Evaluation of Soil Quality and Balancing of Nitrogen Application Effects in Summer Direct-Seeded Cotton Fields Based on Minimum Dataset
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Test Crops
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Measurement Indicators and Methods
2.4.1. Biomass
2.4.2. Yield and Yield Composition Factors
2.4.3. Soil Indicators
2.5. Calculations
2.5.1. Yield Stability Index and Sustainability Index
2.5.2. Minimum Soil Dataset
2.5.3. Soil Quality Evaluation Function
2.5.4. Data Analysis
- (1)
- Root mean square error (RMSE) and standardized root mean square error (nRMSE)where RMSE was the root mean square error, nRMSE was the standardized root mean square error, and Pi was the soil quality index under TDS for each treatment year; Oi was the soil quality index under MDS for each treatment year, was the average soil quality index under MDS, and n was the number of samples. The smaller the RMSE value, the higher the consistency between the soil quality index of MDS and TDS; NRMSE < 10% indicates excellent simulation performance; 10% < nRMSE < 20% indicates good performance; 20% < nRMSE < 30% indicates average performance; and NRMSE > 30% indicates poor performance.
- (2)
- Collaboration index d and determination coefficient R2where d is the synergy index and R2 is the coefficient of determination; the closer the value of d is to 1, the better the effect, and the closer the value of R2 is to 1, the higher the credibility.
2.5.5. Nitrogen Use Efficiency
2.5.6. Soil Barrier Degree
2.6. Statistics and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Establishment of Minimum Soil Dataset
3.2. Soil Quality Evaluation and Effectiveness Verification Based on Minimum Dataset
3.3. The Effect of Different Nitrogen Application Measures on Soil Nutrient Content
3.4. Effects of Different Nitrogen Application Measures on the Source–Sink Relationship During the Cotton Boll Opening Stage
3.5. Effects of Different Nitrogen Application Measures on Cotton Yield and Yield Stability
3.6. The Effect of Different Nitrogen Application Measures on Nitrogen Fertilizer Utilization Efficiency
3.7. Correlation Analysis of Soil Quality Index, Seed Cotton Yield, and Nitrogen Fertilizer Utilization Efficiency
3.8. Importance of Random Forest Model in Predicting Soil Quality Indicators and Analysis of Soil Barrier Degree
4. Discussion
4.1. Construction and Validation of the Minimum Dataset for Cotton Fields Under Different Nitrogen Application Measures
4.2. The Impact of Different Nitrogen Application Measures on Soil Quality
4.3. Balancing Nitrogen Application Measures Based on the Synergistic Improvement in Soil Quality, Yield, and Nitrogen Fertilizer Utilization Efficiency
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sangeeta, B.; Yin, X.; Virginia, S.; Jaehoon, L.; Sindhu, J. Soil aggregate-associated organic carbon and nitrogen response to long-term no-till crop rotation, cover crop, and manure application. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2021, 85, 2169–2184. [Google Scholar]
- Pable, D.; Chatterji, S.; Venugopalan, M.V. Soil quality assessment of two cotton growing agroecological subregions of Vidarbha, Maharashtra. Indian J. Soil Conserv. 2016, 44, 343–349. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Pan, W.; Tang, S.; Ma, Q.; Mi, W.; Wu, L.; Liu, X. Optimizing nitrogen fertilization rate to achieve high yield and high soil quality in paddy ecosystems with straw incorporation. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 375, 124158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Lin, Y.; Liu, X.; Deng, M.; Zhang, P.; Ren, X.; Chen, X. Manure substitution with appropriate N rate enhanced the soil quality, crop productivity and net ecosystem economic benefit: A sustainable rainfed wheat practice. Field Crops Res. 2023, 304, 109164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Yang, H.; Yang, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Fan, Q.; Yang, N.; Wang, K.; Zhang, J.; et al. Different Impacts of Long-Term Tillage and Manure on Yield and N Use Efficiency, Soil Fertility, and Fungal Community in Rainfed Wheat in Loess Plateau. Plants 2024, 13, 3477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nafi, E.; Webber, H.; Danso, I.; Naab, J.B.; Frei, M.; Gaiser, T. Interactive effects of conservation tillage, residue management, and nitrogen fertilizer application on soil properties under maize-cotton rotation system on highly weathered soils of West Africa. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 196, 104473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.; Rashed, R.A. Effect of Syrian Indigenous Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi in Combination with Manure on the Growth of Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2017, 48, 2093–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, D.L.; Wilts, H.D.M.; MacLeod, J.A. Dissolved nitrous oxide emissions associated with agricultural drainage water as influenced by manure application. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1479754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafeez, A.; Ali, S.; Ma, X.; Tung, S.A.; Shah, A.N.; Ahmad, S.; Chattha, M.S.; Souliyanonh, B.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, G. Photosynthetic characteristics of boll subtending leaves are substantially influenced by applied K to N ratio under the new planting model for cotton in the Yangtze River Valley. Field Crops Res. 2019, 237, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Wang, X.; Xie, X.; Yang, D.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Q.; Liu, A.; Tu, X. Complex Microbial Fertilizer Promotes the Growth of Summer-Sown Short-Season-Cultivated Cotton and Increases Cotton Yield in the Yangtze River Basin by Changing the Soil Microbial Community Structure. Agronomy 2025, 15, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Qiu, S.; Thistlethwaite, R.; Yao, X.; Tan, D.; Wang, D.; Yang, G. Optimizing nitrogen application methods and frequency to increase cotton yield in summer direct sown condition. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 213, 118468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.N.; Javed, T.; Singhal, R.K.; Shabbir, R.; Wang, D.; Hussain, S.; Anuragi, H.; Jinger, D.; Pandey, H.; Abdelsalam, N.R.; et al. Nitrogen use efficiency in cotton: Challenges and opportunities against environmental constraints. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 970339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Xia, S.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, R.; Chen, P.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z. Effect of interaction of nitrogen and potassium fertilizer on cotton yield and nitrogen use efficiency and assessment of suitable fertilization level in the Yangtze River Basin. Soil Fertil. Sci. China 2022, 01, 44–46. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Pittaway, P.A.; Antille, D.L.; Melland, A.R.; Marchuk, S. Availability of Nitrogen in Soil for Irrigated Cotton Following Application of Urea and 3,4-Dimethylpyrazole Phosphate-Coated Urea in Concentrated Bands. Plants 2023, 12, 1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajeshkumar, N.K.; Balakrishnan, P.; Naveena, K.; Kumar, K.S.B. Identification of Minimum Data Set for Soil Quality Assessment in Upper Krishna Project Area. Int. J. Agric. Sci. 2016, 8, 3184–3188. [Google Scholar]
