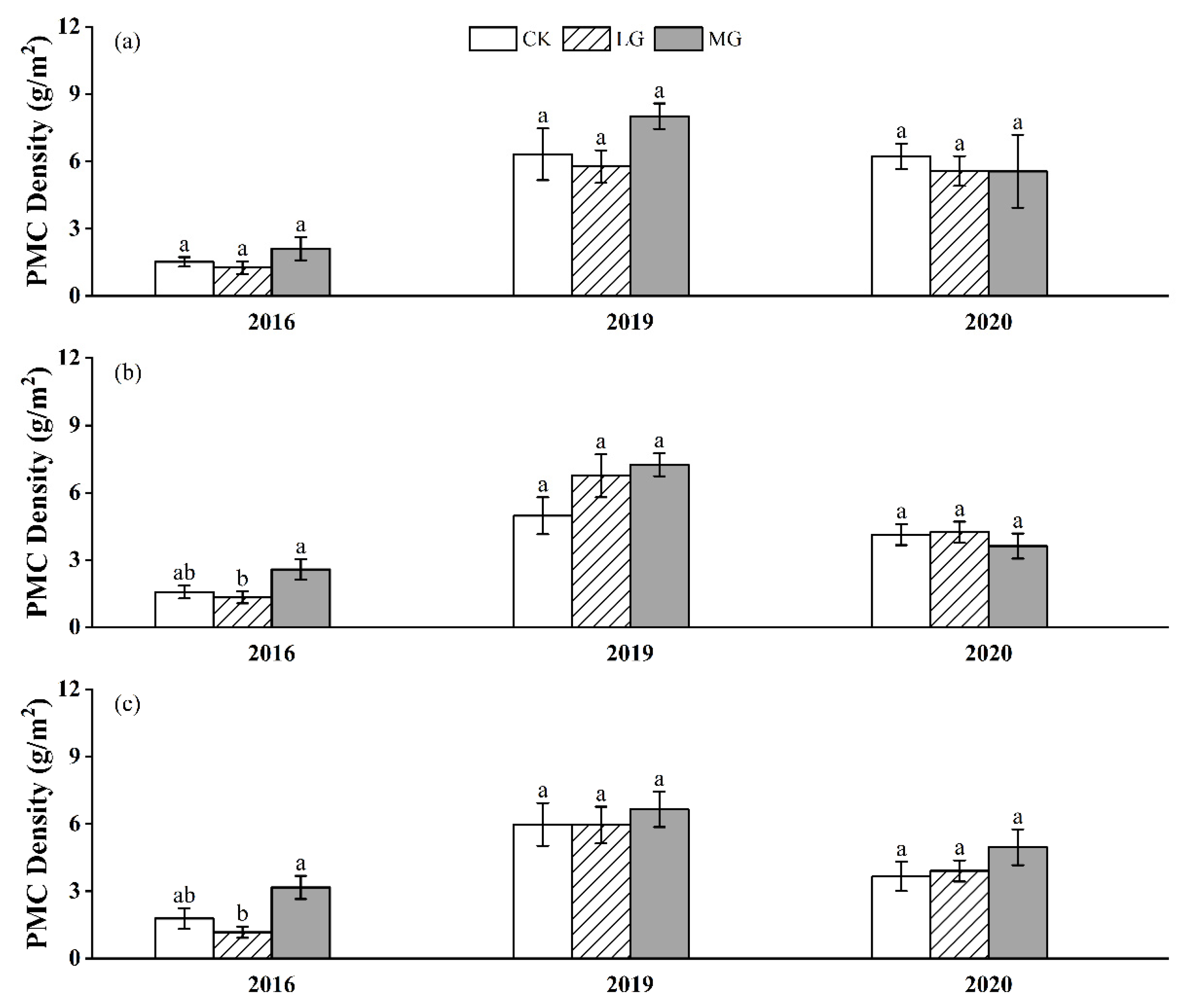
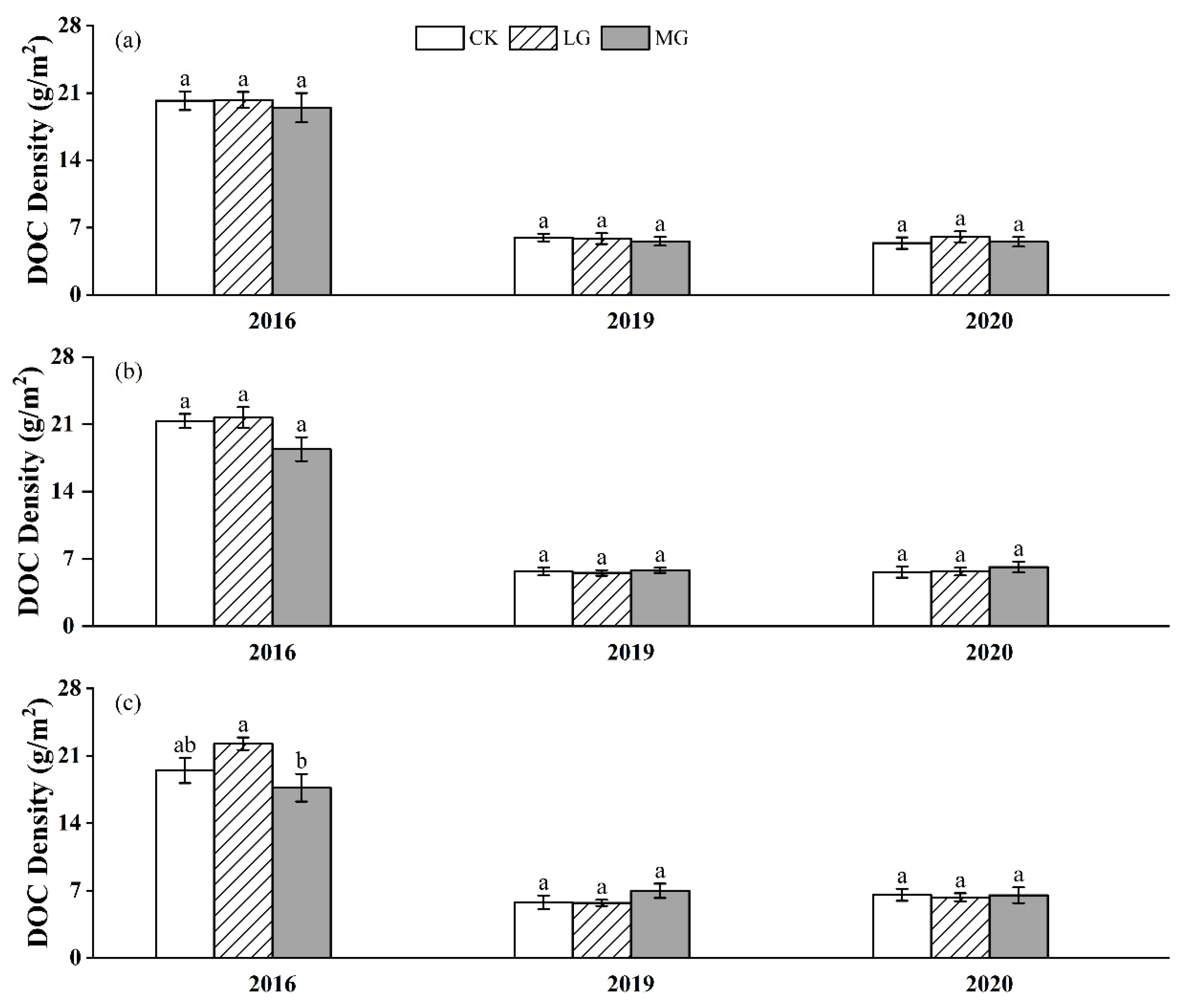
3.2. Labile SOC Fractions
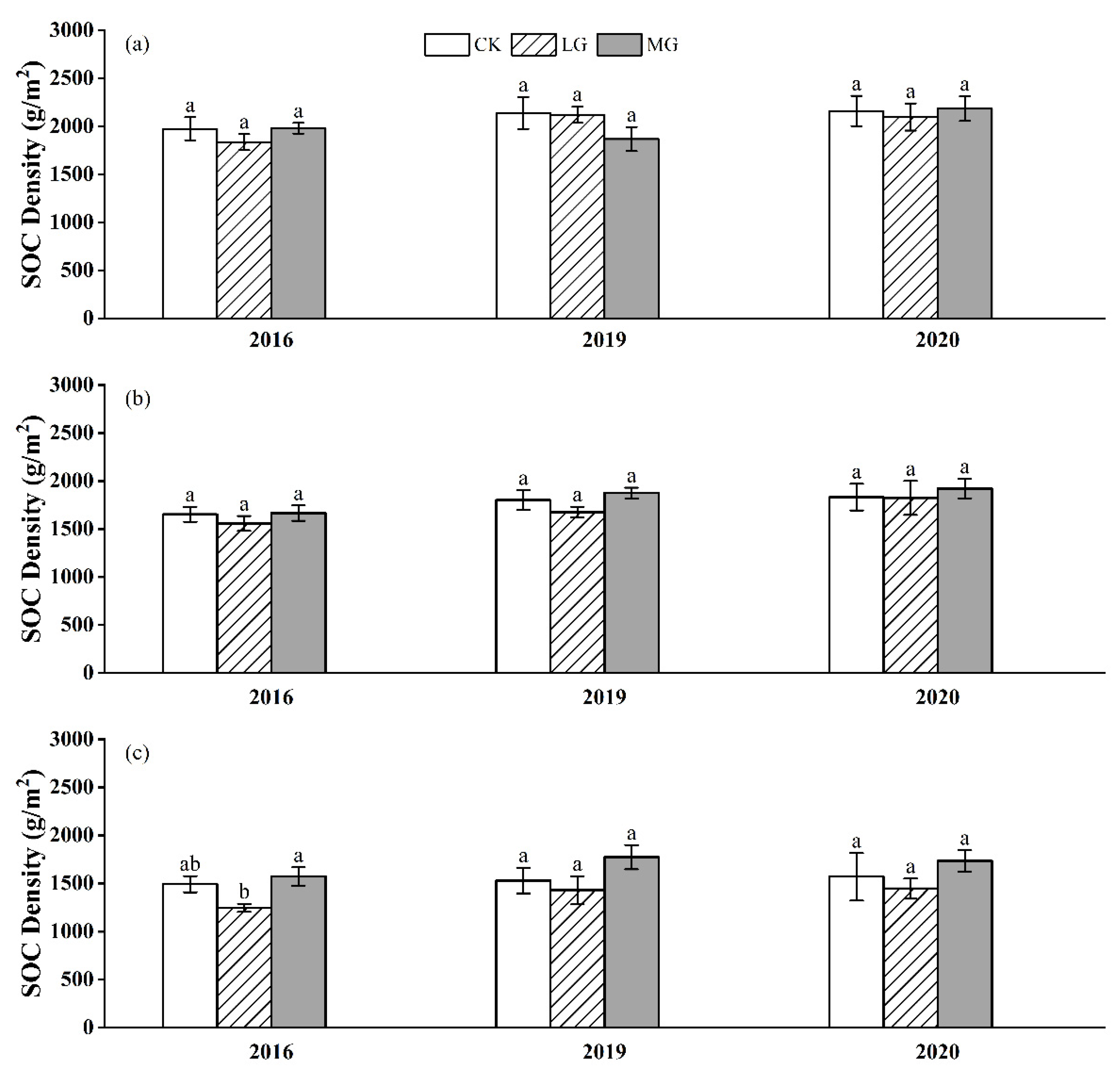
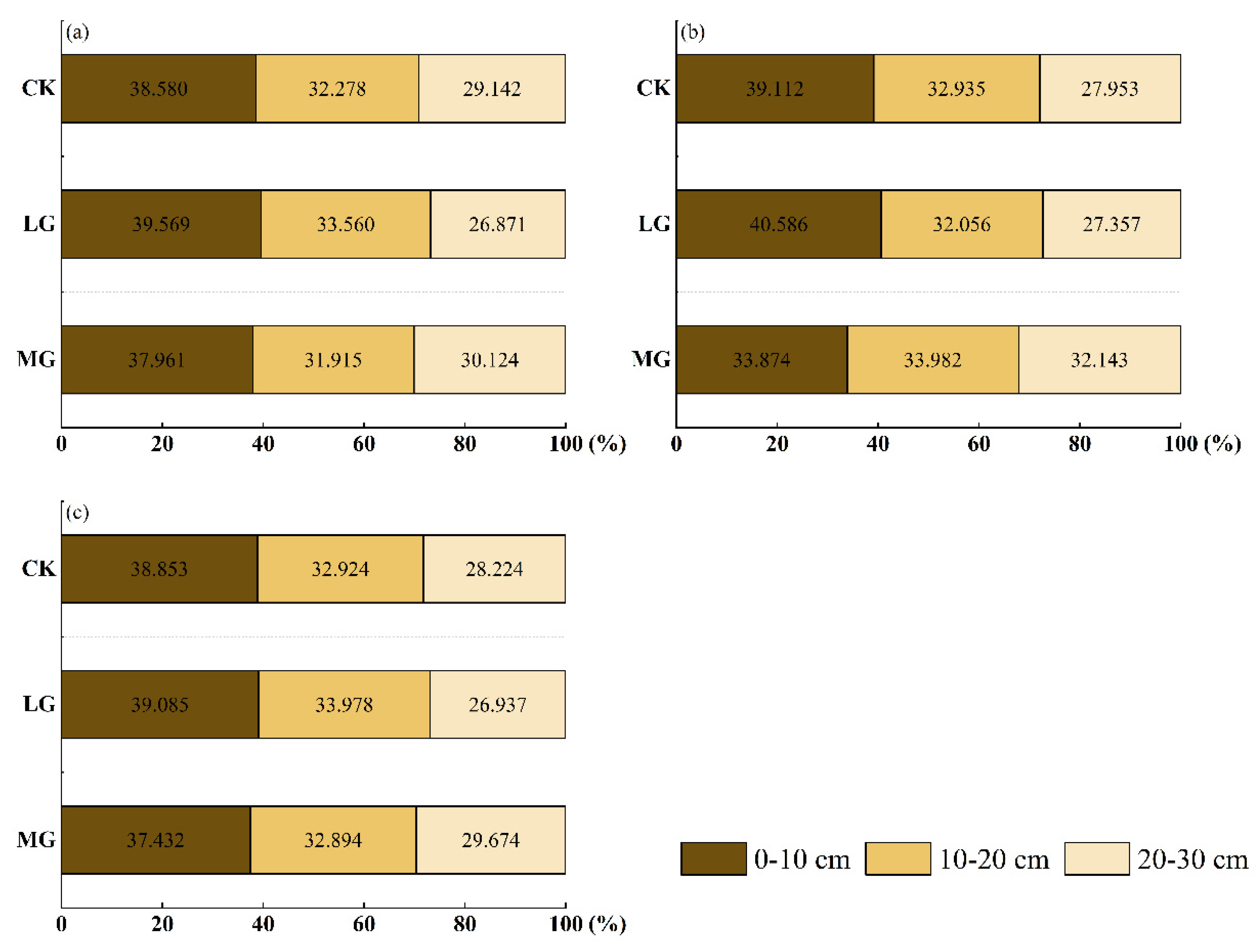
3.3. Total Soil Organic Carbon (SOC)
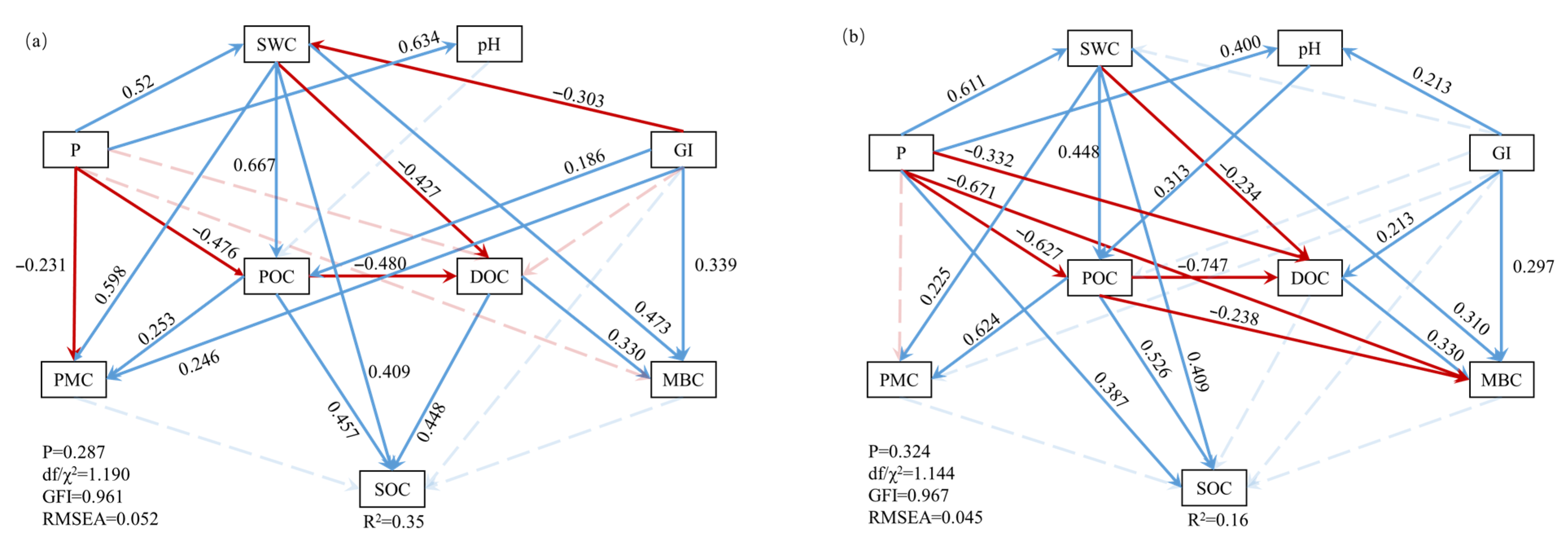
3.4. The Direct and Indirect Effects of Predictor Variables on SOC Density
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Grazing Intensity on AGB and Carbon Density
4.2. Effects of Grazing Intensity on SOC and Labile SOC Fractions
4.3. Effects of Precipitation on SOC and Labile SOC Fractions
4.4. Main Limitations and Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lal, R. Soil Carbon Sequestration Impacts on Global Climate Change and Food Security. Science 2004, 304, 1623–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, M.W.I.; Torn, M.S.; Abiven, S.; Dittmar, T.; Guggenberger, G.; Janssens, I.A.; Kleber, M.; Kögel-Knabner, I.; Lehmann, J.; Manning, D.A.C.; et al. Persistence of soil organic matter as an ecosystem property. Nature 2011, 478, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.B.; Yu, H.X.; Xiao, H.Y.; Wang, T.; Hossain, M.A.; Wu, Y.S.; Yadav, N. Radiocarbon evidence of organic carbon turnover response to grassland grazing: A soil aggregate fraction perspective. Sustain. Horiz. 2024, 12, 100115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, E.; Midwood, A.J.; Millard, P. Through the eye of the needle: A review of isotope approaches to quantify microbial processes mediating soil carbon balance. New Phytol. 2009, 184, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wander, M.M.; Traina, S.J.; Stinner, B.R.; Peters, S.E. Organic and conventional management effects on biologically active soil organic matter pools. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1994, 58, 1130–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, M.E.; Galantini, J.A.; Martínez, J.M.; Limbozzi, F. Labile soil organic carbon for assessing soil quality: Influence of management practices and edaphic conditions. Catena 2018, 171, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Huang, Q. Comprehensive analysis of grazing intensity impacts soil organic carbon: A case study in typical steppe of Inner Mongolia, China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018, 129, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Lou, Y.; Sun, X.; Wang, W.; Baniyamuddin, M.; Zhao, K. Soil organic carbon active fractions as early indicators for total carbon change under straw incorporation. