Cultivated Land Quality Evaluation and Constraint Factor Identification Under Different Cropping Systems in the Black Soil Region of Northeast China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
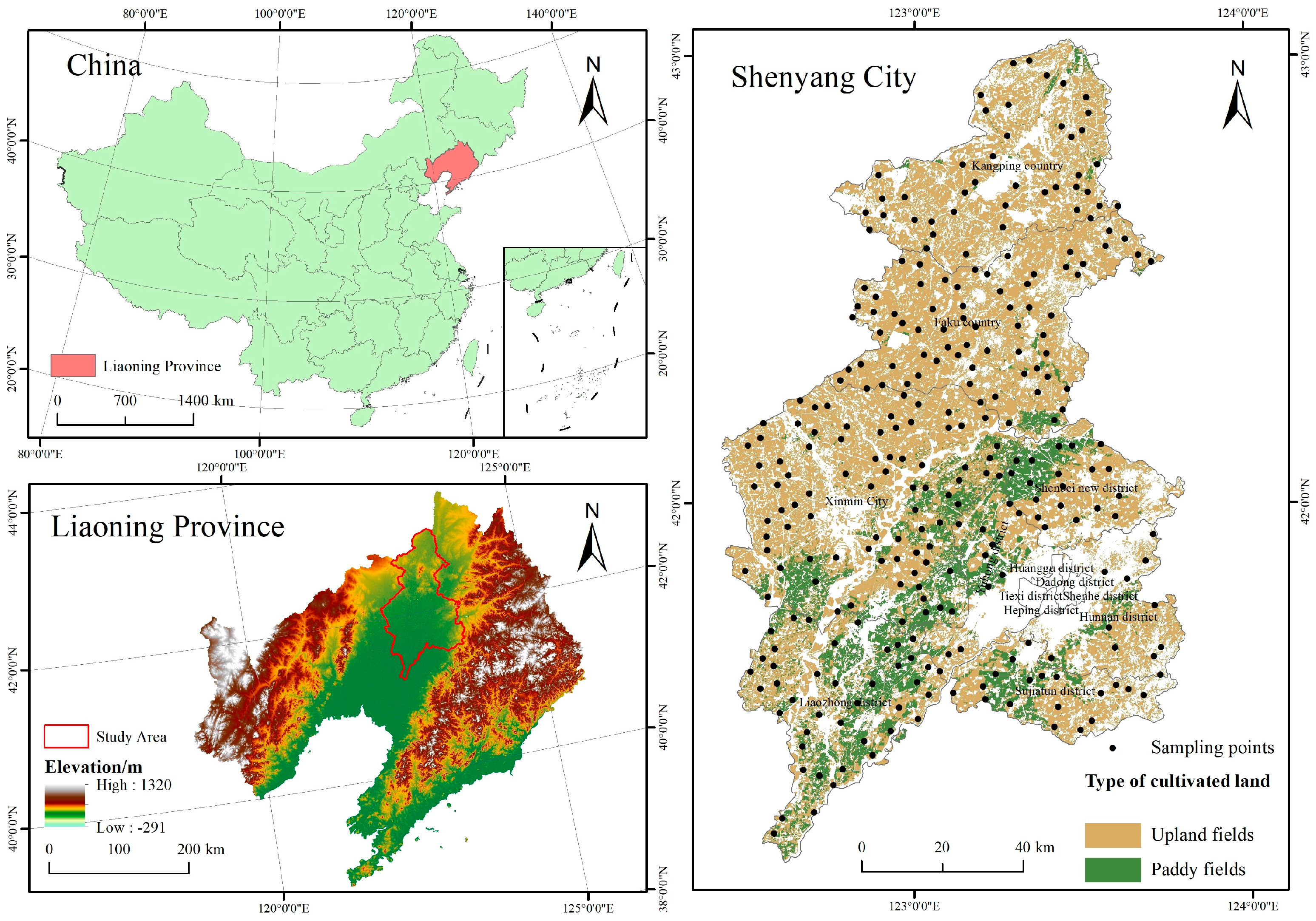
2.1. Study Area and Data Sources
2.2. Evaluation of Cultivated Land Quality
2.2.1. Indicator System and Membership Function Selection
2.2.2. MDS Selection and Weight Calculation
2.2.3. Calculation of the CQI
2.2.4. Validation of MDS Evaluation Accuracy
2.3. Obstacle Factor Diagnosis
2.4. Spatial Interpolation Analysis
2.5. Data Processing
3. Results
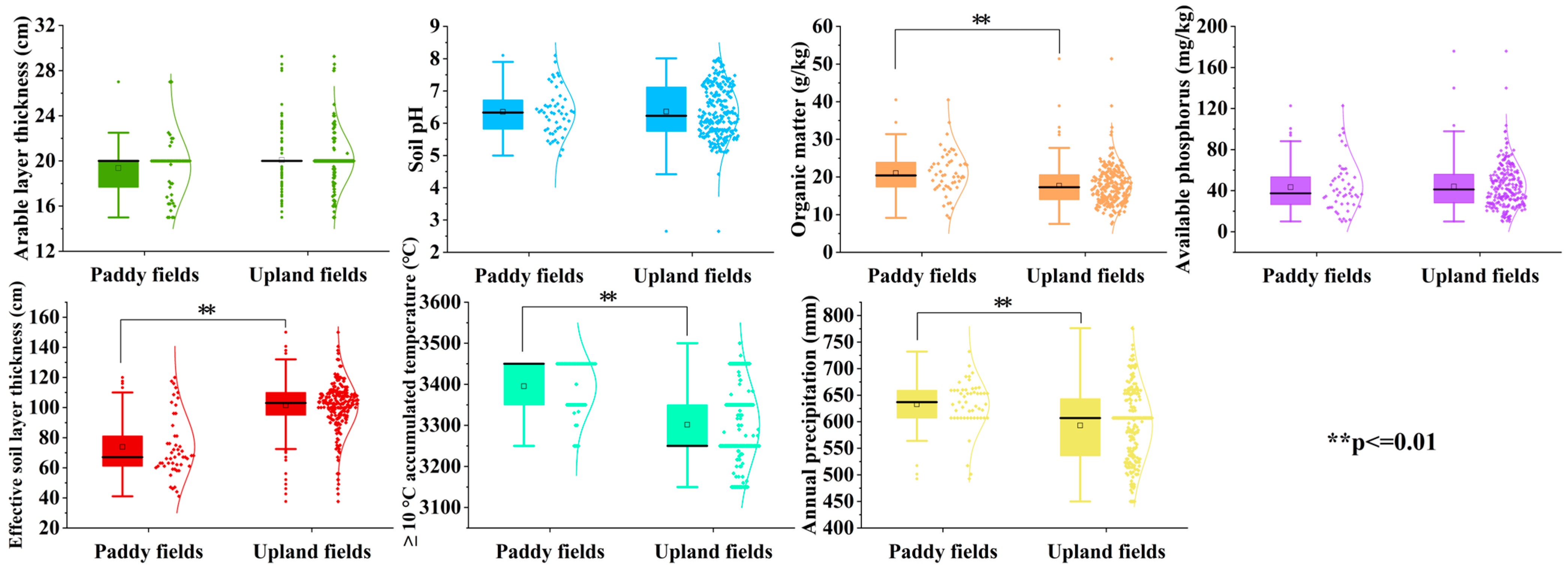
3.1. Descriptive Statistics
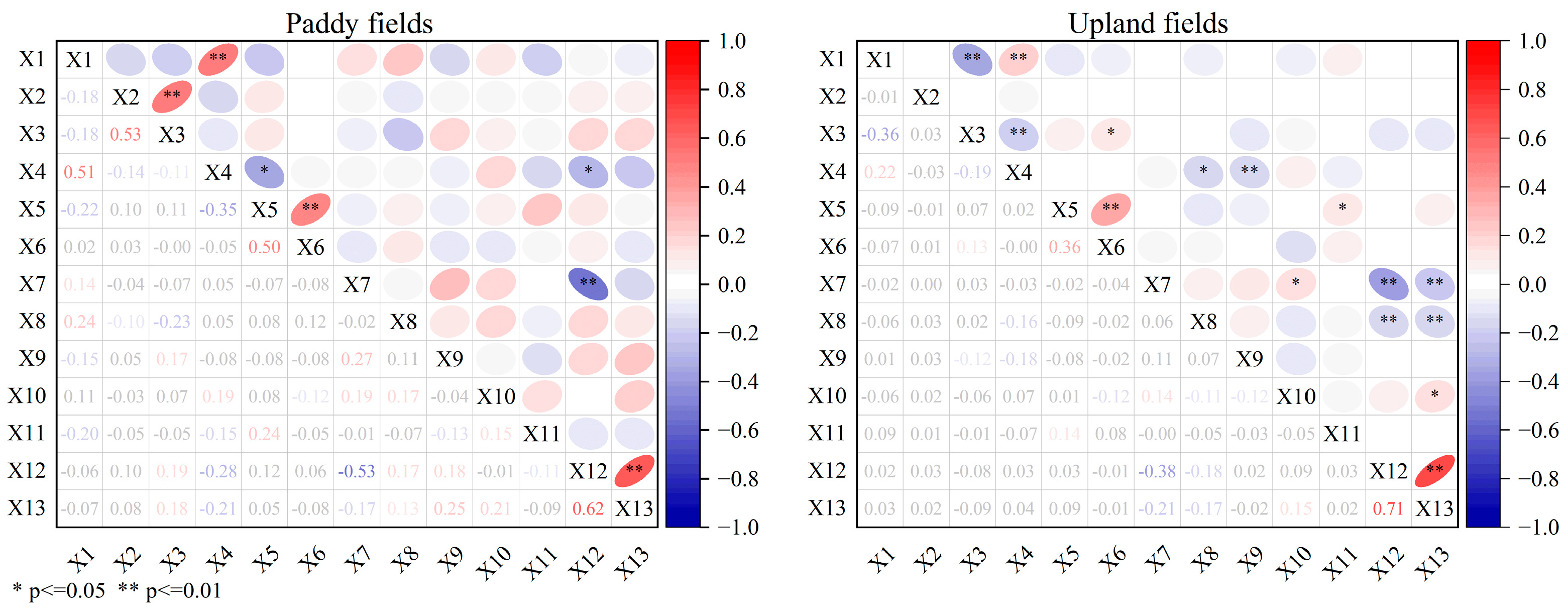
3.2. Construction of the MDS
3.3. Cultivated Land Quality Evaluation
3.3.1. Quantitative Characteristics of Sampled Points CQI
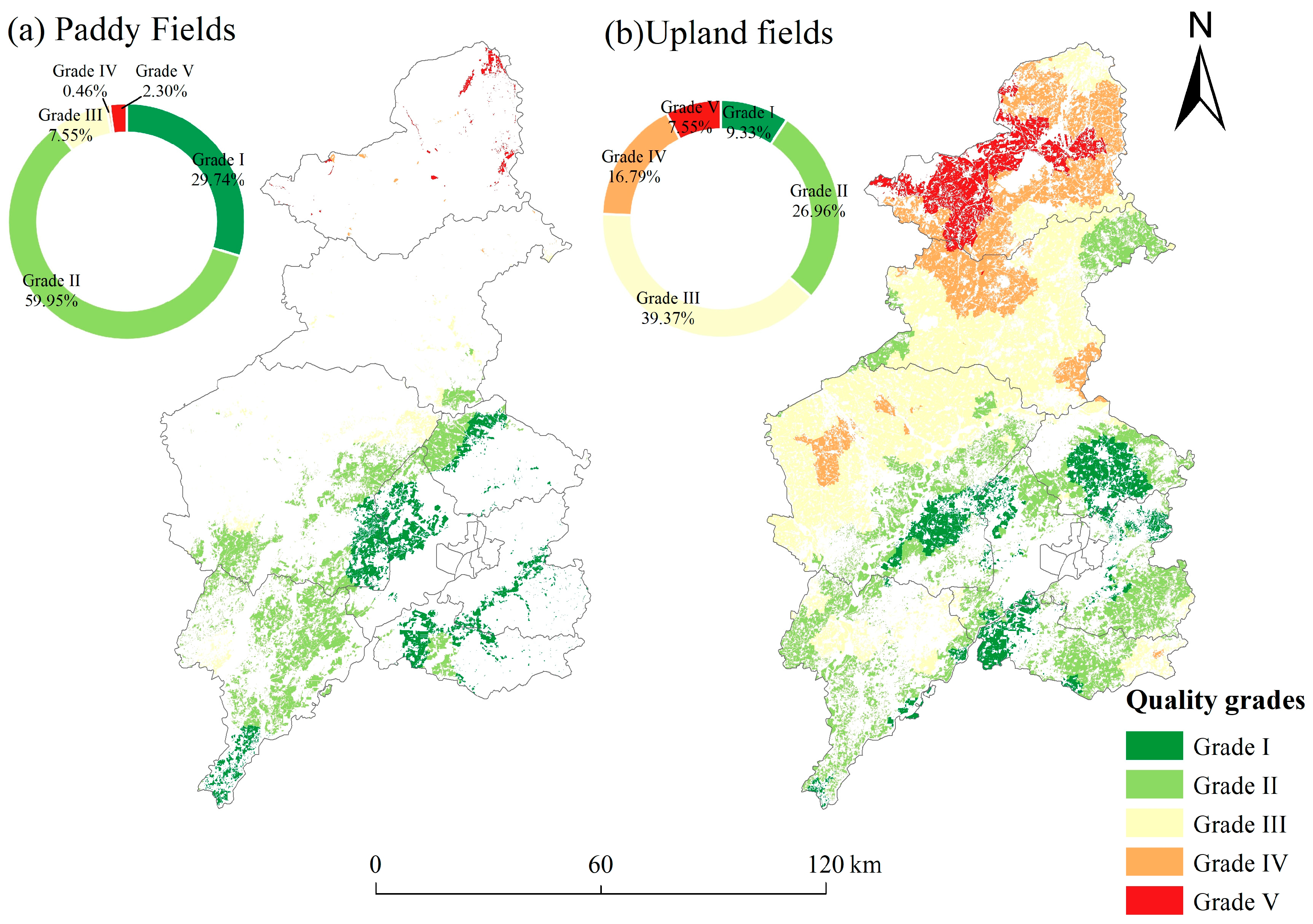
3.3.2. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Cultivated Land Quality
3.3.3. Rationality Validation of the MDS
3.4. Obstacle Factors
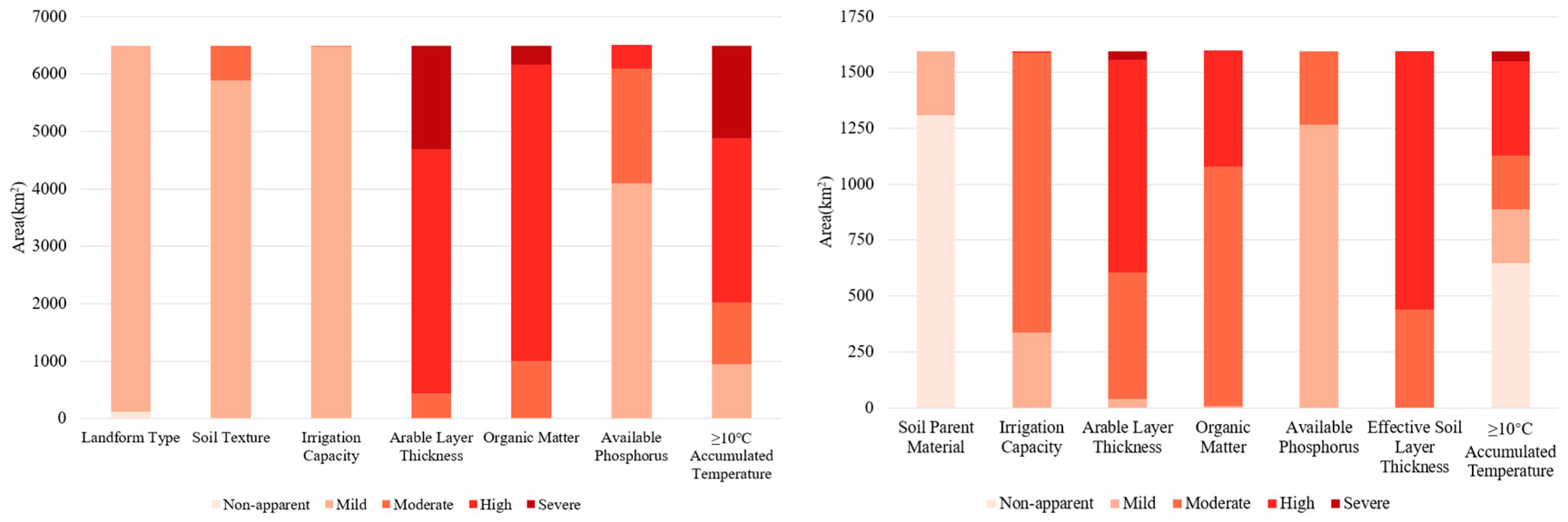
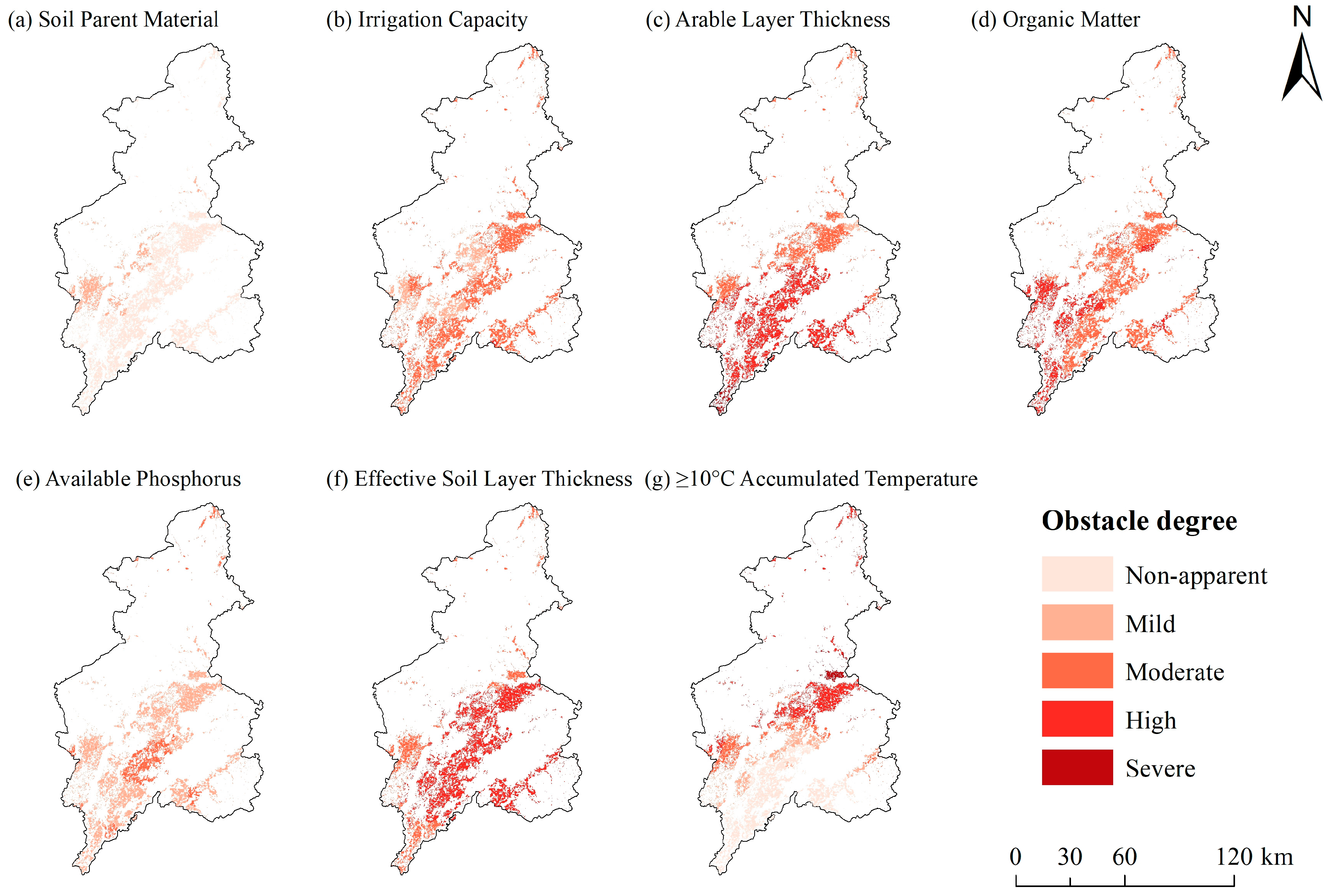
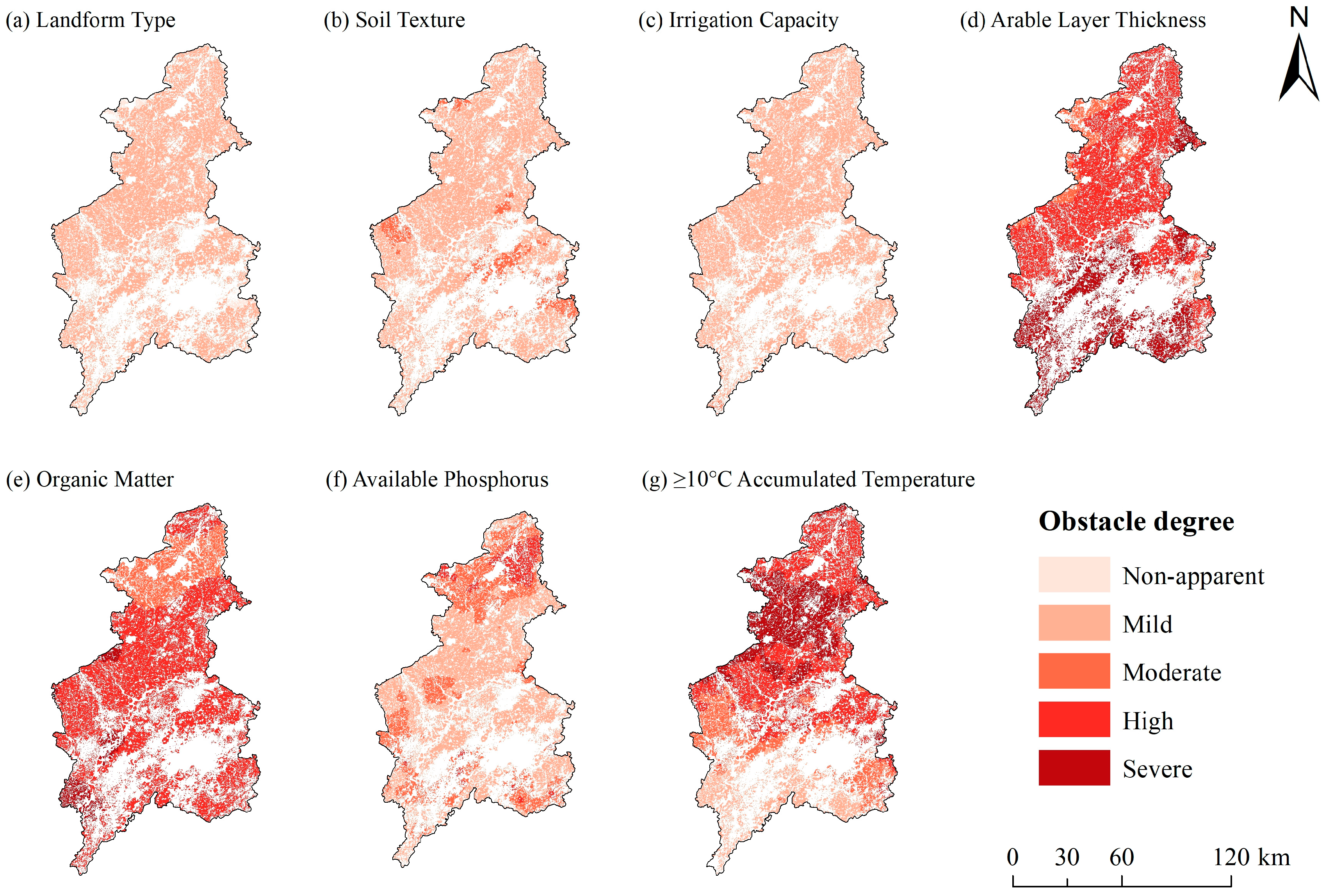
3.4.1. Distribution Characteristics of Obstacle Factors
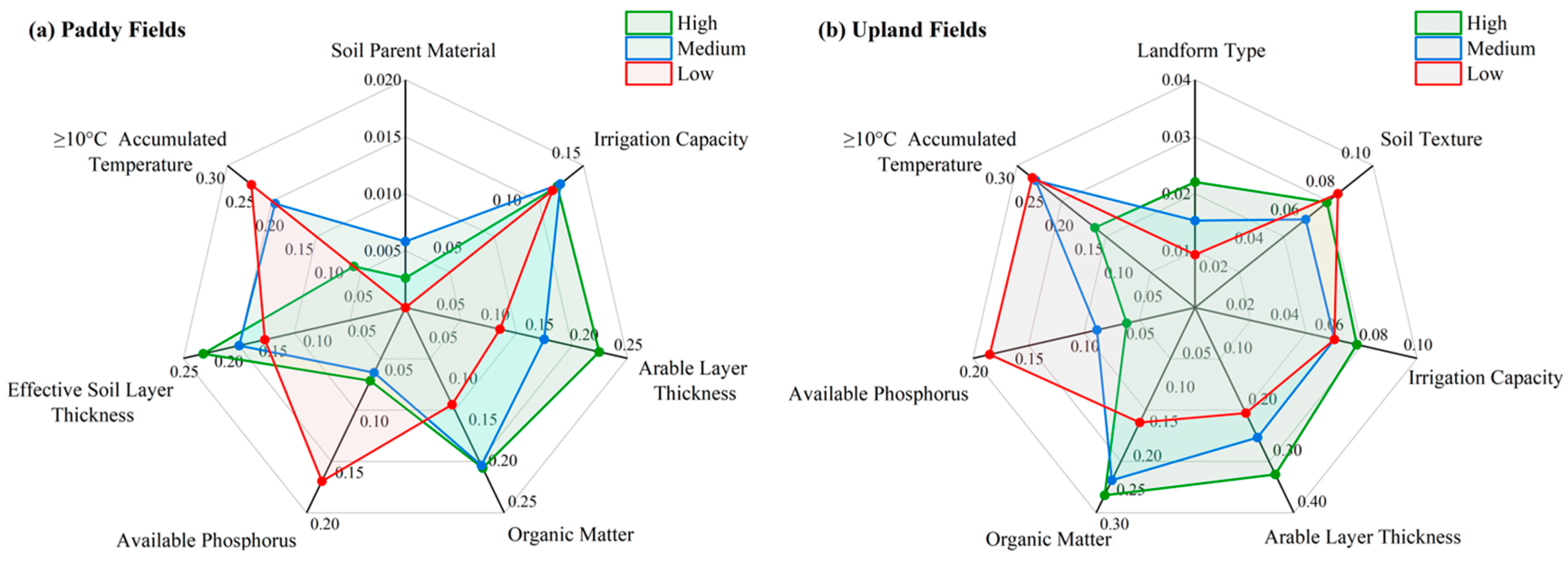
3.4.2. Identification of Major Obstacle Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Cropping Systems on Cultivated Land Quality Indicators
4.2. Impacts of Cropping Systems on Cultivated Land Quality and Obstacle Factors
4.3. Recommendations for Improving Cultivated Land Quality Under Different Cropping Systems
4.4. Implications and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bindraban, P.S.; Stoorvogel, J.J.; Jansen, D.M.; Vlaming, J.; Groot, J.J.R. Land Quality Indicators for Sustainable Land Management: Proposed Method for Yield Gap and Soil Nutrient Balance. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2000, 81, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, P.; Shen, C.; Tang, H.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Y. Knowledge Atlas of Cultivated Land Quality Evaluation Based on Web of Science Since the 21st Century (2000–2023). Land 2024, 13, 1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, R.; Wu, K.; Li, X.; Niu, B.; Li, J. Study on Cultivated Land Quality Evaluation from the Perspective of Farmland Ecosystems. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 139, 108959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlen, D.L.; Mausbach, M.J.; Doran, J.W.; Cline, R.G.; Harris, R.F.; Schuman, G.E. Soil Quality: A Concept, Definition, and Framework for Evaluation (A Guest Editorial). Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1997, 61, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuzaid, A.S.; Mazrou, Y.S.A.; El Baroudy, A.A.; Ding, Z.; Shokr, M.S. Multi-Indicator and Geospatial Based Approaches for Assessing Variation of Land Quality in Arid Agroecosystems. