Dual Mechanisms of Nitrate in Alleviating Ammonium Toxicity: Enhanced Photosynthesis and Optimized Ammonium Utilization in Orychophragmus violaceus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Experimental Design
2.2. Harvest and Biomass Measurements
2.3. Chlorophyll Concentration Determination
2.4. Analysis of Leaf Nitrogen and Carbon Content
2.5. 13C and 15N Analysis
2.6. Quantifying Δ15N Values of NH4+ Assimilation and N Source Partitioning
2.7. Quantifying the Absolute Nitrogen and Carbon Accumulation in Leaves
2.8. Quantifying Leaf Nitrogen from NO3−/NH4+ Assimilation
2.9. Statistical Analysis
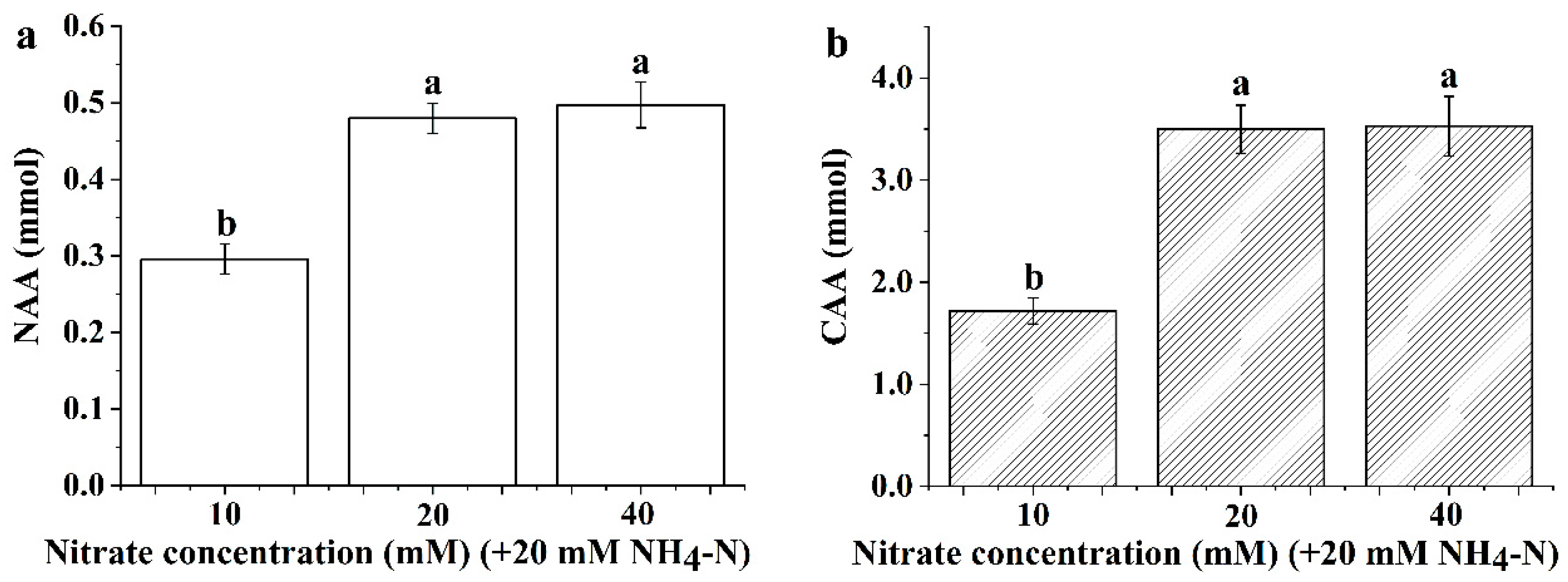
3. Results
3.1. Growth Characteristics
3.2. Chlorophyll Concentrations
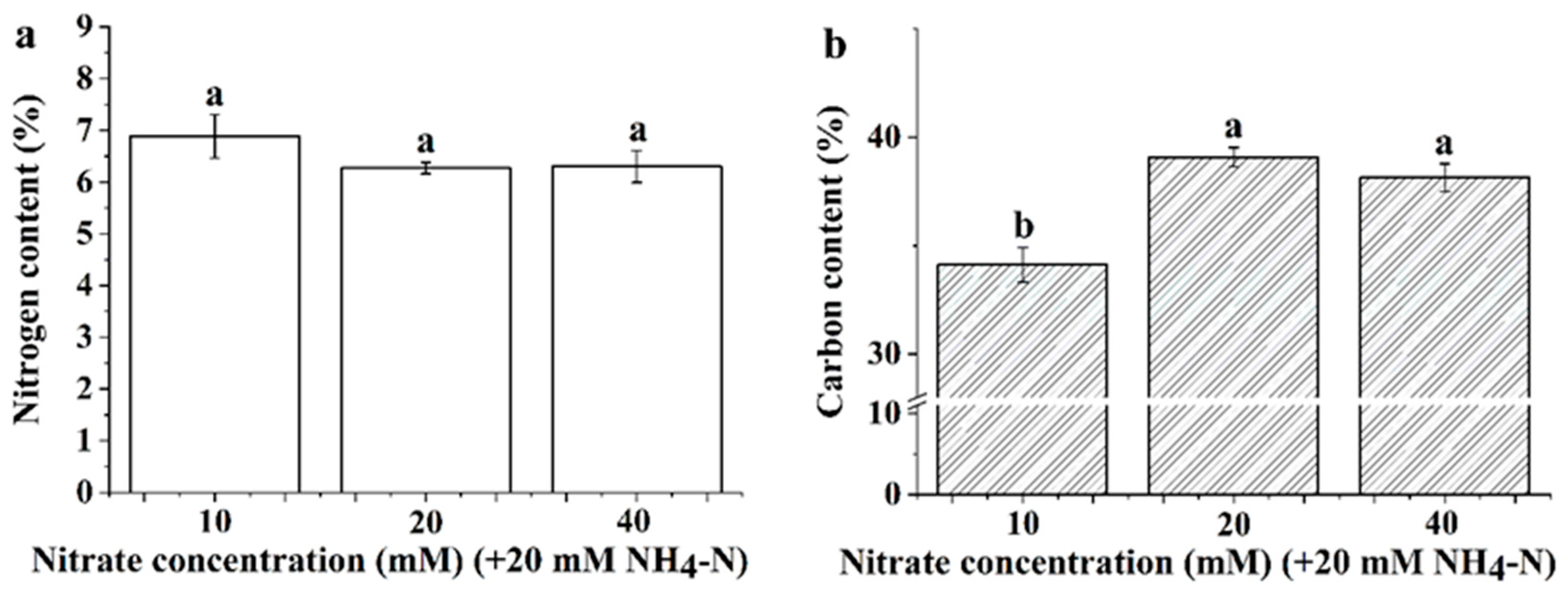
