Rare Earth Elements in Tropical Agricultural Soils: Assessing the Influence of Land Use, Parent Material, and Soil Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Do Eucalyptus and pasture in long-established agricultural lands increase REE concentrations in southeastern Brazilian soils?
- Which predictors (land cover, parent material, soil properties) best explain variations in soil REE content?
- What is the relative influence of these predictors on REE distribution?
2. Materials and Methods
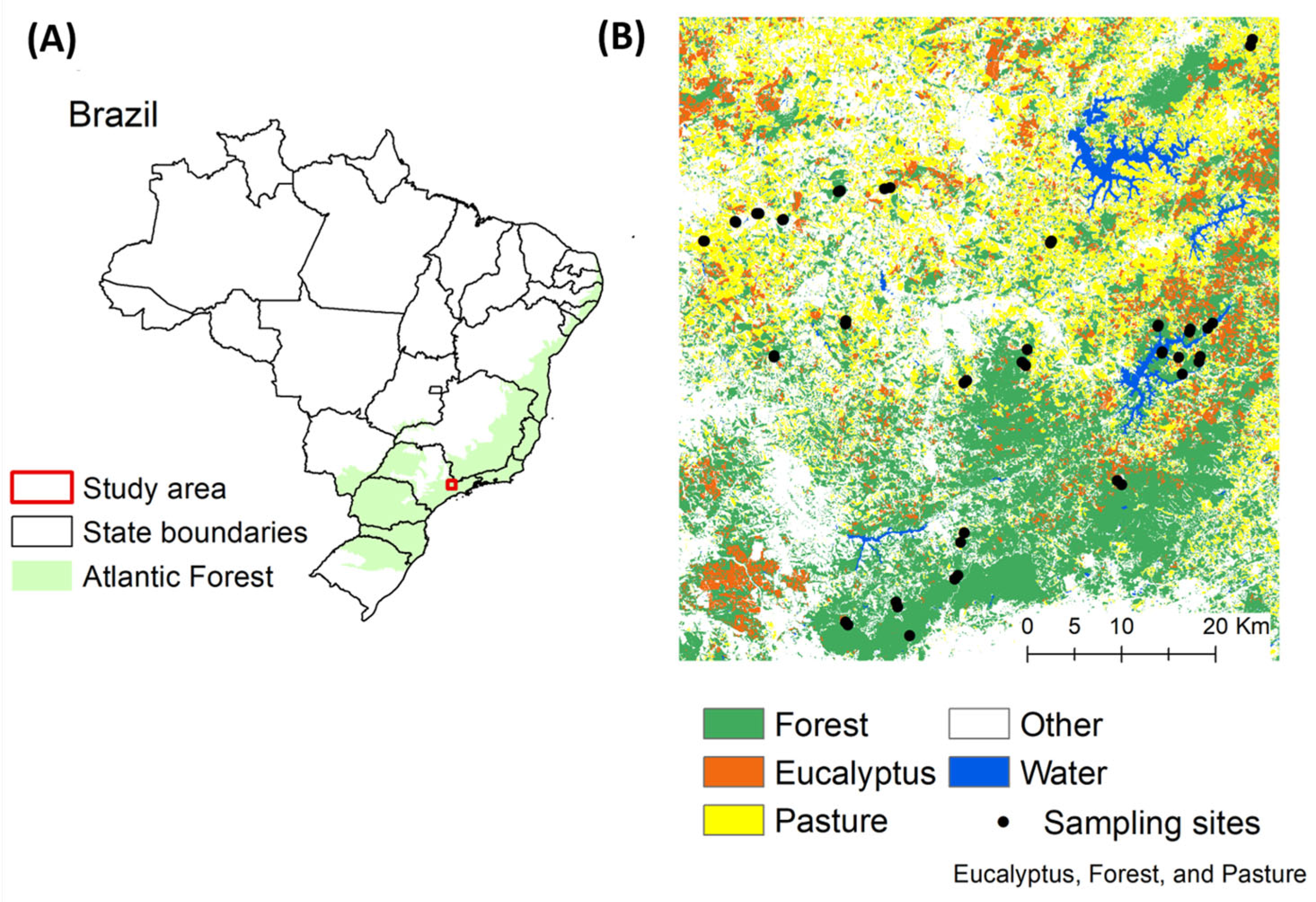
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Soil Sampling and Analysis of Structural and Physicochemical Properties
2.3. Determination of Rare Earth Elements (REEs)
2.4. Normalized Patterns and Fractionation of REEs, Including Ce and Eu Anomalies
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
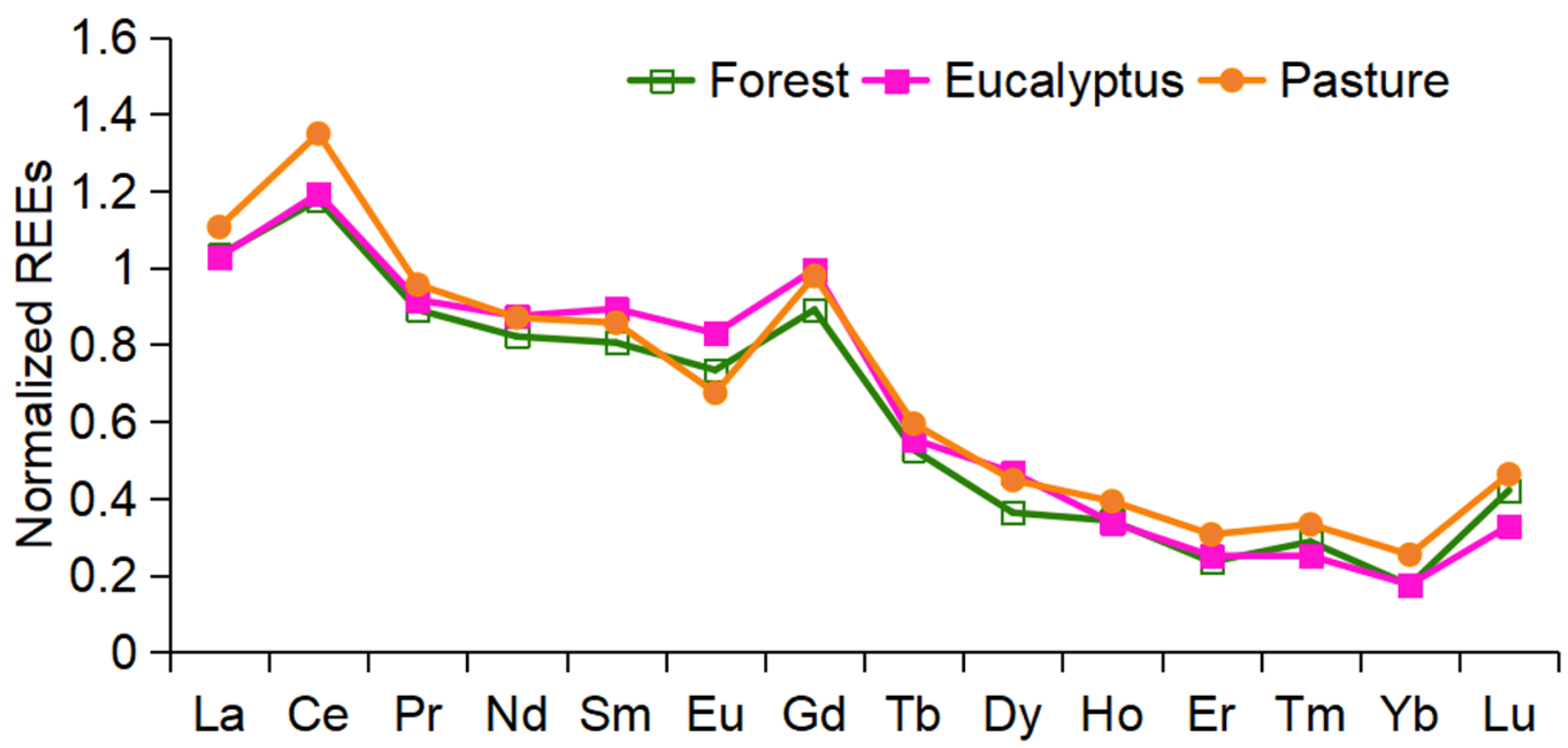
3.1. REE Distribution Across Land Cover Types and Parent Materials
3.2. Influence of Land Cover Types, Parent Materials, and Soil Properties on REE Content
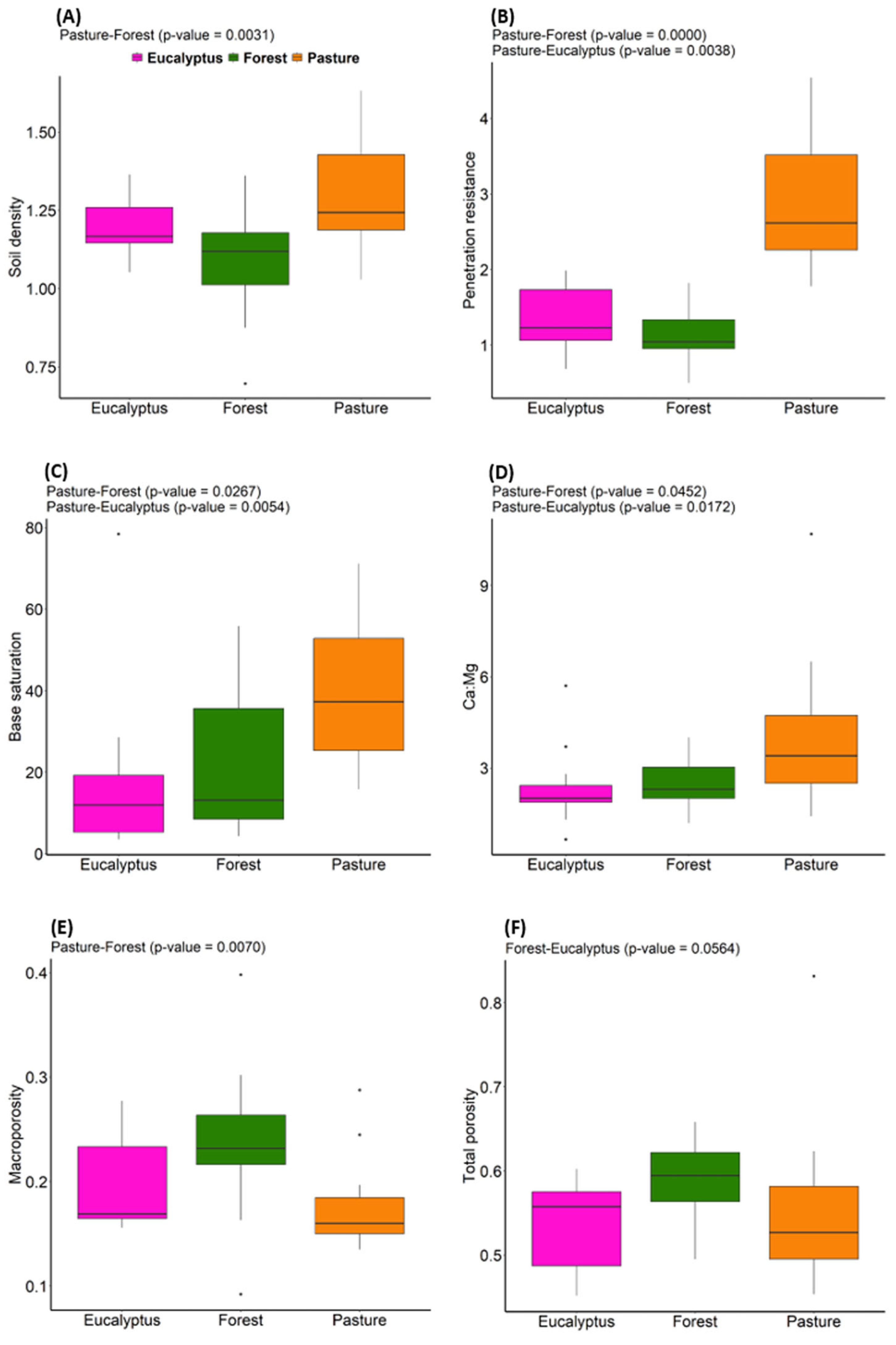
3.3. Soil Properties Across Land Cover Types
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rashid, A.; Schutte, B.J.; Ulery, A.; Deyholos, M.K.; Sanogo, S.; Lehnhoff, E.A.; Beck, L. Heavy Metal Contamination in Agricultural Soil: Environmental Pollutants Affecting Crop Health. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Yang, L.; Zhang, C.; Xiao, X.; Lyu, X. Early warning of heavy metals contamination in agricultural soils: Spatio-temporal distribution and future trends in the Hexi Corridor. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 160, 111908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, M.D.; Fernandes, A.C.; Alves, R.S.; Alves, D.A.; Barbosa Júnior, F.; Batista, B.L.; Ribeiro, M.C.; Hornos Carneiro, M.F. Effects of native forest and human-modified land covers on the accumulation of toxic metals and metalloids in the tropical bee Tetragonisca angustula. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 215, 112147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wuana, R.A.; Okieimen, F.E. Heavy Metals in Contaminated Soils: A Review of Sources, Chemistry, Risks and Best Available Strategies for Remediation. ISRN Ecol. 2011, 2011, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angon, P.B.; Islam, M.S.; Kc, S.; Das, A.; Anjum, N.; Poudel, A.; Suchi, S.A. Sources, effects and present perspectives of heavy metals contamination: Soil, plants and human food chain. Heliyon 2024, 10, e28357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nde, S.C.; Félicité, O.M.; Aruwajoye, G.S.; Palamuleni, L.G. A meta-analysis and experimental survey of heavy metals pollution in agricultural soils. J. Trace Elem. Miner. 2024, 9, 100180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowiak, K.; Lisiak, M.; Kanclerz, J.; Budka, A.; Mleczek, M.; Niedzielski, P.; Adamska, A.; Janicka, E. Relations between rare earth elements accumulation in Taraxacum officinale L. and land use in an urban area—A preliminary study. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 94, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, W.V.; Ramos, S.J.; Melo, L.C.; Braz, A.M.; Dias, Y.N.; Almeida, G.V.; Fernandes, A.R. Levels and environmental risks of rare earth elements in a gold mining area in the Amazon. Environ. Res. 2022, 2011, 113090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, F.B.; Nascimento, C.W.; Álvarez, A.M.; Araújo, P.R. Inputs of rare earth elements in Brazilian agricultural soils via P-containing fertilizers and soil correctives. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 232, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paye, H.D.; Mello, J.W.; Mello, J.W.; Mascarenhas, G.M.; Gasparon, M.; Gasparon, M. Distribution and fractionation of the rare earth elements in Brazilian soils. J. Geochem. Explor. 