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2011, 47, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardgett, R.D.; Bullock, J.M.; Lavorel, S.; Manning, P.; Schaffner, U.; Ostle, N.; Chomel, M.; Durigan, G.; Fry, E.L.; Johnson, D.; et al. Combatting global grassland degradation. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 720–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.S.; Xu, F.W. Root, not aboveground litter, controls soil carbon storage under grazing exclusion across grasslands worldwide. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 3326–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.P.; Han, S.J.; Zheng, Y.H.; Zhang, X.M.; Wu, H.H.; Cui, J.F.; Xiao, C.W.; Han, X.G. Fencing facility affects plant species and soil organic carbon in temperate steppes. Catena 2021, 196, 104928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.Y.; Hu, Z.M.; Lai, D.Y.F.; Han, D.R.; Wang, M.; Liu, M.; Zhang, M.; Guo, M.Y. Light grazing facilitates carbon accumulation in subsoil in Chinese grasslands: A meta-analysis. Glob. Change Biol. 2020, 26, 7186–7197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, J.A.; Svenning, J.C.; Georgiou, K.; Malhi, Y. Can large herbivores enhance ecosystem carbon persistence? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2022, 37, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Terrer, C.; Li, J.; Cao, Y.; Yang, S.; Liu, D. Historical impacts of grazing on carbon stocks and climate mitigation opportunities. Nat. Clim. Change 2024, 14, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Kan, H.M.; Yang, G.W.; Zhang, Y.J. Changes in plant, soil, and microbes in a typical steppe from simulated grazing: Explaining potential change in soil C. Ecol. Monogr. 2015, 85, 269–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.H.; Bai, Y.F.; Wang, W.W.; Qu, G.P.; Deng, Z.H.; Li, R.C.; Zhao, J.X. Warm- and cold-season grazing affect plant diversity and soil carbon and nitrogen sequestration differently in Tibetan alpine swamp meadows. Plant Soil 2021, 458, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McSherry, M.E.; Ritchie, M.E. Effects of grazing on grassland soil carbon: A global review. Glob. Change Biol. 2013, 19, 1347–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Ren, C.; Shelton, S.; Wang, Z.; Pang, G.; Chen, J.; Wang, J. Grazing intensity influence soil microbial communities and their implications for soil respiration. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 249, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, D.; Shi, P.; Zhang, X.; Zou, C.B. Effects of grazing exclusion on carbon sequestration and plant diversity in grasslands of China—A meta-analysis. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 94, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.F.; Wu, J.G.; Clark, C.M.; Pan, Q.M.; Zhang, L.X.; Chen, S.P.; Wang, Q.B.; Han, X.G. Grazing alters ecosystem functioning and C:N:P stoichiometry of grasslands along a regional precipitation gradient. J. Appl. Ecol. 2012, 49, 1204–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, C.H.; Strickland, M.S.; Hutchings, J.A.; Bianchi, T.S.; Flory, S.L. Grazing enhances belowground carbon allocation, microbial biomass, and soil carbon in a subtropical grassland. Glob. Change Biol. 2018, 24, 2997–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, N.P.; Zhang, Y.H.; Yu, Q.; Chen, Q.S.; Pan, Q.M.; Zhang, G.M.; Han, X.G. Grazing intensity impacts soil carbon and nitrogen storage of continental steppe. Ecosphere 2011, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesmeier, M.; Barthold, F.; Blank, B.; Kögel-Knabner, I. Digital mapping of soil organic matter stocks using Random Forest modeling in a semi-arid steppe ecosystem. Plant Soil 2011, 340, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damien, H.; Nathalie, V.; Frederique, L.; Gael, A.; Julien, P.; Catherine, P.C.; Isabelle, B.; Pascal, C. How does soil particulate organic carbon respond to grazing intensity in permanent grasslands? Plant Soil 2015, 394, 239–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Molen, M.K.; Dolman, A.J.; Ciais, P.; Eglin, T.; Gobron, N.; Law, B.E.; Meir, P.; Peters, W.; Phillips, O.L.; Reichstein, M.; et al. Drought and ecosystem carbon cycling. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2011, 151, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Kim, S.; Han, S.H.; Chang, H.; Du, D.; Son, Y. Precipitation affects soil microbial and extracellular enzymatic responses to warming. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 120, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannenberg, S.A.; Anderegg, W.R.L.; Barnes, M.L.; Dannenberg, M.P.; Knapp, A.K. Dominant role of soil moisture in mediating carbon and water fluxes in dryland ecosystems. Nat. Geosci. 2024, 17, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhao, X.; Li, G.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X. Review on responses of grassland plant-soil to precipitation and management measures in arid and semi-arid areas of China. J. Desert Res. 2025, 45, 131–140. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, G.Y.; Zhou, X.H.; He, Y.H.; Shao, J.J.; Hu, Z.H.; Liu, R.Q.; Zhou, H.M.; Hosseinibai, S. Grazing intensity significantly affects belowground carbon and nitrogen cycling in grassland ecosystems: A meta-analysis. Glob. Change Biol. 2017, 23, 1167–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Viscarra Rossel, R.A.; Shi, Z. Distinct controls over the temporal dynamics of soil carbon fractions after land use change. Glob. Change Biol. 2020, 26, 4614–4625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Gong, J.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, J.; Zhang, W.; Song, L. Grazing directly or indirectly affect shoot and root litter decomposition in different decomposition stage by changing soil properties. Catena 2022, 209, 105803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Gong, J.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, L.; Hou, X. Growth–defense trade-off regulated by hormones in grass plants growing under different grazing intensities. Physiol. Plant. 2019, 166, 553–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.Y.; Xu, X.X.; Liu, W.Z.; Chen, T.L. Dynamic changes of soil moisture in loess hilly and gully region under effects of different yearly precipitation patterns. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2008, 19, 1234–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, R.; Lyu, W.; Yi, F.; Liu, Y.; Chang, H.; Sun, H.; Liu, Y. Evaluating the implementation effects of grassland ecological conservation subsidy and reward policies: A case study of xilinhot city, Inner Mongolia. Anim. Husb. Feed Sci. 2015, 36, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, E.D.; Brookes, P.C.; Jenkinson, D.S. An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass-C. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1987, 19, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellert, B.H.; Bettany, J.R. Calculation of organic matter and nutrients stored in soils under contrasting management regimes. Can. J. Soil Sci. 1995, 75, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, K.C.; He, J.S.; Zhang, S.T.; Lechowicz, M.J. Tradeoffs between forage quality and soil fertility: Lessons from Himalayan rangelands. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 234, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.Y.; Kelsey, K.C.; Yan, Y.; Sun, J.; Wang, X.D.; Cheng, G.W.; Neff, J.C. Effects of grazing on ecosystem structure and function of alpine grasslands in Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau: A synthesis. Ecosphere 2017, 8, e01656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, B.D.; Dong, X.J.; Nyren, P.E.; Nyren, A. Effects of grazing intensity, precipitation, and temperature on forage production. Rangel. Ecol. Manag. 