3.3. Leaf Nitrogen and Carbon Content
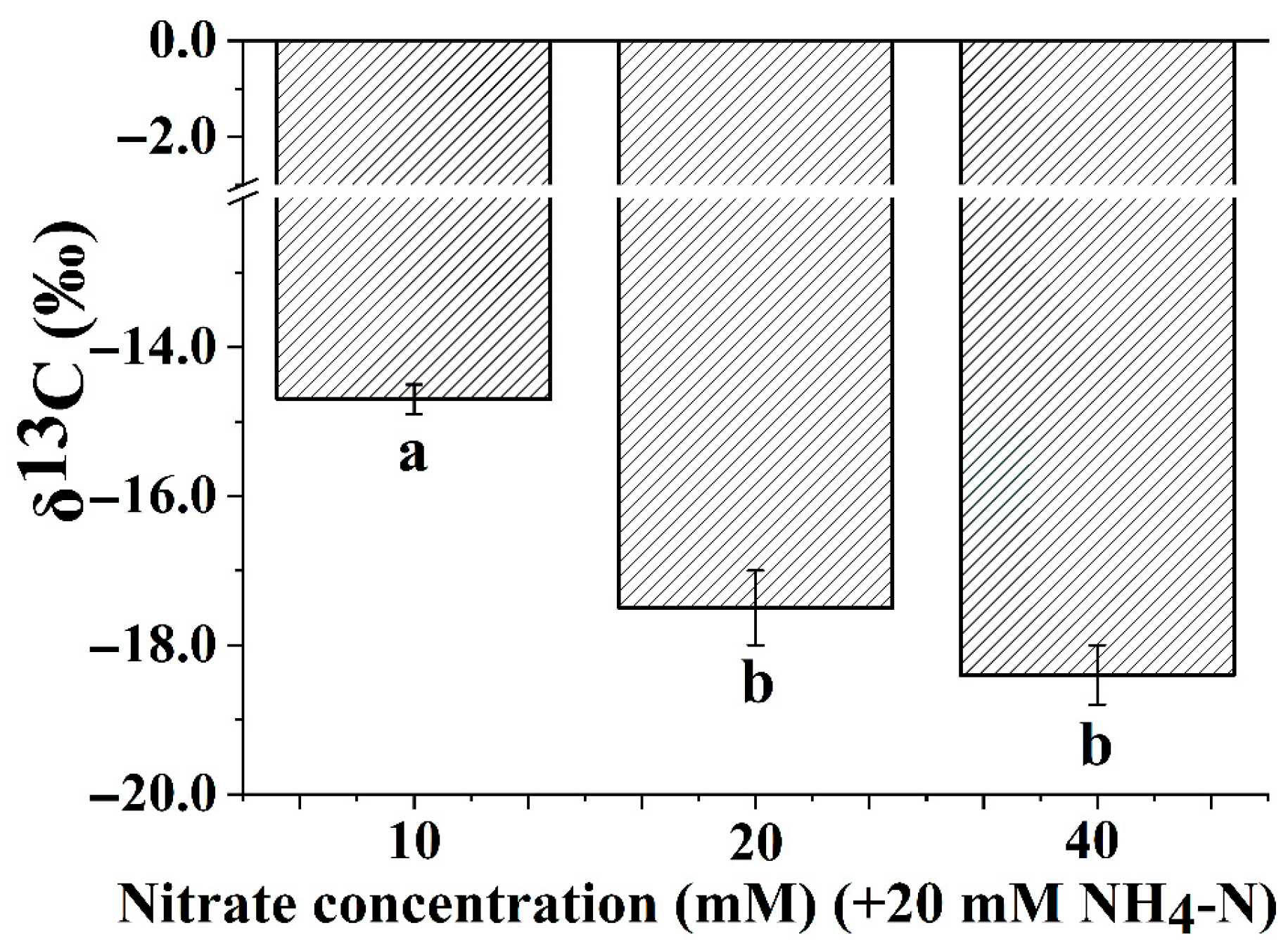
3.4. Leaf Carbon Isotope Composition
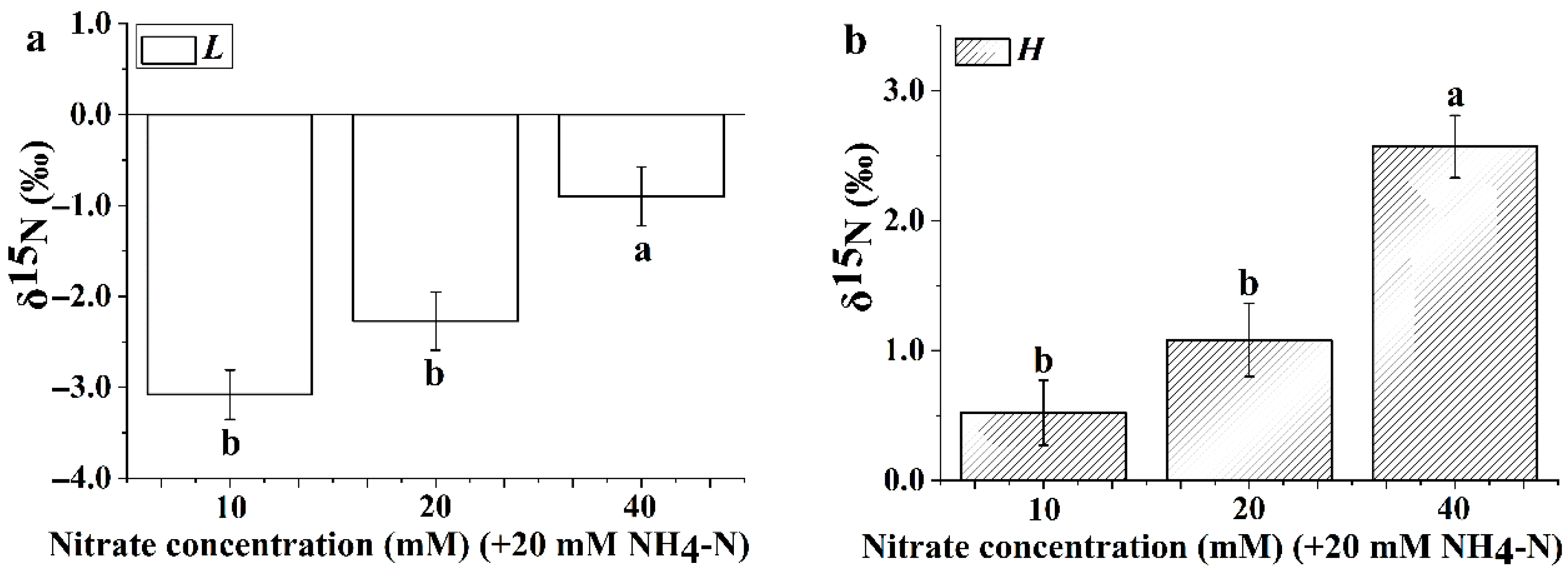
3.5. Leaf Nitrogen Isotope Composition
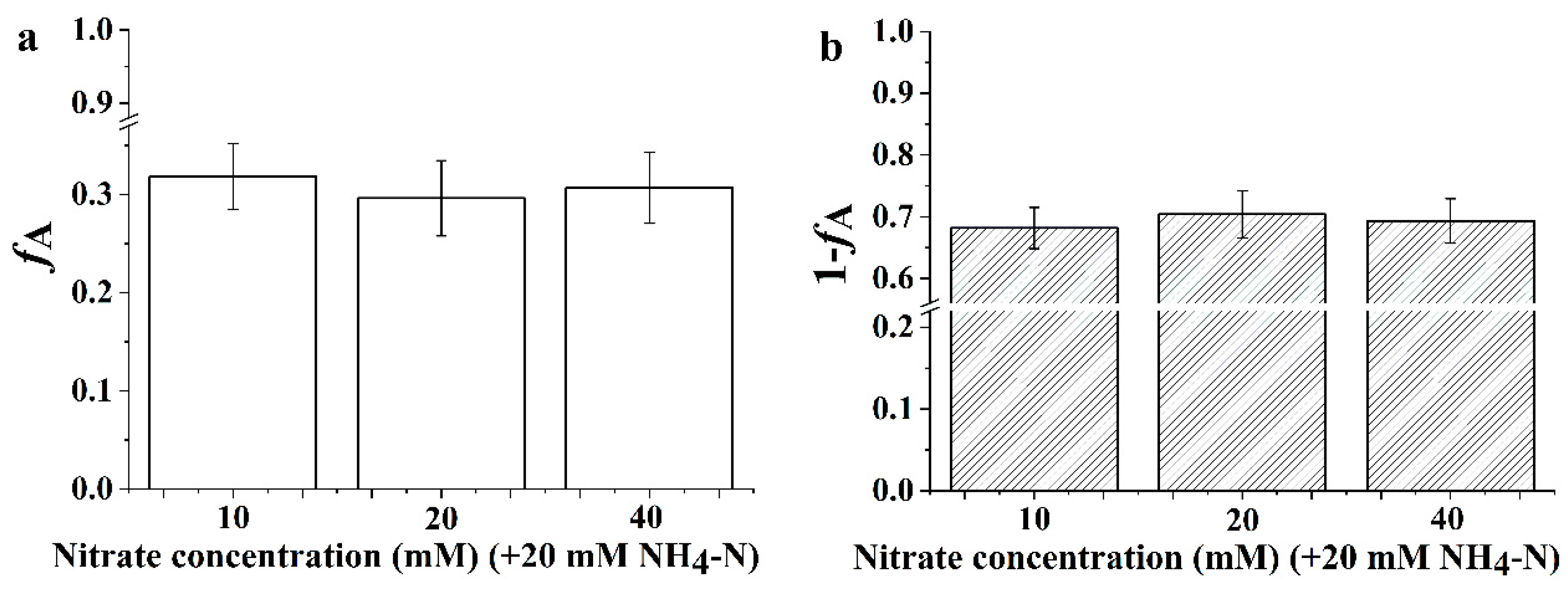
3.6. The Proportion of Inorganic Nitrogen Utilization
3.7. The δ15N and Δ15N of Ammonium Assimilation
3.8. Absolute Nitrogen and Carbon Accumulation in the Leaves
3.9. Leaf Nitrogen Accumulation Amount Resulting from Nitrate/Ammonium Assimilation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salsac, L.; Chaillou, S.; Morot-Gaudry, J.F.; Lesaint, C.; Jolivet, E. Nitrate and ammonium nutrition in plants. Plant Physiol. Bioch. 1987, 25, 805–812. Available online: https://hal.science/hal-02727402/ (accessed on 6 July 2025).
