Identification of the Embryogenesis Gene BBM in Alfalfa (Medicago sativa) and Analysis of Its Expression Pattern
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
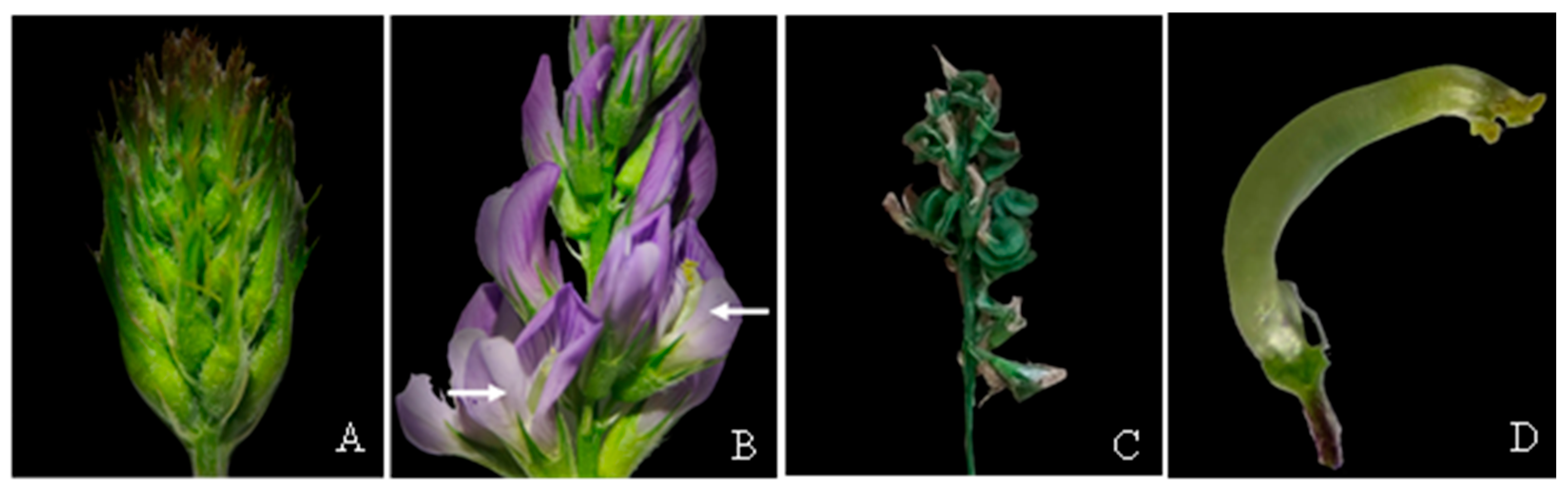
2.1. Plant Materials and Treatments
2.2. Identification of Target Genes
2.3. Cloning of Target Genes
2.4. Bioinformatics Analysis of MsBBM Protein
2.5. MsBBM Overexpression Vector Construction and Subcellular Localization
2.6. Real-Time Fluorescence Quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR) Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification and Cloning of Alfalfa BBM Genes
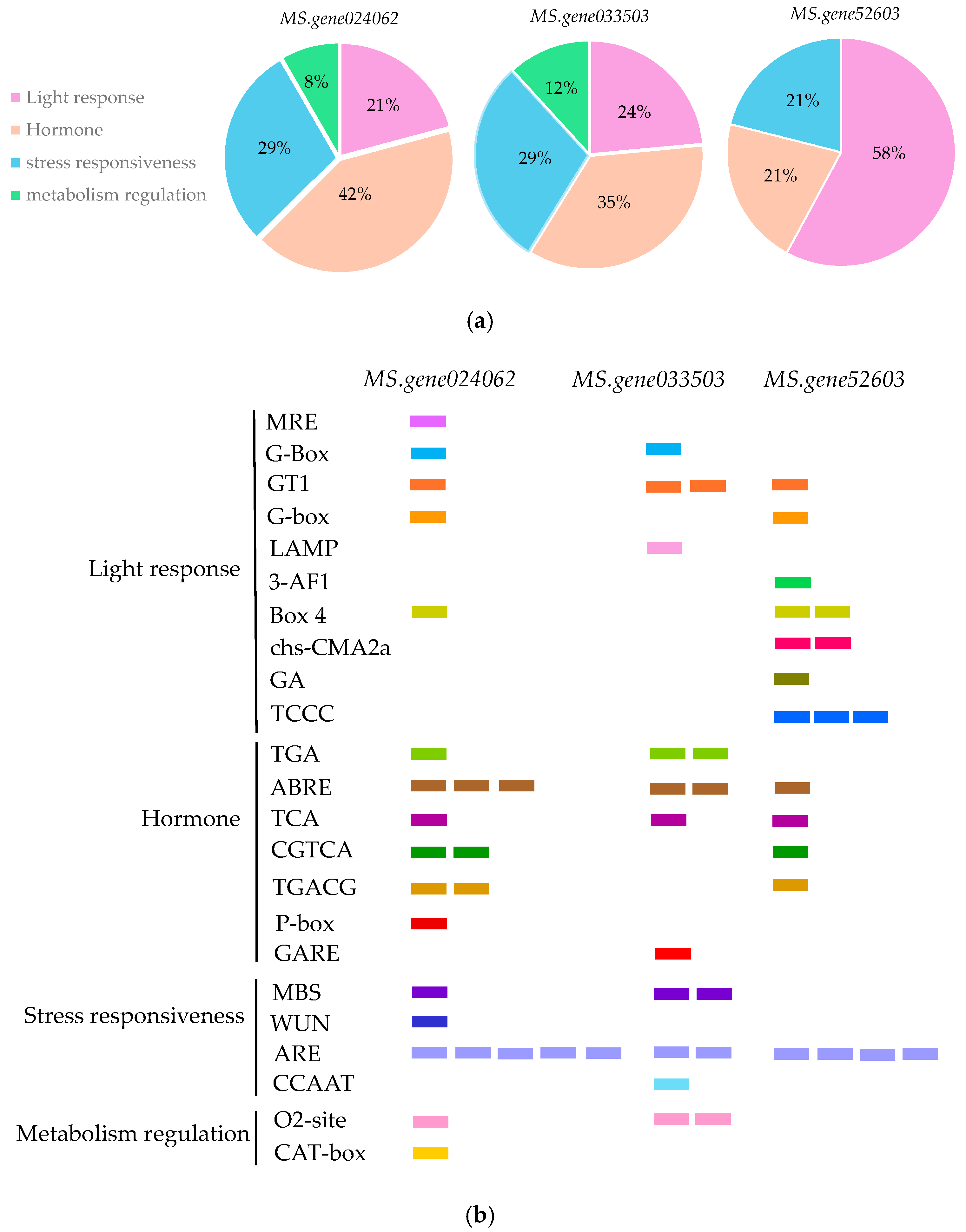
3.2. Analysis of Cis-Acting Elements in Alfalfa BBM Gene Promoters
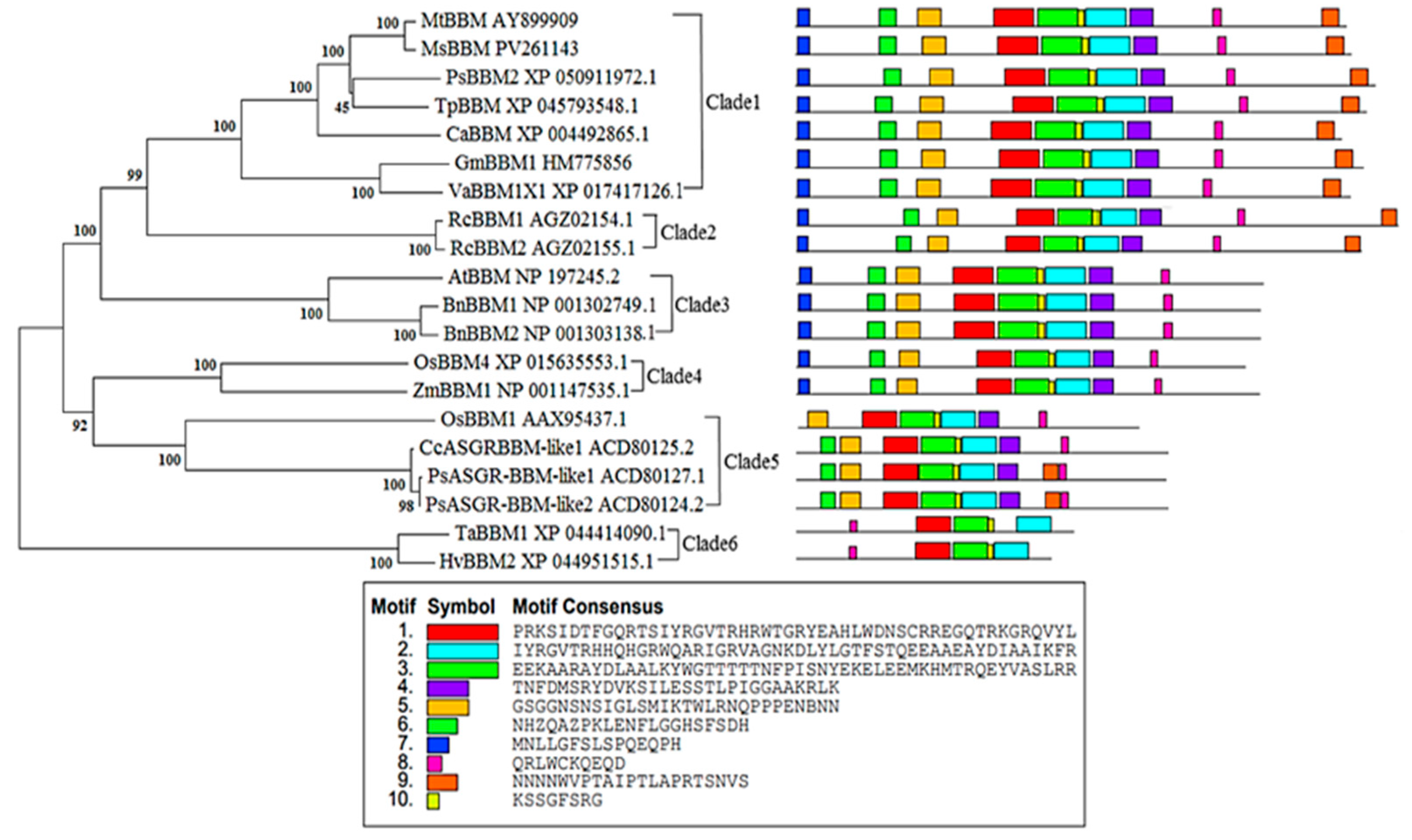
3.3. Phylogenetic Tree Construction and Motif Analysis of Alfalfa MsBBM
3.4. Subcellular Localization of Alfalfa MsBBM Protein
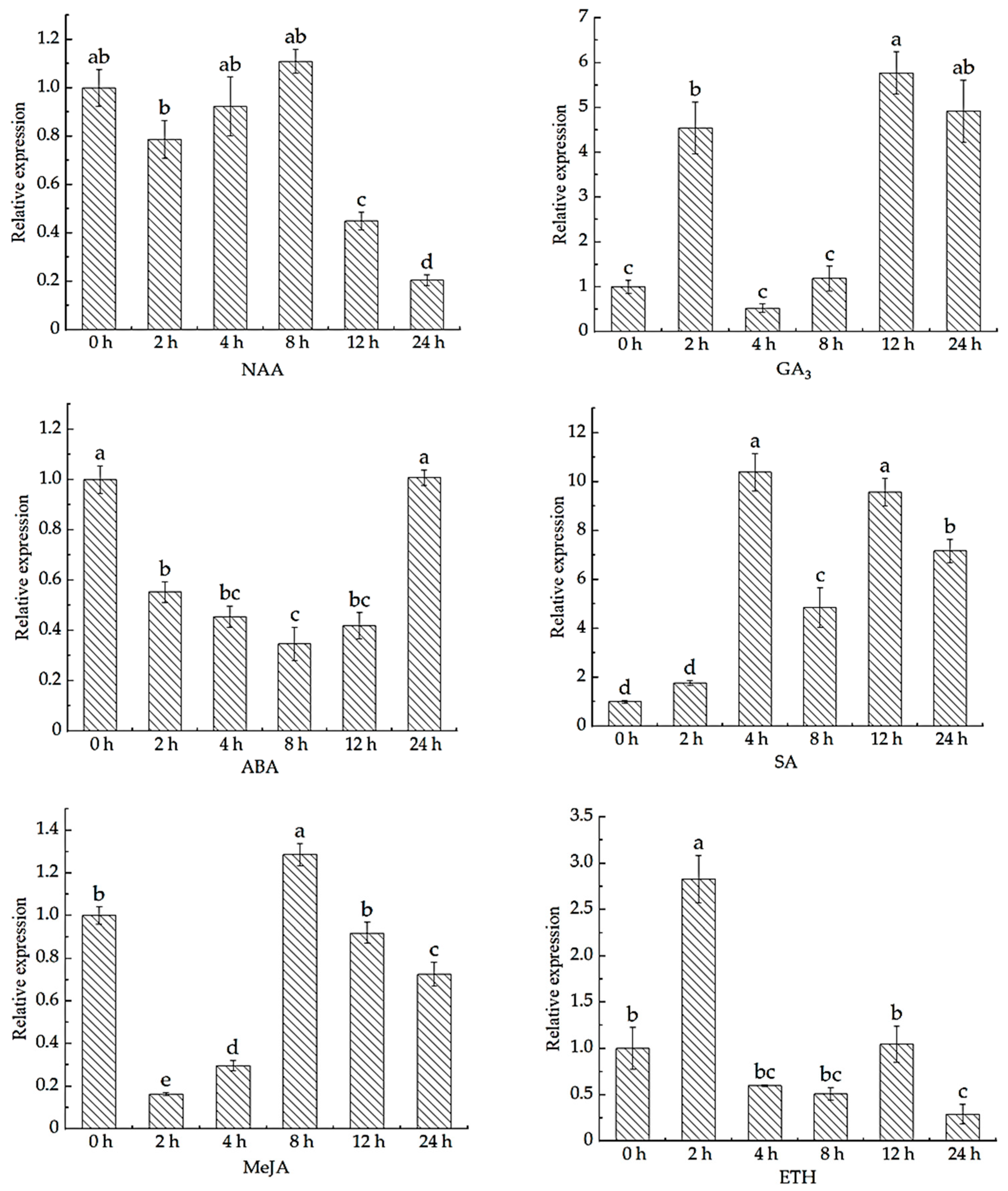
3.5. Analysis of MsBBM Gene Expression Pattern
4. Discussion
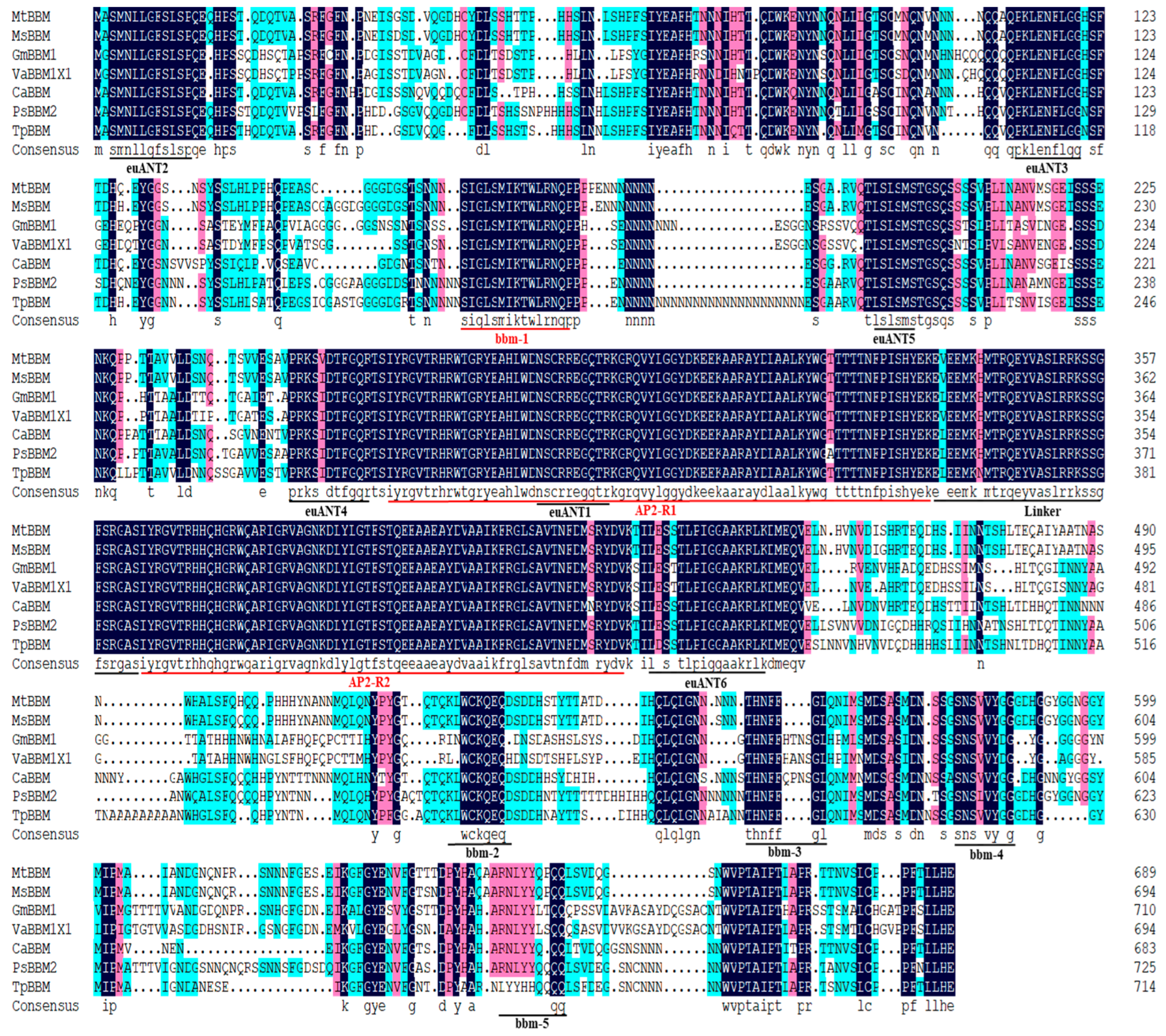
4.1. Characteristics of Conserved Domains and Motifs in Alfalfa MsBBM Protein
4.2. Analysis of MsBBM Gene Expression Pattern in Alfalfa
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NAA | Naphthalene Acetic Acid |
| GA3 | Gibberellic Acid |
| ABA | Abscisic Acid |
| SA | Salicylic acid |
| MeJA | Methyl jasmonate |
| ETH | Ethylene |
References
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Lei, W. Advances in basic biology of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.): A comprehensive overview. Hortic. Res. 2025, 12, uhaf081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.P.