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chase, J.M.; Blowes, S.A.; Knight, T.M.; Gerstner, K.; May, F. Ecosystem Decay Exacerbates Biodiversity Loss with Habitat Loss. Nature 2020, 584, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, F.; Jiao, S.; Yu, Y.; Wang, X.; Shao, T. Cultivated Land Quality Assessment and Obstacle Factors Diagnosis in Changtu County, Northeast China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2024, 35, 5065–5077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasu, D.; Tiwary, P.; Chandran, P. A Novel and Comprehensive Soil Quality Index Integrating Soil Morphological, Physical, Chemical, and Biological Properties. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 244, 106246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wu, L.; Chen, D.; Li, M.; Wei, C. Soil Quality Assessment of Different Camellia Oleifera Stands in Mid-Subtropical China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 113, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-D.; Wang, H.-Y.; Zhou, J.-M.; Xing, L.; Zhu, B.-S.; Zhao, Y.-C.; Chen, X.-Q. Minimum Data Set for Assessing Soil Quality in Farmland of Northeast China. Pedosphere 2013, 23, 564–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Hu, W.; Li, M.; Wang, S.; Chu, L. Network Analysis Was Effective in Establishing the Soil Quality Index and Differentiated among Changes in Land-Use Type. Soil Tillage Res. 2025, 246, 106352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Sun, Z.; Ouyang, Z.; Han, D.; Li, F. A Comparison of Soil Quality Evaluation Methods for Fluvisol along the Lower Yellow River. CATENA 2017, 152, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Chen, J.; Hu, H.; Zhou, M.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhu, L.; Jiang, X.; Wang, J. Soil Quality Evaluation of Different Land Use Modes in Small Watersheds in the Hilly Region of Southern Jiangsu. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 160, 111895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.; Li, Z.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, B.; Gui, J. A Comprehensive Evaluation of Soil Quality in the Three River Headwaters Region, China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2024, 54, e03155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Li, Q.; Zhou, D. Selecting the Minimum Data Set and Quantitative Soil Quality Indexing of Alkaline Soils under Different Land Uses in Northeastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616–617, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Sun, M.; Xu, N.; Sun, G.; Zhao, M. Land Use Change from Upland to Paddy Field in Mollisols Drives Soil Aggregation and Associated Microbial Communities. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 146, 103351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Liu, G.; Huang, C.; Liu, Q. Soil Quality Assessment in Yellow River Delta: Establishing a Minimum Data Set and Fuzzy Logic Model. Geoderma 2019, 334, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Ge, T.; Zhu, Z.; Luo, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, M.; Yan, Z.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Kuzyakov, Y. Comparing Carbon and Nitrogen Stocks in Paddy and Upland Soils: Accumulation, Stabilization Mechanisms, and Environmental Drivers. Geoderma 2021, 398, 115121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.-L.; Gong, Z.-T. Pedogenic Evolution of Paddy Soils in Different Soil Landscapes. Geoderma 2003, 115, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Jiao, W.; MacBean, N.; Rulli, M.C.; Manzoni, S.; Vico, G.; D’Odorico, P. Dryland Productivity under a Changing Climate. Nat. Clim. Change 2022, 12, 981–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Wang, C.; Ying, C.; Mei, S.; Tong, T.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Q. Research on Cultivated Land Quality Restriction Factors Based on Cultivated Land Quality Level Evaluation. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zhao, R.; Zhan, Y. Land Comprehensive Carrying Capacity of Major Grain-Producing Areas in Northeast China: Spatial–Temporal Evolution, Obstacle Factors and Regulatory Policies. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, D.; Pei, J.; Wang, J. Temporal-spatial changes in cultivated land quality in a black soil region of Northeast China. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2020, 28, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, L.A. Fuzzy Sets. Inf. Control 1965, 8, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doran, J.W.; Parkin, T.B. Defining and Assessing Soil Quality. In Defining Soil Quality for a Sustainable Environment; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 1994; pp. 1–21. ISBN 978-0-89118-930-5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Tong, M.; He, Y.; Han, X.; Wang, L. A Comprehensive, Locally Adapted Soil Quality Indexing under Different Land Uses in a Typical Watershed of the Eastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahin, H.S.; Abuzaid, A.S.; Abdellatif, A.D. Using Multivariate Analysis to Develop Irrigation Water Quality Index for Surface Water in Kafr El-Sheikh Governorate, Egypt. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 17, 100532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Liu, J.; Tang, H.; Sun, X.; Liu, S.; Tang, X.; Ding, Z.; Ma, M.; Ci, E. Establishing a Soil Quality Index to Evaluate Soil Quality after Afforestation in a Karst Region of Southwest China. CATENA 2023, 230, 107237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhu, M.; Lu, J.; Zhou, Q.; Ma, W. Evaluation of Ecological City and Analysis of Obstacle Factors under the Background of High-Quality Development: Taking Cities in the Yellow River Basin as Examples. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 118, 106771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wackernagel, H. Ordinary Kriging. In Multivariate Geostatistics: An Introduction with Applications; Wackernagel, H., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; pp. 79–88. ISBN 978-3-662-05294-5. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Islam, M.U.; Jiang, F. The Effect of Deep-Tillage Depths on Crop Yield: A Global Meta-Analysis. Plant Soil Environ. 2023, 69, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, D.; Dai, G.; Chen, Y.; Yu, G. Optimal Tillage Depths for Enhancing Rice Yield, Quality and Lodging Resistance in the Rice Production Systems of Northeast China. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsos, T.M.; Menexes, G.C.; Eleftherohorinos, I.G.; Alexandridis, T.K. Using Block Kriging as a Spatial Smooth Interpolator to Address Missing Values and Reduce Variability in Maize Field Yield Data. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Hu, Y.; Xia, Y.; Zheng, S.; Ma, C.; Rui, Y.; He, H.; Huang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Ge, T.; et al. Contrasting Pathways of Carbon Sequestration in Paddy and Upland Soils. Glob. Change Biol. 2021, 27, 2478–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X. Economic Potential of Biomass Supply from Crop Residues in China. Appl. Energy 2016, 166, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ge, T.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, S.; Luo, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, P.; Gavrichkova, O.; Xu, X.; Wang, J.; et al. Carbon Input and Allocation by Rice into Paddy Soils: A Review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 133, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Hall, S.J. Elevated Moisture Stimulates Carbon Loss from Mineral Soils by Releasing Protected Organic Matter. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keiluweit, M.; Nico, P.S.; Kleber, M.; Fendorf, S. Are Oxygen Limitations under Recognized Regulators of Organic Carbon Turnover in Upland Soils? Biogeochemistry 2016, 127, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Ge, T.; Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Hu, Y.; Wu, J.; Su, Y.; Kuzyakov, Y. Effects of Biotic and Abiotic Factors on Soil Organic Matter Mineralization: Experiments and Structural Modeling Analysis. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2018, 84, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelico, R.; Ceglie, A.; He, J.-Z.; Liu, Y.-R.; Palumbo, G.; Colombo, C. Particle Size, Charge and Colloidal Stability of Humic Acids Coprecipitated with Ferrihydrite. Chemosphere 2014, 99, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, X.; Yu, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Zou, Y. Iron-Bound Organic Carbon Is Conserved in the Rhizosphere Soil of Freshwater Wetlands. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 149, 107949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Lv, T.-F.; Chen, Y.; Westby, A.P.; Ren, W.-J. Soil Physicochemical and Biological Properties of Paddy-Upland Rotation: A Review. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 856352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinoto, Y.; Otani, R.; Matsunami, T.; Maruyama, S. Analysis of the Shallow Root System of Maize Grown by Plowing Upland Fields Converted from Paddy Fields: Effects of Soil Hardness and Fertilization. Plant Prod. Sci. 2021, 24, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Zhang, L.; Hao, L.; Sun, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, C. Spatiotemporal Trends of Urban Heat Island Effect along the Urban Development Intensity Gradient in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 544, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Jia, X.; Shao, M.; Chen, L.; Han, G.; Zhang, G. Phases and Rates of Iron and Magnetism Changes during Paddy Soil Development on Calcareous Marine Sediment and Acid Quaternary Red-Clay. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uga, Y.; Sugimoto, K.; Ogawa, S.; Rane, J.; Ishitani, M.; Hara, N.; Kitomi, Y.; Inukai, Y.; Ono, K.; Kanno, N.; et al. Control of Root System Architecture by DEEPER ROOTING 1 Increases Rice Yield under Drought Conditions. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1097–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumhálová, J.; Kumhála, F.; Kroulík, M.; Matějková, Š. The Impact of Topography on Soil Properties and Yield and the Effects of Weather Conditions. Precis. Agric. 2011, 12, 813–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Ge, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Liang, T.; Bolan, N.; Lischeid, G.; Rinklebe, J. Influence of Soil Properties, Topography, and Land Cover on Soil Organic Carbon and Total Nitrogen Concentration: A Case Study in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau Based on Random Forest Regression and Structural Equation Modeling. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 821, 153440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wankmüller, F.J.P.; Delval, L.; Lehmann, P.; Baur, M.J.; Cecere, A.; Wolf, S.; Or, D.; Javaux, M.; Carminati, A. Global Influence of Soil Texture on Ecosystem Water Limitation. Nature 2024, 635, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.F.; Fansler, S.J.; Campbell, T.P.; Bond-Lamberty, B.; Smith, A.P.; RoyChowdhury, T.; McCue, L.A.; Varga, T.; Bailey, V.L. Soil Texture and Environmental Conditions Influence the Biogeochemical Responses of Soils to Drought and Flooding. Commun. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ji, C.; Ma, W.; Wang, S.; Wang, S.; Han, W.; Mohammat, A.; Robinson, D.; Smith, P. Significant Soil Acidification across Northern China’s Grasslands during 1980s–2000s. Glob. Change Biol. 2012, 18, 2292–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scudiero, E.; Corwin, D.L.; Morari, F.; Anderson, R.G.; Skaggs, T.H. Spatial Interpolation Quality Assessment for Soil Sensor Transect Datasets. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2016, 123, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Li, Q.; Gao, J.; Lin, Q.; Xu, Q.; Groffman, P.M.; Yu, S. Non-Algorithmically Integrating Land Use Type with Spatial Interpolation of Surface Soil Nutrients in an Urbanizing Watershed. Pedosphere 2017, 27, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Soil Carbon Sequestration Impacts on Global Climate Change and Food Security. Science 2004, 304, 1623–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Bai, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, F. Phosphorus Dynamics: From Soil to Plant. Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 997–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco-Canqui, H.; Lal, R. Crop Residue Removal Impacts on Soil Productivity and Environmental Quality. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2009, 28, 139–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Conant, R.T.; Paul, E.A.; Paustian, K. Stabilization Mechanisms of Soil Organic Matter: Implications for C-Saturation of Soils. Plant Soil 2002, 241, 155–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Han, Y.; Zhou, J.; Liu, J.; Wu, J. Mapping Farmland Soil Organic Carbon Density in Plains with Combined Cropping System Extracted from NDVI Time-Series Data. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 142120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, T.; Das, B.; Chakraborty, D.; Singh, V.K.; Das, D.; Aggarwal, P. Development and Evaluation of a Novel Soil Quality Analysis Framework for Rice-Wheat Cropping System in the Indo-Gangetic Plains of India 2023. SSRN Electron. J. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaeman, Y.; Maftuáh, E.; Sukarman, S.; Neswati, R.; Nurdin, N.; Basuki, T.; Suriadi, A.; Vasenev, I. Influence of Land-Use Type on Black Soil Features in Indonesia Based on Soil Survey Data. Land 2025, 14, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uthappa, A.R.; Devakumar, A.S.; Das, B.; Mahajan, G.R.; Chavan, S.B.; Jinger, D.; Jha, P.K.; Kumar, P.; Kokila, A.; Krishnamurthy, R.; et al. Comparative Analysis of Soil Quality Indexing Techniques for Various Tree Based Land Use Systems in Semi-Arid India. Front. For. Glob. Change 2024, 6, 1322660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Objective | Criterion | Index |
|---|---|---|
| Cultivated land quality | climatic conditions | ≥10 °C accumulated temperature |