- Lal, B.; Sharma, A.; Gupta, A.K.; Singh, S.S.; Chaturvedi, S.K.; Jhariya, M.K. Soil fertility evaluation through farmer knowledge and scientific approaches of Bundelkhand region, Central India. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, prepublish. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami, N.S.; Chavoshi, E.; Ayoubi, S.; Honarjoo, N.; Zeraatpisheh, M. Comprehensive assessment of soil quality in various land uses: A comparative analysis of soil quality index models. Environ. Earth Sci. 2024, 83, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, J.; Miao, Y.; Zhao, T.; Guo, L.; Liu, D. Assessment of soil fertility in Artemisia argyi planting areas in Qichun county based on minimum data set. China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2022, 47, 3738–3748. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Pan, B.; Dai, L.; Tian, A. Selection of the minimum data set and quantitative soil quality indices for different azalea forest communities in southwestern China. Plant Soil 2024, 511, 463–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duraisamy, V.; Gopal, T.; Sonalika, S.; Benukantha, D.; Abhishek, J.; Prasad, S.R.; Ravindra, N.; Pramod, T.; Karunakaran, K.; Padikkal, C. A minimum data set of soil morphological properties for quantifying soil quality in coastal agroecosystems. CATENA 2020, 198, 105042. [Google Scholar]
- Mohaghegh, P.; Naderi, M.; Mohammadi, J. Determination of Minimum Data Set for Assessment of Soil Quality:A Case Study in Choghakhur Lake Basin. J. Water Soil 2017, 30, 1232–1243. [Google Scholar]
- Ram, S.S.; Kumar, K.D.; Pradip, D.; Singha, M.B. Identification of Minimum Data Set Under Balanced Fertilization for Sustainable Rice Production and Maintaining Soil Quality in Alluvial Soils of Eastern India. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2017, 48, 2170–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davtian, N.; Ménot, G.; Bard, E.; Poulenard, J.; Podwojewski, P. Consideration of soil types for the calibration of molecular proxies for soil pH and temperature using global soil datasets and Vietnamese soil profiles. Org. Geochem. 2016, 101, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volchko, Y.; Norrman, J.; Rosèn, L.; Norberg, T. A minimum data set for evaluating the ecological soil functions in remediation projects. J. Soils Sediments 2014, 14, 1850–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Hu, Q.; Tang, W.; Wang, X.; Lu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, T.; Kong, X. Effects of N fertilizer rate and planting density on short-season cotton yield, N agronomic efficiency and soil N using 15N tracing technique. Eur. J. Agron. 2022, 138, 126546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mng’omba, S.A.; Akinnifesi, F.K.; Kerr, A.; Salipira, K.; Muchugi, A. Growth and yield responses of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) to inorganic and organic fertilizers in southern Malawi. Agrofor. Syst. 2017, 91, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, Q.; Lin, C.; He, C.; Zhong, S.; Li, Y.; Xin, J. Establishing a minimum data set of soil quality assessment for cold-waterlogged paddy field in Fujian Province, China. J. Appl. Ecol. 2015, 26, 1461–1468. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Nan, H.; Feng, K. Effects of reduced chemical fertilizer with organic fertilizer application on soil microbial biomass, enzyme activity and cotton yield. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 31, 173–181. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Qin, Y.; Cheng, H.; Li, Y.; Luo, H. Research on Characteristics of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Loss from Surface Runoff of Cotton Field in Northern Jiangxi Province of Poyang Lake Region. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2022, 24, 166–175. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sahabi, H.; Moradi, R.; Ray, R.L.; Saeidnejad, A.H. Mitigating greenhouse gas emissions in a cotton production system using various management practices. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 115901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Lv, Q.; Tang, Q. Impact of bio-organic fertilizer and reduced chemical fertilizer application on physical and hydraulic properties of cucumber continuous cropping soil. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2022, 14, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, K.; Khan, N.; Khan, M.U.; Yazdan Saleem, F.; Rashid, A. Impact of tillage and nitrogen on cotton yield and quality in a wheat-cotton system, Pakistan. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2014, 60, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochester, I.J.; Constable, G.A. Nitrogen-fertiliser application effects on cotton lint percentage, seed size, and seed oil and protein concentrations. Crop Pasture Sci. 2020, 71, 831–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Joshi, R.K.; Mishra, A.; Kumar, S.; Hansda, P.; Garkoti, S.C. Treeline ecotone drives the soil physical, bio-chemical and stoichiometry properties in alpine ecosystems of the western Himalaya, India. Catena 2024, 239, 107950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iseas, M.S.; Sainato, C.M.; Romay, C. Supplemental irrigation in the humid Pampean region: Effects on soil salinity, physical properties, nutrients and organic carbon. Soil Tillage Res. 2025, 248, 106421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benes, E.; Fodor, M.; Kovács, S.; Gere, A. Application of Detrended Fluctuation Analysis and Yield Stability Index to Evaluate Near Infrared Spectra of Green and Roasted Coffee Samples. Processes 2020, 8, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awio, T.; Senthilkumar, K.; Ibrahim, A.; Corbeels, M.; Saito, K. Yield stability of four staple crops of sub-Saharan Africa: Analysis of long-term trials. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosystems 2025, 130, 329–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Tu, J.; Zhang, F.; Ran, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, W.; Chen, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q. Soil health assessment of urban forests in Nanchang, China: Establishing a minimum data set model. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2025, 206, 109795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, U.K.; Warrington, D.N.; Bhardwaj, A.K.; Bar-Tal, A.; Kautsky, L.; Minz, D.; Levy, G.J. Evaluating impact of irrigation water quality on a calcareous clay soil using principal component analysis. Geoderma 2007, 144, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, D.S.W.; Naves, S.M.L.; Cesar, A.J.; Francisco, A.G.S.; Moreira, C.B.; Ângelo, C.M.; Nilton, C. Soil quality assessment using erosion-sensitive indices and fuzzy membership under different cropping systems on a Ferralsol in Brazil. Geoderma Reg. 2021, 25, e00385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaspour-Gilandeh, M.; Abbaspour-Gilandeh, Y. Modelling soil compaction of agricultural soils using fuzzy logic approach and adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) approaches. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2019, 5, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkacha, A.; Douaoui, A.; Younes, K.; Sawda, C.E.; Alsyouri, H.; Zahab, S.E.; Grasset, L. Investigating the Impact of Salinity on Soil Organic Matter Dynamics Using Molecular Biomarkers and Principal Component Analysis. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebonye, N.M. Exploring the novel support points-based split method on a soil dataset. Measurement 2021, 186, 110131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, H.; Noh, B. SolarNexus: A deep learning framework for adaptive photovoltaic power generation forecasting and scalable management. Appl. Energy 2025, 391, 125848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanap, S.; Patil, M.A.; Wandre, S.S.; Dalavi, P.N. Estimation of Crop Evapotranspiration of Wheat Using Remote Sensing & GIS Based Crop Coefficient. Asian J. Adv. Agric. Res. 2025, 25, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askari, I.B.; Ahsaee, H.G.; Shahsavar, A.; Keshtegar, B. Machine learning-based multi-objective optimization of a carbon dioxide direct-expansion geothermal heat pump comprising an internal heat exchanger and expander. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2025, 274, 126699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Feng, W.; Chen, J.; Zheng, C.; Zhang, L.; Nie, T. Critical Nitrogen Dilution Curve for Diagnosing Nitrogen Status of Cotton and Its Implications for Nitrogen Management in Cotton–Rape Rotation System. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, L.; He, X.; Lv, G. Evaluation of Soil Quality and Analysis of Barriers of Protection Forests along Tarim Desert Highway Based on a Minimum Data Set. Land 2024, 13, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yemefack, M.; Jetten, V.G.; Rossiter, D.G. Developing a minimum data set for characterizing soil dynamics in shifting cultivation systems. Soil Tillage Res. 2005, 86, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raiesi, F. A minimum data set and soil quality index to quantify the effect of land use conversion on soil quality and degradation in native rangelands of upland arid and semiarid regions. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 75, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyolanu, O.D. Application of the Concept of Minimum Data Sets to Soil Quality Assessment for Crop Production in Southwestern Nigeria. Int. J. Plant Soil Sci. 2017, 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatano, R.; Mukumbuta, I.; Shimizu, M. Soil Health Intensification through Strengthening Soil Structure Improves Soil Carbon Sequestration. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slaton, N.A.; Lyons, S.E.; Osmond, D.L.; Brouder, S.M.; Culman, S.W.; Drescher, G.; Gatiboni, L.C.; Hoben, J.; Kleinman, P.J.; McGrath, J.M.; et al. Minimum dataset and metadata guidelines for soil-test correlation and calibration research. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2021, 86, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samira, H.; Nafiseh, Y.; Bagher, F.M.; Atefeh, S. Soil quality assessment of paddy fields (in Northern Iran) with different productivities: Establishing the critical limits of minimum data set indicators. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 30, 10286–10296. [Google Scholar]
- Govaerts, B.; Sayre, K.D.; Deckers, J. A minimum data set for soil quality assessment of wheat and maize cropping in the highlands of Mexico. Soil Tillage Res. 2005, 87, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yang, S. Soil quality assessment in different dammed-valley farmlands in the hilly-gully mountain areas of the northern Loess Plateau, China. J. Arid. Land 2021, 13, 777–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandel, S.; Hadda, M.S.; Mahal, A.K. Soil Quality Assessment Through Minimum Data Set Under Different Land Uses of Submontane Punjab. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2018, 49, 658–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namr, K.I.; Lahbib, S.B.; Rerhou, B.; Masmoudi, Y.A.; Hajjaj, H.; Said, B.A. Comparative scoring indicators methods of different soil types to modelling soil quality through constructing Minimum Data Set in the Doukkala irrigated perimeter—Western region of Morocco. Environ. Earth Sci. 2025, 84, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maji, P.; Mistri, B. Comparative assessment of soil quality dynamics using SQI modelling approach: A study in rice bowl of West Bengal, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavarin-Pineda, Y. Soil quality in volcanic soils in a forest biosphere reserve in Mexico. Soil Water Res. 2021, 16, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravali, E.; Konde, N.M.; Bhoyar, S.M.; Kanase, N.; Singh, A.; Thite, M.D.; Shrirao, T. Effect of Different Tillage and Organic Inputs on Soil Properties and Yield of Cotton on Vertisols. Asian J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2024, 10, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Ye, Z.; Li, H.; Lyu, S.; Wang, L.; Zhou, C. Effects of combined application of biochar and nitrogen fertilizer on soil quality of summer maize-winter wheat system. J. Appl. Ecol. 2023, 34, 442–450. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Rout, K.K.; Sahoo, S.; Mukhi, S.K.; Mohanty, G.P. Assessment of Quality of Different Organic Manures used by the Farmers of Khurda District in Orissa and their Effect on Microbial Activity of an Acid Soil. J. Indian Soc. Soil Sci. 2012, 60, 30–37. [Google Scholar]
- Polychronaki, E.; Douma, C.; Giourga, C.; Loumou, A. Assessing Nitrogen Fertilization Strategies in Winter Wheat and Cotton Crops in Northern Greece. Pedosphere 2012, 22, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Huang, W.; Chen, J.; Wu, F.; Jia, Y.; Han, Y.; Wang, G.; Feng, L.; Li, X. Cover crops and N fertilization affect soil ammonia volatilization and N2O emission by regulating the soil labile carbon and nitrogen fractions. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 340, 108188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Zhang, L.; He, X.; Chen, X.; Cui, Z. Long-term optimization of crop yield while concurrently improving soil quality. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 897–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Zhang, J.; Chang, F.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Luan, H.; Qi, G.; Guo, S. Effects of nitrogen reduction combined with bio-organic fertilizer on soil bacterial community diversity of red raspberry orchard. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0283718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khuspure, J.A.; Kaware, D.; Bhoyar, S.M. Impact of Different Organic Manures Application on Soil Microbial Population and Soil Fertility under Cotton Cultivation. Trends Biosci. 2016, 8, 1519–1524. [Google Scholar]
- Koocheki, A.; Mahallati, M.N.; Moradi, R.; Alizadeh, Y. Evaluation of Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency of Maize and Cotton Intercropping under Different Nitrogen Levels. Iran. J. Field Crops Res. 2015, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Han, G.; Duan, Y.; Han, R.; Shen, X.; Wang, C.; Zhao, L.; Nie, M.; Du, H.; Yuan, X.; et al. Effects of Different Organic Fertilizer Substitutions for Chemical Nitrogen Fertilizer on Soil Fertility and Nitrogen Use Efficiency of Foxtail Millet. Agronomy 2024, 14, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Ma, J.; Wu, L.; Li, X.; Xu, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Bai, L.; Wang, Z. Effect of Organic Manure on Crop Yield, Soil Properties, and Economic Benefit in Wheat-Maize-Sunflower Rotation System, Hetao Irrigation District. Plants 2024, 13, 2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saikia, P.; Bhattacharya, S.S.; Baruah, K.K. Organic substitution in fertilizer schedule: Impacts on soil health, photosynthetic efficiency, yield and assimilation in wheat grown in alluvial soil. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 203, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, A.; Liang, H.; McBride, S.G.; Yuan, P.; Ali, I.; Zaman, M.; Zeeshan, M.; Khan, R.; Akhtar, K.; Wei, S.; et al. Manure applications combined with chemical fertilizer improves soil functionality, microbial biomass and rice production in a paddy field. Agron. J. 2022, 114, 1431–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannoulis, K.D.; Bartzialis, D.; Skoufogianni, E.; Danalatos, N.G. Innovative Nitrogen Fertilizers Effect on Cotton Cultivation. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2020, 51, 869–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, E.A.; Omara, P.; Iboyi, J.E.; Mulvaney, M.J.; Carter, E.; Wood, C.W.; Sharma, L.; Singh, H. Optimizing nitrogen rates for rainfed cotton on sandy loam soils of Florida. Agron. J. 2025, 117, e70046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhan, J.; Feng, K.; Qi, J.; Nan, H. Higher yield sustainability and soil quality by reducing chemical fertilizer with organic fertilizer application under a single-cotton cropping system. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1494667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.; Hou, C.; Cui, H. Inversion Models for Orchard Soil Nutrient Content Using Near- Infrared Spectroscopy. Innov. Appl. AI 2025, 2, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

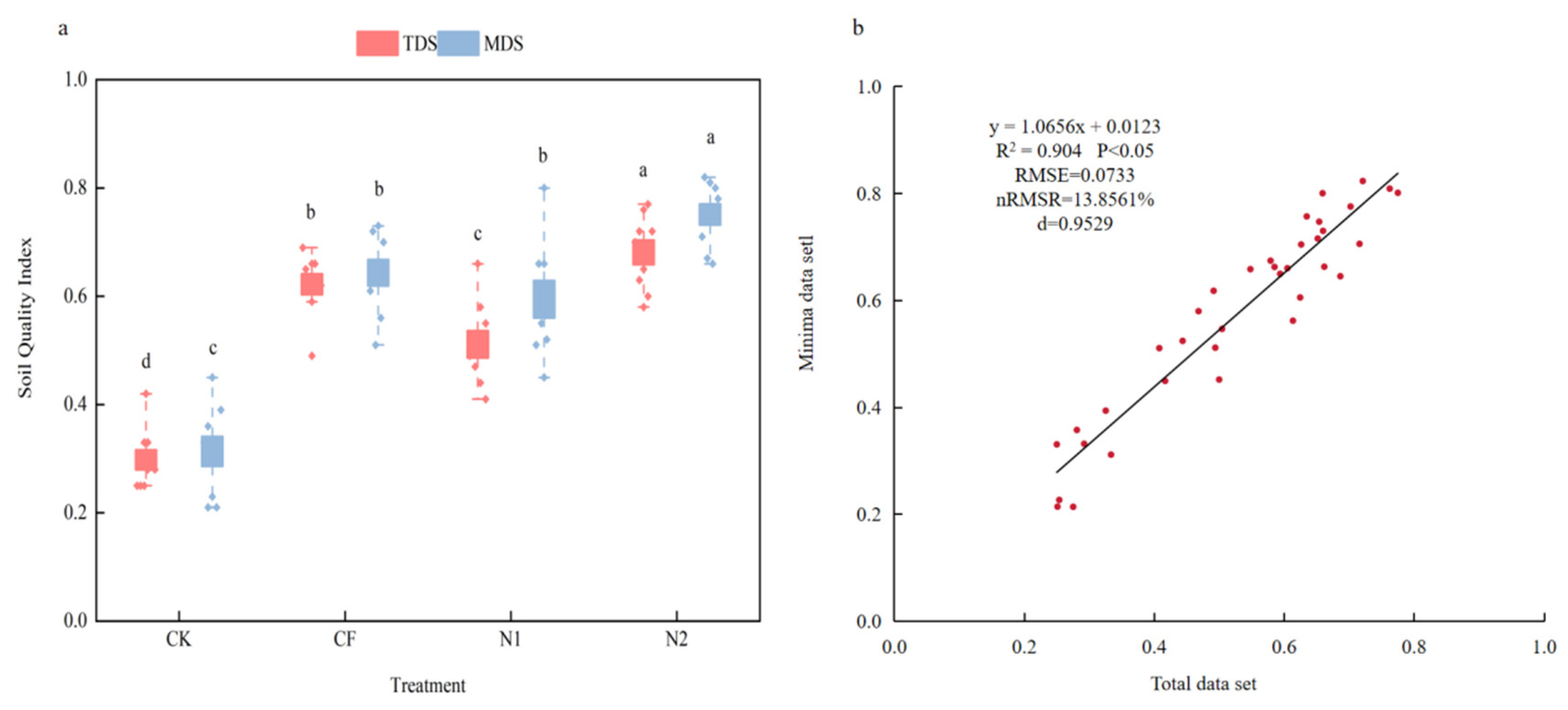
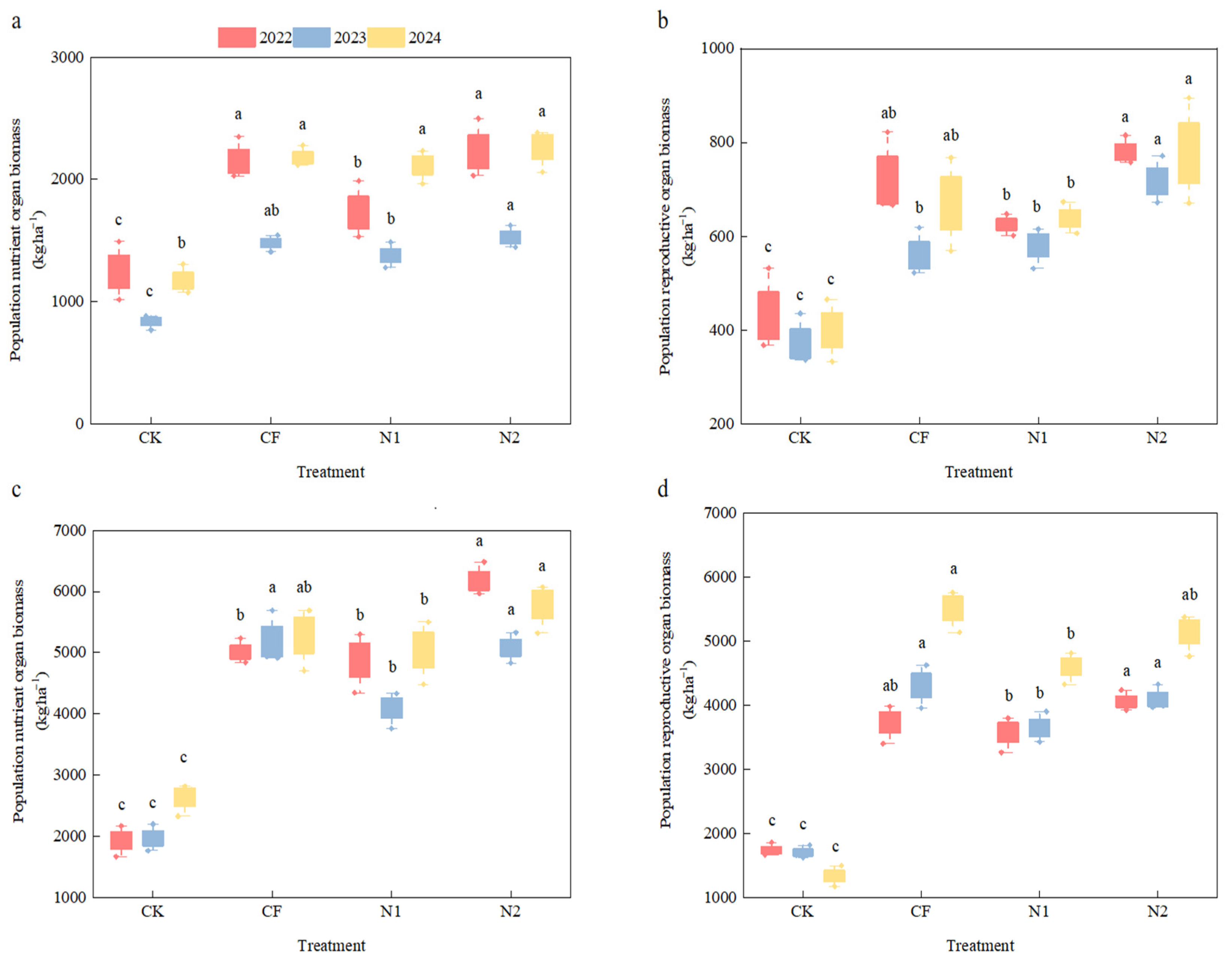

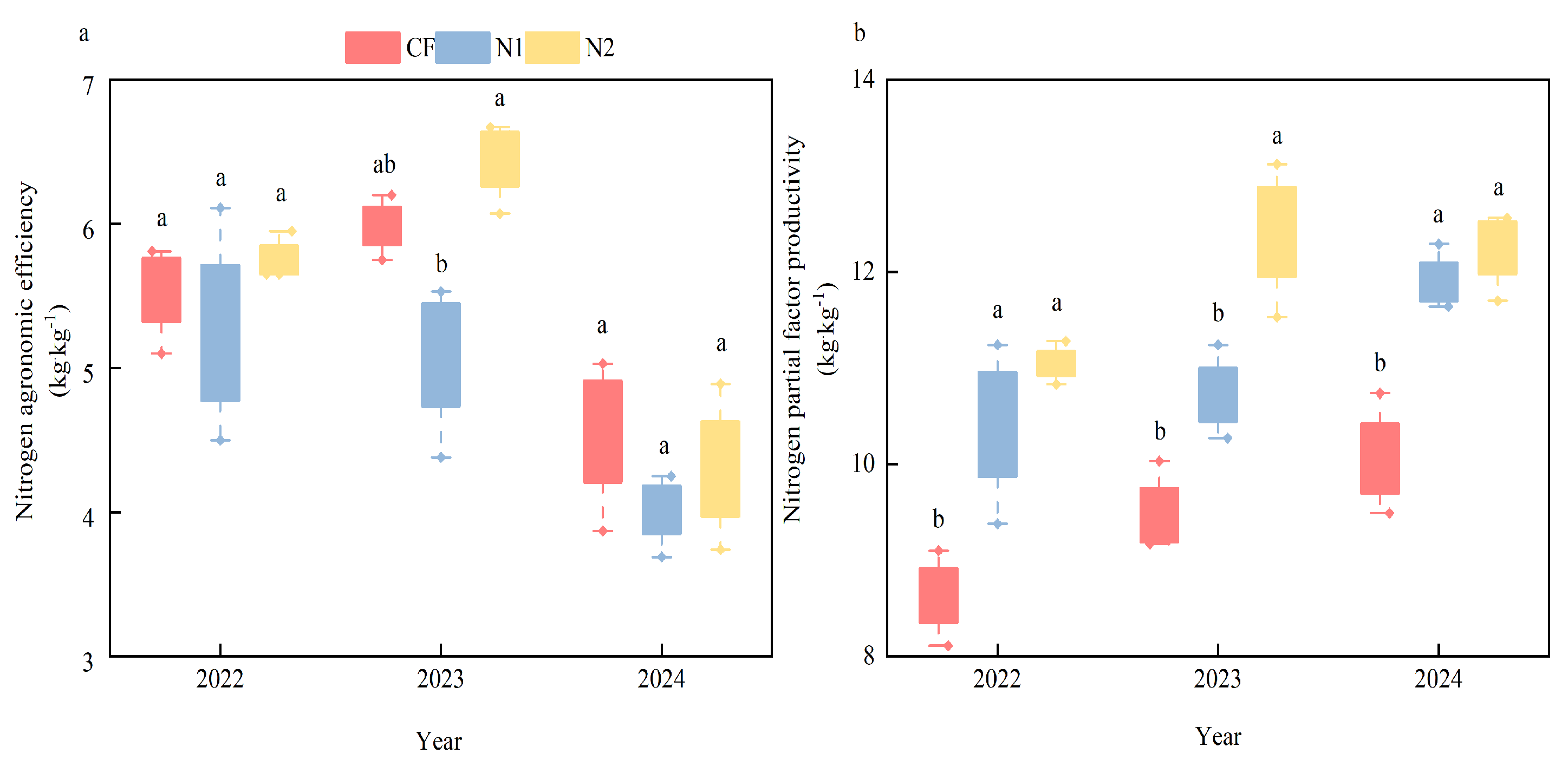


| OM/(g·kg−1) | TN/(g·kg−1) | TP/(g·kg−1) | TK/(g·kg−1) | AP/(mg·kg−1) | AK/(mg·kg−1) | NH4-N/(mg·kg−1) | NO3-N/(mg·kg−1) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.15 | 0.66 | 0.82 | 19.05 | 15.09 | 211.24 | 2.89 | 7.04 | 7.74 |
| Treatment | Application Rate of Nitrogen /(kg·ha−1) | Application Rate of Phosphate /(kg·ha−1) | Application Rate of Potassium /(kg·ha−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0 | 144 | 315 |
| CF | 345 | 144 | 315 |
| N1 | 276 | 144 | 315 |
| N2 | 276 | 144 | 315 |
| Soil Indicators | Principal Component Load Value | Norm Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | ||
| SBD | −0.46 | 0.79 | −0.22 | 0.19 | 1.63 |
| TP1 | 0.46 | −0.79 | 0.22 | −0.19 | 1.63 |
| SMC | −0.15 | 0.28 | 0.76 | −0.09 | 1.15 |
| pH | 0.09 | −0.09 | 0.68 | 0.39 | 1.03 |
| TN | 0.68 | 0.35 | −0.01 | −0.50 | 1.80 |
| TP2 | 0.49 | 0.50 | −0.21 | −0.05 | 1.41 |
| TK | 0.62 | 0.10 | 0.33 | −0.22 | 1.60 |
| NO3-N | 0.64 | −0.16 | −0.49 | 0.18 | 1.72 |
| NH4-N | 0.50 | −0.28 | −0.38 | 0.26 | 1.40 |
| AN | 0.68 | −0.07 | −0.10 | −0.34 | 1.71 |
| AP | 0.75 | 0.09 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 1.84 |
| AK | 0.61 | 0.25 | 0.29 | 0.22 | 1.59 |
| OM | 0.92 | 0.17 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 2.25 |
| SOC | 0.94 | 0.19 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 2.31 |
| C/N | 0.79 | −0.03 | 0.06 | 0.50 | 1.99 |
| Data Set Classification | Soil Index | Common Factor Variance | Weight | Membership Function Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TDS | SBD | 0.931 | 0.09 | Anti S-type |
| TP1 | 0.931 | 0.09 | S-type | |
| SMC | 0.688 | 0.06 | Parabolic | |
| pH | 0.635 | 0.06 | Parabolic | |
| TN | 0.834 | 0.08 | S-type | |
| TP2 | 0.539 | 0.05 | S-type | |
| TK | 0.553 | 0.05 | S-type | |
| NO3-N | 0.708 | 0.07 | S-type | |
| NH4-N | 0.539 | 0.05 | S-type | |
| AN | 0.596 | 0.06 | S-type | |
| AP | 0.579 | 0.05 | S-type | |
| AK | 0.564 | 0.05 | S-type | |
| OM | 0.869 | 0.08 | S-type | |
| SOC | 0.925 | 0.09 | S-type | |
| C/N | 0.871 | 0.08 | S-type | |
| MDS | SBD | 0.434 | 0.13 | Anti S-type |
| SMC | 0.675 | 0.20 | Parabolic | |
