Carbon Footprint and Energy Balance Analysis of Rice-Wheat Rotation System in East China
Abstract
1. Introduction
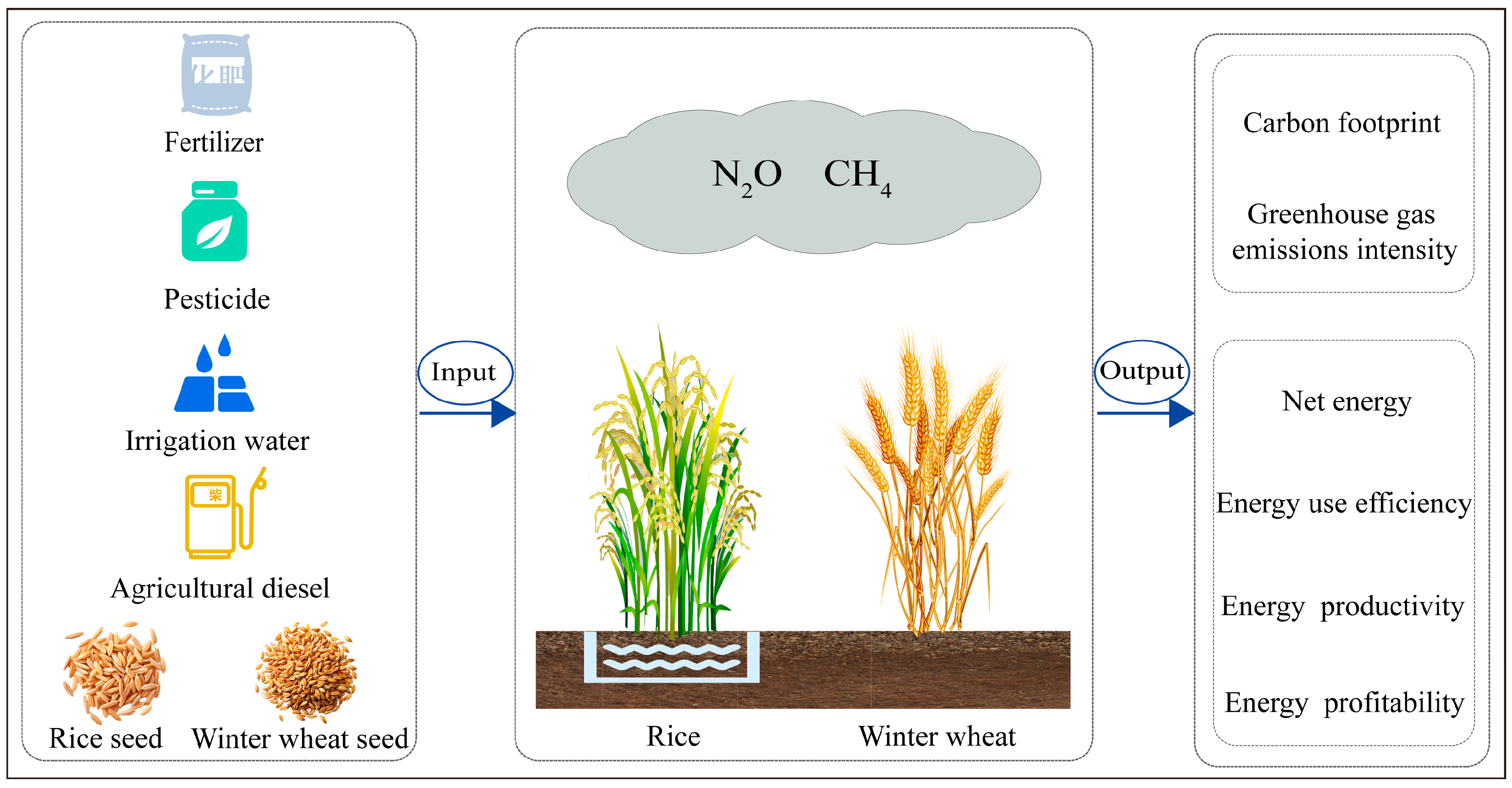
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. Carbon Footprint
| Emission Source | Emission Factor | Unit | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen fertilizer production and transportation | 8.3 | kg CO2 eq kg−1 | [21,22,23,24,25,26,27] |
| Phosphate fertilizer production and transportation | 0.79 | kg CO2 eq kg−1 | [21,23,24,25,26,27,28] |
| Potassium fertilizer production and transportation | 0.55 | kg CO2 eq kg−1 | [21,23,24,25,26,27,28] |
| Compound fertilizer production and transportation | 2.47 | kg CO2 eq kg−1 | [22,29] |
| Pesticide production and transportation | 19.12 | kg CO2 eq kg−1 | [21,30] |