2007, 60, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Gong, J.; Li, X.; Ding, Y.; Shi, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Dong, J. Plant phosphorus demand stimulates rhizosphere phosphorus transition by root exudates and mycorrhizal fungi under different grazing intensities. Geoderma 2022, 423, 115964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönbach, P.; Wan, H.; Gierus, M.; Bai, Y.; Müller, K.; Lin, L.; Susenbeth, A.; Taube, F. Grassland responses to grazing: Effects of grazing intensity and management system in an Inner Mongolian steppe ecosystem. Plant Soil 2011, 340, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulick, A.G.; Johnson, R.A.; Pollock, C.G.; Hillis-Starr, Z.; Bolten, A.B.; Bjorndal, K.A. Recovery of a cultivation grazer: A mechanism for compensatory growth of Thalassia testudinum in a Caribbean seagrass meadow grazed by green turtles. J. Ecol. 2021, 109, 3031–3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.J.; Dang, X.H.; Gao, Y.; Ren, X.M.; Ding, Y.L.; Wang, M. Interactive effects of wind speed, vegetation coverage and soil moisture in controlling wind erosion in a temperate desert steppe, Inner Mongolia of China. J. Arid Land 2018, 10, 534–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, B.; Xie, G.D.; Zhai, X.; Sun, H.L. Vegetation cover changes and sand -fixing service responses in the sandstorm source control area. Environ. Dev. 2020, 34, 100455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patoine, G.; Eisenhauer, N.; Cesarz, S.; Phillips, H.R.P.; Xu, X.F.; Zhang, L.H.; Guerra, C.A. Drivers and trends of global soil microbial carbon over two decades. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duo, X.; Xu, Z.; Yang, L.; Qi, Q.; Yang, H.; Li, Z. The influencing factors and control strategies of soil labile organic carbon in opencast coal mine reclamation. J. Nat. Resour. 2024, 39, 2735–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garten, C.T.; Classen, A.T.; Norby, R.J. Soil moisture surpasses elevated CO2 and temperature as a control on soil carbon dynamics in a multi-factor climate change experiment. Plant Soil 2009, 319, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enriquez, A.S.; Cremona, M.V. Particulate organic carbon is a sensitive indicator of soil degradation related to overgrazing in Patagonian wet and mesic meadows. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 26, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewins, D.B.; Lyseng, M.P.; Schoderbek, D.F.; Alexander, M.; Willms, W.D.; Carlyle, C.N.; Chang, S.X.; Bork, E.W. Grazing and climate effects on soil organic carbon concentration and particle-size association in northern grasslands. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walse, C.; Berg, B.; Sverdrup, H. Review and synthesis of experimental data on organic matter decomposition with respect to the effect of temperature, moisture, and acidity. Environ. Rev. 1998, 6, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Si, J.; Jia, B.; He, X.; Zhou, D.; Wang, C.; Qin, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, L. Changes of soil carbon along precipitation gradients in three typical vegetation types in the Alxa desert region, China. Carbon Balance Manag. 2024, 19, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hu, X. Woody plant reduces soil organic carbon controlled by precipitation. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 377, 124581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.N.; Zhu, Q.A.; Zhan, W.; Xu, Y.Y.; Zhu, E.X.; Gao, Y.H.; Li, S.Q.; Zheng, Q.Y.; Zhu, D.; He, Y.X.; et al. The linkage between vegetation and soil nutrients and their variation under different grazing intensities in an alpine meadow on the eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 110, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.J.; Dai, G.H.; Liu, T.; Jia, J.; Zhu, E.X.; Liu, C.Z.; Zhao, Y.P.; Wang, Y.; Kang, E.Z.; Xiao, J.; et al. Understanding the mechanisms and potential pathways of soil carbon sequestration from the biogeochemistry perspective. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2024, 67, 3386–3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.Y.; Li, F.R.; Chen, S.K.; Zhang, H.R.; Li, G.D. Dynamics of vegetation and soil carbon and nitrogen accumulation over 26 years under controlled grazing in a desert shrubland. Plant Soil 2011, 341, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Chen, S.; Hu, R.; Li, Y. Aggregate stability and size distribution of red soils under different land uses integrally regulated by soil organic matter, and iron and aluminum oxides. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 167, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Zheng, Y.; Martinsen, V.; Liang, C.; Mulder, J. Effect of Grazing Exclusion and Rotational Grazing on Soil Aggregate Stability in Typical Grasslands in Inner Mongolia, China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 844151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobbágy, E.G.; Jackson, R.B. The vertical distribution of soil organic carbon and its relation to climate and vegetation. Ecol. Appl. 2000, 10, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, O.A.; Kumar, S.S.; Hussain, N.; Wani, A.I.A.; Babu, S.; Alam, P.; Rashid, M.; Popescu, S.M.; Mansoor, S. Multi-scale