- Xu, G.H.; Fan, X.R.; Miller, A.J. Plant nitrogen assimilation and use efficiency. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2012, 63, 153–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaheer, M.; Zafar, Z.U.; Athar, H.U.R.; Bano, H.; Amir, M.; Khalid, A.; Manzoor, H.; Javed, M.; Iqbal, M.; Ogbaga, C.C.; et al. Mixing tannery effluent had fertilizing effect on growth, nutrient accumulation, and photosynthetic capacity of some cucurbitaceous vegetables: A little help from foe. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2023, 30, 28947–28960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Britto, D.T.; Kronzucker, H.J. NH4+ toxicity in higher plants: A critical review. J. Plant Physiol. 2002, 159, 567–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachiya, T.; Watanabe, C.K.; Fujimoto, M.; Ishikawa, T.; Takahara, K.; Kawai-Yamada, M.; Uchimiya, H.; Uesono, Y.; Terashima, I.; Noguchi, K. Nitrate addition alleviates ammonium toxicity without lessening ammonium accumulation, organic acid depletion and inorganic cation depletion in Arabidopsis thaliana shoots. Plant Cell Physiol. 2012, 53, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, L.G.; Zhang, Y.X.; Zhang, B.; Li, H.W.; Wang, Z.H.; Si, J.H.; Fan, S.J.; Feng, B. Does energy cost constitute the primary cause of ammonium toxicity in plants? Planta 2022, 256, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.; Fang, X.M.; Xiao, C.B.; Huang, X.M.; Su, J.R.; Li, J.; Wang, J.F.; Wang, S.M.; Luan, S.; He, K. Kinase SnRK1.1 regulates nitrate channel SLAH3 engaged in nitrate-dependent alleviation of ammonium toxicity. Plant Physiol. 2021, 186, 731–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, W.Y.; Zhang, Y.X.; Si, J.S.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, S.J.; Xia, H.Y.; Kong, L.A. Nitrate alleviates ammonium toxicity in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) by regulating tricarboxylic acid cycle and reducing rhizospheric acidification and oxidative damage. Plant Signal Behav. 2021, 16, 1991687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; He, K.; Kleist, T.; Chen, F.; Luan, S. Anion channel SLAH3 functions in nitrate-dependent alleviation of ammonium toxicity in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ. 2015, 38, 474–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.Y.; Wu, Y.Y.; Su, Y.; Li, H.T. Implication of quantifying nitrate utilization and CO2 assimilation of Brassica napus plantlets in vitro under variable ammonium/nitrate ratios. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Britto, D.T.; Kronzucker, H.J. Futile cycling at the plasma membrane: A hallmark of low-affinity nutrient transport. Trends Plant Sci. 2006, 11, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczerba, M.W.; Britto, D.T.; Balkos, K.D.; Kronzucker, H.J. Alleviation of rapid, futile ammonium cycling at the plasma membrane by potassium reveals K+-sensitive and-insensitive components of NH4+ transport. J. Exp. Bot. 2008, 59, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hachiya, T.; Inaba, J.; Wakazaki, M.; Sato, M.; Toyooka, K.; Miyagi, A.; Kawai-Yamada, M.; Sugiura, D.; Nakagawa, T.; Kiba, T.; et al. Excessive ammonium assimilation by plastidic glutamine synthetase causes ammonium toxicity in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.X.; Ding, M.D.; Xu, F.Y.; Afzal, M.R.; Chen, X.; Zeng, H.Q.; Yan, F.; Zhu, Y.Y. Involvement of plasma membrane H+-ATPase in the ammonium-nutrition response of barley roots. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2018, 181, 878–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, R.; Ariz, I.; Cruz, C.; Moran, J.F. Review: Mechanisms of ammonium toxicity and the quest for tolerance. Plant Sci. 2016, 248, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alencar, V.T.C.B.; Lobo, A.K.M.; Carvalho, F.E.L.; Silveira, J.A.G. High ammonium supply impairs photosynthetic efficiency in rice exposed to excess light. Photosynth Res. 2019, 140, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Gao, J.; Shi, S.; He, X.; Dai, T. Impaired electron transfer accounts for the photosynthesis inhibition in wheat seedlings (Triticum aestivum L.) subjected to ammonium stress. Physiol. Plantarum 2019, 167, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.X.; Li, Y.X.; Tian, Z.W.; Hu, J.L.; Adkins, S.; Dai, T.B. Changes of oxidative metabolism in the roots of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) seedlings in response to elevated ammonium concentrations. J. Integr. Agri. 2021, 20, 1216–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murashige, T.; Skoog, F. A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plantarum 1962, 15, 473–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessini, K.; Lachaal, M.; Cruz, C.; Soltani, A. Role of ammonium to limit nitrate accumulation and to increase water economy in Wild Swiss chard. J. Plant Nutr. 2009, 32, 821–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.B.; Sun, D.D.; Liu, B.B.; Fang, X.M.; Li, P.C.; Jiang, Y.; He, M.M.; Li, J.; Luan, S.; He, K. Nitrate transporter NRT1. 1 and anion channel SLAH3 form a functional unit to regulate nitrate-dependent alleviation of ammonium toxicity. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2022, 64, 942–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.Y.; Wu, Y.Y.; Hang, H.T. Differential contributions of NO3−/NH4+ to nitrogen use in response to a variable inorganic nitrogen supply in plantlets of two Brassicaceae species in vitro. Plant Methods 2019, 15, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olaitan, M.M.; Mangse, G.; Ogbaga, C.C.; Uthman, T.O. Gibberellic acid influences growth indices and biochemical parameters in micropropagated Ocimum gratissimum L. explants. J. Med. Plants Econ. Dev. 2022, 6, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serret, M.D.; Trillas, M.I.; Matas, J.; Araus, J. The effect of different closure types, light, and sucrose concentrations on carbon isotope composition and growth of Gardenia jasminoides plantlets during micropropagation and subsequent acclimation ex vitro. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. 1997, 47, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, M.H. Carbon isotope fractionation in plants. Phytochemistry 1981, 20, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.E.; Ni, L.Y.; Xie, P.; Xu, J.; Zhang, M. Effects of moderate ammonium enrichment on three submersed macrophytes under contrasting light availability. Freshwater Biol. 2011, 56, 1620–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Wang, H.J.; Wang, H.Z.; Li, Y.; Liang, X.M.; Xu, C.; Jeppesen, E. Does the responses of Vallisneria natans (Lour.) Hara to high nitrogen loading differ between the summer high-growth season and the low-growth season? Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601, 1513–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, R.D. Physiological mechanisms influencing plant nitrogen isotope composition. Trends Plant Sci. 2001, 6, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalcsits, L.A.; Buschhaus, H.A.; Guy, R.D. Nitrogen isotope discrimination as an integrated measure of nitrogen fluxes, assimilation and allocation in plants. Physiol. Plantarum 2014, 151, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoneyama, T.; Kamachi, K.; Yamaya, T.; Mae, T. Fractionation of nitrogen isotopes by glutamine synthetase isolated from spinach leaves. Plant Cell Physiol. 1993, 34, 489–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Guy, R.D. Isotopic composition and concentration of total nitrogen and nitrate in xylem sap under near steady-state hydroponics. Plant Cell Environ. 2020, 43, 2112–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsaadawi, I.S.; Al-Hadithy, S.M.; Arif, M.B. Effects of three phenolic acids on chlorophyll content and ions uptake in cowpea seedlings. J. Chem. Ecol. 1986, 12, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousfi, S.; Serret, M.D.; Araus, J.L. Comparative response of δ13C, δ18O and δ15N in durum wheat exposed to salinity at the vegetative and reproductive stages. Plant Cell Environ. 2013, 36, 1214–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, J. Introduction to Error Analysis, the Study of Uncertainties in Physical Measurements; University Science Books: Sausalito, CA, USA, 1997; Available online: https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1997ieas.book.....T/abstract (accessed on 6 July 2025).