| Irrigation water | 0.29 | kg CO2 eq m−3 | [31] |
| Agricultural diesel | 3.75 | kg CO2 eq kg−1 | [32] |
| Winter wheat seed transportation | 0.11 | kg CO2 eq kg−1 | [33] |
| Rice seed transportation | 0.78 | kg CO2 eq kg−1 | [34,35] |
2.2.1. N2O Direct and Indirect Emissions
2.2.2. CH4 Emission
2.2.3. Greenhouse Gas Emissions Intensity
2.3. Energy Balance
| Energy Input/Output | Energy Factor | Unit | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen fertilizer production and transportation | 91.0 | MJ kg−1 | [42] |
| Phosphate fertilizer production and transportation | 13.3 | MJ kg−1 | [42] |
| Potassium fertilizer production and transportation | 9.0 | MJ kg−1 | [42] |
| Compound fertilizer production and transportation | 37.77 | MJ kg−1 | [42] |
| Pesticide production and transportation | 102.0 | MJ kg−1 | [42] |
| Irrigation water | 1.02 | MJ m−3 | [43] |
| Agricultural diesel | 44 | MJ kg−1 | [42] |
| Winter wheat seed transportation | 5.57 | MJ kg−1 | [42] |
| Rice seed transportation | 15.1 | MJ kg−1 | [42] |
| Energy Output | |||
| Wheat yield | 16.3 | MJ kg−1 | [42] |
| Rice yield | 15.9 | MJ kg−1 | [44] |
2.4. Statistics and Analysis of Data
3. Results
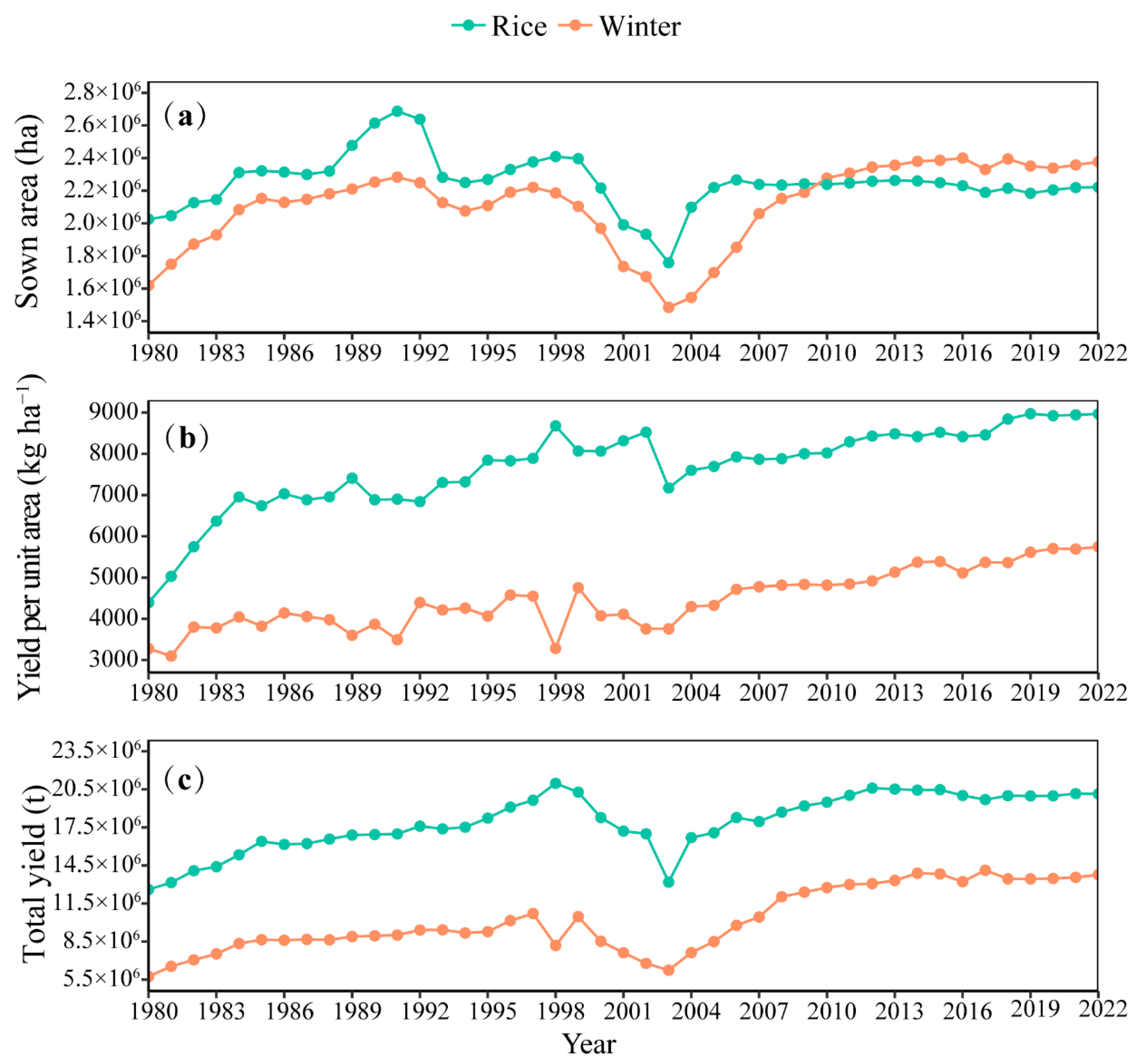
3.1. Sown Area, Yield per Unit Area, Total Yield of Rice-Wheat System
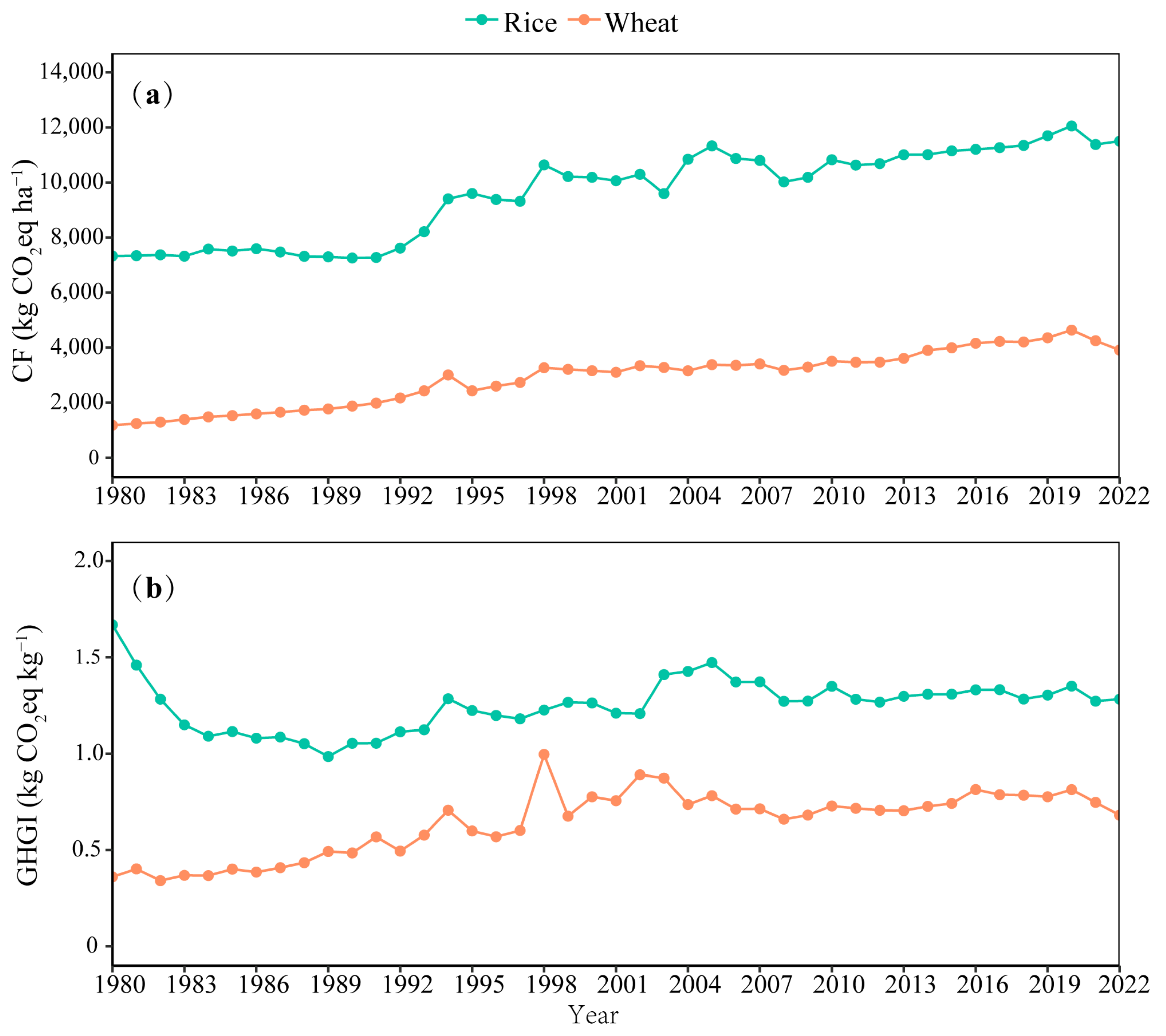
3.2. Carbon Footprint of Rice-Wheat System
3.2.1. Carbon Footprint and Greenhouse Gas Emissions Intensity
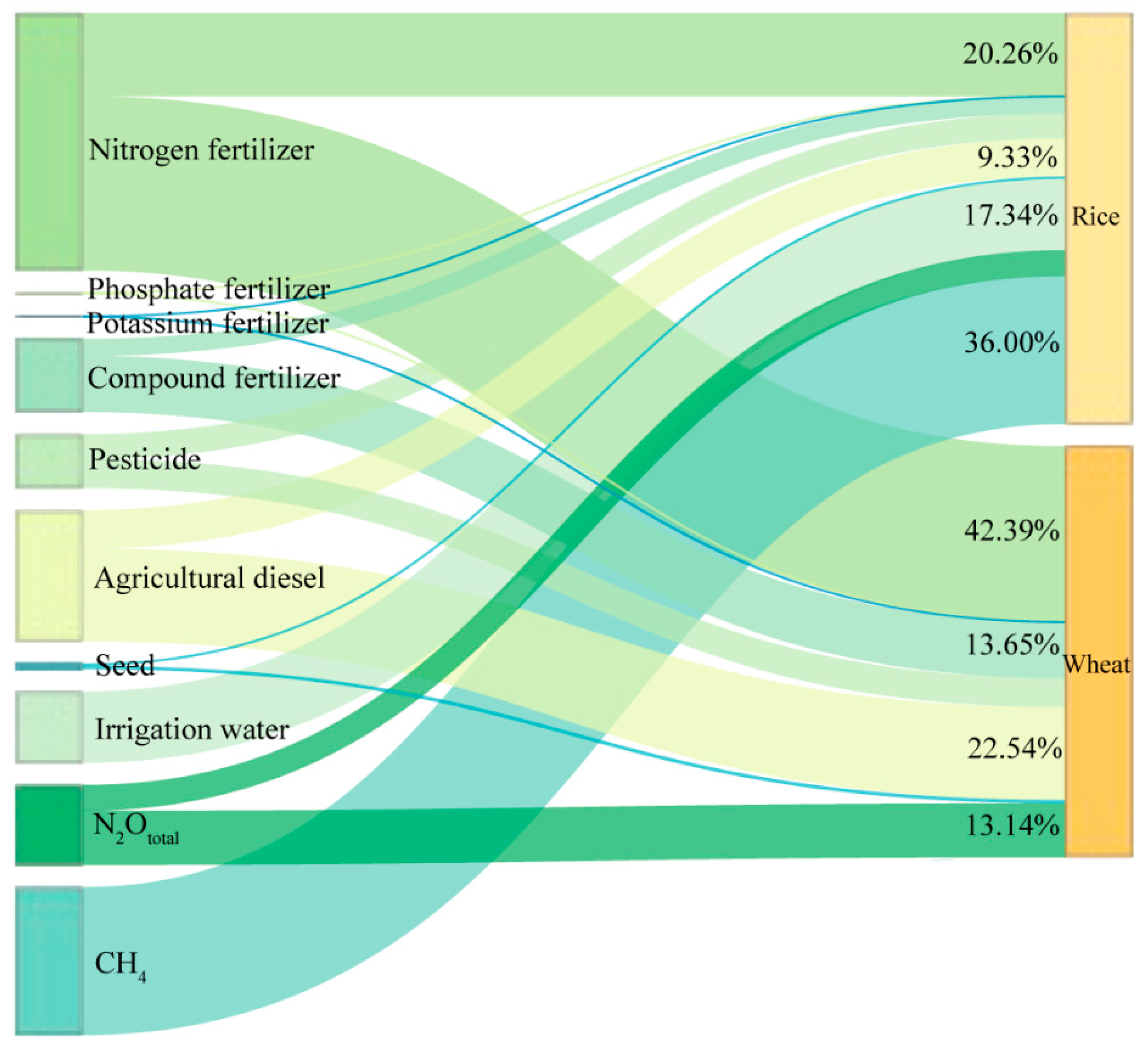
3.2.2. Direct and Indirect Greenhouse Gas Emissions
3.3. Energy Balance of Rice-Wheat System
3.3.1. Net Energy, Energy Use Efficiency, Energy Productivity, and Energy Profitability
3.3.2. The Energy Input of Rice and Wheat
4. Discussion
4.1. Sown Area and Yield of Rice and Wheat
4.2. Carbon Footprint, Greenhouse Gas Emissions Intensity and Agricultural Materials
4.3. Energy Balance and Energy Input
4.4. Future Prospects
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, H.C.; Dai, Q.G.; Guo, B.W.; Wu, W.G. Research on the Double Maturity of Rice and Wheat in China; Phoenix Sci. Press: Nanjing, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Jiangsu Provincial People’s Government. Jiangsu Statistical Yearbook. Available online: https://tj.jiangsu.gov.cn/2021/index.htm (accessed on 29 May 2025).