2016, 161, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brilhante, S.A.; da Silva, Y.J.; de Medeiros, P.L.; do Nascimento, C.W.; da Silva, Y.J.; Ferreira, T.O.; Otero, X.L.; Silva, A.H.; Sousa, M.G.; Alcântara, V.; et al. Geochemistry of rare Earth elements in rocks and soils along a Cretaceous volcano-sedimentary Basin in Northeastern Brazil. Geoderma Reg. 2024, 26, e00756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martina, A.; Ferroni, L.; Marrocchino, E. The Soil–Plant Continuity of Rare Earth Elements: Their Interactions with Plant Structures and Processes. J. Xenobiot. 2025, 15, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, Y.J.; Nascimento, C.W.; Silva, Y.J.; Biondi, C.M.; Silva, C.M. Rare Earth Element Concentrations in Brazilian Benchmark Soils. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Solo 2016, 40, e0150413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, P.G.; Dinali, G.S.; Boldrin, P.; de Carvalho, T.S.; de Oliveira, C.; Ramos, S.J.; Siqueira, J.O.; Moreira, C.G.; Guilherme, L.R. Rare Earth Elements (REEs) Rich-Phosphate Fertilizers Used in Brazil are More Effective in Increasing Legume Crops Yield Than Their REEs-Poor Counterparts. Int. J. Plant Prod. 2021, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, S.J.; Dinali, G.S.; Oliveira, C.D.; Martins, G.C.; Moreira, C.G.; Siqueira, J.O.; Guilherme, L.R. Rare Earth Elements in the Soil Environment. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2016, 2, 28–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bispo, F.H.; de Menezes, M.D.; Fontana, A.; Sarkis, J.E.; Gonçalves, C.M.; de Carvalho, T.S.; Curi, N.; Guilherme, L.R. Rare earth elements (REEs): Geochemical patterns and contamination aspects in Brazilian benchmark soils. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 289, 117972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turra, C.; Fernandes, E.A.N.; Bacchi, M.A. Evaluation on rare earth elements of Brazilian agricultural supplies. J. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2011, 3, 86–92. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, Y.J.; Oliveira, E.B.; Silva, Y.J.; Nascimento, C.W.; Silva, T.D.; Boechat, C.L.; Teixeira, M.P.; Barbosa, R.S.; Singh, V.P.; Sena, A.F. Quality reference values for rare earth elements in soils from one of the last agricultural frontiers in Brazil. Sci. Agri. 2021, 78, e20200069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, C.G.; Carvalho, T.S.; de Oliveira, C.; Abreu, L.B.; Castro, A.C.; Ribeiro, P.G.; Bispo, F.H.; Boutin, C.; Guilherme, L.R. Ecological risk assessment of cerium for tropical agroecosystems. Chemosphere 2019, 221, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereto, C.; Baudrimont, M.; Coynel, A. Global natural concentrations of Rare Earth Elements in aquatic organisms: Progress and lessons from fifty years of studies. Sci. Total. Environ. 2014, 222, 171241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, N.; Mittermeier, R.A.; Mittermeier, C.G.; Fonseca, G.A.; Kent, J. Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature 2000, 403, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montagnana, P.C.; Alves, R.S.; Garófalo, C.A.; Ribeiro, M.C. Landscape heterogeneity and forest cover shape cavity-nesting hymenopteran communities in a multi-scale perspective. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2021, 56, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CPRM. Geologia do Brasil. 2004. Available online: https://metadados.snirh.gov.br/geonetwork/srv/api/records/4de151f5-6d20-4e87-b49c-c9b0ea65440c (accessed on 17 July 2024).