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, W.X.; Zhang, J.Y.; Xie, W.G.; Wang, Y.R.; Nan, Z.B. Some scientific issues of forage breeding in China. Acta Pratacult. Sin. 2021, 30, 184–193. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, E.; Li, Y.F.; Tang, D.; Lv, Y.X.; Liu, Z.G.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, D.Z. A strategy for generating rice apomixis by gene editing. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2019, 61, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riechmann, J.L.; Meyerowitz, E.M. The AP2/EREBP family of plant transcription factors. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 379, 633–646. [Google Scholar]
- Boutilier, K.; Offringa, R.; Sharma, V.K.; Kieft, H.; Ouellet, T.; Zhang, L.; Hattori, J.; Liu, C.M.; van Lammeren, A.A.M.; Miki, B.L.A.; et al. Ectopic expression of BABY BOOM triggers a conversion from vegetative to embryonic growth. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 1737–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouakfaoui, S.E.; Schnell, J.; Abdeen, A.; Colville, A.; Labbe, H.; Han, S.; Miki, B. Control of somatic embryogenesis and embryo development by AP2 transcription factors. Plant Mol. Biol. 2010, 74, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shivani; Awasthi, P.; Sharma, V.; Kaur, N.; Kaur, N.; Pandey, P.; Tiwari, S. Genome-wide analysis of transcription factors during somatic embryogenesis in banana (Musa spp.) cv. Grand Naine. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulinska-Lukaszek, K.; Tobojka, M.; Adamiok, A.; Kurczynska, E.U. Expression of the BBM gene during somatic embryogenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Biol. Plant 2012, 56, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, C.; Liu, Z.; Heidmann, I.; Supena, E.D.J.; Fukuoka, H.; Joosen, R.; Lambalk, J.; Angenent, G.; Scorza, R.; Custers, J.B.M.; et