| Annual precipitation | ||
| Profile characteristics | Effective soil layer thickness | |
| Arable layer thickness | ||
| Site condition | Texture configuration | |
| Parent material | ||
| Landform type | ||
| Nutrient status | Organic matter | |
| Available phosphorus | ||
| Soil physical and chemical property | Soil pH | |
| Soil texture | ||
| Soil management | Irrigation capacity | |
| Drainage capacity |
| Function Type | Index | Upland Fields Function Parameters | Paddy Fields Function Parameters | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| xmin | r1 | r2 | xmax | xmin | r1 | r2 | xmax | ||
| more is better | ≥10 °C accumulated temperature | 3150 | 3500 | 3250 | 3450 | ||||
| Annual precipitation | 450 | 776 | 492.67 | 732 | |||||
| Effective soil layer thickness | 37.65 | 150 | 41.1 | 120 | |||||
| Arable layer thickness | 15 | 29.25 | 15 | 27 | |||||
| Organic matter | 7.55 | 40 | 9.15 | 40 | |||||
| Available phosphorus | 10 | 40 | 10.03 | 40 | |||||
| optimal range | Soil pH | 4.35 | 6.8 | 6.8 | 9.69 | 4.35 | 6.8 | 6.8 | 9.69 |
| Index | Attribute | Membership Degree | Index | Attribute | Membership Degree |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Texture configuration | Upper loose lower tight | 1.00 | Soil texture | Medium loam | 1.00 |
| Spongy | 0.90 | Light loam | 0.88 | ||
| Sandwich | 0.80 | Heavy loam | 0.84 | ||
| Compact | 0.70 | Sandy loam | 0.71 | ||
| Upper tight lower loose | 0.60 | Clay soil | 0.60 | ||
| Thin layer | 0.50 | Sandy soil | 0.48 | ||
| Loose | 0.40 | Irrigation capacity | Fully satisfy | 1.00 | |
| Parent material | Alluvium, loess and loess-like parent material | 1.00 | Satisfy | 0.90 | |
| Sediments, fluvial and lacustrine alluvium | 0.80 | Basically satisfy | 0.80 | ||
| Glacial deposits and colluvium | 0.70 | Not satisfy | 0.40 | ||
| Residual deposits, aeolian deposits, crystalline salts and laterite | 0.50 | Drainage capacity | Fully satisfy | 1.00 | |
| Landform type | Alluvial plain, diluvial plain, alluvial-diluvial plain, and alluvial fan plain | 1.00 | Satisfy | 0.90 | |
| Erosional plain | 0.80 | Basically satisfy | 0.70 | ||
| Hilly land | 0.70 | Not satisfy | 0.30 | ||
| Low-relief mountains | 0.60 |
| Index | Group | Norm | TDS | MDS | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC-1 | PC-2 | PC-3 | PC-4 | PC-5 | PC-6 | Weight | Weight | |||
| ≥10 °C accumulated temperature | 1 | 0.723 | 0.245 | −0.498 | −0.039 | 0.155 | −0.057 | 1.387 | 0.089 | 0.164 |
| Irrigation capacity | 2 | 0.358 | −0.658 | 0.021 | 0.075 | 0.378 | 0.312 | 1.203 | 0.083 | 0.124 |
| Arable layer thickness | 3 | −0.397 | 0.134 | 0.673 | −0.061 | 0.287 | 0.167 | 1.132 | 0.077 | 0.163 |
| Parent material | 4 | 0.445 | 0.014 | 0.398 | 0.567 | −0.265 | 0.031 | 1.131 | 0.077 | 0.147 |
| Effective soil layer thickness | 4 | 0.078 | −0.382 | 0.198 | −0.523 | −0.278 | 0.467 | 1.019 | 0.078 | 0.148 |