- Raij, B.V.; Andrade, J.C.; Cantarella, H.; Quaggio, J.A. Análise Química para Avaliação da Fertilidade de Solos Tropicais, 1st ed.; Instituto Agronômico: Campinas, Brasil, 2001; 285p. [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira, P.C.; Donagemma, G.K.; Fontana, A.; Teixeira, W.G. Manual de Métodos de Análise de Solos, 3rd ed.; Embrapa: Brasília, Brasil, 2017; 574p. [Google Scholar]
- Otto, R.; Silva, A.P.; Franco, H.C.; Oliveira, E.C.; Trivelin, P.C. High soil penetration resistance reduces sugarcane root system development. Soil. Tillage Res. 2011, 117, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. EPA. Method 3051A (SW-846): Microwave Assisted Acid Digestion of Sediments, Sludges, and Oils; Revision 1; U.S. EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- McLennan, S.M. Rare Earth Elements in Sedimentary Rocks: Influence of Provenance and Sedimentary Processes. In Geochemistry and Mineralogy of Rare Earth Elements; Lipin, B.R., McKay, G.A., Eds.; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 1989; pp. 169–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourmand, A.; Dauphas, N.; Ireland, T.J. A novel extraction chromatography and MC-ICP-MS technique for rapid analysis of REE, Sc and Y: Revising CI-chondrite and Post-Archean Australian Shale (PAAS) abundances. Chem. Geol. 2012, 291, 38–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bau, M.; Dulski, P. Distribution of yttrium and rare-earth elements in the penge and kuruman iron-formations, transvaal supergroup, South Africa. Precambrian Res. 1996, 79, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grawunder, A.; Merten, D.; Büchel, G. Origin of middle rare earth element enrichment in acid mine drainage-impacted areas. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 6812–6823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migaszewski, Z.M.; Gałuszka, A.; Dołęgowska, S. Rare earth and trace element signatures for assessing an impact of rock mining and processing on the environment: Wiśniówka case study, south-central Poland. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 24943–24959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migaszewski, Z.M.; Gałuszka, A.; Dołęgowska, S. Extreme enrichment of arsenic and rare earth elements in acid mine drainage: Case study of Wiśniówka mining area (south-central Poland). Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 898–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, K.R.; Green, R.H. Statistical Design and Analysis For A Biological Effects Study. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1988, 46, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuur, A.F.; Ieno, E.N.; Walker, N.; Saveliev, A.A.; Smith, G.M. Mixed Effects Models and Extensions in Ecology with R. Statistics for Biology and Health; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Mihajlovic, J.; Rinklebe, J. Rare earth elements in German soils—A review. Chemosphere 2018, 205, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, J.; Vitorino, L.C.; Fabrega Gonçalves, R.; Corrêa Côrtes, M.; Souza Cruz Alves, R.; Cezar Ribeiro, M.; Garcia Collevatti, R. Matrix dominance and landscape resistance affect genetic variability and differentiation of an Atlantic Forest pioneer tree. Landsc. Ecol. 2022, 37, 2481–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, T.C.; Londe, V.; Zanini, A.M.; Rodrigues, R.R. Comparative recovery of soil microbial activity and invertebrate abundance and richness in abandoned and planted pastures in Southeastern Brazil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 203, 105683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suguituru, S.S.; Silva, R.R.; Souza, D.R.; Munhae, C.D.; Morini, M.S. Ant community richness and composition across a gradient from Eucalyptus plantation to secondary Atlantic Forest. Biota Neotrop. 