processes influencing global carbon storage and land-carbon-climate nexus: A critical review. Pedosphere 2023, 33, 250–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Norby, R.J.; Ledford, J.; Weltzin, J.F. Responses of soil respiration to elevated CO2, air warming, and changing soil water availability in a model old-field grassland. Glob. Change Biol. 2007, 13, 2411–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockett, B.F.T.; Prescott, C.E.; Grayston, S.J. Soil moisture is the major factor influencing microbial community structure and enzyme activities across seven biogeoclimatic zones in western Canada. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 44, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Feng, W.; Luo, Y.; Baldock, J.; Wang, E. Soil organic carbon dynamics jointly controlled by climate, carbon inputs, soil properties and soil carbon fractions. Glob. Change Biol. 2017, 23, 4430–4439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Van Meerbeek, K.; Yue, K.; Ni, X.; Desie, E.; Heděnec, P.; Yang, J.; Wu, F. Responses of soil C pools to combined warming and altered precipitation regimes: A meta-analysis. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2023, 32, 1660–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.H.; Xu, X.; Ju, C.H.; Chen, H.Y.H.; Wilsey, B.J.; Luo, Y.Q.; Fan, W. Long-term, amplified responses of soil organic carbon to nitrogen addition worldwide. Glob. Change Biol. 2021, 27, 1170–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.Y.; Niu, B.; Hu, Y.L.; Luo, T.X.; Zhang, G.X. Warming and increased precipitation indirectly affect the composition and turnover of labile-fraction soil organic matter by directly affecting vegetation and microorganisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 714, 136787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Xu, Z.W.; Yang, S.; Li, X.B.; Top, E.M.; Wang, R.Z.; Zhang, Y.G.; Cai, J.P.; Yao, F.; Han, X.G.; et al. Responses of Soil Bacterial Communities to Nitrogen Deposition and Precipitation Increment Are Closely Linked with Aboveground Community Variation. Microb. Ecol. 2016, 71, 974–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtson, P.; Bengtsson, G. Rapid turnover of DOC in temperate forests accounts for increased CO2 production at elevated temperatures. Ecol. Lett. 2007, 10, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Qiu, S.-J.; Liu, J.-T.; Liu, Q.; Lu, Z.-H. Roles of soil dissolved organic carbon in carbon cycling of terrestrial ecosystems: A review. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2012, 23, 1407–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.J.; Zhao, F.Z.; Shi, Z.; Chen, J.; Han, X.H.; Yang, G.H.; Feng, Y.Z.; Ren, G.X. Differential responses of soil microbial biomass and carbon-degrading enzyme activities to altered precipitation. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 115, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.Q.; Peñuelas, J.; Yue, K.; Zhou, Z.H.; Yan, P.; Heděnec, P.; Zhang, H.; Ji, Y.K.; Ma, N.; Chang, S.X.; et al. Asymmetric responses of litter decomposition to altered precipitation: Double evidence from field experiments and global synthesis. Innov. Geosci. 2025, 3, 100117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Soil Depth | Predictor | Direct Effect | Indirect Effect | Total Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–10 cm | GI | 0.005 | −0.090 | −0.085 |
| P | - | 0.085 | 0.085 | |
| SWC | 0.409 | 0.117 | 0.526 | |
| pH | - | 0.062 | 0.062 | |
| POC | 0.457 | −0.186 | 0.271 | |
| MBC | 0.083 | - | 0.083 | |
| PMC | 0.167 | - | 0.167 | |
| DOC | 0.448 | 0.027 | 0.475 | |
| 10–20 cm | GI | −0.067 | 0.152 | 0.084 |
| P | 0.387 | −0.197 | 0.189 | |
| SWC | - | 0.117 | 0.117 | |
| pH | - | 0.09 | 0.090 | |
| POC | 0.526 | −0.239 | 0.287 | |
| MBC | 0.180 | - | 0.180 | |
| PMC | −0.177 | - | −0.177 | |
| DOC | 0.116 | - | 0.116 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Li, X.; Li, M.; Li, X.; Dang, D.; Wang, K.; Dou, H.; Lyu, X. Interannual Variability in Precipitation Modulates Grazing-Induced Vertical Translocation of Soil Organic Carbon in a Semi-Arid Steppe. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1839. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081839
Liu S, Li X, Li M, Li X, Dang D, Wang K, Dou H, Lyu X. Interannual Variability in Precipitation Modulates Grazing-Induced Vertical Translocation of Soil Organic Carbon in a Semi-Arid Steppe. Agronomy. 2025; 15(8):1839. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081839
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Siyu, Xiaobing Li, Mengyuan Li, Xiang Li, Dongliang Dang, Kai Wang, Huashun Dou, and Xin Lyu. 2025. "Interannual Variability in Precipitation Modulates Grazing-Induced Vertical Translocation of Soil Organic Carbon in a Semi-Arid Steppe" Agronomy 15, no. 8: 1839. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081839
APA StyleLiu, S., Li, X., Li, M., Li, X., Dang, D., Wang, K., Dou, H., & Lyu, X. (2025). Interannual Variability in Precipitation Modulates Grazing-Induced Vertical Translocation of Soil Organic Carbon in a Semi-Arid Steppe. Agronomy, 15(8), 1839. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081839