al. Heterologous expression of the BABY BOOM AP2/ERF transcription factor enhances the regeneration capacity of tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.). Planta 2007, 225, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, K.; Wu, E.; Wang, N.; Hoerster, G.; Hastings, C.; Cho, M.J.; Scelonge, C.; Lenderts, B.; Chamberlin, M.; Cushatt, J.; et al. Morphogenic regulators Baby boom and Wuschel improve monocot transformation. Plant Cell 2016, 28, 1998–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y. Capturing heterosis: Progress towards achieving apomixis in sorghum. In Proceedings of the Plant and Animal Genome XXV Conference, San Diego, CA, USA, 14–18 January 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mookan, M.; Nelson-Vasilchik, K.; Hague, J.; Kausch, A.P. Selectable marker independent transformation of recalcitrant maize inbred B73 and sorghum P898012 mediated by morphogenic regulators BABY BOOM and WUSCHEL2. Plant Cell Rep. 2017, 36, 1477–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.F.; Conner, J.; Guo, Y.P.; Ozias-Akins, P. Haploidy in tobacco induced by PsASGR-BBML transgenes via parthenogenesis. Genes 2020, 11, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Maas, L.; Figueiredo, D.; Zhong, Y.; Reis, R.; Li, M.; Horstman, A.; Riksen, T.; Weemen, M.; Liu, H.; et al. BABY BOOM regulates early embryo and endosperm development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2201761119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conner, J.A.; Podio, M.; Ozias-Akins, P. Haploid embryo production in rice and maize induced by PsASGR-BBML transgenes. Plant Reprod. 