| TN | 0.668 | 0.19 | S-type | |
| SOC | 0.982 | 0.28 | S-type | |
| C/N | 0.688 | 0.20 | S-type |
| Soil Index | Treatment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | CF | N1 | N2 | |
| SBD | 1.40 ± 0.02 a | 1.38 ± 0.01 ab | 1.37 ± 0.02 ab | 1.33 ± 0.03 b |
| TP1 | 47.30 ± 0.83 b | 48.01 ± 0.56 ab | 48.13 ± 0.89 ab | 49.85 ± 1.14 a |
| SMC | 14.45 ± 1.32 a | 12.70 ± 1.18 b | 13.69 ± 1.35 ab | 13.67 ± 1.07 ab |
| pH | 7.78 ± 0.07 ab | 7.68 ± 0.09 b | 7.94 ± 0.05 a | 7.93 ± 0.07 a |
| TN | 0.73 ± 0.02 b | 0.94 ± 0.04 a | 0.93 ± 0.03 a | 0.94 ± 0.02 a |
| TP2 | 0.81 ± 0.02 b | 0.98 ± 0.05 a | 0.91 ± 0.04 ab | 1.05 ± 0.07 a |
| TK | 19.55 ± 0.51 c | 21.41 ± 0.45 b | 22.04 ± 0.29 ab | 22.51 ± 0.47 a |
| NO3-N | 4.31 ± 0.26 c | 6.77 ± 0.30 a | 5.76 ± 0.39 b | 6.10 ± 0.36 ab |
| NH4-N | 4.50 ± 0.16 c | 5.93 ± 0.35 a | 4.91 ± 0.20 bc | 5.29 ± 0.30 ab |
| AN | 91.00 ± 1.90 c | 111.89 ± 1.86 a | 101.33 ± 2.87 b | 104.33 ± 2.79 b |
| AP | 11.30 ± 0.40 b | 16.43 ± 0.60 a | 12.31 ± 0.61 b | 16.96 ± 0.33 a |
| AK | 316.89 ± 11.31 b | 343.22 ± 9.09 b | 331.22 ± 7.94 b | 391.33 ± 11.29 a |
| OM | 6.78 ± 0.26 c | 9.62 ± 0.18 b | 9.42 ± 0.19 b | 10.66 ± 0.23 a |
| SOC | 5.15 ± 0.12 c | 8.18 ± 0.20 b | 7.84 ± 0.23 b | 9.25 ± 0.07 a |
| C/N | 7.04 ± 0.10 c | 8.83 ± 0.34 b | 8.45 ± 0.36 b | 9.92 ± 0.21 a |
| Year | Treatment | Seed Cotton Yield/(kg·ha−1) | Single Boll Weight/g | Boll Density/(Bolls·m−2) | Lint Percent/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 | CK | 1065.50 ± 51.72 b | 3.98 ± 0.10 b | 38.30 ± 3.15 b | 41.45 ± 0.22 b |
| CF | 2978.76 ± 98.85 a | 4.57 ± 0.08 a | 79.40 ± 3.27 a | 42.72 ± 0.25 a | |
| N1 | 2874.50 ± 150.76 a | 4.63 ± 0.13 a | 71.80 ± 2.26 a | 42.62 ± 0.35 a | |
| N2 | 3049.50 ± 36.28 a | 4.69 ± 0.10 a | 75.80 ± 3.74 a | 43.15 ± 0.08 a | |
| 2023 | CK | 1201.00 ± 67.33 c | 4.05 ± 0.04 b | 46.30 ± 2.40 c | 41.37 ± 0.39 b |
| CF | 3267.00 ± 96.94 a | 5.23 ± 0.03 a | 93.80 ± 4.26 a | 42.41 ± 0.66 a | |
| N1 | 2958.00 ± 78.21 b | 5.30 ± 0.22 a | 78.70 ± 2.82 b | 42.27 ± 0.27 a | |
| N2 | 3425.50 ± 129.32 a | 5.34 ± 0.08 a | 92.10 ± 4.38 ab | 42.56 ± 0.43 a | |
| 2024 | CK | 1898.00 ± 59.52 b | 4.43 ± 0.08 b | 44.73 ± 3.88 b | 44.82 ± 0.75 a |
| CF | 3470.64 ± 126.34 a | 5.37 ± 0.31 a | 60.55 ± 3.85 a | 44.10 ± 0.02 a | |
| N1 | 3283.76 ± 54.94 a | 5.06 ± 0.15 ab | 56.07 ± 2.27 a | 44.45 ± 1.01 a | |
| N2 | 3381.06 ± 75.70 a | 5.43 ± 0.35 a | 56.55 ± 3.40 a | 44.54 ± 0.49 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qin, Y.; Feng, W.; Zheng, C.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Nie, T. Evaluation of Soil Quality and Balancing of Nitrogen Application Effects in Summer Direct-Seeded Cotton Fields Based on Minimum Dataset. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1763. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081763
Qin Y, Feng W, Zheng C, Chen J, Wang Y, Zhang L, Nie T. Evaluation of Soil Quality and Balancing of Nitrogen Application Effects in Summer Direct-Seeded Cotton Fields Based on Minimum Dataset. Agronomy. 2025; 15(8):1763. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081763
Chicago/Turabian StyleQin, Yukun, Weina Feng, Cangsong Zheng, Junying Chen, Yuping Wang, Lijuan Zhang, and Taili Nie. 2025. "Evaluation of Soil Quality and Balancing of Nitrogen Application Effects in Summer Direct-Seeded Cotton Fields Based on Minimum Dataset" Agronomy 15, no. 8: 1763. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081763
APA StyleQin, Y., Feng, W., Zheng, C., Chen, J., Wang, Y., Zhang, L., & Nie, T. (2025). Evaluation of Soil Quality and Balancing of Nitrogen Application Effects in Summer Direct-Seeded Cotton Fields Based on Minimum Dataset. Agronomy, 15(8), 1763. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081763