- Evans, R.D.; Bloom, A.J.; Sukrapanna, S.S.; Ehleringer, J.R. Nitrogen isotope composition of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill. cv. T-5) grown under ammonium or nitrate nutrition. Plant Cell Environ. 1996, 19, 1317–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárdenas-Navarro, R.; Adamowicz, S.; Robin, P. Diurnal nitrate uptake in young tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.) plants: Test of a feedback-based model. J. Exp. Bot. 1998, 49, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matt, P.; Geiger, M.; Walch-Liu, P.; Engels, C.; Krapp, A.; Stitt, M. The immediate cause of the diurnal changes of nitrogen metabolism in leaves of nitrate-replete tobacco: A major imbalance between the rate of nitrate reduction and the rates of nitrate uptake and ammonium metabolism during the first part of the light period. Plant Cell Environ. 2001, 24, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.Y.; Wu, Y.Y. The δ15N response and nitrate assimilation of Orychophragmus violaceus and Brassica napus plantlets in vitro during the multiplication stage cultured under different nitrate concentrations. Acta Geochim. 2017, 36, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boschiero, B.N.; Mariano, E.; Azevedo, R.A.; Trivelin, P.C.O. Influence of nitrate-ammonium ratio on the growth, nutrition, and metabolism of sugarcane. Plant Physiol. Bioch. 2019, 139, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarasketa, A.; González-Moro, M.B.; González-Murua, C.; Marino, D. Nitrogen source and external medium pH interaction differentially affects root and shoot metabolism in Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.H.; Li, G.J.; Kronzucker, H.J.; Baluška, F.; Shi, W.M. Ammonium stress in Arabidopsis: Signaling, genetic loci, and physiological targets. Trends Plant Sci. 2014, 19, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safaei, F.; Alirezalu, A.; Noruzi, P.; Alirezalu, K. Phytochemical and morpho-physiological response of Melissa officinalis L. to different NH4+ to NO3-ratios under hydroponic cultivation. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, X.H.; Chen, Y.L. The physiological response of photosynthesis to nitrogen deficiency. Plant Physiol. Bioch. 2021, 158, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shilpha, J.; Song, J.; Jeong, B.R. Ammonium phytotoxicity and tolerance: An insight into ammonium nutrition to improve crop productivity. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronzucker, H.J.; Britto, D.T.; Davenport, R.J.; Tester, M. Ammonium toxicity and the real cost of transport. Trends Plant Sci. 2001, 6, 335–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hachiya, T.; Noguchi, K. Integrative response of plant mitochondrial electron transport chain to nitrogen source. Plant Cell Rep. 2011, 30, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, C.B.; Fang, Y.; Wang, S.M.; He, K. The alleviation of ammonium toxicity in plants. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2023, 65, 1362–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Yan, L.; Zhang, W.; Yi, C.; Haider, S.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Xu, F.S.; Ding, G. Nitrate alleviates ammonium toxicity in Brassica napus by coordinating rhizosphere and cell pH and ammonium assimilation. Plant J. 2024, 117, 786–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, H.M.; Fan, X.R.; Miller, A.J.; Xu, G.H. Plant nitrogen uptake and assimilation: Regulation of cellular pH homeostasis. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 4380–4392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Hsu, P.K.; Tsay, Y.F. Uptake, allocation and signaling of nitrate. Trends Plant Sci. 2012, 17, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.Z.; Tian, W.H.; Liu, X.X.; Lin, X.Y.; Jin, C.W.; Zheng, S.J. Alleviation of proton toxicity by nitrate uptake specifically depends on nitrate transporter 1.1 in Arabidopsis. New Phytol. 