2011, 11, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brancalion, P.H.; Amazonas, N.T.; Chazdon, R.L.; Melis, J.; Rodrigues, R.R.; Silva, C.C.; Sorrini, T.B.; Holl, K.D. Exotic eucalypts: From demonized trees to allies of tropical forest restoration? J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 57, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Azimi, G. Impact of particle size and associated minerals on rare earth desorption and incorporation mechanisms in a South American ion-adsorption clay. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 16216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Metwally, A.; Abdel-Bary, A.; El-Azib, A.; Ragab, A. Geochemistry and REE tetrad effect of the acidic volcanics and associated stream sediments, southeast G. El-Hadid area, Central Eastern Desert, Egypt. Arab. J. Geosci. 2024, 17, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, H.N.; Coêlho, J.J.; Dubeux Júnior, J.C.; Santos, E.R.; Cunha, M.V.; Mello, A.C.; Santos, M.V. Soil chemical changes and resemblances in a chronosequence rainforest-sugarcane-pastureland in the Atlantic Forest biome. CERNE 2020, 26, 444–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, F.P.; Silva, I.R.; Novais, R.F.; Barros, N.F.; Neves, J.C. Alterations of soil chemical properties by eucalyptus cultivation in five regions in the Rio Doce Valley. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Solo 2010, 34, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, V.S.; Cardoso, I.M.; Fernandes, O.R.; Rocha, G.C.; Simas, F.N.; Moura, W.D.; Santana, F.C.; Veloso, G.V.; Luz, J.M. The establishment of a secondary forest in a degraded pasture to improve hydraulic properties of the soil. Soil. Tillage Res. 2020, 198, 104538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, P.H.D.; de Almeida, G.L.P.; Pandorfi, H.; de Lima, R.P.; de Medeiros, V.W.C.; da Silva, J.L.B.; de Melo, A.A.S.; Coutinho, A.S. Assessment spatial soil physical properties under rotational cattle grazing in Northeastern Brazil. CATENA 2024, 240, 108002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benevenute, P.A.; Morais, E.G.; Souza, A.A.; Vasques, I.C.; Cardoso, D.P.; Sales, F.R.; Severiano, E.D.; Homem, B.G.; Casagrande, D.R.; Silva, B.M. Penetration resistance: An effective indicator for monitoring soil compaction in pastures. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Predictor Variables (R < 7) | Response Variables (R < 7) |
|---|---|
| Soil physical variables Soil density Total porosity Macroporosity Microporosity Fine sand Total sand Penetration resistance Hydraulic conductivity Silty Clay | Rare earth elements Europium Cerium Lutetium Yttrium |
| ∑LREEN/∑HREEN ∑LREE ∑HREE ∑REE δCe δEu LaN/YbN LaN/SmN SmN/YbN | |
Soil chemical variables Potassium content Phosphorus content Carbon stock Ca:Mg |
| Eucalyptus (Avg ± SD) | Forest (Avg ± SD) | Pasture (Avg ± SD) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Europium (mg·kg−1) | 0.89 ± 0.60 | 0.79 ± 0.59 | 0.72 ± 0.39 |
| Cerium (mg·kg−1) | 94.98 ± 68.67 | 93.63 ± 39.59 | 107.40 ± 35.48 |
| Lutetium (mg·kg−1) | 0.14 ± 0.12 | 0.18 ± 0.10 | 0.20 ± 0.13 |
| Yttrium (mg·kg−1) | 7.60 ± 9.53 | 5.40 ± 2.97 | 7.60 ± 7.43 |