- Yu, X.L.; Zhang, F.M.; Fang, Y.Q.; Lu, Y.Y.; Zhang, K.D.; Ni, T. Simulation and reduction of CH4 flux emission in a rice-wheat rotation system in the Huai River Basin, China. J. Agro-Environ.Sci. 2023, 42, 2346–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.J.; Chen, L.B.; Cheng, W.X.; Li, Y.P.; Li, T.; Smith, P.; Cheng, K. Synergistic effects of climate change and nitrogen use on future nitric oxide emissions from China’s croplands. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 377, 124643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, J.; Zhang, C.; Hu, M.J.; Sun, T.C. Accounting for greenhouse gas emissions in the agricultural system of China based on the Life Cycle Assessment method. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matuštík, J.; Kočí, V. What is a footprint? A conceptual analysis of environmental footprint indicators. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 285, 124833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.P.; Li, D.; Lu, H.W.; Feng, S.S.; Nie, Q.W. Trends, distribution, and impact factors of carbon footprints of main grains production in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.J.; Deng, A.X.; Shang, Z.Y.; Tang, Z.W.; Chen, C.Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.J. Characteristics of carbon emission and ap-proaches of carbon mitigation and sequestration for carbon neutrality in China’s crop production. Acta Agron. Sin. 2022, 48, 930–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, G.J.; Ji, H.T.; Cheng, K.; Liu, M.Q.; Jiang, Y.; Hu, Z.K.; Zhang, Y.F.; Hu, N.J.; Tang, R.D.; Hu, F. Analysis on carbon footprint and nitrogen footprint of paddy field rotation pattern in Jiangsu Province. J. Nanjing Agric. Univ. 2023, 46, 510–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Miao, S.J.; Qiao, Y.F. Evaluating the carbon footprint of the rice-wheat rotation system based on localized parameters in Jiangsu Province. Energy Environ. Sci. 2023, 32, 1682–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, R.L.; Lin, B.Q. Energy efficiency and production technology heterogeneity in China’s agricultural sector: A meta-frontier approach. Technol. Forecast. Soc. 2016, 109, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Kong, Z.Y.; Liu, Y.Z.; Li, N.; Yang, X.L.; Zhuang, M.H. A high-resolution energy use efficiency assessment of China’s staple food crop production and associated improvement potential. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 188, 113789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Peng, S.B. Trends in the economic return on energy use and energy use efficiency in China’s crop production. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 70, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Peng, S.B.; Wang, D.; Man, J.G. Evaluation of the energy budget and energy use efficiency in wheat production under various crop management practices in China. Energy 2018, 160, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.Q.; Zhang, L.; Liu, H.Y.; Nie, L.X. Energy assessment of different rice-wheat rotation systems. Food Energy Secur. 2021, 10, e284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, C.Q.; Bai, Y.C.; You, L.Y.; Yi, Y.L.; Huang, F.; Li, X.X. Life cycle energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions of wheat-rice rotation system with straw returning. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2015, 34, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.J.; Yuan, Z.; Geng, Y.; Ren, J.; Jiang, S.; Sheng, H.; Gao, L. Temporal trends and spatial patterns of energy use efficiency and greenhouse gas emissions in crop production of Anhui Province, China. Energy 2017, 133, 955–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, M.; Panday, S.C.; Meena, V.S.; Yadav, R.P.; Singh, S.; Parihar, M.; Mishra, P.K.; Bisht, J.K.; Pattanayak, A. Long-term tillage and irrigation management practices: Impact on carbon budgeting and energy dynamics under rice–wheat rotation of Indian mid-himalayan region. Conservation 2022, 2, 388–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.Y.; Zhao, J.; Jia, H.; Zhao, J.C.; Lu, J.; Zhao, M.Y.; Chu, Q.Q. Seeking sustainable pathway of crop production by opti-mizing planting structures and management practices from the perspective of water footprint. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 843, 157091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wei, H.H.; Zhang, M.L.; Yang, Y.; Huang, Y.L.; Chai, N.; Zhang, X.L.; Zhang, K.Q.; Li, F.M.; Guo, S.Q.; et al. Adopting plastic film mulching system in the food-energy-water-carbon nexus to the sustainable dryland agriculture. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 306, 109183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Yue, S.; Wang, G.; Meng, Q.; Wu, L.