2016, 211, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filella, I.; Serrano, L.; Serra, J.; Peñuelas, J. Evaluating wheat nitrogen status with canopy reflectance indices and discriminant analysis. Crop Sci. 1995, 35, 1400–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochieng, W.A.; Xian, L.; Nasimiyu, A.T.; Muthui, S.W.; Ndirangu, L.N.; Otieno, D.O.; Wan, T.; Liu, F. Exploring the ammonium detoxification mechanism of young and mature leaves of the macrophyte Potamogeton lucens. Aquat. Toxicol. 2021, 237, 105879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Gao, J.W.; Yong, J.W.H.; Liu, Y.F.; Cao, D.; He, X.H. Glutamate over-accumulation may serve as an endogenous indicator of tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle suppression under NH4+ nutrition in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) seedlings. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2020, 177, 104130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, F.; Hajiboland, R.; Nikolic, M. Multiple mechanisms are involved in the alleviation of ammonium toxicity by nitrate in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Plant Soil 2024, 503, 451–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szal, B.; Podgórska, A. The role of mitochondria in leaf nitrogen metabolism. Plant Cell Environ. 2012, 35, 1756–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchanan, B.B.; Gruissem, W.; Jones, R.L. Biochemistry and Molecular Biology of Plants, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: West Sussex, UK, 2015; Available online: https://www.wiley.com/en-us/Biochemistry+and+Molecular+Biology+of+Plants%2C+2nd+Edition-p-9781118502198 (accessed on 6 July 2025).


| Parameters | Inorganic Nitrogen Concentration | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM NO3-N + 20 mM NH4-N | 20 mM NO3-N + 20 mM NH4-N | 40 mM NO3-N + 20 mM NH4-N | |
| Increased biomass (g/plantlet FW) | 2.525 ± 0.084 b | 4.178 ± 0.369 a | 4.070 ± 0.251 a |
| Leaf DW (g) | 0.060 ± 0.003 b | 0.107 ± 0.006 a | 0.111 ± 0.008 a |
| Parameters | Inorganic Nitrogen Concentration | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM NO3-N + 20 mM NH4-N | 20 mM NO3-N + 20 mM NH4-N | 40 mM NO3-N + 20 mM NH4-N | |
| Chl a (mg/g FW) | 0.163 ± 0.008 b | 0.564 ± 0.037 a | 0.647 ± 0.047 a |
| Chl b (mg/g FW) | 0.081 ± 0.005 b | 0.295 ± 0.013 a | 0.322 ± 0.012 a |
| Chl a + b (mg/g FW) | 0.243 ± 0.004 b | 0.859 ± 0.049 a | 0.969 ± 0.057 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, K.; Li, H.; Hang, H.; He, X.; Wu, Y. Dual Mechanisms of Nitrate in Alleviating Ammonium Toxicity: Enhanced Photosynthesis and Optimized Ammonium Utilization in Orychophragmus violaceus. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1789. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081789
Zhang K, Li H, Hang H, He X, Wu Y. Dual Mechanisms of Nitrate in Alleviating Ammonium Toxicity: Enhanced Photosynthesis and Optimized Ammonium Utilization in Orychophragmus violaceus. Agronomy. 2025; 15(8):1789. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081789
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Kaiyan, Haitao Li, Hongtao Hang, Xinhua He, and Yanyou Wu. 2025. "Dual Mechanisms of Nitrate in Alleviating Ammonium Toxicity: Enhanced Photosynthesis and Optimized Ammonium Utilization in Orychophragmus violaceus" Agronomy 15, no. 8: 1789. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081789
APA StyleZhang, K., Li, H., Hang, H., He, X., & Wu, Y. (2025). Dual Mechanisms of Nitrate in Alleviating Ammonium Toxicity: Enhanced Photosynthesis and Optimized Ammonium Utilization in Orychophragmus violaceus. Agronomy, 15(8), 1789. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081789