2017, 30, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Han, D.F.; Cheng, D.H.; Chen, J.F.; Tian, S.J.; Wang, J.F.; Liu, M.; Yuan, L. AtRKD5 inhibits the parthenogenic potential mediated by AtBBM. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2024, 66, 1517–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozias-Akins, P.; Roche, D.; Hanna, W.W. Tight clustering and hemizygosity of apomixis-linked molecular markers in Pennisetum squamulatum implies genetic control of apospory by a divergent locus that may have no allelic form in sexual genotypes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 5127–5132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozias-Akins, P.; Akiyama, Y.; Hanna, W.W. Molecular characterization of the genomic region linked with apomixis in Pennisetum/Cenchrus. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2003, 3, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conner, J.A.; Gunawan, G.; Ozias-Akins, P. Recombination within the apospory specific genomic region leads to the uncoupling of apomixis components in Cenchrus ciliaris. Planta 2013, 238, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horstman, A.; Willemsen, V.; Boutilier, K.; Heidstra, R. AINTEGUMENTA-LIKE proteins: Hubs in a plethora of networks. Trends Plant Sci. 2014, 19, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steffen, J.G.; Kang, I.H.; Macfarlane, J.; Drews, G.N. Identification of genes expressed in the Arabidopsis female gametophyte. Plant J. 2007, 51, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conner, J.A.; Mookkan, M.; Huo, H.; Chae, K.; Ozias-Akins, P. A parthenogenesis gene of apomict origin elicits embryo formation from unfertilized eggs in a sexual plant. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 11205–11210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gualtieri, G.; Conner, J.A.; Morishige, D.T.; Moore, L.D.; Mullet, J.E.; Ozias-Akins, P. A segment of the Apospory-Specific Genomic Region is highly microsyntenic not only between the apomicts Pennisetum squamulatum and buffelgrass, but also with a rice chromosome 11 Centromeric-Proximal Genomic Region. Plant Physiol. 2006, 140, 963–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mieulet, D.; Jolivet, S.; Rivard, M.; Cromer, L.; Vernet, A.; Mayonove, P.; Pereira, L.; Droc, G.; Courtois, B.; Guiderdoni, E.; et al. Turning rice meiosis into mitosis. Cell Res. 2016, 26, 1242–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanday, I.; Skinner, D.; Yang, B.; Mercier, R.; Sundaresan, V. A male-expressed rice embryogenic trigger redirected for asexual propagation through seeds. Nature 2019, 565, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chahal, L.S.; Conner, J.A.; Ozias-Akins, P. Phylogenetically Distant BABY BOOM Genes from Setaria italica Induce Parthenogenesis in Rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 863908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Liu, C.; Chen, X.; Lu, H.W.; Wang, J.; Yang, S.L.; Wang, K.J. Synthetic apomixis with normal hybrid rice seed production. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zeng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Huang, L.; Tang, B.; Zhang, H.; Hao, F.; Liu, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; et al. Allele-aware chromosome-level genome assembly and efficient transgene-free genome editing for the autotetraploid cultivated alfalfa. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, R.