| ∑LREEN/∑HREEN | 3.16 ± 1.27 | 2.87 ± 0.99 | 2.73 ± 0.99 |
| ∑LREE (mg·kg−1) | 177.84 ± 118.87 | 174.07 ± 72.58 | 193.08 ± 80.81 |
| ∑HREE (mg·kg−1) | 9.03 ± 6.31 | 8.05 ± 3.32 | 9.42 ± 4.82 |
| ∑REE (mg·kg−1) | 186.88 ± 124.51 | 182.12 ± 75.30 | 202.50 ± 85.40 |
| δCe | 1.27 ± 0.59 | 1.47 ± 0.96 | 1.97 ± 1.79 |
| δEu | 1.72 ± 1.31 | 1.36 ± 0.73 | 1.64 ± 2.30 |
| LaN/YbN | 7.38 ± 4.17 | 6.93 ± 4.00 | 4.68 ± 1.78 |
| LaN/SmN | 1.20 ± 0.22 | 1.27 ± 0.32 | 1.23 ± 0.24 |
| SmN/YbN | 6.17 ± 3.51 | 5.36 ± 3.03 | 3.81 ± 1.45 |
| Land Cover Types | ||
|---|---|---|
| REEs | R | Significance (p-Value) |
| Europium | −0.08 | 0.01 |
| Cerium | 0.09 | 0.00 |
| Lutetium | 0.02 | 0.00 |
| Yttrium | −0.02 | 0.01 |
| LREEN/HREEN | 0.02 | 0.00 |
| ∑LREE | 0.02 | 0.00 |
| ∑HREE | −0.01 | 0.00 |
| ∑REE | 0.02 | 0.00 |
| δCe | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| δEu | 0.07 | 0.00 |
| LaN/YbN | −0.01 | 0.01 |
| LaN/SmN | 0.01 | 0.00 |
| SmN/YbN | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Geological Types | ||
| REEs | R | Significance (p-Value) |
| Europium | 0.20 | 0.00 |
| Cerium | 0.02 | 0.00 |
| Lutetium | 0.03 | 0.00 |
| Yttrium | 0.18 | 0.00 |
| LREEN/HREEN | 0.15 | 0.00 |
| ∑LREE | 0.14 | 0.00 |
| ∑HREE | 0.19 | 0.00 |
| ∑REE | 0.14 | 0.00 |
| δCe | 0.05 | 0.00 |
| δEu | 0.24 | 0.00 |
| LaN/YbN | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| LaN/SaN | 0.31 | 0.00 |
| SaN/YbN | −0.04 | 0.01 |
| Yttrium | DAICc | df | Weight | Mult R2 | Adj R2 |
| Parent material | 0.00 | 10 | 0.98 | 0.48 | 0.37 |
| ∑HREE | DAICc | df | Weight | Mult R2 | Adj R2 |
| Phosphorus: land cover types | 0.00 | 7.0 | 0.95 | 0.34 | 0.26 |
| δCe | DAICc | df | Weight | Mult R2 | Adj R2 |
| Ca:Mg | 0.00 | 3.0 | 0.71 | 0.17 | 0.15 |
| δEu | DAICc | df | Weight | Mult R2 | Adj R2 |
| Parent material | 0.00 | 10 | 0.85 | 0.42 | 0.30 |
| LaN/SaN | DAICc | df | Weight | Mult R2 | Adj R2 |
| Parent material | 0.00 | 10 | 0.99 | 0.49 | 0.38 |
| SaN/YbN | DAICc | df | Weight | Mult R2 | Adj R2 |
| Clay | 0.00 | 3.0 | 0.80 | 0.13 | 0.11 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Castellano, G.R.; Santos, J.S.d.; Zanatta, M.B.T.; Alves, R.S.C.; Souza, Z.M.d.; Ribeiro, M.C.; Menegário, A.A. Rare Earth Elements in Tropical Agricultural Soils: Assessing the Influence of Land Use, Parent Material, and Soil Properties. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1741. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071741
Castellano GR, Santos JSd, Zanatta MBT, Alves RSC, Souza ZMd, Ribeiro MC, Menegário AA. Rare Earth Elements in Tropical Agricultural Soils: Assessing the Influence of Land Use, Parent Material, and Soil Properties. Agronomy. 2025; 15(7):1741. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071741
Chicago/Turabian StyleCastellano, Gabriel Ribeiro, Juliana Silveira dos Santos, Melina Borges Teixeira Zanatta, Rafael Souza Cruz Alves, Zigomar Menezes de Souza, Milton Cesar Ribeiro, and Amauri Antonio Menegário. 2025. "Rare Earth Elements in Tropical Agricultural Soils: Assessing the Influence of Land Use, Parent Material, and Soil Properties" Agronomy 15, no. 7: 1741. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071741
APA StyleCastellano, G. R., Santos, J. S. d., Zanatta, M. B. T., Alves, R. S. C., Souza, Z. M. d., Ribeiro, M. C., & Menegário, A. A. (2025). Rare Earth Elements in Tropical Agricultural Soils: Assessing the Influence of Land Use, Parent Material, and Soil Properties. Agronomy, 15(7), 1741. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071741