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Li, S.; Zhang, F.; Chen, X. Closing the yield gap could reduce projected greenhouse gas emissions: A case study of maize production in China. Glob. Change Biol. 2013, 19, 2467–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.F.; Dou, Z.X.; He, P.; Ju, X.T.; Powlson, D.; Chadwick, D.; Norse, D.; Lu, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; et al. New technologies reduce greenhouse gas emissions from nitrogenous fertilizer in China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 110, 8375–8380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, X.H.; Nie, Z.R.; Zuo, T.Y. Life cycle emission inventories for the fuels consumed by thermal power in China. China Environ. Sci. 2005, 25, 632–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. 2006 IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories. National Greenhouse Gas Inventories Programme; IGES: Hayama, Japan, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, B.R.; Nie, Z.R.; Di, X.H.; Zuo, T.Y. Life cycle inventories of fossil fuels in China(II): Final life cycle inventories. Mod. Chem. Ind. 2006, 26, 59–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2011.
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Energy Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2011.
- Brentrup, F.; Pallière, C. GHG Emission and Energy Efficiency in European Nitrogen Fertilizer Production and Use; International Fertiliser Society: York, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.M.; Lan, Y. A comparative study on carbon footprints between plant- and animal-based foods in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 2581–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.G.; Audsley, E.; Sandars, D.L. Determining the Environmental Burdens and Resource Use in the Production of Agricultural and Horticultural Commodities. Available online: https://www.silsoe.cranfield.ac.uk (accessed on 29 May 2025).
- Wang, J.X.; Rothausen, S.G.S.A.; Conway, D.; Zhang, L.; Xiong, W.; Holman, I.P.; Li, Y. China’s water-energy nexus: Green-house-gas emissions from groundwater use for agriculture. Environ. Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 014035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Cui, Z.; Fan, M.; Peter, V.; Zhao, M.; Ma, W.Q.; Wang, Z.L.; Zhang, W.J.; Yan, X.Y.; Yang, J.C.; et al. Producing more grain with lower environmental costs. Nature 2014, 514, 486–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, T.O.; Marland, G. A synthesis of carbon sequestration, carbon emissions, and net carbon flux in agriculture: Comparing tillage practices in the United States. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2002, 91, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Linquist, B.A.; Wilson, L.T.; Cassman, K.G.; Stuart, A.M.; Pede, V.; Miro, B.; Saito, K.; Agustiani, N.; Aristya, V.E.; et al. Sustainable Intensification for a Larger Global Rice Bowl. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 7163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Song, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Wei, W.; Li, S.; Yu, Y. The characteristics of yield-scaled methane emission from paddy field in recent 35-year in China: A meta-analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 161, 1044–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2021—The Physical Science Basis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- He, S.N.; Chen, Y.; Xiang, W.; Chen, X.W.; Wang, X.L.; Chen, Y. Carbon and nitrogen footprints accounting of peanut and peanut oil production in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 291, 125964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.Q.; Guo, Y.T.; Wang, R.; Wang, N.J.; Li, C.; Chu, X.S.; Feng, H.; Chen, H.X. Carbon footprint of a winter wheat-summer maize cropping system under straw and plastic film mulching in the Loess Plateau of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 794, 148590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; Ciais, P.; Smith, P.; Yan, X.Y.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Liu, S.W.; Li, T.T.; Zou, J.W. The role of rice cultivation in changes in atmospheric methane concentration and the Global Methane Pledge. Glob. Change Biol. 2023, 29, 2776–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.Q.; Harrison, M.T.; Liu, K.; Nie, L.X. Dry direct-seeded rice-wheat rotation system: Lower water and carbon footprint and higher carbon production efficiency and net ecosystem economic benefits. Field Crops Res. 2024, 309, 109323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Jin, W.; Chen, X.; Song, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Kong, L.; Huang, Z.; Liu, R.; Du, X. Effect of soybean inclusion in cropping systems on productivity, profitability, and carbon footprints: A case study from the Huang-Huai-Hai plain. Energy 2025, 316, 134422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F. Agricultural Ecology; China Agricultural University Press: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Meena, R.S.; Pradhan, G.; Kumar, S.; Lal, R. Using industrial wastes for rice-wheat cropping and food-energy-carbon-water-economic nexus to the sustainable food system. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 187, 113756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, B.; Panda, B.B.; Gautam, P.; Raja, R.; Singh, T.; Mohanty, S.; Shahid, M.; Tripathi, R.; Kumar, A. Input-output energy analysis of rainfed rice-based cropping systems in eastern India. Agron. J. 2015, 107, 1750–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.G.; Pei, X.X.; Dang, J.Y.; Zhang, D.Y. Research progress on high-yield, high-quality and high-efficiency ecological culti-vation of wheat by micro-spray (drip) irrigation and fertilizer integration. Crops 2022, 206, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.C.; Zhu, C.C.; Huo, Z.Y.; Xu, K.; Jiang, X.H.; Chen, H.C.; Gao, S.Q.; Li, D.J.; Zhao, C.M.; Dai, Q.G.; et al. Advantages of yield formation and main physiological and ecological characteristics of rice planted in potting machines. TCSAE 2013, 29, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.P. Effect of Mechanized Planting Methods on the Productivity of Rice and Annual Grain Production. Ph.D. Thesis, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.P.; Chen, J.J.; Liu, S.G.; Xin, H.B.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, M.W.; Lu, P.L. Study on yield and quality characteristics of conventional Japonica rice varieties in high sand soil areas along the Yangtze River in Jiangsu. China Seed Ind. 2024, 43, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.F.; Xu, K.; Ding, C.Q.; Wang, L.J.; Chen, X.H.; Gu, K.J.; Wei, G.B.; Li, C.Y.; Wu, L.Q.; Zhou, Q.; et al. Creation and Application of Key Technologies for High-Yield, High-Efficiency and Green Cultivation of Rice-Wheat. Available online: https://kxyjy.njau.edu.cn/info/1143/10990.htm (accessed on 29 May 2025).
- Wang, R.Q.; Zhang, R.; Cheng, M.H.; He, Z.T.; Wang, J.H.; Fan, D.J.; Chen, S.Q. Breeding of a wheat variety Yangfumai 20 with high yield, high quality and early-maturing. China Seed Ind. 2024, 43, 135–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, S.X.; Tu, M.; Huang, Y.G.; Zhu, S.S. Effects of N, P, K fertilizer application on grain yield, quality, nutrient uptake and utilization of T Xiangyou 557. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2020, 48, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.K.; Li, J.Q.; Li, W.W.; Wen, C.X.; Gao, S.; Wang, Y.H.; Liu, D.; Xu, L.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Z.H.; et al. Higher rice productivity and lower paddy nitrogen loss with optimized irrigation and fertilization practices in a rice-upland system. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 374, 109176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X.Q.; Nyamdavaa, M.; Zhang, F.S. The transformation of agriculture in China: Looking back and looking forward. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.Y.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, X.; Qi, W.; Sun, Q.; Wang, L.W. Spatiotemporal pattern and driving factors of grain production in Jiangsu Province. Econ. Geogr. 2018, 38, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.T.; Zhang, Y. An analysis of the evolution of the spatial and temporal pattern of crop planting structure in Jiangsu Province. China Rice 2023, 29, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.H.; Han, L.; Xie, J.N.; Jin, H.; Liu, C.Y.; Fan, J.L. Study on the carbon footprint dynamics and composition of major agricultural crops in Jiangsu Province. J. Nanjng Univ. Inf. Sci. Technol. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2022, 14, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L. Carbon Footprint Analysis of Agriculture in Jiangsu Province: An Example of Rice-Wheat Annual Rotation System. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, H.Y.; Zhu, X.C.; Huang, S.; Linquist, B.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Wassmann, R.; Minamikawa, K.; Martinez-Eixarch, M.; Yan, X.Y.; Zhou, F.; et al. Greenhouse gas emissions and mitigation in rice agriculture. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 716–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.Y.; Qin, T.; Du, X.Z.; Sheng, F.; Li, C.F. Effects of irrigation regime and rice variety on greenhouse gas emissions and grain yields from paddy fields in central China. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 250, 106830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment. Second Biennial Update Report on Climate Change of the People’s Republic of China. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/ydqhbh/wsqtkz/201907/P020190701765971866571.pdf (accessed on 29 May 2025).