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Li, M.; Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, W.; Zhang, T.; Yu, L.X.; He, F.; et al. Genome assembly of alfalfa cultivar zhongmu-4 and identification of SNPs associated with agronomic traits. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2022, 20, 14–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.; Du, H.; Chen, Z.; Lu, H.; Zhu, F.; Chen, H.; Meng, X.; Liu, Q.; Liu, P.; Zheng, L.; et al. The chromosome-level genome sequence of the autotetraploid alfalfa and resequencing of core germplasms provide genomic resources for alfalfa research. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1250–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Kang, W.J.; Wu, F.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Bu, H.; Hu, T.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z. Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals new insight of Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) cultivars in response to abrupt freezing stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 798118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Su, J.B.; Duan, S.; Ao, Y.; Dai, J.R.; Liu, J.; Wang, P.; Li, Y.G.; Liu, B.; Feng, D.R.; et al. A highly efficient rice green tissue protoplast system for transient gene expression and studying light/chloroplast-related processes. Plant Methods 2011, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, W.N.; Xu, T.Y.; Miao, J.M.; Li, Y.Z. Screening of Reference Genes in Different Tissues and Hormone Treatments of Alfalfa. Grassl. Turf 2024. Available online: http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/62.1156.S.20240521.1243.002.html (accessed on 22 June 2025).