| Organic matter | 5 | 0.210 | 0.420 | 0.424 | −0.090 | 0.565 | −0.216 | 1.087 | 0.080 | 0.122 |
| Available phosphorus | 6 | 0.173 | 0.522 | 0.150 | −0.192 | 0.094 | 0.604 | 1.041 | 0.076 | 0.131 |
| Eigenvalues | 2.680 | 1.876 | 1.517 | 1.300 | 1.243 | 1.090 | ||||
| Variance/% | 20.614 | 14.428 | 11.667 | 10.002 | 9.560 | 8.385 | ||||
| Cumulative variance/% | 20.614 | 35.043 | 46.710 | 56.712 | 66.272 | 74.658 | ||||
| Index | Group | Norm | TDS | MDS | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC-1 | PC-2 | PC-3 | PC-4 | PC-5 | Weight | Weight | |||
| ≥10 °C accumulated temperature | 1 | 0.834 | 0.077 | −0.288 | −0.176 | 0.012 | 1.299 | 0.107 | 0.163 |
| Landform type | 2 | −0.222 | 0.620 | −0.240 | 0.247 | −0.300 | 1.001 | 0.084 | 0.140 |
| Irrigation capacity | 2 | 0.138 | 0.570 | 0.461 | 0.013 | 0.218 | 0.959 | 0.079 | 0.060 |
| Soil texture | 3 | 0.222 | −0.325 | 0.561 | 0.059 | −0.389 | 0.942 | 0.082 | 0.154 |
| Arable layer thickness | 4 | −0.427 | −0.154 | 0.113 | 0.619 | 0.301 | 1.020 | 0.091 | 0.162 |
| Available phosphorus | 4 | 0.381 | −0.189 | −0.022 | 0.714 | 0.086 | 1.011 | 0.092 | 0.180 |
| Organic matter | 5 | −0.129 | −0.165 | −0.365 | −0.144 | 0.678 | 0.907 | 0.086 | 0.141 |
| Eigenvalues | 2.198 | 1.648 | 1.352 | 1.248 | 1.166 | ||||
| Variance/% | 16.906 | 12.676 | 10.402 | 9.598 | 8.968 | ||||
| Cumulative variance/% | 16.906 | 29.582 | 39.984 | 49.582 | 58.550 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.; Sun, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, S.; Zhou, W.; Qian, F.; Liu, Y.; Tang, H.; Huang, Y. Cultivated Land Quality Evaluation and Constraint Factor Identification Under Different Cropping Systems in the Black Soil Region of Northeast China. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081838
Liu C, Sun Y, Liu X, Xu S, Zhou W, Qian F, Liu Y, Tang H, Huang Y. Cultivated Land Quality Evaluation and Constraint Factor Identification Under Different Cropping Systems in the Black Soil Region of Northeast China. Agronomy. 2025; 15(8):1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081838
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Changhe, Yuzhou Sun, Xiangjun Liu, Shengxian Xu, Wentao Zhou, Fengkui Qian, Yunjia Liu, Huaizhi Tang, and Yuanfang Huang. 2025. "Cultivated Land Quality Evaluation and Constraint Factor Identification Under Different Cropping Systems in the Black Soil Region of Northeast China" Agronomy 15, no. 8: 1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081838
APA StyleLiu, C., Sun, Y., Liu, X., Xu, S., Zhou, W., Qian, F., Liu, Y., Tang, H., & Huang, Y. (2025). Cultivated Land Quality Evaluation and Constraint Factor Identification Under Different Cropping Systems in the Black Soil Region of Northeast China. Agronomy, 15(8), 1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081838