- Zhang, Z.W.; Qin, X.B.; Fan, J.L.; Wei, X.H.; Wan, Y.F.; Wang, J.M.; Liao, Y.L.; Lu, Y.H. Applicability and abatement potential assessment of alternate wet and dry CH4 mitigation technology in major rice cropping regions in Hunan Province of China. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2022, 38, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Carrijo, D.; Huang, S.; Chen, J.; Balaine, N.; Zhang, W.; Groenigen, K.J.V.; Linquist, B. Water management to mitigate the global warming potential of rice systems: A global meta-analysis. Field Crops Res. 2019, 234, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.M.; Kim, G.W.; Kim, P.J.; Kim, S.Y. Comparison of net global warming potential between continuous flooding and midseason drainage in monsoon region paddy during rice cropping. Field Crops Res. 2016, 193, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.P.; Peng, S.B. Input-output energy analysis of rice production in different crop management practices in central China. Energy 2017, 141, 1124–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.X.; Langer, V.; Høgh-Jensen, H.; Egelyng, H. Life cycle assessment of fossil energy use and greenhouse gas emissions in Chinese pear production. J. Clean. Prod. 2010, 18, 1423–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Tong, Y.Q.; Liu, Q.; Zang, H.D.; Yang, Y.D.; Qi, Z.Q.; Zeng, Z.H. Characterization of temporal and spatial changes in global rice production and analysis of trade trends. J. South. Agric. 2022, 53, 1776–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China. Implementation Plan for Agricultural and Rural Emissions Reduction and Carbon Sequestration. Available online: https://www.moa.gov.cn/govpublic/KJJYS/202206/t20220630_6403715.htm (accessed on 29 May 2025).
- Zhang, Y.; Gu, J.Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, W.L.; Zhang, W.Y.; Gu, J.F.; Liu, L.J.; Yang, J.C.; Zhang, H. Carbon footprint of major grain crops in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River during 2011–2022. J. Appl. Ecol. 2023, 34, 3364–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, M.H.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Y.F.; Wang, L.G.; Lu, X. Agricultural machinery could contribute 20% of total carbon and air pollutant emissions by 2050 and compromise carbon neutrality targets in China. Nat. Food 2024, 6, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daba, N.A.; Huang, J.; Shen, Z.; Han, T.F.; Alam, M.A.; Li, J.W.; Tadesse, K.A.; Gilbert, N.; Kebede, E.; Legesse, T.G.; et al. Green manure substitution for chemical nitrogen reduces greenhouse gas emissions and enhances yield and nitrogen uptake in rice-rice cropping systems. Field Crops Res. 2025, 322, 109715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.J.; Feng, B.; Zhang, D.T.; Zou, J.; Yang, Y.H.; Rees, R.M.; Topp, C.F.E.; Hu, S.Y.; Qiao, B.W.; Huang, W.H.; et al. Optimizing N applications increases maize yield and reduces environmental costs in a 12-year wheat-maize system. Field Crops Res. 2025, 322, 109741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Huang, Z.; Mu, Y.X.; Song, S.K.; Zhang, Y.C.; Tao, Y.; Nie, L.X. Alternate wetting and drying maintains rice yield and reduces global warming potential: A global meta-analysis. Field Crops Res. 2024, 318, 109603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.B.; Yang, Y.T.; Zhu, X.L.; Shen, W.Y.; Zhu, Z.K.; Ge, T.D.; Xia, L.L.; Ma, J.; Lv, S.H.; Xu, H. Combining water-saving and drought-resistant rice with plastic film mulching mitigates CH4 emissions with higher net economic benefits. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2024, 202, 107372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, D.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, L. Carbon Footprint and Energy Balance Analysis of Rice-Wheat Rotation System in East China. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1778. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081778
Wu D, Shen Y, Zhang Y, Zhang T, Zhang L. Carbon Footprint and Energy Balance Analysis of Rice-Wheat Rotation System in East China. Agronomy. 2025; 15(8):1778. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081778
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Dingqian, Yezi Shen, Yuxuan Zhang, Tianci Zhang, and Li Zhang. 2025. "Carbon Footprint and Energy Balance Analysis of Rice-Wheat Rotation System in East China" Agronomy 15, no. 8: 1778. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081778
APA StyleWu, D., Shen, Y., Zhang, Y., Zhang, T., & Zhang, L. (2025). Carbon Footprint and Energy Balance Analysis of Rice-Wheat Rotation System in East China. Agronomy, 15(8), 1778. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081778