- Kim, S.; Soltis, P.S.; Wall, K.; Soltis, D.E. Phylogeny and domain evolution in the APETALA2-like gene family. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2006, 23, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, T.; Suzuki, K.; Fujimura, T.; Shinshi, H. Genome-wide analysis of the ERF gene family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Physiol. 2006, 140, 411–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakuma, Y.; Liu, Q.; Dubouzet, J.G.; Abe, H.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. DNA-binding specificity of the ERF/AP2 domain of Arabidopsis DREBs, transcription factors involved in dehydration- and cold-inducible gene expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 290, 998–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, D.; Ohme-Takagi, M.; Sarai, A. Unique mode of GCC box recognition by the DNA-binding domain of ethylene-responsive element-binding factor (ERF domain) in plant. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 26857–26861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, R.C.; Betzner, A.S.; Huttner, E.; Oakes, M.P.; Tucker, W.Q.J.; Gerentes, D.; Perez, P.; Smyth, D.R. AINTEGUMENTA, an APETALA2-like gene of Arabidopsis with pleiotropic roles in ovule development and floral organ growth. Plant Cell 1996, 8, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Okamuro, J.K.; Caster, B.; Villarroel, R.; Van Montagu, M.; Jofuku, K.D. The AP2 domain of APETALA2 defines a large new family of DNA binding proteins in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 7076–7081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aida, M.; Beis, D.; Heidstra, R.; Willemsen, V.; Blilou, I.; Galinha, C.; Nussaume, L.; Noh, Y.S.; Amasino, R.; Scheres, B. The PLETHORA genes mediate patterning of the Arabidopsis root stem cell niche. Cell 2004, 119, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Chen, M.; Chen, X.; Xu, Z.; Guan, S.; Li, L.C.; Li, A.; Guo, J.; Mao, L.; Ma, Y. Phylogeny, gene structures, and expression patterns of the ERF gene family in soybean (Glycine max L.). J. Exp. Bot. 2008, 59, 4095–4107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilichak, A.; Luu, J.; Jiang, F.; Eudes, F. Identification of BABY BOOM homolog in bread wheat. Agric. Gene 2018, 7, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.F.; Kou, Y.P.; Gao, B.; Soliman, T.M.A.; Xu, K.D.; Wang, X.Q.; Wang, F.X. Identification and functional analysis of BABY BOOM genes from Rosa canina. Biol. Plant 2014, 58, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavuz, C.; Çalışkan, M.E. Identification of BABY BOOM-like genes (SbBBM) in Sorghum [(Sorghum bicolor) L. Moench]. Cereal Res. Commun. 2022, 50, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, K.; Sun, X.; Li, Y. Isolation and characterization of larch BABY BOOM2 and its regulation of adventitious root development. Gene 2019, 690, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, R.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, P.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y. GmBBM7 promotes callus and root growth during somatic embryogenesis of soybean (Glycine max). Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2023, 37, 2238833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.P.; Sun, X.M.; Han, H.; Li, Y. Isolation, characterization and expression analysis of the BABY BOOM (BBM) gene from Larix kaempferi×L. olgensis during adventitious rooting. Gene 2014, 551, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.L.; Tang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Yang, Q.P. Cloning and expression of BABY BOOM gene in Dendrocalamus farinosus. J. Bamboo Res. 2019, 38, 24–31. [Google Scholar]
- Bui, L.T.; Pandzic, D.; Youngstrom, C.E.; Wallace, S.; Irish, E.E.; Szovenyi, P.; Cheng, C.L. A fern AINTEGUMENTA gene mirrors BABY BOOM in promoting apogamy in Ceratopteris richardii. Plant J. 2017, 90, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanday, I.; Santos-Medellín, C.; Sundaresan, V. Rice embryogenic trigger BABY BOOM1 promotes somatic embryogenesis by upregulation of auxin biosynthesis genes. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horstman, A.; Li, M.; Heidmann, I.; Weemen, M.; Chen, B.; Muino, J.M.; Angenent, G.C.; Boutilier, K. The BABY BOOM transcription factor activates the LEC1-ABI3-FUS3-LEC2 network to induce somatic embryogenesis. Plant Physiol. 2017, 175, 848–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.D.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, Z.Y.; Li, Q.; Yang, H.Q.; Luan, S.; Li, J.M.; He, Z.H. Auxin controls seed dormancy through stimulation of abscisic acid signaling by inducing ARF-mediated ABI3 activation in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 15485–15490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, D.; Datta, S.; Mitra, S.; Nag Chaudhuri, R. ABSCISIC ACID INSENSITIVE 3 promotes auxin signalling by regulating SHY2 expression to control primary root growth in response to dehydration stress. J. Exp. Bot. 2024, 75, 5111–5129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Xu, J.; Zheng, C.; Yang, Y.Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, R.R.; Ren, X.T.; Wei, S.W.; Aziz, U.; Du, J.B.; et al. Abscisic acid inhibits primary root growth by impairing ABI4-mediated cell cycle and auxin biosynthesis. Plant Physiol. 2023, 191, 265–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Caruso, L.V.; Downie, A.B.; Perry, S.E. The embryo MADS domain protein AGAMOUS-Like 15 directly regulates expression of a gene encoding an enzyme involved in gibberellin metabolism. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 1206–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Ji, H.; Burnie, W.; Perry, S.E. Gene regulation by the AGL15 transcription factor reveals hormone interactions in somatic embryogenesis. Plant Physiol. 2016, 172, 2374–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, F.; Dong, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; Liu, J.; Li, H. The gibberellin signaling negative regulator RGA-LIKE3 promotes seed storage protein accumulation. Plant Physiol. 2021, 185, 1697–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valencia-Lozano, E.; Ibarra, J.E.; Herrera-Ubaldo, H.; de Folter, S. Osmotic stress-induced somatic embryo maturation of coffee Coffea arabica L., shoot and root apical meristems development and robustness. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Li, Q.; Chen, Z.; Lv, Q.; Bao, F.; Wang, X.; He, Y. Regulatory Mechanism of ABA and ABI3 on Vegetative Development in the Moss Physcomitrella patens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.H.; Toda, E.; Kobayashi, M.; Kudo, T.; Koshimizu, S.; Takahara, M.; Iwami, M.; Watanabe, Y.; Sekimoto, H.; Yano, K.; et al. Expression of genes from paternal alleles in rice zygotes and involvement of OsASGR-BBML1 in initiation of zygotic development. Plant Cell Physiol. 2019, 60, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiyosue, T.; Ohad, N.; Yadegari, R.; Hannon, M.; Dinneny, J.; Wells, D.; Katz, A.; Margossian, L.; Harada, J.J.; Goldberg, R.B.; et al. Control of fertilization-independent endosperm development by the MEDEA polycomb gene in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 4186–4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Wrobel-Marek, J.; Heidmann, I.A.; Horstman, A.; Chen, B.; Reis, R.; Angenent, G.C.; Boutilier, K. Auxin biosynthesis maintains embryo identity and growth during BABY BOOM-induced somatic embryogenesis. Plant Physiol. 2022, 188, 1095–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Software Name | Analysis Project | Website |
|---|---|---|
| PlantCARE | Promoter analysis | https://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/plantcare/html/ (accessed on 10 August 2024) |
| MEME | Conservative structural domain analysis | https://meme-suite.org/meme/ (accessed on 11 August 2024) |
| MEGA 7.0 | Phylogenetic analysis | https://www.megasoftware.net/ (accessed on 12 August 2024) |
| DNAMAN 8 | Multiple Sequence Alignment | https://www.lynnon.com/ (accessed on 13 August 2024) |
| Gene ID | Chr | ORF Length (bp) | Full-length Gene (bp) | AA Length | Number of Exons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MS.gene024062 | Chr7.1 | 2085 | 3845 | 694 | 9 |
| MS.gene033503 | Chr7.3 | 2088 | 3983 | 695 | 9 |
| MS.gene52603 | Chr7.4 | 2091 | 3978 | 696 | 9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Yu, J.; Miao, J.; Yue, W.; Xu, T. Identification of the Embryogenesis Gene BBM in Alfalfa (Medicago sativa) and Analysis of Its Expression Pattern. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1768. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081768
Li Y, Yu J, Miao J, Yue W, Xu T. Identification of the Embryogenesis Gene BBM in Alfalfa (Medicago sativa) and Analysis of Its Expression Pattern. Agronomy. 2025; 15(8):1768. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081768
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yuzhu, Jiangdi Yu, Jiamin Miao, Weinan Yue, and Tongyu Xu. 2025. "Identification of the Embryogenesis Gene BBM in Alfalfa (Medicago sativa) and Analysis of Its Expression Pattern" Agronomy 15, no. 8: 1768. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081768
APA StyleLi, Y., Yu, J., Miao, J., Yue, W., & Xu, T. (2025). Identification of the Embryogenesis Gene BBM in Alfalfa (Medicago sativa) and Analysis of Its Expression Pattern. Agronomy, 15(8), 1768. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081768





